大前庭水管综合征家系SLC26A4基因突变分析
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:563.70 KB
- 文档页数:7

GJB2、SLC26A4基因相关耳聋儿童的听力损失特点分析崔庆佳;孙喜斌;戴朴;黄丽辉;王国建;张媛;杨影;康东洋;杜延顺;赵丽萍;黄莎莎;张伟【摘要】Objective To determine the audiological characteristics in 832deaf children with biallelic causative mutations in GJB2 ,SLC26A4gene .Methods The 832 patients received deafness gene screening ,553 were GJB2 gene biallelic causative mutations ,279 were SLC26A4 gene biallelic causative mutations .Patients were divided into four groups according to ages of hearing loss onset :<1 ,1~3 ,3~6 ,6~12 years old ,and the audiological character-istics and prevalence of GJB2 ,SLC26A4 gene mutations at different ages of onset .Results The prevalence of GJB2 gene mutations at four groups was 37 .97% (210/553) ,38 .34% (212/553) ,16 .27% (90/553) ,7 .41% (41/553) ,re-spectively ;the prevalence of SLC26A4 gene mutations at four groups was 25 .45% (71/279) ,44 .80% (125/279) , 20 .07% (56/279) ,9 .67% (27/279) ,respectively .The difference between GJB2 and SLC26A4 gene was significant(P=0 .001) .The prevalence of profound hearing loss with GJB2 gene mutations at four groups were 66 .67%(140/210) ,61 .32% (130/212) ,47 .78% (43/90) ,41 .46%(17/41) ,respectively .The difference was significant (P=0 .004) ,while the difference in 279 patients with SLC26A4 gene mutations was not statistically significant (P= 0 . 083) .Conclusion The age of hearing loss onset in patients with biallelic causative mutations in GJB 2 or SLC26A4 gene refers to 0~3 years -old ,hearing loss in patients with GJB2 ,SLC26A4 gene mutations gives priority to pro-found .The age of hearing loss onsetis smaller ,the ratio of profound hearing loss is higher .Patients with severe and profound hearing impairment should be performed the genetic testing when the age of onset under 12 .%目的:探讨明确为GJB2、SLC26A4基因相关耳聋儿童的听力损失特点。

•138 •屮华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志202丨年 2 月第56 #第2 期(:丨丨in J ()t»>rhim>lar>ng»l Head Neck Surg, M>mar> 2021. V»l. 56, V>. 2•新技术新材料-Goldengate尚通量耳聋基因芯片在大如庭水管综合征中的有效性验证及应用分析吴宏蒋璐刘畅刘亚兰龙梦琦梅凌云贺楚峰蔡鑫章陈红胜冯永中南大学湘雅医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科耳鼻咽喉科重大疾病研究湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410008冯永现在南华大学附属长沙中心医院耳鼻咽喉科410004通信作者:冯永,Email:***********************oni【摘要】目的将Goldengale高通量耳聋基因芯片应用于大前庭水管综合征患者,验证芯片的准确性及有效性,为制定更加详细的大前庭水管综合征遗传检测策略提供参考方法2016年8月至2018年2月利用本研究团队研发的Goldmgate高通迓耳聋检测芯片,检测丨5例确诊为大前庭水管综合征耳浮患者及60例健康人对照样本,并•利用S anyr测序法验证芯片检测结果所有大前庭水管综合征患者均进行57X26,44基因测序,并与芯片结果进行对比分析结果12/15患者通过芯片检测出.S’LC26,44椹W突变,通过芯片检测和SAC26.料基因直接测序共检出9种突变,其中7种突变被两种方法均检出,该芯片可检测出基W1*£接测序法所提供的等位基因信息的93.33%( 28/30)除•S/X26.44基因以外,丨5例大前庭水管综合征患者通过芯片还同时检测出、PC’/)///5、m C7、M V Y沁以及线粒体基丨大丨的突变,并均经过S anyr测序法得到验证结论Goldengate*高通量耳聋基W芯片具有检测潰盖广、准确性高等特点,可作为大前庭水管综合征患者的初步检测手段【关键词】大前庭水管综合征;基因芯片基金项目:湖南f t「丨然科学基•金(20丨7JJ3476)Validation and analysis of Goldengate high-throughput deafness gene chip in detecting thepatients with enlarged vestibular aq u e d u ct syndrom eWu Hong, Jiang Lu, Liu Chang, Liu Yalan, Long Mengqi, Mei Lingyun, He Chufeng, Cai Xinzhang,Chen Hongsheng, Feng YongDepartment of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery, Xiangya Hospital, Central SouthUniversity, Key Laboratory of Otorhinolaryngology, Hunan Province, Changsha 410008, ChinaFeng Yong is now in the Department o f Otorhinolaryngology, Changsha Central Hospital, University ofSouth China, Changsha 410004, ChinaCorresponding author: Feng Yong, Email: ***********************【A bstract 】Objective To verify the accuracy and effectiveness of Goldengatehigh-throughput deafness gene chip in detecting the patients with enlarged vestibular aqueductsyndrome(EVAS), and to provide a reference for genetic detection strategy of EVAS. Methods FromAugust 2016 to February 2018, 15 patients with EVAS and 60 normal controls were detected byGoldengate high-throughput deafness detection chip developed by our team, and the results wereverified by Sanger sequencing. SLC26A4gene sequencing was carried out in all the patients withEVAS. Results 12/15 of patients with EVAS were detected mutations of SLC26A4gene. Ninem utations were detected by chip detection and SLC26A4gene direct sequencing, seven of whichD O I: 10.3760/l 15330-20200302-00150收稿日期2020-03-02 本文编辑金昕引用本文:吴宏,蒋璐.刘畅,等.Goldengate高通量耳聋基W芯片在大前庭水管综合征中的有效性验证及应用分析I J1.中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2021. 56(2): 138-143.丨)()丨:10.3760/(ma. j.cn115330-20200302-00150.中 $丨〔鼻咽喉头颈外f’l H、202 I<丨'2 ).j 第 56 卷第2 期(Ihin .1()t«>rhi!i〇Unyng()l Head N<-ck Smg. I rhruary 2021, \Ol. 56. No. 2•139 •were detected by both methods. The chip could detect 93.33%(28/30) of the allele informationprovided by SLC26A4gene direct sequencing. In addition to SLC26A4gene, m utations of G]B2,PCDH15, TMC1, MY06and mitochondrial genes were detected in 15 patients with EVAS. Theseresults were verified by Sanger sequencing. Conclusion Goldengate high-throughput deafnessgene chip possesses the traits of wide coverage and high accuracy, which can be used as apreliminary detection method for patients with EVA S.【K e y w o r d s】Vestibular aqueduct enlargement syndrome; Gene chipFund program:Hunan Natural Science Foundation Project(2017)J3476)耳聋是最常见的感觉神经性疾病:|,据报道,全球有2.5亿人患有中度以上听力损失2 :中国每 年约有3万先天性听力损失患儿出生:3]。

感音神经性耳聋患者大前庭导水管综合征相关SLC26A4基因IVS7-2A>G的全序列分析李琦;黄德亮;朱庆文;袁永一;方如平;戴朴【期刊名称】《中华医学遗传学杂志》【年(卷),期】2010(027)006【摘要】目的对携带SLC26A4基因IVS7-2A>G单杂合突变感音神经性耳聋患者进行 SLC26A4基因的全序列检测,以期发现除IVS7-2A>G以外的其他突变.方法应用直接测序法对80例携带IVS7-2A>G单杂合突变的感音神经性耳聋患者进行SLC26A4基因进行全序列测序.结果 80例患者中47例发现另1个突变位点,其余33例未发现复合杂合突变,IVS7-2A>G单杂合突变找到另外1个突变的比例为58.8%(47/80).发现了 3个新的突变,分别是5+2T>A、14-2A>G和1825del G,最为常见的5种突变为H723R(20%)、T410M(5%)、15+5G>A(5%)、L676Q(5%)、N392Y(3.75%).第17外显子是突变发生种类最多的外显子.结论SLC26A4基因IVS7-2A>G单杂合突变者应该进行其他突变的筛查,SLC26A4基因复合突变可以解释部分的耳聋原因.%Objective To investigate the whole sequence of the SLC26A4 gene in moderate to profound sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) patients with IVS7-2A>G mutation of the gene in China.Methods Whole SLC26A4 gene sequence was analyzed by direct sequencing in 80 SLC26A4 gene IVS7-2A>G mutation carriers for the occurrence of a second mutation in the gene. Results Forty-seven out of the 80 patients were found to have a second heterozygous mutation, whereas a single IVS7- 2A> G mutation could be responsible for SNHL inthe remaining 33 patients. Three novel mutations, 5+ 2T>A,14-2A>G and 1825del G, were identified. The five most common mutations includeH723R (20%),T410M (5%), C. 1705+5G>A (15+5G>A) (5%), L676Q(5%), and N392Y (3. 75%). Exon 17 harbored the most types of compound heterozygosity with the IVS7 - 2A>G mutation. Conclusion A Chinese specific SLC26A4 diversity was found, and comparable SLC26A4 contributing to deafness. This study suggested that if a heterozygous SLC26A4 mutation is found in a patient with deafness, other exons of the SLC26A4 gene should be analyzed. Furthermore, double heterozygosity of theSLC26A4 gene may also account for some of the disease phenotype.【总页数】6页(P610-615)【作者】李琦;黄德亮;朱庆文;袁永一;方如平;戴朴【作者单位】210008,南京医科大学附属南京儿童医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科;210008,南京医科大学附属南京儿童医院儿童听力中心;中国人民解放军总医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科;中国人民解放军总医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科;中国人民解放军总医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科;210008,南京医科大学附属南京儿童医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科;中国人民解放军总医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科【正文语种】中文【相关文献】1.30例大前庭水管综合征患者 SLC26A4基因诊断与听性脑干电位特性分析2.大前庭水管综合征患者的SLC26A4基因诊断3.大前庭水管综合征家系特征与SLC26A4基因分析4.27个省市聋校学生基于SLC26A4基因IVS7-2A>G突变的全序列分析5.河南两地区聋儿教育机构患者大前庭水管相关SLC26A4基因热点突变筛查分析因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。




大前庭水管综合征及其相关的基因—SLC26A4赵亚丽翟所强王秋菊中国人民解放军总医院耳鼻咽喉研究所(北京100853)临床和流行病学研究表明,每1000名新生儿中就有1名先天性耳聋的患儿。
大前庭水管综合征(largevestibularaqueductsyndrome,LVAS)是先天性耳聋的一种。
1978年,Valvassori和Clemis[1]在对3700例颞骨连续分层摄片中发现,有50例前庭水管扩大,并将其命名为大前庭水管(dilatedvestibularaqueduct,DVA),又将临床上伴感音神经性听力损失等症状者称“大前庭水管综合征”。
近年,随着CT、MRI以及分子遗传学的发展,对此病的认识已经从影像学诊断、临床表现、发展到了分子诊断的水平。
1大前庭水管综合征的临床表现、发病机理及诊断大前庭水管是儿童感音神经性聋最常见的内耳畸形,由其导致的大前庭水管综合征是一种独立性疾病,除了前庭水管扩大外,不合并其它畸形,属于非综合征型耳聋。
其临床表现为波动性感音神经性听力损失,多呈进行性下降。
可从出生后至青春期这一年龄段内任何时期开始起病,但多数为出生后几年内发病。
发病突然或隐匿,通常之前有感冒、轻微颅外伤或其他使颅内压增高的病史。
约81%-94%的患者为双侧发病,单侧发病者少见[2]。
听力受损以高频为主,听力图多为下降型,少数为平坦型,无一例为上升型[3]。
听力下降的程度与前庭水管的大小无关,可表现为从接近正常到极重度聋。
并且,双耳听力可不对称。
大多数患者仅表现为听力损失,只有少数患者伴有前庭症状,约占29%,但有人认为前庭症状少见可能与发病人群多为幼儿有关[4]。
目前,关于前庭水管扩大导致感音神经性聋的致病机理还不是很清楚,通常有三种假说:(1)内淋巴液返流学说,前庭水管扩大时,往往同时伴有内淋巴管和内淋巴囊的异常扩大,突然的脑压变化,迫使两层脑膜间内淋巴囊内容返流入耳蜗,囊内高渗内淋巴进入耳蜗基底周,损伤神经感觉上皮,产生感音神经性耳聋。
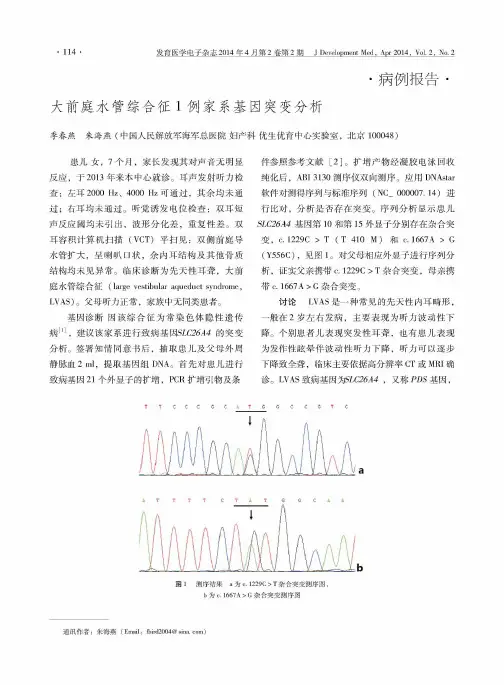
114筮宣匡堂皇王盘查至Q!垒生垒旦箜至鲞箜至塑』望!!!!!卫坐!堕坐鱼:垒匹垫!垒:y!!至:盟!.兰大前庭水管综合征1例家系基因突变分析病例报告季春燕朱海燕(中国人民解放军海军总医院妇产科优生优育中心实验室,北京100048)患儿女,7个月,家长发现其对声音无明显反应,于2013年来本中心就诊。
耳声发射听力检查:左耳2000H z、4000H z可通过,其余均未通过;右耳均未通过。
听觉诱发电位检查:双耳短声反应阈均未引出,波形分化差,重复性差。
双耳容积计算机扫描(V C T)平扫见:双侧前庭导水管扩大,呈喇叭口状,余内耳结构及其他骨质结构均未见异常。
临床诊断为先天性耳聋,大前庭水管综合征(1ar ge ves t i b ul ar aqueduc t syndr om e,L V A S)。
父母听力正常,家族中无同类患者。
基因诊断因该综合征为常染色体隐性遗传病u J,建议该家系进行致病基H SLC26A4的突变分析。
签署知情同意书后,抽取患儿及父母外周静脉血2m l,提取基因组D N A。
首先对患儿进行致病基因21个外显子的扩增,PC R扩增引物及条件参照参考文献[2]。
扩增产物经凝胶电泳回收纯化后,A B I3130测序仪双向测序。
应用D N A st ar 软件对测得序列与标准序列(N C一000007.14)进行比对,分析是否存在突变。
序列分析显示患儿SL C26A4基因第10和第15外显子分别存在杂合突变,c.1229C>T(T410M)和c.1667A>G (Y556C),见图1。
对父母相应外显子进行序列分析,证实父亲携带c.1229C>T杂合突变,母亲携带c.1667A>G杂合突变。
讨论L V A S是一种常见的先天性内耳畸形,一般在2岁左右发病,主要表现为听力波动性下降。
个别患者儿表现突发性耳聋,也有患儿表现为发作性眩晕伴波动性听力下降,听力可以逐步下降致全聋,临床主要依据高分辨率C T或M R I确诊。

135例大前庭导水管耳聋患者SLC26A4基因突变分析于晓宇;林妘;许军;杨涛;吴皓【摘要】Objective To investigate the mutation spectrum of SLC26A4 and to elucidate molecular mechanisms un-derlying non-syndromic hearing loss associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct in east China by screening for SLC26A4 gene mutations.Methods Blood samples and clinical data were collected from 135 unrelated EVA probands and screening of coding regions of the SLC26A4 gene was performed by nested polymerase chain reaction followed by Sanger sequencing.Results One hundred(74.07%)probands carried two SLC26A4 mutant alleles and ten(7.41%)had one SLC26A4 mutant allele, while no mutation was detected in the rest twenty-five (18.52%) patients.A total of 51 types of SLC26A4 mutations were identified with c.919-2A>G and p.H723R being the most common mutations account-ing for 50%(105/210)and 10.48%(22/210)of mutant alleles,respectively.Conclusions Consistent with previous re-ports,c.919-2A>G is most prevalent in Chinese.Further research will be needed to investigate other genetic factors that may contribute to the pathogenesis of EVA given the fact that a large percentage of patients lack mutations in the SLC26A4 coding region in one or both alleles.%目的研究华东地区非综合征性大前庭导水管耳聋患者SLC26A4基因的突变情况,以进一步了解其突变谱,为阐明EVA的分子机制和指导基因诊断提供依据.方法通过巢式聚合酶链式反应扩增目的片段和Sanger测序对135例明确诊断的散发非综合征性EVA耳聋患者SLC26A4基因的外显子及侧翼序列进行变异检测.结果在135例EVA耳聋患者中,明确为SLC26A4双等位基因突变致病的占74.07%(100/135),单等位基因突变的占7.41%(10/135),18.52%(25/135)的患者未检测到任何SLC26A4基因突变.共检出51种SLC26A4基因突变,其中, c.919-2A>G突变和p.H723R突变最常见,分别占总检出突变的50%(105/210)和10.48%(22/210).结论与既往报道一致,c.919-2A>G突变为中国人群SLC26A4基因的最常见变异.有相当一部分患者未检出SLC26A4双等位基因突变,提示可能有其他致病因子参与EVA的发生,有待进一步研究阐明.【期刊名称】《中华耳科学杂志》【年(卷),期】2018(016)002【总页数】5页(P160-164)【关键词】大前庭导水管;SLC26A4;耳聋;基因诊断【作者】于晓宇;林妘;许军;杨涛;吴皓【作者单位】上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,上海交通大学医学院耳科学研究所,上海市耳鼻疾病转化医学重点实验室;上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,上海交通大学医学院耳科学研究所,上海市耳鼻疾病转化医学重点实验室;上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,上海交通大学医学院耳科学研究所,上海市耳鼻疾病转化医学重点实验室;上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,上海交通大学医学院耳科学研究所,上海市耳鼻疾病转化医学重点实验室;上海交通大学医学院附属第九人民医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科,上海交通大学医学院耳科学研究所,上海市耳鼻疾病转化医学重点实验室【正文语种】中文【中图分类】R764大前庭导水管(Enlarged vestibular aqueduct,EVA)是与儿童感音神经性聋相关的最常见的内耳畸形[1]。

新生儿SLC26A4基因热点突变筛查及结果分析目的:利用耳聋基因芯片筛查,出生听力筛查正常新生儿中SLC26A4基因热点突变的发生频率,检出携带者。
方法:研究对象为1823例出生听力筛查正常新生儿,采集出生72h后足跟血,以PCR与耳聋芯片技术,检测滤纸干血斑,检测SLC26A4耳聋基因8个热点突变位点。
结果:检出携带者 19例,检出率 1.04%。
SLC26A4 基因 IVS7-2A>G 杂合突变型 16例(0.88%),2168A>G 杂合突变型 1 例(0.05%),1229C>T杂合突变型1例(0.05%),IVS15+5G>A杂合突变型1例(0.05%)。
结论:听力筛查正常的新生儿,仍有携带大前庭导水管综合征相关耳聋基因的风险,建议出生时进行SLC26A4热点基因检测,预防大前庭导水管综合征相关的听力下降。
关键词:大前庭导水管综合症;耳聋;听力筛查;基因突变大前庭导水管综合征( large vestibular aqueduct syndrome,LVAS) 是以前庭导水管扩大伴有感音神经性聋或混合性聋为特征的疾病,占感音神经性聋患者的1%-12%1-2,是儿童先天性耳聋的主要原因之一。
随着对遗传的深入研究,大量致聋基因突变位点被确认,为遗传性耳聋筛查及诊断提供了基础,SLC26A4是明确的致聋基因,与大前庭水管综合征(large vestibular aqueduct syndrome LVAS)发病有关3。
本调查采用耳聋基因芯片对我院1823 例听力筛查正常新生儿进行耳聋基因筛查,为大前庭导水管综合征的早期诊断、干预和预防提供理论依据。
1.对象与方法1.1 对象选取2019年8月~2019年9月间收集新生儿筛查标本1823例,均为福建省妇幼保健院出生听力筛查正常新生儿,均无明显畸形,无怀孕病毒感染史,并签订听力筛查与基因检测知情同意书。
72h后采集足跟血滴于干燥的滤纸片上,完全渗透,血斑不小于8mm,自然晾干后置4℃冰箱保存。
听觉是一种通过大脑皮层分析后获得的声音感觉,一旦听觉系统中的任何部位发生结构或功能障碍均可导致程度不等的听力损失,包括传导性、感音神经性和混合性等听力损失。
其中感音神经性聋的病因很多,常见的病因有先天性因素、感染性因素、药物中毒性因素、职业性因素、外伤性因素、肿瘤、梅尼埃病、突发性聋、老年性退行性变、听觉中枢病变以及贫血、免疫反应等全身性疾病。
在感音神经性聋中尤以因内耳病变引起的感音性聋较多见,而且大部分耳聋发生在出生以后,甚至出现在成年以后,这其中包括一部分畸形和遗传性聋。
大前庭水管综合征是一种非常常见的听力损失疾病,此病属先天畸形但多于后天发病。
1 概述1.1 定义大前庭水管综合征(large vestibular aqueductsyndrome, LVAS)是一种以渐进性波动性听力下降为主的先天性内耳畸形性听力障碍,可同时伴有反复发作的耳鸣或眩晕等一系列临床症候群,听力检查通常表现为感音神经性聋,也有少部分患者表现为混合性聋。
这是20世纪70年代末随着CT技术问世而被发现的一种内耳畸形致聋疾病,1978年被正式命名为LVAS。
前庭水管是一个细小的骨性管道,从前庭延伸到颞骨的岩部,包裹着充满了内淋巴液的膜性内淋巴管,其作用是将前庭的膜迷路与颞骨内的内淋巴囊相连,正常的前庭水管是维持内淋巴液代谢所必需的。
胚胎时期的发育异常可导致前庭水管扩大,进而由于扩大的前庭导水管引起一系列的临床症状,但目前致病原因还不十分明确。
1.2流行病学资料据保守估计,至少有1%~1.5%的感音神经性聋和有平衡问题的病人会有大前庭水管综合征。
也有报道表明,5%~7%不明原因的感音神经性聋患者可能*基金项目:我国耳神经疾病早期干预措施及规范化治疗方案研究,十五科 技攻关(2004BA720A18-02)作者单位:首都医科大学附属北京同仁医院 北京 100730 北京市耳鼻喉科研究所 耳鼻咽喉头颈科学教育部重点实验室(首都医科大学)作者简介:刘博 硕士 主任医师;研究方向:听力、眩晕疾病 大前庭水管综合征(Ⅰ)*——基本概念和基础研究Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome(I) ——Basic concepts and research■刘 博 LIU Bo【中图分类号】R764.3 【文献标识码】A 【文章编号】1672-4933(2008)04-0058-04编者按 目前,大前庭水管综合征被认为是导致儿童耳聋的主要原因之一,但由于该病起病隐匿,加之患儿存在不同程度的残余听力和可能存在的传导性聋成分,易被许多临床医师所忽视和误诊,进而耽误该病的早期诊断并错过最佳的有效治疗期,最终导致严重的不可恢复的感音神经性聋。
大前庭水管综合征SLC26A4基因突变临床研究山西医科大学硕士学位论文大前庭水管综合征SLC26A4基因突变临床研究姓名:席宏申请学位级别:硕士专业:耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科学指导教师:张芩娜2011-03-15 山西医科大学硕士学位论文大前庭水管综合征 SLC26A4 基因突变分析摘要目的: 应用耳聋基因芯片对非综合征性感音性神经性耳聋患者进行分子病因学研究。
在临床上可以形成一个将临床听力学特征性的表现,与影像学和致病基因的突变检测相结合的一个系统的诊断流程。
研究方法: 采集聋哑学校和门诊散发病例的非综合症性耳聋患者 102 人的外周血,提取基因组DNA,应用耳聋基因芯片检测中国人中常见的大前庭水管综合征基因(亦称 PDS 基因或SLC26A4 基因)的两个热点突变,包括 IVS7-2A〉G 和 2168A〉G。
结果: 在非综合征行耳聋患者中 SLC26A4 基因突变占 16.39,且 SLC26A4 突变的患者 CT 检查均证实为大前庭水管扩大。
且 CT 证实为大前庭的患者,有 95.36基因检测 SLC26A4 突变阳性,SLC26A4 基因中的 IVS7-2A〉G 位点突变的比率高,占 78.95。
结论:本实验102例非综合征性耳聋患者SLC26A4基因突变率达到16.4,证实了SLC26A4是非综合征性耳聋的易感基因。
运用耳聋基因芯片对非综合征性重度和极重度耳聋患者的突变检出率与解放军总医院的相关报告一致(21)。
SLC26A4基因检测可作为重度和极重度非综合征性耳聋患者的临床检查项目。
本课题对非综合征性耳聋患者都采用CT检查与基因芯片筛查,二者吻合率达94.12,说明SLC26A4基因检测可作为重度和极重度非综合征性耳聋患者的临床检查项目。
筛查该基因有助于该病的预防、诊断和治疗。
关键词:大前庭水管综合征 SLC26A4基因突变基因芯片II山西医科大学硕士学位论文 Abstract Objective: we will analyze the auditory data andgenetic characteristics the geneticdiagnostic kit of hereditary deafness based on DNA microarray. Methods: 61 moderate to profound NSHL patients were included in this study. Theirgenomic DNA samples were extracted from peripheral blood and detected with theDNA microarray which is able to perform mutation detection of 2 hot-spot mutationsin the most common pathologic genes SLC26A4 IVS7-2A〉G G 2168A〉simultaneously. Results: Of 61 patients1016.39 were found out to be carriers of SLC26A4 pathogenicgene mutation .Among them IVS7-2A〉G homozygous mutation in9cases compoundheterozygous mutation in 1 cases 2168A〉Gheterozygous mutation in 1cases. Conclusion: In the 61 NSHL patients the SLC26A4 mutation’s quotiety is 16.39. the resultas same as the PLA General Hospital. the genetic diagnostic kit of hereditarydeafness based on DNA microarray appears to have some inherent advantages ingenetic diagnosis of NSHL its features of easy manipulation standardization andpopularization endue it perfect prospect in clinical application. Key words: Large vestibular aqueduct syndrome SLC26A4 gene Mutation DNAmicroarray III 山西医科大学硕士学位论文英文缩写词索引缩写英文全称中文全称NSHL Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss 非综合征性耳聋LVAS Large Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome大前庭水管综合征EVA Enlargement of the vestibular aqueduct 前庭导水管扩大PDS Pendredsyndrome Pendred 综合征PCR Polymerase Chain Reaction 聚合酶链反应CT Computerized Tomography 电脑断层扫描ABR Auditory Brainstem Response 听觉脑干反应ASSR Auditory Steady StateResponse 听觉稳态反应SLC26A4 Solute carrierfamily 26 member 4 溶质载体家族 26 个,会员 4HHL Hereditary Hearing Loss 遗传性耳聋 IV 学位论文独创性声明本人声明,所呈交的学位论文系在导师指导下本文独立完成的研究成果。
一例大前庭水管综合征患儿的SLC26A4基因突变研究孙东兰;常立甲;曹琴英;穆卫红;张艳华;高虹;方芳;于湄;赵丽娟;张静;米冬青【期刊名称】《中华医学遗传学杂志》【年(卷),期】2017(034)003【摘要】Objective To analyze mutations of SLC26A4 gene and explore their origins for a patient with enlarge vestibuar aqueductsyndrome.Methods Clinical data and peripheral venous blood samples were collected from the patient and her parents.Genome DNA was extracted from the peripheral blood.All of the 21 exons of the SLC26A4 gene were amplified with PCR and subjected to directly sequencing.Results The patient was found to have carried two mutant alleles of the SLC26A4 gene,namely c.1522A>G and c.1229C>>T,which were inherited from her father and mother,respectively.Conclusion SLC26A4 c.1522A>G is likely to be a pathogenic mutation.Above results may facilitate genetic counseling and prenatal diagnosis for this family.%目的对1例大前庭水管综合征患儿进行SLC26A4基因突变位点分析,以明确其突变类型和突变形式,并探讨其突变来源和传递规律.方法收集大前庭水管综合征患儿及其父母的临床资料及血样,提取基因组DNA,聚合酶链反应进行SLC26A4基因的全序列扩增,扩增产物纯化后测序.应用Sequencing Analysis Software等软件进行生物信息学分析、比对.结果测序结果提示患儿为SLC26A4c.1522A>G和c.1229C>T的复合杂合突变,父亲为SLC26A4 c.1522A>G杂合突变,母亲为SLC26A41229C>T杂合突变.结论SLC26A4 c.1522A>G变异可能是该患儿的致病基因突变,本研究结果对于该家庭的再生育及患儿将来的婚育有指导意义.【总页数】3页(P390-392)【作者】孙东兰;常立甲;曹琴英;穆卫红;张艳华;高虹;方芳;于湄;赵丽娟;张静;米冬青【作者单位】050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心;050011 石家庄市第四医院产前诊断中心【正文语种】中文【相关文献】1.前庭导水管扩大耳聋人群中SLC26A4单等位基因突变的出现率及致病相关性研究2.大前庭水管综合征家系SLC26A4基因突变分析3.大前庭水管综合征4个家系SLC26A4基因突变分析4.SLC26A4基因突变致前庭水管扩大听力损失机制的研究进展5.大前庭水管综合征的基因诊断和SLC26A4基因突变分析因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。