中级微观经济-Chapter21_Cost_Curves
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.04 MB
- 文档页数:51

关键词:成本曲线
总成本曲线(total cost curve):总成本函数的图像。
可变成本曲线(variable cost curve ):可变成本函数平均成本曲线(average total cost curve ):
平均可变成本曲线(average variable cost curve ):
平均固定成本曲线(average fixed cost curve ):厂边际成本曲线(marginal cost curve ):厂商边际成
不变成本F c v (y )可变成本
c(y) 是厂商的总成本函数。
y F
y (y)
y F
(y)
y F
(y)
c(y)
总成本函数平均总成本平均成本函数平均不变成本函数度量的是每单位产量的不变成本,平均可变成本函数度量的是每单位产量的可变成v +
平均固定成本
AFC(y)
y 平均固定成本曲线
当产出水平提高的时候将最终导致一个企业的平均可变成本上升。

1、绝对优势(Absolute advantage)如果一个国家用一单位资源生产的某种产品比另一个国家多,那么,这个国家在这种产品的生产上与另一国相比就具有绝对优势。
2、逆向选择(Adverse choice)在此状况下,保险公司发现它们的客户中有太大的一部分来自高风险群体。
3、选择成本(Alternative cost)如果以最好的另一种方式使用的某种资源,它所能生产的价值就是选择成本,也可以称之为机会成本。
4、需求的弧弹性( Arc elasticity of demand)如果P1和Q1分别是价格和需求量的初始值,P2 和Q2 为第二组值,那么,弧弹性就等于-(Q1-Q2)(P1+P2)/(P1-P2)(Q1+Q2)5、非对称的信息(Asymmetric information)在某些市场中,每个参与者拥有的信息并不相同。
例如,在旧车市场上,有关旧车质量的信息,卖者通常要比潜在的买者知道得多。
6、平均成本(Average cost)平均成本是总成本除以产量。
也称为平均总成本。
7、平均固定成本( Average fixed cost)平均固定成本是总固定成本除以产量。
8、平均产品(Average product)平均产品是总产量除以投入品的数量。
9、平均可变成本(Average variable cost)平均可变成本是总可变成本除以产量。
10、投资的β(Beta)β度量的是与投资相联的不可分散的风险。
对于一种股票而言,它表示所有现行股票的收益发生变化时,一种股票的收益会如何敏感地变化。
11、债券收益(Bond yield)债券收益是债券所获得的利率。
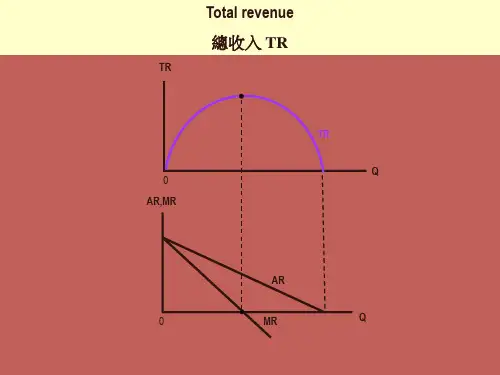
12、收支平衡图(Break-even chart)收支平衡图表示一种产品所出售的总数量改变时总收益和总成本是如何变化的。
收支平衡点是为避免损失而必须卖出的最小数量。
13、预算线(Budget line)预算线表示消费者所能购买的商品X和商品Y的数量的全部组合。



中级微观经济学题库第一章市场1.1 假定市场中最初有5单位公寓,而其中的一个单位变成了公共品。
(a)假设需求者A决定买下该公共物品。
使得公寓的需求等于供给的最高价格是多少?最低价格是多少?在表中的A列中填入你的答案。
然后计算一下,如果B,C,…决定购买该公共品时公寓的均衡价格。
(b)假设在每个保留价格下有两个需求者,共有10套公寓。
供给等于需求的最高价格是多少?假设这些公寓中的一套变成了公共品,这一最高价格还是均衡价格吗?需求者 A B C D E F G H最高价最低价1.2 现在假定有一个垄断者拥有所有的公寓,他要决定能够最大化他的收入的价格和数量。
(a)如果该垄断者租出1,2,…,8套公寓,在下表中填写他能获得的最高价格和收入。
(假定他必须对所有的公寓索要同样的价格。
)(b)从A到F中,哪些人租到了公寓?(c)如果法律要求垄断者刚好租出5套公寓,为了最大化收入,他索要的价格将是多少?(d)哪些人会租到公寓?(e)假定该房东可以向每个人索要不同的价格,并且他知道每个人的保留价格。
如果他将5套公寓全部租出,他能获得的最大收入是多少?(f)如果5套公寓都租出去了,哪些人租到了公寓?数量 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8价格收入第二章预算约束2.1 在波罗的海附近的一个小国中,只有三种商品:土豆、肉丸和果酱。
在过去的近50年里,价格都十分稳定。
土豆每袋2克朗,肉丸每坛4克朗,果酱每罐6克朗。
(a)一个叫Gunnar的公民,他每年有360克朗的收入,写出他的预算方程。
令P、M、J分别代表Gunnar在一年中所消费的土豆的袋数、肉丸的坛数和果酱的罐数。
(b)该国的公民一般都十分聪明,但是他们不擅长乘以2的计算。
这使得购买土豆成为了一件令许多公民痛苦的困难事情。
因此该国决定引入一种新的货币单位,使得土豆成为计价物。
一代土豆要花费一单位的新货币,但相对价格与过去一样。
用新货币表示的肉丸价格是多少?(c)用新货币表示的果酱价格是多少?(d)要使Gunnar能够买得起变革之前他所消费的相同的商品束,他以新货币表示的收入必须是多少?(e)写出Gunnar的新预算方程。

(完整版)范⾥安中级微观经济学中级微观经济学1. 维克⾥拍卖定义:维克⾥拍卖的⽅式类似密封拍卖,但有⼀个重要区别:商品由报价最⾼的竞价⼈获得,但他只需要按第⼆⾼的报价⽀付。
换句话说,报价最⾼的投标⼈得到了拍卖商品,但是他不需要按照他⾃⾝的报价⽀付,⽽是按照报价第⼆⾼的⼈的报价⽀付。
特点:密封报、同时报价、价⾼者得、赢家⽀付次⾼价分析:我们分析⼀个只有两个投标⼈的特殊情形。
这两⼈的对商品的评价分别为 1v 和2v ,他们在纸条上写下的报价分别为1b 和2b 。
投标⼈1的期望收益为:如果21v >v ,最⼤化胜出的概率;也就是设置11v b =。
如果21v <v ,最⼩化胜出的概率;也就是设置11v b =。
任意情况,Telling the truth is best 。
2. 帕累托有效率如果可以找到⼀种配置,在其他⼈的境况没有变坏的情况下,的确能使⼀些⼈的境况变得更好⼀些,那么,这就叫做帕累托改进;如果⼀种配置⽅法存在帕累托改进,他就称为帕累托低效率;如果⼀种配置⽅法不存在任何的帕累托改进,他就称为帕累托有效率的。
3. 价格歧视,第⼀、⼆、三级价格歧视1.价格歧视:按不同价格销售不同单位产品的做法称为价格歧视 2.⼀、⼆、三级价格歧视:第⼀级价格歧视:是指垄断企业按不同价格出售不同产量,⽽且这些价格可能因⼈⽽异。
这种价格歧视有时⼜称为完全价格歧视。
第⼆级价格歧视:是指,垄断企业按不同价格出售不同产量,但是购买相同数量的每个⼈⽀付价格是相同的。
因此,价格按购买数量制定,⽽不是因⼈⽽异。
最常见的情形是⼤宗购买时可以享受折扣。
第三级价格歧视:是指垄断企业的销售价格因⼈⽽异,但对于同⼀个⼈来说,每单位产品的售价是相同的。
这种价格歧视最常见。
例如:对⽼年⼈打折,对学⽣打折等。
4. 消费者剩余消费者剩余:是指购买者的⽀付意愿减去购买者的实际⽀付量。
消费者剩余衡量了购买者⾃⼰感觉到所获得的额外收益。
5. 显⽰偏好原理1.显⽰偏好:假定:(1)所有消费者的偏好都是严格凸性的,因此对于⼀个预算线来说都有且只有⼀个最优消费束。



中级微观经济学复习Budget constraint预算约束Consumption bundles: a list of numbers of goods and servicesthe objects of consumers choice。
消费束:一系列商品和服务的组合,消费者选择的东西。
消费束是我们研究选择问题中涉及到的全部商品(或服务)The budget set of the consumer: the consumer’s affordable consumption bundles,(x1,x2) satisfying p1x1 + p2x2≤m.预算集:既定价格和收入下消费者能负担得起的所有消费束的集合。
Composite good: take x2 as everything else,the dollars spent on other goods.复合商品:它代表除商品1之外所有其他的消费品Budget line: the set of bundles that cost exactly m :p1x1+ p2x2= m预算线:是指恰好将收入m 花费完的预算集预算线的斜率:为了多消费一些商品1,你必须放弃一些商品2 的消费。
放弃消费商品2 的机会是多消费商品1 的经济成本,这样的经济成本以预算线的斜率衡量预算线的变动Budget Line Changes:Change in income收入增加会使预算线向外平行移动,收入下降会使预算线向内平行移动。
Changes in prices商品1 价格上升,预算线会变得更陡峭,商品2价格上升,预算线会变得更平缓观点:完全平衡的通货膨胀(即所有商品价格和收入都按相同比率上升),不会改变任何人的预算集,因此也不会改变任何人的最优选择。
(tp1)x1+(tp2)x2= tmPreference 偏好Consumer Preferences:Consumer ranks consumption bundles by his satisfaction from use of goods,irrelevant to the prices。

1 BUDGET CONSTRAINT1.A poor person who has an income of $1000 receives $100 worth offood stamps. Draw the budget constraint if the food stamp recipient can sell these coupons on the black market for less than their face value.2.Since 1979, recipients have been given food stamps. Before 1979,however, people bought food stamps at a subsidized rate. For example, to get $1 worth of food stamps, a household paid about 15¢(the exact amount varied by household characteristics and other factors). What is the budget constraint facing an individual if that individual may buy up to $100 per month in food stamps at 15¢per each $1 coupon. 3.During his first year at school, Ximing buys eight new collegetextbooks at a cost of $50 each. Used books cost $30 each. When the bookstore announces a 20% increase in new texts and a 10% increase in used texts next year, Ximing’s father offers him $80 extra. Is Ximing better off, the same, or worse off after the price change? Why?2 PREFERENCES1. Julia consumes cans of anchovies, A, and boxes of biscuits, B. Each ofher indifference curves reflects strictly diminishing marginal rates of substitution. Where A = 2 and B = 2, her marginal rate of substitution between cans of anchovies and boxes of biscuits equals -1. Will sheprefer a bundle with three cans of anchovies and a box of biscuits to a bundle with two of each? Why?2. What assumption or assumptions rule out the following phenomenon:Geoffrey has a bundle consisting of 6 apples and 8 raspberries. He states that if he is given 1 more apple, he will ask for 3 more raspberries to keep him indifferent between his old bundle and the new bundle that he will have after he receives the 1 additional apple.3. Draw indifference curves for the following people:a) John says: “I get no satisfaction from 1 ounce of vermouth or 3 ouncesof gin, but 1 ounce of vermouth and 3 ounces of gin (a martini) really turn me on.”b) Steve says: “I will not cut my hair to please my boss unless she paysme. My price is $300 plus $1 for every 1/8 inch of hair that is cut. In other words, for every $1 above $300 that the boss pays me, I will cut 1/8 inch off my hair.”c) In Part b of this problem, what is the marginal rate of substitutionbetween dollars and hair in the region below and above $300?d) Ann says: “I enjoy beer and pretzels, but after 12 beers, any additionalbeer makes me sick.”4. Jeffrey is five years old. He likes candy and hates spinach. He isallowed 2 candy bars a day, but his mother offers him 1 additional candy bar for every 2 ounce of spinach he eats.a) On these terms, Jeffrey eats 3 ounces of spinach and 3.5 candy barseach day. Using indifference curves, illustrate his optional choice.b) Suppose that Jeffrey’s mother does not give him 2 “free” candy barseach day but still gives him 1 candy bar for every 2 ounce of spinach he eats. Would his spinach consumption be greater or smaller than in Part a? Explain your answer.4 CHOICE1. Tara has a utility function U(B, Z) = ABαZβ, Where A, α, andβareconstraints, B is burritos, and Z is pizzas. If the price of burritos, p B is $2 and the price of pizzas, p Z is $1, what is Tara’s optimal bundle?2. Assume that there are two goods in the world: apples and raspberries.Say that Geoffrey has a utility function for these goods of the following type, where r denotes the quantity of raspberries and a the quantity if apples: U = r·a.a)Draw an indifference curve that is defined by this utility function andhas a utility level of 2500.b)What is the marginal rate of substitution between the raspberries andthe apples when Geoffrey consumes 50 raspberries and 50 apples?What is the marginal rate of substitution between these two goods when Geoffrey consumes 100 raspberries and 50 apples?c)If the price of raspberries is $1 per unit and the price of apples is $1per unit and Geoffrey has $100 to spend, what bundle of raspberries and apples will he buy? Is the marginal rate of substitution equal to the ratio of the prices of these goods in the optimal bundle? If not, why not?d)If the unit prices of the raspberries and the apples are $4 and $3,respectively, what bundle of raspberries and apples will Geoffrey buy with his income of $100?3. Steve’s utility function is U = BC, where B = veggie burgers per weekand C= packs of cigarettes per week. What is his marginal rate of substitution if veggie burgers are on the vertical axis and cigarettes are on the horizontal axis? Steve’s income is $120, the price of a veggie burger is $2, and that of a pack of cigarettes is $1. How many burgers and how many packs of cigarettes does Steve consume to maximize his utility? When a new tax raises the price of a burger to $3, what is his new optimal bundle? Illustrate your answers in a graph.5 DEMAND1.Roger’s utility function is U = B1/4Z3/4, his income is Y, the price of Bis p B, and the price of Z is p Z. Derive his demand curves.2.Derive Roger’s Engel curve for B for the utility given in problem 2.7 CONSUMER’S SUPPLUS1.If the inverse demand function is p = a–bQ, what is the consumersurplus if price is a/2?2.If the supply function is Q = Apη, what is the producer surplus if priceis p*?9 EQUILIBRIUM1.In 1998, a virus killed more than half the oysters used to producepearls in the world’s busiest undersea factory. Use a diagram to indicate why the price of pearls rose 18%. How did the equilibrium quantity change?2.Increasingly, instead of advertising in newspapers, individuals andfirms use Web sites that offer free classified ads, such as , , , and portals like Yahoo and America Online.Using a supply-and-demand model, explain what will happen to the equilibrium levels of newspaper advertising as the use of the Internet grows. Will the growth of the Internet affect the supply curve, the demand curve or both? Why?3.The U.S. supply of frozen orange juice comes from Florida and Brazil.What is the effect of a freeze that damages oranges in Florida on the price of frozen orange juice in the U.S. and on the quantities of orange juice sold by Floridian and Brazilian firms?4.The supply of corn by the U.S. is Q a= a + bp, and the supply by therest of the world is Q r = c + ep. What is the world supply?5. A rent control law limits the price of an apartment. What is the likelyeffect of such a law in the short run? What is the likely effect of the law in the long run? Be sure to discuss the quantity and quality of apartments available for rent.6.The government wants to drive the price of soybeans above theequilibrium price, p1 to p2. It offers growers a payment of x to reduce their output from Q1(the equilibrium level) to Q2, which is the quantity demanded by consumers at p2. How large must x be for growers to reduce output to this level? What are the effects of this program on consumers, farmers, and total welfare? Compare this approach to (a) offering a price support of p2, (b) offering a price support and a quota set at Q1, and (c) offering a price support and a quota set at Q2.10 TECHNOLOGY1.Michelle’s business produces ceramic cups using labor, clay, and akiln. She can manufacture 25 cups a day with one worker and 35 with two workers. Does her production process illustrate diminishing returns to scale or diminishing marginal returns to scale? What is the likely explanation for why output doesn’t increase proportionatelywith the number of workers?2. Suppose that the production function is q = L 3/4K 1/4.a. What is the average product of labor ,holding capital fixed at K ?b. What is the marginal product of labor?c. Does this production function have increasing, constant, or decreasing returns to scale?3. A good recipe for a French dish called ceviche requires 16 ounces of fillet of red snapper, 3 ounces of lime juice, 1 ounce of coriander, and 8 ounces of Bermuda onion. This combination of inputs is expressed in the following production function:1243min ,,,1638z z z y z ⎧⎫=⎨⎬⎩⎭ In this production function, z 1 is fillet of red snapper, z 2 is lime juice, z 3 is coriander, and z 4 is Bermuda onion. The unit of measure for each input is the ounce, and the unit of measure for ceviche (the output) is the quantity produced by the recipe. If a restaurant has on hand 32 ounces of snapper, 9 ounces of lime juice, 5 ounces of coriander, and 48 ounces of onion, how many “units ” of ceviche can it produce?4. Construct a total product curve for a function that exhibits diminishing marginal product throughout. Then construct another total product curve for a function that exhibits initially constant and subsequently diminishing marginal product. Below the graphs of these two total products curve, derive the corresponding average and marginalfunctions. Check to see that the curves you have drawn are consistent with what you know about the relationship between the average and marginal product curves.11 PROFIT MAXIMIZATION1.You have 60 minutes to take an exam with two questions. You want tomaximize your score. Toward the end of the exam, the more time you spend on either question, the fewer extra points per minutes you get for that question. How should you allocate time between the two questions?(Hint: Think about producing an output of a score on the exam using inputs of time spent on each of the problem)2. A competitive firm’s production function is y = L + 2LK + K. What isits marginal revenue product of labor?3.A firm’s production function is y = ALαKβ. What is the firm’s marginalrevenue product of labor?1L2, 4.A competitive firm has the production of function Q= 20L–4 where Q is the number of units of output produced and L is the number of units of labor (the only input) used. The output price is $2, the wage rate is $1, and the firm faces a fixed cost of $100.a)What is the profit-maximizing quantity of labor demanded by thefirm?b)What is the firm’s profit in the short run?c)If, in the long run, the output price changes so that profits are zero,what is the quantity of labor demanded in the long run?5.A competitive firm has the production function. Q = LαKβ, where Q isthe number of units of output produced, L is the number of units of labor used, and K is the number of units of capital used. The output price p, the wage rate w, and the cost of capital r are given. Assume that α > 0, β > 0, and 0 < ( α + β ) < 1.a)What is the firm’s profit-maximizing quantity of labor if the quantityof capital is fixed at K?b)What is the firm’s profit-maximizing level of capital if both capitaland labor are variable? (Hint: Use the profit-maximizing capital-labor ratio K/L to substitute for the level of labor.)12 COST MINIMIZATION1.Assume that a firm produces 90 units of output using 9 units of inputX and 9 units of input Y. The f irm’s technological possibilities can be represented by the production function Q = 10X1/2Y1/2.a)If the price of X is $8 and the price of Y is $16, is the inputcombination of 9 units of X and 9 units of Y the most efficient way to produce 90 units of output?b)What must the ratio of input prices be for this input combination to beefficient?c)Assume that the price of X is $1 and the price of Y is $2. Derive theleast-cost way to produce 400 units of output.2.A medical center produces health services using two inputs: hospitalbeds and labor. There is a government regulation restricting the number of beds to B. Assume that the medical center is currently usingB beds and L units of labor to produce Q1 units of health services. Alsoassume that the medical center plans to expand its output to Q2 units of health services. Prepare a diagram to show how this government regulation restricting the number of hospital beds would affect the efficiency of delivering health services.3.A trucking firm’s output is measured by the number m of truck-milesmoved per day. The firm’s operating costs are as follows:i.wages of trucks, $w per hourii.cost of gasoline, $p per galloniii.fuel consumption, g= A+ Bs, where g is gallons of gasoline per truck-mile, s is the speed at which a truck is driven, and A and B are constantsa)Derive the total variable cost function of the firm if it has an unlimitednumber of trucks.b)What does the cost function look like if the firm has only one truckand that truck can be driven for a maximum of ten hours per day?4.A college student is considering whether to operate a lawn-mowingbusiness for the summer or work in a business owned by her family.Her time is worth $w1 per hour and she can work as many hours as she chooses in the family business at this rate. If she starts her own business, she will have to buy gasoline for her lawn mower at a price of $w2 per gallon. She can rent a small mower for $w3 per hour. The mower cuts a 12-inch swath of lawn and uses 1/3 gallon of gasoline per hour. With this mower, she can cut 10,000 square feet of lawn in an hour. (Use 10,000 square feet as the units of measurement for output.) Our college student can rent a large mower for $w4 per hour.This mower uses 1 gallon of gasoline per hour and cuts 3 units of lawn per hour.a)Verify that the production function for the two mowers are as follows:y = min{z1, 3z2, z3}y = 3min{z1, z2, z4}Assume that z1 is hours of labor, z2 is gallons of gasoline, and z3 and z4are the hours of the small mower and the large mower, respectively.b)Derive the cost functions.c)Show that using the small mower is a cheaper way to cut grass if 2w1 <w4 – 3w3. Why is this result independent of the price of gasoline?d)How high a price must our college student receive for cutting a unit oflawn in order to induce her to set up her own lawn-mowing firm ratherthan work in the family business?e)Assume that a firm uses two types of input in the production of acertain commodity. What is the maximum output if the marginal product of input is MP1 = 100X2 –X1 and the marginal product of input2 is MP2 = 100X1 –X2, the total amount that can be spent on inputs is$1,000, the price of input 1 is $2, and the price of 2 is $5?13 COST CURVES1.The only variable input a janitorial service firm uses to clean offices isworkers who are paid a wage, w, of $8 an hour. Each worker can clean four offices in an hour. Use math to determine the variable cost, the average variable cost, and the marginal cost of cleaning one more office. Draw a diagram to show the average cost, and marginal cost curves.2.Gail works in a flower shop, where she produces 10 floralarrangements per hour. She is paid $10 an hour for the first eight hours she works and $15 an hour for each additional hour she works. What is the firm’s cost function? What are its AC, AVC, and MC functions?Draw the AC, AVC, and MC curves.3.A firm has two plants that produce identical output. The cost functionsare C1 = 10y– 4y2 + y3and C2 = 10y– 2y2 + y3.b.At what output levels does the average cost curve of each plant reachits minimum?c. If the firm wants to produce 4 units of output, how much should it produce in each plant?4. A firm that makes widgets must build a plan that will cost $10,000. The plant will be able to produce up to 10,000 units, at which point its capacity will be reached and a new plant will be needed. The total cost function for each plant (including the fixed cost of building the plant) is C (y ) = 10,000 – x 1/2/100.a) Determine the cost function for this firm.b) Is this cost function subadditive over the range of outputs from 1 unit to 10,000 units? Is it subadditive for all levels of output?14 FIRM SUPPLY1. If a competitive firm ’s cost function is C (y ) = 100 + 10y – y 2 + 31y 3, what is the firm ’s marginal cost function? What is the firm ’s profit- maximizing condition?2. If a competitive firm ’s cost function is C (y ) = a + by + cy 2 + dy 3, where a , b , c , and d are constants, what is the firm ’s marginal cost function? What is the firm ’s profit-maximizing condition?3. Consider a firm with a total cost curve of TC = 1,000 + q 3/3 – 2q 2 + 6q . a) What is the lowest price at which this firm will want to supply a positive amount to the market in the short run?b) At the “lowest price”, how much will be supplied?c) How much will be supplied in the short run if the price is $10?4. What is the effect on firm and market equilibrium of a law requiring afirm to give its workers six months’ notice before it can shut down its plant?15 INDUSTRY SUPPLY1. Each firm in a competitive market has a cost function of C = 16 + y2.The market demand function is Q = 24–y. Determine the equilibrium price, quantity per firm, market quantity, and number of firms.2. Assume that the taxi industry in the town of New City is perfectlycompetitive. Also assume that the constant marginal cost of a taxi ride is $5 per trip and that each taxi is capable of making 20 trips a day. We will let the demand function for taxi rides each day be D(p) = 1,100 –20p.a)What is the perfectly competitive price of a taxi ride?b)How many rides will the citizens of New City make every day?c)How many taxis will operate in New City?Assume that every taxi that operates in New City has a special license. Therefore, the number of such licenses is the same as the number of taxis that you calculated in Part c of this problem. Further assume that the demand for taxi rides has increased and is now D(p) =1,200 - 20p. The cost of operating a taxi is still $5 per ride, and the number of taxis has not changed.d)Calculate the price that will equate demand with supply.e)Calculate the profit that each taxi will earn on a ride.f)Calculate the daily profit of each taxi. (Hint: Continue to assume thateach taxi can make only 20 rides a day)3. A competitive market has an unlimited number of potential suppliersproducing the same output, and each supplier has a long-run average cost function of AC= q2 –4q+ 6 and a long-run marginal cost function of MC = 3q2 – 8q + 6.a) Find the equilibrium quantity q produced by each firm in the long run.b) Find the long-run equilibrium price.4. Assume that a very large number of firms in an industry all have accessto the same production technology. The total cost function associated with this technology is TC(Q) = 40Q–24Q2 + 4Q3. If the demand function for the industry’s product is Q = 19 –P, how many firms will produce positive amounts of output at a competitive (that is, zero profit) equilibrium?5. Assume that a certain small town contains a large number ofwidget-producing firms. All the firms buy oil from the same refinery.Firm 1 is situated very close to the refinery, and the other firms are located 50 miles away. Firm 1 pays $18 per barrel for the oil, while theother firms pay $18 per barrel plus a transportation charge of $.05 cents a mile, or a total of $20.50 per barrel.To produce four widgets, a firm needs 1/10 barrel of oil, 1/2 hour of labor, and the use of one machine. The cost of labor is $10 per hour, and the necessary machine can be rented for $5 per hour. No firm has the capacity to produce more than 100 units of widgets.a)Derive the supply curve for firm1. Derive the supply curve for all theother firms.b)What is the equilibrium price?c)Does any firm earn economic rent (that is, extra economic profit) inthe industry?d)Does firm 1 affect the price of widgets in the industry? If not, whynot?e)Suppose that there is no capacity limit. What will the equilibrium pricebe?f)Will firm 1 affect the price when there is unlimited capacity?16 MONOPOLY1.Show that after a shift in the demand curve, a monopoly’s price mayremain constant but its output may rise.2.When is a monopoly unlikely to be profitable?(Hint: Discuss therelationship between market demand and average cost)3.The inverse demand curve a monopoly faces is p = 100 - Q. The firm’scost curve is C(Q) = 10 + 5Q. What is the profit-maximizing solution?4.How does your answer to Problem 3 change if C(Q) = 100 + 5Q?5.A monopoly’s production function is: y = L1/2K1/2, where L is labor andK is capital. The demand function is p = 100–y. The wage, w, is $1 per hour, and the rental cost of capital, r, is $4.a.Derive the long-run total cost curve equation as a function of y.b.What quantity maximizes this firm’s profit?c.Find the optimal input combination that produces the profit-maximizing quantity. Illustrate with a graph.6. Suppose that a monopolist faces a demand curve of P = 100 - 2Q. Herfirm has costs of C(Q) = 5Q2.a) What is the revenue function for this monopolist?b) What is the marginal revenue function?c) What is the marginal cost function?d) What is the profit-maximizing output for this monopolist?e) What is the maximum profit this firm can make?f) If this monopolist has to pay a permission free of $150 to the stategovernment in order to start the business, will her optimal level of output change? If not, why not?17 FACTOR MARKETS1.A monopsony faces a supply curve: w = 10 + x. What is its marginalexpenditure curve?18 OLIGOPOLY1.What is the duopoly Cournot equilibrium if the market demandfunction is Q = 1000–1000p, and each firm’s marginal cost is $0.28 per unit?2. Consider a duopolistic market with two firms, A and B, facing ademand curve of p = 1 –q A–q B. Assume that initially each firm has access to the same technology with constant returns to scale and that the cost of production is C A = q A/2 for firm A and C B= q B/2 for firm B.a) What is the profit function for each firm?b) Graph the reaction functions for firms.c) What is the equilibrium outputs?d) Assume that the initial output levels of the two firms are given by pointX(3/10, 4/10) and Y(1/10, 2/10). Show in a graph the process of change in the output levels of the two firms and the point at which their output levels converge.3. A duopoly faces a market demand of p= 120–Q. Firm 1 has aconstant marginal cost of MC1 = 20. Firm 2’s constant marginal cost is MC2 = 40. Calculate the output of each firm, market output, and price if there is (a) a collusive equilibrium or (b) a Cournot equilibrium.4. Assume that there are two firms in a market, firm 1 and firm 2. Thetotal demand for the identical product they make is p = 200 – 2(q1 + q2), where q1 is the output of firm 1 and q2 is the output of firm 2. The production costs of firm 1 and firm 2 are C1 = q12and C2 = q22, respectively.a) Assume that firm 2 decides to produce either 20, 40, 60, or 100 units ofoutput. Show the demand curve and the marginal revenue curve facing firm 1 in each of these situations, assuming that the output levels will remain unchanged once they are chosen.b) Define the output that represents the best (the profit-maximizing)response of firm 1 to each of the output levels chosen by firm 2.19 EXCHANGE1.Initially, Michael has 10 candy bars and 5 cookies, and Tony has 5candy bars and 10 cookies. After trading, Michael has 12 candy bars and 3 cookies. In an Edgeworth box, label the initial Allocation A and the new Allocation B. Draw some indifference curves that are consistent with this trade being optimal for both Michael and Tony. 2.In a pure exchange economy with two goods, G and H, the two tradershave Cobb-Douglas utility functions. Amos’s utility is U a =(G a)α(H a)1-α, and Elise’s is U e = (G e)β(H e) 1-β, what are their marginalrates of substitution?3. Continuing with problem 3: between them, Amos and Elise own 100 units of G and 50 units of H . Thus if Amos has G a and H a , Elise has G e =100 – G a and H e = 50 – H a . Solve for their contract curve.4. Arnold and Brigitte are marooned on a deserted island. Arnold has exactly one unit of Xylose and Brigitte has exactly one unit of Yam. Their preferences between these two items are represented by the following two equations:1/32/31/21/2A A AB B B U X Y U X Y =⋅=⋅In these equations, X A and Y A are the consumption of Xylose and Yam by Arnold. Similarly, X B and Y B are the consumption of Xylose and Yam by Brigitte.a) Is the following allocation Pareto-optimal? Explain why or why not.1211,,,2323A AB B X Y andX Y ==== b) If Arnold and Brigitte were to trade between themselves, would they be able to attain this allocation as a competitive equilibrium? What would be the equilibrium price ratio of Xylose to Yam? Would Arnold and Brigitte be able to afford this allocation at the equilibrium prices, given their endowments? If not, what kind of income transfer would be necessary?5. Two people trade two goods that they cannot produce. Suppose that one consumer ’s indifference curves are bowed away from the origin – the usual type of curves – but the other ’s are concave to the origin.In an Edgeworth box, show that a point of tangency between the two consumers’indifference curves is not a Pareto-efficient bundle.(Identify another allocation that Pareto dominates.)6.The demands for two goods depend on the prices of Good 1 and Good2, p1 and p2, Q1 = 15 – 3p1 + p2, Q2 = 6 – 2p2 + p1, but each supply curve depends on only its own price: Q1 = 2 + p1, Q2 = 1 + p2. Solve for the equilibrium: p 1, p2, Q1, and Q2.20 PRODUCTION1. Assume that you have exactly 100 hours of labor to allocate betweenproducing good X and good Y. Your output of goods X and Y depends solely on the hours of labor you spend in the following way:X=and Y=a)If you can sell your output of goods X and Y at the fixed prices P X = 10and P Y= 5, how much of goods X and Y would you produce to maximize your profits?b)Now assume further that you have the following utility function:U=If you can trade a bundle of goods X and Y that you produce in the market at fixed prices of P X = 10 and P Y = 5, what bundle would you produce and what bundle would you consume to maximize your utility?Are you a net demander and a net supplier of the two goods? Draw adiagram to depict what is happening.2. Suppose that the production possibilities frontier for cheeseburgers (C)and milk-shakers (M) is given by C + 2M = 600.a) Graph this function.b) Assuming that people prefer to eat two cheeseburgers with everymilk-shaker, how much of each product will be produced? Indicate this point in your graph.c) Assuming that this fast-food economy is operating efficiently, whatprice ratio (P C/P M) will prevail?21 WELFARE1. Suppose that society used the “opposite”of a Rawlsian welfarefunction: it tried to maximize the well-being of the best-off member of society. Write this welfare function. What allocation maximizes welfare in this society?2. Assume that Bob has a utility function of U = 8X1 + 1X2 – 3X3 and Joanhas a utility function of U = –2X1 + 7X2 + 5X3. Consider the following allocation:a)Is this allocation envy free?b)Is this allocation Pareto-optimal?c)Find a Pareto-optimal allocation, and determine whether it is envyfree.d)Do you think that the allocation in Part c of this problem is desirable?Why or why not?22 EXTERNALITIES1.Suppose that the only way to reduce pollution from paper productionis to reduce output. The government imposes a tax equal to the marginal harm from the pollution on the monopoly producer. Show that the tax may raise welfare.2.Suppose that the inverse demand curve for paper is p = 200–y, theprivate marginal cost (unregulated competitive market supply) is MC p = 80 + Q, and the marginal harm from gunk is MC g = y.a.What is the unregulated competitive equilibrium?b.What is the social optimum? What specific tax (per unit of output orgunk) results in the social optimum?c.What is the unregulated monopoly equilibrium?d.How would you optimally regulate the monopoly? What is theresulting equilibrium?3. A soot-spewing factory that produces steel windows is next to a。
/portalweb/appmanager/portal/semTSINGHUA UNIVERSITYSCHOOL OF ECONOMICS AND MANAGEMENT中级微观经济学2004年秋季学期Intermediate MicroeconomicsFall Semester 2004星期三Wednesday9:50 am —12:15pm六教 6A018任课教师:清华大学经济管理学院教授李稻葵Professor David D. Li助教:姜超, 冯俊新,江红平,梅松课程网页Course Web-Page:→分类讨论→中级微观经济学用户名: s311 密码:pe4028联系方式:李稻葵E-mail: lidk@电话: 6277-2126;办公室: 舜德楼南211H答疑时间: 预约姜超S972260@ 冯俊新fengjx@江宏平jianghp@ 梅松meis@习题课以及答疑时间: 星期一 & 星期二Monday & Tuesday19:00 pm —21:00 pm伟伦楼北5081.课程简介微观经济学是现代经济学的基础. 其核心理论体系之完美, 可以和物理学的牛顿力学相媲美; 其主要研究方法广泛应用于经济学的各个分支; 其思维方式,渗透了现代社会科学的主要学科. 本课程的目的就是给学生打下一个扎实的微观经济学基础, 欣赏其理论之完美和独特的思维方式, 并熟练地掌握微观经济学系统的分析工具.2.教学风格本课程属于经济学核心课程, 力求与国际最高标准接轨. 教学的文字材料(包括教材, 讲稿, 习题和考试等), 以英文为主; 口头表达以汉语为主.3.教材教材为:Hal R. Varian: Intermediate Microeconomics A Modern Approach. Sixth Edition W.W. Norton & Company. New York, NY. 2003.习题来自其附本:Theodore C. Bergstrom and Hal R. Varian: Workouts in Intermediate Microeconomics. Sixth Edition W.W. Norton & Company. New York, NY. 2003.4.习题课对大多数同学而言, 参加习题课是学好本课程的关键. 习题课上还会布置随堂习题, 成绩计入总成绩. 如果有的同学感到可以比较轻松地完全掌握教学内容, 可以选择不参加少量习题课和部分随堂习题, 不会影响总成绩, 总成绩地计算办法见下.除第一周和国庆节长周末之外, 每周将安排两节内容相同但时间不同的习题课, 大家可以任选其一参加. 具体时间另行通知.5.课程要求及考核标准微观经济学的特点是思想性与方法性并重, 要学好这门课, 学生们一定要下功夫彻底理解基本概念和基本原理, 不仅懂, 而且会讲,会用, 然后练习解题. 解题时要举一反三, 多动脑筋总结经验.根据微观经济学的这些特点, 本课程采取以下考核方式:1)随堂习题 (比重 20%) : 在习题课上进行. 题目来自Theodore C.Bergstrom and Hal R. Varian: Workouts in Intermediate MicroeconomicsSixth Edition W.W. Norton & Company. New York, NY. 2003.随堂习题的目的是鼓励学生在课下做习题, 多练习.随堂习题的总成绩是每人8个最高的随堂习题的平均值.2)期中考试 (比重 30%): 题目也将与上述习题集有关.3)期末考试 (比重 50%): 按清华大学的给定时间进行.Class ScheduleNote:Chapters refer to Hal R. Varian: Intermediate Microeconomics AModern Approach. Sixth Edition W.W. Norton & Company. New York, NY. 2003.September 15 Introduction and Overview of the CourseChapter 1 The MarketChapter 2 Budget ConstraintSeptember 22 Chapter 3 PreferencesChapter 4 UtilityChapter 5 ChoiceSeptember 29 Chapter 6 DemandChapter 7 Revealed PreferenceOctober 6 (No Class --- National Day Long Weekend)October 13Chapter 8 Slutsky EquationChapter 9 Buying and sellingOctober 20 Chapter 10 Intertemporal ChoiceChapter 11 Asset MarketsChapter 12 UncertaintyChapter 13 Risky AssetsOctober 27 Chapter 14 Consumer’s SurplusChapter 15 Market DemandChapter 16 EquilibriumNovember 3 Mid-Term ExamNovember 10Chapter 18 TechnologyChapter 19 Profit MaximizationChapter 20 Cost MinimizationNovember 17Chapter 21 Cost CurvesChapter 22 Firm SupplyChapter 23 Industry Supply November 24Chapter 24 MonopolyChapter 25 Monopoly BehaviorChapter 26 Factor Markets December 1 Chapter 27 OligopolyChapter 28 Game Theory December 8 Chapter 30 ExchangeChapter 31 ProductionDecember 15 Chapter 32 WelfareChapter 33 ExternalitiesChapter 35 Public Goods December 22 Chapter 36 Asymmetric InformationChapter 17 AuctionsDecember 29 Course Integration任课教师简介李稻葵(David D. Li) 1985年毕业于清华大学经济管理学院管理信息系统专业,同年由学院推荐参加国家教委组织的留美经济学考试(即, 邹至庄经济学留学计划),出国留学. 1985到1986,为美国哈佛大学国际发展研究所(HIID)访问学者. 1986年入该校经济系攻读博士, 从师艾里克马斯金,安德烈史莱法,以及亚诺什科尔耐, 主修经济理论,公司金融, 和比较经济学. 1992年获哈佛大学哲学博士(经济学)学位. 1992至1999任美国安娜堡密西根大学经济系助理教授并兼任该校中国研究中心研究员. 1997至1998, 从密西根大学请假,任美国斯坦福大学胡佛研究所国家研究员,从事中国经济改革的制度变迁研究. 1999至2004年长期聘为香港科技大学经济系副教授,并任该校经济发展研究中心副主任.李稻葵曾兼任世界银行中国社会保障体制改革研究项目顾问 (1989), 国际<<比较经济学杂志>> (Journal of Comparative Economics)编委 (2000-03), 中国留美经济学会(CES)会长 (2001-02), 清华大学经济管理学院特聘教授(2002-03). 现兼任(欧洲)经济政策研究中心(CEPR), 美国密西根大学威廉戴维森研究所 (The William Davidson Institute)研究员; 国际《经济学通報》(Economics Bulletin),中国<<经济研究>>,香港《中国评论》(The China Review)等学术杂志的编委; 国际比较经济研究会执行理事; 南开大学,四川大学,西南财经大学兼职教授。
经济学习笔记第21章消费者选择理论一、重要名词解释预算约束线:对消费者可以支付得起的消费组合的限制,又称消费可能线和价格线。
无差异曲线:一条表示给消费者带来相同满足程度的消费组合的曲线。
边际替代率MRS:消费者愿意以一种物品交换另一种物品的比率。
完全替代品:无差异曲线为直线的两种物品。
完全互补品:无差异曲线为直角形的两种物品。
收入效应:当价格的某种变动使消费者移动到更高或更低无差异曲线时所引起的消费变动。
替代效应:当价格的某种变动使消费者沿着一条既定的无差异曲线变动到有新边际替代率的一点时所引起的消费变动。
正常物品:收入增加引起需求量增加的物品。
低档物品:收入增加引起需求量减少的物品。
吉芬物品:价格上升引起需求量增加的物品。
二、重要摘抄1.预算约束线的斜率衡量的是消费者用一种物品换另一种物品的比率,也是两种物品的相对价格。
在任何一条既定的无差异曲线的所有点上,消费者的满足程度相同。
无差异曲线代表消费者偏好,具有四个特征:消费者对较高无差异曲线的偏好大于较低的无差异曲线;无差异曲线向右下方倾斜;无差异曲线不相交;无差异曲线凸向原点。
无差异曲线凸向原点,反映了消费者更愿意放弃他已大量拥有的那一种物品。
无差异曲线的形状告诉我们消费者用一种物品交换另一种物品的意愿。
当物品很容易相互替代时,无差异曲线呈现出较小的凸性;当物品难以替代时,无差异曲线呈现出很大的凸性。
其中两种极端的情况是:边际替代率不变、无差异曲线都是直线的情况下,两种物品是完全替代品;无差异曲线为直角形的情况下,两种物品是完全互补品。
2.预算约束衡量了消费者能买得起什么,偏好衡量了消费者想要什么。
消费者可以达到的最高无差异曲线(图中的I2)是正好与预算约束线相切的那条无差异曲线,相切的点被称为最优点,在这个点上,边际替代率MRS等于两种物品的相对价格。
图1 消费者最优点相对价格是市场愿意用一种物品交换另一种物品的比率,而边际替代率是消费者愿意用一种物品交换另一种物品的比率。