北京邮电大学物理实验绪论课(20101-5学分新)
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:4.32 MB
- 文档页数:66

可编辑修改精选全文完整版大学物理第六版上册北京邮电大学出版课后答案详解1、行驶的汽车关闭发动机后还能行驶一段距离是因为汽车受到惯性力作用[判断题] *对错(正确答案)答案解析:汽车具有惯性2、用如图所示的装置做“探究小车速度随时间变化的规律”实验:1.小车从靠近定滑轮处释放.[判断题] *对错(正确答案)3、马德堡半球实验测出了大气压,其大小等于760mm高水银柱产生的压强[判断题]对错(正确答案)答案解析:托里拆利实验最早测出了大气压强4、11.小敏学习密度后,了解到人体的密度跟水的密度差不多,从而她估测一个中学生的体积约为()[单选题] *A.50 m3B.50 dm3(正确答案)C.50 cm3D.500 cm35、9.在某原子结构模型示意图中,a、b、c是构成该原子的三种不同粒子,能得出的结()[单选题] *A.a和c数量不相等B.b决定原子种类C.质量集中在c上D.a和c之间存在吸引的力(正确答案)6、4.静止在水平地面上的物体受到向上的弹力是因为地面发生了形变.[判断题] *对(正确答案)错7、下列有关力做功的说法中正确的是()[单选题]A.用水平力推着购物车前进,推车的力做了功(正确答案)B.把水桶从地面上提起来,提水桶的力没有做功C.书静止在水平桌面上,书受到的支持力做了功D.挂钩上的书包静止时,书包受到的拉力做了功8、1.与头发摩擦过的塑料尺能吸引碎纸屑。
下列与此现象所反映的原理相同的是()[单选题] *A.行驶的汽车窗帘被吸出去B.挤压后的吸盘吸在光滑的墙上C.用干燥的双手搓开的塑料袋会吸在手上(正确答案)D.两个表面光滑的铅块挤压后吸在一起9、下列措施中,能使蒸发减慢的是()[单选题]A.把盛有酒精的瓶口盖严(正确答案)B.把湿衣服晾在通风向阳处C.用电吹风给湿头发吹风D.将地面上的积水向周围扫开10、停放在水平地面上的汽车对地面的压力和地面对车的支持力是平衡力[判断题] *对错(正确答案)答案解析:相互作用力11、52.“凿壁偷光”原指凿穿墙壁,让邻舍的烛光透过来,后用来形容家贫而勤奋读书。
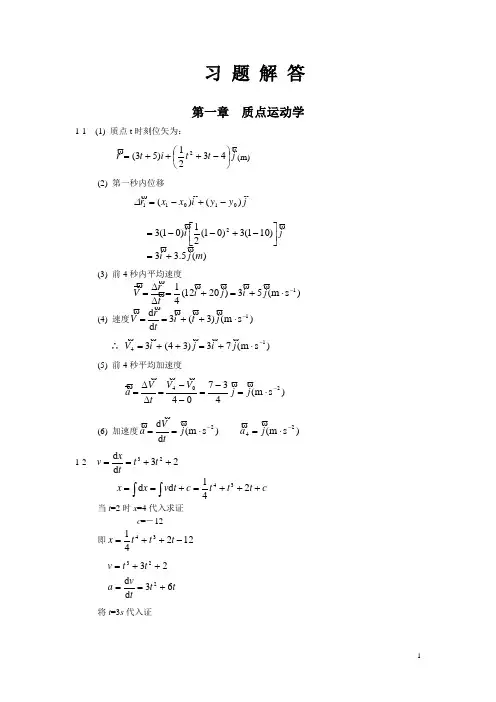
习 题 解 答第一章 质点运动学1-1 (1) 质点t 时刻位矢为:j t t i t r ⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-+++=4321)53(2(m)(2) 第一秒内位移j y y i x x r)()(01011-+-=∆)(5.33)101(3)01(21)01(32m j i ji +=⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡-+--=(3) 前4秒内平均速度)s m (53)2012(411-⋅+=+=∆∆=j i j i t r V(4) 速度)s m ()3(3d d 1-⋅++==j t i t r V∴ )s m (73)34(314-⋅+=++=j i j i V(5) 前4秒平均加速度)s m (43704204-⋅=-=--=∆∆=j j V V t V a (6) 加速度)s m ()s m (d d 242--⋅=⋅==j a j tV a1-2 23d d 23++==t t txv c t t t c t v x x +++=+==⎰⎰241d d 34 当t =2时x =4代入求证 c =-12 即1224134-++=t t t xtt tv a t t v 63d d 23223+==++= 将t =3s 代入证)s m (45)s m (56)(414123133--⋅=⋅==a v m x1-3 (1) 由运动方程⎩⎨⎧+==ty t x 2342消去t 得轨迹方程0)3(2=--y x(2) 1秒时间坐标和位矢方向为 m y m x 5411==[4,5]m: ︒===3.51,25.1ααxytg(3) 第1秒内的位移和平均速度分别为)m (24)35()04(1j i j i r+=-+-=∆)s m (2411-⋅+=∆∆=j i tr V(4) 质点的速度与加速度分别为i t Va j i tr V8d d ,28d d ==+==故t =1s 时的速度和加速度分别为 2111s m 8,s m 28--⋅=⋅+==i a j i V1-4 该星云飞行时间为a 1009.2s 1059.61093.31074.21046.910177915⨯=⨯=⨯⨯⨯⨯ 即该星云是101009.2⨯年前和我们银河系分离的. 1-5 实验车的加速度为g)(25m/s 1047.280.13600101600223≈⨯=⨯⨯==t v a 基本上未超过25g.1.80s 内实验车跑的距离为)(m 40080.13600210160023=⨯⨯⨯==t v s1-6 (1)设第一块石头扔出后t 秒未被第二块击中,则2021gt t v h -= 代入已知数得28.9211511t t ⨯-=解此方程,可得二解为s 22.1s,84.111='=t t第一块石头上升到顶点所用的时间为s 53.18.9/15/10===g v t m由于m t t >1,这对应于第一块石头回落时与第二块相碰;又由于m t t <'1这对应于第一块石头上升时被第二块赶上击中.以20v 和'20v 分别对应于在t 1和'1t 时刻两石块相碰时第二石块的初速度,则由于2111120)(21)(t t g t t v h ∆∆---= 所以184.1)184.1(8.92111)(2121121120--⨯⨯+=∆-∆-+=t t t t g h v m /s 2.17=同理.122.1)122.1(8.92111)(2121121120--⨯⨯+=-'-'+='t t t t g h v ∆∆ m/s)(1.51=(2) 由于'>=123.1t s t ∆,所以第二石块不可能在第一块上升时与第一块相碰.对应于t 1时刻相碰,第二块的初速度为3.184.1)3.184.1(8.92111)(2122122120--⨯⨯+=--+="t t t t g h v ∆∆ m/s)(0.23=1-7 以l 表示从船到定滑轮的绳长,则t l v d /d 0-=.由图可知22h l s -=于是得船的速度为02222d d d d v s h s t l h l lts v +-=-==负号表示船在水面上向岸靠近. 船的加速度为3202022d d d d d d s v h tl v h l ll t v a -=⎥⎥⎦⎤⎢⎢⎣⎡⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛--== 负号表示a 的方向指向岸边,因而船向岸边加速运动.1-8 所求位数为522422221048.9601.0)106(44⨯=⨯⨯⨯==ππωg r n g r1-9 物体A 下降的加速度(如图所示)为222m/s 2.024.022=⨯==t h a 此加速度也等于轮缘上一点在s 3='t 时的切向加速度,即)m/s (2.02='t a在s 3='t 时的法向加速度为)m/s (36.00.1)32.0()(2222=⨯='='=R t a R v a t n1-10 2m /s 2.1=a ,s 5.00=t ,m 5.10=h .如图所示,相对南面,小球开始下落时,它和电梯的速度为m/s)(6.05.02.100=⨯==at v以t 表示此后小球落至底板所需时间,则在这段时间内,小球下落的距离为2021gt t v h +=电梯下降的距离为习题1-9图 习题1-10图2021at t v h +='又20)(21t a g h h h -='-= 由此得s 59.02.18.95.1220=-⨯=-=a g h t而小球相对地面下落的距离为2021gt t v h += 259.08.92159.06.0⨯⨯+⨯= m 06.2= 1-11 人地风人风地v v v+=画出速度矢量合成图(a)又人地风人风地02v v v +'=,速度矢量合成如图(b )两图中风地v应是同一矢量.可知(a )图必是底角为︒45的等腰直角三角形,所以,风向应为西北风,风速为人地人地风地00245cos v v v =︒=)s m (23.41-⋅=1-12 (1) v LvL t 22==(2) 22212u v vLu v L u v L t t t -=++-=+= 1212-⎥⎥⎦⎤⎢⎢⎣⎡⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=v u v L(3) v Lv L t t t '+'=+=21,如图所示风速u 由东向西,由速度合成可得飞机对地速度v u v +=',则22u v V -='.习题1-12图习题1-11图2221222⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛-=--='=v u v L uv L v L t 证毕1-13 (1)设船相对岸的速度为V '(如图所示),由速度合成得V u V +='V 的大小由图1.7示可得αβcos cos u V V +'=即332323cos cos -=⨯-=-='αβu V V 而1212sin sin =⨯=='αβu V 船达到B 点所需时间)s (1000sin =='='=D V DV OB t βAB 两点之距βββsin cos D Dctg S == 将式(1)、(2)代入可得m)(1268)33(=-=D S(2) 由αβsin 101sin 3u V D t ⨯='=船到对岸所需最短时间由极值条件决定0cos sin 11d d 2=⎪⎭⎫⎝⎛-=αααu t 即 2/,0c o s παα==故船头应与岸垂直,航时最短.将α值代入(3)式得最短航时为s)(500105.021012/sin 101333m in=⨯=⨯=⨯=s u t π (3) 设l OB =,则ααββsin cos 2sin sin 22u uV V u D V D V D l -+=''==欲使l 最短,应满足极值条件.习题1-13图a a uV V u u D l '⎢⎢⎣⎡''-+-='cos sin cos 2d d 22αα 0cos 2sin sin 2222=⎥⎦⎤'-+''+αuV V u a a uV 简化后可得01cos cos 222=+'+-'αuVV u a即 01cos 613cos 2=+'-'αa 解此方程得32cos ='α︒=='-2.4832cos 1α 故船头与岸成︒2.48,则航距最短.将α'值代入(4)式得最小航程为222222m in 321232322321000cos 1cos 2⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-⨯⨯⨯-+='-'-+-=ααu uv v u D lkm)(5.1m 105.13=⨯= AB 两点最短距离为km)(12.115.122min min =-=-=D l S第二章 质点动力学2-1 (1)对木箱,由牛顿第二定律,在木箱将要被推动的情况下如图所示,x 向:0cos m ax m in =-f F θ y 向:0sin m in =--Mg F N θ 还有 N f s m ax μ=解以上三式可得要推动木箱所需力F 的最小值为θμθμsin cos s s min -=MgF习题2-1图在木箱做匀速运动情况下,如上类似分析可得所需力F 的大小为θμθμsin cos k k min -=MgF(2)在上面m in F 的表示式中,如果0sin cos s →-θμθ,则∞→m in F ,这意味着用任何有限大小的力都不可能推动木箱,不能推动木箱的条件是0sin cos s ≤-θμθ由此得θ的最小值为s1arctanμθ=2-2 (1)对小球,由牛顿第二定律x 向:ma N T =-θθsin cosy 向:0cos sin =-+mg N T θθ 联立解此二式,可得N)(32.3)30sin 8.930cos 2(5.0)sin cos (=︒+︒⨯⨯=+=ααg a m T N)(74.3)30sin 230cos 8.9(5.0)sin cos (=︒-︒⨯⨯=+=ααa g m N由牛顿第三定律,小球对斜面的压力N)(74.3=='N N(2)小球刚要脱离斜面时N =0,则上面牛顿第二定律方程为mg T ma T ==θθsin ,cos由此二式可解得2m/s 0.1730tan /8.9tan /=︒==θg a2-3 要使物体A 与小车间无相对滑动,三物体必有同一加速度a ,且挂吊B 的绳应向后倾斜。

课程教学大纲系别:基础教学部适用专业:通信与信息工程系(通信工程、电子信息工程、信息工程专业)电子与自动化系(电子科学与技术、物流、机械与自动化专业)课程名称:大学物理实验编者:汪成编写日期:2011年05月审核人:年月日《大学物理实验》课程教学大纲课程编号:121·02211课程名称:中文:大学物理实验英文:physical experiment课程类别:公共必修课总学时: 16学时总学分:1学分适用对象:适用于通信与信息工程系一年级下学期及电子与自动化系二年级上学期的学生。
课程性质:物理学是一门以实验为基础的科学。
物理规律的发现、物理理论的建立,来自于严格的科学实验,并受到实验的检验。
实践证明,物理实验是物理学发展的动力。
在物理学的发展进程中,物理实验和物理理论始终是相互促进、相互制约、共同发展的。
大学物理实验课是高等理工科院校对学生进行基本训练的必修课程,与大学物理理论课一起构成基础物理学知识统一的整体。
由于大学物理实验具有完整的、科学的实验教学课程体系,因此也是一门独立的课程。
是学生进入大学后接受系统实验技能训练的开端,也是后续实验课的基础。
课程目标:按照国家教育部颁布的《高等学校工科本科物理实验课程教学基本要求》,明确了本课程的教学任务是:使学生在中学物理实验的基础上,按照循序渐进的原则,学习物理实验知识和方法,得到实验技能的训练,从而初步了解科学实验的主要过程和基本方法,为今后的学习和工作奠定良好的实验基础。
具体说:(一)知识性目标:本课程通过对实验现象的观察、测量和分析,学习物理实验知识,学习和加深对物理学原理的理解,并使学生初步了解科学实验的主要过程与基本方法和技能,为今后的学习和工作奠定良好的实验基础。
(二)技能性目标:培养学生独立进行科学实验的能力,如通过课前阅读教材或资料准备实验以培养学生的自学能力;通过实验操作培养学生理论联系实际的动手能力;通过观察、分析现象培养学生的思维判断能力;通过正确处理实验数据、撰写合格实验报告培养科研总结能力;通过灵活运用已有知识进行实验设计培养创新能力等。

The Report Of the College Physics ExperimentExperiment 1:optical lever mirror method to measure Young'smodulus of the metalPurpose:1. Master the principle of measuring the small length changes with optical levermirror.2.Learn how to eliminate the systematic errors with symmetric measurement.3.Learn how to estimate the errors to each measured value in accordance with theactual situation.4.Train to deal data with different methods and construction.Theory:Objects should engender deformation more or less by the external force. It is theelastic deformation which will disappear promptly after withdrawing the externalforce when the force is no more than a certain limits. The objects will restore arestituted internal stress after occurring elastic deformation.There is a section S, length L 0 of the equably rod- like (wire-like) material, whenit stretched by the pulling force F, it elongates L Δ, stress is measured as the force per unit cross sectional area ofS F ; and strain is the increase in length of unit length of LL Δ. According to Hook’s Law, the strain rod -like (wire-like)material burdened is proportional to the burdened stress:0ΔL L Y S F Fig. 1 the optical lever Where Y is the coefficient depended on the characterization of the materials .Themodulus is thenFig. 1 the optical leverknown as Young’s modulus (Y). and hence: LS FL Y Δ0 (1) This experiment is to measure the Young ’s modulus of a kind of model steel, in which F can be determined by the calculated weight of weight, sectional area S can be get by calculating the diameter of the wire measured with micrometer screw gouge, 0L can be measured by conventional measurement apparatus such as meter and so on. But L Δis difficult to measure accurately for its small length change used ordinary apparatus. So we choose amplification ——“optical lever mirror” to measure this small change L Δ. The optical lever mirror physical diagram is Fig. 1Fig.2 the principle of optical lever mirrorFig.2 is the principle chart of measuring the tiny length change by optical lever mirror. The left curled object is the optical lever mirror, M is a reflector, b is the so- called short – optical lever mirror arm length, O is fixed- side of b-side, the other side b will rise or fall when the measured object elongating or shortening, and change the direction of normal line of M. The original wire length is 0L , from the right adjusted telescope we can see the reading of scale imagine of M of 1n , while the steel is elongated, from the telescope we can see the reading of scale imagine of M: 2n . In this way, the tiny wire elongation is L Δ, the corresponding angle change of the optical Db MΔn=n-nOlever mirror is θ, and the reading change of scale imagine of M is 21Δn n n -=. Be reversible by the optical path that light lever angle should be θ2. Using the geometric method in Fig.2 we can get:bL ∆=≈θθtg (2) D n D n n ∆=-=≈1222tg θθ (3) Hence n Db L ∆=∆2 (4) Where 12n n n -=∆, equivalent to the displacement of the long arm of optical lever mirror. bD 2 is the magnification of optical lever mirror, as D >> b, so ∆n >> ∆L, that means we get linear amplification of the small amount, and enhance the measurement accuracy of L ∆.This measurement is known as amplification. This amplification has a wide range of applications in designing all kinds of testing equipment for its advantage of stable performance, high precision, linear amplification and so on.Taking into account the wire by the external force there is a lag effect of flexibility, as to say that the steel can’t be due immediately to the elongated length of i L (i i L L L ∆+=0) when it is elongated, but only to the elongation of i i L L δ-. Similarly, the steel can’t be reduced to the length of L i when once the stretching force of the wire has been reduced, but only reduced to i i L L δ+. Therefore the measured length of the wire by the experiment is not the actual elongated or contracted length. In order to eliminate the systematic errors by the lag effect of flexibility, the measurement should be included a symmetrical measurement process of increasing the tensile strength and reducing the tensile strength. To the experiment, we can get this to increase or reduce the weights, we can take average amount of the stretching of wire as long as increase or reduce a corresponding weight to eliminate the effects of lagged volume. That is:[]()()[]i i i i i i L L L L L L L L L L L ∆+=+∆++-∆+=+=0002121δδ减增Procedure:(1)Attach 2kg hanger for weights to end of the wire to remove any irregularities. Adjust the three foot screws under the Young’s modulu s chassis, and observe the standard ruler on the platform at the same time until the middle of the platform is at the level of state.(2)Regulate the location of the optical lever mirror. Take the optical lever mirror on the platform, the two front feet on the cross- platform, the rear foot on the cylindrical casing of the lower end of the fixed wire (the rear foot must be placed on the edge of the metal casing, but not on the location of the gap),and let the mirror of optical lever mirror to be basic vertical or slight angle, as shown in Fig. 1.(3)Adjust the telescope. Place the telescope about 2m away from the optical lever mirror. Loose the fixed screw of telescope and move up or down to let the mirror of optical lever mirror and the telescope are on the same height. Take aim at the mirror of optical lever mirror along the tube axis above the telescope. Shift the fixed position of the telescope until we can see the scale imagine from the optical lever mirror. And then observe from the eyepiece. Adjust the eyepiece to see the cross wire clearly and finally revolve the focusing hand wheel to flexible the telescope in the tube until we can see the ruler scale clearly from the telescope.(4)Observe the stretch change. Attach 2kg hanger for weights to the end of the wire as the beginning, and take the telescope reading of 0n . Load the measured wire with successive kilogram weights, taking the telescope reading after each addition ——76543210n ,n ,n ,n ,n ,n ,n ,n . Unload kilogram by kilogram, and read thetelescope at each stage ——01234567n ,n ,n ,n ,n ,n ,n ,n ''''''''. Note: Add or subtract the weight lightly to avoid a relatively large vibration. After adding or subtracting the weight, the wire will have a scalable micro-vibration, and we should read after the steel gradually becoming stable.(5)Measure the distance b from the front foot to the rear foot of optical lever mirror. Rent the 3 feet of the optical lever mirror in white paper. Draw the connection of the two front feet and then measure the vertical distance from the rear foot to theline with the vernier scale.(6)Measure the diameter of the wire at several points about 3-5 times along its length and find a mean value. This measurement must be done carefully with a micrometer screw-gauge and note the zero error each time.(7)Use meter ruler to measure the distance D from the plane mirror to the scale.(8)Use meter ruler to measure the original length of wire.(9)Notes①The wire must be clamped tightly at the both side, at one hand to reduce the system error, and at the other hand to avoid falling down to damage the test devices.②Don ’t move the telescope and the table in the measuring and reading process, or you must start measuring again.③Keep the measured wire straight so as to avoid misusing the measuring process for the elongation, resulting in measurement error.④Keeping the weight should be 1kg and don ’t touch the mirror in the measuring progress.⑤You must adjust the telescope in a certain scope to avoid damaging it.Data and the resultsKG △x=0.05 CM1.0F =仪镜尺距(he distance from the ruler to the mirror)D =150 mm ; △x仪= 0.05 CMThe wire length:L1(上读数) / cm L2(下读数)/cm 钢丝长度L/cm7.8 42.2 34.4The diameter of the wire:First record=0.02 mm ; △d仪=0.004 mm次数 1 2 3 4 5 6diameter ofthe wire/mm0.80 0.81 0.81 0.85 0.85 0.82光杠杆常数b=85.17 mm ;△b仪=0.002 mmgraphical method:F(*9.80N)10.0 11.5 13.0 14.5 16.5 17.5 19.0 20.5 22.0 23.5 25.0 26.5△x/c m 2.0152.1952.3552.512.7552.943.163.4053.613.834.0054.20The discuss of this experiment and my experiment:After this experiment I know that we should use plot to obtain the value of Y in this experiment.Eliminating the systematic errors in the experiment is also very important.I think that I have learned how to eliminate the systematic errors with symmetric measurement.I also have learned that how to estimate the errors to each measured value in accordance with the actual situation.To deal data withdifferent methods and construction is the purpose that we must get.。



北京邮电大学物理实验课程设计实验报告大学物理实验课程设计实验报告姓名:郑友行学号:10211388 班级:309重力加速度的测定一、实验任务:精确测定北京地区的重力加速度二、实验要求:测量结果的相对不确定度不超过5%三、物理模型的建立及比较初步确定有以下六种模型方案:方法一、用打点计时器测量所用仪器为:打点计时器、直尺、带钱夹的铁架台、纸带、夹子、重物、学生电源等. 利用自由落体原理使重物做自由落体运动.选择理想纸带,找出起始点0,数出时间为t的P点,用米尺测出OP的距离为h,其中t=0.02秒×两点间隔数.由公式h=gt2/2得g=2h/t2,将所测代入即可求得g.方法二、用滴水法测重力加速度调节水龙头阀门,使水滴按相等时间滴下,用秒表测出n个(n取50—100)水滴所用时间t,则每两水滴相隔时间为t′=t/n,用米尺测出水滴下落距离h,由公式h=gt′2/2可得g=2hn2/t2.方法三、取半径为R的玻璃杯,内装适当的液体,固定在旋转台上.旋转台绕其对称轴以角速度ω匀速旋转,这时液体相对于玻璃杯的形状为旋转抛物面重力加速度的计算公式推导如下:取液面上任一液元A,它距转轴为x,质量为m,受重力mg、弹力N.由动力学知:Ncosα-mg=0(1)Nsinα=mω2x(2)两式相比得tgα=ω2x/g,又tgα=dy/dx,∴dy=ω2xdx/g,∴y/x=ω2x/2g.∴g=ω2x2/2y. .将某点对于对称轴和垂直于对称轴最低点的直角坐标系的坐标x、y测出,将转台转速ω代入即可求得g.方法四、光电控制计时法调节水龙头阀门,使水滴按相等时间滴下,用秒表测出n个(n取50—100)水滴所用时间t,则每两水滴相隔时间为t′=t/n,用米尺测出水滴下落距离h,由公式h=gt′2/2可得g=2hn2/t2.方法五、用圆锥摆测量所用仪器为:米尺、秒表、单摆. 使单摆的摆锤在水平面内作匀速圆周运动,用直尺测量出h(见图1),用秒表测出摆锥n转所用的时间t,则摆锥角速度ω=2πn/t 摆锥作匀速圆周运动的向心力F=mgtgθ,而tgθ=r/h所以mgtgθ=mω2r由以上几式得:g=4π2n2h/t2. 将所测的n、t、h代入即可求得g 值.方法六、单摆法测量重力加速度在摆角很小时,摆动周期为:则通过对以上六种方法的比较,本想尝试利用光电控制计时法来测量,但因为实验室器材不全,故该方法无法进行;对其他几种方法反复比较,用单摆法测量重力加速度原理、方法都比较简单且最熟悉,仪器在实验室也很齐全,故利用该方法来测最为顺利,从而可以得到更为精确的值。



习题 1选择题(1) 一运动质点在某瞬时位于矢径),(y x r的端点处,其速度大小为(A)dt dr (B)dt r d(C)dtr d ||(D) 22)()(dt dy dt dx[答案:D](2) 一质点作直线运动,某时刻的瞬时速度s m v /2 ,瞬时加速度2/2s m a ,则一秒钟后质点的速度(A)等于零 (B)等于-2m/s (C)等于2m/s (D)不能确定。
[答案:D](3) 一质点沿半径为R 的圆周作匀速率运动,每t 秒转一圈,在2t 时间间隔中,其平均速度大小和平均速率大小分别为(A)t R t R 2,2 (B) tR2,0 (C) 0,0 (D) 0,2tR[答案:B]填空题(1) 一质点,以1 s m 的匀速率作半径为5m 的圆周运动,则该质点在5s 内,位移的大小是 ;经过的路程是 。
[答案: 10m ; 5πm](2) 一质点沿x 方向运动,其加速度随时间的变化关系为a=3+2t (SI),如果初始时刻质点的速度v 0为5m ·s -1,则当t 为3s 时,质点的速度v= 。
[答案: 23m ·s -1](3) 轮船在水上以相对于水的速度1V 航行,水流速度为2V,一人相对于甲板以速度3V 行走。
如人相对于岸静止,则1V 、2V 和3V的关系是 。
[答案: 0321 V V V]一个物体能否被看作质点,你认为主要由以下三个因素中哪个因素决定:(1) 物体的大小和形状; (2) 物体的内部结构; (3) 所研究问题的性质。
解:只有当物体的尺寸远小于其运动范围时才可忽略其大小的影响,因此主要由所研究问题的性质决定。
下面几个质点运动学方程,哪个是匀变速直线运动?(1)x=4t-3;(2)x=-4t 3+3t 2+6;(3)x=-2t 2+8t+4;(4)x=2/t 2-4/t 。
给出这个匀变速直线运动在t=3s 时的速度和加速度,并说明该时刻运动是加速的还是减速的。

大学物理实验模拟试题五一、填空题:1.物理学从本质上说是一门____科学,物理规律的发现和物理理论的建立,都必须以严格的____为基础。
并受到____的检验。
2.测量的四要素是______、____、____和____.3.误差按性质可分为____ 和____误差.4.表示重复测量数据离散程度的是____度,它属于____误差,用____误差(偏差)来描述它比较合适。
5.指出下列各数的有效数字的位数.(1) 0。
05cm 是____,(2)mm 310321.4-⨯是____位,( 3)周长R π2=中的2是____,( 4)kg )012.0842.3(±中的kg 842.3是____位.6.计算 =⨯+01.0647.9326.000.100____ ,其中00.100=____,0.326+9.647=____,=+647.9326.000.100____。
7.分光仪的四大组成部分是____、____、____和____。
8.在牛顿环实验的调节过程中,若发现视场中半明半暗,应调节____,若发现视场非常明亮.但却调节不出于涉环,其原因是____,若干涉环不够清晰应调节____________。
9.试举出米尺(类)外的三种测量长度的仪器(具) :(l)____(2)____(3)________10.在落球法测液体的粘度系数中,要测小球的运动过度,这个速度应是小球作____运动的速度;如果实验时。
液体中有气泡,可能使这个速度____,从而使η值的测量值____.二、选择题:1、选出下列说法的正确者().A .可用仪器最小分度或最小分度的一半作为该仪器的一次测量的误差;B .可以用仪器精度等级估算该仪器一次测量的误差;C .只要知道仪器的最小分度值,就可以大致确定仪器误差的数量级;D .以上三种说法都正确.2.测量一约为1.5伏特的电压时要求其结果的相对误差小于1。
5%,则应选用下列哪一种规格的伏特表()。
大学物理实验模拟试题一一、填空题(总分42分,每空1分)1. 测量结果的有效数字的位数由 和 共同决定。
2. 50分度的游标卡尺,其仪器误差为 。
3. 量程为10mA 电流表,其等级为1。
0,当读数为6。
5mA 时,它的最大误差为 。
4. 不确定度 表示 . 5. lg35.4= .6. 在分光计实验中,望远镜的调节用的是 法.7. S 是表示多次测量中每次测量值的 程度,它随测量次数n 的增加变化很 ,N S 表示偏离真值的多少,它随测量次数n 的增加变化很 。
8. 在杨氏模量实验中,若望远镜的叉丝不清楚,应调节望远镜 的焦距,若观察到的标尺像不清楚则应调节望远镜 的焦距。
钢丝的伸长量用 法来测定。
9. 计算标准偏差我们用 法,其计算公式为 。
10.表示测量数据离散程度的是 精密度 ,它属于 偶然 误差,用 误差(偏差)来描述它比较合适.11.用20分度的游标卡尺测长度,刚好为15mm ,应记为 mm 。
12.根据获得测量结果的不同方法,测量可分为 测量和 测量;根据测量的条件不同,可分为 测量和 测量.13.电势差计实验中,热电偶的电动势与温差的关系为 关系,可用法、 法和 法来求得经验方程。
14.789。
30×50÷0.100= .15.10.1÷4。
178= 。
16.2252= 。
17.用分光仪测得一角度为300,分光仪的最小分度为1,,测量的结果为 。
18.对于连续读数的仪器,如米尺、螺旋测微计等,就以 作为仪器误差。
19.分光计测角度时由于度盘偏心引起的测量角度误差按正弦规律变化,这是 误差.20.在示波器内部,同步、扫描系统的功能是获得 电压信号,这种电压信号加在 偏转板上,可使光点匀速地沿X 方向从左向右作周期性运动.21.系统误差有 确定性 的特点,偶然误差有 随机性 的特点。
22.在测量结果的数字表示中,由若干位可靠数字加上 位可疑数字,便组成了有效数字。
习题十10-1 一半径r =10cm 的圆形回路放在B =0.8T 的均匀磁场中.回路平面与B垂直.当回路半径以恒定速率tr d d =80cm ·s -1 收缩时,求回路中感应电动势的大小.解: 回路磁通 2πr B BS m ==Φ 感应电动势大小40.0d d π2)π(d d d d 2====tr rB r B ttm Φε V10-2 一对互相垂直的相等的半圆形导线构成回路,半径R =5cm ,如题10-2图所示.均匀磁场B =80×10-3T ,B 的方向与两半圆的公共直径(在Oz 轴上)垂直,且与两个半圆构成相等的角α 当磁场在5ms 内均匀降为零时,求回路中的感应电动势的大小及方向.解: 取半圆形cba 法向为i, 题10-2图则 αΦcos 2π21B R m =同理,半圆形adc 法向为j,则αΦcos 2π22B R m =∵ B 与i夹角和B 与j 夹角相等,∴ ︒=45α则 αΦcos π2R B m =221089.8d d cos πd d -⨯-=-=Φ-=tB RtmαεV方向与cbadc 相反,即顺时针方向.题10-3图*10-3 如题10-3图所示,一根导线弯成抛物线形状y =2ax ,放在均匀磁场中.B与xOy 平面垂直,细杆CD 平行于x 轴并以加速度a 从抛物线的底部向开口处作平动.求CD 距O 点为y 处时回路中产生的感应电动势.解: 计算抛物线与CD 组成的面积内的磁通量⎰⎰=-==aym y B x x y B S B 0232322d )(2d 2ααΦ∴ v y Bty y Btm 21212d d d d ααε-=-=Φ-=∵ ay v 22=∴ 212y a v =则 ααεaByy a yBi 8222121-=-= i ε实际方向沿ODC .题10-4图10-4 如题10-4图所示,载有电流I 的长直导线附近,放一导体半圆环MeN 与长直导线共面,且端点MN 的连线与长直导线垂直.半圆环的半径为b ,环心O 与导线相距a .设半圆环以速度v 平行导线平移.求半圆环内感应电动势的大小和方向及MN 两端的电压NM UU -.解: 作辅助线MN ,则在MeNM 回路中,沿v方向运动时0d =m Φ ∴ 0=MeNM ε 即 MN MeN εε=又∵ ⎰+-<+-==ba ba MN ba b a Ivl vB 0ln2d cos 0πμπε所以MeN ε沿NeM 方向,大小为ba b a Iv-+ln20πμM 点电势高于N 点电势,即ba b a IvU U N M -+=-ln20πμ题10-5图10-5如题10-5所示,在两平行载流的无限长直导线的平面内有一矩形线圈.两导线中的电流方向相反、大小相等,且电流以tI d d 的变化率增大,求:(1)任一时刻线圈内所通过的磁通量; (2)线圈中的感应电动势. 解: 以向外磁通为正则 (1) ]ln[lnπ2d π2d π2000da db ab Ilr l r Ir l r Iab b ad d m +-+=-=⎰⎰++μμμΦ(2) tIb a b d a d l t d d ]ln [ln π2d d 0+-+=-=μΦε 10-6 如题10-6图所示,用一根硬导线弯成半径为r 的一个半圆.令这半圆形导线在磁场中以频率f 绕图中半圆的直径旋转.整个电路的电阻为R .求:感应电流的最大值.题10-6图解: )cos(2π02ϕωΦ+=⋅=t r B S B m∴Bfr f r B r B t r B tm m i 222202ππ22π2π)sin(2πd d ===+=-=ωεϕωωΦε∴ RBf r RI m 22π==ε10-7 如题10-7图所示,长直导线通以电流I =5A ,在其右方放一长方形线圈,两者共面.线圈长b =0.06m ,宽a =0.04m ,线圈以速度v =0.03m ·s -1垂直于直线平移远离.求:d =0.05m 时线圈中感应电动势的大小和方向.题10-7图解: AB 、CD 运动速度v方向与磁力线平行,不产生感应电动势. DA 产生电动势⎰==⋅⨯=A D Ivb vBb l B v d2d )(01πμεBC 产生电动势)(π2d )(02d a I vbl B v CB+-=⋅⨯=⎰με∴回路中总感应电动势8021106.1)11(π2-⨯=+-=+=ad dIbvμεεεV方向沿顺时针.10-8 长度为l 的金属杆ab 以速率v 在导电轨道abcd 上平行移动.已知导轨处于均匀磁场B中,B 的方向与回路的法线成60°角(如题10-8图所示),B的大小为B =kt (k 为正常).设t =0时杆位于cd 处,求:任一时刻t 导线回路中感应电动势的大小和方向.解: ⎰==︒=⋅=22212160cos d klvt lv kt Blvt S B m Φ∴ klvt tm -=-=d d Φε即沿abcd 方向顺时针方向.题10-8图10-9 一矩形导线框以恒定的加速度向右穿过一均匀磁场区,B的方向如题10-9图所示.取逆时针方向为电流正方向,画出线框中电流与时间的关系(设导线框刚进入磁场区时t =0). 解: 如图逆时针为矩形导线框正向,则进入时0d d <Φt,0>ε;题10-9图(a)题10-9图(b)在磁场中时0d d =tΦ,0=ε;出场时0d d >tΦ,0<ε,故t I -曲线如题10-9图(b)所示.题10-10图10-10 导线ab 长为l ,绕过O 点的垂直轴以匀角速ω转动,aO =3l 磁感应强度B 平行于转轴,如图10-10所示.试求: (1)ab 两端的电势差; (2)b a ,两端哪一点电势高? 解: (1)在Ob 上取dr r r +→一小段则 ⎰==320292d lOb l B r rB ωωε同理 ⎰==32181d lOa l B r rB ωωε∴ 2261)92181(l B l B Ob aO ab ωωεεε=+-=+=(2)∵ 0>ab ε 即0<-b a U U ∴b 点电势高.题10-11图10-11 如题10-11图所示,长度为b 2的金属杆位于两无限长直导线所在平面的正中间,并以速度v平行于两直导线运动.两直导线通以大小相等、方向相反的电流I ,两导线相距2a .试求:金属杆两端的电势差及其方向. 解:在金属杆上取r d 距左边直导线为r ,则 ba b a Ivr ra rIv l B v ba ba BAAB -+-=-+-=⋅⨯=⎰⎰+-lnd )211(2d )(00πμπμε∵ 0<AB ε ∴实际上感应电动势方向从A B →,即从图中从右向左,∴ ba ba Iv U AB -+=ln 0πμ题10-12图10-12 磁感应强度为B的均匀磁场充满一半径为R 的圆柱形空间,一金属杆放在题10-12图中位置,杆长为2R ,其中一半位于磁场内、另一半在磁场外.当tB d d >0时,求:杆两端的感应电动势的大小和方向.解: ∵ bc ab ac εεε+=tB R B R ttab d d 43]43[d d d d 21=--=-=Φε=-=tab d d 2ΦεtB R B R td d 12π]12π[d d 22=--∴ tB R R ac d d ]12π43[22+=ε∵0d d >tB∴ 0>ac ε即ε从c a → 10-13 半径为R 的直螺线管中,有dtdB >0的磁场,一任意闭合导线abca ,一部分在螺线管内绷直成ab 弦,a ,b 两点与螺线管绝缘,如题10-13图所示.设ab =R ,试求:闭合导线中的感应电动势.解:如图,闭合导线abca 内磁通量)436π(22R R B S B m-=⋅= Φ∴ tB R R i d d )436π(22--=ε∵ 0d d >tB∴0<i ε,即感应电动势沿acba ,逆时针方向.题10-13图题10-14图10-14 如题10-14图所示,在垂直于直螺线管管轴的平面上放置导体ab 于直径位置,另一导体cd 在一弦上,导体均与螺线管绝缘.当螺线管接通电源的一瞬间管内磁场如题10-14图示方向.试求:(1)ab 两端的电势差;(2)cd 两点电势高低的情况.解: 由⎰⎰⋅-=⋅l S t Bl Ed d d d 旋知,此时旋E 以O 为中心沿逆时针方向.(1)∵ab 是直径,在ab 上处处旋E与ab 垂直 ∴ ⎰=⋅ll 0d旋∴0=ab ε,有b a U U =(2)同理, 0d >⋅=⎰l Ecddc旋ε∴ 0<-c d U U 即d c U U >题10-15图10-15 一无限长的直导线和一正方形的线圈如题10-15图所示放置(导线与线圈接触处绝缘).求:线圈与导线间的互感系数.解: 设长直电流为I ,其磁场通过正方形线圈的互感磁通为⎰==32300122ln π2d π2aa Ia r rIa μμΦ∴ 2ln π2012aIM μΦ==10-16 一矩形线圈长为a =20cm ,宽为b =10cm ,由100匝表面绝缘的导线绕成,放在一无限长导线的旁边且与线圈共面.求:题10-16图中(a)和(b)两种情况下,线圈与长直导线间的互感.解:(a)见题10-16图(a),设长直电流为I ,它产生的磁场通过矩形线圈的磁通为2ln π2d 2πd 020)(12Iarr Ia S B bbS μμΦ⎰⎰==⋅=∴ 6012108.22ln π2-⨯===aNIN M μΦ H(b)∵长直电流磁场通过矩形线圈的磁通012=Φ,见题10-16图(b) ∴ 0=M题10-16图题10-17图10-17 两根平行长直导线,横截面的半径都是a ,中心相距为d ,两导线属于同一回路.设两导线内部的磁通可忽略不计,证明:这样一对导线长度为l 的一段自感为πμl L 0=Inaa d -.解: 如图10-17图所示,取r l S d d = 则 ⎰⎰-----=--=-+=ad aad aad d aa d Il r r rIl r l r I r πI )ln(ln2πd )d11(π2d ))d (π22(0000μμμμΦaa d Il-=lnπ0μ∴ aa d lI L -==lnπ0μΦ10-18 两线圈顺串联后总自感为1.0H ,在它们的形状和位置都不变的情况下,反串联后总自感为0.4H .试求:它们之间的互感. 解: ∵顺串时 M L L L 221++= 反串联时M L L L 221-+='∴ M L L 4='-15.04='-=L L M H10-19图10-19 一矩形截面的螺绕环如题10-19图所示,共有N 匝.试求: (1)此螺线环的自感系数;(2)若导线内通有电流I ,环内磁能为多少? 解:如题10-19图示 (1)通过横截面的磁通为 ⎰==baab NIhr h r NIlnπ2d π200μμΦ磁链 ab Ih N N ln π220μΦψ==∴ ab h N IL lnπ220μψ==(2)∵ 221LIW m =∴ ab hI N W m ln π4220μ=10-20 一无限长圆柱形直导线,其截面各处的电流密度相等,总电流为I .求:导线内部单位长度上所储存的磁能. 解:在R r <时 20π2RI B rμ=∴ 4222002π82RrI Bw m μμ==取 r r V d π2d =(∵导线长1=l ) 则 ⎰⎰===RRm I Rr r I r r w W 0204320π16π4d d 2μμπ。