11规则值班机工英语听力与会话 朗读
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:5.56 MB
- 文档页数:6


Unit 1 Familiarisation on boardI W arming-updeck, bridge, galley, hospital, cabin, office, corridorII Reading Aloud1.What is the captain doing?----He is making an announcement to the passengers.2.How should the passengers do in case of emergency?----They should obey the orders given on the public address system.3. Can you memorise all the spaces that safety regulations do not permit passengers to enter?----Y es, I can. Such as navigating bridge, engine room, maneuvering areas, cargo rooms and compartments, service rooms, all areas and spaces marked “crew only”, all closed ,sealed or roped off areas, spaces and rooms and car decks.IV SpeakingPart A Read and LearnFine, like my new job, vessel, Chief Officer, a list of jobs, play chess, read a book, another cadet, listen to musicGet up, 0700, breakfast, 0730, bridge, take over the watch from the Chief, 0750, drink coffee, 1030, hand over to the 2nd Officer, noon, lunch, 1215,listen to music, 1300, sleep, 1400, everything, finePart BPrompt card 11. What’s your date of birth?----My date of birth is August 1st, 1992.2. What’s your seaman’s book number?----My seaman’s book number is L 396767.3.How many members are there in your family?What are their occupations (What do they do?)----3.They are my father, my mother and I. (They are my wife, my son/daughter and I.)----My father and my mother are farmers/ workers. My wife is a teacher. I am a seaman.4. What’s your daily work?----There are many works, such as keep the watch, check the equipment on the bridge, take charge of the life-saving and fire-fighting equipment and so on.5. What are your spare time activities?----Play basketball, play chess, listen to the music and so on.Prompt card21.What’s your favorite port you have ever called at?----My favorite port is Dalian/I like Dalian best.2.What’s your favorite TV program?----My favorite TV program is CCTV-news.3.What’s your favorite website?----My favorite website is / .4.What’s your favorite sport?----My favorite sport is playing basketball.5.What’s your favorite food?----My favorite food is bread/rice/meat.Part C Presentationfive decks, engine room below first deck, first deck, laundry, galley, storeroom, second deck, hospital, ratings’messroom, office, third deck, pilot’s cabin, Chief Officer’s cabin, officer’s messroom, fouth deck, radio room,master’s cabin, Chief Engineer’s cabinUnit 2 Ship OrdersI W arming-up1.Can you list some ship orders?----Y es, I can. Such as the wheel orders, engine orders, anchoring orders, mooring orders and so on.2.What should you do when you are given a specific ship’s order?----Firstly, repeat the order. Secondly, carry out the order correctly. Thirdly, report.3. Describe briefly the following pictures in relation to ship’s various orders.----In the first picture we can see an officer giving the wheel order; the second picture shows the telegraph order; The third picture is the anchor order and the fourth is the mooring order.II Reading Aloud1.What is the main idea of this short passage?----How to respond and carry out the wheel orders correctly.2.What should be the helmsman do if the vessel does not answer the wheel?----He should report immediately.IV SpeakingPart A Listening—Based Speaking TasksTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.What is this dialogue about?----It is about anchoring operation.2.What did the captain ask the chief officer to do in the beginning of thedialogue?----Go with the bosun to the forward station and standby the port anchor for letting go.3.How is the cable leading in the end of the dialogue?----Ten o’clock.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----The procedures of anchoring are as following:1) Standby the port anchor for letting go.2) Walk back the anchor to just above the water and hold it on the brake.3) Use engine.4) Take the sounding.5) Let go port anchor.6) Lead the cable to ten o’clock, medium weight.7) Five shackles in the water.8) Bring it up.9) Hoist anchor signal.Task 3:Suppose you were the captain or chief mate, retell the dialogue in the form of a monologue.同上Part B W ork-place Communication TaskPrompt card 1----Midships.----Midships. Wheel’s amidships.(Wheel’s port five. Wheel’s port twenty. Wheel hard- a-port. Course steady. Engine full ahead. Engine half ahead. Engine slow ahead. Port engine dead slow ahead. Engines stopped. Engine standby.)Prompt card2同上Part C Topic Presentation TasksTask1: Ship’s ordersA.the basic ship’s ordersmon ship’s orders in each categoryC.caution in executing the ordersThere are four kinds of ship’s orders, such as wheel orders, engine orders, anchoring orders, mooring orders.Wheel orders involve Midships, Port five, Steady and so on. Engine orders involve Full ahead, Stop engines, Standby engine and so on. Anchoring orders involve Standby port anchor for letting go, Let go port anchor, How is the cable leading and so on. Mooring orders involve Heave on headline, Stop heaving, Let go headline and so on.Please note: All these ship’s orders should be repeated, carried out and reported correctly and immediately.Task 2:Ship’s Anchoring Operation6.responsibilities of the crew involved7.basic anchoring orders and meaningsC any other relevant information pertaining to anchoringIn anchoring operation the captain gives the orders. The chief officer and carpenter carry out the orders on the spot and report accordingly.There are many anchoring orders, for example, Stand by port/starboard/both anchors for letting go. It means stand by relevant anchors for letting go. Let go port/starboard/both anchors. It means “Drop the relevant anchors accordingly.” Stand by for heaving up. It means “Get ready to pick up the anchor.”The length of the anchor cable should be five to seven times the depth of water. The operators should hoist the anchor signals according to the COLREG.Task3:Ship’s Mooring and Unmooring OperationA.responsibilities of the crew involvedB.basic mooring and unmooring ordersC.safety and other relevant information relating to mooring and unmooringoperationThe captain gives the order. The chief officer and the second officer carry out the orders and report accordingly.There are many mooring and unmooring orders, for example, Send out the headlines; Make fast fore and aft ; Stop heaving; and so on.The operators should check the lines regularly and ensure that they are in good condition. The crew members should put on the gloves, helmet, safety shoes and so on.Unit 3 PilotageI W arming-up1. Can you describe the details of the construction of Pilot Ladder according to the following diagram?----The pilot ladder consists of 3 parts: steps, spreaders, side ropes. The length of each step is 48cms and its thickness is 11.5cms. The space between the steps is 30-38cms. The minimum length of the spreader is 180cms.The diameter of the side rope is 18mms. The pilot ladder is always used with a manrope. The diameter of the manropeis 28mms.2. What equipment should be ready when pilot is boarding?----The pilot ladder and manropes.II Reading Aloud1. What is the main idea of the passage?----It is about the preparations of entering a port and receving the pilot.2. What should you prepare when your vessel is ready to receive pilot?----The pilot ladder, manropes, boat rope, heaving line and lights.IV SpeakingPart A Listening—Based Speaking TasksDialogue 1 Entering Port (1)Task 1: Listen carefully and answer the following questions:1.How has the pilot ladder been rigged?----It has been rigged on the starboard side, one meter above the waterline.2.What time will the pilot arrive?----The pilot will arrive at 0920.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----This is a dialogue between Pilot Station and officers on ship. They were speaking on Channel 06. The pilot would be on station 0920 and ask the vessel to rig the pilot ladder on starboard side, one meter above the waterline.Dialogue 2 Entering Port (2)Task 1: Listen carefully and answer the following questions:1.What did the captain tell the pilot?----He told the pilot the engine speed and ship’s course..2.What did the pilot hope?----The pilot hoped the fishing boats wouldn’t cross the route.3.What berthing information will the Third Mate inform the Chief Mate of?----Bring the ship to berth on starboard side and prepare the flags.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with yourpartner either in pair or group work.----This is a dialogue between pilot and captain. The vessel was entering port under pilot’s order.There were many fishing boats around. The pilot asked the vessel to hoist flags and berth on the starboard alongside.Dialogue 3 Station on the Bridge for Leaving PortTask 1: Listen carefully and answer the following questions:1.Why should the anchor be prepared according to the pilot’s order?----Because it can be dropped to slacken the speed in case of emergency.2.Please describe the details of unmooring operation according to the dialogue. ----First, fore and aft, single up with the head line and stern line. Then, let go all lines. Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----The captain asked officers to single up with headline and stern line under pilot’s order. The officers carried out the orders given and stood by starboard anchor in case of emergency.Part B W ork-place Communication Task1.----What is your ship’s name, call sign, type, flag, gross tonnage and LOA?----My ship’s name is Dahlia, call sign VRCP7, type container ship, flag Hongkong, gross tonnage 28927 tons and LOA 220ms.2.----Which VHF Channel do you work on?----CH 12.3.----What is your ETA at Singapore Pilot Station?----24/05/2011 1230 LT.4.----What is your draught fore and aft?----My draft is 11.5m forward 12.0m aft.5.----What is your last port and next port of call?----Hong Kong, Jeddah.6.----How is the pilot ladder rigged?----It is rigged on starboard side, 2 meters above water.7.----Which side will the pilot boat get alongside?----Port side.Part C Topic Presentation TasksTask1: Describe the procedures of pilotage.A.the general procedures for pilot requestB.the preparations for receiving the pilotC.the general rules for pilotageBefore arrival at a port, contact the pilot station directly or through your agent in advance, making sure about the embarking time and embarkation place of the pilot.prepare the pilot ladder or gangway and take some safety measures. Get the throwing line and life buoy ready and put them beside the pilot ladder, andensure to have sufficient lights at nightWhen the pilot arrives at the boarding place, you will make a lee side for the pilot boat. The duty officer should wait for receiving the pilot on board. The captain should tell the ship’s particulars to the pilot.Task 2:Describe the proper way of using VHFA How to operate VHF set properB general rules of using VHFC rules of using VHF Channel 16First you will pick up the receiver and set the calling channel, and then press the button on the receiver handle and speak. If the channel is not chosen when VHF is turned on, it will automatically turn to channel 16. VHF should be used correctly and properly, and according to the Radio Regulations the following should be avoided:1)Non-essential transmissions.2)Transmitting without correct identification.3)Use of offensive language etc.Y ou must remember that Channel 16 is publicly used for calling by all the relative parties. If there is an emergency, all other uses of channel 16 must stop. Before calling on channel 16 you should make a careful check that no Mayday emergency exists.In short, VHF procedure at sea always be conducted as follows:1) keep a listeningwatch at all times on channel 16; 2) Use a dual-watch facility to listen on any other required channel. 3) Use channel 16 to establish contact only and as soon as the contact is established, turn to another channel as requested at once.Unit 4 Berthing and UnberthingI W arming-upCan you tell your partner about all the lines shown below?And write down in full the orders that match with the diagrams A-D.----Y es,I can. They are headlines, fore to aft spring, breast line, aft to fore spring and stern lines.A. single up fore and aftB. Let go forward.C. Single up aft to stern line.D. Let go all lines.II Reading Aloud1. What is the main idea of the passage?----It is about the importance of proper use of VHF channels and limitation factors in determining range.2. What can cause the transmission and receiving range of VHF signals greater? ----High pressure and increased humidity.IV SpeakingPart A Listening—Based Speaking TasksDialogue 1 Talking in the VHF Radio before Entering PortTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.Why did MV. Shinzan Maru reduce her speed?---Due to traffic.2.How long will it take to enter the Uraga Traffic Route entrance at the speedof 10 knots?----Two hours.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with yourpartner either in pair or group work.----The vessel reduces her speed from 12 knots to 10 knots because she will arrive earlier than her ETA. An hour later, the vessel calls Tokyo MARTIS on VHF , her present position is 10 miles from No.1 buoy, her ETA is 0930.Dialogue 2 Preparing the Mooring LinesTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.Who was responsible for operating winches?----Sailor Ramos.2.Who was directing the operation of preparing the mooring lines?----Bosun.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----Bosun was directing the operation of preparing the mooring lines. Sailor Ramos was standing by the winch. The rest of the sailors, Avarro and Perez were manning the ropes.Dialogue 3 Station on the Bridge for Leaving PortTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.What did the pilot want to check on the bridge?----The engine.2.What should the officer on watch pay attention to before testing engine in harbour?----The gangway should be clear.3.What details should be included in the pilot card?----Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----The officers on the bridge tested the engine for leaving port. The pilot came to the bridge to show how to unmoor and unberth.Part B W ork-place Communication TaskChief:Which side is alongside?Captain:Port side.Chief:Which is the first line to be made fast?Captain:Spring.Chief:Where will the tug be made fast?Captain:Starboard bow.Chief:Is the ship positioned?Captain:No,please shift 5 meters forward.Chief:Heave/Slack away forward line?Captain: Heave/Slack.Part C Topic Presentation TasksTask1: Describe the responsibilities as a watch officer while the ship is at anchor.A.Regular operations for anchor watch.B.Emergency handling in case of draggingC.conclusionAs regular operations , someone is arranged on anchor watch.At night the watchman will check up on the anchoring situation every hour,and we post someone on anchor watch in bad weather.the watchman will conduct the duties as followHave visual inspections to see if the vessel is dragging.If dragging occur immediate action the following:1) Turn on the GPS, VHF channel 16 ,the electronic depth sounder, wind instruments, boat speed indicator, the radar and take EBL and Range on two landmarks and write them down2) Get some fenders ready for use and check up on the ground tackle. Stand by engine and steer out of the anchorage if necessary.In general, keep a sharp lookout for other vessels’ positions in the vicinity of our vessel; and keep an eye on the depth, wind speed and direction as well as speed indicators. If any dragging situations occur, alert everyone on board the vessel andtake immediate action efficiently.Task 2:Describe the proper way of using VHFA. How to operate VHF set properB. general rules of using VHFC. rules of using VHF Channel 16(重题)Task3: Describe the procedures before arrival at a port.A. the preparations from the bridge.B. the preparations from the engine roomC. the preparations from the deckBefore arrival at a port, the captain should inform every department to do the preparatory work for entering port, such as arranging relative persons to check and test the navigation equipment, emergency equipment, anchor and steering gear etc. Autopilot should be changed to manual pilot, and a listening watch should kept on VHF channel 16.For the engine room, everything must also be well prepared for standing by engine.The deck crew members should stand by anchor and get heaving line and mooring lines ready for berthing, and also get ready for the pilot ladder and life buoy for th e pilot’s safe embarkation. Meanwhile hoist the flags and signals as required.Unit 5 Loading and UnloadingI W arming-upII Reading Aloud1.What equipment is used to load and discharge cargo?----Cranes on the quay or the ship’s derricks.2.Can you draw a sketch according to the passage?----Y es, I can.The main structure of the ship is the hull, within the hull are the tween decks or platform. The derricks are fitted to masts. The front part of a ship is calledthe bow and the rear part is called the stern. The engine is fitted near the bottom of the ship. The right side of a ship facing the bow is called the starboard side and the other side is the port side.IV SpeakingPart A Listening—Based Speaking TasksDialogue 1 Talk with the Foreman on DeckTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.What’s the matter with the No.6 hold as the foreman said?----Seawater is leaking from the topside tank in Hold No.6.2.How does the third mate go down into the hold?----He will use aft spiral ladder to go down inside.3.What damage happened to the hold?----The bottom part of the spiral ladder is broken.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----Foreman told the third officer that seawater was leaking from the topside in Hold No.6. It didn’t seem to be leaking very much. The third officer would use aft spiral ladder to go down inside. He found the bottom part of the spiral ladder was broken. Dialogue 2Complaining to the Driver of the Cargo LoaderTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.What is the matter with the ship?----The ship is listing to starboard side.2.How would the driver deal with the matter?----He will load on the port side..3.What would the third officer do if he finds the driver does not do a good job?----He will have the Chief Officer file a complaint.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----The ship was listing to starboard because No.3 hatch was overloaded by the driver. So the third officer asked the foreman to warn the driver. The driver would load on theport side. Otherwise, the third officer would have the Chief officer file a complaint. Dialogue 3 Lashing down the cargo on a Container shipTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.What ‘s the matter in Bay No.3?----The lashing bars in Bay No.3 were loose.2.Why didn’t the worker want to do the job?----Because he didn’t think it was his job.3.What would the worker do?----He would tighten up the lashing bars.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.---- The lashing bars in Bay No.3 were loose.The third officer asked the worker to tighten them up, but he didn’t think it was his job.After disputing, the worker had to do it according to third officer’s order.Part B W ork-place Communication TaskDuty officer:What is this reefer container location?Foreman:It is 220282.Duty officer:Is reefer motor aft or forward/Foreman:Aft.Duty officer:How about lashing condition?Foreman:Some lashing bars are loosened. Some twistlocks are unlocked.Unit 6 NavigationI W arming-up3 13 1 114 15 8 7 12 9 16 5 14 6 2 10II Reading Aloud4)What is the main idea of this passage?----The officer orders the helmsman to turn the wheel and the helmsman should repeat all orders given to him.Then,the helmsman should report the course and counter the swing of the ship.2.What should the helmsman do when he completed his turn at the wheel?----He should state clearly the course to be steered to the relieving helmsman and repeats the course to the officer of the watch when reporting that he has been relieved.3.what can cause the ship heading to change when the ship is on voyage?----The wind and waves, as well as the action of the propeller, tend to cause the ship heading to change.IV SpeakingPart A Listening—Based Speaking TasksDialogue 1 Navigation in a Narrow ChannelTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:8.Why did the ship reduce her speed?----Because she was getting closer to the ship ahead.9.What should the Master expect from the OOW on arriving at the bridge?----the course and speed of the ship ahead.10.What is the original course and speed?----The course is 236 degrees, the speed is 12 knots.Task 2: Listen again, note down the main idea and then role play with your partner either in pair or group work.----Our ship reduced speed because the ship ahead reduced hers and we are getting closer.The driftwood was found by port bow.The boat safely passed it according to the captain’s wheel orders.Dialogue 2Bad visibilityTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.What condition is it around the ship?----In poor visibility there is a vessel ahead off our starboard bow with the same speed as us.2.Why is it important to sound fog signals?----Give warning of her position.Task 2: Listen again and discuss with your partner the following topics:3.When should an OOW notify the master immediately to the bridge? Pleaselist some.----Bad visibility, other ships in the vicinity, a ship approaching and so on.4.What action should be taken by OOW in poor visibility?----Reduce speed, Sound fog signals, Watching the radar and so on.Dialogue 3 An engine problemTask 1: Listen to the dialogue and answer the questions below:1.What problem has happened in the engine room?----The main engine has a slight problem.2.Why did the master come up to the bridge?----He directed the third officer to stop engine to repair the fuel valves.Task 2: Listen again and discuss with your partner the following topics:1.What signals should be displayed in day time and in night time when your ship is not under command?---- Two black balls in day time,two red lights in night time.Part B W ork-place Communication TaskA.We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that we deviate from steering course: we went aground.B. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that present tide height is below prediction: we went aground.C. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that the depth indicated in the chart were by no means to be trusted: we went aground.D. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that the chart we used is obsolete: we went aground.E. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that we are running into shoals: we went aground.F. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that we misread the echo-sounder data: we went aground.G. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that the draught of our vessel is too deep: we went aground.H. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that the echo-sounderis not functioning: we went aground.I. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that we are lack of local knowledge: we went aground.J. We had been warned about these waters and soon found out that sea state,swell and wind are too strong: we went aground.Part C Topic Presentation tasksTask 1: Describe the duties of watch-keeping when underway.A General rules as to watch-keepingB Items to be checked and monitored each watch.C Special attention for bridge watch-keepingThe officer in charge of the navigational watch shall:1) keep the watch on the bridge2)in no circumstances leave the bridge until properly relieved3) continue to be responsible for the safe navigation of the ship, despite the presence of the master on the bridge, until informed specifically that the master has assumed that responsibility and this is mutually understood; and4) notify the master when in any doubt as to what action to take in the interest of safety.During the watch the course steered, position and speed shall be checked at sufficiently frequent intervals, using any available navigational aids necessary, to ensure that the ship follows the planed course.The officer in charge of navigational watch shall have full knowledge of the safety and navigational equipment on board and make effective use of them. A proper lookout and security watch shall be kept and a record shall be maintained.Task 2: Describe the bridge shift change.A The conditions which must be satisfied before taking over a bridge watch.B The procedures for shift change.C Special attention for shift change.The officer in charge of the bridge watch shall not hand over the watch to the relieving officer if there is reason to believe that the latter is not capable of carrying out the watch-keeping duties effectively, in which case the master shall be notified.The relieving officer shall ensure that the members of the relieving watch are fully capable of performing their duties, particularly as regards their adjustment to night vision. Reliving officers shall not take over the watch until their vision is fully adjusted to the light condition.Prior to taking over the watch relieving officers shall satisfy themselves as to the ship’s estimated or true position and confirm its intended track, course and speed, and UMS controls as appropriate and shall note any dangers to navigation expected to be encountered during their watch.If at any time the officer in charge of bridge watch is to be relieved when a manoeuvre or other action to avoid any hazard is taking place, the relief of that officer shall be deferred until such action has been completed.Task 3: Describe the differences between navigating in a narrow channel and in a traffic separation scheme.A The rules in navigating in a narrow channel.B The rules in navigating in a traffic separation scheme.C The major differences in terms of technical navigationa.) A vessel proceeding along the course of a narrow channel shall keep as near to the outer limit of the channel which lies on her starboard side as is safe and practicable.b.) A vessel using a traffic separation scheme shall proceed in the appropriate traffic lane in the general direction of traffic flow for that lane and so far as practicable keep clear of a traffic separation line or separation zone.c.) Navigating in narrow channel requires great skill. Since it might be crowded with heavy traffic, a sharp look-out shall always be kept. Before entering the narrow channel, duty officer shall familiarize themselves by consulting relevant sailing directions and other nautical publications.。



值班机工英语听力与会话Lesson 1 Daily English:1.What is your name?My name is _______.2.How old are you?I am XXX.3.What is your marital status?I am XXX.4.How many people are there in your family? There are four people in my family.5.How long have you worked on board?I have worked on board for two years.6.How many countries have you ever been to?I have been to two countries.7.Do you like your job?Yes。
I like my job.8.What is your favorite color?XXX blue.9.Which season do you like best?I like spring the best.10.What kind of music do you like?I like pop music.Lesson 2 XXX:1.How many departments are there on board? There are two XXX.2.What is the difference een port and starboard?Port is the left side of the ship and starboard is the right side.3.What is the meaning of bow?Bow is the front part of the ship.4.What is the meaning of stern?XXX is the back part of the ship.5.What is the meaning of deck?Deck is the floor of the ship.The n of clarifier is to remove solid impurities from oil。

11规则轮机员任评估大纲之轮机英语听力与会话《轮机英语听力与会话》一、编写目的1.实现STCW公约马尼拉修正案的履约工作;全面考核船员英语交流能力是否达到适任其职务的要求,包括英语听力理解能力,口语表述能力以及需要掌握的英语词汇量的要求。
2.更新大纲内容,切实提高船员英语交流能力,适应航运发展需求。
二、编写原则1.依据公约要求确定考核体系结构,预防应试教育,实现教考分离;2.紧密联系船员实际工作中英语交流需要,重视英语交流能力。
3.以现行大纲为基础,充分考虑履行《STCW 公约》2010马尼拉修正案的要求以及不同职务船员,即轮机长,大管轮和二、三管轮,在实际工作中履行其职责时在英语听力理解,口语表达方面的英语交流能力适任需求4.划分考核知识点细目,以指导命题。
三、基本要求听力与会话评估要求:听力理解能力:能够听懂并理解《STCW 公约》对无限航区的各级别海员职务要求的船舶内部日常生活和及听懂通过VHF和其他无线电和电子通信设备所进行的业务英语交流内容,包括机舱日常业务,应急情况下用语,安全和保安等行为过程中的英语口语交际内容。
能够听懂语速为每分钟100-150词的口语交流内容,掌握中心大意,理解其中的重要事实,细节和关键性信息点。
口语表述能力:能够进行《STCW 公约》对无限航区的各级别海员职务要求的有效的面对面的口语沟通,包括日常生活交流,船上业务工作交流,以及安全和保安等场景中的英语口语交流内容。
能够掌握并使用与机舱作业相关的《标准航海通信用语》(SMCP),发音基本准确,语言基本流畅,表意基本完整。
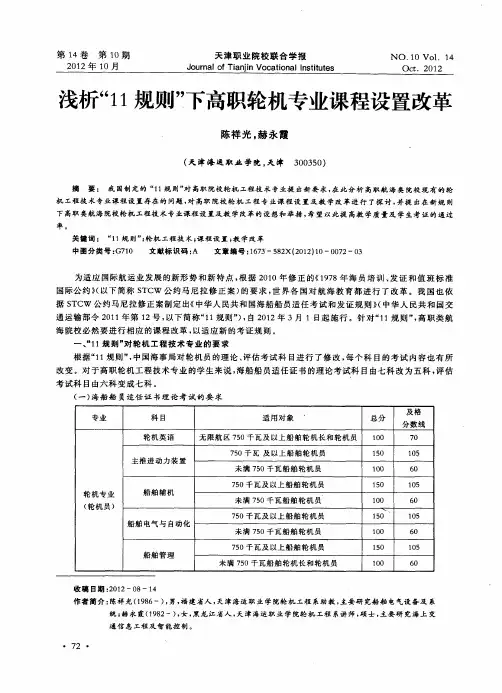
轮机英语听力与会话评估纲要适用对象891 892 893无限航区750KW及以上船舶轮机长无限航区750KW及以上船舶大管轮无限航区750KW及以上船舶二/三管轮1公共用语1.1 日常用语√√√1.2日常对外业务用语√√√1.3 船东面试时用语√√√2机舱日常业务2.1主机系统2.1.1轮机设备部件名称√√√2.1.2主机燃油系统操作与管理√√√2.1.3主机冷却水系统操作与管理√√√2.1.4主机润滑油系统操作与管理√√√2.1.5主机起动空气系统操作与管理√√√2.1.6主机运行工况监测√√√2.1.7主机换气、增压系统操作与管理√√√2.1.8主机故障排除√√√2.1.9主机维护保养√√√2.1.10主机智能设备操作√√√2.2辅助设备2.2.1锅炉的操作与管理√√√2.2.2发电柴油机的操作与管理√√√2.2.3空调和制冷系统的操作与管理√√√2.2.4空压机的操作与管理√√√2.2.5造水机的操作与管理√√√2.2.6分油机的操作与管理√√√2.2.7油水分离器的操作与管理√√√2.2.8焚烧炉的操作与管理√√√2.2.9生活污水处理装置的操作与管理√√√2.2.10舵机的操作与管理√√√2.2.11压载水系统操作与管理√√√2.2.12舱底水系统操作与管理√√√2.2.13甲板机械的维护与管理√√√2.2.14电气设备的操作与管理√√√2.2.15电气设备的安全注意事项√√√2.2.16消防水系统的操作与管理√√√2.2.17生活日用水系统的操作与管理√√√3 与驾驶台联系3.1值班人员交流√√√3.2备车√√√3.3试车√√√3.4完车√√√3.5对车钟√√√3.6对时√√√3.7试舵√√√3.8轮机长与船长的对话√4 应急情况下的用语4.1主机故障应急用语√√√4.2失电应急用语√√√4.3船舶消防应急用语√√√4.4碰撞应急用语√√√4.5机舱进水应急用语√√√4.6撤离现场与弃船应急用语√√√4.7溢油应急用语√√√4.8人员伤亡与救护应急用语√√√5对外业务联系用语5.1加油5.1.1加油程序用语√√√5.1.2加油前的准备用语√√√5.1.3加油中的注意事项用语√√√5.1.4加油数量的核对及争议的处理用语√√√5.2修船、监造、交接船5.2.1核对修理项目√√√5.2.2确定修理要求与标准√√√5.2.3修理质量与争议的处理√√√5.2.4坞修√√√5.2.5修理设备的调试√√√5.2.6造船规范讨论√√5.2.7船舶交接√√√5.3机损报告、机损检查与各项检验√√√5.4物料和备件5.4.1物料和备件的申请√√√5.4.2物料和备件接收√√√6 PSC\ISM检查用语6.1 PSC一般性检查6.1.1各种证书的名称及内容√√6.1.2油类记录簿的记录与内容√√√6.2 PSC详细检查6.2.1机器、设备操作性检查√√√6.2.2救生与消防演习现场检查√√√6.2.3职务规则用语√√√6.3 ISM检查用语6.3.1 ISM体系文件的检查√√√6.3.2与体系文件相关的记录的检查√√√6.3.3与ISM审核官员的会话√√√6.3.4 ISM条款问答√√√四、轮机英语听力与会话评估考试说明听力评估考试总时间:20-30分钟满分:100分;及格分:60分题型:听力单句单选题,听力对话单选题,听力短文理解题各职级题型分数比例分布如下:无限航区职位听力单句理解比例听力对话理解比例听力短文理解比例轮机长20% 30% 50%大管轮30% 30% 40%二、三管轮40% 40% 20%会话评估考试总时间:15-30分钟满分:100分;及格分:60分题型:听力单选题,短文朗读,回答问题,口述题,听力短文理解题各职级题型分数比例分布如下:无限航区职位短文朗读话题口述问题回答轮机长20% 20% 60%大管轮20% 20% 60%二、三管轮20% 20% 60%。



值班机工英语听力与会话口述题部分值班机工英语听力与会话口述20分1. Make a brief self-introduction. 作一个自我介绍。
(包括了自我介绍、家庭family、学习经历education experience、工作经历working experience)I’m glad to introduce myself.很高兴能介绍我自己。
My name is_______.我叫……I’m___ years old.我今年……岁。
There are 3 people in my family, my father, my mother, and myself.我家里有三口人,爸爸、妈妈还有我。
I’m married/ single。
I love my family.I will graduate from Guangzhou Seaman School this year.我将从广州海员学校毕业。
So I haven’t worked on board before.因此我还没有上船的经历。
2. Talk about the departments on board ship.谈一谈船上的部门。
There are two departments on board ship. The deck department and the engine department.船上有两个部门,甲板部和轮机部。
They are very important.它们都很重要。
In the deck department, there are chief officer, second officer, third officer and some sailors. 在甲板部,有大副、二副、三副还有一些水手。
The chief officer is the head of the deck department.大副是甲板部的负责人。

中华人民共和国海船船员适任考试培训教材航海英语听力与会话(船长)学习笔记Unit 1 general English(通用英语)Lesson 1 shipboard everyday life(船上的日常生活)I Warming-up (预热)Read the diary by Captain Keith Townley.The ship is nearly full but there is room for a bit more cargo before crossing the pacific to Los Angeles. Our last call here will be Yokohama, Japan.Good news. The pilot boarding time has been changed from 0600 to 0800 which is a bit more civilized and means there will be a chance for breakfast as well.0930 all fast in Yokohama. A nice day with a straight forward pilotage and a simple berth approach. Very cautious pilot-pleasantly common in Japan-and although sometimes a few minutes slower, undoubtedly much safer.1430 everything done, paperwork too, so we can set sail for the US. Looking forward to ten days at sea though the weather predictions are not looking too good.Questions for discussion1.What is the ship’s last call of the voyage?2.Why is the captain happy that the pilot boarding time has been changed?3.What does the captain think of the Japanese pilots in general?4.What is the ship’s next port of call?diary ['daiəri] n.日记, 日记簿a bit more多一点civilized['sivilaizd] a.文明的, 有礼的cautious ['kɔ:ʃəs] adj.谨慎的, 十分小心的pleasantly ['plezntli]adv. 愉快地, 友好地, 亲切地, 客气地,合意地paperwork ['peipəˌwə:k] n.文书工作prediction[pri'dikʃәn]n.预言, 预报set sail for开船, 动身vt.启航,驶往阅读船长基思·汤利的日记。
船员最新11规则-船员培训、考试部分《11规则》及其配套文件,基本构成了一个完整体系。
(一)一个部令:《中华人民共和国海船船员适任考试和发证规则》(二)一个履约准备通知:《关于做好STCW公约马尼拉修正案履约准备工作有关事项的通知》(海船员〔2011〕923号)(三)一个实施办法:《<中华人民共和国海船船员适任考试和发证规则>实施办法》(四)一个过渡期办法:《关于STCW公约马尼拉修正案过渡规定的实施办法》(五)一个培训合格证书签发管理办法:《中华人民共和国海船船员培训合格证书签发管理办法》(六)一个健康证签发管理办法:《中华人民共和国海船船员健康证书签发管理办法》(七)一套适任标准:包括适任考试大纲、评估纲要和规范等。
(八)一套质量管理规则:《中华人民共和国船员教育和培训质量管理规则》、《中华人民共和国船员管理质量管理规则》、《中华人民共和国船员教育、培训和管理质量管理体系审核实施细则》和《中华人民共和国船员教育、培训和管理质量管理体系审核员管理规定》二、《11规则》与《培训合格证签发管理办法》的主要变化船员培训适任考试船上见习证书船员培训1.岗位适任培训:(1)取消了学历的要求,强化适任培训。
除了三副升二副、三管升二管职务签证外,均需要参加岗位适任培训(包括航区扩大和吨位或功率提高),并且参加岗位适任培训前需要取得航海资历,资历的真实性由船员本人声明、培训机构审核。
《11规则》这种调整并不是降低现有的标准和要求,而是理清理顺相关法规规章之间的法律关系,同时也是以人为本、实事求是的体现。
《11规则》并没有否定航海教育的作用,而是按航海教育和培训的不同层次和类型,采取差别管理的模式区别对待,体现在接受不同航海教育与培训的学生在船员职业生涯起点上的公平。
(2)增加了新的适任岗位和适任标准按照STCW公约马尼拉修正案的要求,《11规则》增加了电子电气员、电子技工、高级值班水手和高级值班机工的岗位适任培训,在船长和驾驶员适任标准中增加了驾驶台资源管理、电子海图等要求,在轮机长和轮机员适任标准中增加机舱资源管理要求。
船员职务晋升说明船员职务晋升说明非航海工科毕业生从普通海员到高级海员的晋升示意图。
1.符合水手(机工)报考条件答:报考水手(机工)一般应满足下列条件:(1)男性,年龄18—35周岁,无不良行为记录,热爱航海事业。
(2)初中及以上文化程度,具有一定的英语基础。
(3)身高1.65以上,无色盲、无色弱,船舶驾驶专业(三副、水手)裸眼视力不低于1.0,船舶轮机专业(三管、机工)裸眼视力不低于0.8;无口吃、无平足,肝功能正常,无慢性病和传染病,符合海员体检标准。
1.1 水手(机工)的培训时间多长?培训地点在何地?答:水手(机工)的培训时间一般为4个月。
专业培训必须在国家海事局指定的具有相应资质的培训机构进行,具体培训地点由船员公司与培训机构联系。
1.2 水手(机工)经过培训是否都能取得各种证书?淘汰率多大?答:经过面试合格的一般都能取得各种证书。
成绩不合格者有多次补考机会,从以往招收的水手(机工)看,淘汰率不超过1%。
1.3 水手(机工)的实习时间多长?实习费用和待遇如何?答:实习时间6个月。
实习费用和待遇签协议时面谈。
1.4 水手培训设置哪些课程?答:基本安全、水手值班(主要项目:模拟驾驶台操舵、信号旗识别等)、水手工艺(绳结、撇缆、高空作业、插钢丝等)、航海英语、英语听力与会话。
1.5 机工培训设置哪些课程?答:基本安全、船舶柴油机、船舶辅机、船舶电气、轮机管理、机工值班(主要项目:柴油机、辅机拆装及主辅机运行管理)、机工英语、英语听力与会话、金工工艺(车床、钳工、焊工)。
1.6 水手的职责是什么?答:值班水手,即甲板部日常营运和工作中的支持级人员。
主要从事:(1)航行和靠离泊时的舵手,兼协助了望;(2)靠离泊时的带解缆;(3)懂得各种船用信号灯和信号旗的使用;(4)甲板部日常维修和保养的具体操作;(5)起卸船吊和开关舱作业;(6)引水梯和舷梯的安全收放。
1.7 机工的职责是什么?答:值班机工,即轮机部日常营运和工作中的支持级人员。
2016年1月上旬刊值班机工英语听力与会话评估通过率的提高策略徐继男(大连航运职业技术学院辽宁大连116047)【摘要】根据交通运输部《中华人民共和国海船船员适任考试和发证规则》(简称11规则)的要求,通过值班机工听力与会话评估考试,获取值班机工适任证书,是学生成为值班机工的必备条件。
笔者将采用经验总结法,提出了如何改善值班机工听力与会话这门课程的教学方法,以提高评估通过率,并使学生达到真正意义上的适任。
【关键词】评估考试教学经验提高策略【中图分类号】H31【文献标识码】A【文章编号】2095-3089(2016)01-0125-01随着世界贸易的发展,我国海员在航运战线上扮演着日益重要的角色,与此同时,对各个级别海员的英语应用水平,尤其是听、说能力也提出了更高的要求,值班机工作为海员队伍的成员,也不例外。
因此,在STCW公约马尼拉修正案的背景下,要不断加强对值班机工英语听力与会话这方面能力的培训。
一、评估内容及目的1.评估考试的内容评估内容包括公共用语、机舱业务日常用语、与驾驶台联系用语、应急情况用语、加油用语、PSC检查用语、ISM/ISPS检查用语以及机舱维护保养用语。
具体以听力考试(词汇、单句、短对话以及长对话)和口语考试(朗读题、问答题及口述题)两种题型出现。
2.评估考试的目的通过评估,检验被评估者掌握值班机工英语听力与会话的相关知识和技能并能正确进行操作和应用的能力,以满足STCW公约马尼拉修正案及中华人民共和国海事局海船船员适任考试评估的有关要求。
[1]二、实际教学经验笔者在一线教学中发现一些影响通过率的因素。
首先,基础英语学习方面。
本门评估课程的前续课程是基础英语。
在实际教学过程中,发现学生对专业英语期待性较强,对基础英语不够重视,基础的语言单位掌握不到位;其次,课程设置方面。
一方面,这门课程的评估考试难度略低,安排课时较少,导致学习质量得不到保证。
另一方面,依据11新规则并为保证学生的实习工作,轮机管理专业学生的三管轮大证考试安排在大三上学期的期末,造成这门课程的上课时间往往与三管轮大证考试准备冲突。