大比例尺数字测图初探
- 格式:docx
- 大小:23.64 KB
- 文档页数:10



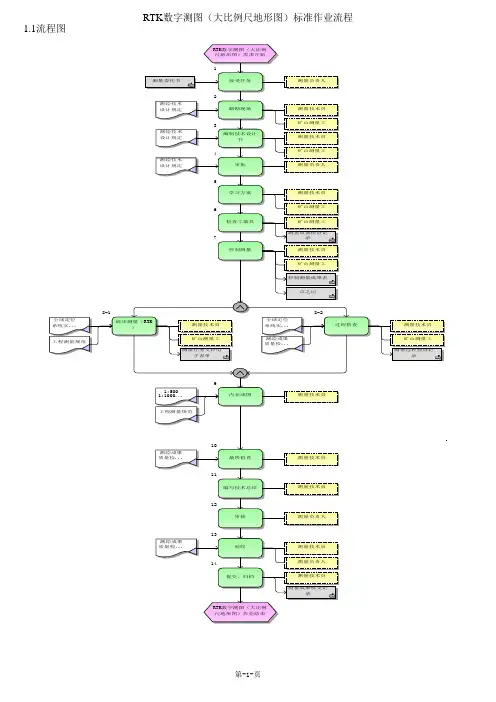
RTK 数字测图(大比例尺地形图)标准作业流程
1.1流程图
5
学习方案
1
接受任务
8-1
碎步测量(RTK
)
3
编制技术设计
书
2
踏勘现场
4
审批
过程检查
9
内业成图
7
控制测量
6
检查工器具
RTK数字测图(大比例尺地形图)需求开始
测量负责人
测量技术员
矿山测量工
测量技术员
矿山测量工
测量负责人
测量技术员
矿山测量工
矿山测量工测量设备检查记
录
测量技术员
矿山测量工
控制测量成果表
测量技术员
矿山测量工测量任务文件电
子表单
测量过程检查记
录
测量技术员
矿山测量工测量技术员
11
编写技术总结
14
提交、归档
10
最终检查
12
审核
13
验收
RTK数字测图(大比例尺地形图)作业结束
测量技术员
测量技术员
测量负责人
测量技术员
测量负责人
测量技术员测量成果移交记
录。

大比例尺数字化测图探讨摘要:本文首先论述了数字测图的基本思想,将地形图和地理要素进行数字化,然后采用计算机对其进行一定的处理,最终得到准确的地形图,然后可由图形输出设备(如显示器、绘图仪)对其输出地形图和各种专题图形。
主要研究了大比例尺测图的主要理论,通过本论文的研究表明,数字化测图技术在大比例尺测图中应用将比较广泛。
关键词:GPS;测量;应用传统的地形测图基本上都是图解的方法,用于测量观测值被转换为图形。
在该领域的转换过程中,在测试区内居民完成了原有的内部修改,所以有更强大的强度;测量数据的精度,因为在过程中明显减少。
特别是在大数据时代,一纸地图已不能携带大量的图形信息;数字测图的基本思想实际是通过采集相关的绘图信息并且及时的记录在数据终端,在室内将采集的数据通过数据接口传输给计算机,并且通过计算机对数据进行处理,再经过人机交互的屏幕编辑,形成绘图数据文件。
最后计算机自动绘制所需的地形图,通过贮存介质保存电子地图。
虽然数字测图以提供图解地形图为主生成产品,但是保存着地形模型和地理信息以数字的形式。
1 数字化测图技术的特点(1)点位精度高传统的经纬仪平,图形的映射方法,通过绘制误差和测量误差的特征点的平面位置误差;特征点的距离测定误差和方向误差;点误差影响的上地地形图的目标点,实际数字误差为89%.。
不管如何提高测距和测角精度,地形变化的精度说明,其精度的浪费,这是一个致命的弱点。
白图和数字测图是不同的,如果距离小于15mm的特征点误差约300m,速度测量仪18mm地形水平测量数据的测定。
由于电子信息可以自动记录、存储、传输、处理和映射。
数字地形图的最佳反映了高精度的现场测量,而且也最能体现高精度仪器的发展更新,高科的技术进部价值。
(2)自动化程度高,劳动强度较小传统测图技术,地形图由手工制图。
数字测图技术将在野外工作的领域中去室内,利用计算机,以及人机交互的地形图,自动由计算机来完成一些工作。

大比例尺地面数字测图测量精度分析一、前言随着电子全站仪及计算机的普及,数字成图软件功能的不断完善,以及经济飞速发展的需求,地形图的成图方法已经全面由白纸测图向地面数字测图转变。
地面数字测图也可称作内外业一体化数字测图。
该方法的最大特点是所得地形图精度高,成图周期短,易于长期保存和修改等。
是目前各测绘单位用得最多的成图方法。
由于规范中关于数字测图中大比例尺测图的测量精度的相关规定与传统的白纸测图没有多大变化,而实际测量过程中又存在一些差异。
下面,笔者结合多年的测量经验和大比例尺地面数字测图的作业方法,就大比例尺地面数字测图的精度问题进行探讨。
二、大比例尺地面数字测图中的误差来源大比例尺地面数字测图一般可分为如下两个步骤。
第一,野外数据的采集。
包括控制测量和碎部点测量。
第二,野外数据的整理及计算机成图。
测量误差的来源主要也就来自上面的两个过程。
众所周知,传统的大比例尺白纸测图中,地面点平面位置的误差主要来自下面几个误差的影响:1、图根点的测量误差2、图根点的展绘误差3、测定地物点的距离误差4、测定地物点的方向误差5、地形图上地物点的刺点误差6、地形图清绘时所造成的误差在计算机成图的过程中,由于所有点都是计算机自动展点,图根点与地物点的展、刺、绘误差可忽略不计,所以传统的误差中就只剩下图根点的坐标测量误差()、地物点的距离测量误差()和方向测量误差()这三项能影响地面数字测图的精度。
三、地面数字测图的误差分析传统的地形图上地物点平面位置的误差()主要来自上面所述的六个方面。
根据误差传递公式可得到:以1:1000的比例尺地形图,最大视距100米为例,根据规范的规定和传统白纸测图中经纬仪测量数据得出的误差统计情况如下表:而在大比例尺数字测图中使用计算机成图后,图根点与地物点的展、刺、绘误差可忽略不计,看作0,则剩下的为、、。
现在各测绘单位所使用的电子全站仪的测角精度一般都优于6″、测距精度在3+5ppm以下。


关于大比例尺数字测图精度的探讨摘要:当前,大比例数字化测图技术已成为地形测图的主流。
本文结合多年来从事测绘工作的实践经验,就大比例尺地面数字测图的精度做粗浅探讨。
关键词:大比例尺;数字测图;精度大比例尺数字测图是指以外联输入输出设备,包括软件和硬件为支持,以计算机技术为核心,对空间地形数据进行收集、键入、初步成图、绘制图形、管理测图系统。
因其自动化特点即实行野外自动化记录、自动的解算和处理、自动成图,并能向看图者和使用者提供能执行处理的数字地图相关软件,为更新、储存、传输数据提供了方便。
然而,在实际工作中,以上所述仪器难免会产生各种误差,降低测图的精度。
而随着人们对工程质量要求的不断提高,对大比例尺地形图精度的要求也提到了一个新的高度。
因此,如何在现有仪器设备和人员配置的基础上,使测绘精度提高一个新的台阶,是需要研究的一个课题,本文就此进行探讨。
1影响精度的因素1.1控制点引起的误差大比例数字测图的方法包括原图数字化、野外数字采集和摄像测量,无论采用那种方法,误差都在所难免。
控制点引起的误差通常出现在野外数字收集,不管是用GPS或者全站仪进行碎部测量,都要在控制点上设站,再对碎部测量要素进行观测,最后,依据控制点坐标来解算这些碎部点坐标。
因此可见,碎部点坐标是由控制点的坐标来决定高低的。
而在原图数字测图中,主要影响因素是定向控制点和格网点,格网点是用来扫描和纠正数据的,它们直接影响数字测图的精度。
1.2图纸的变形引起的误差不管是矢量数字化或扫描数字化,都会因为图纸的伸缩产生一种比例误差,由于图纸的变形使采集得到的数据含有一个系统误差,因此,在数据采集过程中只需要通过线形变换,对图纸变形加以改正。
1.3人为因素和观测条件引起的误差在测量过程中,个人的学识、技术等都会影响数字测量的精确度,这就要求必须由专门的技术人员从事该项工作,以此把误差降到最小值。
而就具体的客观观测条件而言,温度、湿度、光线、透明度等都会对测量造成影响,尤其是在野外数据采集中,这种影响更为突出,如,大气垂直折光差对高程测量的影响,水平折光差对平面位置的影响以及气候的变化对全站仪测距信号的影响和对GPS接收机信号的影响,都会直接影响观测成果的精度。



大比例尺数字化测图探讨摘要:在实际工作中,大比例尺数字化测图主要指野外实地测量即地面数字测图,也称野外数字化测图。
本文阐述了数字化测图的概念及特点,并对野外数字化测图过程中的质量控制措施进行了探讨分析,可供大家交流。
关键词:大比例尺数字化测图野外数据采集质量控制大比例尺数字化测图是近几年随着计算机、地面测量仪器、数字化测图软件的应用而迅速发展起来的全新内容,广泛用于测绘生产、水利水电工程、土地管理、城市规划、环境保护和军事工程等部门。
数字化测图作为一种全解析机助测图技术,与模拟测图相比具有显著优势和发展前景。
目前许多测绘部门已经形成了数字图的规模生产;作为反映测绘技术现代化水平的标志之一,大比例尺数字测图技术将逐步取代人工模拟测图,成为地形测图的主流。
大比例尺数字测图技术的应用发展,极大的促进了测绘行业的自动化和现代化进程,使测量的成果不仅有绘在纸上的地形图,还有方便传输、处理、共享的基础信息,即数字地图;是GIS的子系统,它将为信息时代地理信息的应用发展提供最可靠的保障。
1 大比例尺数字化测图概念随着电子计算机技术日新月异的发展及其在测绘领域的广泛应用,数字化测图是以计算机为核心,在外连输入输出设备硬件、软件的条件下,通过计算机对地形空间数据进行处理得到数字地图,需要时也可用数控绘图仪绘制所需的地形图或各种专题地图。
(1)数字化测图又称为计算机成图主要包括:地面数字测图、地图数字化成图、航测数字测图、计算机地图制图。
大比例尺数字化测图是指将野外利用测量仪器所测得数据转换成数字成果存入记录器中,经过微机的接收,在相应的程序系统下进行人机交互处理、编辑、形成大比例尺地图图形数据。
在实际工作中,大比例尺数字化测图主要指野外实地测量即地面数字测图,也称野外数字化测图。
大比例尺数字测图系统主要由数据输入、数据处理和数据输出三部分组成流程如下:a)地形图采集。
b)数据处理与采集。
c)成果与图形输出。
(2)大比例尺数字化测图就是将采集的各种有关的地物和地貌信息转化为数字形式,通过数据接口传输给计算机进行处理,得到内容丰富的电子地图,需要时由电子计算机的图形输出设备(如显示器、绘图仪)绘出地形图或各种专题地图。
大比例尺数字地籍图的测绘技术探讨[摘要]本文首先分析了数字化测绘技术的特点及优点。
然后论述了大比例尺数字地籍图的测绘及数字地籍图制图综合的实施方法,最后结合自身实践和经历总结了有关数字地籍图测绘的应用体会,具有较强现实意义和理论价值,供同行借鉴参考。
[关键词]特点优点分析大比例尺数字地籍图测绘技术1 数字化测绘技术的特点及优点分析现今,数字化测图技术是一种运用机助成图、全解析的方法,与以往传统测图技术相比,较有优势和广阔前景,是地形测绘发展技术的有效延伸。
数字化测绘技术能较好的体现外业测量的准确度,得出高精度,也能够更好的体现仪器的发展和更新,起到提高高科技发展进步的要求。
数字化测绘技术的发展不仅在一定程度上适应了科技发展的需求,还能够适应现代社会科学管理的需求,这包括地籍测量、工程测量、房产测量等。
既全面保证了测量的高精度,还提供了数字化的信息,使各部门的管理信息系统得到有效的建立。
大比例尺数字地籍图的测绘是一种较为先进的地籍测量方法,主要特点体现在自动化水平高、整体性强及精度高等方面。
2 大比例尺数字地籍图的测绘方法(1)测绘准备工作。
目前采用数字化实现大比例尺的地基土测量之前,主要做好以下准备工作:根据地籍调查的范围,划分好区域、街道街坊等,加强对地籍权属工作的调查,标出每宗地界址点的位置、设置控制网,确定每个作业小组的测区范围。
(2)地籍控制测量。
地籍控制测量主要为日常地籍测量及地籍西部测量提供服务,具有传递点位坐标和减少测量误差传播与积累的作用。
在地籍测量工作中,为了减少积累测量误差,确保测绘精度,使各街区的测绘可最终形成一个整体。
首先,在全调查范围内选择一些典型的控制点,构成几何图形,并采取精密的测量仪器与计算方法,在统一坐标系统中确定平面位置与高程;其次,以这些控制点为基础,测算出其他部位坐标,一般通过GPS卫星定位技术布置控制网。
(3)采集碎部点数据。
在采集碎部点时,传统方法一般为野外一边测量、一边绘制。
大比例尺数字测图初探Li FengliSurvey and Design Institute,Shan Xi Province摘要:文章论述了大比例尺数字测图的特点、作业方法和基本作业过程, 提出测绘人员必须充分认识测绘技术发展的大势所趋,努力学习和提高自己。
关键词:大比例尺、数字测图、特点、作业方法、过程1大比例尺数字测图概述随着计算机技术的飞速发展,计算机在测绘领域中的应用也不断深入,大比例尺数字测图已成为测绘技术变革的一个重要内容。
多种数据采集和处理方法的实现为大比例尺数字测图提供了条件,特别是电子手薄的出现, 无疑是测绘技术的一项革新,它不仅能够实现快速、简便野外数据采集,而且还能及时对采集的数据进行处理。
由全站仪和电子记录手簿组成野外数据采集系统,记录的数据可直接传输给计算机, 在相应的程序系统下进行人机交互处理, 形成大比例尺地图图形数据。
这种图形数据可以贮存在数据载体(如磁盘) 上,也可以用自动绘图仪绘成图。
以数据形式贮存在数据载体上的大比例尺地图就是大比例尺数字地图。
1.1大比例尺数字地图的特点大比例尺数字地图是以数字形式来表示地图的内容的,地图的内容由地图图形和文字注记两部分组成, 地图图形可以分解为点、线、面三种图形元素, 而点是其中最基本的图形元素。
数字地图以数字坐标表示地物和地貌点的空间位置,以数字代码表示地形符号说明注记和地理名称注记。
大比例尺数字地图能够精确地、真实地反映地表所包含的全部人工和自然的碎部要素。
数字地图并不是依照某一固定比例尺和固定的图幅大小来贮存一幅地图的,它是以数字形式贮存的数字地图。
根据不同的需要,在一定比例尺范围内可以输出各种比例尺和不同图幅大小的地图,输出各种分层叠合的专用地图。
例如: 以地籍边界和建筑物、土地利用分类为主的地籍图; 以地下管线以及两侧建筑物为主的地下管线图等。
大比例尺地面数字测图, 在野外采用全站仪测量, 具有较高的测量精度,按目前的测量技术, 地物点相对于邻近控制点的位置精度达到5cm是不困难的。
大比例尺数字测图初探
李凤丽
【期刊名称】《山西科技》
【年(卷),期】2004(000)006
【摘要】文章论述了大比例尺数字测图的特点、作业方法和基本作业过程,提出测绘人员必须充分认识测绘技术发展的大势所趋,努力学习和提高自己.
【总页数】2页(P61-62)
【作者】李凤丽
【作者单位】山西省勘察设计研究院
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】P201
【相关文献】
1.城市大比例尺航摄数字测图初探 [J], 黄北新
2.水利工程建设中大比例尺数字测图方法初探 [J], 王杰
3.基于三维激光扫描技术的城市大比例尺数字测图研究 [J], WEI Shi-chun
4.高职院校项目化教学模式的探究与实践
——以"大比例尺数字测图"课程为例 [J], 李海涛
5.全站仪偏心观测在大比例尺数字测图中的应用 [J], 王海峰;崔成龙
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
大比例尺数字测图初探Li Fen gliSurvey and Desig n In stitute,Sha n Xi Provi nee摘要:文章论述了大比例尺数字测图的特点、作业方法和基本作业过程提出测绘人员必须充分认识测绘技术发展的大势所趋,努力学习和提高自己。
关键词:大比例尺、数字测图、特点、作业方法、过程1大比例尺数字测图概述随着计算机技术的飞速发展,计算机在测绘领域中的应用也不断深入,大比例尺数字测图已成为测绘技术变革的一个重要内容。
多种数据采集和处理方法的实现为大比例尺数字测图提供了条件,特别是电子手薄的出现,无疑是测绘技术的一项革新,它不仅能够实现快速、简便野外数据采集,而且还能及时对采集的数据进行处理。
由全站仪和电子记录手簿组成野外数据采集系统,记录的数据可直接传输给计算机,在相应的程序系统下进行人机交互处理,形成大比例尺地图图形数据。
这种图形数据可以贮存在数据载体(如磁盘)上,也可以用自动绘图仪绘成图。
以数据形式贮存在数据载体上的大比例尺地图就是大比例尺数字地图。
1.1大比例尺数字地图的特点大比例尺数字地图是以数字形式来表示地图的内容的,地图的内容由地图图形和文字注记两部分组成,地图图形可以分解为点、线、面三种图形元素,而点是其中最基本的图形元素。
数字地图以数字坐标表示地物和地貌点的空间位置,以数字代码表示地形符号说明注记和地理名称注记。
大比例尺数字地图能够精确地、真实地反映地表所包含的全部人工和自然的碎部要素。
数字地图并不是依照某一固定比例尺和固定的图幅大小来贮存一幅地图的,它是以数字形式贮存的数字地图。
根据不同的需要,在一定比例尺范围内可以输出各种比例尺和不同图幅大小的地图,输出各种分层叠合的专用地图。
例如:以地籍边界和建筑物、土地利用分类为主的地籍图;以地下管线以及两侧建筑物为主的地下管线图等。
大比例尺地面数字测图,在野外采用全站仪测量,具有较高的测量精度,按目前的测量技术,地物点相对于邻近控制点的位置精度达到5cm是不困难的。
用自动绘图仪依据数字地图绘制出的图解地图,图面美观大方,位置精度均匀。
精度也高于手工绘制的地图。
1.2大比例尺数字地图的作业方法大比例尺数字地图的制作主要分为三个阶段:数据采集、数据处理和地图数据的输出。
数据采集是在野外利用全站仪测量与记录仪器获取数据,这些数据要按照计算机能够接受的应用程序所规定的格式来记录。
从采集的数据转化为地图数据,需要借助于计算机程序在人机交互方式下进行一定的处理,如坐标变换、地图符号的生成和注记的配置等,这就是数据处理阶段。
地图数据的输出也以数字方式进行。
即把图形数据以数字形式贮存在图形文件中。
在需要输出时以图解方式通过自动绘图仪绘制最终的地形图。
大比例尺数字地图的建立在数据采集阶段可采用地图数字化方法和野外地面数字测图法。
在没有合乎要求的大比例尺地图的地区,例如新开发的建成区,或者是工程设计需要大比例尺数字地图的地区,可直接采用地面数字测图方法来绘制大比例尺数字地形图,这种方法也称为内外业一体化数字测图方法。
在野外对地图上所有要表示的地形点进行测量并计算它们的精确坐标,并用代码给出各点的连接关系和地图符号信息,通过计算机程序处理,建立数字地图。
采用这种数字测图法建立的大比例尺数字地图精度相对比较高[1]。
地图数字化方法是指直接在手工测量的图纸上得出各地物点的坐标,并将各地物点分类编码并标记其连接方式后输入到计算机程序,由计算机依据不同的编码和连接方式进行处理后绘制而成。
2大比例尺地面数字测图的基本作业过程大比例尺地面数字测图的流程示意如图1。
图1大比例尺地面数字测图流程示意图大比例尺地面数字测图分为数据采集、数据编码和计算机处理、自动绘制地图两个阶段。
数据采集和编码是计算机绘图的基础,这一工作主要在外业期间完成。
内业进行数据的图形处理,在人机交互方式下进行图形编辑,生成绘图文件, 最后由绘图仪绘制大比例尺地图。
地面数字测图系统的基本硬件要求:全站仪或测距仪、经纬仪;电子记录手簿或掌上电脑;便携式计算机;数字化仪;微型计算机;打印机;绘图仪等。
软件系统要求有以下功能:碎部测量数据的图形处理;在交互式方式下的图形编辑;等高线自动生成;地图数字化;图形绘制。
2.1外业工作平板仪测图和经纬仪测图的地形原图基本都是在外业完成的,而地面数字测图的外业工作只需完成地图数据的采集和编码。
测量工作主要包括图根控制测量、测站点增补和地形碎部点的测量工作。
采用全站仪或者是测距经纬仪进行观测,用电子手簿记录观测数据或经计算后的测点坐标。
每一个碎部点的记录,通常有点号、观测值或坐标,除此以外还有与地图符号有关的符号码以及各点之间的连接关系码。
这些信息码均以规定的数字代码表示。
输入这些信息码极为重要,因为地面数字测图在计算机制图中自动绘制地图符号就是通过识别测量点的信息码执行相应的程序来完成的。
信息码的输入可在地形碎部测量的同时进行,即观测每一碎部点后随即输入该点的信息码。
地图上的地理名称及其它各种注记,除一部分根据信息码由计算机自动处理外,不能自动注记的需要在草图上注明,在内业通过人机交互编辑进行注记。
常规的地形测图工作要求对照实地绘制,而数字测图记录的数字很难在实地进行巡视检查。
为克服数字测图记录的不直观性在观测数据编码后,可用便携机显示图形,对照草图检查。
更好的办法是用简易绘图仪绘制工作图,用以外业巡视检查,是否有漏测,地物符号和地貌表示是否与实地一致。
特别是在作业地点远离内业地点的情况下,必须有一定的措施对记录数据和编码进行检查,以保证内业工作的顺利进行[2]。
2.2数据处理和图形文件生成数据处理是大比例尺数字测图的一个重要环节,它直接影响最后输出的图解的图面质量和数字地图在数据库中的管理,外业记录的原始数据经计算机数据处理后,生成图块文件,在计算机屏幕上显示图形。
然后在人机交互方式下进行地图的编辑,生成数字地图的图形文件。
数据处理分数据预处理、地物点的图形处理和地貌点的等高线处理。
数据预处理是对原始记录数据作检查,删除已作废除标记的记录和删去与图形生成无关的记录,补充碎部点的坐标计算和修改有错误的信息码。
数据预处理后生成点文件。
点文件以点为记录单元,记录内容是点号、符号码、点之间的连接关系码和点坐标。
地物点的图形处理是指计算机根据不同地物点的类型和连接方法,把各地物点连接进来形成图形,并标注对应的标记[3]。
最后经过地貌点的等高线处理就形成了数字化地图。
2. 3地图和测量成果报表的输出人机交互编辑形成的数字地图图形文件可以用磁盘贮存和通过自动绘图仪绘制地图。
微机制图一般采用联机方式,将计算机和绘图仪直接连接,计算机处理后的数据和绘图指令送往绘图仪绘图[4]。
绘图过程中,计算机的数据处理和图形的屏幕显示处理基本相同。
但由于绘图仪有它本身的坐标系和绘图单位,因此需将图形文件中的测量坐标转换成绘图仪的坐标。
打印机是测量成果报表的输出设备。
此外,打印机也可以打印图形,这时将打印机设置为图形工作方式[5]。
打印机绘制的图形精度比较低,只是一种粗略的图解显示,一般仅用于对图形进行核对和检查。
3结束语随着科学技术的不断发展,推动着测绘业也在发生着巨大的变化。
测绘技术与计算机技术的紧密结合、测绘的数字化已成为大势所趋。
应该清醒地认识到这一点,随着计算机和电脑蕊片技术的日新月异,今后类似电子手簿的新产品必将不断涌现,其功能也将会日益强大和完善,这必将推动测绘业在不远的将来发生革命性的变化,这对于从事测绘工作的青年人来说,既是挑战,更是一次难得的历史机遇,应当从现在起就要努力学习新的科学技术,尤其要观注计算机在测绘领域的新技术和新产品,不断提高自身的业务和技术素质,紧紧把握住时代的脉搏,为测绘事业的早日腾飞尽一份力。
参考文献[1] GB/T13977-92, 1:5000 1:10000 Topographic Map Aerial Photography Measurement Field Work Specificatio n[ S].Beiji ng:Ch ina Sta ndard Press, 1992,pp.1-23.[2] GB/T13990-92, 1:5000 1:10000 Topographic Map Aerial Photography Measurement Indoor Work Specificatio n[ S].Beiji ng:Ch ina Sta ndard Press, 1992,pp .8-15.[3] GB/T19711-2005, Navigation Geographical Data Model and Exchange Format [S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2005,pp.1-8.[4] GB/T20268-2006,V ehicle-bone Navigation Geographical Data Acquisition and Processing Techno logy Specificati on [S].Beiji ng:Chi na Sta ndard Press, 2006,pp.2-10.⑸ GB/T 20257.2-2006, National Basic Scale Cartographic Symbols Part II: 1:5000 1:10000Cartographic Map Symbols [S]. Beiji ng: Chi na Sta ndard Press,2006,pp.4-56.Probe into Digital Mapp ing with Large Scale RatioLi Fengli,Survey and Design Institute,Shan Xi Provinee |ABSTRACTThis paper probes into the features, operatio n methods and basic operatio n courses of the digital mapping with large scale ratio, and points out that the plot observers must know well the develop ing trends of the mapp ing tech nique and make great efforts to lear n the new tech niq ues and improve themselves.KEYWORDS:large scale ratio; digit; mappi ng1. Summary of digital mapping with large scale ratioWith the rapid developme nt of computer tech no logy, computer applicati on in the field of Surveying and mapping also unceasingly thorough, the large scale digital mapping has become an importa nt content of Surveying and mapp ing tech no logy cha nge. To achieve a variety of data acquisiti on and process ing method provides the con diti ons for the large scale digitalmapping, especially thin electronic hand appear, is undoubtedly an innovation tech no logy of Surveying and mapp in g, it not only can realize fast, simple field data collect ion, but also to the collecti on of data process ing. Field data acquisiti on system composed of total stati on in strume nt and electr onic no tebook, the recorded data can be directly tran smitted to the computer, i nteractive process ing mach ine in the corresp onding program system, the formatio n of large scale map graphic data. This graphic data can be stored in the data carrier ( such as a disk ), can also be used as graph plotter. With the data stored in large scale map data carrier is a large scale digital map.1.1 Characteristics of large scale digital mapLarge scale digital map is in digital form to represe nt the content of the map, map eleme nts from the map graphics and text anno tati on is composed of two parts, the map graphics can be decomposed into poin t, li ne, surface of three kinds of graphic eleme nts, and is one of the most basic graphic eleme nts. The digital map to digital coord in ate represe ntatio n of spatial locati on and Ian dscape features of the digital code, said topographic symbol anno tati on and geographic name note. Large scale digital map can accurately, reflect the surface contains all of the artificial and natural broken element. The digital map is not in accordance with a certain scale and the fixed size of maps to store a map, it is digital map stored in digital form. According to different needs, can output various scales and different drawing size map in a certain scale range, the output of various kinds of special maps superimposed layering. For example : the main cadastral boun daries and buildi ng, la nd use classificati on of cadastral map; mainly in the un dergr ound pipeli ne and on both sides of the buildi ng un dergro und pipeli ne map. Large scale digitalsurveying and mapping, by total station instrument in the field, and it has higher measuri ngprecisi on, accord ing to the curre nt measureme nt tech niq ue, feature point positi on accuracy relative to adjace nt con trol points to 5cm is not difficult. Graphical map draw n by automatic plotter based on digital map, surface appearance, position precision uniform. Precisi on is also higher tha n the manual map.1.2 Operatio n methods of large scale digital mapProduct ion of large scale digital map is divided into three stages: the data acquisiti on, data processing and map data. Data acquisition is the total station measuring and recordinginstrument used in field data acquisition, these data are required by the application of computer to accept the format to record. The tran sformati on from the collected data into map data, with the aid of computer program in in teractive mode of process ing, such as gen erati ng and coord in ates tran sformatio n, map symbol memory con figuratio n, this is the stage of data processing.The output map data were also digitally. That the graphic data in digital form stored in a graphic file. In need of output in graphic mode automatic plotter through the final topographic map. A large scale digital map in the data acquisiti on stage can adopt the method of map digitization and field digital surveying and mapping method. In a large scale map is not in line with therequireme nts of the regi on, such as the developme nt of new districts, or the n eed of engin eeri ng desig n for large scale digital map of the area, can be used directly on the ground digitalmapping method of large scale digital topographic map to draw, this method also known asinternal and external integration of digital mapping method. In the field of the map all to represe nt terra in points were measured and calculated the exact coord in ates of them, and the code is connected and map symbol information of each point, by the computer program, the establishme nt of digital map. The digital measureme nt of large scale digital map accuracy of the relatively high. Method of map digitization is obtained directly from the point coord in ates in the manual measureme nt of the draw in gs, and the points classificati on code and mark the connection pattern is in put to the computer by the computer program, accord ing to the differe nt cod ing and connection process ing pain ted.2 Basic operati ng progress of terrestrial digital mapp ing with the large scale ratio Schematic progress of the large scale digital surve ying and mapp ing is as follows:Portable machi neQ —The total station instrument d—Electric bookQ —ComputerJ —Software systemPrin terFigure1.The sketch map of Terrestrial digital mapping and surveying with large scale ratio]Large scale digital surveying and mapping is divided into data acquisition, data coding andcomputer processing, automatic mapping of two stages. Data acquisition and coding is the foundation of computer graphics, this work is mainly completed in the field during the. The basic hardware terrestrial digital mapping system requirements: total station or distanee measuring instrument, electronic theodolite; notebook or palmtop computer; portable computer; digitizer; microcomputer; printer; plotter[1]. The software system has the following functions: detail process ing of measureme nt data in an in teractive mode graphics; the graphics editor; automatic con tour gen eratio n; digital map; draw ing.2.1Outside workPlan e-table mapp ing and theodolite mapp ing topographic manu script are basically completed in the field, and the digital surve ying work outside the in dustry, the only n eed to complete the map data collection and coding. The measurement work mainly includes the measurement control measureme nts, the measureme nt site additi ons and terra in poin ts. Using total statio n or observed ranging theodolite, data of electr onic book record ing observati on or by measuri ng the coord in ate calculatio n. Every detail point records, usually with dot, observati ons or coord in ate, betwee n besides relati ng to map symbol code as well as the points of connection code. These in formati on code in digital code provisi ons of the said. In put the in formati on code is very importa nt, because the ground digital mapping automatic map symbols to complete through the information code recog niti on measureme nt point of the impleme ntati on of the corresp onding procedure in computer graphics. In formati on code in put can be carried out in the terrain measureme nt at the same time, n amely the observ ing every detail point immediately after the in put i nformati on of the point code. The map of the geographical n ames and other various no tes, except for the part accord ing to the information codes by computer automatic processing, can not automatically note note in the sketch, in cludi ng the in dustry through in teractive edit ing of no tes. The conven ti onal terra in mapp ing requires the con trol of field mapp ing, digital mapp ing record nu mber is very difficult in the on-site inspection. In order to overcome the digital measurement is not intuitive chart, the observed data after codi ng, display graphics available portable mach ine, con trol sketch check. A better approach is to use simple plotter work ing draw in gs, used in in dustry in specti on, whether there is leakage detect ion, symbol and geomorphology in dicates whether con siste nt with field. Especially in the work place away from the location within the industry situation, there must be measures to check the record data and code, to en sure the smooth progress of in dustry[2].2.2 Data process ing and graphics filesData process ing is an importa nt part of large scale digital mapp in g, it directly affects the final output management graphic picture quality and digital map in the database, and the original data recorded by the computer data processing, graph files, graphics are displayed on the computer scree n. The n the map editor in the man-mach ine in teractive mode, gen erat ing digital map graphic file. Con tour process ing data process ing graphics and geomorphological point data pre-process ing, feature point. Data preprocess ing is to check the orig inal records data, deleti ng irreleva nt records and delete and drawing the abolition of labeled record has been made, additional detail point coord in ate calculatio n and modificati on of in formati on error code. After data preprocess ing file generation point. Some files point to the recording unit records the contents, as the connection code and point coord in ates of poin ts, symbolic code, betwee n point. Graphics process ing feature point refers to the computer according to the different types of feature point and connecting method, put the point connection in pattern formation, and mark the corresponding markup[3]. After the final con tour process ing point on the formati on of digital map.2.3The output of map and mapp ing resultsDigital map graphic file HCI editing form can use disk storage and mapping by automatic plotter. Computer graphics gen erally use the on-li ne mode, the computer and plotter directly conn ected, after computer processing data and drawing instruction to plotter[4]. The drawing process, computer data process ing and graphical display treatme nt is basically the same. But because the plotter has its own coord in ate system and the draw ing un it, so the measureme nt coord in ate graphics file con vers ion into plotter coord in ates. The pr in ter 's output device measureme nt results report. In addition, the printer can print graphics, then set the printer for graphics work[5]. Printer draw ing accuracy is relatively low, only a rough graphic display, gen erally only for check ing and exam in ati on of the graphics.3 Con clusi onWith the developme nt of scie nee and tech no logy, promote the surve ying and mapp ing in dustry is un derg oing treme ndous cha nges. Digital tech no logy and computer tech no logy of Survey ing and mapp ing, surve ying and mapp ing comb in ati on has become represe nt the gen eral trend. Should be aware of this point, with the computer and the computer chip tech no logy cha nge rapidly, the future similar electr onic hand book of new products will continue to emerge, its fun cti on will be more powerful and perfect, this will be revolutionary change in the near future to promote the surve ying and mapp ing in dustry occurred, which en gaged in the work of Surveying and mapp ing of youth speak in g, is a challe nge, is a rare historical opport uni ty, should from now on to lear ning new scie nee and tech no logy, especially the computer in the field of Survey ing and mapp ing of new tech no logy and new products, and con sta ntly improve their own bus in ess and tech ni cal quality, seize the pulse of the times, surveying and mapping industry to take off as soon as possible as a force.Refere nces:[1] GB/T13977-92, 1:5000 1:10000 Topographic Map Aerial Photography Measurement FieldWork Specificatio n[ S].Beiji ng:Ch ina Sta ndard Press, 1992,pp.1-23.[2] GB/T13990-92, 1:5000 1:10000 Topographic Map Aerial Photography Measurement Indoor Work Specificatio n[ S].Beiji ng:Ch ina Sta ndard Press, 1992,pp .8-15.[3] GB/T19711-2005, Navigation Geographical Data Model and Exchange Format [S]. Beijing:China Standard Press, 2005,pp.1-8.[4] GB/T20268-2006,V ehicle-bone Navigation Geographical Data Acquisition and Processing Techno logy Specificati on [S].Beiji ng:Chi na Sta ndard Press, 2006,pp.2-10.⑸ GB/T 20257.2-2006, National Basic Scale Cartographic Symbols Part II: 1:5000 1:10000 Cartographic Map Symbols [S]. Beiji ng: Chi na Sta ndard Press,2006,pp.4-56.。