宏观经济学(叶航)浙江大学精品课程在线播放
- 格式:doc
- 大小:13.50 KB
- 文档页数:4


可编辑修改精选全文完整版《宏观经济学教程》教材习题参考答案第一章总产出二、分析与思考1,在总产值中包含着中间产品的价值,如果以各部门的产值总和来合算总产出,则会出现重复计算。
2,因为这只是证券资产的交易,在这种交易中获得的利润或蒙受的损失与本期生产无关。
3,可能会,因为销售的产品可能是上年生产的产品。
GDP与GNP应该以后者,即本年生产的最终产品为口径。
因为它是用来衡量国家当年总产出水平的量的。
4,不是,因为个人可支配收入是GNP或GDP中减去折旧、间接税、公司利润、社会保障支付、个人所得税,再加上转移支付得到的。
5,购买住宅属于投资行为,因为西方国家的消费者购买或建造住宅一般都是使用银行贷款,而且住宅也像企业的固定资产一样,是一次购买、长期使用、逐步消耗的。
6,一般中间产品在当期生产中全部被消耗掉,其价值完全包含在产品的销售价格中。
而,固定资产在生产过程中则是被逐步消耗的,计入当期产品生产成本的仅仅是固定资产中部分被消耗掉的价值,即折旧。
7,不是。
因为总支出包括消费,投资,政府购买和净出口,并不只是在消费最终产品上。
8,不是。
总产出包括的是净出口,对外贸易规模大,如果进口大于出口,则总产出规模不会因对外贸易规模大而变大。
9,可以。
因为名义GDP与实际GDP的比率是消费价格平减指数,平减指数可以衡量物价水平变化,所以可用来衡量通货膨胀率。
10,不一定。
因为购买力平价在计算时有样本选择的典型性与权重确定上的困难,不能很好地反映两国货币实际比率。
三、计算题1,解:Y = C + I + G + NXGNP=8000+5000+2500+2000-1500=16000NNP= GNP-折旧NNP=16000-500=15500NI= NNP-间接税NI=15500-2000=13500PI=NI-公司未分配利润-公司所得税和社会保险税 + 政府转移支付PI=13500+500=14000DPI=PI-个人所得税DPI=14000-(3000-2000)=13000第二章 消费、储蓄与投资二、分析与思考1,不包括公共产品的消费。





pptx目录•宏观经济学概述•国民收入与经济增长•货币银行体系与货币政策传导机制•财政政策与政府支出乘数效应•国际经济关系与汇率制度选择•总需求-总供给模型与宏观经济政策效果•开放经济条件下宏观经济政策协调•经济增长理论及其在中国实践应用宏观经济学概述宏观经济学研究对象与特点研究对象特点总量分析,关注经济总体的变化趋势和规律;政策导向,为政府制定经济政策提供理论依据。
宏观经济学与微观经济学关系相互联系区别宏观经济学发展历程及主要流派发展历程主要流派国民收入与经济增长国民收入核算体系介绍010203国民收入定义与分类核算方法与数据来源国民收入核算的意义经济增长理论包括古典经济增长理论、新古典经济增长理论和内生增长理论等,探讨经济增长的源泉、机制和影响因素。
经济增长政策实践包括财政政策、货币政策、产业政策和科技创新政策等,通过调节总需求、优化资源配置、提高生产效率等手段促进经济增长。
经济增长与可持续发展经济增长应注重可持续性,避免资源过度消耗和环境破坏,实现经济、社会和环境的协调发展。
经济增长理论与政策实践失业、通货膨胀与货币政策目标失业类型与原因通货膨胀类型与影响平下降等。
货币政策目标与工具货币银行体系与货币政策传导机制货币银行体系定义由中央银行、商业银行、其他金融机构及金融市场组成的复杂系统。
中央银行职能发行货币、制定货币政策、维护金融稳定、提供金融服务。
商业银行作用吸收存款、发放贷款、办理结算等业务,是货币政策传导的重要渠道。
其他金融机构与金融市场保险公司、证券公司、信托公司等,提供多样化金融服务,促进资金融通。
货币银行体系概述及功能货币政策工具及其运用策略货币政策工具种类存款准备金率、利率、公开市场操作等。
存款准备金率调整策略通过调整存款准备金率,影响商业银行信贷规模,进而调控货币供应量。
利率政策运用通过调整存贷款利率,影响居民储蓄和企业投资,达到调控经济的目的。
公开市场操作方式中央银行在公开市场上买卖国债等有价证券,调节市场流动性。

可编辑修改精选全文完整版宏观经济学课件chapter02Macroeconomics, 6e (Blanchard/Johnson)Chapter 2: A Tour of the Book2.1 Multiple Choice Questions1) Fill in the blank for the following: GDP is the value of all ________ produced in a given period.A) final and intermediate goods and services produced by the private sector onlyB) final goods and servicesC) final and intermediate goods and services, plus raw materialsD) all of the aboveE) none of the aboveAnswer: BDiff: 12) When using the income approach to measure GDP, the largest share of GDP generally consists ofA) interest income.B) labor income.C) indirect taxes.D) profits.E) capital income.Answer: BDiff: 13) For this question, assume that 1980 is the base year. Given macroeconomic conditions in the United States over the past three decades, we know thatA) nominal GDP is always smaller than real GDP since 1980.B) real GDP and nominal GDP would be equal for the entire period.C) real GDP is larger than nominal GDP from 2002 to 2008.D) real GDP and nominal GDP were equal in 1980.E) none of the aboveAnswer: DDiff: 24) Suppose nominal GDP increased in a given year. Based on this information, we know with certainty thatA) real output has increased.B) the price level (GDP deflator) has increased.C) real output and the price level (GDP deflator) have both increased.D) either real output or the price level (GDP deflator) have increased.E) real output has increased and the price level has decreased.Answer: DDiff: 25) Use the following information to answer this question. If nominal GDP rises from $100 trillion to $120 trillion, while the GDP deflator rises from 2.0 to 2.2, the percentage change in real GDP is approximately equal toA) -10%.B) 10%.C) 20%.D) 9.1%.E) 0%.Answer: DDiff: 26) Hedonic pricing isA) the way that luxury goods are priced in a market economy.B) the tendency for the inflation rate to rise by greater and greater amounts.C) the tendency for nominal GDP to rise when the price level rises.D) the process of translating nominal GDP into real GDP.E) the process of pricing individual characteristics of a good or service.Answer: EDiff: 17) In a given year, suppose a company spends $100 million on intermediate goods and $200 million on wages, with no other expenses. Also assume that its total sales are $800 million. The value added by this company equalsA) $200 million.B) $300 million.C) $500 million.D) $700 million.E) $800 million.Answer: DDiff: 28) A firm's value added equalsA) its revenue minus all of its costs.B) its revenue minus its wages.C) its revenue minus its wages and profit.D) its revenue minus its cost of intermediate goods.E) none of the aboveAnswer: DDiff: 29) Suppose you are provided with the following data for yourcountry for a particular month: 200 million people are working, 20 million are not working but are looking for work, and 40 million are not working and have given up looking for work. The official unemployment rate for that month isA) 7.7%.B) 9.1%.C) 10%.D) 23%.E) 30%.Answer: BDiff: 110) In the United States, someone is classified as unemployed if he or sheA) does not have a job.B) does not have a job, or else has a job but is looking for a different one while continuing to work.C) does not have a job, has recently looked for work, and is collecting unemployment insurance.D) does not have a job, and is collecting unemployment insurance.E) none of the aboveAnswer: EDiff: 111) An individual is said to be a discouraged worker if he or sheA) is working, but prefers not to work.B) is working part time, but would prefer a full time job.C) is working in jobs she/he is not suited for.D) wants to work, and is actively searching for a job.E) wants to work, but has given up searching for a job.Answer: EDiff: 112) Which of the following tends to occur when the unemployment rate increases?A) a reduction in the labor force participation rateB) a reduction in the number of discouraged workersC) an increase in the number of employed workersD) all of the aboveE) none of the aboveAnswer: ADiff: 113) Labor income's share in an advanced country is likely to beA) 70%.B) 45%.C) 29%.D) 10%.E) none of the aboveAnswer: ADiff: 214) The labor force in the United States is defined asA) the total number of individuals who are employed.B) the sum of the total number of individuals who are employed and the officially unemployed.C) the sum of the total number of individuals who are employed, the officially unemployed, and discouraged workers.D) the total number of individuals who are 16 years old and older, but not retired.E) none of the aboveAnswer: BUse the information provided below to answer the following questions.Suppose a country using the United States' system of calculating official unemployment statistics has 100 million people, of whom 50 million are working age. Of these 50 million, 20 million have jobs. Of the remainder: 10 million are actively searching for jobs; 10 million would like jobs but are not searching; and 10 million do not want jobs at all.15) Refer to the information above. The labor force isA) 20 million.B) 40 million.C) 60 million.D) 80 million.E) 100 million.Answer: CDiff: 216) Refer to the information above. The labor force participation rate isA) .2.B) .3.C) .4.D) .6.E) .8.Answer: DDiff: 217) Refer to the information above. The official unemployment rate isA) .1.B) .2.D) .4.E) .66.Answer: CDiff: 218) The GDP deflator provides a measure of which of the following?A) the ratio of GDP to the size of the populationB) the ratio of GDP to the number of workers employedC) the ratio of nominal GDP to real GDPD) the price of a typical consumer's basket of goodsE) real GDP divided by the aggregate price levelAnswer: CDiff: 119) Which of the following calculations will yield the correct measure of real GDP?A) divide nominal GDP by the consumer price indexB) divide the GDP deflator by the consumer price indexC) multiply nominal GDP by the consumer price indexD) multiply nominal GDP by the GDP deflatorE) none of the aboveAnswer: EDiff: 220) The prices for which of the following goods are included in both the GDP deflator and the consumer price index?A) goods bought by householdsB) goods bought by firmsC) good bought by governmentsD) goods bought by foreign households (i.e., exports)E) all of the aboveAnswer: ADiff: 221) Suppose we switch the base year from 2000 to 2008. This change in the base year will causeA) nominal GDP in every year to increase.B) nominal GDP in every year to decrease.C) both nominal and real GDP in every year to decrease.D) real GDP in every year to decrease.E) none of the aboveAnswer: EDiff: 222) Pure inflation occurs whenA) nominal wages rise faster than all prices.B) all prices rise faster than nominal wages.C) all prices and nominal wages rise by the same percentage.D) the GDP deflator and Consumer Price Index rise by the same percentage.E) none of the aboveAnswer: CDiff: 223) One of the reasons macroeconomists have concerns about inflation is that inflation causesA) real GDP to rise.B) nominal GDP to fall.C) wages to rise as fast as prices.D) real GDP to exceed nominal GDP.E) none of the aboveAnswer: EDiff: 124) Changes in GDP in the short run are caused primarily byA) demand factors.B) supply factors.C) technology.D) capital accumulation.E) all of the aboveAnswer: ADiff: 225) Changes in GDP in the medium run are determined primarily byA) demand factors.B) supply factors.C) monetary policy.D) all of the aboveAnswer: BDiff: 226) Changes in GDP in the long run are determined primarily byA) monetary policy.B) fiscal policy.C) demand.D) all of the aboveE) none of the aboveAnswer: EDiff: 227) Which of the following prices will be used when calculating the rate of growth of real GDP between the year's 2005 and 2006 using the chain method?A) prices in the base year (2002)B) prices in 2005C) prices in 2006D) the average of prices in 2005 and 2006E) prices in 2005, 2006, and in 2002 (the base year)Answer: DDiff: 228) Which of the following factors is NOT believed to affect output in the long run?A) technologyB) monetary policyC) the size of the labor forceD) the capital stockAnswer: BDiff: 129) The Okun's law shows the relationship betweenA) inflation and unemployment rate.B) output growth and unemployment.C) inflation and output growth.D) output growth and money supply.Answer: BDiff: 230) The Phillips curve describes the relationship betweenA) output growth and unemployment.B) inflation and output growth.C) output growth and money supply.D) inflation and unemployment .Answer: DDiff: 231) Prices for which of the following are included in the GDP deflator, but not included in the Consumer Price Index?A) firms' purchases of new equipmentB) intermediate goods and servicesC) consumption of goodsD) consumption of servicesAnswer: ADiff: 132) Macroeconomists are concerned about changes in the unemployment rate because changes in the unemployment rate provide information aboutA) the state of the economy.B) the welfare of those who are unemployed.C) none of the aboveD) both A and BAnswer: DDiff: 133) Based on the notation presented in Chapter 2, which of the following expressions represents nominal GDP?A) Y tB) P t Y tC) Y t/P tD) $Y t/P tAnswer: BDiff: 134) Deflation generally occurs when which of the following occurs?A) the consumer price index is greater than the GDP deflatorB) the consumer price index decreasesC) the rate of inflation falls, for example, from 4% to 2%D) nominal GDP does not changeAnswer: BDiff: 135) During the mid-1980s, we observed a significantreduction in oil prices. In the United States, we would expect that this reduction in oil prices would causeA) a larger reduction in the CPI compared to the GDP deflator.B) an equal reduction in the CPI and GDP deflator.C) a larger reduction in the GDP deflator compared to the CPI.D) no change in the CPI and a reduction in the GDP deflator.Answer: ADiff: 236) Suppose nominal GDP in 2009 does not change (compared its previous level in 2008). Given this information, we know with certainty thatA) real GDP increased during 2009.B) the GDP deflator increased during 2009.C) both the GDP deflator and real GDP fell during 2009.D) more information is needed to answer this question.Answer: DDiff: 237) During the late 1990s, Japan experienced reductions in the GDP deflator. Given this information, we know with certainty thatA) real GDP fell during these periods.B) real GDP did not change during these periods.C) the overall price level in Japan decreased during these periods.D) both real GDP and the overall price level decreased during these periods. Answer: CDiff: 238) Hedonic pricing is used toA) convert nominal values to real values.B) calculate the difference between nominal GDP and real GDP.C) measure the rate of change in real GDP.D) obtain chain-weight indexes.E) none of the aboveAnswer: EDiff: 139) GDP in current dollars is equivalent to which of the following?A) real GDPB) GDP in terms of goodsC) GDP in 2000 dollarsD) GDP in constant dollarsE) none of the aboveAnswer: EDiff: 140) Which of the following does NOT represent real GDP?A) GDP in current dollarsB) GDP in terms of goodsC) GDP in base year dollarsD) GDP in constant dollarsAnswer: ADiff: 141) which of the following represents real GDP?A) GDP in constant dollarsB) GDP in terms of goodsC) GDP in base year dollarsD) all of aboveAnswer: ADiff: 142) According to convention, a recession is referred to if an economy goes throughA) at least two consecutive quarters of negative growthB) at least three consecutive quarters of negative growthC) at least four quarters of negative growthD) at least two consecutive months of negative growthAnswer: ADiff: 143) Based on the notation presented in Chapter 2, which of the following expressions represents real GDP?A) Y tB) P t Y tC) Y t/P tD) $Y t/P tAnswer: ADiff: 144) Measures of aggregate output have been published on a regular basis in the United States sinceA) 1947.B) 1933.C) 1917.D) 1946.Answer: ADiff: 145) Which of the following about capital income is NOT correct?A) it refers to a firm's revenue.B) it is also called profit income.C) it goes to the firms.D) it accounts for less than 35% of income in advancedcountries.Answer: ADiff: 146) Which of the following about the Phillips curve is NOT correct?A) It shows the relation between GDP growth and unemployment.B) It has been redefined as a relation between the change in the rate of inflation and the unemployment rate.C) It was first explored by A. W. Phillips.D) The curve is downward sloping.Answer: ADiff: 12.2 Essay Questions1) Explain the three ways GDP can be measured.Answer: GDP can be measured three ways. First, GDP represents the market value of the final goods and services produced in the economy during a given period. This would be obtained by adding C, I, G, and NX. Second, GDP is the sum of the value added by firms. The value added for a firm equals the value of the production (at that stage of the production process) minus the value of the intermediate goods (excluding labor services). The final value of aggregate output can be calculated by either summing the value of all final goods and services OR by summing the value added of all goods and services at each stage of production. And finally, GDP is also the sum of all incomes earned in a given period.2) First, define nominal GDP and real GDP. Second, is it possible for nominal GDP in a year to be less than real GDP in the same year? Explain.Answer: Nominal GDP represents the value of goods and services produced using current prices. Real GDP measures the value of the same goods and services using some base year prices. It is possible for nominal GDP to be less than real GDP in a given year. Given the definitions of the two variables, this will occur if prices in that year are simply less than prices in the base year. If, for example, the base year is 2002, it will generally be the case that nominal GDP will be less than real GDP for those years prior to 2002 given that prices have generally risen in all years. 3) Explain whether it is possible for nominal GDP to increase and real GDP to decrease in the same period.Answer: Nominal GDP can rise because either the price level is rising or the real quantity of goods and services produced has increased. Nominal GDP can increase while real GDP falls if the increase in the aggregate price level is larger (in a proportionate sense) than the drop in real economic activity.4) Explain the difference between the unemployment rate and the participation rate.Answer: The unemployment rate is the percentage of the labor force (those employed and unemployed) that is unemployed. The participation rate is the percentage of the working age population that is in the labor force.5) Explain how the existence of discouraged workers alters the extent to which the official unemployment provides an accurate measure of the use of labor resources.Answer: Discouraged workers are those individuals who have decided to stop searching for employment because they have become "discouraged" about employment opportunities. At some point, these individuals will no longer be considered as part of the labor force. The existence of discouraged workers willcause the official unemployment rate to provide an under-estimate of the underutilization of labor.6) Briefly explain why the reported official unemployment rate in Spain in 1994 may have provided an over-estimate of unemployment in Spain.Answer: The relatively high unemployment rate in Spain is partly the result of a relatively large underground economy. The underground economy is that part of the economy not measured in official statistics. After taking into account those individuals who are "employed" in the underground economy, the unemployment rate in Spain would have been lower (but still relatively high).7) What are the social and economic implications of unemployment? Explain.Answer: Economic implications: signal of economic activity and measure of the utilization of labor. Social implications: the emotional and psychological suffering that occurs as a result of being unemployed.8) Explain what factors cause changes in output in: (1) the short run; (2) medium run; and (3) long run.Answer: In the short run, demand factors primarily cause changes in output. In the medium run, factors such as the technology, amount of capital, and the skill and size of the labor force (supply factors) affect output. And in the long run, the education system, saving rate, and role of government affect economic activity.9) Will the CPI and GDP deflator always move together? Explain.Answer: No they will not. Some of the goods included in the GDP deflator (some investment goods) are not included in theCPI. Some of the goods included in the CPI (foreign goods) are not included in the GDP deflator.10) Explain how inflation can lead to distortions.Answer: First, not all prices and wages adjust automatically when inflation occurs. Second, variations in relative prices (which occur when there is not pure inflation) can lead to uncertainty. Inflation can also lead to distortions if the tax system is not adjusted when inflation occurs (e.g. nominal income tax brackets).11) Explain why economists care about inflation.Answer: Inflation will cause relative prices to change. It will also cause changes in the distribution of income. Inflation will lead to other distortions such as tax distortions and uncertainty.12) Explain Okun's Law.Answer: It shows the relationship between GDP growth and unemployment rate. If output growth is high, unemployment will decrease.13) Explain the Phillips curve.Answer: It shows the negative relationship between inflation rate and unemployment rate. After 1970s, it was redefined as the relationship between the change in the rate of inflation and the unemployment rate.14) Explain why the Phillips curve on average is downward sloping.Answer: When unemployment becomes very low, the economy is likely to overheat and this will lead to upward pressure on inflation.15) Explain why economists care about unemployment.Answer: First, they care about unemployment because of its direct effect on the welfare of the unemployed. Unemployment is often associated with financial and psychological suffering.Second, they care about unemployment because it provides a signal that the economy may not be using some of its resources efficiently.16) Can an economy maintain high output growth, low unemployment, and low inflation at the the same time? Explain.Answer: It would be very hard to achieve the three objectives at the same time. High output growth leads to low unemployment, which is likely to put pressure on inflation.。

目录•宏观经济学基本概念与原理•经济增长理论与政策分析•失业、通货膨胀与货币政策•国际贸易与汇率制度研究•政府财政收支平衡与公共债务管理•当代宏观经济热点问题透视宏观经济学基本概念与原理宏观经济学定义及研究对象宏观经济学定义研究整体经济现象,包括国民经济总量、国民收入、就业、通货膨胀、国际收支等问题的一门学科。
研究对象整个国民经济活动,包括生产、消费、投资、政府购买和净出口等方面。
国民收入核算体系与方法国民收入核算体系包括国内生产总值(GDP)、国民生产总值(GNP)、国民收入(NI)等指标的核算体系。
核算方法生产法、支出法和收入法。
其中,生产法是从生产过程中创造的货物和服务价值入手,核算国内生产总值;支出法是从最终使用的角度衡量核算期内产品和服务的最终去向;收入法是从生产过程创造收入的角度,根据生产要素在生产过程中应得的收入份额反映最终成果。
总供给与总需求模型01总供给指一个国家或地区在一定时期内(通常为1年)由社会生产活动实际可以提供给市场的可供最终使用的产品和劳务总量。
02总需求指一个国家或地区在一定时期内(通常1年)由社会可用于投资和消费的支出所实际形成的对产品和劳务的购买力总量。
03总供给与总需求模型描述总供给和总需求之间相互作用和影响的模型,用于分析经济中的均衡产出和价格水平。
货币市场与资本市场均衡货币市场指期限在1年以内的短期金融市场,主要功能是调节短期资金融通。
资本市场指期限在1年以上的长期金融市场,主要功能是筹集长期资金。
货币市场与资本市场均衡指货币市场和资本市场在利率和资金供求等方面达到平衡状态,使得整个经济体系能够稳定运行。
经济增长理论与政策分析经济增长核算及影响因素经济增长核算方法01通过国民收入核算体系,对经济增长进行定量评估,包括实际GDP、人均GDP等指标。
经济增长影响因素02分析影响经济增长的主要因素,如资本积累、劳动力投入、技术进步等。
经济增长核算的意义03揭示经济增长的来源和动力,为制定经济政策提供依据。
•宏观经济学概述•国民收入与经济增长•失业与通货膨胀问题探讨•货币政策与财政政策实践应用目录•国际收支与汇率制度改革进展•宏观经济政策效果评价及展望01宏观经济学概述宏观经济学定义与特点定义特点以整个国民经济为考察对象,关注总量指标如GDP、失业率、通货膨胀率等;研究经济波动、经济增长、国际经济等宏观层面的问题。
宏观经济学研究对象国民收入决定失业与通货膨胀经济周期与经济增长国际经济研究对象不同分析方法不同政策目标不同相互联系01020304宏观经济学与微观经济学关系02国民收入与经济增长国民收入定义指一个国家或地区在一定时期内(通常为一年)所有常住单位从事生产活动所创造的增加值的总和。
采用国内生产总值(GDP)作为衡量国民收入的主要指标,通过生产法、收入法和支出法三种方法进行核算。
从生产过程中创造的货物和服务价值入手,剔除生产过程中投入的中间产品的价值,得到增加值。
也称分配法,按收入法计算的国内生产总值是从生产过程创造收入的角度,对常住单位的生产活动成果进行核算。
是从最终使用的角度反映国内生产总值最终使用去向的一种方法。
最终使用包括货物和服务的最终消费、资本形成总额和净出口三部分。
核算方法收入法支出法生产法国民收入概念及核算方法经济增长理论与政策目标经济增长理论研究解释经济增长规律和影响制约因素的理论,包括古典经济增长理论、新古典经济增长理论和新经济增长理论等。
政策目标促进经济持续、稳定、协调发展,提高人民生活水平,实现充分就业,保持物价稳定,推动社会全面进步。
实现途径通过增加投资、提高生产效率、优化产业结构、推动技术创新和制度创新等方式实现经济增长。
为起飞创造前提阶段开始积累起飞所需的社会基础设施和公共基础设施,如交通、通讯、电力等。
成熟阶段追求生活质量阶段人们更加关注生活质量和环境保护,绿色经济和可持续发展成为重要议题。
传统社会阶段生产力水平低下,以农业为主导产业,经济增长缓慢。
起飞阶段高额群众消费阶段居民消费水平显著提高,对高品质商品和服务的需求增加,推动经济向更高水平发展。
宏观经济学(叶航)浙江大学精品课程在线播放
宏观经济学(叶航)浙江大学精品课程名称:宏观经济学(叶航)浙江大学
分类:经济管理
观看人数:3054
TAG:
时间:2013/4/14 21:32:05
收藏:更多3 1: 优酷01导论02导论03导论04导论05导论06导论07总产出08总产出09总产出10总产出11消费、储蓄和投资12消费、储蓄和投资13消费、储蓄和投资14消费、储蓄和投资15消费、储蓄和投资16货币需求与货币供给17货币需求与货币供给18货币需求与货币供给19货币需求与货币供给20货币需求与货币供给21货币需求与货币供给22货币需求与货币供给23有效需求决定模型24有效需求决定模型25有效需求决定模型26有效需求决定模型27有效需求决定模型28有效需求决定模型29IS-LM模型30IS-LM模型31IS-LM模型32IS-LM模型33IS-LM模型34AD-AS模型35AD-AS模型36AD-AS模型37AD-AS模型38通货膨胀39通货膨胀40通货膨胀41通货膨胀42通货膨胀43通货膨胀44通货膨胀45通货膨胀46经济增长47经济增长48经济增长49经济增长50经济
增长51经济增长52经济增长53经济增长54经济增长55经济周期56调控的技巧与艺术57调控的技巧与艺术58调控的技巧与艺术59调控的技巧与艺术60宏观调控三十年61宏观调控三十年62宏观调控三十年63宏观调控三十年64宏观调控三十年65宏观调控三十年66宏观调控三十年67宏观调控三十年68宏观经济学流派69宏观经济学流派70宏观经济学流派宏观经济学(叶航)浙江大学介绍
宏观经济学(叶航)浙江大学精品课程
叶航,浙江大学经济学院教授、博士生导师,致力于经济学的跨学科研究,涉及领域主要包括行为经济学、实验经济学、效用与偏好理论、神经元经济学、神经元伦理学、演化博弈理论与演..
为了突出教材的逻辑性,还对传统教材的章节和内容作了较大的调整。
其中主要有:把消费、储蓄和投资列为宏观经济变量篇中专门的一章(第二章),而消费、储蓄和投资对宏观经济的影响则放在第四章有效需求决定模型中加以介绍。
有效需求决定是凯恩斯宏观经济理论的灵魂,因此我们对这一章的内容进行了较大的调整和充实,以便读者能够比较系统和全面地掌握这一理论的精髓。
在介绍IS—LM模型(第四章)和A —AS模型(第五章)时,突出了模型的数理推
导,以便读者对这两个重要的分析工具能够有一个更深刻的理解。
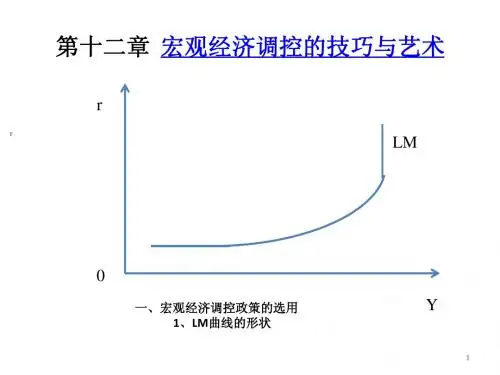
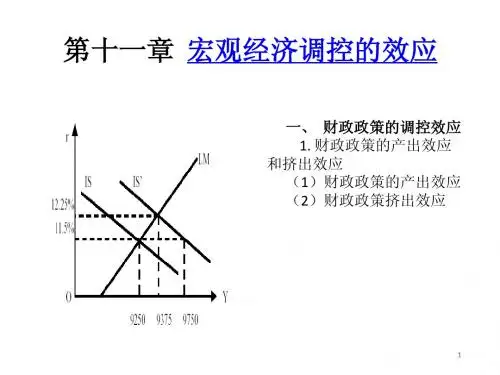
我们对宏观经济调控的内容进行较大的扩充,一是把IS—LM的政策效应分析列为单独一章(第十一章),以便有更大的空间来展开论述;二是专门增加了一章(第十二章),对宏观经济调控的技巧与艺术进行分析。
认为,政府对宏观经济的调控,既是一个重要的理论问题,也是一个重要的实践问题,它对读者把握宏观经济的发展具有十分重要的现实意义。
在宏观经济学流派中,增加了对新凯恩斯主义的介绍。
新凯恩斯主义是20世纪80年代以后兴起的,其代表人物如斯蒂格利茨和曼昆等人都是当代美国最活跃的经济学家。
导论
第一节宏观经济学概述
第二节宏观经济学的产生与发展
第一篇宏观经济变量
第一章总产出
第一节总产出核算的指标
第二节总产出核算的方法
第三节总产出核算的校正
练习与思考
第二章消费、储蓄与投资
第一节消费、消费函数与消费倾向
第二节储蓄、储蓄函数与储蓄倾向
第三节投资、投资函数与投资的边际效率练习与思考
第三章货币流通
第一节货币需求
第二节货币供给
第三节货币市场的均衡
练习与思考
第二编宏观经济模型
第四章有效需求决定模型
第一节有效需求与充分就业。