第9章1重量分析法
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:232.00 KB
- 文档页数:27


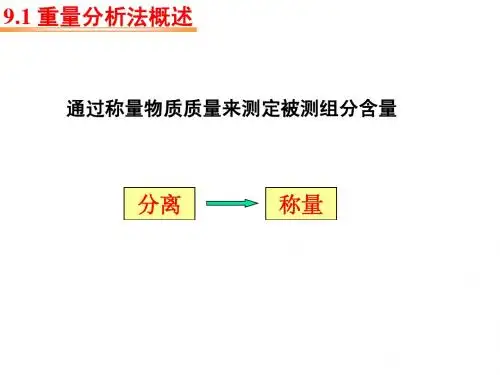
第九章重量分析法第一节概述测定时先用适当的方法将被测组分与试样中的其他组分分离,然后转化为一定的称量形式,称重,从而求得该组分的含重量分析法是直接用分析天平称量而获得分析结果第二节挥发法挥发法:是利用被测组分具有挥发性,或将它转化为挥发性物质来进行挥发组分含量测定的方法挥发重量法又分为直接法和间接法一、直接法直接挥发法:是利用加热等方法使试样中挥发性组分逸出,用适宜的吸收剂将其全部吸收,称量吸收剂的增量来计算该组分含量的方法常用高氯酸镁来吸收逸出的水分常用苏打石灰用于吸收逸出的CO2在直接法测定中,若有几种挥发性物质并存时,应选用适当的吸收剂,定量地吸收被测物而不吸收其他共存物药典中经常要检测炽灼残渣的限量,以控制某些药品的质量。
取一定量被检药品,经过高温炽灼,出去挥发性物质后,称量剩下来的不挥发无机物,称为炽灼残渣所测定的虽不是挥发物,但仍属直接挥发法二、间接法间接挥发法:是利用加热等方法使试样中挥发性组分逸出以后,称量其残渣,有样品的减量来计算该挥发组分的含量干燥法:测定固体物质中的水分含量试样中水分挥发的难易取决于水在试样中存在的状态其次取决于环境空间的干燥程度固体物质中水的存在状态分为(1)引湿水(湿存水)(2)包埋水(3)吸入水(4)结晶水(5)组成水引湿水:固体表面吸附的水分这种水在一定湿度下随物质的性质、粉碎程度以及空气的湿度而定物质的表面积大、颗粒细、吸水性强以及空气的湿度大,则吸附愈显著所有固体物质放在空气中都会或多或少地带有这种水分包埋水:从水溶液中得到的晶体,长可在晶体内的空穴内保持藏水分这种水分与外界不通,很难除尽,可将颗粒研细或用高温烧除吸入水:一些具有亲水胶体性质的物质(硅胶、纤维素、淀粉、和明胶),内部有很大的扩胀性,内表面积很大,能大量吸收水分有时需采用70-100度真空干燥适用于试样易变质和水分较难挥发的试样干燥剂干燥:能升华或受热不稳定、容易变质的物质只要试样的相对蒸汽压高于干燥剂的相对蒸汽压,试样就能继续失水,直至达到平衡用干燥剂干燥法来测定水分,因为达到平衡需要较长时间,而且不易达到完全干燥的目的,所以该法少用盛有干燥剂的密闭容器,在重量分析中经常被用作短时间存放刚从烘箱或高温炉取出的热的干燥器皿或试样,目的是在低湿度的环境中冷却,减少吸水,以便称量但十分干燥的试样不宜在干燥器中长时间放置,尤其是很细的粉末,由于表面吸附作用,可使它吸收一些水分第三节液-液萃取法液-液萃取法(溶剂萃取法):是把待测物质从一个液相转移到另一个液相以达到分离的目的一、基本原理(一)萃取分离的本质亲水性:一般无机盐类都是离子型化合物,具有易溶于水难溶于有机溶剂的性质,这种性质称为~疏水性:许多有机化合物没有极性或极性很弱,这类化合物难溶于水而易溶于有机溶剂,这种性质称为~反萃取:有时需要把在有机溶剂中的物质再转入水中,就要把疏水性转化为亲水性,这种过程称为~萃取和反萃取配合使用,可提高萃取分离的纯净度(二)分配定律分配平衡:在萃取分离中,溶质在两相中的浓度达到平衡时,称为~分配系数:溶质A在两相中的平衡浓度[A]有机相和[A]水相的比值K称为~(三)分配比分配定律适用的溶质只限于固定不变的化合状态分配比:表示溶质A在两相中各种存在形式的总浓度之比,用D表示浓度对分配比的影响,主要是溶质于溶液中电离或聚合发生变化而分配比值发生改变(四)萃取效率萃取效率:萃取的完全程度,常用萃取百分率E%表示E%值大小与分配比D和两相体积比V水/V有有关如果D一定且较小时,V水/V有越小,E%越大要使V水/V有较小可以增加V有,实际中采用多次萃取的方法随着萃取次数的不断增多,萃取率的提高将越来越有限(五)分离因子与分离系数若A是萃取目的物,B是希望除去的物质,萃取平衡后,有机相中两组分的比以S B/A=Q B*E B/Q A*E AS B/A值(分离因子)越小,说明萃取所得A组分中混入的B组分越少,分离效果越好两组分分配比D A与D B的比值越大,可使分离因子S B/A越小,分离效果越好分配系数:两组分分配比的比值称为~,以β表示β=D/D于1,就有可能得到满意的分离二、萃取类型(一)有机化合物利用“相似相溶”原则(二)离子缔合物机酸根等4一些金属阳离子可用适当的配位剂,形成没有或很少配位水分子的配位阳离子,再与电荷密度小的阴离子缔合,即可成为疏水性的离子缔合物而被萃取(三)金属配位化合物一些金属阳离子能与有机配位体生成不带电荷的配位化合物,称为疏水性指点,可以从水中析出,亦可被有机溶剂萃取第四节沉淀法沉淀形式与称量形式可以相同,也可以不同Eg:用重量法测定SO42-,加BaCl2为沉淀剂,沉淀形式和称量形式都是BaSO4两者不同,在Ca2+的测定中,沉淀形式是CaC2O4*H20炽灼后所得的称量形式是CaO,两者不同对沉淀形式与称量形式要求具有以下几个条件:沉淀溶解损失的量应不超出分析天平的称量误差范围,这样才能保证反应定量完全(2)(3)为此尽量希望获得粗大的晶形沉淀。

专业英语词汇-----分析化学第一章绪论分析化学:analytical chemistry定性分析:qualitative analysis定量分析:quantitative analysis物理分析:physical analysis物理化学分析:physico-chemical analysis仪器分析法:instrumental analysis流动注射分析法:flow injection analysis;FIA顺序注射分析法:sequentical injection analysis;SIA化学计量学:chemometrics第二章误差的分析数据处理绝对误差:absolute error相对误差:relative error系统误差:systematic error可定误差:determinate error随机误差:accidental error不可定误差:indeterminate error准确度:accuracy精确度:precision偏差:debiation,d平均偏差:average debiation相对平均偏差:relative average debiation标准偏差〔标准差〕:standerd deviation;S相对平均偏差:relatibe standard deviation;RSD变异系数:coefficient of variation误差传递:propagation of error有效数字:significant figure置信水平:confidence level显著性水平:level of significance合并标准偏差〔组合标准差〕:pooled standard debiation 舍弃商:rejection quotient ;Q化学定量分析第三章滴定分析概论滴定分析法:titrametric analysis滴定:titration容量分析法:volumetric analysis化学计量点:stoichiometric point等当点:equivalent point电荷平衡:charge balance电荷平衡式:charge balance equation质量平衡:mass balance物料平衡:material balance 质量平衡式:mass balance equation第四章酸碱滴定法酸碱滴定法:acid-base titrations质子自递反响:auto protolysis reaction质子自递常数:autoprotolysis constant质子条件式:proton balance equation酸碱指示剂:acid-base indicator指示剂常数:indicator constant变色范围:colour change interval混合指示剂:mixed indicator双指示剂滴定法:double indicator titration第五章非水滴定法非水滴定法:nonaqueous titrations质子溶剂:protonic solvent酸性溶剂:acid solvent碱性溶剂:basic solvent两性溶剂:amphototeric solvent无质子溶剂:aprotic solvent均化效应:differentiatin g effect区分性溶剂:differentiating solvent离子化:ionization离解:dissociation结晶紫:crystal violet萘酚苯甲醇: α-naphthalphenol benzyl alcohol奎哪啶红:quinadinered百里酚蓝:thymol blue偶氮紫:azo violet溴酚蓝:bromophenol blue第六章配位滴定法配位滴定法:compleximetry乙二胺四乙酸:ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid,EDTA 螯合物:chelate compound金属指示剂:metal lochrome indcator第七章氧化复原滴定法氧化复原滴定法:oxidation-reduction titration碘量法:iodimetry溴量法:bromimetry ]溴量法:bromine method铈量法:cerimetry高锰酸钾法:potassium permanganate method条件电位:conditional potential溴酸钾法:potassium bromate method硫酸铈法:cerium sulphate method偏高碘酸:metaperiodic acid高碘酸盐:periodate亚硝酸钠法:sodium nitrite method重氮化反响:diazotization reaction重氮化滴定法:diazotization titration亚硝基化反响:nitrozation reaction亚硝基化滴定法:nitrozation titration外指示剂:external indicator外指示剂:outside indicator重铬酸钾法:potassium dichromate method 第八章沉淀滴定法沉淀滴定法:precipitation titration容量滴定法:volumetric precipitation method 银量法:argentometric method第九章重量分析法重量分析法:gravimetric analysis挥发法:volatilization method引湿水〔湿存水〕:water of hydroscopicity 包埋(藏)水:occluded water吸入水:water of imbibition结晶水:water of crystallization组成水:water of composition液-液萃取法:liquid-liquid extration溶剂萃取法:solvent extration反萃取:counter extraction分配系数:partition coefficient分配比:distribution ratio离子对〔离子缔合物〕:ion pair沉淀形式:precipitation forms称量形式:weighing forms仪器分析概述物理分析:physical analysis物理化学分析:physicochemical analysis仪器分析:instrumental analysis第十章电位法及永停滴定法电化学分析:electrochemical analysis电解法:electrolytic analysis method电重量法:electrogravimetry库仑法:coulo metry库仑滴定法:coulo metric titration电导法:conductometry电导分析法:conductometric analysis电导滴定法:conductometric titration 电位法:potentiometry直接电位法:dirext potentiometry电位滴定法:potentiometric titration伏安法:voltammetry极谱法:polarography溶出法:stripping method电流滴定法:amperometric titration化学双电层:chemical double layer相界电位:phase boundary potential金属电极电位:electrode potential化学电池:chemical cell液接界面:liquid junction boundary原电池:galvanic cell电解池:electrolytic cell负极:cathode正极:anode电池电动势:eletromotive force指示电极:indicator electrode参比电极:reference electroade标准氢电极:standard hydrogen electrode一级参比电极:primary reference electrode饱和甘汞电极:saturated calomel electrode银-氯化银电极:silver silver-chloride electrode液接界面:liquid junction boundary不对称电位:asymmetry potential表观PH值:apparent PH复合PH电极:combination PH electrode离子选择电极:ion selective electrode敏感器:sensor晶体电极:crystalline electrodes均相膜电极:homogeneous membrance electrodes非均相膜电极:heterogeneous membrance electrodes非晶体电极:non- crystalline electrodes刚性基质电极:rigid matrix electrode流流体载动电极:electrode with a mobile carrier气敏电极:gas sensing electrodes酶电极:enzyme electrodes金属氧化物半导体场效应晶体管:MOSFET离子选择场效应管:ISFET总离子强度调节缓冲剂:total ion strength adjustment buffer,TISAB永停滴定法:dead-stop titration双电流滴定法〔双安培滴定法〕:double amperometric titration 第十一章光谱分析法概论普朗克常数:Plank constant电磁波谱:electromagnetic spectrum光谱:spectrum光谱分析法:spectroscopic analysis原子发射光谱法:atomic emission spectroscopy质量谱:mass spectrum质谱法:mass spectroscopy,MS第十二章紫外-可见分光光度法紫外-可见分光光度法:ultraviolet and visible spectrophotometry;UV-vis肩峰:shoulder peak末端吸收:end absorbtion生色团:chromophore助色团:auxochrome红移:red shift长移:bathochromic shift短移:hypsochromic shift蓝〔紫〕移:blue shift增色效应〔浓色效应〕:hyperchromic effect减色效应〔淡色效应〕:hypochromic effect强带:strong band弱带:weak band吸收带:absorption band透光率:transmitance,T吸光度:absorbance谱带宽度:band width杂散光:stray light噪声:noise暗噪声:dark noise散粒噪声:signal shot noise闪耀光栅:blazed grating全息光栅:holographic grating光二极管阵列检测器:photodiode array detector偏最小二乘法:partial least squares method ,PLS褶合光谱法:convolution spectrometry褶合变换:convolution transform,CT离散小波变换:wavelet transform,WT多尺度细化分析:multiscale analysis供电子取代基:electron donating group吸电子取代基:electron with-drawing group第十三章荧光分析法荧光:fluorescence荧光分析法:fluorometryX-射线荧光分析法:X-ray fluorometry原子荧光分析法:atomic fluorometry分子荧光分析法:molecular fluorometry振动弛豫:vibrational relaxation内转换:internal conversion 外转换:external conversion体系间跨越:intersystem crossing激发光谱:excitation spectrum荧光光谱:fluorescence spectrum斯托克斯位移:Stokes shift荧光寿命:fluorescence life time荧光效率:fluorescence efficiency荧光量子产率:fluorescence quantum yield荧光熄灭法:fluorescence quenching method散射光:scattering light瑞利光:R a yleith scattering light拉曼光:Raman scattering lightAbbe refractometer 阿贝折射仪absorbance 吸收度absorbance ratio 吸收度比值absorption 吸收absorption curve 吸收曲线absorption spectrum 吸收光谱absorptivity 吸收系数accuracy 准确度acid-dye colorimetry 酸性染料比色法acidimetry 酸量法acid-insoluble ash 酸不溶性灰分acidity 酸度activity 活度第十四章色谱法additive 添加剂additivity 加和性adjusted retention time 调整保存时间adsorbent 吸附剂adsorption 吸附affinity chromatography 亲和色谱法aliquot 〔一〕份alkalinity 碱度alumina 氧化铝ambient temperature 室温ammonium thiocyanate 硫氰酸铵analytical quality control〔AQC〕分析质量控制anhydrous substance 枯燥品anionic surfactant titration 阴离子外表活性剂滴定法antibiotics-microbial test 抗生素微生物检定法antioxidant 抗氧剂appendix 附录application of sample 点样area normalization method 面积归一化法argentimetry 银量法arsenic 砷arsenic stain 砷斑ascending development 上行展开ash-free filter paper 无灰滤纸〔定量滤纸〕assay 含量测定assay tolerance 含量限度atmospheric pressure ionization(API) 大气压离子化attenuation 衰减back extraction 反萃取back titration 回滴法bacterial endotoxins test 细菌内毒素检查法band absorption 谱带吸收baseline correction 基线校正baseline drift 基线漂移batch, lot 批batch(lot) number 批号Benttendorff method 白田道夫〔检砷〕法between day (day to day, inter-day) precision 日间精密度between run (inter-run) precision 批间精密度biotransformation 生物转化bioavailability test 生物利用度试验bioequivalence test 生物等效试验biopharmaceutical analysis 体内药物分析,生物药物分析blank test 空白试验boiling range 沸程British Pharmacopeia (BP) 英国药典bromate titration 溴酸盐滴定法bromimetry 溴量法bromocresol green 溴甲酚绿bromocresol purple 溴甲酚紫bromophenol blue 溴酚蓝bromothymol blue 溴麝香草酚蓝bulk drug, pharmaceutical product 原料药buret 滴定管by-product 副产物calibration curve 校正曲线calomel electrode 甘汞电极calorimetry 量热分析capacity factor 容量因子capillary zone electrophoresis (CZE) 毛细管区带电泳capillary gas chromatography 毛细管气相色谱法carrier gas 载气cation-exchange resin 阳离子交换树脂ceri(o)metry 铈量法characteristics, description 性状check valve 单向阀chemical shift 化学位移chelate compound 鳌合物chemically bonded phase 化学键合相chemical equivalent 化学当量Chinese Pharmacopeia (ChP) 中国药典Chinese material medicine 中成药Chinese materia medica 中药学Chinese materia medica preparation 中药制剂Chinese Pharmaceutical Association (CPA) 中国药学会chiral 手性的chiral stationary phase (CSP) 手性固定相chiral separation 手性别离chirality 手性chiral carbon atom 手性碳原子chromatogram 色谱图chromatography 色谱法chromatographic column 色谱柱chromatographic condition 色谱条件chromatographic data processor 色谱数据处理机chromatographic work station 色谱工作站clarity 澄清度clathrate, inclusion compound 包合物clearance 去除率clinical pharmacy 临床药学coefficient of distribution 分配系数coefficient of variation 变异系数color change interval 〔指示剂〕变色范围color reaction 显色反响colorimetric analysis 比色分析colorimetry 比色法column capacity 柱容量column dead volume 柱死体积column efficiency 柱效column interstitial volume 柱隙体积column outlet pressure 柱出口压column temperature 柱温column pressure 柱压column volume 柱体积column overload 柱超载column switching 柱切换committee of drug evaluation 药品审评委员会comparative test 比较试验completeness of solution 溶液的澄清度compound medicines 复方药computer-aided pharmaceutical analysis 计算机辅助药物分析concentration-time curve 浓度-时间曲线confidence interval 置信区间confidence level 置信水平confidence limit 置信限congealing point 凝点congo red 刚果红〔指示剂〕content uniformity 装量差异controlled trial 对照试验correlation coefficient 相关系数contrast test 对照试验counter ion 反离子〔平衡离子〕cresol red 甲酚红〔指示剂〕crucible 坩埚crude drug 生药crystal violet 结晶紫〔指示剂〕cuvette, cell 比色池cyanide 氰化物cyclodextrin 环糊精cylinder, graduate cylinder, measuring cylinder 量筒cylinder-plate assay 管碟测定法daughter ion 〔质谱〕子离子dead space 死体积dead-stop titration 永停滴定法dead time 死时间decolorization 脱色decomposition point 分解点deflection 偏差deflection point 拐点degassing 脱气deionized water 去离子水deliquescence 潮解depressor substances test 降压物质检查法derivative spectrophotometry 导数分光光度法derivatization 衍生化descending development 下行展开desiccant 枯燥剂detection 检查detector 检测器developer, developing reagent 展开剂developing chamber 展开室deviation 偏差dextrose 右旋糖,葡萄糖diastereoisomer 非对映异构体diazotization 重氮化2,6-dichlorindophenol titration 2,6-二氯靛酚滴定法differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 差示扫描热量法differential spectrophotometry 差示分光光度法differential thermal analysis (DTA) 差示热分析differentiating solvent 区分性溶剂diffusion 扩散digestion 消化diphastic titration 双相滴定disintegration test 崩解试验dispersion 分散度dissolubility 溶解度dissolution test 溶出度检查distilling range 馏程distribution chromatography 分配色谱distribution coefficient 分配系数dose 剂量drug control institutions 药检机构drug quality control 药品质量控制drug release 药物释放度drug standard 药品标准drying to constant weight 枯燥至恒重dual wavelength spectrophotometry 双波长分光光度法duplicate test 重复试验effective constituent 有效成分effective plate number 有效板数efficiency of column 柱效electron capture detector 电子捕获检测器electron impact ionization 电子轰击离子化electrophoresis 电泳electrospray interface 电喷雾接口electromigration injection 电迁移进样elimination 消除eluate 洗脱液elution 洗脱emission spectrochemical analysis 发射光谱分析enantiomer 对映体end absorption 末端吸收end point correction 终点校正endogenous substances 内源性物质enzyme immunoassay(EIA) 酶免疫分析enzyme drug 酶类药物enzyme induction 酶诱导enzyme inhibition 酶抑制eosin sodium 曙红钠〔指示剂〕epimer 差向异构体equilibrium constant 平衡常数equivalence point 等当点error in volumetric analysis 容量分析误差excitation spectrum 激发光谱exclusion chromatography 排阻色谱法expiration date 失效期external standard method 外标法extract 提取物extraction gravimetry 提取重量法extraction titration 提取容量法extrapolated method 外插法,外推法factor 系数,因数,因子feature 特征Fehling’s reaction 费林反响field disorption ionization 场解吸离子化field ionization 场致离子化filter 过滤,滤光片filtration 过滤fineness of the particles 颗粒细度flame ionization detector(FID) 火焰离子化检测器flame emission spectrum 火焰发射光谱flask 烧瓶flow cell 流通池flow injection analysis 流动注射分析flow rate 流速fluorescamine 荧胺fluorescence immunoassay(FIA) 荧光免疫分析fluorescence polarization immunoassay(FPIA) 荧光偏振免疫分析fluorescent agent 荧光剂fluorescence spectrophotometry 荧光分光光度法fluorescence detection 荧光检测器fluorimetyr 荧光分析法foreign odor 异臭foreign pigment 有色杂质formulary 处方集fraction 馏分freezing test 结冻试验funnel 漏斗fused peaks, overlapped peaks 重叠峰fused silica 熔融石英gas chromatography(GC) 气相色谱法gas-liquid chromatography(GLC) 气液色谱法gas purifier 气体净化器gel filtration chromatography 凝胶过滤色谱法gel permeation chromatography 凝胶渗透色谱法general identification test 一般鉴别试验general notices 〔药典〕凡例general requirements 〔药典〕通那么good clinical practices(GCP) 药品临床管理标准good laboratory practices(GLP) 药品实验室管理标准good manufacturing practices(GMP) 药品生产质量管理标准good supply practices(GSP) 药品供应管理标准gradient elution 梯度洗脱grating 光栅gravimetric method 重量法Gutzeit test 古蔡〔检砷〕法half peak width 半峰宽[halide] disk method, wafer method, pellet method 压片法head-space concentrating injector 顶空浓缩进样器heavy metal 重金属heat conductivity 热导率height equivalent to a theoretical plate 理论塔板高度height of an effective plate 有效塔板高度high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) 高效液相色谱法high-performance thin-layer chromatography (HPTLC) 高效薄层色谱法hydrate 水合物hydrolysis 水解hydrophilicity 亲水性hydrophobicity 疏水性hydroscopic 吸湿的hydroxyl value 羟值hyperchromic effect 浓色效应hypochromic effect 淡色效应identification 鉴别ignition to constant weight 灼烧至恒重immobile phase 固定相immunoassay 免疫测定impurity 杂质inactivation 失活index 索引indicator 指示剂indicator electrode 指示电极inhibitor 抑制剂injecting septum 进样隔膜胶垫injection valve 进样阀instrumental analysis 仪器分析insulin assay 胰岛素生物检定法integrator 积分仪intercept 截距interface 接口interference filter 干预滤光片intermediate 中间体internal standard substance 内标物质international unit(IU) 国际单位in vitro 体外in vivo 体内iodide 碘化物iodoform reaction 碘仿反响iodometry 碘量法ion-exchange cellulose 离子交换纤维素ion pair chromatography 离子对色谱ion suppression 离子抑制ionic strength 离子强度ion-pairing agent 离子对试剂ionization 电离,离子化ionization region 离子化区irreversible indicator 不可逆指示剂irreversible potential 不可逆电位isoabsorptive point 等吸收点isocratic elution 等溶剂组成洗脱isoelectric point 等电点isoosmotic solution 等渗溶液isotherm 等温线Karl Fischer titration 卡尔·费歇尔滴定kinematic viscosity 运动黏度Kjeldahl method for nitrogen 凯氏定氮法Kober reagent 科伯试剂Kovats retention index 科瓦茨保存指数labelled amount 标示量leading peak 前延峰least square method 最小二乘法leveling effect 均化效应licensed pharmacist 执业药师limit control 限量控制limit of detection(LOD) 检测限limit of quantitation(LOQ) 定量限limit test 〔杂质〕限度〔或限量〕试验limutus amebocyte lysate(LAL) 鲎试验linearity and range 线性及范围linearity scanning 线性扫描liquid chromatograph/mass spectrometer (LC/MS) 液质联用仪litmus paper 石蕊试纸loss on drying 枯燥失重low pressure gradient pump 低压梯度泵luminescence 发光lyophilization 冷冻枯燥main constituent 主成分make-up gas 尾吹气maltol reaction 麦牙酚试验Marquis test 马奎斯试验mass analyzer detector 质量分析检测器mass spectrometric analysis 质谱分析mass spectrum 质谱图mean deviation 平均偏差measuring flask, volumetric flask 量瓶measuring pipet(te) 刻度吸量管medicinal herb 草药melting point 熔点melting range 熔距metabolite 代谢物metastable ion 亚稳离子methyl orange 甲基橙methyl red 甲基红micellar chromatography 胶束色谱法micellar electrokinetic capillary chromatography(MECC, MEKC) 胶束电动毛细管色谱法micelle 胶束microanalysis 微量分析microcrystal 微晶microdialysis 微透析micropacked column 微型填充柱microsome 微粒体microsyringe 微量注射器migration time 迁移时间millipore filtration 微孔过滤minimum fill 最低装量mobile phase 流动相modifier 改性剂,调节剂molecular formula 分子式monitor 检测,监测monochromator 单色器monographs 正文mortar 研钵moving belt interface 传送带接口multidimensional detection 多维检测multiple linear regression 多元线性回归multivariate calibration 多元校正natural product 天然产物Nessler glasses(tube) 奈斯勒比色管Nessler’s reagent 碱性碘化汞钾试液neutralization 中和nitrogen content 总氮量nonaqueous acid-base titration 非水酸碱滴定nonprescription drug, over the counter drugs (OTC drugs) 非处方药nonproprietary name, generic name 非专有名nonspecific impurity 一般杂质non-volatile matter 不挥发物normal phase 正相normalization 归一化法notice 凡例nujol mull method 石蜡糊法octadecylsilane chemically bonded silica 十八烷基硅烷键合硅胶octylsilane 辛〔烷〕基硅烷odorless 无臭official name 法定名official specifications 法定标准official test 法定试验on-column detector 柱上检测器on-column injection 柱头进样on-line degasser 在线脱气设备on the dried basis 按枯燥品计opalescence 乳浊open tubular column 开管色谱柱optical activity 光学活性optical isomerism 旋光异构optical purity 光学纯度optimization function 优化函数organic volatile impurities 有机挥发性杂质orthogonal function spectrophotometry 正交函数分光光度法orthogonal test 正交试验orthophenanthroline 邻二氮菲outlier 可疑数据,逸出值overtones 倍频峰,泛频峰oxidation-reduction titration 氧化复原滴定oxygen flask combustion 氧瓶燃烧packed column 填充柱packing material 色谱柱填料palladium ion colorimetry 钯离子比色法parallel analysis 平行分析parent ion 母离子particulate matter 不溶性微粒partition coefficient 分配系数parts per million (ppm) 百万分之几pattern recognition 模式识别peak symmetry 峰不对称性peak valley 峰谷peak width at half height 半峰宽percent transmittance 透光百分率pH indicator absorbance ratio method? pH指示剂吸光度比值法pharmaceutical analysis 药物分析pharmacopeia 药典pharmacy 药学phenolphthalein 酚酞photodiode array detector(DAD) 光电二极管阵列检测器photometer 光度计pipeclay triangle 泥三角pipet(te) 吸移管,精密量取planar chromatography 平板色谱法plate storage rack 薄层板贮箱polarimeter 旋光计polarimetry 旋光测定法polarity 极性polyacrylamide gel 聚丙酰胺凝胶polydextran gel 葡聚糖凝胶polystyrene gel 聚苯乙烯凝胶polystyrene film 聚苯乙烯薄膜porous polymer beads 高分子多孔小球post-column derivatization 柱后衍生化potentiometer 电位计potentiometric titration 电位滴定法precipitation form 沉淀形式precision 精密度pre-column derivatization 柱前衍生化preparation 制剂prescription drug 处方药pretreatment 预处理primary standard 基准物质principal component analysis 主成分分析programmed temperature gas chromatography 程序升温气相色谱法prototype drug 原型药物provisions for new drug approval 新药审批方法purification 纯化purity 纯度pyrogen 热原pycnometric method 比重瓶法quality control(QC) 质量控制quality evaluation 质量评价quality standard 质量标准quantitative determination 定量测定quantitative analysis 定量分析quasi-molecular ion 准分子离子racemization 消旋化radioimmunoassay 放射免疫分析法random sampling 随机抽样rational use of drug 合理用药readily carbonizable substance 易炭化物reagent sprayer 试剂喷雾器recovery 回收率reference electrode 参比电极refractive index 折光指数related substance 有关物质relative density 相对密度relative intensity 相对强度repeatability 重复性replicate determination 平行测定reproducibility 重现性residual basic hydrolysis method 剩余碱水解法residual liquid junction potential 剩余液接电位residual titration 剩余滴定residue on ignition 炽灼残渣resolution 分辨率,别离度response time 响应时间retention 保存reversed phase chromatography 反相色谱法reverse osmosis 反渗透rider peak 驼峰rinse 清洗,淋洗robustness 可靠性,稳定性routine analysis 常规分析round 修约〔数字〕ruggedness 耐用性safety 平安性Sakaguchi test 坂口试验salt bridge 盐桥salting out 盐析sample applicator 点样器sample application 点样sample on-line pretreatment 试样在线预处理sampling 取样saponification value 皂化值saturated calomel electrode(SCE) 饱和甘汞电极selectivity 选择性separatory funnel 分液漏斗shoulder peak 肩峰signal to noise ratio 信噪比significant difference 显著性差异significant figure 有效数字significant level 显著性水平significant testing 显著性检验silanophilic interaction 亲硅羟基作用silica gel 硅胶silver chloride electrode 氯化银电极similarity 相似性simultaneous equations method 解线性方程组法size exclusion chromatography(SEC) 空间排阻色谱法sodium dodecylsulfate, SDS 十二烷基硫酸钠sodium hexanesulfonate 己烷磺酸钠sodium taurocholate 牛璜胆酸钠sodium tetraphenylborate 四苯硼钠sodium thiosulphate 硫代硫酸钠solid-phase extraction 固相萃取solubility 溶解度solvent front 溶剂前沿solvophobic interaction 疏溶剂作用specific absorbance 吸收系数specification 规格specificity 专属性specific rotation 比旋度specific weight 比重spiked 参加标准的split injection 分流进样splitless injection 无分流进样spray reagent 〔平板色谱中的〕显色剂spreader 铺板机stability 稳定性standard color solution 标准比色液standard deviation 标准差standardization 标定standard operating procedure(SOP) 标准操作规程standard substance 标准品stationary phase coating 固定相涂布starch indicator 淀粉指示剂statistical error 统计误差sterility test 无菌试验stirring bar 搅拌棒stock solution 储藏液stoichiometric point 化学计量点storage 贮藏stray light 杂散光substituent 取代基substrate 底物sulfate 硫酸盐sulphated ash 硫酸盐灰分supercritical fluid chromatography(SFC) 超临界流体色谱法support 载体〔担体〕suspension 悬浊液swelling degree 膨胀度symmetry factor 对称因子syringe pump 注射泵systematic error 系统误差system model 系统模型system suitability 系统适用性tablet 片剂tailing factor 拖尾因子tailing peak 拖尾峰tailing-suppressing reagent 扫尾剂test of hypothesis 假设检验test solution(TS) 试液tetrazolium colorimetry 四氮唑比色法therapeutic drug monitoring(TDM) 治疗药物监测thermal analysis 热分析法thermal conductivity detector 热导检测器thermocouple detector 热电偶检测器thermogravimetric analysis(TGA) 热重分析法thermospray interface 热喷雾接口The United States Pharmacopoeia(USP) 美国药典The Pharmacopoeia of Japan(JP) 日本药局方thin layer chromatography(TLC) 薄层色谱法thiochrome reaction 硫色素反响three-dimensional chromatogram 三维色谱图thymol 百里酚〔麝香草酚〕〔指示剂〕thymolphthalein 百里酚酞〔麝香草酚酞〕〔指示剂〕thymolsulfonphthalein ( thymol blue) 百里酚蓝〔麝香草酚蓝〕〔指示剂〕titer, titre 滴定度time-resolved fluoroimmunoassay 时间分辨荧光免疫法titrant 滴定剂titration error 滴定误差titrimetric analysis 滴定分析法tolerance 容许限toluene distillation method 甲苯蒸馏法toluidine blue 甲苯胺蓝〔指示剂〕total ash 总灰分total quality control(TQC) 全面质量控制traditional drugs 传统药traditional Chinese medicine 中药transfer pipet 移液管turbidance 混浊turbidimetric assay 浊度测定法turbidimetry 比浊法turbidity 浊度ultracentrifugation 超速离心ultrasonic mixer 超生混合器ultraviolet irradiation 紫外线照射undue toxicity 异常毒性uniform design 均匀设计uniformity of dosage units 含量均匀度uniformity of volume 装量均匀性〔装量差异〕uniformity of weight 重量均匀性〔片重差异〕validity 可靠性variance 方差versus …对…,…与…的关系曲线viscosity 粘度volatile oil determination apparatus 挥发油测定器volatilization 挥发法volumetric analysis 容量分析volumetric solution(VS) 滴定液vortex mixer 涡旋混合器watch glass 外表皿wave length 波长wave number 波数weighing bottle 称量瓶weighing form 称量形式weights 砝码well-closed container 密闭容器xylene cyanol blue FF 二甲苯蓝FF〔指示剂〕xylenol orange 二甲酚橙〔指示剂〕zigzag scanning 锯齿扫描zone electrophoresis 区带电泳zwitterions 两性离子zymolysis 酶解作用簡體書目錄Chapter 1 Introduction 緒論1.1 The nature of analytical chemistry 分析化學的性質1.2 The role of analytical chemistry 分析化學的作用1.3 The classification of analytical chemistry分析化學的分類1.4 The total analytical process分析全過程Terms to understand重點內容概述Chapter 2 Errors and Data Treatment in Quantitative Analysis 定量分析中的誤差及數據處理2.1 Fundamental terms of errors誤差的根本術語2.2 Types of errors in experimental data實驗數據中的誤差類型2.2.1 Systematic errors 系統誤差2.2.2 Random errors偶然誤差2.3 Evaluation of analytical data分析數據的評價2.3.1 Tests of significance顯著性檢驗2.3.2 Rejecting data可疑值取捨2.4 Significant figures有效數字ProblemsTerms to understand重點內容概述Chapter 3 Titrimetric Analysis滴定分析法3.1 General principles根本原理3.1.1 Relevant terms of titrimetric analysis滴定分析相關術語3.1.2 The preparation of standard solution and the expression of concentration 標準溶液的配製與濃度表示方法3.1.3 The types of titrimetric reactions滴定反應類型3.2 Acid-base titration酸鹼滴定3.2.1 Acid-base equilibria 酸鹼平衡3.2.2 Titration curves滴定曲線3.2.3 Acid-base indicators酸鹼指示劑3.2.4 Applications of acid-base titration酸鹼滴定的應用3.3 Complexometric titration配位滴定3.3.1 Metal-chelate complexes金屬螯合物3.3.2 EDTA 乙二胺四乙酸3.3.3 EDTA titration curves EDTA滴定曲線3.3.4 Metal Ion indicators金屬離子指示劑3.3.5 Applications of EDTA titration techniques EDTA滴定方法的應用3.4 Oxidation-reduction titration氧化還原滴定3.4.1 Redox reactions氧化還原反應3.4.2 Rate of redox reactions氧化還原反應的速率3.4.3 Titration curves滴定曲線3.4.4 Redox indicators氧化還原指示劑3.4.5 Applications of redox titrations氧化還原滴定的應用3.5 Precipitation titration沉澱滴定3.5.1 Precipitation reactions沉澱滴定反應3.5.2 Titration curves滴定曲線3.5.3 End-point detection終點檢測ProblemsTerms to understand重點內容概述Chapter 4 Potentiometry 電位分析法4.1 Introduction簡介4.1.1 Classes and characteristics分類及性質4.1.2 Definition定義4.2 Types of potentiometric electrodes電極種類4.2.1 Reference electrodes 參比電極4.2.2 Indicator electrodes指示電極4.2.3 Electrode response and selectivity電極響應及選擇性4.3 Potentiometric methods and application電位法及應用4.3.1 Direct potentiometric measurement 直接電位法4.3.2 Potentiometric titrations電位滴定4.3.3 Applications of potentiometry 電位法應用ProblemsTerlns to understand重點內容概述Chapter 5 Chromatography色譜法5.1 An introduction to chromatographic methods色譜法概述5.2 Fundamental theory of gas chromatography氣相色譜根本原理5.2.1 Plate theory塔板理論5.2.2 Kinetic theory(rate theory) 速率理論5.2.3 The resolution Rs as a measure of peak separation 分離度5.3 Gas chromatography 氣相色譜5.3.1 Components of a gas chromatograph 氣相色譜儀的組成5.3.2 Stationary phases for gas-liquid chromatography 氣液色譜固定相5.3.3 Applications of gas-liquid chromatography 氣液色譜的應用5.3.4 Adsorption chromatography 吸附色譜5.4 High performance liquid chromatography 高效液相色譜5.4.1 Instrumentation 儀器組成5.4.2 High-performance partition chromatography 高效分配色譜5.5 Miscellaneous separation methods 其他分離方法5.5.1 High-performance ion-exchange chromatography 高效離子交換色譜5.5.2 Capillary electrophoresis 毛細管電泳5.5.3 Planar chromatography 平板色譜ProblemsTerms to understand重點內容概述Chapter 6 Atomic Absorption Spectrometry原子吸收光譜分析法6.1 Introduction 概述6.2 Principles 原理.6.2.1 The process of AAS,resonance line and absorption line 原子吸收光譜法的過程,共振線及吸收線6.2.2 The number of ground atom and the temperature of flame 基態原子數與光焰溫度6.2.3 Quantitative analysis of AAS原子吸收光譜定量分析6.3 Instrumentation 儀器6.3.1 Primary radiation sources 光源6.3.2 Atomizer 原子儀器6.3.3 Optical dispersive systems 分光系統6.3.4 Detectors 檢測器6.3.5 Signal measurements 信號測量6.4 Quantitative measurements and interferences 定量測定及干擾6.4.1 Quantitative measurements 定量測定6.4.2 Interferences 干擾6.4.3 Sensitivity6.5 Applications of AAS原子吸收光譜法的應用ProblemsTerms to understand重點內容概述Chapter 7 Ultraviolet and Visible Spectrophotometry 紫外-可見分光光度法7.1 Introduction簡介7.2 Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectroscopy 紫外-可見吸收光譜7.2.1 Introduction for radiant energy 輻射能簡介7.2.2 Selective absorption of radiation and absorbance spectrum 物質對光的選擇性吸收和吸收光譜7.2.3 Absorbing species and electron transition 吸收物質與電子躍遷7.3 Law of absorption吸收定律7.3.1 Lambert-Beer's law朗伯-比爾定律7.3.2 Absorptivity吸光係數7.3.3 Apparent deviations from Beer's law對比爾定律的明顯偏離7.4 Instruments儀器7.5 General types of spectrophotometer分光光度計種類7.6 Application of UV-Vis absorption spectroscopy 紫外-可見吸收光譜的應用7.6.1 Application of absorption measurement to qualitative analysis 光吸收測定在定性分析上的應用7.6.2 Quantitative analysis by absorption measurements 光吸收測量定量分析法7.6.3 Derivative spectrophotometry 導數分光光度法ProblemsTerms to understand重點內容概述Chapter 8 Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy紅外吸收光譜8.1 Theory of infrared absorption紅外吸收根本原理8.1.1 Dipole changes during vibrations and rotations 振轉運動中的偶極距變化8.1.2 Mechanical model of stretching vibrations 伸縮振動機械模型8.1.3 Quantum treatment of vibrations 振動的量子力學處理、8.1.4 Types of molecular vibrations分子振動形式8.2 Infrared instrument components紅外儀器組成8.2.1 Wavelength selection波長選擇8.2.2 Sampling techniques 採樣技術8.2.3 Infrared spectrophotometers for qualitative analysis 定性分析用紅外分光光度計8.2.4 Other techniques其他技術8.3 The group frequencies of functional groups in organiccompounds 有機化合物官能團的特徵頻率8.4 The factors affecting group frequencies 影響基團特徵吸收頻率的因素8.4.1 Adjacent groups 鄰近基團的影響8.4.2 Hydrogen bonding 氫鍵8.5 Qualitative applications to structural analysis 結構分析的定性應用ProblemsTerms to understand重點內容概述Chapter 9 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 核磁共振波譜法9.1 Theory of nuclear magnetic resonance 核磁共振理論9.1.1 Quantum description of NMR NMR 的量子描述9.1.2 Classical description of NMR NMR 的經典描述9.2 Experimental methods of NMR spectroscopy NMR波譜的實驗方法9.3 The chemical shift of protons in organic compounds 有機化合物中質子的化學位移9.3.1 Souroe of the chemical shift化學位移產生原9.3.3 Environmental effects on the chemical shift of protonNMR spectra 影響NMR波譜中質子化學位移的環境因素9.4 Spin-Spin coupling 自旋-自旋耦合9.4.1 Source of Spin-Spin coupling and splitting 自旋-自旋耦合與裂分的產生原因9.4.2 Coupling constant耦合常數9.4.3 Rule8 governing the interpretation of spectra光譜解析規則9.5 Qualitative applications of proton NMR質子NMR波譜的定性應用.。


第九章重量分析法一、判断题(对的打√, 错的打×)1、沉淀的颗粒越大,溶解度越大。
( )2、AgCl和BaSO4的Ksp值差不多,所以这两类难溶化合物的沉淀类型相同。
( )3、均匀沉淀法可获得颗粒较大的沉淀,是因为在生成沉淀的过程中有效地降低了溶液的相对过饱和度。
( )4、加入适当过量的沉淀剂可降低沉淀的溶解度,但如果沉淀剂过量太多,反而会引起盐效应和络合效应而增加沉淀的溶解度。
( )二、选择题1.重量分析对沉淀形式的要求有哪些( )A、溶解度要小B、要纯净C、相对分子质量摩尔质量要大D、要便于过滤和洗涤E、易于转化为称量形式2.以SO42-作为Ba2+的沉淀剂,其过量应为A、10 %B、10 % ~20 %C、20 % ~ 50 %D、50 % ~ 100 %E、100 % ~200 %3.Ag2CO3的K SP=8.1×10-12,若不考虑CO32-的水解,则Ag2CO3在纯水中的溶解度为A、1.3×10-4 mol·L-1B、3.0×10-4 mol·L-1C、2.0×10-4mol·L -1D、5.2×10-4 mol·L-1E、2.6×10-4 mol·L-14.Sr3(PO4)2的s=1.0×10-8mol/L,则其K SP值为A.1.0×10-30 B.5.0×10-30 C.1.1×10-38 D.1.0×10-125.在一定酸度和一定C2O42-浓度的溶液中,CaC2O4的溶解度为A、S=K SP/C(C2O42-)B、s=C、s= K SP×α C2O4(H) /C(C2O42-)·D、S=6.已知Mg(OH)2的K SP=1.8×10-11,则Mg(OH)2饱和溶液中的pH是A、3.59B、10.43C、4.5;D、9.417.AgCl在HCl溶液中的溶解度,随HCl的浓度增大时,先是减小然后又逐渐增大,最后超过其在纯水中的饱和溶解度。



第9章 重量分析法9.1单项选择题(共25题)9.1.1 用重量法测定氯化物中氯的百分含量,欲使10.0mg AgCl 沉淀相当于1.00%的氯,应称取试样重(g )( ) (Ar (Cl )=35.5 , Mr (AgCl )=143.3)A 、0.1237B 、0.2477C 、0.3711D 、0.4948 9.1.2 用分度值为0.1g 的台秤称取约20g 的物品,最做可记录( )位有效数字。
如用来测定土壤水分,要求称量的相对误差不大于2%,至少应称取土壤试样( )g 。
A 、3—10B 、3—8C 、5—10D 、5—89.1.3 在一定酸度和一定浓度C 2O 42-存在下,CaC 2O 4的溶解度计算公式为( ) A 、224SPC O K S C -=B、S = C 、222424sp C O C O K S C δ--=• D、S =9.1.4 在沉淀反应中,下列说法错误的是( )A 、酸效应会使沉淀的溶解度增大B 、盐效应会使沉淀的溶解度增大C 、络合效应会使沉淀的溶解度增大D 、同离子效应效应会使沉淀的溶解度增大 9.1.5 用沉淀的方法能有效地提高沉淀纯度的是( )A 、混晶共沉淀B 、吸附共沉淀C 、保藏共沉淀D 、后沉淀 9.1.6 利用BaSO 4沉淀的生成重量分析法测定硫的含量,以HCl 调节酸度,优先进入沉淀吸附层的离子是( )A 、SO 42-B 、Cl -C 、H +D 、Ba 2+9.1.7 用重量法测定试样中钙含量时,钙沉淀为草酸钙,高温(1100℃)灼烧后称量,则钙的换算因数为( )A 、24Ca CaC O M F M =B 、3CaCaCO M F M = C 、Ca CaOM F M = D 、24CaC O Ca M F M =9.1.8 PbSO 4沉淀随H 2SO 4浓度增加,溶解度增加的是( )A 、催化反应B 、自动催化反应C 、副反应D 、诱导反应 9.1.9 据BaSO 4测定S ,其换算因数为( ) A 、4BaSOSM F M α=B 、4BaSO SM F M =C 、4S BaSO M F M =D 、4SBaSO M F M α= 9.1.10 利用电解原理,将待测金属在电极上析出,据电解板电解前后重量来测算其含量的方法为( )A 、极谱法B 、络合滴定法C 、重量法D 、沉淀滴定法 9.1.11用重量分析法测Ca 含量,经沉淀加热至550℃时CaCO 3,干燥冷却后称量,则CaCO 3称为( )A 、称量形式B 、沉淀形式C 、被测组分D 、试样 9.1.12 在沉淀重量法中,向溶液中加入一定量的电解质而使沉淀溶解度增加的现象称为( )A 、同离子效应B 、盐效应C 、酸效应D 、络合效应 9.1.13 用沉淀重量法测试样中Ag 含量时往溶液中多加一些沉淀剂HCl ,其目的是( )A 、增大沉淀AgCl 的溶解度B 、减小沉淀AgCl 的溶解度C 、纯化AgCl 沉淀D 、增大溶液酸度9.1.14 在沉淀重量法中,常向溶液中加入大量乙醇、丙酮等有机溶剂,其目的是( )A 、增大溶解度B 、减小溶解度C 、增大溶液极性D 、减小溶液极性9.1.15相对过饱和液(Ca-S)/S增大,易形成()沉淀。

分析化学(第五版)上册武汉大学主编第一章概论第二章分析试样的采集与制备第三章分析化学中的误差与数据处理第四章分析化学中的质量保证与质量控制第五章酸碱滴定第六章络合滴定第七章氧化还原滴定第八章沉淀滴定法与滴定分析小结第九章重量分析法第十章吸光光度法第十一章分析化学中常用的分离与富集方法第一章概论1、答:定义:分析化学是发展和应用各种理论、方法、仪器和策略以获取相关物质在相对时空内的组成和性质的信息的一门科学。
任务:定性、定量、结构。
作用:略2、答:略3、答:取样→分解→测定→计算及评价注:取样的原则:应取具有高度代表性的样品;分解的原则:①防止式样损失;②防止引入干扰。
4、答:Na2B4O7·10H2O的摩尔质量比Na2CO3的大,故选择硼砂作为标定盐酸的基准物质可以使称量误差减小,但是硼砂含10个结晶水不稳定,而碳酸钠摩尔质量小,性质稳定。
6、答:a.偏低b.偏低c.偏低d.无影响e.偏大f.偏小g.偏大h.可能偏大也可能偏小7、答:偏低NaOH O H O C H OH O C H NaOH V M m C 1210002422242222⨯⨯=••因为失水后的H 2C 2O 4中含有比同样质量H 2C 2O 4·2H 2O 更多的能与NaOH 作用的H +,这样测定时消耗V NaOH 增大,所以C NaOH 偏小。
8、答:偏高第二章 分析试样的采集与制备(略)1、答:不对。
应将原始试样全部送交分析部门,再由分析人员对原始试样采用四分法进行缩分,依据经验公式取样,再分解、测定等。
2、答:分解无机试样和有机试样的主要区别在于:无机试样的分解时将待测物转化为离子,而有机试样的分解主要是破坏有机物,将其中的卤素,硫,磷及金属元素等元素转化为离子。
3、答:用NaOH 溶解试样,Fe ,Ni ,Mg 形成氢氧化物沉淀,与Zn 基体分离。
4、答:测硅酸盐中SiO 2的含量时采用碱熔法,用KOH 熔融,是硅酸盐中的硅转化为可溶性的K 2SiO 3,再用容量法测定:测定硅酸盐中Fe ,Al ,Ca ,Mg ,Ti 的含量时,用HF 酸溶解试样,使Si 以SiF 4的形式溢出,再测试液中Fe ,Al ,Ca ,Mg ,Ti 的含量。

第九章 重量分析法思考题与习题1. 沉淀重量法中,对沉淀形式和称量形式的要求?答:①对沉淀形式的要求:溶解度小;易过滤、洗涤;纯度高;易转化为称量形式。
②对称量形式的要求:有确定的化学组成;稳定,不受空气中水分、CO 2和O 2等的影响;称量形式的摩尔质量要大。
2. 简述获得晶形沉淀和无定形沉淀的主要条件。
答:①晶形沉淀的条件:“稀、热、慢、搅、陈”。
②无定形沉淀的条件:“浓、热、快、稀、再’。
3. 为了使沉淀完全,必须加入过量沉淀剂,为什么不能过量太多?答:在沉淀法中,由于沉淀剂通常是强电解质,所以在利用同离子效应保证沉淀完全的同时,还应考虑盐效应的影响,盐效应使沉淀溶解度增大。
有时还应考虑酸效应、配位效应等的影响。
4. 影响沉淀纯度的因素有哪些?简述提高沉淀纯度的措施。
答:影响沉淀纯度的因素主要有两个:共沉淀和后沉淀。
共沉淀包括:表面吸附、混晶、吸留与包藏。
提高沉淀纯度的措施有:选择合理的分析步骤 、降低易被吸附杂质离子的浓度、选择合适的沉淀剂、选择合理的沉淀条件、必要时进行再沉淀等。
5. 计算下列换算因数称量形式 被测组分(1) Al 2O 3 Al(2) BaSO 4 (NH 4)2Fe(SO 4)2·6H 2O(3) Fe 2O 3 Fe 3O 4(4) BaSO 4 K 2SO 4 ·Al 2 (SO 4)3·24H 2O(5) Mg 2P 2O 7 MgO(6) PbCrO 4 Cr 2O 3解:(1) (2) (3) (4) 23AlAl O 2M M ()()444222BaSO NH Fe SO 6H O 2M M 3423Fe O Fe O 2M M ()4242423BaSO K SO Al SO 24H O 4M M(5) (6) 6. 称取0.7089g 不纯的KCl 试样,以过量的AgNO 3处理,得到1.3028gAgCl ,求该试样中KCl 的百分含量。