Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets 双丙戊酸钠缓释片美国药典USP39
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:165.58 KB
- 文档页数:4


Purdue制药公司的处方止痛药OxyContin的标签上将添加黑框警告华盛顿,7月26日(路透社医学新闻)Purdue制药公司的OxyContin(氧可酮)的标签上将印上很明显的警示语,旨在帮助防止不适当的处方、滥用和转向使用问题。
OxyContin是一种被广泛滥用的止痛处方药。
OxyContin的滥用者通常会压碎药丸用鼻吸入或溶解后注射,以避开药物的控释给药系统。
今年早些时候公布的一项报告显示,司法部门认定至少有37例OxyContin滥用死亡事件。
为了突出与OxyContin滥用相关的危险性,FDA周三说,他们已和Purdue制药公司合作在药品的标签上作了不少修改,其中包括添加黑框的警示语,这是处方药中最有力的一种警示。
Purdue制药公司还将向药剂师、医生和其他医务人员发送一封“致亲爱的医务人员”的信,以强调与该药相关的滥用和转向使用问题,并解释标签的变化。
FDA说:“新的警告旨在减少OxyContin被不恰当地用于比许可应用的程度轻的疼痛或其它不该用II级麻醉药的疾病的机会。
在开处方时一定要认真地考虑疼痛是否严重到需治疗的程度,而不仅是引起疼痛症状的疾病本身。
”OxyContin是一种阿片样物质激动剂,和它的“近亲”吗啡一样有成瘾性。
该药被批准用于需较长时间用药物控制的中至重度疼痛的患者。
由于所有的阿片样物质类药物都有滥用、误用和转向使用的问题,所以FDA还鼓励其它生产该类产品的厂商检查他们的药品标签,可能的话也进行修改。
FDA强调还要给那些真正需要止痛药治疗的患者的合理使用留有余地。
Purdue制药公司发言人告诉路透社医学新闻。
“公司很高兴能成为第一个在产品标签上作出这些修改的止痛药生产商。
阿片样物质激动剂的其它生产商还包括强生公司和葛兰素史克公司。
”发言人认为,OxyContin标签修改的范围不大,称这次修改“很大程度上是一次图形设计的改动”,而不是大幅度修改内容。
Purdue制药公司官员过去曾指出,在超过6,000名患者的临床试验中,并没有一人发生OxyContin成瘾。
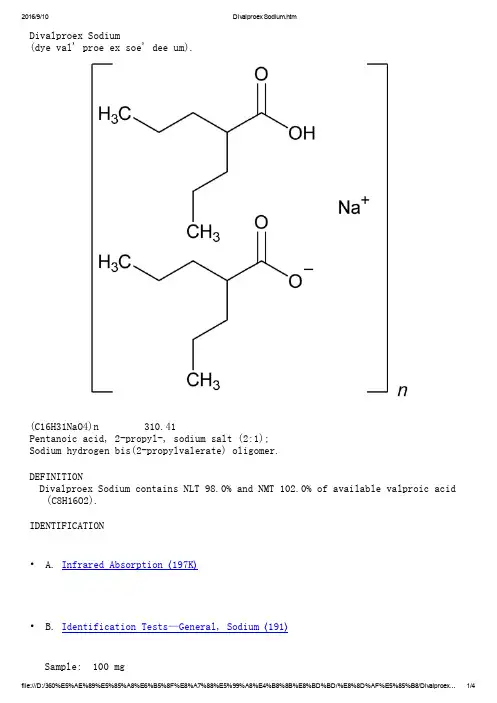
Divalproex Sodium(dye val' proe ex soe' dee um).(C16H31NaO4)n 310.41Pentanoic acid, 2-propyl-, sodium salt (2:1);Sodium hydrogen bis(2-propylvalerate) oligomer.DEFINITIONDivalproex Sodium contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of available valproic acid (C8H16O2).IDENTIFICATION• A. Infrared Absorption 〈197K〉• B. Identification Tests—General, Sodium 〈191〉Sample: 100 mgAnalysis: Ignite the Sample.Acceptance criteria: Meets the requirementsASSAY• ProcedureSolution A: 3.5 g of monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate in 900 mL ofwater. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.5. Dilute with water to 1 L.Mobile phase: Acetonitrile and Solution A (1:1)Impurity stock solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid Related Compound A RS in acetonitrileStandard stock solution: 5.0 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid RS in Mobile phase System suitability solution: 0.5 mg/mL of valproic acid from the Standardstock solution, and 5 µg/mL of valproic acid related compound A from theImpurity stock solution, in Mobile phaseStandard solution: 0.5 mg/mL of USP Valproic Acid RS from the Standard stock solution in Mobile phaseSample solution: 0.5 mg/mL of Divalproex Sodium in Mobile phaseChromatographic system(See Chromatography 〈621〉, System Suitability.)Mode: LCDetector: UV 215 nmColumn: 4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L7Flow rate: 1 mL/minInjection size: 20 µLSystem suitabilitySample: System suitability solution[Note—The relative retention times for valproic acid related compound A and valproic acid are 0.69 and 1.0, respectively.]Suitability requirementsResolution: NLT 5.0 between valproic acid related compound A and valproicacidTailing factor: NMT 1.5 for the valproic acid peakRelative standard deviation: NMT 2.0%AnalysisSamples: Standard solution and Sample solutionCalculate the percentage of available valproic acid (C8H16O2) in the portion of Divalproex Sodium taken:Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × (1/F) × 100 rU=peak area from the Sample solutionrS=peak area from the Standard solutionCS=concentration of USP Valproic Acid RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL)CU=concentration of the Sample solution (mg/mL)Mr1=molecular weight for divalproex sodium repeating unit, 310.41Mr2=molecular weight for valproic acid, 144.21F=number of moles of valproic acid per mole of divalproex sodium repeating unit, 2Acceptance criteria: 98.0%–102.0%IMPURITIESInorganic ImpuritiesDelete the following:• Heavy Metals, Method II 〈231〉: NMT 20 ppm(Official 1-Jan-2018)SPECIFIC TESTS• Water Determination, Method I 〈921〉: NMT 1.0%ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS• Packaging and Storage: Preserve in tight containers. Store at room temperature.• USP Reference Standards 〈11〉USP Divalproex Sodium RSSodium hydrogen bis(2-propylvalerate), oligomer; pentanoic acid, 2-propyl-, sodium salt (2:1).(C16H31NaO4)n 310.41USP Valproic Acid RSUSP Valproic Acid Related Compound A RSAuxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.Topic/Question Contact Expert CommitteeMonograph Heather R. Joyce, Ph.D.Associate ScientificLiaison(301) 998-6792(CHM42015) Chemical Medicines Monographs 4Reference Standards RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129rstech@USP39–NF34 Page 3551Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 36(5) Page 1178 Chromatographic Column—DIVALPROEX SODIUMChromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 39 or NF 34.。

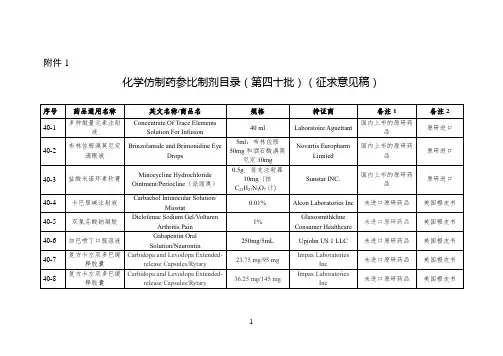
国家药监局关于发布仿制药参比制剂目录(第三十九
批)的通告
文章属性
•【制定机关】国家药品监督管理局
•【公布日期】2021.03.01
•【文号】国家药品监督管理局通告2021年第20号
•【施行日期】2021.03.01
•【效力等级】部门规范性文件
•【时效性】现行有效
•【主题分类】药政管理
正文
国家药品监督管理局通告
2021年第20号
国家药监局关于发布仿制药参比制剂目录(第三十九批)的
通告
经国家药品监督管理局仿制药质量和疗效一致性评价专家委员会审核确定,现发布仿制药参比制剂目录(第三十九批)。
特此通告。
附件:仿制药参比制剂目录(第三十九批)
国家药监局
2021年3月1日附件
仿制药参比制剂目录(第三十九批)。


_______________________________________________________________________________ HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use VIMOVO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for VIMOVO. VIMOVO ™ (naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium) DELAYED RELEASE TABLETS Initial US Approval: April 2010 -----------------------RECENT MAJOR CHANGES------------------------ WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 05/2011 Hypomagnesemia (5.19) WARNING: CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL RISKS See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning Cardiovascular Risk •Naproxen, a component of VIMOVO, may cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may increase with duration of use. Patients with cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease may be at greater risk. (5.1) •VIMOVO is contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery. (4, 5.1) Gastrointestinal Risk•NSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of VIMOVO, cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinal (GI) events. (5.4) -------------------------INDICATIONS AND USAGE------------------------- Relief of signs and symptoms of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and ankylosing spondylitis and to decrease the risk of developing gastric ulcers in patients at risk of developing NSAID associated gastric ulcers (1) ------------------------DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION----------------One tablet twice daily. Use the lowest effective dose. Not recommended in moderate/severe renal insufficiency or in severe hepatic insufficiency. Consider dose reduction in mild/moderate hepatic insufficiency (2) ----------------------DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS----------------Delayed release tablets: 375 mg/20 mg or 500 mg/20 mg of naproxen and esomeprazole magnesium (3) ----------------------------CONTRAINDICATIONS------------------------- •Known hypersensitivity to any component of VIMOVO or substituted benzimidazoles (4) •History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs (4, 5.8, 5.9, 5.13) • Use during the peri-operative period in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4, 5.1) • Late pregnancy (4, 5.10, 8.1) --------------------WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS---------------------- •Serious and potentially fatal cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke. Patients with known CV disease/risk factors may be at greater risk (5.1) •Serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events, which can be fatal. The risk is greater in patients with a prior history of ulcer disease or GI bleeding, and in patients at high risk for GI events, especially the elderly. VIMOVO should be used with caution in these patients (5.4, 8.5) •Treatment should be withdrawn when active and clinically significantbleeding from any source occurs (5.5)•Elevated liver enzymes and, rarely, severe hepatic reactions. Discontinueuse immediately if abnormal liver enzymes persist or worsen (5.11, 8.6, 12.3)•New onset or worsening of pre-existing hypertension. Blood pressureshould be monitored closely during treatment with VIMOVO (5.2, 7.1, 7.4)•Congestive heart failure and edema. VIMOVO should be used with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure (5.3) •Renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury with long-term use. Use VIMOVO with caution in the elderly, those with impaired renal function, hypovolemia, salt depletion, heart failure, liver dysfunction, and those taking diuretics, or ACE-inhibitors. Not recommended for patients with moderate or severe renal impairment (2, 5.6, 5.7, 7.1, 7.4, 8.7) •Anaphylactoid reactions. Do not use VIMOVO in patients with the aspirin triad (5.8) • Serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis, which can be fatal and can occur without warning. Discontinue VIMOVO at first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity (5.9) • Long-term proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of the hip, wrist or spine (5.16) • Symptomatic response to esomeprazole does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy (5.4) • Atrophic gastritis has been noted on biopsy with long-term omeprazole therapy (5.4) • Hypomagnesemia has been reported rarely with prolonged treatment with PPIs (5.19) ---------------------------------ADVERSE REACTIONS-------------- Most common adverse reactions in clinical trials (>5%): erosive gastritis, dyspepsia, gastritis, diarrhea, gastric ulcer, upper abdominal pain, nausea (6.1) To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact AstraZeneca at 1-800-236-9933 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or /medwatch. ----------------------------DRUG INTERACTIONS----------- •Concomitant use of NSAIDs may reduce the antihypertensive effect of ACE Inhibitors, diuretics, and beta-blockers (7.1, 7.4, 7.9) • Concomitant use of NSAIDs increases lithium plasma levels (7.5) • Concomitant use of VIMOVO with methotrexate may increase the toxicity of methotrexate (7.6) • Concomitant use of VIMOVO and warfarin may result in increased risk of bleeding complications. Monitor for increases in INR and prothrombin time (7.7) • Esomeprazole inhibits gastric acid secretion and may interfere with the absorption of drugs where gastric pH is an important determinant of bioavailability (eg, ketoconazole, iron salts and digoxin) (7.11) ---------------------------USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS------- • Pregnancy Category C: VIMOVO should not be used in late pregnancy (4, 5.10, 8.1) • Hepatic Insufficiency: VIMOVO is not recommended in patients with severe hepatic insufficiency (2, 4, 5.11, 8.6, 12.3) • Renal Insufficiency: VIMOVO is not recommended in patients with moderate or severe renal insufficiency (2, 5.6, 5.7, 8.7, 12.3) SEE 17 FOR PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION AND FDA APPROVED PATIENT LABELING OR MEDICATION GUIDE REVISED MAY 2011 FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS* 5.5 Active Bleeding 5.6 Renal Effects Cardiovascular Risk 5.7 Advanced Renal Disease 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE 5.8 Anaphylactoid Reactions 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION 5.9 Skin Reactions 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS 5.10 Pregnancy 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS 5.11 Hepatic Effects 5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS 5.12 Hematological Effects 5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events 5.13 Pre-existing Asthma 5.2 Hypertension 5.14 Concomitant NSAID Use 5.3 Congestive Heart Failure and Edema5.15 Corticosteroid Treatment5.17 Masking of Inflammation and Fever5.18 Laboratory Tests5.19 Hypomagnesemia6 ADVERSE REACTIONS6.1 Clinical Studies Experience6.2 Postmarketing experience7 DRUG INTERACTIONS7.1 ACE-inhibitors7.2 Aspirin7.3 Cholestyramine7.4 Diuretics7.5 Lithium7.6 Methotrexate7.7 Anticoagulants7.8 Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)7.9 Other Information Concerning Drug Interactions7.10 Drug/Laboratory Test Interaction7.11 Interactions related to absorption7.12 Antiretroviral agents7.13 Effects on hepatic metabolism/cytochrome P-450 pathways7.14 Other pharmacokinetic-based interactions8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS8.1 Pregnancy8.2 Labor and Delivery8.3 Nursing Mothers8.4 Pediatric Use8.5 Geriatric Use8.6 Hepatic Insufficiency8.7 Renal Insufficiency10 OVERDOSAGE11 DESCRIPTION12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY12.1 Mechanism of Action12.2 Pharmacodynamics12.3 Pharmacokinetics13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology14 CLINICAL STUDIES16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed1FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Cardiovascular RiskNon-Steroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), a component of VIMOVO, may cause an increased riskof serious cardiovascular thrombotic events,myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal.This risk may increase with duration of use. Patientswith cardiovascular disease or risk factors forcardiovascular disease may be at greater risk [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.1)].VIMOVO is contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypassgraft (CABG) surgery [see Contraindications (4), andWarnings and Precautions (5.1)].Gastrointestinal RiskNSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of VIMOVO, cause an increased risk of seriousgastrointestinal adverse events including bleeding,ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines,which can be fatal. These events can occur at any timeduring use and without warning symptoms. Elderlypatients are at greater risk for serious gastrointestinalevents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].INDICATIONS AND USAGEVIMOVO is a combination product that contains naproxenand esomeprazole. It is indicated for the relief of signs andsymptoms of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis andankylosing spondylitis and to decrease the risk of developinggastric ulcers in patients at risk of developing NSAID-associated gastric ulcers. VIMOVO is not recommended forinitial treatment of acute pain because the absorption ofnaproxen is delayed compared to absorption from othernaproxen-containing products. Controlled studies do notextend beyond 6 months.2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATIONCarefully consider the potential benefits and risks ofVIMOVO and other treatment options before deciding to useVIMOVO. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortestduration consistent with individual patient treatment goals.VIMOVO does not allow for administration of a lower dailydose of esomeprazole. If a dose of esomeprazole lower thana total daily dose of 40 mg is more appropriate, a differenttreatment should be considered.Rheumatoid Arthritis, Osteoarthritis and AnkylosingSpondylitisThe dosage is one tablet twice daily of VIMOVO 375 mgnaproxen and 20 mg of esomeprazole or 500 mg naproxenand 20 mg of esomeprazole.The tablets are to be swallowed whole with liquid. Do notsplit, chew, crush or dissolve the tablet. VIMOVO is to betaken at least 30 minutes before meals.Geriatric PatientsStudies indicate that although total plasma concentration ofnaproxen is unchanged, the unbound plasma fraction ofnaproxen is increased in the elderly. Use caution when highdoses are required and some adjustment of dosage may berequired in elderly patients. As with other drugs used in theelderly use the lowest effective dose [see Use in SpecificPopulations (8.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Patients With Moderate to Severe Renal ImpairmentNaproxen-containing products are not recommended for usein patients with moderate to severe or severe renalimpairment (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min) [seeWarnings and Precautions (5.6, 5.7) and Use in SpecificPopulations (8.7)].Hepatic InsufficiencyMonitor patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairmentclosely and consider a possible dose reduction based on thenaproxen component of VIMOVO.VIMOVO is not recommended in patients with severehepatic impairment because esomeprazole doses should notexceed 20 mg daily in these patients [see Warnings andPrecautions (5.11), Use in Specific Populations (8.6) andClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].Pediatric PatientsThe safety and efficacy of VIMOVO in children youngerthan 18 years has not been established. VIMOVO istherefore not recommended for use in children.3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHSOval, yellow, delayed release tablets for oral administrationcontaining either:• 375 mg enteric coated naproxen and 20 mg esomeprazole (as magnesium trihydrate) tabletsprinted with 375/20 in black, or• 500 mg enteric coated naproxen and 20 mg esomeprazole (as magnesium trihydrate) tabletsprinted with 500/20 in black.4 C ONTRAINDICATIONSVIMOVO is contraindicated in patients with knownhypersensitivity to naproxen, esomeprazole magnesium,substituted benzimidazoles, or to any of the excipients.VIMOVO is contraindicated in patients who haveexperienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions aftertaking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal,anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported insuch patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8, 5.13)].Hypersensitivity reactions, eg, angioedema and anaphylacticreaction/shock, have been reported with esomeprazole use.VIMOVO is contraindicated for the treatment of perioperative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft(CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].VIMOVO is contraindicated in patients in the late stages ofpregnancy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Use inSpecific Populations (8.1)].5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic EventsClinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselectiveNSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown anincreased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thromboticevents, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal.All NSAIDS, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, mayhave a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or riskfactors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimizethe potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treatedwith an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used forthe shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients shouldremain alert for the development of such events, even in theabsence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should beinformed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CVevents and the steps to take if they occur.There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirinmitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic eventsassociated with NSAID use.Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selectiveNSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10–14 daysfollowing CABG surgery found an increased incidence ofmyocardial infarction and stroke [see Contraindications (4)].5.2 H ypertensionNSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of VIMOVO, canlead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to theincreased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides orloop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapieswhen taking NSAIDs. NSAIDs should be used with cautionin patients with hypertension. Blood pressure (BP) should bemonitored closely during the initiation of NSAID treatmentand throughout the course of therapy [see Drug Interactions(7.1, 7.4)].5.3 Congestive Heart Failure and EdemaFluid retention, edema, and peripheral edema have beenobserved in some patients taking NSAIDs and should be usedwith caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.— Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, 5.4 G astrointestinalEffectsand PerforationNSAIDs, including naproxen, a component of VIMOVO, cancause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events includinginflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of thestomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can befatal. While VIMOVO has been shown to significantlydecrease the occurrence of gastric ulcers compared tonaproxen alone, ulceration and associated complications canstill occur.These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with orwithout warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs.Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper GIadverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GIulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDsoccur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3–6months, and in about 2–4% of patients treated for one year.These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasingthe likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some timeduring the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk. The utility of periodic laboratory monitoring has not been demonstrated, nor has it been adequately assessed.VIMOVO should be prescribed with caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk of developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants or antiplatelets (including low-dose aspirin), longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients, and therefore special care should be taken in treating this population.To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID or NSAID-containing product, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.Epidemiological studies of the case-control and cohort design have demonstrated an association between use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of upper gastrointestinal bleeding. In two studies, concurrent use of an NSAID, COX-2 inhibitor, or aspirin potentiated the risk of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.8)]. Although these studies focused on upper gastrointestinal bleeding, bleeding at other sites cannot be ruled out.NSAIDs should be given with care to patients with a history of inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease) as their condition may be exacerbated. Gastrointestinal symptomatic response to therapy with VIMOVO does not preclude the presence of gastric malignancy.Atrophic gastritis has been noted occasionally in gastriccorpus biopsies from patients treated long-term withomeprazole, of which esomeprazole is an enantiomer and acomponent of VIMOVO.Bleeding5.5 A ctiveWhen active and clinically significant bleeding from anysource occurs in patients receiving VIMOVO, the treatmentshould be withdrawn.5.6 Renal EffectsLong-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renalpapillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity hasalso been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins havea compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. Inthese patients, administration of an NSAID may cause adose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and,secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overtrenal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reactionare those with impaired renal function, hypovolemia, heartfailure, liver dysfunction, salt depletion, those takingdiuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly.Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed byrecovery to the pretreatment state.5.7 Advanced Renal DiseaseNo information is available from controlled clinical studiesregarding the use of VIMOVO in patients with advancedrenal disease. Therefore, treatment with VIMOVO is notrecommended in these patients with advanced renal disease.If VIMOVO therapy must be initiated, close monitoring ofthe patient’s renal function is advisable [see Dosage andAdministration (2), Use in Specific Populations (8.7) andClinical Pharmacology (12.3)].5.8 Anaphylactoid ReactionsAnaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients withoutknown prior exposure to either component of VIMOVO.NSAIDs should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad.This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patientswho experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or whoexhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after takingaspirin or other NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].Emergency help should be sought in cases where ananaphylactoid reaction occurs. Anaphylactoid reactions, likeanaphylaxis, may have a fatal outcome.5.9 Skin ReactionsNSAIDs can cause serious skin adverse events such asexfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxicepidermal necrolysis, which can be fatal. These seriousevents may occur without warning. Patients should beinformed about the signs and symptoms of serious skinmanifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued atthe first appearance of skin rash or any other sign ofhypersensitivity.5.10 P regnancyPregnancy Category CIn late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, naproxen, acomponent of VIMOVO, should be avoided because it maycause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus [seeContraindications (4), and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].5.11 Hepatic EffectsBorderline elevations of one or more liver tests may occur inup to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs including naproxen, acomponent of VIMOVO. Hepatic abnormalities may be theresult of hypersensitivity rather than direct toxicity. Theselaboratory abnormalities may progress, may remainessentially unchanged, or may be transient with continuedtherapy. The SGPT (ALT) test is probably the most sensitiveindicator of liver dysfunction. Notable elevations of ALT orAST (approximately three or more times the upper limit ofnormal) have been reported in approximately 1% of patientsin clinical trials with NSAIDs. In addition, rare cases ofsevere hepatic reactions, including jaundice and fatalfulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and hepatic failure, someof them with fatal outcomes, have been reported.A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liverdysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred,should be evaluated for evidence of the development of moresevere hepatic reaction while on therapy with VIMOVO.If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver diseasedevelop, or if systemic manifestations occur (eg,eosinophilia, rash, etc.), VIMOVO should be discontinued.Chronic alcoholic liver disease and probably other diseaseswith decreased or abnormal plasma proteins (albumin) reducethe total plasma concentration of naproxen, but the plasmaconcentration of unbound naproxen is increased. Caution isadvised when high doses are required and some adjustmentof dosage may be required in these patients. It is prudent touse the lowest effective dose for the shortest possibleduration of adequate treatment.VIMOVO is not recommended in patients with severehepatic impairment because esomeprazole doses should notexceed 20 mg daily in these patients [see Dosage andAdministration (2), and Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].5.12 H ematological EffectsAnemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs.This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI bloodloss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis.Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs should havetheir hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit anysigns or symptoms of anemia.NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown toprolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, theireffect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorterduration, and reversible. Patients receiving VIMOVO whomay be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function,such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receivinganticoagulants or antiplatelets, should be carefully monitored. 5.13 Pre-existing AsthmaPatients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. Theuse of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma hasbeen associated with severe bronchospasm, which can befatal. Since cross reactivity, including bronchospasm,between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in suchaspirin-sensitive patients, VIMOVO should not beadministered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivityand should be used with caution in patients with pre-existingasthma.5.14 Concomitant NSAID UseVIMOVO contains naproxen as one of its active ingredients.It should not be used with other naproxen-containingproducts since they all circulate in the plasma as thenaproxen anion.The concomitant use of VIMOVO with any dose of a non-aspirin NSAID should be avoided due to the potential forincreased risk of adverse reactions.5.15 C orticosteroid TreatmentVIMOVO cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroidsor to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abruptdiscontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to diseaseexacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapyshould have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is madeto discontinue corticosteroids and the patient should beobserved closely for any evidence of adverse effects,including adrenal insufficiency and exacerbation ofsymptoms of arthritis.5.165.17 5.185.19 Bone FractureSeveral studies and literature reports indicate that proton pump inhibitor (PPI) therapy is associated with an increased risk for osteoporosis-related fractures of the hip, wrist, or spine. Those patients with the highest risk received high-dose or long-term PPI therapy (a year or longer). Patients should use the lowest effective dose and shortest duration of PPI therapy appropriate to the condition being treated. Patients at risk for osteoporosis-related fractures should be managed according to the established treatment guidelines. Adequate vitamin D and calcium intake is recommended. Masking of Inflammation and FeverThe pharmacological activity of VIMOVO in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, noninflammatory painful conditions.Laboratory TestsBecause serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (eg, eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, VIMOVO should be discontinued.Patients with initial hemoglobin values of 10 g or less who are to receive long-term therapy should have hemoglobin values determined periodically.HypomagnesemiaHypomagnesemia, symptomatic and asymptomatic, has been reported rarely in patients treated with PPIs for at least three months, in most cases after a year of therapy. Serious adverse events include tetany, arrhythmias, and seizures. In most patients, treatment of hypomagnesemia required magnesium replacement and discontinuation of the PPI.For patients expected to be on prolonged treatment or who take PPIs with medications such as digoxin or drugs that may cause hypomagnesemia (e.g., diuretics), health care professionals may consider monitoring magnesium levels prior to initiation of PPI treatment and periodically. [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]。

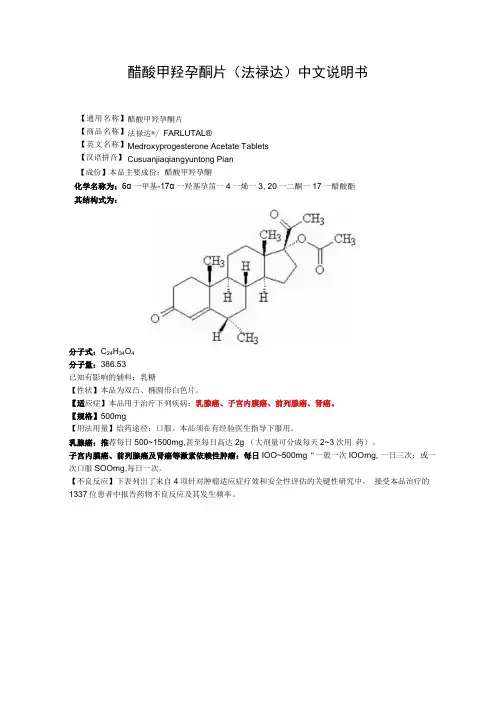
醋酸甲羟孕酮片(法禄达)中文说明书醋酸甲羟孕酮片 法禄达®/ FARLUTAL®Medroxyprogesterone Acetate Tablets Cusuanjiaqiangyuntong Pian 【成份】本品主要成份:醋酸甲羟孕酮化学名称为:6α 一甲基-17α 一羟基孕笛一4一烯一3, 20一二酮一17一醋酸酯 其结构式为:分子式:C 24H 34O 4 分子量:386.53 已知有影响的辅料:乳糖【性状】本品为双凸、椭圆形白色片。
【适应症】本品用于治疗下列疾病:乳腺癌、子宫内膜癌、前列腺癌、肾癌。
【规格】500mg【用法用量】给药途径:口服。
本品须在有经验医生指导下服用。
乳腺癌:推荐每日500~1500mg,甚至每日高达2g (大剂量可分成每天2~3次用 药)。
子宫内膜癌、前列腺癌及肾癌等激素依赖性肿瘤:每日IOO~500mg “一般一次IOOmg, 一日三次;或一次口服SOOmg,每日一次。
【不良反应】下表列出了来自4项针对肿瘤适应症疗效和安全性评估的关键性研究中, 接受本品治疗的1337位患者中报告药物不良反应及其发生频率。
【通用名称】 【商品名称】 【英文名称】 【汉语拼音】报告疑似不良反应在医药产品上市后进行疑似不良反应报告非常重要。
报告疑似不良反应能够对医药产品的获益/风险的平衡进行持续监测。
医护人员需要报告任何可疑的不良反应。
【禁忌】对活性物质或【成份】所列的任何辅料有超敏反应。
本品禁用于具有下述情况的患者:严重肝功能不全,因骨转移出现高钙血症的患者,已知或疑似妊娠,不明原因的子宫不规则出血,己知对本品或其任何辅料过敏,乳腺癌诊断可疑或早期乳腺癌。
【注意事项】本品应该在有经验的肿瘤专科医师监督指导下使用,且患者须进行定期随访。
・应对本品治疗期间发生的意外阴道出血进行仔细检查,明确诊断。
•在送检子宫内膜或宫颈组织时,应告知病理学家(实验室)患者正在使用本品。
Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets» Divalproex Sodium Delayed-Release Tablets contain an amount of divalproexsodium equivalent to not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 percent of the labeled amount of valproic acid (C8H16O2).Packaging and storage—Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at controlled room temperature.USP Reference standards 〈11〉—USP Valproic Acid RSIdentification—The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.Dissolution 〈711〉—acid stage—Medium: 0.08 N hydrochloric acid (prepared by adding 40 mL of hydrochloric acid to 5000 mL of water, adjusting with 2 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 1.2, and diluting with water to 6000 mL); 900 mL.Apparatus 2: 50 rpm.Time: 1 hour.Procedure—At the end of 1 hour, carefully transfer the Tablet to a dissolution vessel containing the Medium of the Buffer stage. [note—Do not perform an analysis of the Medium in the Acid stage.]buffer stage—Medium: pH 7.5 phosphate buffer (prepared by dissolving 40.83 g of monobasic potassium phosphate and 9.84 g of sodium hydroxide in 5000 mL of water,adjusting with 0.08 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 7.5, and diluting with water to 6000 mL); 900 mL.Apparatus 2: 50 rpm.Time: 1 hour.Determine the amount of C8H16O2 dissolved in the Buffer stage by employing the following method.Citrate buffer—Dissolve 0.5 g of citric acid monohydrate and 0.4 g of dibasic sodium phosphate in 1.0 L of water.Potassium phosphate buffer—Dissolve 6.8 g of monobasic potassium phosphate and 1.7 g of sodium hydroxide in 1.0 L of water. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.4 ± 0.1.Mobile phase—Prepare a mixture of Citrate buffer, Potassium phosphate buffer, and acetonitrile (35:35:30). Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0 ± 0.1,and mix. Filter and degas. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography 〈621〉).Standard solution—Prepare a solution of USP Valproic Acid RS in the Medium used in the Buffer stage, having a known concentration of about 0.12 mg per mL. [note —A volume of acetonitrile not exceeding 10.0% of the total volume may be used to dissolve the USP Valproic Acid RS.]Test solution—If necessary, dilute a portion of each filtered solution under test with the Medium used in the Buffer stage to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 0.12 mg per mL.Chromatographic system (see Chromatography 〈621〉)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 210-nm detector and a 3.9-mm × 15-cm column that contains 4-µm packing L11. The flow rate is about 1.2 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1000 theoretical plates; the tailing factoris not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.Procedure—Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Standardsolution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of valproic acid (C8H16O2) dissolved by the formula:900CD(rU / rS)in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Valproic Acid RS in the Standard solution; D is the dilution factor used to prepare the Test solution; and rU and rS are the peak areas of valproic acid obtained from the Testsolution and the Standard solution, respectively.Tolerances—Not less than 80% (Q) of the labeled amount of C8H16O2 is dissolved in 1 hour in the Buffer stage.Uniformity of dosage units 〈905〉: meet the requirements.Assay—Citrate buffer—Dissolve 2.0 g of citric acid monohydrate and 1.6 g of dibasic sodium phosphate in 4.0 L of water.Mobile phase—Prepare a mixture of Citrate buffer and acetonitrile (7:3).Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0 ± 0.1, and mix. Filter and degas.Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography〈621〉).Standard preparation—Prepare a solution of USP Valproic Acid RS in Mobilephase having a known concentration of about 0.5 mg per mL.Assay preparation—Transfer a number of whole Tablets containing the equivalent of about 2500 mg of valproic acid into a 250-mL volumetric flask. Add 150 mL of Mobile phase, and sonicate with frequent swirling for 30 minutes or until the Tablets completely disintegrate. Allow the solution to cool down to roomtemperature, and then dilute with Mobile phase to volume. Transfer 5.0 mL of the resulting solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.Chromatographic system (see Chromatography 〈621〉)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 210-nm detector and a 3.9-mm × 15-cm column that contains 4-µm packing L11. The flow rate is about 0.9 mL per minute. Chromatograph theStandard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1000 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.Procedure—Separately inject equal volumes (about 15 µL) of the Standardpreparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record thechromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of valproic acid (C8H16O2) in the portion of Tablets taken by the formula:5000C(rU / rS)in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Valproic Acid RS in the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the peak areas of valproic acidobtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively. Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs beforecontacting USP.Topic/Question Contact Expert CommitteeMonograph Heather R. Joyce, Ph.D.Associate ScientificLiaison(301) 998-6792(CHM42015) Chemical Medicines Monographs 4Reference Standards RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129rstech@〈711〉Margareth R.C. Marques,Ph.D.Principal ScientificLiaison(301) 816-8106(GCDF2015) General Chapters-DosageForms 2015USP39–NF34 Page 3554Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(1) Page 153Chromatographic Column—DIVALPROEX SODIUM DELAYED-RELEASE TABLETSChromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 39 or NF34.。