CHAPTER 03
Diagnosis and treatment of diabetes
Diagnostic criteria for diabetes
Random (casual) blood glucose level
A blood glucose level of 200 mg/dL (11.1 mmol/L) or higher with symptoms of diabetes such as increased thirst, frequent urination, and unexplained weight loss also indicates diabetes.
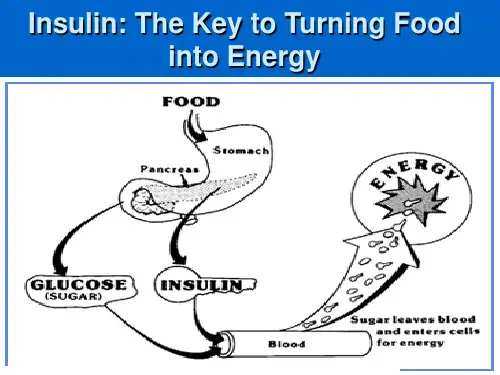
Insulin Deficiency or Resistance
In Type 1 diabetes, there is a significant reduction in insulin production by the pancreas, while in Type 2 diabetes, the body's cells become resistant to insulin, leading to inadequate glucose uptake and utilization.
An HbA1c of 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes. This test measures the average blood glucose level over the past 2-3 months.
Treatment of diabetes
01 02 03
Comorbidities and complications
Diabetes can lead to various serious health complications, including cardiovascular diseases, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, nerve damage, and amputations.