地下水溶质运移第二章
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:416.36 KB
- 文档页数:55


土壤水与溶质的运移Contents5.0 Introduction5.1 Classifying and determining of soil water土壤水的类型划分及土壤水分含量的测定5.2 Energy status of soil water土壤水的能态5.3 Soil water movement土壤水的运动5.4 Solute transportation in soils土壤中的溶质运移Soil water土壤水是土壤的最重要组成部分之一;在土壤形成过程中起着极其重要的作用,在很大程度上参与了土壤内进行的许多物质转化过程:矿物质风化、有机化合物的合成和分解等;作物吸水的最主要来源;自然界水循环的重要环节;非纯水,而是稀薄的溶液,溶有各种溶质,还有胶体颗粒悬浮或分散其中。
Principal sources of soil water●Precipitation——Rain, snow, hail(雹); fog, mist(霜)●Ground water——lateral movement from upslope, upward movement from the underlying rock strata.precipitation Surface devoid of vegetationReachdirectly Vegetated surfaceinterceptedcanopyCanopy throughfall andstemflow atmosphereevaporation infiltration Run offSoil waterDrainage and lostEvapotraspirationThe composition of soil waterSoil water contains a number of dissolved solid and gaseous constituents,many of which exist in mobile ionic form,and a variety of suspended solid components.Base cations(Ca2+, Mg2+, K+, Na+, NH4+)PrecipitationMineral weatheringOrganic matter decomposition Lime and fertilizersourcesH+——a measure of acidity (pH)●CO2Atmosphere ——dissolved in precipitation Soil air ——produced in soil respirationH2O + CO2H2CO3H++ HCO3-Unpolluted rain water: pH>5.6Soil water: pH <5.0●Industrial and urban emission●Organic acids derived from decaying organic material●Released by plants in exchange for nutrient base cations major sourceIron and aluminiumMajor sourcesmineral weatheringacid rainMajor formFe2+, Al3+ionssoluble organic-metallic complexesSoluble anionsNO3-, PO43-Cl-, SO42-HCO3-Mineralisation processesFertilizersAtmosphere sourcesMineral weatheringDissolved organic carbon (DOC) Pollutants (heavy metals et al.)Suspended constitutions☐Small particles of mineral and organic material ☐Often result in discoloration(变污)and increased turbidity(混浊度)of soil water.第一节土壤水的类型划分及土壤水分含量测定Classifying and determining of soil water 一、土壤水分类型及有效性Soil water types and availability土壤水分研究方法能量法数量法从土壤水分受各种力作用后自由能的变化研究水分的能态和运动、变化规律。

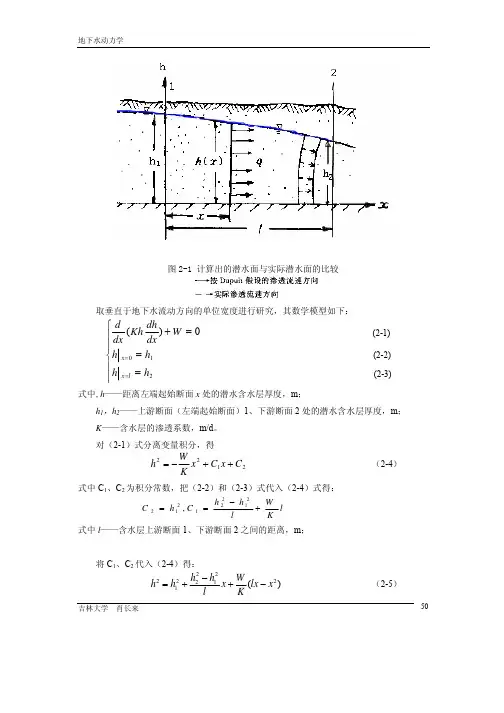
第二章 地下水向河渠的运动一、填空题1. 将_______________上的入渗补给量称为入渗强度.2. 有入渗补给的河渠间含水层中,只要存在分水岭,且两河水位不相等时,则分水岭总是偏向_________一侧。
如果入渗补给强度W >0时,则浸润曲线的形状为____________;当W <0时,则为__________;当W =0时,则为____________。
3. 双侧河渠引渗时,地下水的汇水点靠近河渠________一侧,汇水点处的地下水流速等于_______。
4. 在河渠单侧引渗时,同一时刻不同断面处的引渗渗流速度_______,在起始断面x=0处的引渗渗流速度______,随着远离河渠,则引渗渗流速度__________。
5. 在河渠单侧引渗中,同一断面上的引渗渗流速度随时间的增大_______,当时间趋向无穷大时,则引渗渗流速度_________。
6. 河渠单侧引渗时,同一断面上的引渗单宽流量随时间的变化规律与该断面上的引渗渗流速度的变化规律_______,而同一时刻的引渗单宽流量最大值在________,其单宽渗流量表达式为_______。
二、选择题1.当河渠间含水层无入渗补给,但有蒸发排泄(设其蒸发强度为ε)时,计算任一断面的单宽流量公式,只要将式W x W l l h h K q x +-=-2/)2/()(2121中的W用( )代替即可。
(1) ε; (2) 0; (3) -ε; (4) ε+W2.在有入渗补给,且存在分水岭的河渠间含水层中,已知左河水位标高为H 1,右河水位标高为H 2,两河间距为L ,当H 1>H 2时,分水岭( );当H 1<H 2时,分水岭( );当H 1= H 2时,分水岭( );(1) 位于L/2处; (2) 靠近右河; (3) 靠近左河; (4) 不存在;(5)位于L=0处; (6)位于L 处3.在底板水平,无入渗、无蒸发的河渠间潜水含水层中,当渗流为稳定流,两侧河水位相等时,浸润曲线的形状为( )。

中国海洋大学硕士学位论文二维地下水溶质运移耦合方程组的差分方法姓名:***申请学位级别:硕士专业:计算数学指导教师:***201206二维地下水溶质运移耦合方程组的差分方法摘要本文分析二维地下水溶质运移数学模型的控制方程,在此基础上,建立了求解控制方程的交替方向隐式差分格式。
古典显格式由于稳定性,在时间上限制很大;隐式差分格式和中心差分法需要求解多个未知量,导致计算时占用内存大,求解困难;本文采用的交替方向差分法,每层分两步计算,每步只需求解一个三对角方程组,在计算规模上相当于一维的计算量,并且它与隐式格式有相同的稳定性。
其次控制方程含有非线性系数,为了高精度地模拟模型,本文对非线性系数用三次样条插值逼近,提高了计算精度。
通过数值算例比较证明本文方法可以对地下水溶质运移进行有效的模拟,对解决此类非线性问题有参考价值。
最后分析了线性的溶质运移方程的稳定性。
文章由三部分组成:第一部分为前言。
介绍了地下水模型和求解地下水问题的数值方法的背景和发展状况,以及本文的主要研究内容。
第二部分为地下水溶质运移模型分析。
在这一部分里,介绍了地下水基本假设和根据均衡单元体的质量守恒建立地下水运动的连续方程和溶质运移方程。
再根据二维潜水问题的Dupuit假设,最终形成二维问题的模型。
还对方程中涉及到的参数做了详细的分析。
第三部分为二维地下水模型的有限差分方法。
给出方程的交替方向差分格式和二维时的三次样条插值计算。
对于方程非线性系数我们介绍了两种方法进行逼近,通过数值算例证明两层平均的三次Hermite插值逼近更有效。
最后分析了线性的溶质运移方程的稳定性。
关键词:地下水连续方程;溶质运移方程;交替方向差分方法;样条插值;稳定性;二维地下水溶质运移耦合方程组的差分方法ADIdi如rencemethodforCIlmenSlonaIgroundwatercoupledsystemoftwoandsolutetransportAbstractThispaperanalyzesthecontrolequationsoftwo-dimensionalgroundwatersolutetransport.Onthisbasis,weestablishalternatingdirectionimplicitdiffer—enceschemeofequations.Classicalexplicitdifferenceschemeduestothestabilityofthetimelimit;Theimplicitdifferenceschemeorcentraldifferencemethodre—quiresthesolutionofquitealotofunknownvariables,andthenleadstosolvingdifficultly;Inthispaper:thealternatingdirectiondifferencemethodisused.Eachlaverisdividedintotwostepsaswella8everystepsimplyneedstosolvesatridiagonalequations.Inthescaleofthecalculation,itisequivalenttoone—dimensional.Andhasthesamestabilitywiththeimplicitscheme.Secondly,thecontrolequationcontainsthenonlinearcoefficient,thecubicsplineinterpolationisusedtoapproximateitinordertoimprovethecalculationaccuracy.Thenumer—icalexampleshasprovedthismethodcanbeeffectivetosimulatetheequationofsolutetransportingroundwater.Thisarticlehasreferencevaluetosolvesuchnonlinearissue.Finally,weanalyzethestabilityofthelinearsolutetransportequation.Thearticleconsistsofthreeparts:Thefirstpartisthe-preface.Itdescribesthebackgroundanddevelopmentofnumericalmodelingroundwater.Inaddition,thissectiongivesthemaincontentsofthisarticle.Thesecondpartisthesolutetransportmodelingroundwater.Inthissec—tion,itpresentsthebasicassumptionsofgroundwater.Andweestablishtheequationsofthegroundwaterflowandthesolutetransportaccordingtomassconservationoftheequilibriumunitcell.OnthebasisofDupuitassumption,weultimatelyformattwo-dimensionalmodel.Finallywemakeadetailedanalysisoftheparametersinvolvedintheequation.Thethirdpartisthefinitedifferencemethodoftwo-dimensionalground—watermodel.ItgivesboththealternatingdirectiondifferentialformatoftheⅨoftwo-dimensional.Weintroduceequationsandthecubicsplineinterpolationtwomethodstoapproximationequationofnonlinearcoefficientandnumericalexamplesprovethatthesecondmethodismoreeffective.Finally,thispaperan—alyzesthestabilityofthelinearsolutetransportequations.Keywords:Groundwatercontinuityequation;solutetransportequa-tion;alternatingdirectiondifferencemethod;splineinterpolation;sta-bility;X第1章前言1.1背景介绍地下水是全球水资源的重要组成部分,在社会经济发展中发挥着重要的作用。





地下水溶质运移常用解析解2013年9月目录1 一维迁移问题的解析解 (1)1.1 定浓度注入污染物的一维解析解 (1)1.2初始浓度不为零时定浓度注入污染物的一维解析解 (1)1.3含有一级化学反应问题时定浓度注入的一维解析解 (1)1.4短时注入污染物问题的一维解析解 (2)1.5瞬时注入污染物问题的一维解析解 (2)2 二维迁移问题的解析解 (3)2.1点源连续注入污染物问题的二维解析解 (3)2.2点源连续注入含有一级化学反应问题的二维解析解 (4)2.3点源瞬时注入的二维解析解 (4)2.4点源瞬时注入含有一级化学反应的二维解析解 (4)2.5面源连续注入的二维解析解 (5)2.6面源瞬时注入的二维解析解 (5)3三维迁移问题的解析解 (6)3.1点源瞬时注入的三维迁移问题解析解 (6)3.2立方体源瞬时注入的三维迁移问题的解析解 (6)3.3点源连续注入的三维迁移问题的解析解 (6)3.4 点线面体源下的三维迁移解析解库 (7)参考文献:《多孔介质污染物迁移动力学》,王洪涛,高等教育出版社,2008年3月第一版。
1 一维迁移问题的解析解1.1 定浓度注入污染物的一维解析解exp 2L c ux c erfc erfc D ⎧⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫⎪⎪=+⎨⎬ ⎪⎝⎭⎪⎪⎩⎭式中:x —距注入点的距离;m ; t —时间,d ;C —t 时刻x 处的示踪剂浓度,mg/L ; C 0—注入的示踪剂浓度,mg/L ; u —水流速度,m/d ;D L —纵向弥散系数,m 2/d ; erfc ()—余误差函数。
1.2初始浓度不为零时定浓度注入污染物的一维解析解01exp 2i i L c c ux erfc erfc c c D ⎧⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫-⎪⎪=+⎨⎬ ⎪-⎝⎭⎪⎪⎩⎭式中:c i —初始时刻多孔介质中污染物浓度;mg/L ; 其余参数含义同上。
1.3含有一级化学反应问题时定浓度注入的一维解析解污染物在迁移的同时还发生衰变反应,且符合一级反应动力学过程,反应常数为λ,则:0()()exp exp 222L L c u w x u w x c erfc erfc D D ⎧⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫⎛⎫-+⎪⎪=+⎨⎬ ⎪ ⎪⎝⎭⎝⎭⎪⎪⎩⎭w =式中参数含义同上。
