高英修辞手法Personification
- 格式:doc
- 大小:33.50 KB
- 文档页数:7

An Introduction to Figures of Speech(修辞格)Rhetoric(修辞学、说话技巧)1.Simile(明喻)Simile is an expression of comparison between two different things. It is usually introduced by “as”“as if”or “like”, and sometimes also by “as…as/as…so”, and “resemble” as the signs of comparison.明喻就是打比方,指一事物像另一事物的修辞格。
常用的比喻词有“as” ,“as if”or “like”, and sometimes also by “as…so /as…as”, and “resemble”等1). Mercy drops as the gentle rain from heaven upon the place beneath. —Shakespeare2). Thecheque fluttered to the floor like a bird with a broken wing.3).The apartments were smashed apart as if by a gigantic fist. ------砸得粉碎4). Self-criticism is as necessary to us as air to water.5). As a man whispers, so the breeze makes a low, hissing sound.6). Learning resembles scaling the heights.2. Metaphor(隐喻/暗喻)**Metaphor contains an implied comparison, it calls one thing by the name of another or one thing is described in terms of another.隐喻是一种隐含着比喻的修辞格,它直接把一种事物比为另一种事物,不用比喻词,通常比较含蓄。

英语中的修辞手法总结
英语中的修辞手法包括以下几种:
1. 比喻(Metaphor):用某个事物来比喻另一个事物,使语言更加形象生动。
例子:她的笑容如阳光一般温暖。
2. 拟人(Personification):将无生命的事物赋予人的特征,使表达更具有生动感和感染力。
例子:风儿吹过,树叶纷飞。
3. 对偶(Parallelism):通过平行的句子结构或词语来表达相同的或类似的意思,使句子更有力量和韵律感。
例子:Love is patient, love is kind. It does not envy, it does not boast, it is not proud.
4. 反问(Rhetorical question):表现出说话人的强烈感情和肯定态度,让听者思考并自行找到答案。
例子:难道我们的作品不应该反映现实生活的美好吗?
5. 比较(Comparison):通过将两个不同的事物进行类比,使得听者或读者更容易理解某个观点。
例子:她跑得像一只兔子一样快。
以上是英语中常见的五种修辞手法,当然还有其他一些较少使用的修辞手法,如反语、夸张、卡里加里(Cacophony)等。
这些修辞手法都可以让语言更生动、更有表现力。

高中英语知识点归纳写作修辞手法与语言风格的应用高中英语知识点归纳:写作修辞手法与语言风格的应用英语作为一门广泛使用的语言,其修辞手法与语言风格在写作中发挥着重要作用。
本文将对高中英语中常见的几种修辞手法和语言风格进行归纳和解析,以帮助学生加深对这些知识点的理解和应用。
一、修辞手法1. 比喻(Metaphor)比喻是通过将某一事物与另一事物进行类比来突出事物的某种特点或特征。
常见的比喻手法包括将人物与动物进行类比、将抽象概念与具体物体进行类比等。
例句:Her smile is a ray of sunshine.(她的微笑如阳光一般灿烂)2. 拟人(Personification)拟人是指将无生命的事物赋予人的特点和行为,使文本更加形象生动,增强表达的力度。
例句:The wind whispered through the trees.(风声从树间响起)3. 夸张(Exaggeration)夸张是指将某种情感、事物或特征表述得极端化,以强调其程度或效果,使文章更富有感染力。
例句:I'm so hungry, I could eat a horse.(我饿得可以吃一匹马)4. 对比(Contrast)对比是通过将两个相反的事物或观点进行对比,以突出二者之间的差异和矛盾,从而加深读者对某种主题或观点的理解。
例句:Love is a battlefield, where there's both joy and sorrow.(爱情就像战场,既有欢乐,也有悲伤)二、语言风格1. 积极表达积极表达是指用乐观、积极的语言风格来表达观点、情感或态度,以增强文章的亲和力和说服力。
例句:We should never give up, no matter how difficult the road ahead may be.(无论前方的道路有多困难,我们都不能放弃)2. 简洁明了简洁明了是指用简练、明晰的语言表达思想,避免冗长和复杂的句子,使文章更易于理解和阅读。

一、明喻(simile)是以两种具有相同特征的事物和现象进行对比,表明本体和喻体之间的相似关系,两者都在对比中出现。
常用比喻词like, as, as if, as though等,补充:二、隐喻(metaphor)这种比喻不通过比喻词进行,而是直接将用事物当作乙事物来描写,甲乙两事物之间的联系和相似之处是暗含的。
补充:三、提喻(synecdoche)又称举隅法,主要特点是局部代表全体,或以全体喻指部分,或以抽象代具体,或以具体代抽象。
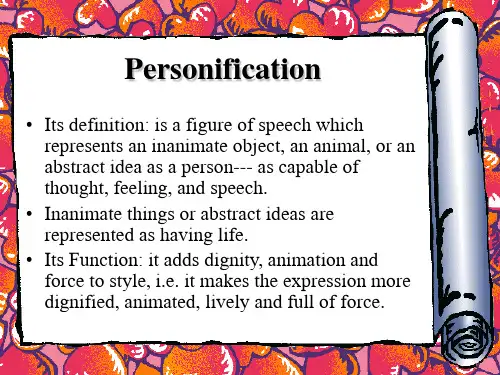
四、拟人(personification)这种修辞方法是把人类的特点、特性加于外界事物之上,使之人格化,以物拟人,以达到彼此交融,合二为一。
五、夸张(hyperbole)这是运用丰富的想象,过激的言词,渲染和装饰客观事物,以达到强调的效果。
六、叠言(rhetorical repetition)这种修辞法是指在特定的语境中,将相同的结构,相同意义词组成句子重叠使用,以增强语气和力量。
七、借代(metonymy)是指两种不同事物并不相似,但又密不可分,因而常用其中一种事物名称代替另一种。
八、双关语(pun)是以一个词或词组,用巧妙的办法同时把互不关联的两种含义结合起来,以取得一种诙谐有趣的效果。
九、拟声(onomatcpocia)是摹仿自然界中非语言的声音,其发音和所描写的事物的声音很相似,使语言显得生动,富有表现力。
十、讽刺(irony)是指用含蓄的褒义词语来表示其反面的意义,从而达到使本义更加幽默,更加讽刺的效果。
十一、通感(synesthesia)是指在某个感官所产生的感觉,转到另一个感官的心理感受。
十二、头韵法(alliteration)在文句中有两个以上连结在一起的词或词组,其开头的音节有同样的字母或声音,以增强语言的节奏感。
英语修辞手法1) Simile:(明喻)It is a figure of speech which makes a comparison between two unlike elements having at least one quality or characteristic (特性)in common. To make the comparison, words like as, as...as, as if and like are used to transfer the quality we associate with one to the other. For example, As cold waters to a thirsty soul, so is good news from a far country./ This elephant is like a snake as anybody can see.2) Metaphor:(暗喻)It is like a simile, also makes a comparison between two unlike elements, but unlike a simile, this comparison is implied rather than stated. For example, the world is a stage./ The diamond department was the heart and center of the store.3) Analogy: (类比)It is also a form of comparison, but unlike simile or metaphor which usually uses comparison on one point of resemblance, analogy draws a parallel between two unlike things that have several common qualities or points of resemblance.4) Personification: (拟人)It gives human form of feelings to animals, or life and personal attributes(赋予) to inanimate(无生命的) objects, or to ideas and abstractions(抽象). For example, the wind whistled through the trees.5) Hyperbole: (夸张)It is the deliberate use of overstatement or exaggeration to achieve emphasis. For instance, he almost died laughing.6) Understatement: (含蓄陈述)It is the opposite of hyperbole, or overstatement. It achieves its effect of emphasizing a fact by deliberately(故意地) understating it, impressing the listener or the reader more by what is merely implied or left unsaid than by bare statement. For instance, It is no laughing matter.7) Euphemism: (委婉)It is the substitution of an agreeable or inoffensive(无冒犯) expression for one that may offend or suggest something unpleasant. For instance, we refer to "die" as” pass away".8) Metonymy (转喻)It is a figure of speech that has to do with the substitution of the mane of one thing for that of another. For instance, the pen (words) is mightier than the sword (forces). 借代(metonymy)是指两种不同事物并不相似,但又密不可分,因而常用其中一种事物名称代替另一种。

Rhetorical Devicessimile 明喻metaphor 暗喻hyperbole 夸张metonymy 转喻synecdoche 借喻mixed metaphor 混合暗喻personification 拟人antithesis 对仗parallelism 排比transferred epithet 转移修饰alliteration 押头韵onomatopoeia 拟声词1.The charm of conversation is that it does not really start from anywhere,and no one has any idea where it will go as it meanders or leaps and sparkles or just glows. (mixed metaphor)2.Perhaps it is because of my upbringing in English pubs that I think barconversation has a charm of its own. (hyperbole)3.The fact that their marriages may be on the rocks, or that their love affairshave broken or even that they got out of bed on the wrong side is simply not a concern. (metaphor)4.They are like the musketeers of Dumas who, although they lived side byside with each other, did not delve into each other's lives.(simile & metaphor)5.The glow of the conversation burst into flames. (metaphor)6.The conversation was on wings. (metaphor)7.Is the phrase in Shakespeare? (synecdoche)8.…that suddenly the alchemy of conversation took place, and all at oncethere was a focus.(metaphor)9.The Elizabethans blew on it as on a dandelion clock.(simile)10.The King's English slips and slides in conversation.(alliteration)11.the sinister corridor of our age(metaphor)我们的时代罪恶的走廊12.Other people may celebrate the lofty conversations in which the greatminds are supposed to have indulged in the great salons of 18th century.(synecdoche)13. I have an unending love affair with dictionaries.(metaphor)14. Otherwise one will bind the conversation. (metaphor)15. We would never have gone to Australia, or leaped back in time to theNorman Conquest. (metaphor)16.The burying-ground is merely a huge waste of hummocky earth, like aderelict building-lot.(simile)17.…and fling over it a little of the dried-up, lumpy earth, which is like brokenbrick.(simile)18. Are they really the same flesh as your self ?(synecdoche)19.They sweat and starve for a few years.(alliteration)20.…and sore-eyed children cluster everywhere in unbelievable numbers, likeclouds of flies. (simile)21. …turning chair-legs at lightning speed. (hyperbole)22.There was a frenzied rush of Jews.(transferred epithet)23.…are working in dark fly-infested booths that look like caves. (simile)24.A white skin is always fairly conspicuous.(synecdoche)25.The soil is exactly like broken-up brick .(simile)26.…winding up the road with a clumping of boots and a clatter of ironwheels.(onomatopoeia)27.Their feet squashed into boots that looked like blocks of wood.(simile)28.And really it was like watching a flock of cattle to see the long column.(simile)29.…while the great white birds drifted ov er them in the opposite direction,glittering like scraps of paper.(simile)30.friend and foe(alliteration)31.(metonymy)32.We shall pay any price, bear any burden…(alliteration)33.United,there is little we cannot do in a host of co-operative ventures.Divided,there is little we can do,for we dare not meet a powerful challenge at odds and split asunder.(antithesis)只要我们团结一致,我们将无所不能,完成众多的合作事业;一旦我们分歧对立,我们将一事无成,因为我们不敢遇见一个与我们意见相左的强大挑战,最后导致四分五裂。

高级英语中的修辞手法总结带课文中例句
高级英语中常见的修辞手法包括:
1. 隐喻(Metaphor):隐喻是一种不直接说明事物,而是通过比较或比喻来暗示某一事物的修辞手法。
例如,“爱情是一座城堡,每个人都在寻找自己的归属”(隐喻,将爱情比喻为城堡)。
2. 反讽(Irony):反讽是一种表面说一套,实际上表达的却是与字面意思
相反的修辞手法。
例如,“我很喜欢去健身房锻炼,只是我的床喜欢把我困住”(反讽,表达的是作者不想去健身房)。
3. 排比(Parallelism):排比是一种通过使用结构相似的句式来表达相近
或相同意思的修辞手法。
例如,“他跳得高,跑得快,游得远”(排比,强调他各方面都很优秀)。
4. 拟人(Personification):拟人是一种将非人类事物赋予人类特性的修辞手法。
例如,“月亮害羞地躲进了云层里”(拟人,将月亮人格化)。
5. 夸张(Hyperbole):夸张是一种通过夸大或缩小事物来表达强烈情感的修辞手法。
例如,“他高兴得像中了彩票一样”(夸张,强调他非常高兴)。
以上是高级英语中常见的修辞手法及例句,希望对你有所帮助。

最权威的国际教育服务平台
资料来源:教育优选 /
SAT 阅读中英文修辞手法(6)
修辞题是SAT 阅读中常见的考点。
本文就为童鞋们全面介绍一下SAT 阅读涉及到的21种修辞手法,其中包括像明喻、类比、拟人、双关等等,建议大家在备考SAT 阅读的时候有针对性地进行复习。
6. Personification 拟人
拟人是把生命赋予无生命的事物,是把人类的特点、特性加于外界事物之上,使之人格化,以物拟人,以达到彼此交融,合二为一。
例如:
(1) She may have tens of thousand of babiesin one summer.(From “ Watching Ants ”) 一个夏天她可能生育成千上万个孩子。
这里用“she ”和“babies ”把蜜蜂比作人类妇女的生育。
(2) My only worry was that January wouldfind me hunting for a job again. 我唯一担心的是,到了一月份我又得去找工作。
英语里常把“年”“月”“日”人格化,赋以生命,使人们读起来亲切生动。


Onomatopoeia (拟声)Alliteration(头韵) Simile(明喻)Metaphor(隐喻)Metonymy(转喻)Irony(反语) Repetition重复Parallelism平行结构: Personification(拟人)Analogy类比1.Onomatopoeia (拟声): to produce sound effectIn describing the sounds heard at the bazaar, the author supplies readers with a batch of verbs and nouns.tinkle bang clash creak squeak rumble grunt groan2.Alliteration(头韵):Clean & Clear;hip hopdull, drilled, docile... (L5)for his hearth and home (L5)3.Simile(明喻): a comparison between two unlike things having at least one quality or characteristic in common.Tenor主体: the subject of the comparisonVehicle喻体: the image of which this idea is conveyedThe vehicle is almost always introduced by the word "like" or "as".1/The bus(tenor主体) went as slowly similarity as a snail(vehicle喻体).2/The water lay grey and wrinkled like an elephant's skin.3/ Her eyes were jet black, and her hair was like a waterfall.4/ I am as busy as a bee.4.Metaphor(隐喻): a comparison between two unlike things, but the comparison is implied rather than stated.Contrary to a simile in which the resemblance between two unlike things is1/Snow clothes the ground.Snow (A---tenor主体) is clothe (B---vehicle喻体).2/Boys and girls, tumbling in the streets and playing, were moving jewels.Boy (A---tenor) is jewel (B---vehicle) .3/ The ship ploughed the sea.Ship (A --- tenor) is plough (B ---vehicle)More examples:She washed us in a river of...burned us... Pressed us ...to shove us away. (L4) stare down any disaster in her efforts... (L4cataract of horrors (L5)rid the earth of his shadow...liberate people from his yoke(L5)5.Analogy(类比) is a form of comparison which draws a parallel between two unlike things that have some common qualities or points of resemblance. It ischiefly used for the purpose of persuasion or for the explanation of an idea or working concept. It is especially helpful in explaining abstract ideas.1/ Just as men are killing such large number of elephants for their tusks that they will soon extinguish, we are using and destroying resources in such a big amount that we are disturbing the balance between daylight and darkness. (L3)6.Metonymy(转喻)is a figure of speech that has to do with the substitution of the name of one thing for that of another. In other words, it involves a “change of name,”the substituted name suggesting the thing meant.Metonymy can be derived from various sources—from names of persons, from animals, professions, locations, place names, etc.Names of personsHave you ever read Mark Twain?John Bull—Britain, or the British peopleUncle Sam—U.S.A.Ivan—the Russian peopleAnimalsThe British Lion—The Polar Bear—ProfessionsThe press—newspapers; journalistsThe bar—the legal professionLocations of government, headquarters, etc.Capitol Hill—legislative branch of US GovernmentThe Pentagon—US military establishmentKremlin—Russian GovernmentWall Street—Hollywood—OthersThe pen—the crown—7.Repetition重复:A/ Repetition of the same word or structure:1/We have but one aim and one single purpose2/ Nothing will turn us---nothing3/ We will never parley, we will never negotiate...4/ This is our policy and this is our declarationB/ Repetition of the same meaning with different words:1/as we shall faithfully and steadfastly2/ We have but one aim, one single irrevocable purpose.8.Parallelism平行结构:1/ The past, with its crimes, its follies, and its tragedies.2/ the return of the bread-winner, of their champion, of their protector3/I see,...I see...I see…4/ We shall fight him by land, we shall fight him by sea, we shall fight him in the air 9..Personification(拟人) is a figure of speech that gives human form or feelings to animals or life and personal attributes to inanimate objects or to ideas and abstractions.A/ use pronounsThe ship (she) the dog (he)B/ other waysNature, land—mother nature; motherland1/ Youth is hot and bold. Age is weak and cold.Youth is wild and age is tame. (by Shakespeare)10.Irony(反语) is a figure of speech that achieves emphasis by saying the opposite of what is meant, the intended meaning of the words being the opposite of their usual senses.Eg.1/Fatty for a thin boy/girl; skinny for someone very fat2/ “I love queuing up.” ( I actually hate it.)。

英语修辞手法举例中英文英语修辞手法是英语写作中常用的技巧,可以让文章更加生动、有力。
以下是几种常见的英语修辞手法及其中英文举例:1. 比喻 (Metaphor)英文解释:A figure of speech that describes something as being something else, in order to emphasize the similarities between the two things.中文解释:一种修辞手法,将一种事物描述成另一种事物,以强调两种事物之间的相似性。
例句: Her voice was music to his ears. (她的声音像是音乐般动听。
)2. 拟人 (Personification)英文解释:A figure of speech in which a non-human object or idea is given human qualities.中文解释:一种修辞手法,将非人类的物体或观念赋予人类的特质。
例句: The wind whispered through the trees. (风吹过树林,低语般的声音在耳边萦绕。
)3. 反问 (Rhetorical question)英文解释:A figure of speech in the form of a question that is asked in order to make a point, rather than to elicit an answer.中文解释:一种修辞手法,以问句的形式表达观点,而不是期望得到回答。
例句: Would you jump off a bridge just because your friends did? (你会因为朋友跳桥而跟随吗?)4. 排比 (Parallelism)英文解释:The use of similar grammatical structures, phrases or words to create a rhythmic and balanced effect.中文解释:一种修辞手法,使用相似的语法结构、短语或单词,以创造节奏感和平衡效果。
高级英语第三版本册1-7课修辞整理
修辞(Rhetoric)是指修词造句的艺术,旨在使文章表达更加
生动、准确。
在英语写作中,修辞手法的运用可以为文本增添色彩
并强化文章逻辑。
以下是本文对高级英语第三版本册1-7课修辞手
法的整理:
1. 比喻(Metaphor):通过将两种不同的事物进行比较来强化
表达。
例:“你是我的太阳”(You are my sunshine)。
2. 拟人(Personification):将非人事物拟人化,使其表现出人
类的特性。
例:“阳光明媚”(The sunshine smiled upon us)。
3. 讽刺(Irony):用反语强调与实际相反的意思。
例:“我今
天看起来真好看,唯一的问题是我感冒了”(I look amazing today. The only problem is that I have a cold.)。
6. 借代(Metonymy):用一个相关的单词或短语来替代原文,起到简洁的效果。
例:“冠军”(champion)代表整个团队获胜。
7. 倍受争议的说法(Euphemism):用含蓄、委婉和微妙的词语或说法来表达直接或难以接受的事情。
例:“真是一个有趣的人”(He is quite a character)。
以上是高级英语第三版本册1-7课修辞手法整理,希望对大家的英语写作有所帮助。
英文中的修辞手法英文中有许多修辞手法,这些手法通过运用特定的语言技巧,可以增强文学作品的表达力和感染力。
以下是一些常见的英文修辞手法:比喻(Metaphor):将两个不同的事物进行比较,以强调它们之间的相似之处,而不使用"like"或"as"。
例如:“时间是一把无情的剑。
”拟人(Personification):赋予非人物以人的特质或行为,使其更具生动性。
例如:“风儿轻轻地低语。
”象征(Symbolism):使用一个事物、符号或象征来代表另一个抽象概念。
例如:“燕子在文学中通常象征着春天和希望。
”暗喻(Metonymy):用一个与所指实体有着密切关联的词汇来替代它。
例如:“白宫发布了一份声明”中的“白宫”代表美国政府。
排比(Parallelism):通过使用相似的句式或结构,强调语言的平衡和韵律。
例如:“我不怕困难,我不怕失败,我不怕挑战。
”双关语(Pun):利用一个词汇项的多义性或相似的发音来制造幽默或引起思考。
例如:“时间飞逝,果然很‘秒’。
”讽刺(Irony):通过言辞上的反讽,表达与字面意义相反的意思。
例如:“这个‘伟大’的计划居然失败了。
”悬念(Suspense):通过保持某种信息的不明确,刺激读者的兴趣,以激发紧张感。
例如:“她打开门,里面的一切都让她惊呆了。
”对仗(Antithesis):将相对或对立的思想或概念通过并列的结构进行强调。
例如:“昨夜寒风凛冽,今朝暖阳明媚。
”比较(Simile):将两个事物通过使用"like"或"as"进行比较,以突显它们之间的相似之处。
例如:“她如同一朵盛开的花。
”这些修辞手法可以单独使用,也可以结合在一起,创造出更为复杂和富有表现力的文学效果。
作家通常根据他们的写作目的,选择最适合表达自己意图的修辞手法。
高级英语1修辞手法汇总修辞手法是英语写作中常用的一种技巧,通过运用修辞手法可以使文章更加生动、富有表现力,增强读者的阅读体验。
在高级英语写作中,修辞手法的运用尤为重要,它可以为文章赋予深度和风格,并提升文章的艺术性和说服力。
下面将介绍几种常见的修辞手法。
一、比喻(Metaphor)比喻是一种通过将一个事物与另一个事物相比较,以便更好地说明或形容某个概念或主题的修辞手法。
它常常用于描述抽象的概念,使之变得更加具体和形象。
例句:1. He is a lion in the battlefield.2. Her smile was a ray of sunshine on a cloudy day.二、拟人(Personification)拟人是一种将非人类的事物或抽象的概念赋予人类的特征和行为的修辞手法。
通过将这些非人类的事物拟人化,可以使文章更生动有趣,增强读者对其中事物的感知和理解。
例句:1. The wind whispered through the trees.2. The flowers danced in the breeze.三、夸张(Hyperbole)夸张是一种通过夸大事物的特征或情况来强调其重要性或影响力的修辞手法。
它常用于诗歌、演讲或幽默作品中,以引起读者的兴趣和共鸣。
例句:1. I've told you a million times not to do that!2. The line for the new iPhone was a mile long.四、反问(Rhetorical question)反问是一种不需要回答的问题,用于引起读者的思考或表达某种意义的修辞手法。
通过将一个问题直接提出,可以引起读者的兴趣和注意,并激发其对文章主题的思考。
例句:1. Do you really think I would believe such a ridiculous story?2. Can you imagine a world without music?五、排比(Parallelism)排比是一种通过重复并列的结构或类似的语法结构来增加修辞效果的修辞手法。
英语的修辞手法英语的修辞手法有很多种,其中一些常见的修辞手法包括:1. 比喻(Metaphor): 指的是用一个事物来比喻另一个事物,从而使语言更加生动、形象。
例如,"She is a lioness in the office." (她是一只办公室中的母狮子。
)2. 拟人(Personification): 指的是将事物或概念拟人化,从而使语言更加生动、形象。
例如,"The mountains were dressed in white and the sky wept tears." (群山披上白色,天空流下泪水。
)3. 排比(Parallelism): 指的是用相似的结构来表达三个或以上的事物,从而使语言更加有力、优美。
例如,"To fish, to hunt, to plant, to harvest, to eat." (钓鱼,打猎,种植,收获,食用。
)4. 夸张(Hyperbole): 指的是用夸张的手法来表达一个事物或概念,从而使语言更加生动、形象。
例如,"She is as fast as lightning." (她快如闪电。
)5. 反问(Rhetorical Question): 指的是用问题的形式来表达一个观点或情感,从而增强语言的力量。
例如,"Isn't life beautiful, floating on the waves of life?" (生活难道不美好吗?在生命的波浪上漂浮。
)6. 讽刺(Satire): 指的是用讽刺的手法来表达对某人或某事的不满或轻蔑,从而引起读者的共鸣。
例如,"The CEO is such a genius that he can even solve the problems of his own company." (CEO如此天才,甚至能解决自己公司的问题。
高级英语修辞总结第一篇:高级英语修辞总结1)Simile:(明喻)是常用as或like等词2)Metaphor:(暗喻)喻词常由:是、就是、成了、成为、变成3)Analogy:(类比)4)Personification:(拟人)5)Hyperbole:(夸张)6)Understatement:(含蓄陈述)7)Euphemism:(委婉)8)Metonymy:(转喻)转喻又称换喻,或借代。
9)Synecdoche(提喻)整体代部分,部分代整体10)Antonomasia(换喻)11)Pun:(双关语)12)Syllepsis:(一语双叙)13)Zeugma:(轭式搭配)把适用于某一事物的词语顺势用到另外一事物上的方法。
在同一个句子里一个词可以修饰或者控制两个或更多的词,它可以使语言活泼,富有幽默感。
14)Irony:(反语)运用跟本意相反的词语来表达此意,却含有否定、讽刺以及嘲弄的意15)Innuendo:(暗讽)16)Sarcasm:(讽刺)17)Paradox:(似非而是的隽语)即短而机智之妙语,名言警句18)Oxymoron:(矛盾修饰)19)Antithesis:(对照)20)Epigram:(警句)21)Climax:(渐进或递升法)22)Anti-climax or bathos:(突降,渐降)23)Apostrophe:(顿呼)24)Transferred Epithet:(移就,转类形容词)就是有意识的把描写甲事物的词语移用来描写乙事物。
一般可分为移人于物、移物于人、移物于物三类。
25)Alliteration:(头韵)头韵是指一组词、一句话或一行诗中重复出现开头音相同的单词,简明生动,起到突出重点,加深印象,平衡节奏,宣泄感情的作用。
26)Onomatopoeia:(拟声)27)Synaesthesia:(通感,联觉,移觉)28)Parallelism(排比,平行)29)Allegory(讽喻,比方,寓言)30)Parody(仿拟)31)Rhetorical question(修辞疑问,反问)32)Rhetorical repetition(叠言)33)Allusion(典故,隐喻)34)anaphora(首语重复法)第二篇:高级英语第一册所有修辞方法及例子总结Personification:1.2.3.4.5.6.7.8.9.10.life dealt him profound personal tragedies...the river had acquainted him with......to literature's enduring gratitude......an entry that will determine his course forever...Bitterness fed on the man who had made the world laugh.Personal tragedy haunted his entire life.Hyperbole Hyperbole is a figure of speech in which exaggeration is used to emphasize a point, to create humor, or to achieve some similar effects1)...takes you...hundreds even thousands of years2)innumerable lamps3)with the dust of centuries4)…5)...cruise through eternal boyhood and...endless summer of freedom...6)America laughed with him.7).The trial that rocked the world8)His reputation as an authority on Scripture is recognized throughout the world.9)Now I was involved in a trial reported the world over.Onomatopoeia:1)creak, squeak, rumble, grunt, sigh, groan, etc.tinkling, banging, clashing2).its anking, heel icking3)appreciative chuckle4)clucked his tongueMetaphor1)2)3)4)5)I had a lump in my throat At last this intermezzo came to an end...I was again crushed by the thought..hen the meaning...sank in, jolting me outof my sad reverie little old Japan adrift amid beige concrete skyscrapers...struggle between kimono and the miniskirtlittle old Japan----traditional floating houses6)I thought that Hiroshima still felt the impactHiroshima----people of Hiroshima, especially those who suffered from the A-bomb(keep her thoughts under control)E.g.1)Whether for him, the arch 3)The Nazi regime is devoid of all theme and principle except and racial domination.a.his wife shot him a swift, warning glance.(give sb.an angry and quick glare)b.The words spat forth with sudden savagery.(the detective said the words suddenly and savagely.)c.Her tone...withered...(become shorter from her frightening voice)d....self-assurance...flickered...(hesitate;move with a quick wavering light emotion)e.The Duchess kept firm tight rein on her racing mind.1)f.Her voice was a whiplash.i.(a heavy blow)2)g.eyes bored into himi.(look at him pointedly or sharply)3)h.I’ll spell it out.a)(explain or speak outfrankly and indetail)4)1.Mark Twain---Mirror of America5)2.Most Americans remember Mark Twain as the father of Huck Finn's idyllic cruisethrough eternal boyhood and Tom Sawyer's endless summer of freedom and adventure.6)3.The geographic core, in Twain's early years was the great valley of the MississippiRiver , main artery of transportation in the young nation's heart.7)4.The cast of characters set before him in his new profession was rich and varied — acosmos.8)Cast of characters: people of various sorts;cosmos: a place where one can find all sortsof characters9)5.Steamboat decks teemed not only with the main current of pioneering humanity, butits flotsam of hustlers, gamblers, and thugs as will.10)current: stream, here not a good choice for the verb teem.11)6.He went west by stagecoach and succumbed to the epidemic of gold and silver fever inNevada 's Washoe region.12)Succumbed…to: gave way to(yielded to, submitted to)the gold and silver rushprevailing in that area.13)7.For eight months he flirted with the colossal wealth available to the lucky and thepersistent, and was rebuffed.Flirted…wealth: did not try hard or persistently enough to get the colossal wealth…14)15)16)17)18)19)20)21)22)23)24)25)26)27)28)29)30)31)32)33)34)failed 8.From the discouragement of his mining failures, Mark Twain began digging his way to regional fame as a newspaper reporter and humorist.6.He went west by stagecoach and succumbed to the epidemic of gold and silver fever in Nevada 's Washoe region.Succumbed…to: gave way to(yielded to, submitted to)the gold and silver rush prevailing in that area.7.For eight months he flirted with the colossal wealth available to the lucky and the persistent, and was rebuffed.Flirted…wealth: did not try hard or persistently enough to get the colossal wealth…failed Digging …fame: working hard to gain regional fameMark Twain honed and experimented with his new writing muscles.Honed: sharpened/exercised.It is not suitable to say “sharpen one's muscles”.saw clearly ahead a black wall of night...the vast basin drained three-quarters of the settled United StatesAll would resurface in his books...that he soakedup...(submarine comes back to the surface, here reappear)When railroads began drying up the demand......took unholy verbal shots...my case would snowball into...our town...had taken on a circus atmosphere.The street...sprouted with...He thundered in his sonorous organ tones.… had not scorched the infidels...…after the preliminary sparring over legalities…The case had erupted on my head.Now Darrow sprang his trump card by calling Bryan as a …But although Malone had won the orato rical duel with Bryan.Then the court broke into a storm of applause that …He accused Bryan of calling for a duel to the death …Irony: a figure of speech in which the meaning literally expressed is the opposite of the meaning intended and which aims at ridicule, humor or sarcasm.1)Hiroshima---the Liveliest City in Japan2)marching backwards to the glorious age of the 16th centuryAnti-climax : the sudden appearance of an absurd or trivial idea following a serious significant ideas and suspensions.This device is usu.aimed at creating comic or humorous effects.1)a town known throughout the world for its---oystersParallelismthe repetition of sounds, meanings and structures serve to order, emphasize, and point out relationsϒϒϒϒ(1)The past, with its crimes, its follies, and its tragedies...(2)the return of the bread-winner, of their champion, of their protector(3)We shall fight him by land, we shall fight him by sea, we shall fight him in the air.(4)are still primordial humanjoys, where maidens laugh and children play.ϒ(5)Let us...Let us...ϒ(6)He hopes...He hopes(7)Behind all this glare, behind all this stormLitotes(double negative)(语轻意重法,间接肯定法)a)A negative before another word to indicate a strong affirmative in the oppositedirection.b).Sarcasm1)ah, yes, for there are times when all pray2)There is some doubt about that.3)His reputation as an authority on Scripture is recognized throughout theworld.Alliteration(头韵)repetition of vowel sound1)2)3)4)its anking, heel ickingRhetorical question1)E.g.… b ut can you doubt what our policy will be?Assonance e.g.when bigots lighted faggots to burn...Repetition –Antithesis(两个结构相似但是意思相反的平行从句便是对偶句)1)E.g.Anyman or state who fights on against Nazidom will have our aid.Any man or state who marches with Hitler is our foe.(E.g.The coward does it with a kiss, the brave man a sword.)2)From them all Mark Twain gained a keen perception of the human race, of the difference between what people claim to be and what they really are.3)...took unholy verbal shots at the Holy Land...4)...a world which will lament them a day and forget them foreverSimilea)b)c)d)e)I see also the dull, drilled, docile, brutish masses of the Hun soldiery plodding...a memory that seemed phonographic...swept the arena like a prairie fire...a palm fan like a sword...The oratorical storm … blew up in the little court in Dayton swept like a fresh wind …Periodic sentence(圆周句)Periodic sentences achieve forcefulness by suspense.The essential elements in the sentence are withheld until the end.松散句把主要意思放在次要意思之前,先说最重要的事情,因而读者在看到最初的几个词后就知道这句话的意思。
高中英语修辞手法1.明喻(Simile)。
通过比较两种事物来表达一种关系,常用的比喻词有“as”“like”“as if”“as though”等。
2.暗喻(Metaphor)。
不直接使用比喻词,而是通过隐喻的方式将一种事物描述为另一种事物,增强语言的表现力。
3.拟人(Personification)。
将无生命的事物赋予人的特征和情感,使语言更加生动形象。
4.夸张(Exaggeration)。
通过放大事物的某些特征来强调其重要性或突出某种情感。
5.头韵(Alliteration)。
通过重复相同的辅音音素来增强语言的音乐性和节奏感。
6.平行法(Parallelism)。
使用结构相似的句子或短语来增强语言的对称性和节奏感。
7.对比(Contrast)。
通过比较两种事物的不同方面来突出其特点。
8.矛盾修辞法(Oxymoron)。
使用看似矛盾的词语来表达一种微妙或深刻的意义。
9.双关(Pun)。
利用词语的多重含义或谐音来制造幽默或讽刺。
10.移情(Empathy)。
通过将读者的情感投射到描述对象上,增强读者的共鸣。
11.排比(Parallelism)。
使用结构相似的句子或短语来增强语言的对称性和节奏感。
12.反问(Rhetorical question)。
通过提出一个看似无解的问题来表达一种强烈的情感或观点。
13.对照(Antithesis)。
通过对比两个意义相反的短语或句子来增强语言的表现力。
14.渐进法(Climax)。
通过逐渐增强语言强度来达到高潮。
15.渐降法(Anticlimax)。
通过逐渐减弱语言强度来达到一种出乎意料的幽默或讽刺效果。
高英修辞手法Personification: 1. The Middle Eastern bazaar takes you...2. dancing flashes3. the beam groan ... and protesting4. where camels lie disdainfully chewing their hay,5. life dealt him profound personal tragedies...6. the river had acquainted him with ...7. ...to literature's enduring gratitude...8. ...an entry that will determine his course forever...9. Bitterness fed on the man who had made the world laugh.10. Personal tragedy haunted his entire life.Hyperbole 1) ... takes you ...hundreds even thousands of ye ars2) innumerable lamps3) with the dust of centuries4) I see the ten thousand villages …5) ...cruise through eternal boyhood and ...endless summer of freedom... 6) America laughed with him.7) . The trial that rocked the world8) His reputation as an authority on Scripture is recognized throughout the world.9) Now I was involved in a trial reported the world over.Onomatopoeia: 1) creak, squeak, rumble, grunt, sigh, groan, etc. tinkling, banging, clashing2) . its clanking, heel clicking3) appreciative chuckle4) clucked his tongueMetaphor 1) I had a lump in my throat ...2) At last this intermezzo came to an end...3) I was again crushed by the thought..4) hen the meaning ... sank in, jolting me out of my sad reve rie5) little old Japan adrift amid beige concrete skyscrapers . ..struggle between kimono and the miniskirt little old Japan---- traditional floating houses6) I thought that Hiroshima still felt Hiroshima----people of Hiroshima, especially those who suffered from the A-bomb E.g.1) Whether for him, the arch anti-Communist, this was riot bowing down in the House of Rimmon2) I suppose they will be rounded up in hordes.3) The Nazi regime is devoid of all theme and principle except appetite and racial domination. 4) Still smarting from many a British whipping5) rid the earth of his shadow and liberated its peoples from hisyoke...a. his wife shot him a swift, warning glance. (give sb. an angry and quick glare)b. The words spat forth with sudden savagery. ( the detective said the words suddenly and savagely.)c. Her tone ...withered... (become shorter from her frightening voice)d. ...self-assurance...flickered... ( hesitate; move with a quick wavering light emotion) e. The Duchess kept firm tight rein on her racing mind.Irony: 1) Hiroshima---the Liveliest City in Japan2) marching backwards to the glorious age of the 16th centuryAnti-climax : the sudden appearance of an absurd or trivial idea following a serious significant ideas and suspensions.1) a town known throughout the world for its---oysters Parallelism the repetition of sounds, meanings and structure s serve to order, emphasize, and point out relation (1) The p ast, with its crimes, its follies, and its tragedies...(2) the return of the bread-winner, of their champion, of th eir protector(3) We shall fight him by land, we shall fight him by sea, we shall fight him in the air.(4) where the means of existence is wrung so hardly from the soil, but where there are still primordial human joys, where maidens laugh and children play.(5) Let us... Let us...(6) He hopes ... He hopes(7) Behind all this glare, behind all this stormLitotes (double negative) (语轻意重法,间接肯定法) a) A negative before another word to indicate a strong af firmative in the opposite direction.b) I had not the slightest doubt where our duty and our poli cy lay.Sarcasm 1) ah, yes, for there are times when all pray2) There is some doubt about that.3) His reputation as an authority on Scripture is recognized throughout the world.Alliteration1) E.g. I see also the dull, drilled, docile, brutish masses2) its clanking, heel clicking3) fighting for his hearth and home4) let us learn the lessonsRhetorical question 1) E.g. … but can you doubt what our policy will be?Assonance I see also the dull, drilled, docile, brutish masse s of the Hun soldiery plodding on like a swarm of crawling lo custs. e.g. when bigots lighted faggots to burn... Repetition E.g. From this nothing will turn us – nothing. 1 That is our policy and that is our declaration.2 the return of the bread-winner, of their champion, of their protector.3 We have but one aim and one single, irrevocable purpose.4 We will never parley; we will never negotiate with Hitler o r any of his gang.Antithesis(两个结构相似但是意思相反的平行从句便是对偶句) 1)E.g. Any man or state who fights on against Nazidom wi ll have our aid. Any man or state who marches with Hitler is our foe.2)From them all Mark Twain gained a keen perception of the h uman race, of the difference between what people claim to be and what they really are.3)...took unholy verbal shots at the Holy Land...4)...a world which will lament them a day and forget them for everSimile a) I see also the dull, drilled, docile, brutish masses of the Hun soldiery plodding on like a swarm of crawling lo custs.b) ...a memory that seemed phonographicc) ...swept the arena like a prairie fired) ...a palm fan like a sword...e) The oratorical storm … blew up in the little court in Day ton swept like a fresh wind …Periodic sentence : 1) E.g. The past, with its crimes, its fo llies, and its tragedies, flashes away.2) if Hitler imagines that his attack on Soviet Russia will cause the slightest divergence of aims or slackening of effor t in the great democracies who are resolved upon his doom, he is woefully mistaken.Euphemism: 1) he commented with a crushing sense of despair o n man's final release from earthly struggles2) He tried soldiering for two weeks with a motley band of Co nfederate guerrillas who diligently avoided contact with the enemy .Metonymy: 1) but for making money, his pen would prove migh tier than his pickaxe2) ...tomorrow the magazines, the books, the newspapers...3) The Christian believes that man came from above. The evolutionist believes that he must have come from below. Ridicule 1) Bryan, ageing and paunchy, was assisted ...2) Bryan mopped his bald dome in silence.3) ...a palm fan like a sword...Transferred epithet 1) e.g. Darrow had whispered throwing a reassuring arm round my shoulder.Oxymoron Malone called my conviction a "victorious defeat" .Pun Darwin is right --- inside.Synecdoche The case had erupted on my head。