西尔斯大学物理双语版答案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:267.50 KB
- 文档页数:6



标准答案及评分标准一.Choice(20分,每题4分)1. a2. b3. c4. d5. a二.Blanks (20分)6. 0.5 (1分) 3 (1分) 1/2 (1分)π/6(2分) 3π or 9.42 (3pts)7. 1.26 (3分)8. 2.26°(3分)9. 3.56×10-28 (3分)10. 1.14eV (3分)三.Questions(10分)11. (5pts)The relativity principle: The laws of physics must be the same in all inertial reference frames. 一切物理规律在惯性系中相同。
(2分)The constancy of the speed of light: The speed of light in vacuum has the same value c in all inertial frames, regardless of the velocity of the observer or the velocity of the source emitting the light. 真空中的光速在任何惯性系中都是c ,与光源或观察者的运动无关。
(3分)12. (5pts)The maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons is independent of light intensity. (2分)No electrons are emitted if the incident light frequency falls below some cutoff frequency fc , whose value is characteristic of the material being illuminated, regardless of the light intensity.(3分)四. Problems (50分)13(10pts) (1) The average transitional kinetic energy 21101.623-⨯==kT K t J ………………… 3pts (2) the rms speed s m MRT v rms /4803≈= ………………… 3pts (3) the internal energy RT i E 2= ………………… 1pts For O 2, i = 5, ………………… 1pts the internal energy 60912≈=RT i E J ………………… 2pts 14(10pts)(1) 1→2: Isothermal expansion )/ln(12V V nRT Q H H = ………………… 2pts 3→4: Isothermal compression )/ln(34V V nRT Q L L = ………………… 2pts (2) 2→3: Adiabatic expansion 1312--=γγV T V T L H ………………… 1pts4 1: Adiabatic compression. 1411--=γγV T V T L H ………………… 1pts Therfore, 4312V V V V = ………………… 1pts HL H L T T Q Q = ………………… 1pts The efficiency of Carnot engine is HL H L T T Q Q -=-=11η ………………… 2pts 15 (17pts)(1) The light path difference isθδs i nd = ………………… 2pts For bright fringesλθδm d ==s i n………………… 2pts The separation between the 2nd-order bright fringe and the 3rd-order bright fringe is423105.523tan tan -⨯==-≈-=∆d D d D d D D D x λλλθθm ………………… 3pts (2) The light path difference is()L n d 1sin -+=θδ ……………………………………… 3ptsFor bright fringes()λθδm L n d =-+=1s i n …………………………… 1pts At the central, point θ=0 ……………………………………… 1ptsThe central point on the viewing screen is now occupied by the seventh bright slid fringe (m =7) ()λδ710sin =-+=L n d ……………………………………… 1pts 61064.6)1/(7-⨯=-=n L λm ……………………………………… 2pts(3) No ……………………………………… 2pts16 (13pts)(1) The period measured by the observers on the spaceship is the propertime. ……………1pts126.020==km T πs ……………4pts (2) The mass and the spaceship is moving at a very high speed relative to the Earth. The effect of special theory of relativity must be taken into account. ………2ptsThe period measured by the observers on the Earth is not the propertime. ……………2ptsAccording to the special theory of relativity,209.0/1220=-=c v T T s ……………4pts。


习题11-1 P 点相对于原点的位矢26=-+p r i j m , P 点到Q 点的位移42∆=-r i j m, 求Q 点相对于原点的位矢并画图.解:设Q 点相对与原点的位矢为Q r ,则:24=+∆=+Q p r r r i j1-2一质点作直线运动,它的运动方程是2ct bt x -=, b , c 是常数. (1) 求此质点的速度和加速度函数;(2) 作出x t -,t υ-和a t -图解:这是一个一维的问题.速度 (2)dx ct b dtυ==-+, 加速度 2d a c dtυ==-. 图略.1-3物体按照29.4t x =的规律运动,x 的单位为米,t 的单位为秒. (1) 计算下列各时间段内的平均速度:1s 到1.1s,1s 到1.01s,1s 到1.001s; (2) 求1s 末的瞬时速度;(3) 解释上述结果解:这也是一个一维的问题.(1) 平均速度 x tυ∆=∆. 1s 到1.1s 内: 224.9 1.1 4.911.11x t υ∆⨯-⨯==∆-=10.29 (m/s ), 1s 到1.01s 内:224.9 1.01 4.911.011x t υ∆⨯-⨯==∆-=9.849(m/s ), 1s 到1.001s 内:224.9 1.001 4.911.0011x t υ∆⨯-⨯==∆-=9.8049(m/s ). (2) 速度 9.8dx t dtυ==. 1-4一质点以110m s -⋅的恒定速率向东运动. 当它刚到达距出发点为d 的一点时,立即以120m s -⋅的恒定速率返回原处. 问: 质点在全过程中的平均速度和平均速率为多少?解:取出发点为原点,向东为x 轴正方向. 从原点到x =d 处,作匀速直线运动,时间 11s t υ∆∆==d/10.从x =d 处返回原点作匀速直线运动,时间22st υ∆∆==d/20 (全过程中,平均速率 12s d d t t t υ∆+===∆∆+∆13.3 (m/s ) 返回原处时,位移x ∆=0,平均速度x tυ∆=∆=0. 1-5 矿井里的升降机由井底从静止开始匀加速上升,经过3s 速度达到13m s -⋅,然后以这个速度匀速上升6s ,最后减速上升经过3s 后到达井口时刚好停止. (1) 求矿井深度;(2) 作出x t -,t υ-和a t -图.解:(1)以井底为原点,向上为x 轴正向.在0—3s 内,升降机作匀加速直线运动:210112x t a t υ∆=+ (1) 2210112a x υυ=+∆. (2)其中00υ=. 由(1)、(2)两式得:1x ∆=4.5(m).在3—9s 内,升降机以1υ=3m/s 作匀加速直线运动,21x t υ∆==18(m/s ) (3)在9—12s 内,升降机作匀减速直线运动231212x t a t υ∆=- (4) 2221232a x υυ=-∆, (5) 其中20υ=. 由(4)和(5)两式得3x ∆=4.5(m)矿井深度 123H x x x =∆+∆+∆=4.5+18+4.5=27(m).1-6湖中有一小船,岸上有人用一根跨过定滑轮的绳子拉船靠岸。



Chapter 23 Exercises23-3 a) For surface S 1, the electric flux is ()()221CL j L k D j C i B S E -=-⋅-+-=⋅=Φ .For surface S 2, the electric flux is ()()222DL k L k D j C i B S E -=⋅-+-=⋅=Φ .For surface S 3, the electric flux is ()()223CL j L k D j C i B S E =⋅-+-=⋅=Φ .For surface S 4, the electric flux is ()()224DL k L k D j C i B S E =-⋅-+-=⋅=Φ.For surface S 5, the electric flux is ()()225BL i L k D j C i B S E -=⋅-+-=⋅=Φ.For surface S 6, the electric flux is ()()226BL i L k D j C i B S E =-⋅-+-=⋅=Φb) The total electric flux is 0654321=Φ+Φ+Φ+Φ+Φ+Φ=Φ.23-6 a) Because the S1 encloses the charge q1, the electric flux through the S1 isb) Because the S2 encloses the charge q2, the electric flux through the S2 isc) Because the S3 encloses the charge q1and q2, the electric flux through the S3 isd) Because the S4 encloses the charge q1 and q3, the electric flux through the S4 ise) Because the S5 encloses the charge q1 ,q2 and q3, the electric flux through the S5 is23-8 a) When the spherical surface ’s radius is 0.500m, the charges q1 and q2 aren ’t closed by this surface, so the electric flux is zero. b) When the spherical surface ’s radius is 1.50m, the second charge q2 is closed by this surface, so the electric flux is)/(1045.01085.81000.426126011C m N q ∙⨯=⨯⨯==Φ---ε)/(1088.01085.81080.726126022C m N q ∙⨯-=⨯⨯-==Φ---ε)/(1043.01085.81080.71000.42612660213C m N q q ∙⨯-=⨯⨯-⨯=+=Φ----ε)/(1072.01085.81040.21000.42612660314C m N q q ∙⨯=⨯⨯+⨯=+=Φ----ε)/(1016.01085.81040.21080.71000.4261266603215C m N q q q ∙⨯-=⨯⨯+⨯-⨯=++=Φ-----εc) When the spherical surface ’s radius is 2.50m, these two charges enclose by the surface, so the electric flux is23-24 a) When r <a, the Gaussian surface doesn’t enclose any electric charges, so the magnitude of electric field is zero.When a <r <b, the Gaussian surface encloses the charge q, so the magnitude of electric field is When b <r <c, because the hollow sphere is a conductor, the electric field is zero inside it. When r>c, the Gaussian surface encloses the charge q, so the magnitude of electric field ise)b)c m N q 2612602/1068.01085.81000.6⨯-=⨯⨯-==Φ--εc m N q q 261266012/10025.01085.81000.61000.4⨯-=⨯⨯-⨯=+=Φ---ε204r qπε=Φ204r q πε=Φc) The negative charge –q is on the inner surface of the hollow sphere. d) The positive charge +q is on the outer surface of the hollow sphere.23-27 a) when r <a, the surface isn ’t closed any charge, so the electric field is E = 0 b) When a <r <b, the surface doesn ’t enclose any charge, so the electric field is E = 0 c) When b <r <c, the surface does enclose the charge +2q, so the electric field isd) When c <r <d, the surface doesn ’t enclose any net charge, so the electric flux is E = 0. e) When r > d, the surface does enclose the charge +2q and +4q, so the electric flux isThe total charge on the inner surface of the small shell is zero. The total charge on the outer surface of the small shell is +2q. The total charge on the inner surface of the large shell is -2q. The total charge on the outer surface of the large shell is +6q.23-28. a) when r <a, the surface doesn ’t closed any charge, so the electric field is E = 0. b) When a <r <b, the surface doesn ’t enclose any charge, so the electric field is E = 0. c) When b <r <c, the surface does enclose the charge +2q, so the electric field isd) When c <r <d, the surface doesn ’t enclose any net charge, so the electric flux is E = 0. e) When r > d, the surface does enclose the charge +2q and -2q, so the electric flux isO a b c d2042r q E πε=202046442r q r q q E πεπε=+=2042r q E πε=042220=-=rq q E πεThe total charge on the inner surface of the small shell is zero. The total charge on the outer surface of the small shell is +2q. The total charge on the inner surface of the large shell is -2q. The total charge on the outer surface of the large shell is zero.23-29. a) when r <a, the surface doesn ’t closed any charge, so the electric field is E = 0. b) When a <r <b, the surface doesn ’t enclose any charge, so the electric field is E = 0. c) When b <r <c, the surface does enclose the charge +2q, so the electric field ise) When r > d, the surface does enclose the charge +2q and -4q, so the electric flux isThe total charge on the inner surface of the small shell is zero. The total charge on the outer surface of the small shell is +2q. The total charge on the inner surface of the large shell is -2q. The total charge on the outer surface of the large shell is -2q.23-33 a) Between the cylinders, using the Gauss ’s law,the electric field isb) At any point outside the outer cylinder, the electric field isc)O a b c2c2042r q E πε=202042442r q r q q E πεπε-=-=⎰=⋅sq s d E 0ε 02ελπl l r E =⋅⋅r E 02πελ=r E 02πελ=。
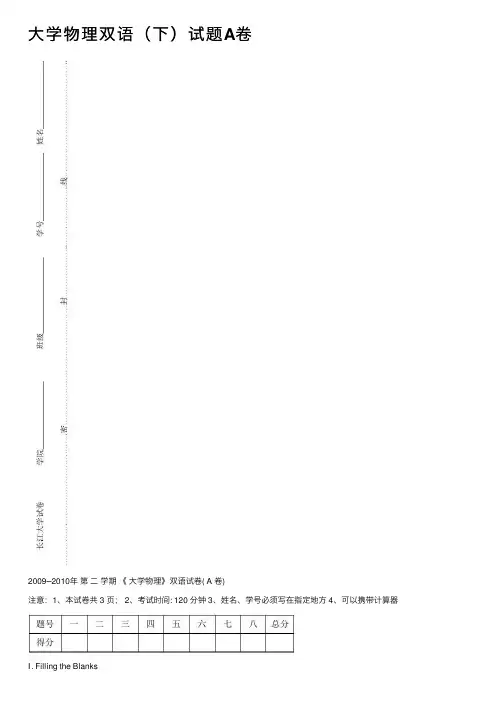
⼤学物理双语(下)试题A卷2009─2010年第⼆学期《⼤学物理》双语试卷( A 卷)注意:1、本试卷共 3 页; 2、考试时间: 120 分钟 3、姓名、学号必须写在指定地⽅ 4、可以携带计算器Ⅰ. Filling the Blanks(每⼩题 2 分,共 20 分)1.⼀空⽓平⾏板容器,两板相距为d ,与⼀电池连接时两板之间相互作⽤⼒的⼤⼩为F ,在与电池保持连接的情况下,将两板距离拉开到3d ,则两板之间的相互作⽤⼒的⼤⼩是2. There is a point charge of electric quantity Q at the center of a cube, the electric flux through one surface of cube is3.如图1,⼀根⽆限长直导线通有电流I ,在P 点处被弯成了⼀个半径为2R 的圆,且P 点处⽆交叉和接触,则圆⼼O 处的磁感强度⼤⼩为_______________,⽅向为______________4. As shown in the figure 2, in the vacuum let the metal sphere with radius R be grounded, place a point charge q with a distance r (r>R) away from the center O of the sphere, the total induced charge on the surface of the metal sphere is5. 如图3所⽰,AOC 为⼀折成形的⾦属导线(AO =OC = L ),位于xoy 平⾯上. 磁感应强度为B 的匀强磁场垂直于xoy 平⾯. 当AOC 以速度v 沿x 轴正向运动时,导线上A 、C 两点间的电势差U AC = ,当以速度v 沿y 轴正向运动时A 、C两点中点电势⾼.6.⼀空⽓平⾏板电容器,接电源充电后电容器中储存的能量为W 0,在保持电源接通的条件下,在两极间充满相对电容率为r ε的各向同性均匀电介质,则该电容器中储存的能量W 为________________7. The period of a pendulum(单摆) is measured to be 3.0s in the reference frame of the pendulum. The period when measured by an observer moving at a speed of 0.95c relative to the pendulum is8.把⼀个静⽌质量为0m 的粒⼦,由静⽌加速到0.6v c =(c 为真空中的光速)需做功为Ⅱ.Choose the Correct Answer(每⼩题 3 分,共 30 分)1. 如图4所⽰,在真空中半径分别为R 和2R 的两个同⼼球⾯,其上分别均匀地带有电量+2q 和-2q ,今将⼀电量为+Q 的带电粒⼦从内球⾯处由静⽌释放,则该粒⼦到达外球⾯时的动能为:()(A)04Qq Rπε.(C) 08Qq Rπε. (D)038QqRπε.2.In following statements which one is correct ( ) (A) The electric potential is definitely zero at the point where the electric field2qFigure 4Figure 3is zero.(B) The electric potential is non-zero at the point where the electric field is not zero.(C) The electric field is definitely zero at the point where the electric potential is zero.(D) The electric field is definitely zero in this area where the electric potential is constant3.有两个长直密绕螺线管,长度及线圈匝数均相同,半径分别为r 1和r 2.管内充满均匀介质,其磁导率分别为µ1和µ2.设r 1∶r 2=1∶2,µ1∶µ2=4∶1,当将两只螺线管串联在电路中通电稳定后,其⾃感系数之⽐L 1∶L 2与磁能之⽐Wm 1∶Wm 2分别为: ( )(B) L 1∶L 2=1∶2,Wm 1∶Wm 2 =1∶1 (C) L 1∶L 2=1∶2,Wm 1∶Wm 2 =1∶2 (D) L 1∶L 2=2∶1,Wm 1∶Wm 2=2∶14. One circular wire loop carries a clockwise current I in a uniform magnetic field B directed to the right as in the figure5. If B increases, what will happen to the net magnetic force and the torque on the current loop,respectively? ( ) (A) increase, increase (B) both keep the same (C) keep the same, decrease (D) keep the same, increase 5. 尺⼨相同的铁环与铜环所包围的⾯积中,通以相同变化率的磁通量,则环中: ( ) (A) 感应电动势相同,感应电流相同 (B) 感应电动势不同,感应电流不同 (C) 感应电动势相同,感应电流不同 (D) 感应电动势不同,感应电流相同Figure 56. The segment of wire in Figure 6 carries a current of I, where the radius of the circular arc is R, the magnitudeof the magnetic field at the origin O is ( )(A) R I 80µ (B) R I 40µ (C) RI πµ80 (D) R Iπµ207. 半径分别为2R 和R 的两个⾦属球,相距很远. ⽤⼀根长导线将两球连接,并使它们带电.在忽略导线影响的情况下,两球表⾯的电荷⾯密度之⽐为: ( )(A) 1/2 (B) 4 (C) 1/4 (D) 28. Which of the following statements is NOT true: ( ) (A) No two electric field lines can cross each other(B) The electric field vector is tangent to the electric field line at each point. (C) Magnetic field lines are always closed curves(D) The magnetic fields can be produced by current, so magnetic fields have sources9. 在某地发⽣两件事,静⽌位于该地的甲测得时间间隔为3s ,若相对甲以4c/5(c 表⽰真空中光速)的速率作匀速直线运动的⼄测得时间间隔为:(A) 2.4s (B) 4s (C) 3.6s (D) 5s ( )10. A spaceship is measured to be 120.0 m long and 20.0 m in diameter while at rest relative to an observer. If this spaceship now flies by the observer with a speed of 0.99c, the diameter does the observer measure is ( ) (A) 17m (B) 19m (C) 15m (D) 20mⅢ.如图7所⽰,两个同⼼的均匀带电球⾯,内球⾯半径为R 1,带电量Q 1,外球⾯半径为R 2,带电量为Q 2.设⽆穷远处为电势零点,求(1)空间各处电场强度的分布;(2)在内球⾯内,距中⼼为r 处的P 点的电势。

Chapter 24 exercises:24-3 a) When the speed of q 2 is 22.0m/s, the kinetic energy of q 2 is21121mv K =; the potential energy of system is 102114r q q U πε=.According to the conservation of energy , when the two spheres are 0.400m apart, the energy is22221mvK =, 202124r q q U πε=. 2211U K U K +=+. We get the speed of q 2 iss m v /5.122=.b) When the q 2 closes to the q 1, the speed of q 2 will slowly until its zero. So the system energy is113U K U +=;10212130214214r q q mv r q q πεπε+=. The distance between the two charges ism r 323.03=.24-7 a) When q 3 is placed at x = +10.0cm, the potential energy of system isJr q q r q q r q q U U U U 7129912991299303120321021*******.310.01085.814.341000.21000.410.01085.814.341000.2)1000.3(20.01085.814.34)1000.3(1000.4444----------⨯-=⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯+⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯-+⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯-⨯⨯=++=++=πεπεπεb) When the potential energy of the system is zero, the q 3 is placed 0444303120321021321=++=++=r q q r q q r q q U U U U πεπεπε3312321210r q q r q q r q q ++=; 2.023=+r rm r 0743.03=.24-9 If zero net work is required to place the three charges at the corners of the triangle, the third charge must be0444000='+'+rq q rq q rqq πεπεπε, 2q q -='.24-25 a) The electron will move with an acceleration to the center of the ring. After through the center, the electron will leave it until the speed is zero. Then it will return to the center and through it to move other side. So the electron will do oscillation.b) According to the conservation of energy, we get K U =,2002144mvReq req =-πεπε.2311291922129191011.92115.01085.814.341024106.130.015.01085.814.341024106.1v⨯⨯⨯=⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯--+⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯--------s m v /1067.17⨯=.24-26 We can suppose the zero potential energy at point p. The distance of point p is R. So we get the initial energy of proton is 2121ln2mv Rr q K U +=+πελ. The final energy of proton isR r q U '=ln202πελ. According to the conservation of energy, we know 22121mv U U =-.221ln2mv r r q ='πελ. The final distance between the line and the proton is cm r 8.15='.24-57 a) Take V = 0, r = b, when r < a, the potential isab dr rr d E r d E r d E V babrarbaln2200πελπελ==⋅+⋅=⋅=⎰⎰⎰⎰.When a < r < b, the potential is rb dr rV brln2200πελπελ==⎰.When r > b, the potential is v = 0.b) Between the inner cylinder and outer cylinder, the electric field is rE 02πελ=. So thepotential difference is ⎰==baab ab dr rV ln2200πελπελ.c) Use Eq. (24-23), we get ()()r a b V r b b rdrdV r E ab 1/ln 220⋅=⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛-⨯⨯-=-=πελ.24-73 a) Use the small element on the rod xdq dV 04πε=, at point P , we getxa x aQ xa x xdxxdq dV V ax xax x+=+====⎰⎰⎰++ln4ln4440000πεπελπελπε.b) At point R, we get⎪⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛++=+===⎰⎰⎰2002201ln 444y a y a a Q yx dxrdqdV V aπεπελπε.c) In part a, when the x is much larger than a, we can think the charged rod like a point charge, so the potential is xQ V 04πε=. In part b, the potential is yQ V 04πε=.24-78 a) From the equation ()2223),,(z y x A z y x V +-=, we can get at any point the electricfield is ()k z j y i x A k z V j y V i x V E 262+--=⎪⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛∂∂+∂∂+∂∂-=. b) At point()()m z y x 250.0,0,0,,=, the potential is )(0625.01V A V ⨯=. At point()()0,0,0,,=z y x , the potential is 02=V . The work done by the electric force isW q V V =-)(21. 651050.10625.01000.6--⨯⨯⨯=⨯A ; 640=Ac) At the point ()()m z y x 250.0,0,0,,=, the electric field is k k E320250.02640-=⨯⨯-=.d) In every plane parallel to the xz-plane, the equation is changed()2223640,,z x yz y x V +=+.So the equipotential contours are circles.e) The radius of the equipotential contour corresponding to V =1280V and y = 2.00m ism r 74.3)00.236401280(212=⨯+=.。

大学物理英语教材答案I. Multiple Choice Questions1. A2. D3. B4. C5. A6. B7. C8. D9. A10. BII. True or False Questions1. False2. True3. True4. False5. True6. False7. True8. False9. True10. FalseIII. Short Answer Questions1. Define Newton's First Law of Motion.Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue moving in a straight line at a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.2. Explain the concept of potential energy.Potential energy is the stored energy possessed by an object due to its position or condition. It is dependent on factors such as height, elasticity, and chemical composition. Potential energy can be converted into other forms of energy, such as kinetic energy, when the object begins to move or undergoes a change.3. What is the difference between speed and velocity?Speed is a scalar quantity that represents how fast an object is moving, regardless of its direction. It is calculated by dividing the distance traveled by the time taken. Velocity, on the other hand, is a vector quantity that includes both speed and direction. It describes the rate at which an object changes its position in a specific direction.4. State the law of conservation of energy.The law of conservation of energy states that energy can neither be created nor destroyed, but it can be transformed from one form to another or transferred from one object to another. The total amount of energy in a closed system remains constant over time.5. What is the difference between elastic and inelastic collisions?In an elastic collision, both momentum and kinetic energy are conserved. The total combined mass and velocity of the objects before the collision equal the total combined mass and velocity of the objects after the collision. In an inelastic collision, momentum is conserved, but kinetic energy is not. Some of the kinetic energy is lost, usually in the form of sound, heat, or deformation.IV. Problem-Solving Questions1. A car travels a distance of 200 km in 4 hours. Calculate its average speed.Average speed = total distance / total timeAverage speed = 200 km / 4 hoursAverage speed = 50 km/h2. A ball is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of 20 m/s. Calculate the maximum height reached by the ball. (Assume no air resistance)Using the kinematic equation:vf^2 = vi^2 + 2as0^2 = (20 m/s)^2 - 2 * 9.8 m/s^2 * h400 = 19.6hh = 400 / 19.6h ≈ 20.41 m3. A force of 50 N is applied to an object with a mass of 5 kg. Calculate the acceleration of the object.Using Newton's second law of motion:F = m * a50 N = 5 kg * aa = 50 N / 5 kga = 10 m/s^24. A block of mass 2 kg slides down a frictionless inclined plane with an angle of 30 degrees. Calculate the acceleration of the block.Using the component of gravity along the incline:F = m * am * g * sin(theta) = m * aa = g * sin(theta)a = 9.8 m/s^2 * sin(30 degrees)a ≈ 4.9 m/s^25. A ball is dropped from a height of 20 meters. Calculate the time it takes for the ball to hit the ground. (Assume no air resistance)Using the kinematic equation:s = vi * t + (1/2) * a * t^20 = 0 * t + (1/2) * 9.8 m/s^2 * t^220 = 4.9 m/s^2 * t^2t = sqrt(20 / 4.9)t ≈ 2.02 secondsV. ConclusionIn conclusion, this set of answers provides solutions to the multiple choice, true or false, short answer, and problem-solving questions found in the university physics English textbook. By understanding and applying the fundamental principles of physics, students will be able to grasp the various concepts discussed in the textbook.。
Chapter 3 –Electric Field, Potential and DC CircuitDeadline: 12/14 1pmName: Student ID: Session ID (1001 or 1002):1.The drawing shows a ray of light traveling from pointA to point B, a distance of 4.60 m in a material thathas an index of refraction n1. At point B, the lightencounters a different substance whose index ofrefraction is n2 = 1.63. The light strikes the interface atthe critical angle of θc = 48.1°. How much time does ittake for the light to travel from A to B?Solution:The time it takes for the light to travel from A to B is equal to the distance divided by the speed of light in the substance. The distance is known, and the speed of light v in the substance is equal to the speed of light c in a vacuum divided by the index of refraction n1(Equation26.1). The index of refraction can be obtained by noting that the light is incident at thecritical angle θc (which is known). According to Equation 26.4, the index of refraction n1 isrelated to the critical angle and the index of refraction n2 by12c/sinn nθ=.The time t it takes for the light to travel from A to B isDistance Speed of lightin the substance dtv==(1)The speed of light v in the substance is related to the speed of light c in a vacuum and theindex of refraction n1 of the substance by v = c/n1(Equation 26.1). Substituting thisexpression into Equation (1) gives11d n d dt c v cn ===⎛⎫ ⎪⎝⎭(2)Since the light is incident at the critical angle θc , we know that 1c 2sin n n θ= (Equation 26.4). Solving this expression for n 1 and substituting the result into Equation (2) yields()2c 181.634.60 m sin sin 48.1 3.3610 s 3.0010 m/sn d d n t c c θ−8⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪ ⎪︒⎝⎭⎝⎭====⨯⨯2. A film of oil lies on wet pavement. The refractive index of the oil exceeds that of the water. The film has the minimum nonzero thickness such that it appears dark due to destructive interference when viewed in red light (wavelength = 640.0 nm in vacuum). Assuming that the visible spectrum extends from 380 to 750 nm, for which visible wavelength(s) in vacuum will the film appear bright due to constructive interference?Solution:When the light strikes the film of oil from above, the wave reflected from the top surface of thefilm undergoes a phase shift that is equivalent to one-half of a wavelength, since the light travels from the smaller refractive index of air toward the larger refractive index of oil. On the other hand, there is no phase shift when the light reflects from the bottom surface of the film, since the light travels from the larger refractive index of oil toward the smaller refractive index of water. Thus, the net phase change due to reflection from the two surfaces is equivalent to one-half of a wavelength in the film. This half-wavelength must be combined with the extra distance 2t traveled by the wave reflected from the bottom surface, where t is the film thickness. Thus, the condition for destructive interference is3511filmfilm film film2222Extra distance Half-wavelength Condition for traveled by wave net phase change destructive interferencein the filmdue to reflection2, , , t λλλλ+=Note that the left-hand side of this equation is greater than 1film2λ. Thus, the right-hand side must also be greater than 1film 2λ. The smallest value that is greater than 1film2λ is the term 3film2λ. Therefore, we have that 31film film222= t λλ+, or film 2 = t λ. Since()film vacuum film film /640.0 nm /n n λλ== (see Equation 27.3), the condition for destructiveinterference becomesfilm film640.0 nm2t n λ==(1)The condition for constructive interference is1filmfilm2Extra distance Condition for Half-wavelengthtraveled by wave constructive net phase change in the filminterferencedue to reflection2 t m λλ''+=1, 2, 3,4m =where filmλ' is the wavelength that produces constructive interference in the film. Solving this relation for 2t gives()()vacuum 11film 22film2t m m n λλ''=−=− (2)Setting Equations (1) and (2) equal to each other and solving for vacuum λ' yields()vacuum 1vacuum 21film film 2640.0 nm 640.0 nm or m n n m λλ''=−=− For m = 1, vacuum λ'=1280 nm; for m = 2, vacuum λ'= 427 nm; for m = 3, vacuum λ'= 256 nm.Values of m greater than 3 lead to values of vacuum λ' that are smaller than 256 nm. Thus, theonly wavelength in the visible spectrum (380 to 750 nm) that will give constructive interference is 427 nm .3. The central bright fringe in a single-slit diffraction pattern has a width that equals the distancebetween the screen and the slit. Find the ratio λ/W of the wavelength λ of the light to the width W of the slit. Solution:19. REASONING The angle θ at which a darkfringe is located in the diffraction pattern of asingle slit is specified by sin m Wλθ=(Equation 27.4), where 1,2,3,...m =, λ is the wavelength of the light, and W is the width of the slit. The drawing at the right shows the angle θ and the positions of the slit and the screen. The width of the central bright fringe is determined by the location first dark fringe()1m = on either side of midpoint of thecentral bright fringe. As the drawing shows, the distance between the midpoint of the central bright fringe and the first dark fringe is y , so the width of the central fringe is 2y .Using Equation 27.4 for the first-order dark fringes (m = 1) and referring to the drawing, we see that22sin (1)y WL yλθ==+Since the distance L between the slit and the screen equals the width 2y of the central bright fringe, this equation becomes()2210.44752yWy y λ===+4. There are four charges, each with a magnitude of 3.0 μC . Two are positive and two are negative.The charges are fixed to the corners of a 0.45-m square, one to a corner, in such a way that the net force on any charge is directed toward the center of the square. Find the magnitude of the net electrostatic force experienced by any charge.Solution:In order for the net force on any charge to be directed inward toward the center of the square, the charges must be placed with alternate + and – signs on each successive corner. The magnitude of the force on any charge due to an adjacent charge located at a distance r isMidpoint of central bright fringeW θyLFirst dark fringe()()()229226228.9910N m /C 3.010C 0.40N 0.45m k q F r−⨯⋅⨯===The forces due to two adjacent charges are perpendicular to one another and produce aresultant force that has a magnitude ofadjacent 0.57 N F ===The magnitude of the force due to the diagonal charge that is located at a distance of is(diagonal 22220.40 N0.20 N 22k qk qF r ====since the diagonal distance is The force F diagonal is directed opposite to F adjacent(since the diagonal charges are of the same sign). Therefore, the net force acting on any of the charges is directed inward and has a magnitudeF net = F adjacent – F diagonal = 0.57 N – 0.20 N = 0.37 N5. The drawing shows an electron entering the lower left side of a parallel plate capacitor andexiting at the upper right side. The initial speed of the electron is 6.00 × 106 m/s. The capacitor is 2.00 cm long, and its plates are separated by 0.150 cm. Assume that the electric field between the plates is uniform everywhere and find its magnitude.Solution:According to 0/E F q = (Equation 18.2) and y F ma = (Equation 4.1), we have00y ma F E q q == (1)From kinematics we know that the electron’s displacement in the upward direction at the time t that it exits the capacitor is 20.150 10 m y −=⨯ and is given by 122y y a t = (Equation 3.5b with 00 m /s y v = since the electron is initially not moving in the y direction). We can solve this equation to obtain 22/y a y t = and substitute this result into Equation (1):2002y ma m yE q q t==(2) We also know that the electron’s displacement in the horizontal direction at the time t that it exits the capacitor is 22.00 10 m x −=⨯ and is given by 0x x v t =, since the horizontal speed of the electron is 60 6.00 10 m /s x v =⨯ and remains constant during the motion. We can solve this equation to obtain 0/x t x v = and substitute this result into Equation (2):()202220000222/x x m yv m y m y E q t q x q x v === (3)With 190 1.60 10 C q e −=−=−⨯ as the electron charge and 319.11 10 kg m −=⨯ as the electron mass, Equation (3) gives()()()()()23126202219209.11 10 kg 20.150 10 m 6.00 10 m /s 21540 N/C 1.60 10 C 2.00 10 m x m yv E q x −−−−⨯⨯⨯===−−⨯⨯This result is negative, because the electric field points downward in the drawing thataccompanies the problem, which is the direction that we assumed to be the negative y direction. The magnitude of the electric field, then, is 1540 N/C .6. What is the magnitude of electric field at location P , which has a distance of r above aninfinitely large plate with uniform density of charge λ (charge of the plate in a unit area)?SOLUTIONWe may select any columns passing through the plate as a closed surface. If the area of the top cover is A, then by Gauss Law:2E∙A=λA ε0So the electric field strengthE=λ2ε0One interesting thing is that E does not change with the distance of the point to the plate. This is the reason why we can generate an even electric field by large plates.7.We have discussed in lecture that the electric potential at a point near an infinitely long straightline with evenly distributed charges can only take locations 1 m away as reference and be calculated by V=−λ2πε0ln r. Here λis the density of charge (charge taken by unit length of the line), and r is the distance of the point to this line. If right below the point, another point charge Q with charge q is added (see the drawing), what should be the new relationship between V and r?SOLUTIONThe major reason why we cannot add the electric potential caused by the line and the charge is that they are related to different reference. So if we can calculate the electric potential generated by the point charge rated to 1 m away, then they can be added together.Now we know the electric potential at P generated by the point charge related to infinitely far point:V p=k q rLet r0=1m, the electric potential at 1 m generated by the point charge related to infinitely far point:V0=k q r0So the electric potential at P generated by the point charge related to 1 m far away is:V p−V0=k qr−kqr0So the electric potential at P generated by both point charge and line related to 1 m far away is:V=V l−V p−V0=k qr−kqr0−λ2πε0ln r=14πε0(qr−qr0−2λln r)(Both forms are correct.)8.Capacitor A and capacitor B both have the same voltage across their plates. However, theenergy of capacitor A can melt m kilograms of ice at 0 °C, while the energy of capacitor B can boil away the same amount of water at 100 °C. The capacitance of capacitor A is 9.3 μF. What is the capacitance of capacitor B?SOLUTIONBy fusing and vaporizing the same amount of water, the energy stored in two capacitor should follow:E A E B =L FL V=333kJ/kg2260kJ/kgThe energy stored in capacitor can be calculated by:E A=12C A V2E B=12C B V2SoC B=C A L VL F=9.3μF2260kJ/kg333kJ/kg=63.1μF9.Two cylindrical rods, one copper and the other iron, are identical in lengths and cross-sectionalareas. They are joined end to end to form one long rod. A 9.0-V battery is connected across the free ends of the copper-iron rod. What is the voltage between the ends of the copper rod?REASONING AND SOLUTION The voltage VCubetween the ends of the copper rod is givenby Ohm’s law as VCu = IRCu,where RCuis the resistance of the copper rod. The current I in thecircuit is equal to the voltage V of the battery that is connected across the free ends of the copper-iron rod divided by the equivalent resistance of the rod. The copper and iron rods are joined end-to-end, so the same current passes through each. Thus, they are connected in series, so the equivalent resistance R S is R S = R Cu + R Fe . Thus, the current isS Cu FeV V I R R R ==+The voltage across the copper rod isCu Cu CuCu Fe VV IR RR R ==+The resistance of the copper and iron rods is given by R Cu = ρCu L /A and R Fe = ρFe L /A , wherethe length L and cross-sectional area A are the same for both rods and ρCu and ρFe denote the resistivites. Substituting these expressions for the resistances into the equation above and using resistivities from Table 20.1 yieldCu CuCuFe 8Cu 889.0V (1.7210m)14V 1.7210m 9.710m V V V ρρρ−−−⎛⎫= ⎪ ⎪+⎝⎭⎛⎫=⨯Ω⋅= ⎪⨯Ω⋅+⨯Ω⋅⎝⎭.10. To save on heating costs, the owner of a greenhouse keeps 675 kg of water around in barrels.During a winter day, the water is heated by the sun to 12.0 ℃. During the night the water freezes into ice at 0 ℃ in nine hours. Suppose the night lasts for 9 hours. What is the minimum ampere rating of an electric heating system (240 V) that would make water temperature back to 12.0 ℃ through the night?REASONING AND SOLUTION The energy Q 1 that is released when the water cools from an initial temperature T to a final temperature of 0.0 °C is given by Equation 12.4 as Q 1 = cm (T – 0.0 °C). The energy Q 2 released when the water turns into ice at 0.0 °C is Q 2 = mL f , where L f is the latent heat of fusion for water. Since power P is energy divided by time, the power produced is12f(0.0)Q Q cm T C mL P tt+−︒+==The power produced by an electric heater is, according to Equation 20.6a, P = IV .Substituting this expression for P into the equation above and solving for the current I , we getf4(0.0)(4186J/kg C )(675kg)(12.0C )(675kg)(33.510J/kg)33A3600s (9.0h)(240V)h cm T C mL I tVI −︒+=⋅︒︒+⨯==⎛⎫ ⎪⎝⎭11. A 90.0-Ω and a 40.0-Ω resistor are connected in parallel. When this combination is connectedacross a battery, the current delivered by the battery is 0.294 A. When the 40.0-Ω resistor is disconnected, the current from the battery drops to 0.116 A. Determine (a) the emf and (b) the internal resistance of the battery REASONING AND SOLUTION a. In the first case the parallel resistance of the 75.0 Ω and the 45.0 Ω resistors have anequivalent resistance that can be calculated using Equation 20.17:p p 111or27.790.040.0R R =+=ΩΩΩOhm’s law, Emf = IR gives Emf = (0.294 A)(27.7 Ω + r ), orEmf = 8.14 V + (0.294 A)r(1)In the second case, Emf = (0.116 A)(90.0 Ω + r), orEmf = 10.44 V + (0.116 A)r(2) Multiplying Equation (1) by 0.116 A, Equation (2) by 0.294 A, and subtracting yieldsEmf = 11.9 Vb. Substituting this result into Equation (1) and solving for r gives r = 12.8 Ω.12.None of the resistors in the circuit shown in the drawing is connected in series or in parallelwith one another. Find (a) the current I5 and the resistances (b)R2 and (c)R3SOLUTIONa. The sum of the currents flowing into the battery must equal the sum of the currents flowing outof the battery:25135132into the out of the battery batteryso 9.0 A 12.0 A 6.0 A 15.0 A I I I I I I I I +=+=+−=+−=b. To apply Kirchhoff’s loop rule to loop CAB (see the drawing), we imagine traversing theloop counter-clockwise. Observing the + and − signs encountered along the way, we see that the potential rises when we cross the battery, and drops when we cross each resistor. The sum of the potential rises must equal the sum of the potential drops, so we have that1122Potential Potential rises drops VI R I R =+ (1)Solving Equation (1) for R 2, we obtain()()1122112275.0 V 9.0 A 4.0 or 6.5 6.0 A V I R I R V I R R I −−Ω=−===Ωc. This time, we apply the loop rule to loop CAED (see the drawing), traversing it clockwise. This procedure yields3355Potential Potential rises drops VI R I R =+ (2)Solving Equation (2) for R 3, we obtain()()5533553375.0 V 15.0 A 2.2 or 3.5 12.0 A V I R I R V I R R I −−Ω=−===Ω。
1. S: 2kv dtdva -==2kv dxdvv dt dx dx dv -==k d x v dvxx vv -=⎰⎰)(ln00x x k v v--= )(00x x k e v v --= (answer)2. S: j t i t dt rd v )3cos 15()3sin 15(+-== jt i t dtv d a )3sin 45()3cos 45(-+-==()()j t i t j t i t v r)3cos 15()3sin 15()3sin 5()3cos 5(+-⋅+=⋅j j t t i i t t⋅⋅+⋅⋅-=)3c o s 3s i n 75()3sin 3cos 75( 0= (proved c)3. S: dtdv v m k m f a =-==dt mkv dv t t v v -=⎰⎰0)(0t mkv t v -=0)(ln t m ke v t v -=0)( (answer) D: t m k e v dtdxv -==0dt e v dx t m k tt x -⎰⎰=00)(0kmv x e kmv ekmv t x t m k t t mk 0max 00),1()(=-=-=--4. S: )()32(j y d i dx j i x r d f dw+⋅+=⋅=dy xdx dw w fi32+==⎰⎰dy xdx 323342⎰⎰--+== -6 J (answer)5. S: 23230.60.4)0.30.4(t t t t t dtddt d +-=+-==θω, t t t dtddt d 60.6)30.60.4(2+-=+-==ωα 0.40300.60.4)0(2=⨯+⨯-=ω (answer of a)0.28)0.4(30.40.60.4)0.4(2=⨯+⨯-=ω rad/s (answer of a ) 60.266)0.2(=⨯+-=α rad/s 2 (answer of b )t t 60.6)(+-=α is time varying not a constant (answer of c) 6. S: ω20031222ML L v m L mv +⋅= MLmv ML L mv 4343020==ω (answer a))c o s 1(2)31(21m a x 22θω-=LMg ML ]1631[cos 2221maxgLM v m -=-θ (answer b) 7. G: m =1.0g, M =0.50kg, L =0.60m, I rod =0.0602m kg ⋅,s rod /5.4=ωR:I sys , v 0S: I sys =I rod +(M+m)L2=0.060+(0.50+0.0010)×0.602= 0.24 2m kg ⋅(answer)the system ’s angular momentum about rotating axis is conservative in the collision.sysI L mv ω=0s m mL I v sys/108.160.00010.024.05.430⨯=⨯⨯==ω (answer )D: The bullet momentum 0v m p=(before impact), its angular momentumabout rotating axis can be expressed as L mv 0(a scalar) 8. S:γ==00.800x xt v c -∆==0811800.600 3.0010t t γ∆=∆=⨯⨯ 9. S: 202202)(mc E cp E E γγ==+=222c p m c m c m c =10. S: 0i n t =-=∆n e t n e t W Q E n e t n e t W Q = 1(3010)(4.0 1.0)2=-- J 30= (answer)11. S: from nRT PV =and K T A 300= we can get:KT K T C B 100300== (answer of a)Change of internal energy between A and B:0)(23int =-=∆A B T T k n E (answer of b)The net work of the cycle:))(100300()13(2121m N AC BC W ⋅-⋅-=⋅=J 200= (answer of c) From the first law : W E Q +∆=int we can derive:the net heat of the whole cycle is J W Q 200== (answer)12. S: 131)(320===⎰⎰∞F v Av dv Av dv v p F33FvA =(answer of a ) F F v a v g v Av dv vAv v F4341420===⎰13. G: T 1=T 2=T , m 1, p 1, v rms,1, m 2, p 2=2p 1, v avg,2 = 2v rms,1 R: m 1 / m 2 S: v avg,2 =1.602m kTv rms,1 = 1.731m kTv avg,2 = 2v rms,167.4)60.173.12(221=⨯=m m (answer) 14. S: dE int =dQ – dWd Q = dE int + dW = n C v dT+pdV VdVnR T dT nC dV T p T dT nC T dQ dS v v +=+==if i f v VV v T T V V nR T T nC V dVnR T dT nC ds S f i filnln +=+==∆⎰⎰⎰ 15. S: dA E q θεcos 0⎰=212100)0.60100(1085.8⨯-⨯⨯=- C 61054.3-⨯= 16. S: 2041)(r Qr E πε=(R < r <∞) dr rQ dr r E udV dU 2022208421πεπε=⋅== RQ r dr Q udV U R0220288πεπε===⎰⎰∞(answer) RQ r dr Q U r r Rεπεεπε02202*88==⎰∞(answer ) 18. S: in the shell of r – r + drdr r R r dV r dq 204)/1()(πρρ-==)34(31)/(4)(4303200r Rr dr R r r dq r q r-=-==⎰⎰πρπρfrom the shell theorems , within the spherical symmetry distribution )34(12)(41)(20020r Rr Rr r q r E -==ερπε (answer of b)R r r R Rdr dE 320)64(12*00=⇒=-=ερ 00200*max 9])32(3324[12)(ερερRR R R R r E E =-⨯== 19. S: j yV i x V V gradV y x E∂∂-∂∂-=-∇=-=),( )0.20.2(y x x VE x +-=∂∂-= x yV E y 0.2-=∂∂-= )/(480.2)0.20.2()0.2,0.2(m V j i j x i y x E--=-+-=20. S: Q in = - q , Q out = q (answer ) 1010241241)0(R qq V q πεπε==104)0(R qV in πε-=204)0(R q V o u t πε=)0()0()0()0(out in q V V V V ++= )11(4210R R q +=πε21. S: from the planar symmetry and superposition principle, Emust in normal direction of the plates and 1σ,2σ,3σ,4σ must be const. Fromcharge conservationA Q S =+)(21σσ ⇒ SQ A=+21σσ (1) B Q S =+)(43σσ ⇒ SQ B=+43σσ (2) Apply Gauss ’ law in the closed surface shown in Fig. 032=+σσ (3)within the metal, 0=p Ewhich leads to002222432104030201=-++⇒=-++σσσσεσεσεσεσFrom(1), (2), (3), (4) yield:⎪⎪⎩⎪⎪⎨⎧-=-=+==S Q Q SQ Q B AB A 223241σσσσ (answer of a) (6 points) 004030201122222εεσεσεσεσS Q Q E BA p -=--+= (1 point) 004030201222222εεσεσεσεσS Q Q E BA p +=+++=(1 point) (answer of b) d S Q Q d E d E V BA p AB 012ε-==⋅= (2 points) (answer of c)27.33()(32)18w F x dx x dx J ==+=⎰⎰;at x=3m212W mV =, 6/V m s =。