西尔斯大学物理双语版题目
- 格式:doc
- 大小:124.50 KB
- 文档页数:7

英文版物理题以下就是小编给大家盘点的英文版物理题,仅供大家参考。
以下是一些英文版物理题:1.A50kg block is resting on a frictionless horizontal surface.A force of100N is applied to the block in the horizontal direction.What is the acceleration of the block?2.An object is thrown vertically upwards with an initial velocity of20m/s.忽略空气阻力,计算该物体达到最高点所需的时间和高度。
3.A ball is thrown horizontally with a velocity of10m/s from a height of5m.Calculate the horizontal distance the ball travels before hitting the ground.4.A10kg mass is attached to a spring with a spring constant of50N/m.The mass is displaced 0.2m from its equilibrium position and released. Calculate the maximum speed of the mass as it oscillates back and forth.5.A current of5A flows through a resistor witha resistance of10Ω.Calculate the potential difference across the resistor.These are just a few examples of英文版物理题.The specific questions and topics will depend on the level of physics and the course curriculum.。


大学物理英语教材题库Introduction:Physics is a fundamental subject that plays a crucial role in understanding the laws and principles that govern the natural world. For university students studying physics, it is important to have access to a comprehensive and reliable textbook that not only covers the core concepts but also offers a variety of practice questions. In this article, we will explore the importance of a physics textbook in English, specifically designed for university students.Section 1: Benefits of a Physics Textbook in English1.1 Enhanced Language Skills:Studying physics in English can improve language proficiency, particularly in scientific terminology and usage. A physics textbook in English enables students to develop their reading and comprehension skills, as well as expand their vocabulary within the context of physics.1.2 Global Perspective:English is the international language of science, and having a physics textbook in English allows students to access a wider range of resources and research materials. It provides exposure to scientific advancements and discoveries from around the world, fostering a global perspective in the field of physics.1.3 Preparation for Academic and Professional Success:With English being the dominant language in academic and professional settings, a physics textbook in English equips students with the necessary language skills for higher education and future scientific careers. It prepares students for international collaborations, conferences, and research work.Section 2: Features of an Effective Physics Textbook2.1 Comprehensive Coverage:An ideal physics textbook should cover all the essential topics and concepts in a systematic and thorough manner. It should include detailed explanations, diagrams, and examples to facilitate understanding. Additionally, it should provide practice questions to reinforce learning.2.2 Relevance to University Curriculum:The content of a physics textbook should align with the university curriculum to ensure that students are studying relevant and up-to-date material. It should follow a logical progression, building upon previously learned topics and preparing students for advanced physics courses.2.3 Engaging and Interactive Elements:To sustain student interest, a physics textbook should incorporate interactive elements such as online simulations, videos, or supplementary materials. These features enhance the learning experience and provide opportunities for hands-on exploration of physics concepts.2.4 Diversity of Question Types:A good physics textbook should contain a diverse range of question types, including multiple-choice, numerical, conceptual, and problem-solving questions. This variety allows students to develop a comprehensive understanding of physics principles and practice different problem-solving techniques.Section 3: Importance of a Physics Question Bank3.1 Assessment Preparation:A physics question bank serves as a valuable resource for exam preparation. It provides students with a wide range of practice questions that cover different topics and difficulty levels. Students can assess their understanding and identify areas for improvement through regular practice.3.2 Reinforcement of Concepts:Practice questions in a physics question bank reinforce the understanding of key concepts and principles. By attempting various types of questions, students can solidify their knowledge and develop problem-solving skills, ultimately leading to better performance in exams.3.3 Self-paced Learning:A physics question bank allows students to learn at their own pace. They can choose specific topics or question types to focus on, enabling personalized learning and targeted improvement in areas of weakness. This flexibility promotes independent learning and self-motivation.Conclusion:In conclusion, a physics textbook in English designed for university students plays a vital role in enhancing language skills, providing a global perspective, and preparing students for academic and professional success.An effective physics textbook should have comprehensive coverage, relevance to the curriculum, engaging elements, and a diverse range of question types. Additionally, a physics question bank is essential for assessment preparation, concept reinforcement, and self-paced learning. By utilizing these resources, students can excel in their study of physics and develop a strong foundation for future endeavors in the field.。

Beijing University of Posts and TelecommunicationsUniversity PhysicsDepartment of Physics School of Science2006Professor XiaoguangZhangReference BooksPhysics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics: D. C. Giancoli. (高等教育出版社)Sears and Zemansky’s University Physics: 西尔斯物理学,Young & Freedman, (机械工业出版社)《大学物理学》(五本),张三慧,(清华大学出版社)《大学物理学》(三本),吴百诗主编,(高等教育出版社) 习题指导书——《吴百诗大学物理学习题分析与解答》,李存志等,(高等教育出版社)。
Chapter 1 Introduction and VectorsImportant contentsSignificant figures (有效数字).¾How to denote the significant figures for a number?¾Scientific notation.¾How to treat the number of significant figures when multiplying or dividing, and adding or subtracting.SI unit system (单位制).¾Base units & derived units; 7 base units for SI unit system.¾The standards of Length, Time, and Mass.¾Unit prefixes.Dimensions and Dimensional analysis (量纲与量纲分析).¾Check an equation by dimensional consistency.Order-of-magnitude.§1 Measurements, Estimating (Self taught)The transmission speed for optical fiber telecommunicationsAmerican standard: SONET (synchronous optical network).International standard: SDH (synchronous digital hierarchy).bit rate for OC-768 (STM-256)=39.813 Gbit/s ≈40Gbit/s, the bit period T B ≈25 ps20.0 ps/div40 Gbit/s RZ code50.0 ps/div10 Gbit/s RZ codeThe screens of an oscilloscopeAn older unit of length used for atomic scale: angstrom (A)In Bohr theory of hydrogen, the orbits of the electron around the proton are quantized: r n =n 2a 0The smallest radius a 0is called the Bohr Radius .。
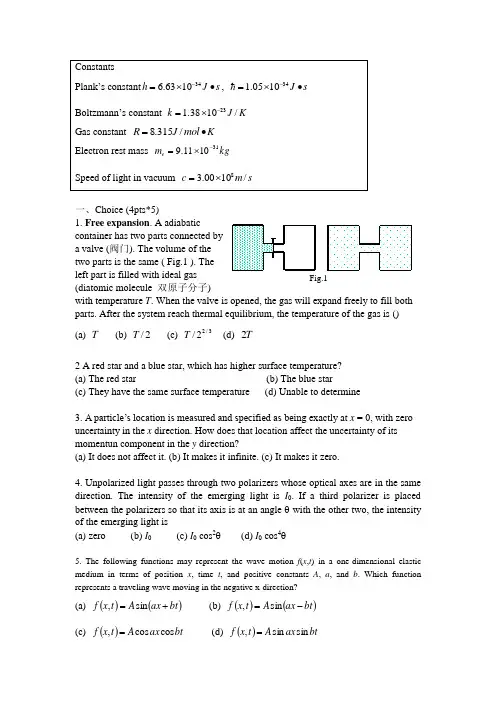
一、Choice (4pts*5)1. Free expansion . A adiabaticcontainer has two parts connected bya valve (阀门). The volume of thetwo parts is the same ( Fig.1 ). Theleft part is filled with ideal gas (diatomic molecule 双原子分子)with temperature T . When the valve is opened, the gas will expand freely to fill both parts. After the system reach thermal equilibrium, the temperature of the gas is () (a) T (b) 2/T (c) 3/22/T (d) T 22 A red star and a blue star, which has higher surface temperature?(a) The red star (b) The blue star(c) They have the same surface temperature (d) Unable to determine3. A particle’s location is measured and specified as being exactly at x = 0, with zero uncertainty in the x direction. How does that location affect the uncertainty of its momentun component in the y direction?(a) It does not affect it. (b) It makes it infinite. (c) It makes it zero.4. Unpolarized light passes through two polarizers whose optical axes are in the same direction. The intensity of the emerging light is I 0. If a third polarizer is placed between the polarizers so that its axis is at an angle θ with the other two, the intensity of the emerging light is(a) zero (b) I 0 (c) I 0 cos 2θ (d) I 0 cos 4θ5. The following functions may represent the wave motion f (x ,t ) in a one-dimensional elastic medium in terms of position x , time t , and positiveconstants A , a , and b . Which function represents a traveling wave moving in the negative x-direction?(a) ()()bt ax At x f +=sin , (b) ()()bt ax A t x f -=sin ,(c) ()bt ax A t x f cos cos ,= (d) ()bt ax A t x f sin sin ,=Fig.1二、Blanks (20pts)6. (8 pts) A 500 g mass is undergoing simple harmonic oscillation that is described by the following equation for its position x (t ) from equilibrium:()⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡+=rad 0.6rad/s 0.6cos )m 50.0()(ππt t x The amplitude A of the oscillation is m. The frequency of the oscillation is Hz. The period T of the oscillation is s. The phase of oscillator at t = 0 s is rad. The maximum speed of the oscillator is m/s .7. (3pts) When Newton ring apparatus is immersed in a liquid, the diameter of the eighth dark ring decreases form 2.92cm to 2.60cm, the refractive index of the liquid is .8. (3pts) In single slit diffraction experiment, 680nm light falls on a slit 0.0345mm wide. The angular width of the center diffraction peak is .9. (3pts) The angular separation of the two components of a double star is 8×10-3 rad and the light from the double stat har a wavelength of 550 nm. According to the Rayleigh criterion, the smallest diameter of a telescope mirror that will resolve the double star is ______ m.10. (3pts) The De Broglie wavelength of a electron moving at 5.9×106m/s is .三、Questions (10pts)11. (5pts) The oceans contains a tremendous amount of thermal energy. Why, in general, it is not possible to put it into useful work.12. (5pts) what are the two postulates of Einstein ’s Special Theory of Relativity?四、Problems (50pts)13. (10pts) For 1 mole O 2 at room temperature (20℃),(1) what is the average transitional kinetic energy of the molecules?(2) what is the rms speed of the molecules?(3) what is the internal energy of the gas?14. (10pts) The PV diagram of the cycle in Carnot ’s engine is shown in Fig 2. The Carnot cycle has 4 processes:1 2: Isothermal expansion with addition of heat |Q H |;2→3: Adiabatic expansion;3→4: Isothermal compression with heat |Q L | flowing out;4→1: Adiabatic compression.(1) Calculate |Q H | and |Q L |. (Suppose the gas is n mole) (2) Show that the efficiency of Carnot engine is H LT T -=1ηFig.215 (17pts) In the double - slit interference experiment (Fig. 3a), 550 nm light falls on the double-slit with two very narrow slit 0.10 mm apart. A viewing screen is 1.0 m far from the double-slit.(1) What is the separation between the 2nd-order bright fringe and the 3rd-order bright fringe?(2) A thin flake of mica (云母, n =1.58) is used to cover one slit of a double – slit (Fig. 3b). The central point on the viewing screen is now occupied by what had been the seventh bright slid fringe (m =7) before the mica was used. What is the thickness L of the mica?(3) Is the separation between adjacent bright fringes changed?16 (13 pts) A 1 kg mass oscillates on the end of a spring whose spring constant is k =2500N/m. If this system is in a spaceship moving pass the Earth with a speed of 0.8c, what ’s the period of the system seen by (1) the observers on the spaceship; (2) the observers on the Earth L 0.11mm 1.0m Fig. 3b 0.11mm1.0mFig. 3az。

大学物理试题(国外英文资料)College physics examination questionsFirst, the multiple-choice questions: (39 points)1. (3 points)The acceleration of a particle moving at a radius of R is the magnitude of the acceleration (V means the velocity of a particle at any time)(A) (B)(C) (D) [[]]2. (3 points)An object of mass m falls from the air and is affected by gravity as well as a resistance proportional to the square of velocity. The coefficient of proportionality is k, and K is the normal number. The closing velocity of the falling object (i.e., the speed at which the final object moves at uniform speed) will be(A) (B)(C) GK (D) [[]]3. (3 points)A spring oscillator of M quality is placed horizontally at rest in equilibrium. As shown, a bullet with a mass of M is injected into the oscillator at a horizontal velocity and then moved along with it. If the level is smooth, then the maximum potential energy of the spring is(A) (B)(C) (D) [[]]4. (3 points)A child of the quality of M stands on the edge of a horizontal platform with a radius of R. The platform can rotate freely through a vertical, smooth, fixed axis through its center. The moment of inertia is J. Both the platform and the child are stationary at the start. When the child suddenly moves counter clockwise toward the edge of the platform at a rate of V relative to the ground, the angular velocity and the rotation direction of the platform relative to the ground are(A) clockwise.(B) counter clockwise.(C) clockwise.(D) counter clockwise. [...]5. (3 points)Two different ideal gases, if their most probable rates are equal, their(A) equal to the average rate, root mean square speed equal.(B) equal to the average rate, root mean square speed is not equal.(C) the average rate is not equal, the root mean square speed equal.(D) the average rate is not equal, not equal to the root mean square speed. [...]6. (3 points)According to the second law of thermodynamics:(A) work can be converted to heat, but heat can not be converted to power.(B) heat can be transferred from a hot object to a cryogenic substance, but not from a cryogenic object to a high temperature object.(C) irreversible processes are processes that cannot proceed in the opposite direction.(D) all spontaneous processes are irreversible. [...]7. (3 points)There are several explanations for the interpretation of Gauss's theorem:(A) if the Gauss surface is zero everywhere, there is no charge in the plane.(B) if the Gauss surface has no charge, then the Gauss surface is zero everywhere.(C) if there is no zero on the Gauss surface, there must be charges in the Gauss plane.(D) if there is a net charge in the Gauss plane, the electric flux through the Gauss surface must not be zero.(E) Gauss's theorem applies only to electric fields with high symmetry. [...]8. (3 points)The radius of the cross section of a long straight wire is a, and a thin cylinder with a radius of B is coaxially arranged outside the conductor, and the two of them are insulated from each other. And the outer cylinder is grounded as shown. The electric charge per unit length of the wire is +, and the potential of the earth is zero. Then the field strength and the electric potential of the P point (Op=r) between the twoconductors are respectively:(A)(B)(C)(D) [[]]9. (3 points)The square coils with side lengths are respectively represented by two modes of current I (wherein the AB and CD are coplanar with the square), and in these two cases, the magnetic induction intensity of the coil at the center of the coil is respectively(A)(B)(C)(D) [[]]10. (3 points)The picture shows four charged particles in the same direction perpendicular to the magnetic field line, and the deflection trajectory of the magnetic field is injected into the uniformmagnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is perpendicular to the surface of the O,The trajectory of the four particles is equal in mass and the magnitude of the electric energy is equal. In that case, the trajectory of the negatively charged particles with the largest kinetic energy is(A) Oa (B) Ob(C) Oc (D) Od [...]11. (3 points)A mass of simple harmonic vibration on the X axis, the amplitude of A = 4cm, T = 2S cycle, its equilibrium position is taken as the origin of coordinates, if t=0 the first moment of the particle by x= 2cm, and to the negative direction of X axis motion is second 2cm particle by x= at the moment(A) 1s (B) (2/3) s(C) (4/3) s (D) 2S [[]]12. (3 points)Using wedge interference method can detect surface defects, when the wavelength of monochromatic parallel light vertical incident, if the interference fringes observed as shown in the figure, each part of the fringe vertex exactly with left fringeof the straight part of the tangent line, then the surface of the workpiece and bending at the corresponding part of the fringe(A) raised, and the height is (B) raised, and the height is...(C) depressions, and the depth is (D) depressions, and the depth is []13. (3 points)A beam of light is a mixture of natural light and polarized light, let it through a vertical polarizer, if this incident beam axis rotating polarizer, the measured transmission light intensity maximum is 5 times the minimum value, then the incident beam in natural light and polarized light intensity ratio is(A) 1 / 2 (B) 1 / 5(C) 1 / 3 (D) 2 / 3Two, fill in the blanks: (46 points)1. (3 points)Let the particles move along the X axis. When the initial condition is t=0, the initial velocity is v0=0, and the coordinate x0=10 is a=4t. Then the equation of motion is.2. (3 points)Under the action of constant force F, an object moves in a straight line. The equation of motion is x=A-Bt+ct2 (A, B, C is constant), and the mass of the object should be m=.3. (3 points)At a constant speed, the quality of M ship, respectively, forward and backward at the same time the level of two throws of equal mass (m) objects thrown two objects relative to the ship the same rate (U) expression of the ship and try to write in the process of the system of the law of conservation of momentum (don't have Jane, for reference).4. (5 points)As shown in the figure, a homogeneous consolidation in a thin rod end ball, and can rotate around a horizontal smooth fixed shaft O to rotate, there is a bullet along with the horizontal angle direction and embedded in the ball hit, then hit in the process of conservation, cricket, bullets, rod system, the reason is. The process of cricket bat and ball increased after being hit in the conservation on cricket, bullets, rod, earth system.5. (3 points)At room temperature, the pressure of the ideal gas of 1 moldiatomic molecules is P, and the volume is V, and the average kinetic energy of the gas molecule is.6. (3 points)If the pressure and volume of an ideal gas remain constant, but the mass and temperature change, then can the internal energy change?.7. (3 points)The thermodynamic temperature of a high temperature heat source is n times of the thermodynamic temperature of a low temperature heat source. In a Kano cycle, the heat delivered by a gas to a cryogenic heat source is twice as much as that obtained from a high temperature heat source.8. (3 points)A simple harmonic wave propagates along the positive direction of the X axis. The relation curves between the vibration velocity and time at two points of X1 and X2 are shown as follows (a) and (b), and the distance between X1 and X2 is known as (lambda lambda).9. (3 points)White light (4000-7000) vertical incidence of 4000 slits per centimeter of grating, can produce the level of the complete visible spectrum.10. (3 points)A charged metal ball, when it is surrounded by a vacuum, stores the electrostatic energy of Wo and keeps its energy constant,It is immersed in an infinite isotropic homogeneous dielectric with relative dielectric constant, when its electrostatic energy is We =.11. (6 points)The three basic assumptions of Bohr's theory of hydrogen atoms are:(1),(2),(3).12. (5 points)An electron at a rate of motion of 0.99c (electron rest mass of 9.11 * 1031kg), then the total electron energy is J, the kinetic energy of classical mechanics and relativistic electron kinetic energy ratio.13. (3 points)Static mass is me the potential for electronic, electrostaticfield accelerated U12, without considering the effect of relativity, the De Broglie wavelength lambda = E.Three. Calculation questions: (65 points)1. (10 points)The equation of motion of a known particle is (as a constant),Find (1) the trajectory equation and velocity of the particle(2) the velocity of a particle and the rotation direction ofa particle(3) the relation between the acceleration of a particle and the vector?2. (10 points)M was a short tube, with a length of hard straight rod suspension as shown in figure L, quality can be ignored, with ether droplets Sheng tube, pipe with mass m cork closed, when the heating tube cork in the ether vapor pressure to fly out, hanging around the tube O in the vertical plane for a complete circular motion, then the minimum speed of the cork flew out for? If you change a hard straight pole into a string, what if?3. (10 points)Having two concentric spherical shells with a radius of insulation for each other, and when the + Q is given to the inner ball:(1) the charge distribution and electric potential of the outer sphere;(2) re insulating the ball after grounding, the charge distribution and the electric potential of the outer sphere(3) then, the inner sphere is grounded, the charge distribution of the inner sphere and the potential of the outer sphere4. (10 points)As shown in the figure, the plane charged ring two coplanar, the inner and outer radius are respectively R1, R2 and R2, R3, the outside of the ring to a second N2 RPM clockwise, inside the ring to a second N1 rpm counterclockwise. If the charge surface density is the ratio of the N1 to the N2, the magnetic induction intensity at the center of the circle is zero.5. (10 points)As shown in the figure, the current long straight conductor for I, a B C D rectangular frame with a long straight conductorcoplanar, and the a D A D C / B a B edge D side is fixed, a and C B to speed without friction uniform translational t=0, a, B and C D side edge coincidence, set line inductance negligible.(1) for example, i=I0, seek the electromotive force in a B, a, B, two points, which point has high potential?(2) the total induced electromotive force in the wire frame when the a b t is moved to the position shown by i=I0cos omega.6. (10 points)A plane harmonic wave propagates along the negative direction of the Ox axis, the wavelength is lambda, and the vibration law of the particle at P is shown in figure.(1) seeking the vibration equation of particle at P;(2) find the wave equation of this wave;(3) in the figure, the vibration equation of the particle at the coordinate origin O is calculated.7. (5 points)In the experiment of single slit Fraunhofer diffraction for white, second bright fringe center is measured at the wavelength of third level bright fringe center and thewavelength for the red wavelength for overlap.Second pageThree hundred and thirty-oneSouth China University of TechnologyIn 2004, I studied the master's degree entrance examination papers(the answer to the test paper is invalid. Please answer it on the answer sheet. After the test, this volume must be returned with the answer sheet.)Subject name: General PhysicsApplicable profession: Philosophy of science and technology Common pageFirst page。
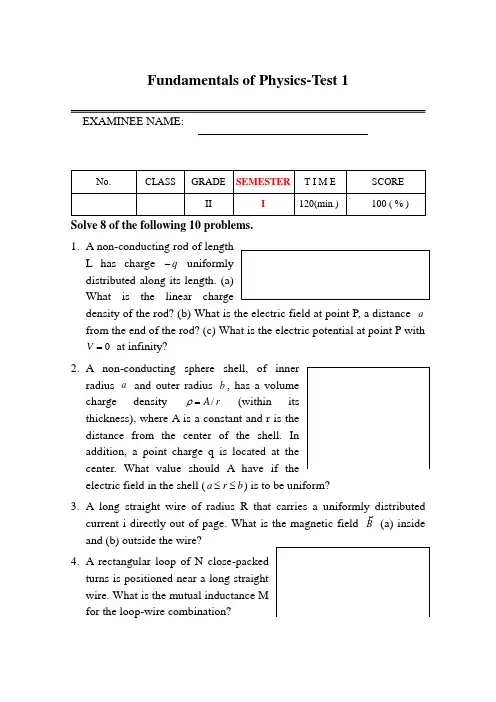
Fundamentals of Physics-Test 1EXAMINEE NAME:Solve 8 of the following 10 problems.1. A non-conducting rod of length L has charge q - uniformlydistributed along its length. (a)What is the linear chargedensity of the rod? (b) What is the electric field at point P, a distance a from the end of the rod? (c) What is the electric potential at point P with 0=V at infinity?2. A non-conducting sphere shell, of inner radius a and outer radius b , has a volumecharge density r A /=ρ (within itsthickness), where A is a constant and r is thedistance from the center of the shell. Inaddition, a point charge qis located at thecenter. What value should A have if theelectric field in the shell (br a ≤≤) is to be uniform?3. A long straight wire of radius R that carries a uniformly distributed current i directly out of page. What is the magnetic field B (a) inside and (b) outside the wire?4. A rectangular loop of N close-packedturns is positioned near a long straightwire. What is the mutual inductance Mfor the loop-wire combination?5. A broad beam of light of wavelength 600nm is sent directly downward through a glass plate (n=1.5) that, with a plastic plate (n=1.2), forms a thinwedge of air which acts as thin film. Anobserver looking down through the topplate sees the fringe pattern shows asthe Figure. With dark fringes centeredon ends A and B. (a) What is thethickness of the wedge at B? (b) How many dark fringes will the observer see if the air between the plates is replaced with water (n=1.33)?6. A diffraction grating is made up of slits of width 300nm with separation 900nm. The grating is illuminated by monochromatic plane waves of wavelength nm 600=λ at normal incidence. (a) How many diffraction maxima are there in the full pattern? (b) What is the width of a spectral line observed in the first order if the grating has 1000 slits?7. A clock moves along the x axis at a speed of 0.600c and reads zero as it passes the origin. (a) Calculate the Lorentz factor. (b) What time does the clock read as it passes x=180m?8. What is the speed of a particle (a) whose kinetic energy is equal to twice its rest energy and (b) whose total energy is equal to twice its rest energy?9. (a) If the work function for a certain metal is 1.8eV , what is its stopping potential for light of wavelength 400nm? (b) What is the maximum speed of electrons emitted via the photoelectric effect as they leave the metal surface (s m c C e s J h /100.3,106.1,1063.681934⨯=⨯=⋅⨯=--)?10. W hat is (a) the momentum and (b) the de Broglie wavelength of an electron whose kinetic energy is 120 eV (,1011.931kg m e -⨯= J eV 19106.11-⨯=)?。

![《物理双语教学习题课》[Solutions]Chapter 1 – NEW PROBLEMS](https://uimg.taocdn.com/139121090740be1e650e9a9e.webp)
Chapter 1– NEW PROBLEMS solutionsN1A million milligrams comprise a kilogram, so 2.3 kg/week is 2.3 x 106 mg/week. Figuring 7 days a week, 24 hours per day, 3600 second per hour, we find 604800 seconds are equivalent to one week. Thus, (2.3 x 106)/(604800) = 3.8 mg/s.N2If we estimate the “typical” large domestic cat mass as 10 kg, and the “typical” atom (in the cat) as 10 u ≈ 2 x 10-26 kg, then there are very roughly (10 kg)/( 2 x 10-26 kg) ≈5 x 1026 atoms. This is close to being a factor of a thousand greater than Avogradro’s number. Thus this is roughly a kilomole of atoms.N3The volume of one unit is 1 cm3 = 1 x 10-6 m3, so the volume of a mole of them is6.02 x 1023 cm3 = 6.02 x 1017 m3. The cube root of this number gives the edge length: 8.4 x 105 m3. This is equivalent to roughly 840 kilometers.N4(a)The volume of the cloud is (3000 m)π(1000 m)2 = 9.4 x 109 m3. Since each cubicmeter of the cloud contains from 50 x 106 to 500 x 106 water drops, then we conclude that the entire cloud contains from 4.7 x 1018 to 4.7 x 1019 drops. Since the volume of each drop is 4π(10 x 10-6 m)3 = 4.2 x 10-15 m3, then the total volume of water in a3cloud is from 2000 to 20000 m3.(b) Each liter is a thousand cubic centimeters (equivalently, a liter is a thousandth of acubic meter), so the amount of water estimated in part (a) would fill from two million to twenty million bottles.(c)At 1000 kg for every cubic meter, the mass of water is from two million to twentymillion kilograms. The coincidence in numbers between the results of parts (b) and(c) of this problem is due to the fact that each liter has a mass of one kilogram whenwater is at its normal density (under standard conditions).N5Equation 1-9 gives (to very high precision!) the conversion from atomic mass units to kilograms. Since this problem deals with the ratio of total mass (1.0 kg) divided by the mass of one atom (1.0 u, but converted to kilograms), then the computation reduces to simply taking the reciprocal of the number given in Eq.1-9 and rounding off appropriately. Thus, the answer is 6.0 ⨯ 1026.N6(a)Dividing 750 mile s by the expected “40 miles per gallon” leads the tourist to believethat the car should need 18.8 gallons (in the U.S.) for the trip.(b)Dividing the two numbers given (to high precision) in the problem (and rounding off)gives the conversion between U.K. and U.S. gallons. The U.K. gallon is larger than the U.S gallon by a factor of 1.2. Applying this to the result of part (a), we find the answer for part (b) is 22.5 gallons.N7The volume of the filled container is 24000 cm3 = 24 liters, which (using the conversion given in the problem) is equivalent to 50.7 pints (U.S). The expected number is therefore in the range from 1317 to 1927 Atlantic oysters. Instead, the number received is in the range from 406 to 609 Pacific oysters. This represents a shortage in the range of roughly 700 to 1500 oysters (the answer to the problem). Note that the minimum value in our answer corresponds to the minimum Atlantic minus the maximum Pacific, and the maximum value corresponds to the maximum Atlantic minus the minimum Pacific.N8A week is 7 days, each of which has 24 hours, and an hour is equivalent to 3600 seconds. Thus, two weeks (a fortnight) is 1209600 s. By definition of the micro prefix, this is roughly 1.21 ⨯ 1012μs.N9(a)The difference between the total am ounts in “freight” and “displacement” tons,(8-7)(73) = 73 barrels bulk, represents the extra M&M’s are shipped. Using theconversions in the problem, this is equivalent to (73)(0.1415)(28.378) = 293 U.S.bushels.(b)The difference between the total amounts in “register” and “displacement” tons,(20-7)(73) = 949 barrels bulk, represents the extra M&M’s are shipped. Using the conversions in the problem, this is equivalent to (949)(0.1415)(28.378) = 3811 U.S.bushels.N10One gry is equivalent to (1/10)(1/12)(72 points) = 0.60 point. Thus, 1 gry2 = (0.60gry2 = 0.18 point2.point)2 = 0.36 point2. Therefore, 12N111460 slugs is equivalent to (1460)(14.6) = 21316 kg. Referring now to the corn, a U.S. bushel is 35.238 liters. Thus, a value of 1 for the corn-hog ratio would be equivalent to 35.238/21316 = 0.00165 in the indicated metric units. Therefore, a value of 5.7 for the ratio corresponds to 0.0094 in the indicated metric units.N12(a)The receptacle is a volume of (40)(40)(30) = 48000 cm3 = 48 L = (48)(16)/11.356 =67.63 standard, which is a little more than 3 nebuchadnezzars (the largest bottleindicated). The remainder, 7.63 standard, is just a little less than 1 methuselah.Thus, the answer to part (a) is 3 nebuchadnezzars and 1 methuselah.(b)Since 1 methuselah.= 8 standard, then the extra amount is 8 - 7.63 = 0.37 standard, or0.26 L.N13According to Appendix D, a nautical mile is 1.852 km, so 24.5 nautical miles is 45.374 km. Also, according to Appendix D, a mile is 1.609 km, so 24.5 miles is 39.4205 km.The difference is 5.95 km.N14(a)We look at t he first (“cahiz”) column: 1 fanega is equivalent to what amount of cahiz?We note from the already completed part of the table that 1 cahiz equals a dozenfanega. Thus, 1 fanega = 112cahiz, or 8.33 ⨯ 10-2 cahiz. Similarly, “1 cahiz = 48cu artilla” (in the already completed part) implies that 1 cuartilla = 148cahiz, or 2.08 ⨯10-2 cahiz. Continuing in this way, the remaining entries in the first column are 6.94 ⨯ 10-3 and 3.47 ⨯ 10-3. In the second (“fanega”) column, we similarl y find 0.250, 8.33 ⨯ 10-2, and 4.17 ⨯ 10-2for the last three entries. In the third (“cuartilla”) column, we obtain 0.333 and 0.167 for the last two entries. Finally, in the fourth (“almude”)column, we get 12= 0.500 for the last entry.(b)Since the conversion table indicates that 1 almude is equivalent to 2 medio, then ouramount of 7.00 almude must be equal to 14.0 medio.(c)Using the value (1 almude = 6.94 ⨯ 10-3 cahiz) found in part (a), we conclude that7.00 almude is equivalent to 4.86 ⨯ 10-2 cahiz.(d)Since each decimeter is 0.1 meter, then 55.501 cubic decimeters is equal to 0.055501m3 or 55501 cm3. Thus, 7.00 almude = 7.0012fanega = 7.0012(55501 cm3) = 3.24 ⨯ 104cm3.N15The volume of the section is (2500 m)(800 m)(2.0 m) = 4.0 x 106 m3. Letting “d” stand for the thickness of the mud after it has (uniformly) distributed in the valley, then its volume there would be (400 m)(400 m)d. Requiring these two volumes to be equal, we can solve for d. Thus, d = 25 m. The volume of a small part of the mud over a patch of area of 4.0 m2 is (4.0)d = 100 m3. Since each cubic meter corresponds to a mass of 1900 kg (stated in the problem), then the mass of that small part of the mud is 1.9 ⨯ 105kg.N16(a)Presuming that a French decimal day is equivalent to a regular day, then the ratio ofweeks is simply 10/7 or (to 3 significant figures) 1.43.(b)In a regular day, there are 86400 seconds, but in the French system described in theproblem, there would be 105 seconds. The ratio is therefore 0.864.N17There are 86400 seconds in a day, and if we estimate somewhere between 2 and 4 seconds between exhaled breaths, then the answer (for the number of dbugs in a day)is 2 ⨯ 104 to 4 ⨯ 104.N18(a)It should be clear that the first column (unde r “wey”) is the reciprocal of the first row– so that 910 = 0.900,340= 7.50 ⨯ 10-2, and so forth. Thus, 1 pottle = 1.56 ⨯ 10-3 weyand 1 gill = 8.32 ⨯ 10-6 wey are the last two entries in the first column. In the second column (under “chaldron”), clearly we have 1 chaldron = 1 caldron (that is, theentries along the “diagonal” in the table must be 1’s). To figure how many chaldron are equal to one bag, we note that 1 wey = 10/9 chaldron = 40/3 bag so that 112chaldron = 1 bag. Thus, the next entry in that second column is 112= 8.33 ⨯ 10-2.Similarly, 1 pottle = 1.74 ⨯ 10-3 chaldron and 1 gill = 9.24 ⨯ 10-6 chaldron.In the third column, we have 1 chaldron = 12.0 bag, 1 bag = 1 bag, 1 pottle = 2.08 ⨯ 10-2 bag, and1 gill = 1.11 ⨯ 10-4 bag. In the fourth column, we find 1 chaldron = 576 pottle, 1 bag= 48 pottle, 1 pottle = 1 pottle, and 1 gill = 5.32 ⨯ 10-3 pottle. In the last column, we obtain 1 chaldron = 1.08 ⨯ 105 gill, 1 bag = 9.02 ⨯ 103 gill, 1 pottle = 188 gill, and, of course, 1 gill = 1 gill.(b)Using the information from part (a), 1.5 chaldron = (1.5)(12.0) = 18.0 bag. And sinceeach bag is 0.1091 m3 we conclude 1.5 chaldron = (18.0)(0.1091) = 1.96 m3.N19Two jalapeño peppers have spiciness = 8000 SHU, and this amount multiplied by 400 (the number of people) is 3.2 x 106 SHU, which is roughly ten times the SHU value for a single habanero pepper. More precisely, 10.7 habanero peppers will provide that total required SHU value.。

Chapter 24 exercises:24-3 a) When the speed of q 2 is 22.0m/s, the kinetic energy of q 2 is21121mv K =; the potential energy of system is 102114r q q U πε=.According to the conservation of energy , when the two spheres are 0.400m apart, the energy is22221mvK =, 202124r q q U πε=. 2211U K U K +=+. We get the speed of q 2 iss m v /5.122=.b) When the q 2 closes to the q 1, the speed of q 2 will slowly until its zero. So the system energy is113U K U +=;10212130214214r q q mv r q q πεπε+=. The distance between the two charges ism r 323.03=.24-7 a) When q 3 is placed at x = +10.0cm, the potential energy of system isJr q q r q q r q q U U U U 7129912991299303120321021*******.310.01085.814.341000.21000.410.01085.814.341000.2)1000.3(20.01085.814.34)1000.3(1000.4444----------⨯-=⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯+⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯-+⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯-⨯⨯=++=++=πεπεπεb) When the potential energy of the system is zero, the q 3 is placed 0444303120321021321=++=++=r q q r q q r q q U U U U πεπεπε3312321210r q q r q q r q q ++=; 2.023=+r rm r 0743.03=.24-9 If zero net work is required to place the three charges at the corners of the triangle, the third charge must be0444000='+'+rq q rq q rqq πεπεπε, 2q q -='.24-25 a) The electron will move with an acceleration to the center of the ring. After through the center, the electron will leave it until the speed is zero. Then it will return to the center and through it to move other side. So the electron will do oscillation.b) According to the conservation of energy, we get K U =,2002144mvReq req =-πεπε.2311291922129191011.92115.01085.814.341024106.130.015.01085.814.341024106.1v⨯⨯⨯=⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯--+⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯⨯--------s m v /1067.17⨯=.24-26 We can suppose the zero potential energy at point p. The distance of point p is R. So we get the initial energy of proton is 2121ln2mv Rr q K U +=+πελ. The final energy of proton isR r q U '=ln202πελ. According to the conservation of energy, we know 22121mv U U =-.221ln2mv r r q ='πελ. The final distance between the line and the proton is cm r 8.15='.24-57 a) Take V = 0, r = b, when r < a, the potential isab dr rr d E r d E r d E V babrarbaln2200πελπελ==⋅+⋅=⋅=⎰⎰⎰⎰.When a < r < b, the potential is rb dr rV brln2200πελπελ==⎰.When r > b, the potential is v = 0.b) Between the inner cylinder and outer cylinder, the electric field is rE 02πελ=. So thepotential difference is ⎰==baab ab dr rV ln2200πελπελ.c) Use Eq. (24-23), we get ()()r a b V r b b rdrdV r E ab 1/ln 220⋅=⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛-⨯⨯-=-=πελ.24-73 a) Use the small element on the rod xdq dV 04πε=, at point P , we getxa x aQ xa x xdxxdq dV V ax xax x+=+====⎰⎰⎰++ln4ln4440000πεπελπελπε.b) At point R, we get⎪⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛++=+===⎰⎰⎰2002201ln 444y a y a a Q yx dxrdqdV V aπεπελπε.c) In part a, when the x is much larger than a, we can think the charged rod like a point charge, so the potential is xQ V 04πε=. In part b, the potential is yQ V 04πε=.24-78 a) From the equation ()2223),,(z y x A z y x V +-=, we can get at any point the electricfield is ()k z j y i x A k z V j y V i x V E 262+--=⎪⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛∂∂+∂∂+∂∂-=. b) At point()()m z y x 250.0,0,0,,=, the potential is )(0625.01V A V ⨯=. At point()()0,0,0,,=z y x , the potential is 02=V . The work done by the electric force isW q V V =-)(21. 651050.10625.01000.6--⨯⨯⨯=⨯A ; 640=Ac) At the point ()()m z y x 250.0,0,0,,=, the electric field is k k E320250.02640-=⨯⨯-=.d) In every plane parallel to the xz-plane, the equation is changed()2223640,,z x yz y x V +=+.So the equipotential contours are circles.e) The radius of the equipotential contour corresponding to V =1280V and y = 2.00m ism r 74.3)00.236401280(212=⨯+=.。

Exercise:1. A particle moving along x axis starts from x 0 with initial velocityv 0. Its acceleration can be expressed in a =-kv 2 where k is a knownconstant. Find its velocity function v =v (x ) with the coordinate x asvariable.2. A particle moves in xy plane with the motion function asj t i t t r )3sin 5()3cos 5()(+=(all in SI). Find (a) its velocity )(t v and (b)acceleration )(t a in the unit-vector notation. (c) Show that v r⊥.3. A bullet of mass m is shot into a sand hill along a horizontalpath, assume that the drag of the sand is kv f -=, find the velocityfunction v(t) if 0)0(v v = and the gravitation of the bullet can beignored.4. what work is done by a conservative force j i x f 32+= thatmoves a particle in xy plane from the initial position j i r i 32+= to the final position j i r f 34--=. All quantities are in SI.5. The angular position of a point on the rim of a rotating wheel isgiven by 320.30.4t t t +-=θ, where θ is in radians and t is inseconds. Find (a) its angular velocities at t=0s and t =4.0s? (b)Calculate its angular acceleration at t =2.0s. (c) Is its angularacceleration constant?6. A uniform thin rod of mass M and length L can rotate freelyabout a horizontal axis passing through its top end o (231ML I =). Abullet of mass m penetrates the rod passing its center of masswhen the rod is in vertical stationary. If the path of the bullet ishorizontal with an initial speed v o before penetration and 20v after penetration . Show that (a) the angular velocity of the rod just after the penetration is MLmv 430=ω. (b) Find the maximum angular max θ the rod will swing upward after penetration.7. A 1.0g bullet is fired into a block (M=0.50kg) that is mountedon the end of a rod (L=0.60m). The rotational inertia of the rodalone about A is 206.0m kg ⋅. The block-rod-bullet system thenrotates about a fixed axis at point A. Assume the block is smallenough to treat as a particle on the end of the rod. Question: (a)What is the rotational inertia of the block-rod-bullet system aboutA? (b) If the angular speed of the system about A just after thebullet ’s impact is 4.5rad/s , What is the speed of the bullet justbefore the impact?8. A clock moves along the x axis at a speed of 0.800c and readszero as it passes the origin. (a) Calculate the Lorentz factor γbetween the rest frame S and the frame S* in which the clock isrest. (b) what time does the clock read as it passes x =180m ?9. What must be the momentum of a particle with mass m sothat its total energy is 3 times rest energy?10. Ideal gas within a closed chamber undergoes the cycle shownthe Fig. Calculate Q net the net energy added to the gas as heatduring one complete cycle.11. One mole of a monatomic ideal gas undergoes the cycleshown in the Fig. temperature at state A is 300K.(a). calculate the temperature of state B and C.(b). what is the change in internal energy of the gas between stateA and state B? (int E )(c). the work done by the gas of the whole cycle .(d). the net heat added to the gas during one complete cycle.12. The motion of the electrons in metals is similar to the motionof molecules in the ideal gases. Its distribution function of speedis not Maxwell ’s curve but given by.⎩⎨⎧=0)(2Av v pthe possible maximum speed v F is called Fermi speed. (a)plot the distribution curve qualitatively. (b) Express the coefficientA in terms of v F . (c) Find its average speed v avg .13. Two containers are at the same temperature. The firstcontains gas with pressure 1p , molecular mass 1m , and rmsspeed 1rms v . The second contains gas with pressure 12p , molecularmass 2m , and average speed 122rm s avg v v =. Find the mass ratio21m m .14. In a quasi-static process of the ideal gas, dW =PdV andd E int =nC v dT . From the 1st law of thermodynamics show that thechange of entropy i f v i fT T nC V V nR S ln ln +=∆ .Where n is the numberof moles, C v is the molar specific heat of the gas at constantvolume, R is the ideal gas constant, (V i , T i ) and (V f , T f ) . are theinitial and final volumes and temperatures respectively.15. It is found experimentally that the electric field in a certainregion of Earth ’s atmosphere is directed vertically down. At analtitude of 300m the field is 60.0 N /C ; at an altitude of 200m , thefield is 100N /C . Find the net charge contained in a cube 100m onedge, with horizontal faces at altitudes of 200m and 300m .Neglect the curvature of Earth.16. An isolated sphere conductor of radius R with charge Q . (a)Find the energy U stored in the electric field in the vacuum outsidethe conductor. (b) If the space is filled with a uniform dielectrics ofknown r ε what is U * stored in the field outside the conductorthen?17. Charge is distributed uniformly throughout the volume of aninfinitely long cylinder of radius R. (a) show that, at a distance rfrom the cylinder axis (r<R), r E 02ερ=, where ρis the volume charge density. (b) write the expression for E when r>R .18. A non-uniform but spherically symmetric distribution ofcharge has a volume density given as follow:⎩⎨⎧-=0)/1()(0R r r ρρwhere 0ρ is a positive constant, r is the distance to the symmetric center O and R is theradius of the charge distribution. Within the charge distribution (r <R ), show that (a) the charge contained in the co-center sphere ofradius r is )34(31)(430r Rr r q -=πρ, (b) Find the magnitude of electricfield E (r ) within the charge (r < R ). (c) Find the maximum field E max =E (r *) and the value of r *.19. In some region of space, the electric potential is the followingfunction of x,y and z: xy x V 22+=, where the potential is measuredin volts and the distance in meter . Find the electric field at thepoint x=2m, y=2m . (express your answer in vector form)20. The Fig. shows a cross section of an isolated spherical metalshell of inner radius R 1 and outer radius R 2. A point charge q is located at a distance 21R from the center of the shell. If the shell is electrically neutral, (a) what are the induced charges (Q in , Q out )on both surfaces of the shell? (b) Find the electric potential V(0) atthe center O assume V (∞)=0.21. Two large metal plates of equal areaare parallel and closedto each other with charges Q A , Q B respectively. Ignore the fringingeffects, find (a) the surface charge density on each side of bothplates, (b) the electric field atp 1, p 2 . (c) the electric potentialA and B)22.In a certain region of space, the electric potential is ()2=-+where A,B,C are positive constant. The ,,,V x y z Axy Bx Cyelectric field is ; at which point is the electric field equal to zero .23. A 9.60-μC point charge is at the center of a cube with sides of length 0.500m. The electric flux through one of the six faces of the cube is ; the answer would be if the sides were of length 0.250m.。