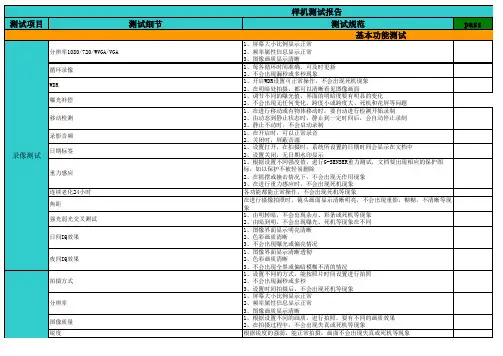
名正行车记录仪测试用例
- 格式:xls
- 大小:94.00 KB
- 文档页数:35

行车记录仪使用说明书功能键(五键)说明一(1)电源键/屏幕背光开关键(2)菜单键/模式键(3)UP键(4)DOWN键(5)OK键(6)摄像头(7)TF槽(8)AVIN接口(9)USB电源接口(10)LCD显示屏(11)复位孔一、功能简介1、使用行车录像功能启动汽车发动机,记录仪自动启动并开启录像功能,录像指示灯闪烁。
当图标显示为红色且时间走动时,按“OK键”暂停/开始录像功能。
关闭汽车发动机,记录仪自动保存录像内容并关机,录像的视频分段保存于TF卡上。
当TF卡存储满后记录仪将覆盖较早前录制的视频。
【注意】a.记录的时间段可自行在菜单中设置为1/2/3/5档,如果选择为“1/2/3/5”分钟这四个档中的任意一档时,当TF卡存储满后记录仪将覆盖较早前录制的影像。
b.前、后摄像头的录像文件和拍照文件分别保存于TF卡中的前录“ VIDEOA”、后录“VIDEOB” 。
2、使用拍照功能在录像界面按“M键”可进入拍照模式,点击0K键可拍摄一张照片。
如需返回主录像界面,短按“M键”两次返回。
在录像界面长按“M键”可进入“拍照设置”菜单,按“上下键”选择,按“0K键”确认,可进行拍照功能设置。
3、视频回放在录像界面按“M键两次”进入回放模式。
按上/下键找到需要回放的视频和照片,按“0k”键进行视频回放。
4、一键锁定功能在录像中,短按M键加锁当前视频,已加锁的文件,加锁图标为“”,文件锁定后将不会被覆盖。
5、键静音功能在录像模式,按“下键”开启或关闭录音。
【提示】设置会自动保存,再次开机后无需设置静音功能。
6、摄像头画面切换功能在录像界面或拍照界面。
按“上键”进行前/后拉界面以及画中画进行切换。
7、时间/日期设定在记录仪界面长按“M键”进入功能设置界面,短按“M键”一次后按“下键”选择“日期/时间”,按“OK键”确认,“上下键”选择年月日后,按“M键”退出设置。
【注意】为了有效记录行车安全事故的取证的日期和时间,在使用本机前请先设置正确的时间。

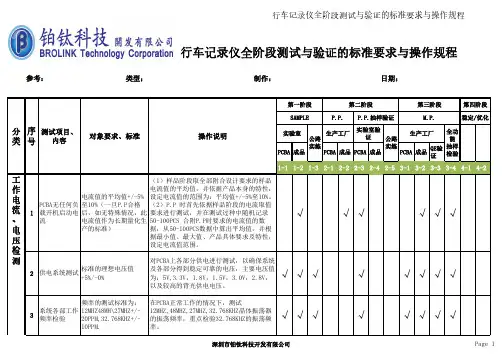
深圳酷达通讯有限公司行车记录仪硬件测试规范编制:范宝停审核:聂建军批准:张中月编号: KUDA-QE-001版本/状态:V1.0生效日期镜片强度测试(镜片粘接类产品)1.将记录仪整机放入高温试验箱85℃±2℃/8h,然后取出进行镜片粘接强度测试;2.在记录仪镜面取上下左右靠近镜片边缘处四点,在四点处粘接扎带,扎带靠近镜片边缘约 10mm,使用拉力计进行垂直拉力测试;3.拉力数值 30N,速度为20mm/min,拉拔方向要求垂直于镜片表面;镜片无脱落、翘起,镜片与面壳间无粘贴分离、脱胶等不良;34)环境可靠性测试测试项目测试方法判定标准样品数量低温存储测试1.将连接完毕的记录仪整机放入低温试验箱,-30℃/240h,注意:对于吸盘连接结构式记录仪需吸附在平面玻璃并悬空倒挂;2.试验结束恢复至室温后接通标称电源电压、接入信号正常工作;试验过程中吸盘粘贴牢靠,无脱落;试验后检查记录仪的外观结构、主要功能和数据记录,应无异常3生效日期整箱振动测试初始检测合格后,将试验样品按照出货外箱包装要求进行打包,依如下顺序采用松紧带固定在振动台面上进行随机振动试验:底面(3 面)朝下固定方式试验 30min、顶面(1 面)朝下固定方式试验 10min、侧面(4面或2 面)朝下固定方式试验 10min、前后面(5 面或 6 面)朝下固定方式试验 10min;试验条件如下表1.包装外箱、内盒不得出现严重破损、变形或散乱;2.产品无外观和功能不良;一箱频率( Hz )功率谱密度g²/Hz1.0Hz 0.00014.0Hz 0.01100.0Hz 0.01200.0Hz 0.001生效日期整箱跌落测试1.初始检测合格后,将试验样品按照出货外箱包装要求进行打包,跌落至水泥地面,跌落顺序为:一角、三菱、六面,各二次;2.跌落时应遵循以下要求:跌落最易碎的面的结合处一角(纸箱接合处,三个棱的结合点);检跌落从结合点辐射到的三条边(三菱);跌落一个最小的面、跌落这个最小面的反面,跌落一个中等的面、跌落这个中等面的反面、跌落一个最大面、跌落这个最大面的反面(六面);1.试验后外箱及内盒不得出现严重破损(破损不大于 15mm)、变形或散乱(包装材料还能正常包装样品,内盒物品不得出现散乱);2.产品无外观和功能异常;一箱8)表面处理验证。

深圳酷达通讯有限公司行车记录仪硬件测试规范编制:范宝停审核:聂建军批准:张中月编号: KUDA-QE-001版本/状态:V1.0生效日期喇叭/ 白燥/粉燥测试1、参考标准 IEC-268-1 ,GBT9396-1996测试条件依据器件的规格的额定功率下测试 96 小时2、扫频仪1、测试后功能正常,扫频接受有噪声不良4镜片强度测试(镜片粘接类产品)1.将记录仪整机放入高温试验箱85℃±2℃/8h,然后取出进行镜片粘接强度测试;2.在记录仪镜面取上下左右靠近镜片边缘处四点,在四点处粘接扎带,扎带靠近镜片边缘约 10mm,使用拉力计进行垂直拉力测试;3.拉力数值 30N,速度为20mm/min,拉拔方向要求垂直于镜片表面;镜片无脱落、翘起,镜片与面壳间无粘贴分离、脱胶等不良;34)环境可靠性测试测试项目测试方法判定标准样品数量生效日期插拔耐久测试1.测试点:母座和数据线线材公头端;2.插拔速率不超过 12.5mm/min,插拔频率20-30 次/min,插入力小于30N;3. 插拔耐久次数:1000 次测试完成后线材接头无明显磨损,接触良好,功能正常 57)包装可靠性测试测试项目测试方法判定标准数量整箱振动测试初始检测合格后,将试验样品按照出货外箱包装要求进行打包,依如下顺序采用松紧带固定在振动台面上进行随机振动试验:底面(3 面)朝下固定方式试验 30min、顶面(1 面)朝下固定方式试验 10min、侧面(4面或2 面)朝下固定方式试验 10min、前后面(5 面或 6 面)朝下固定方式试验 10min;试验条件如下表1.包装外箱、内盒不得出现严重破损、变形或散乱;2.产品无外观和功能不良;一箱频率( Hz )功率谱密度g²/Hz生效日期8)表面处理验证铅笔硬度测试1 在常温下用三菱 2H 铅笔以45°的菱角在实验样品表面划 3-5 条划痕2.璃镜材质6H,亚克力材质2H,PC材质 1H3、将铅笔笔芯在纱布上磨平将样品平衡的房在测试治具上每划一条线转动一次铅笔测试完成后样品表面不允许有明显划痕2纸带摩擦测试1、测试要求:负重 175g电镀,喷涂为 300 圈,橡胶漆50 圈将样品平衡的房在测试治具上,固定好避免移动2、电镀件和喷涂件测试 50 圈检查一次,橡胶漆每 10 圈检查一次测试后样品不能露底材2百格测试用百格刀在样品表面划100 个小网格(1mm*1mm)每条划痕应深及表面涂层的底层用 32M610 胶纸牢牢粘着测试的小网格,注意胶带粘住处不留气泡,待静置 2min 抓抓胶带两端,以垂直的方向迅速扯下胶带测试后样品整块油漆脱落的网格数要求小于 5 块,网络边缘的油漆脱落的网格数要求小于15 块2。

行车记录仪测试用例测试用例:行车记录仪用例1:启动行车记录仪前提条件:行车记录仪已安装且电源已连接1.用户按下行车记录仪的电源按钮。
2.验证行车记录仪是否成功开机。
3.验证行车记录仪是否显示正常的启动界面。
用例2:录制行车视频前提条件:行车记录仪已启动并连接了储存设备1.验证行车记录仪是否处于录制状态。
2.验证行车记录仪是否能够正常捕捉和存储行车视频。
3. 验证视频文件的格式是否正确,如.mp4等。
4.验证录制的视频文件是否能够正常播放。
用例3:拍摄行车照片前提条件:行车记录仪已启动并连接了储存设备1.验证行车记录仪是否处于拍照模式。
2.验证行车记录仪是否能够正常捕捉和存储行车照片。
3. 验证照片文件的格式是否正确,如.jpg等。
4.验证拍摄的照片是否清晰,不模糊或遮挡。
用例4:自动停车监控前提条件:行车记录仪已启动并连接了车辆电源和储存设备1.用户将车辆熄火。
2.验证行车记录仪是否能够检测到车辆熄火状态。
3.验证行车记录仪是否能够自动进入停车监控模式。
4.验证停车监控模式下是否能够自动录制视频或拍摄照片。
用例5:紧急事件记录前提条件:行车记录仪已启动并连接了车辆电源和储存设备1.在行驶过程中,用户遇到紧急事件,如碰撞、急刹车等。
2.验证行车记录仪是否能够自动检测到紧急事件。
3.验证行车记录仪是否能够自动保存紧急事件前后的行车视频。
4.验证行车记录仪是否能够保存紧急事件的准确时间和GPS位置信息。
用例6:存储检查前提条件:行车记录仪已启动并连接了储存设备1.验证行车记录仪的储存设备是否可读写。
2.验证行车记录仪是否能够自动清理储存设备上的旧视频或照片。
3.验证行车记录仪是否能够自动分割并保存录制的视频文件以避免储存设备满载。
用例7:设备设置前提条件:行车记录仪已启动并连接了储存设备1.用户进入行车记录仪的设置菜单。
2.验证用户是否能够正确设置行车记录仪的录制分辨率、帧率、循环录制等参数。
3.验证用户是否能够正确设置行车记录仪的时间、日期、语言等参数。

目录前言 (1)产品保证 (2)产品概述 (3)产品特性 (4)产品示意图 (5)按键功能 (6)操作指南 (7)摄影模式 (8)拍照模式 (9)回放模式 (10)系统设置 (11)产品参数 (12)附件清单 (13)安全注意事项 (14)简易疑难排解 (15)一、前言感谢您购买新科行车记录仪。
本手册将详细说明如何正确使用行车记录仪,同时提供给您详细的产品信息,包括操作、注意事项及技术规格等,使用前请仔细阅读本手册。
我们希望本产品能满足您的需求并长期服务于您!二、产品保证本产品经严格测试,性能合乎规定,使用过程中有任何问题和疑问,请致电全国免费电话:400-850-0528,专业的技术指导24小时为您服务。
三、产品概述本产品是采用最新科技设计而成的数字高清行车记录仪,可以录制像素分辨率高达1920*1080PFULL HD的高解析影像。
本产品安装方便打开包装拿出产品专用支架装到机器相对应的接口处,然后直接吸在前挡风玻璃上,接上电源把车充插到点烟器上直接使用方可。
后拉镜头撕开双面胶贴在后挡风玻璃中上端位置,然后把后拉镜头一段接口对应机器处连接上方可使用。
和传统的摄影机相比较,本产品录制的FULL HD高清影像,可以记录更加完美的视频画面。
本产品支持汽车启动自动录像,可定时循环录像,移动侦测自录像,灵敏度可调碰撞感应,支持录像锁定,录像自动覆盖。
本产品安装简单,牢固可靠,不影响驾驶人视线。
高清影像使用micro SD卡存储,最大支持32G扩展。
使用本产品,享受真正的HD画质生活。
电脑操作系统:Windows 2000/XP/Vista/Windows 7,MAC OS*10.3.6以上四、产品特性⏹1920*1080P影像。
⏹200W CMOS感光芯片。
⏹140度广角全玻镜头。
⏹高保真语音播报。
⏹具有多种场景白平衡补偿功能。
⏹前置200W像素摄像头,后置可录制100W摄像头。
⏹内置麦克风/喇叭。
⏹支持移动侦测。

汽车行驶记录仪检定装置操作规程打开电源开关,屏幕显示产品名称以及版本信息等,按任意键后,即进入主测试菜单。
在主测试菜单,按“↑”,“↓”光标键选择所需要的测试项目(注:被选中的测试项为反白显示),按“开始”键既进入测试参数设置菜单,请按照欲进行的测试项目的实际情况正确设置测试参数。
按“↑”,“↓”光标键选择测试参数项目,按“←”,“→”光标键设置正确的测试参数。
按“↑”,“↓”“←”,“→”选择要输入的数字。
输入完成后按“F2”键保存,或者选中”保存”后按“开始”键保存,按“结束”键退出这次设置。
1.1.1 应接GPS天线1.1.2 应设置参数:车牌号1.1.3 测试操作:●在主测试菜单,按“↑”,“↓”光标键选择“车速试验”,按“开始”键进入测试参数设置菜单,根据试验目的,正确设置测试参数。
●按“开始”键进入测试界面。
●此时屏幕右上侧显示即时车速。
右下侧图形区显示即时速度曲线。
左下侧文本区显示“NO.00”,表示第1次测试。
(按“↑”“↓”光标键,可以修改该值。
)●此时屏幕左上侧开始显示“测试距离”和“测试时间”。
●系统自动对行驶距离进行监视,当行驶距离达到“测试距离”时,测试过程自动结束(也可以按“结束”键提前结束测试)。
屏幕显示测试结果。
测试结果依次为:“测试距离”、“测试时间”、“平均速度”、“最大速度”。
●按“↑”键可以循环查看测试过程的V-T和V-S曲线,当一条曲线在一屏中显示不开时,可以按“→”键循环查看曲线的其余部分。
●按“打印”键可以将测试结果打印出来,再次按“打印”键可以将V-T和V-S曲线打印出来。
按“结束”键,则可以开始一次新的测试,再次按“结束”键,则返回主测试菜单。
1.2 道路试验1.2.1 应接GPS天线1.2.2 应设置参数:车牌号1.2.3 测试操作:●在主测试菜单,按“↑”,“↓”光标键选择“道路试验”,按“开始”键进入测试参数设置菜单,根据试验目的,正确设置测试参数。


车载行驶记录仪软件测试工具设计与实现Chapter 1 Introduction- Background and motivation- Problem statement- Objectives and scope- Research questions- MethodologyChapter 2 Literature Review- Definitions of car driving recorder software testing tools- Existing car driving recorder software testing tool- Evaluation of current software testing tools- Introduction to software testing techniquesChapter 3 Requirements Analysis- Requirements gathering- System architecture design- Functional and non-functional requirements- Use case diagramChapter 4 Design and Implementation- Design of the car driving recorder software testing tool- Implementation of the car driving recorder software testing tool - Testing of the car driving recorder software testing tool- User interface designChapter 5 Testing and Validation- Testing strategies- Validation of the car driving recorder software testing tool- Results and analysis- Limitations and future workChapter 6 Conclusion- Summary of the research work- Contribution of the work- Conclusions and recommendations- Future research directions.Chapter 1: IntroductionBackground and MotivationCar driving recorders have become increasingly popular over the years, providing drivers with a comprehensive view of their driving experience. With the increasing demand for these devices, there has been a corresponding increase in the development of software to support them. However, car driving recorder software testing tools are still in their early stages of development.Software testing is an important process that ensures software quality and reliability. Without proper testing, software can contain errors or bugs that can impact the device's performance and potentially cause harm to users. Therefore, it is essential to develop effective software testing tools for car driving recorders to ensure their safe and efficient operation.Problem StatementWith an increasing number of car driving recorder software applications available on the market, it is becoming challenging for developers to test and ensure the quality of these tools comprehensively. The absence of proper testing tools can result in software errors, which can cause performance issues, data loss, and, more importantly, pose a significant risk to the safety of driversand their passengers. Developing a robust car driving recorder software testing tool will help mitigate these risks significantly. Objectives and ScopeThe primary objective of this thesis is to design and develop a car driving recorder software testing tool that can help identify errors and bugs in the software. This thesis aims to develop a flexible, user-friendly, and efficient software testing tool for car driving recorder software developers.The scope of this thesis is limited to the development of a software testing tool for car driving recorders. The tool will analyze the software's functionality and identify any errors, bugs, or performance issues before the software is released to the public. The tool will analyze the usability, security, and performance of the software.Research Questions- What are the current car driving recorder software testing tools available in the market?- What are the limitations of the current software testing tools?- What are the software testing techniques used for car driving recorder software?- How can a software testing tool be designed and developed specifically for car driving recorder software?MethodologyThis thesis will employ a mixed-methods research approach, comprising qualitative and quantitative research methods. Secondary data will be collected to review the literature, includingexisting literature on software testing tools and techniques for car driving recorders. Furthermore, empirical data will be collected through surveys, interviews, and experiments to develop and validate the software testing tool. The development process will be conducted using an Agile software development methodology.Chapter 2: Literature Review2.1 Car Driving Recorder Software Testing ToolsCar driving recorder software testing tools are designed to ensure the software's integrity and performance. There are several software testing tools available in the market, such as Selenium, Appium, and TestComplete, that can be used for car driving recorder software testing. However, these tools have certain limitations that make them unsuitable for testing car driving recorder software.2.2 Limitations of Current Software Testing ToolsThe current software testing tools used for car driving recorder software testing have limitations that make them unsuitable for the task. For instance, Selenium has limitations in testing mobile applications. TestComplete, on the other hand, requires a high level of expertise to use, making it less accessible to developers with limited testing knowledge.2.3 Software Testing Techniques for Car Driving Recorder SoftwareSeveral software testing techniques can be used to test car driving recorder software, such as functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and usability testing.Functional testing involves testing the software's functionalities to ensure they are working as intended. Performance testing involves testing the software's performance to determine its speed, scalability, and stability. Security testing involves identifying and mitigating security-related risks, while usability testing involves evaluating the software's user interface and user experience.2.4 Development of a Software Testing Tool for Car Driving Recorder SoftwareDeveloping a software testing tool for car driving recorder software requires a comprehensive understanding of the software's functionality, user requirements, and business goals. The tool should be designed to be flexible, user-friendly, and efficient. Agile methodologies can be used to ensure the project's timely and successful completion.2.5 SummaryIn summary, several software testing tools are available in the market for car driving recorder software testing. However, these tools have limitations that make them unsuitable for the task. Software testing techniques such as functional testing, performance testing, security testing, and usability testing can be used to test car driving recorder software. Developing a software testing tool for car driving recorder software requires a comprehensive understanding of the software's functionalities, user requirements, and business goals. Agile methodologies can be used to ensure the successful completion of the project within the settimeline.Chapter 3: Methodology3.1 Research DesignThis study will use a mixed-methods research design, which will involve both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods. The quantitative data will be collected through survey questionnaires and the qualitative data through interviews.3.2 ParticipantsThe participants in this study will be developers who have experience in developing car driving recorder software. The participants will be recruited through industry associations and social media platforms.3.3 Data CollectionThe data will be collected through two methods: survey questionnaires and interviews. The survey will be administered online and will capture quantitative data such as demographic information, experiences, and opinions on software testing tools for car driving recorder software. The interviews will be conducted online or in-person and will generate qualitative data on the developers' experiences, opinions, and challenges in testing car driving recorder software.3.4 Data AnalysisThe quantitative data collected through the survey will be analyzed using statistical methods such as descriptive statistics, correlations, and regression analysis, to identify the relationship between the variables. The qualitative data collected through interviews will be analyzed using content analysis to identify themes and patterns in the data.3.5 Ethical ConsiderationsThe study will adhere to ethical guidelines and principles such as anonymity, confidentiality, informed consent, and voluntary participation. All participants will be informed of the purpose, procedures, and risks involved in the study before giving their consent to participate.3.6 LimitationsThe main limitation of this study is the small sample size of participants. Additionally, the results will be limited to the experiences and opinions of the selected developers and may notbe generalizable to the broader population of software developers. 3.7 Importance of the StudyThis study is significant because it will provide insights into the challenges, experiences, and opinions of developers regarding software testing tools for car driving recorder software. The findings of this study can inform the development of specialized testing tools for car driving recorder software that address the identified challenges and meet the requirements of developers. Additionally, the study can guide the industry in the developmentof best practices in software testing.Chapter 4: Results4.1 Demographic CharacteristicsA total of 50 developers participated in the survey, with an even split between men and women. The majority of participants (76%) had over five years of experience in software development, and 68% had experience developing car driving recorder software.4.2 Experience with Testing ToolsWhen asked about their experience with testing tools for cardriving recorder software, 56% of participants reported using open-source testing tools, 32% used commercial testing tools, and 12% used in-house testing tools. The most commonly used open-source testing tool was Selenium, while the most commonly used commercial testing tool was HP Unified Functional Testing (UFT).4.3 Opinions on Importance of TestingParticipants were asked about their opinions on the importance of testing in the development of car driving recorder software. Over 90% of respondents believed that testing was either very important or somewhat important in ensuring the quality of software. Furthermore, 80% of respondents believed that testing could help identify potential safety issues in car driving recorder software.4.4 Challenges in Testing Car Driving Recorder Software Participants were asked about the challenges they faced when testing car driving recorder software. The most common challenge identified by participants was the lack of standard testing protocols (76%), followed by difficulty in testing the integration of software with hardware components (68%), and the complexity of testing for safety-critical features (62%).4.5 Opinion on the Ideal Testing ToolWhen asked about their opinion on the ideal testing tool for car driving recorder software, 50% of participants stated that a specialized tool that addresses the unique requirements of car driving recorder software would be ideal. Additionally, 30% of participants suggested that a combination of open-source and commercial testing tools could be used to test different aspects of car driving recorder software.4.6 Themes from InterviewsThe interviews conducted with five developers revealed three main themes in their experiences and opinions on testing car driving recorder software. The first theme was the importance of safety testing, with all participants highlighting the need for rigorous testing to ensure that car driving recorder software does not pose a safety risk to drivers or passengers. The second theme was the need for specialized testing tools that can handle the complexity of testing for car driving recorder software. Finally, the third theme was the importance of collaboration between software developers and hardware engineers to ensure the integration of software and hardware components is tested effectively.4.7 Limitations of the StudyThe main limitation of this study is the small sample size of participants, which may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the study relied on self-report data, which can be subject to biases and errors in recall.4.8 Implications for PracticeThe findings of this study highlight the need for specialized testing tools that can address the unique challenges of testing car driving recorder software. Additionally, the study emphasizes the importance of safety testing and collaboration between software developers and hardware engineers. The development of standard testing protocols could also help to address the challenge identified by participants regarding the lack of standard testing protocols. Overall, the findings of this study can inform the development of best practices in software testing for car driving recordersoftware.Chapter 5: Conclusion and Future Directions5.1 ConclusionThis study aimed to explore the current practices, challenges, and opinions regarding software testing for car driving recorder software. The findings of this study suggest that testing is considered very important in ensuring the quality and safety of car driving recorder software. However, developers face challenges such as the lack of standard testing protocols, difficulty in testing the integration of software with hardware components, and the complexity of testing for safety-critical features.Developers also have varied experience with testing tools, with open-source tools such as Selenium and commercial tools such as HP Unified Functional Testing (UFT) being the most commonly used. There is a need for specialized testing tools that can handle the complexity of testing car driving recorder software and the integration of software with hardware components. Collaboration between software developers and hardware engineers is also essential to ensure effective testing.5.2 Future DirectionsThe findings of this study suggest several directions for future research in software testing for car driving recorder software. One potential area of research is the development of specialized testing tools that can address the unique challenges of testing this type of software. Additionally, the development of standard testing protocols could help to ensure consistency and reliability in software testing.Another area of research could be the exploration of new, innovative testing methods that can better address the challenges of testing car driving recorder software. For example, the use of simulation and virtual environments could provide a safer and more controlled testing environment for safety-critical features.Furthermore, additional research can be conducted to explore the role of collaboration between software developers and hardware engineers in testing car driving recorder software. This can help to identify best practices for effective collaboration and communication between teams, which can ultimately lead to better software testing and improved software quality.Overall, this study provides a foundation for future research in software testing for car driving recorder software. The results suggest the need for continued innovation and collaboration in this field to ensure the safety and quality of these important software systems.。
一、镜头性能指标
1.光学有效像素总数
2. 色彩还原准确度
3.白平衡度
4.亮度
5.坏点&黑点&彩色点
6. 动态范围
7. 几何失真
8. 对角线视场
9. 帧频
二、测试环境
测试应在如下的测试环境中进行:
1. 暗室:测试的环境照度应小于1 Ix 勒克斯(Luxes)
2. 拍摄时测试图卡表面照度范围应在700~1200 Ix 勒克斯(Luxes)之间,
在D65 光源色温下,测试图卡上任何一点的照度与测试图卡中心照度差不大于10%;在其他色温下,测试图卡上任何一点的照度与测试图卡中心照度差不大于30%
3. 光源应采取必要的遮光措施,防止光源直射镜头。
4.测试图卡周围(包括放置测试图卡的置具)应是低照度,减少炫光,测试时应尽量避免外界光线照射。
5.测试图卡背景采用黑或吸光型中性灰。
6.测试中可使下列标准色温:D65 光源色温6500K、泛光灯色温3400K。
实际测试环境的色温标准偏差应不大于200K。
色温从2700k-7500k 可调换,国际照明学会(CIE)所认可的七色人工E 光。
7. 温度20±2℃,相对湿度50±20%。
三、测试治具
1.标准光源灯
2.反射式灯光箱
3. 照度计
4.分光式色度计
5.反射式光密度计
6. 帧频测试仪
7.放大镜
8.显微镜
9. 测试图卡:分辨率测试图卡,色彩测试图卡,几何失真测试图卡,灰阶测试图卡。
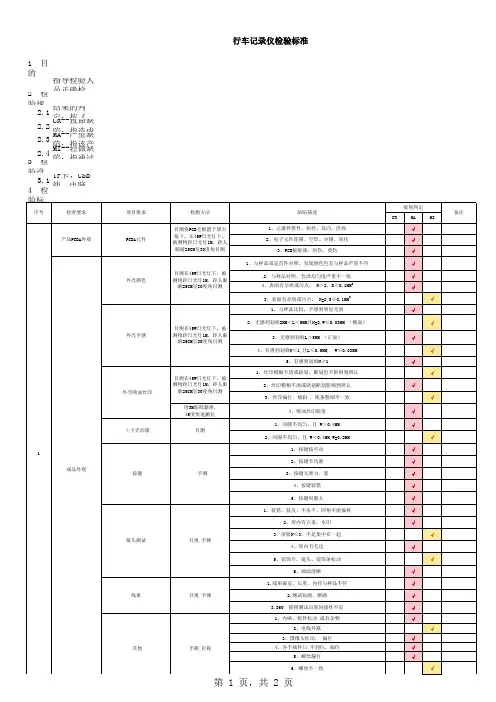
行车记录仪检验指导书作业内容1.0准备工作:标准样品,校正电源电压并插上车充(电源电压12V)。
2.0作业步骤:2.1.首先看产品外观:外壳有刮痕长度>3.0mm,不见底色拒收。
面壳和底壳缝隙间距>0.3mm拒收;外壳有刮痕,见底色拒收,气泡或污点、杂点直径>Φ0.20mm拒收,面壳与底壳的断差>0.3mm拒收;2.2.把记录仪在工作台上轻敲其底部(确认产品内部有无异物)并摇动镜头转轴确认松紧适中,无卡死异常,然后插入车充,记录仪自动开机,观察显示屏有无异常(开机LOGO,白屏,不开机),拔出车充,记录仪会在约15秒左右关机。
2.3.插入TF卡,按开机键进入工作状态,按REC/SNAP键进入录像模式,对着记录仪说话,录制6—10秒钟;2.4.按MODE转换到拍照模式,拍摄几张照片;2.5.再一次按MODE进入本机回放,对刚才所录像的视频和拍照的图片进行回放;按上下键选择播放文件(观察是否清晰,上下键有无作用);2.6.插入A V输出线,在电视上可看到刚才所录像的视频和拍照的图片(如图2);2.7.在录像模式下按MENU进入菜单打开夜视功能,LED会发亮,菜单各项参数是否正确(参照样机)2.8.循环覆盖:在录像时当内存满了会自动删除之前的旧文件;2.9.可移动磁盘:电脑上的USB线插入USB口就可以连上电脑充当读卡器功能2.10.按复位键恢复到出厂时状态;2.11.检验OK后把产品摆放整齐进入下一道工序…。
图1图2注意事项1.1.回放录像时,声音是否清晰1.2.桌面保持整洁。
预防刮伤产品工具仪器序号名称型号/参数用量序号名称型号/参数用量1 可调电源RXN3030D 1 4 车充5V 12 TF卡2G以上标准卡 1 5 液晶电视有A V输入口 13 电脑XP系统 1 6制表/日期审核/日期批准/日期。
行车记录仪测试标准行车记录仪是一种可以记录车辆行驶过程中的视频、声音和其他相关数据的设备,它可以为车主提供行车安全保障,同时也可以作为事故证据的重要来源。
然而,由于市场上行车记录仪种类繁多,质量参差不齐,因此需要制定一套行车记录仪测试标准,以保证其质量和性能。
首先,行车记录仪的视频录制功能是其最基本的功能之一。
在测试时,需要对其视频录制的清晰度、色彩还原度、广角度等进行全面的评估。
清晰度是指录制视频的清晰程度,色彩还原度是指录制视频的色彩还原的真实程度,广角度则是指行车记录仪能够录制的视野范围。
这些指标的测试可以通过专业的视频测试设备和标准测试画面来进行。
其次,行车记录仪的声音录制功能也是需要被测试的重点之一。
在测试时,需要对其录制声音的清晰度、抗干扰能力等进行评估。
清晰度是指录制声音的清晰程度,抗干扰能力则是指行车记录仪在复杂环境下录制声音的稳定性。
这些指标的测试可以通过专业的声音测试设备和标准测试声音来进行。
另外,行车记录仪的数据存储和保护功能也是需要被测试的重点之一。
在测试时,需要对其存储介质的可靠性、数据写入速度、数据保护能力等进行评估。
存储介质的可靠性是指行车记录仪的存储介质是否稳定可靠,数据写入速度是指行车记录仪的数据录制速度,数据保护能力则是指行车记录仪在意外断电或者碰撞时对数据的保护能力。
这些指标的测试可以通过专业的存储介质测试设备和标准测试程序来进行。
最后,行车记录仪的外观设计和安装稳定性也是需要被测试的重点之一。
在测试时,需要对其外观设计的美观度、材质质量、安装稳定性等进行评估。
美观度是指行车记录仪的外观设计是否符合美学标准,材质质量是指行车记录仪的材质是否坚固耐用,安装稳定性则是指行车记录仪在安装后是否稳定不易松动。
这些指标的测试可以通过专业的外观设计评估设备和安装稳定性测试设备来进行。
综上所述,行车记录仪的测试标准应包括视频录制功能、声音录制功能、数据存储和保护功能、外观设计和安装稳定性等多个方面。