英语基础写作讲义
- 格式:docx
- 大小:17.42 KB
- 文档页数:6

雅思基础写作精讲班第1讲讲义基础写作基本框架Procedure of writing:How to distribute the time of 40 minutes一、议论文真题类型分类:练习题目:1. Studying the English language in an English-speaking country is the best but not the only way to learn the language. Do you agree?2. To what extent is nuclear technology a danger to life on Earth? What are the benefits and risks associated with its use?3. Describe some of the problems that overpopulation causes, and suggest at least one possible solution.4. Discuss the causes and some effects of widespread drug use by young people in modern day society. Make any recommendations you feel are necessary to help fight youth drug abuse.5. Scientific and technological advances have changed our lives. But some scientists in some fields say that scientists are not able to find solutions to the problems they havecreated. To what extent do you agree or disagree?6. Intelligent machines such as robots are increasingly being used. They can do many things that used to be done by human. Discuss the benefits and dangers.7. In order to solve the problems of traffic jam and air pollution, government is determined to raise the price of petrol. Do you believe it isthe best way? What other methods can you recommend?确定关键词Procedure of writing:How to distribute the time of 40 minutes一、议论文真题类型分类:练习题目:1. Studying the English language in an English-speaking country is the best but not the only way to learn the language. Do you agree?2. To what extent is nuclear technology a danger to life on Earth? What are the benefits and risks associated with its use?3. Describe some of the problems that overpopulation causes, and suggest at least one possible solution.4. Discuss the causes and some effects of widespread drug useby young people in modern day society. Make any recommendations you feel are necessary to help fight youth drug abuse.5. Scientific and technological advances have changed our lives. But some scientists in some fields say that scientists are not able to find solutions to the problems they have created. To what extent do you agree or disagree?6. Intelligent machines such as robots are increasingly being used. They can do many things that used to be done by human. Discuss the benefits and dangers.7. In order to solve the problems of traffic jam and air pollution, government is determined to raise the price of petrol. Do you believe it is the best way? What other methods can you recommend?雅思基础写作精讲班第2讲讲义07年真题回顾2. 真题思路扩展brainstorming(1)specific: I. from abstract to personal: air travel, oneself study—group study, fast food-traditional food (2)general: economy, environment, efficiency, safety, pleasure, science and technology避开主题句错误类型3. 确定主题句:ascertain topic sentencesI. Some mistakes of the thesis statement or topic sentences:(1)The subject of this paper will be my parents.(2)My parents have been the most influential people in my life.(3)My parents had only one child.(4)My parents helped me grow in important ways, although in other respects I was limited.4. 开始动笔写作:1. format: block,2. pencil3. handwriting: clean and clear4. time control: 34m5. 装饰和改错:decoration and correction(1)After I cashed my paycheck. I treated myself to dinner.(2)The instructor told everyone in the room to be quiet his favorite show was on.(3)How you react to the incident reveal what side you stand on.(4)The crowd has surged forward, showing their excitement.(5)There are more and more people go abroad nowadays.(6)The student who had sat down quickly put on the headphones. 雅思基础写作精讲班第3讲讲义必备模板第二种模板形式(五段式)雅思基础写作精讲班第4讲讲义Mixed typesMethod:Successful introduction:1. “Knowledge is power,” wrote Francis Bacon long ago.Today college students are hard at study to acquire all kinds of skills, such as English, computer, and driving.People, however, cannot reach a general consensus on what subjects should be attached more importance to,academic or practical.( academic subjects Vs. practical subjects) (As the old saying goes)Art is long, life isshort;(Rudyard Kipling wrote) East is east, and West is west, and never the twain shall meet!; Experience is the father of wisdom and memory the mother; Knowledge isa treasure, but practice is the key to it; Knowledgeadvances by steps, not by leaps; Great works areperformed not by strength but by perseverance; Genius is nothing but labor and diligence.2. What can be done to solve the problem of watershortage? Surely, modern people frequently are plagued with this question. As for me, there are three methods as followings.(the problem of water shortage)3. Is the history of no avail to modern society? Recentdiscussions concerning the function of history haveraised some very real doubts in the minds ofcontemporary people. As far as I am concerned, we can benefit a lot form the past.(whether history is useful to cotemporary society)4. A recent survey reports that there were about one thirdof college graduates who could not find an ideal job in2005. This fact prompts us to make a thorough analysis of the root reason of this alarming phenomenon.(theissue of unemployment of graduates)5. It is generally agreed that the main responsibility ofteachers is to pass on knowledge to students. As a result, if students can do well in academic subjects, theirteachers are qualified enough. However, I assert thatassisting students in distinguishing right from wrong is more significant for teachers.(the relationship between students and teachers)6. With the development of computer technology, books, asa traditional medium, are more and more challenged.Many libraries are faced with such a dilemma, whether they should invest on computers or on books. With every aspect taken into consideration, I believe that to invest on computers would be a better choice.(investment inbooks or computers for a library)Successful body:1. One main reason for water shortage is lack of theawareness of water conservation. For example, moreoften than not we can come across such a phenomenon that a person turns a faucet on and forgets to turn it off.Precious water has been totally squandered. (theproblem of water shortage)2. Smoking should be banned without any hesitation for it israther detrimental to people’s health. Cigarette smokecontains nicotine, several cancer producing or irritatingsubstances and carbon monoxide gas. Damage to the lining of the bronchial tubes is much more among cigarettesmokers than non smokers, even when there is no obvious disease. Some of these changes are considered to bepre-cancerous. Lung function is generally reduced among cigarette smokers. Cigarette smoking is a greater hazard than other factors---such as community air pollution—in the causation of lung cancer and chronic bronchitis.(nosmoking)3 Due to great strides of modern technology, dramatictransformations have taken place in our life. In the past, if we were anxious to contact friends, we had to drop in on them in person, which was inconvenient andtime-consuming. Now, fashionable cell phones can be an efficient bridge between acquaintances.(the benefit of modern technology)4. There are a lot of benefits of raising dogs. First, dogscontribute to the health of their owners. Often theirdemands for walks and play improve their owner’sexercise routine. In fact, statistics show that dog owners get more regular exercise than non-dog owners do. Also, they enhance health simply be being around to bepetted. Second, they provide a means for parents toteach their children responsibility. When parents givechildren a dog, they provide them the opportunity tofulfill the responsibilities of walking, feeding, and caring for its other needs. Finally and most important of all,dogs enhance the well-being and emotional stability of families. Older people who live alone especially rely on dogs to give them enjoyment and company. Childrenalso find a great deal of comfort in their dogs. As anexample, a family dog helps a little boy adapt when his mother leaves him with a sitter and goes towork..(advantage of keeping pets)5.lot of advantages. Firstly, after three or four years ofschooling, students can undoubtedly acquire valuableexpertise, which is essential to their future jobs. As weknow, through compulsory and optional courses,students lay a solid foundation in a particular field andare confident to solve the relevant problemsconfronted.(benefits of college education)6. By contrast, the opponents argue that its drawbacksshould not be ignored. For one thing, some existingmajors are so out of date that they serve no purpose for the future job. In such a dilemma, there is no doubt that graduation means exactly unemployment. If whatstudents learn in colleges is only theoreticalargumentation definitely unconnected with reality, what is the point in wasting such prime time? (drawbacks of college education)Successful conclusion:1. The extinction of species, the shortage of lumber anddrug ingredients, the reduction of oxygen and theincrease of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere all signal that we cannot afford to lose any moreforests.(protection of forests)2. To stop losing more forests, we should educate people,especially those who have destroyed and who are going to destroy forests for one reason or another, in why forestsmust exist on the earth. (protection of forests)雅思基础写作精讲班第5讲讲义写作的素材素材Topics:1. If a five-year old commits a crime, should his/her parents have the responsibility and are punished? What is the age of a child when parents no longer bear the responsibility for children's behavior? /Unlike other countries, police in UK donot carry guns. Some think it leaves citizen unprotected, while others think it reduces the overall violence in our society. Discuss both the views.2. We know that university graduates should earn higher salary than less well-educated members, so in this way they should pay all the full cost. /Quality of people that we need in our society can’t be learned in universities and other academic institutions. To what extent do you agree or disagree?3. International tourism creates tension rather than understanding between people from different cultures. To what extent do you agree or disagree?/ Government should build new buildings in a traditional way in order to protect traditional culture.4. The government should control the amount of violence in films and on television in order to decrease the violent crimes in society. To what extent do you agree or disagree? / Billions of money is spent on the space research. Some people say that it should be spent on improving the living standard of the people on the earth. Do you agree or disagree?5. Wild animals have no place in the 21st century, and the protection is a waste of resource. Agree or disagree? /Some people think killing animals for food is cruel and unnecessary and some people think is essential for dairy diet. To what extent what do you think about the both issues?6. Nowadays motorized flight is considered as the most important and influential invention in the world. Not any other invention has such a significant impact on our lives. Agree?/ Maintaining public library is a waste of money, because computer technology has already replaced its function. Do you agree or disagree?7. Traffic and housing problems in major cities could be solved by moving large companies and factories with their employees to the countryside. To what extent do you agree or disagree?/ The environmental problem is so serious to most countries and individuals that it needs the international cooperation. Do you agree or disagree?8. Mass media have a significant influence on our life and this is a negative development. Do you agree or disagree?/ Do thenegative effects of some international media such as TV and magazine for example overweigh the positive effects?Topic Word:I.1. society: Society is flooded with unhealthy substance in the mass media, such as violence and pornography, therefore having inevitably downside effect on people, Citizens are preoccupied by money worship to make profits by hook or by crook; parents never discipline children strictly, divorce rate rockets, children are in need of solicitude, youngsters fall victim to prevalent domestic violence and are prone to aggressive impulse; students are heavily encumbered by knowledge acquisition, psychological education has been neglected, confronted with frustration, children have no efficient outlet to alleviate stress.素材(2)犯罪处罚2. Government should mount a crackdown on crime and bring criminals to justice, the aim is to reform those who have gone astray, offenders can turn over a new leaf and are endowed withproficiency in a particular line, inferiority complex and psychological shadow should be avoided, delinquents harbor vengeful sentiments against others and society as a whole, lawbreakers resume committing crimes or committing suicide.II.1. students can acquire academic qualification, learners can develop expertise, pupils have practical ability to apply what they have learned to society; campus and dormitory life instill discipline into students, living together can cultivate cooperation and strengthen the skill of interpersonal relationship, learners get tolerant of others, schooling can help students tell right from wrong2. course framework ought to be more flexible, such as more optional subjects rather than compulsory ones, interests can be aroused, subjects are practical and related to future jobs, learners should be more motivated, they have convenient access to relevant information of majors.III.1. advantage: cultures are mutually beneficial, theycan pool and share resources, the platform of exchange of ideas will assist diverse countries in comprehending actual state of affairs of distinct cultures, globalization will facilitate mutual understanding and dispel misunderstanding; disadvantage: the conflict between mainstream and marginal cultures will result in lesser-known cultures on the verge of extinction, the world is turned into a similar and monotonous entity.2. tradition is precious and unique, it symbolizes identity of a nation, people in the homeland are bristled with pride, for example, Forbidden City, fantastic buildings witness resplendent culture of feudalism, the Bastille, time-honored prison appreciates glorious history of French Revolution; peaceful coexistence between tradition and modernity should be guaranteed, tradition serves as places of tourist interests and boost the development of economy, we can invest money in the conservation of tradition and promote the education of protecting tradition.雅思基础写作精讲班第6讲讲义第四大主题1. the ultimate purpose of government is to serve the people, dispelling adverse substance is the obligation, authority should make overall planning and give consideration to the interests of all sides in adopting policies, it can exercise executive power if necessary.V.1. animals are in an unfavorable situation, they are entitled to the right of subsistence and deserve impartial treatment, it is unjustifiable to expropriate the right of living,2. humans enjoy the right of priority, in medical field, human beings can carry out clinical experiment on laboratory animals, they can achieve breakthrough in medical treatment, vivisection is justifiable.3. a reciprocal relationship is strongly recommended, equilibrium in biosphere and harmonious development can be beneficial to each other, they are indispensable to each other,1. white-hot technology transforms the life of drudgery into a convenient and comfortable one, entertainment at a finger’s click is not beyond our wildest dream, the means of communications, traffic, and information have been changed dramatically, humans are more confident about the future2. people adhere to hedonist philosophy and become indolent, declined ability is accompanying the progress; humans are heavily dependent on modern science, they become alienated, environment falls victim to advance of science and technology, environmental pollution has been aggravated.素材7VII.1. modern society are flooded with one-off products, such as chopsticks, shopping bags, and purified water bottles, some of them are non-biodegradable, industry, fossil fuel in industrial development is widely applied, petrol, coal, gas, the increase of carbon dioxide leads to global warming and air pollution, it will deplete ozone layer, farming, fertilizer andpesticide give rise to erosion of soil.2. government should pursue strict policy and popularize biodegradable packaging, coordination should be ensured among various countries, education will fire the masses with enthusiasm for environmental protection.VIII.1. Readers are thoroughly informed of current affairs, they can have access to up-to-date information and enjoy the right to know the truth, the freedom of speech will be guaranteed.2. Because of lack of professional ethics, shameless and unscrupulous journalists always carry gloomy news, such as murder, to promote circulation, paparazzo(singular), hordes of paparazzi(plural), invade privacy, chequebook journalism leads to sham news, the mass media follow the fashion and pander to the low taste, it encourages vulgar interests雅思基础写作精讲班第7讲讲义写作中必备的词汇和句式词汇和句式:第一:1.appalling/drug-related/commit/tackle crime, turn to crime: bored youngsters turn to crime. hardened criminal, teach criminals salutary lessons, unwilling victims, fall victim to,2.decent education, enter higher education, education authority, education resources, encyclopedic knowledge, broaden knowledge,3. alien/indigenous/dominant/mainstream culture, assimilate the culture, experience culture shock, a mutual exchange of ideas, facilitate communication, eco-friendly tourismernment agency/backing, guarantee equality, maximize efficiency, supplement meagre income,5.prove medically beneficial for human beings, endangered animals, laboratory animals, slaughter animals,6. white-hot technology, communication/telecommunications technology, treat the world with difference,7. safeguard the environment, damage the environment, environment issues/protection, pollution of the environment, fragile balance, sit in traffic jam, strike a balance8.tabloid journalism, fashion/literary/science journalism, the world of journalism, information bombard, create serious disturbance to people, accurate information, misleading advertisements, classified advertisements,第二:1. give rise to/lead to/arouse a heated discussion/perplexity; when it comes to.., it is commonly believed that…; one indisputable fact is that….;it goes without saying that…; it cannot be denied that…; recently, …has been brought into focus; with the rapid of development of…, …has gained an ever-increasing popularity in modern people’s life;…..is not strange to modern people.I assert…; in my opinion…; what I emphasize is that…;2. the reasons are multiple, it is manifest that…., it is conceded that…, in other words, that is to say, for example.3. from what has been discussed above…, taking into account all the points.., from the above-mentioned facts,.. I am convinced that..第四种词汇第三:alarming issue/ thorny problem, crucial reason/contributing factor, profound impact/ disruptive influence, charismatic culture/ time-honored tradition, beneficialinterest/spectacular result, persistent effort/genuine dilemma, pollution prevention/prevailing attitude, efficient solution/mass production, harmoniousrelationship/sustainable development, rosy picture/ monotonous routine, infallible methodology, severepenalty/impending crisis, draconian measure/appropriate punishment, widespread phenomenon/current situation, rampant corruption/petty crime, improperly undoubtedly, inevitably, indiscriminately, absolutely, responsibly第四:1.In addition/additionally: Computers provide efficient work. In addition, they make our life more colorful.Furthermore/further: This method can, furthermore, be used in environmental protection. Moreover: private cars are cheap and, moreover, it can improve our life. In other words: Killing live animals is cruel, a murder in other words.2. Hence: The cost of transport is a major expense for a person. Hence job location is an important consideration. Consequently: Globalization is a widespread phenomenon and consequently the domestic culture has been affected. Thereupon: Nature will revenge on humans. Thereupon people begin to realize the power of nature.3.Whereas: Smoking is something personal whereas it will affect others’ right. Conversely: S ome policemen prefer to carry guns when on duty; conversely others are reluctant to do that.4.Although/though: Although some young men really have no idea of what a new culture is, they absorb it without any reservation. Granted: Granted that the deed is not perfect, the disadvantages are outweighed by the advantages.5. for example, specifically: Specifically, the departmentwanted answers to the following questions.6. On condition that: Television enrich our lives a lot on condition that we are not addicted to it. Given that: Given that pets have become an indispensable part of some people’s life, the key is to coordinate the relationship between them.雅思基础写作精讲班第8讲讲义第六种词汇positive words:1. strive for a harmonious society/greater efficiency/striveto do something争取2. take suitable/timely steps to address this problem.采取合适/及时的措施3. top the central government's agenda.位于…最重要的位置4. assist sb in sth.在…方面帮助5. play an increasingly more integral role in wealthdistribution.起到越来越整体的作用6. contribute to sth/doing做出贡献7. implement the policy执行8. exert a positive/baneful effect on9. embark on reform and opening开始做…10. t ake initiative to eliminate negative effects.主动做…11. l aunch a spate of stringent measures发动,采取12. n avigate one’s way through the difficult situation.通过13. P roblems triggered by income composition are easy toresolve.解决/ muster enough resolve to quit smoking.鼓起勇气/Distribution of wealth is tainted and distorted by corruption must be redressed.纠正14. P roblems arising from development-based factors can berelieved and eased.减轻/ improve and ease减轻 thedifficulties and frustrations faced by travelers15. e liminate/ weed out 消除the structure of unscientificdesign.16. u tilize利用 their rich resources.17. i mprove/upgrade/optimize改善 the conditions18. f acilitate 推动the country's future sustainabledevelopment.19. b oost 推进the employment20. s houlder 承担起greater social responsibilities/bridge 消除,减少the cultural differences./ sth is mirrored by被反映21. m ake a difference有很重要的作用22. a vail oneself of something利用23. a bide by traffic rules遵守24. e nhance their job opportunities/enrich one’s life丰富,提高25. a spire to careers in finance/aspire to study abroad努力想要26. v oice their support for the movement表示了27. m ake efforts to do努力做事情28. h elp with 帮助weight loss and control; improve 改善fitness; reduce 减少stress, and of course save 节省money on petrol and parking.29. m inimize 减轻air and noise pollution, traffic accidents,oil consumption, road repairs and beautifies cities. 30. T hose measures, coupled with 与…一起advanced science andtechnology, will be taken without any delay.31. H ouse prices will start to calm down, saving the sector.下降32. T he current campaign to curb控制 the use of tobacco shouldbe stepped up.加速33. n urture/ cultivate a great number of learned people/培养,培育34. F igures released 公布on World No Tobacco Day serve as asource of frustration for everyone who wants to curb smokingin China.35. a slew of/a spate of/ a skyrocketing number of多数量第五:negative words:1. fail to do没能做…2. be a heache to…对于..是个难题3. pose a potential threat to residents' health.有潜在的威胁4. mean a formidable battle to do艰苦的斗争5. is now confronted with the same question that haunts/ beplagued with/be afflicted with (overpopulation/youth drug abuse/traffic accidents) 受到…问题的困扰6. be detrimental to sth对..有害7. focus attention on/bring something to somebody's attention引起…注意8. be blind to this point注意不到,忽视9. be of no avail没有用处10. crack down on(严厉的处罚) smoking in public places andpenalize(处罚) those who sell cigarettes to juveniles.11. exert a negative effect on sth有负面的影响12. exacerbate income disequilibrium/ The situation wascompounded by…加剧了13. squander natural resources浪费14. deprive sb of sth剥夺15. We believe that car tax should be scrapped.废除16. If it is hard to rein in控制17. The move has aroused controversy引起争论18. Apart from that, numerous factors are to blame for thecurrent situation. 责备19. We must stop pampering children纵容20. take various measures to tackle such malpractices处理玩忽职守21. Air pollution has turned into a major hazard affecting urbanresidents' quality of life. 巨大的危险影响了.22. an apparent total lack of明显的完全缺乏23. social and economic disequilibrium/ gauge(衡量) incomeinequality/disparity不平衡24. the severity of the pollution levels严重性25. lung damage and respiratory problems肺部损害以及呼吸问题26 be mind-boggling/ a problem of mind-boggling complexity令人难以置信的27. People cannot help but wonder why efforts to cut the numberof smokers have proven to be so futile. 没有效果的28. Smokers are six times more likely to be infertile(不生育的)and have a greater chance of becoming disabled,(残疾的) while women who smoke have a higher chance ofcontracting(得…病) breast cancer.29. looming environmental and public health disaster逐渐显现的30. leave others to the mercy of market forces受到..控制31. The abuse(滥用) of power for financial gain veils behind(隐藏)monopolies32. a hard nut to crack is that..困难是…33. Emissions from car exhausts have been found to be one ofthe major sources of urban air pollution. 尾气的排放34. carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide二氧化碳,一氧化碳35. We have no reason to be optimistic about the improvementof urban air quality. 对..不乐观第六:同义必备词:66. youth, teenager, minor, fledgling67. the old, elderly, grizzled, grey-headed68. conserve, preserve保存,如:We must conserve our waterresources for future generations.69. assure, ensure(insure), guarantee, pledge, avouch保证,如:Government should assure consumers of the quality of commodities. /It is important to insure that universities have enough funds to carry out important research inscience subjects./ The law guarantees equal rights for men and women./ The new government pledged to reduce crime./ Some criminals avouched that they themselves wereinnocent.70. Ideal, aspiration(beyond normal expectation), ambition(aparticular end)理想,雄心71. compare with/to, contrast, analogize(elaboration on thefunction of families in social life, sociologists like to analogists them to the cells of a human body.) 比较72. change, alter, modify(change of function), convert into,transform(appearance),改变73. argue, controversy(long-continued argument),dispute(angry manner), debate(formal argument)争论74. standard, criterion, gauge, yardstick标准75. inevitable, inescapable, unavoidable难免76. wealth, property, assets, fortune财富77. attend, take part in, participate in(formal), partake in,join in,参与。


高考英语写作讲义:万能语料之连接词的高级表达1. 表目的●So as to●With an aim to●In anticipation of例句:基础版:The international cooperation is expected to be strengthened, in order to build a harmonious world of common prosperity.为了建设一个共同繁荣的和谐世界,我们需要加强国际合作。
升级版:1. The international cooperation is expected to be strengthened, so as to build a harmonious world of common prosperity.2. The international cooperation is expected to be strengthened, with an aim to builda harmonious world of common prosperity.3. The international cooperation is expected to be strengthened, in anticipationof building a harmonious world of common prosperity.注In anticipation of后面的动词需要变成动名词2. 表因果●Since●For that reason●Thus (doing)例句:基础版:Innovation lights the way to infinite possibility, so we should give our imagination free rein.创新通向无限可能,所以我们应该让想象力自由驰骋。
升级版:1. Since innovation lights the way to infinite possibility, we should give our imagination free rein.2. Innovation lights the way to infinite possibility. For that reason, we should give our imagination free rein.3. Innovation lights the way to infinite possibility, thus making it necessary to give our imagination free rein.3. 表转折●Conversely●On the flip side●While/whereas例句:基础版:Money is a good thing. However, too much pursuit of it will subject us to its slavery.钱是个好东西,但过分追求就会使我们沦为金钱的奴隶。



雅思考虫基础写作讲义1. 雅思考试概述雅思考试是国际英语测试系统(International English Language Testing System)的简称,是全球范围内用于评估非英语国家学生英语能力的一项标准化测试。
该考试分为雅思学术考试和雅思普通考试,学术考试主要用于申请留学,而普通考试主要用于移民和就业。
雅思考试由剑桥大学、英国文化协会和澳大利亚考试委员会联合主办,被许多国家和组织所认可。
2. 如何备考雅思写作在备考雅思写作时,了解考试要求和技巧是至关重要的。
其中,考虫(Kaochong)的雅思写作讲义可以被认为是备考雅思写作的“基石”,提供了系统且全面的备考内容。
该讲义从写作基础到高级写作技巧都有涉及,对于备考考生而言是一份非常宝贵的资料。
下面将对考虫的雅思写作讲义进行深入解读。
3. 考虫雅思写作讲义的基础部分考虫的雅思写作讲义首先从写作的基本结构开始介绍,包括如何组织思路、如何构建段落、如何展开论述等内容。
这一部分内容对于初学者来说尤为重要,因为一个清晰、有逻辑、结构合理的作文是取得高分的基础。
在这部分内容中,考虫提到了写作的基础知识,例如主题句、论点、论据和结论等。
这些基础知识的掌握,可以帮助考生在写作时更加得心应手,写出结构清晰、逻辑严谨的文章。
4. 关于写作技巧的讲解在讲义的第二部分,考虫详细介绍了写作的技巧,包括如何使用丰富的词汇和句型、如何进行论证和举例、如何进行逻辑推理等。
这一部分内容的掌握可以让考生的文章更加生动、具有说服力,同时也可以提高文章的语言表达水平。
考虫还介绍了一些常用的写作模板和句型,这些模板和句型的掌握可以帮助考生提高写作效率,同时也可以提高写作的质量。
5. 个人观点和总结通过对考虫的雅思写作讲义的深入解读,我深刻认识到了写作在雅思考试中的重要性。
考虫提供的讲义内容全面、系统,既包括了写作的基础知识,也包括了高级写作技巧,对于备考考生而言是一份难得的宝藏。

考研基础班网络课堂写作讲义北京新东方学校王江涛第一节考研写作总论一、课程安排:1、考研写作总论:评卷实例、复习计划、学习方法、大纲解读2、应用文:书信类、告示类3、段落写作:真题透视、框架结构、启承转合4、两图写作(00、03、06、07)5、一图写作(98、01、02、04、05)6、图表作文二、评卷实例:2001年真题Directions:Among all the worthy feelings of mankind, love is probably the noblest, but everyone had his/her own understanding of it.There has been a discussion recently on the issue in a newspaper. Write an essay to the newspaper to1) show your understanding of the symbolic meaning of the picture below,2) give a specific example, and3) give your suggestion as to the best way to show love.1、20分范文:Among all the worthy feelings of mankind, love is probably the noblest. It is of the utmost importance to the human beings. Everybody not only needs love, but also should give love.As is described in the picture, “love is a lamp which is brighter in darker places.” This is indeed true. People in darker places need more light than ordinary people. Maybe even a dim lightcan give them much hope for a better life and progress. Maybe even a dim light can give them much hope for a better life and progress. Maybe just a thread of light will call forth their strength and courage to step out of their difficulties.For instance when someone is starving to death, just a little food and water from you may save his life. Or when a little girl in a poor rural area drops out of school because of poverty, just a small sum of money from you may support her to finish her schooling and change her life, you have given love which is like a lamp in a dark place where light is most needed.So to sum up, we should offer our help to all who are in need. We expect to get love from others and we also give love to others so when you see someone in difficulty or in distress and in need of help, don’t hesitate to give your love to him. I believe then the relationship between people will be harmonious and our society will be a better place for us to live in.2、18分范文It is generally believed that love is a hot topic which is most talked about. This is true not only in China but also in other countries. We live in different countries, speak different languages, but love is something common to us all. But how to show love may be different with different people in different countries. This is something we should give more thought to.As is shown in the picture, love is like a lamp which shines brightest in dark places. This tells us a simple truth: Love is like a lamp. It is most valuable when it is most needed. For example, once I saw a foreign lady get lost in the street. She could not speak Chinese and nobody seemed to be able to help her. Though my English is not very good and I am a shy person, I thought she needed help very much. I asked her what she wanted. She told me she lost her way, so I showed her the way to her hotel. It was a small thing but she thanked me very much because my help was needed very much. My help was like a lamp in dark places.I think we all should be like a lamp in a dark place, showing our love, giving our help to others, even to strangers. In this way, we can make this world a harmonious and peaceful world.三、复习计划:1、考前复习:1)攻克词汇:2)精研真题:词汇、句子结构、选项设置、英译汉、背诵3)适当模考:2、写作练习:3、时间分配:1)14:00-14:15 写作A节2)14:15-14:50 写作B节3)14:50-16:00 阅读A节4)16:00-16:20 完型填空5)16:20-16:40 阅读B节6)16:40-17:00 阅读C节第二节应用文一、学习方法:(一)提高实力:1、十遍精读:1)精彩词汇2)精彩词组3)精彩句型4)句子结构:简单句(主干+修饰成分)、从句、时态、冠词、主谓一致5)段落结构:总分总,主题句+论证(+小结)6)关联词:小作文3-5个,大作文5-7个7)同义替换:词汇+句型8)代词替换:it, that, they9)精彩观点:10)原因建议:2、背诵:滚瓜烂熟、脱口而出、多多益善3、默写:发现写作弱点4、中译英:提高写作实力5、写作:模仿(二)掌握技巧:万能框架二、大纲解读:(一)评价目标:考生应能写不同类型的应用文,包括私人和公务信函、备忘录、摘要、报告等,还应能写一般描述性、叙述性和说明或议论性的文章。

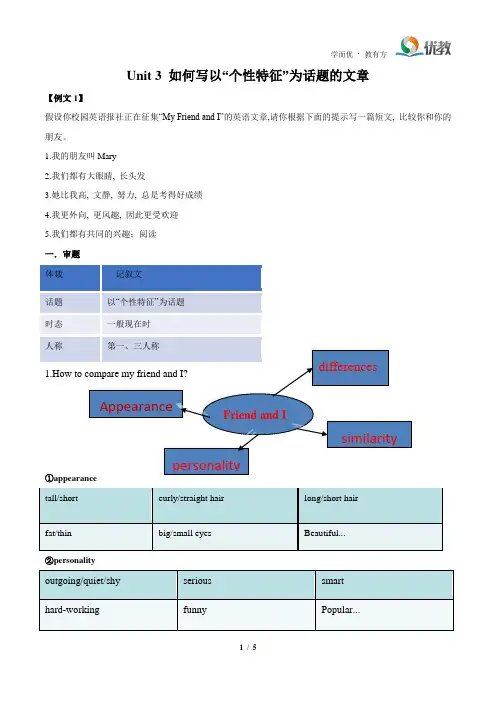
Unit 3 如何写以“个性特征”为话题的文章【例文1】假设你校园英语报社正在征集“My Friend and I”的英语文章,请你根据下面的提示写一篇短文, 比较你和你的朋友。
1.我的朋友叫Mary2.我们都有大眼睛, 长头发3.她比我高, 文静, 努力, 总是考得好成绩4.我更外向, 更风趣, 因此更受欢迎5.我们都有共同的兴趣:阅读 一.审题 体裁 记叙文话题 以“个性特征”为话题 时态 一般现在时 人称第一、三人称1.How to compare my friend and I?①appearancetall/shortcurly/straight hairlong/short hairfat/thinbig/small eyes Beautiful...②personalityoutgoing/quiet/shy serious smart hard-workingfunnyPopular...Friend and IAppearancedifferencespersonalitysimilarity二.文章布局开头:引出人物 以“ She / He is my friend./She and I are friends.”引出正文:相同和不同点 In some ways, we are similar, but in other ways, we are different.结尾:总结 We are different in some ways, but we are close friends....三.遣词造句 ①词汇库相似similar; 不同的different; 直的straight; 外向的outgoing; 风趣的funny; 受欢迎的popular; 安静的quiet; 努力的hard-working; 亲密的close; 喜欢like/enjoy; 不喜欢dislike; 锻炼exercise; 兴趣hobby/interest ②短语箱与...相似be similar to; 与...不同be different from; 对...感兴趣be interested in; 锻炼do sports/do exercise; 取得好成绩get good grades; 受欢迎的be popular with ; 擅长be good at;和...分享share ...with; 交朋友make friends; 和...一样the same as/as...as ③链接句型1. I am more outgoing than my sister.2. Tina thinks she works harder than me.3. I am taller now than I was two years ago.4. He likes to do the same things as me.5. A good friend is talented in music.6. My best friend, Larry is quite different from me7. And we can talk about and share everything.8. I am shy, so it ’s not easy for me to make friends.9. My brother is as serious as my sister 四.作文模板___________ is my best friend. We are in the same class/school.In some ways, we are similar to each other. We both__________________________________________. (We are as...as.....) What ’s more, we are interested in______________________. However, in other ways, we are different. She is ____________ than me. I am ____________________. Besides,___________________________.文章段落结构We look different from each other in some ways, but we are close friends.And we can talk about and share everything.五.参考范文Mary is my best friend. We are in the same class/school.In some ways, we are similar to each other. We both have big eyes and straight hair. What’s more, we are interested in reading. However, in other ways, we are different. She is taller than me. I am more outgoing and funnier, so I am more popular with my classmates. She is quieter and more hard-working, so she often gets better grades.We look different from each other in some ways, but we are close friends. And we can talk about and share everything.【例文2】Compare yourself now and two years ago.In the past Now1. a primary school student2. short and thin3.talk less4.painting4.reading 1.a middle school student2.tall and stronger3.outgoing4.reading5.play sports一.作文模板I am really different from what I was like two years ago. Two years ago, I was a primary school student, but now I am a student from middle school.In the past, I was_____________. I disliked/liked_______________________. I was interested in____________. However, I have changed a lot. Now, I look _______________. I become __________________.I still enjoy________________.I really like what I look like now.二.参考范文I am really different from what I was like two years ago. Two years ago, I was a primary school student, but now I am a student from middle school.In the past, I was short and thin. I disliked to talk with others, so I had few friends. I was interested in painting. However, I have changed a lot. Now, I look taller and stronger, that’s because I often do sports. I become more outgoing, so I make a lot of friends. But I still enjoy reading.I really like what I look like now.课后练习(一)根据表格, 写出“我”和“Nick”在学习, 爱好, 等方面的相同和不同之处。

一、词汇讲解2018 年浙江省新高考写作基础能力练习讲义必修一unit3part31.stubbornadj.顽固的,固执的;顽强的或有决心的;坚持的;棘手的比较级:stubborner最高级:stubbornest【派生词】stubbornlyadv.倔强地,顽强地,顽固地【派生词】stubbornnessnoun[U]倔强,顽强;牛性;牛脾气;犟劲anizev.组织;安排;规划;建立组织【派生词】organizer-iser n.组织者,编制者,发起人;[生]形成体;〈口〉公文柜,(分类记事的)备忘记事簿;[计]整理器【派生词】organizationn.组织;机构;团体;【派生词】organizationaladj.组织的;编制的3.determinevt.&vi.(使)下决心,(使)做出决定(~onsth/todosth决定,决心(做某事))vt.决定,确定;判定,判决;使决定;限定vi.[主用于法律]了结,终止,结束【派生词】determinationn.决心;决定,确定;[物]测定,计算【派生词】determinedadj.确定的;坚定的;毅然的v.确定;决定;(使)下决心,(使)做出决定(determine的过去式和过去分词);使决定【派生词】determinedlyadv.坚决地;坚定地;断然地;决然地4.journey(Journeytothe West西游记)n.旅行,旅程行期;历程,过程vi.旅行,出游vt.在…旅行或旅行到过…【近义词辩词】1)journey指经由陆路、空路或海路,从一地到另一地的旅程,如:ajourneyofover2,000miles(2,000多英里的旅程)。
表示旅行到某个地方用journey,这是文雅的用法:Thenightsbecamecolderastheyjourneyednorth(他们北上的过程中,夜晚变得越来越冷)。
2)voyage通常指乘船或乘坐飞行器进行的长途旅行:thevoyagetothemoonin1972(1972年的登月之旅)。

小学英语写作基础【大小写规则】一、英文书写规则1.句首第一个字母要大写。
例:We have lunch at twelve o’clock every day.2.“I ”在句中任何位置都要大写。
例:My sister and I are twins.3.人名、国家名、地名等专有名词第一个字母要大写。
例:Sue, Liu Dehua, China, Shanghai4.表示语种、国籍的名词或形容词第一个字母要大写。
例:Chinese, English5.人名前的称呼、职务或头衔第一个字母要大写。
例:Mr. Wang, Miss Li6.星期、月份的第一个字母要大写。
例:Sunday, September7.节日中实词的第一个字母要大写例:Children’s Day, the Spring Festival【标点符号使用规则】1. 句号“.”(1)用于除疑问句或感叹句以外的句子末尾。
例:I e from China.(2)用于缩写后例:p.m., Jun. 27th2. 逗号“,”(1)用于分隔所列词语,不过在and之前常常省略。
例:He likes strawberries, pears and apples.(2)书写对话时用于某某说等词语前。
例:”I’m so happy,”she says.3. 问号“?”用于问句末尾。
例:What’s your name?4. 感叹号“!”用于表示惊讶、欣喜、愤怒、震惊或其他强烈感情的句子末尾。
例:That’s great!5. 撇号“’”(1)与s连用表示所有格。
例:Mary’s schoolbag注意:对于以s结尾的复数名词,只加’。
例:the boys’schoolbag (2)在缩写中表示字母或数字的省略。
例:I am=I’m(3)主语与have got/ has got的缩写:He has got=He’s got6. 连字符“”(1)将两个或两个以上的词组成复合词。
对症(甲状腺机能减退症)——找方手册甲状腺机能减退症(简称“甲减”)是由于甲状腺激素绝对或相对不足,以致机体代谢过程降低的症群。
由于发病年龄不同,临床表现各异,一般可分为:(l)呆小病(又称克汀病),发病始于'胎儿及新生儿;(2)幼年型甲减,发病始于青春发育期以前;(3)成年型甲减,发病始于青春发育期以后。
三型严重时均可引起粘蛋白和粘多糖在皮肤浸润,表现为粘液性水肿。
前二型临床表现则主要为发育迟缓及智能障碍。
本节主要阐述成年型甲减,其主要症状为畏寒、乏力、表情淡漠、反应迟钝,面色苍白、体重增加、眼睑浮肿、毛发稀疏、皮肤干燥、声音嘶哑、食欲差、便秘、性欲减退等。
严重者可引起心包、胸腔积液,甚至发生粘液性水肿昏迷,可危及生命。
现代医学认为常见病因为甲状腺发育异常,多有家族史倾向;甲状腺激素合成异常系常染色体隐性遗传;甲状腺病变;放射性碘治疗后;长期饮食中缺碘或药物使甲状腺激素合成障碍等。
本病诊断主要依据临床症状及实验室检查。
血清T3、T4浓度水平测定、甲状腺碘131摄取率等甲状腺功能检查。
一般均降低;基础代谢率降低,血胆固醇升高。
甲减诊断明确后需做血清TSH测定、TRH 测试,以进一步确定原发病变在甲状腺、垂体或下丘脑。
现代医学对本病主要采用甲状腺激素的替代疗法、对症疗法等。
本病中医属“虚劳”、“水肿”范畴。
虚劳是指元气亏损、气血不足、脏腑受损所致的慢性疾病,其中以脾肾二虚为多见,表现为面色苍白、表情淡漠、畏寒乏力、毛发稀疏、皮肤干燥、声音嘶哑。
水肿是由于脾气亏虚、水湿停聚、泛滥横逆而成。
肾阳不足则开阖不利,不能化气行水,以致水液停聚,泛滥于肌肤也可形成水肿,可见眼睑浮肿,体重增加,甚至心包胸腔积液等一系列脾肾阳虚症状。
1.[处方名称]张氏甲减方[功能主治](l)方功能温中健脾,扶阳补肾,主治脾肾阳虚型甲状腺机能减退症。
(2)方功能健脾利湿,平肝;主治肝旺脾虚型甲状腺机能减退症。
[处方组成](1)附子6克、干姜3克、肉桂2.l克、党参15克、茶苓9克、白术9克、炙甘草4.5克,水煎服。
Unit3李仕才一、词汇讲解1.flowvi.流;垂;流出;(谈话、文体等)流畅n. 流动~ (ofsth/sb);滔滔不绝;涨潮;连贯vt.使泛滥;淹没;排出【习语】go with the flow(informal) 随大溜to be relaxed and not worry about what you should do2.persuadevt.& vi. 说服;劝说;使相信;使信服persuade sb (into sth/into doing sth)(out of sth/out of doing sth)【近义词辨析】persuade 说服、劝说:I tried to persuade her to see a doctor.我极力劝她去看医生。
convince (~ sb/yourself (of sth)) 使确信、信服:He convinced me he was right.他使我相信他是正确的。
advise 给某人出主意:I will do as you have advised.我会照你说的去做。
3.graduatevi. 渐变;渐渐变为(与 into 连用);渐渐消逝(与 away 连用);取得资格(与 as 连用);vt. 授予学位或毕业证书;从…接受学位;分成等级;标以刻度;n.<美>毕业生;<英>大学毕业生;(已经取得学士学位正在攻读高级学位的)研究生;量筒;adj. <美>毕业了的,研究生的;有(学士)学位的;I have strong education, degree from the university, graduate school and the law school.我有较强的教育,从大学学位,研究生院和法学院。
【派生词】graduationn. 毕业;毕业典礼;刻度,分度;分等级【派生词】gradualadj. 渐进的,渐(升)降的;倾斜度小的;逐次的,逐渐的;平缓的n. 弥撒升阶圣歌;弥撒圣歌集【派生词】graduallyadv. 逐步地,渐渐地;按部就班地;日趋;冉冉4.schedulen. 时刻表,进度表;清单,明细表;预定计划;目录 = timetablevt. 排定,安排~ sth (for sth);将…列表~ sth (assth);为…作目录The meeting is scheduled for Friday afternoon.会议安排在星期五下午。
英语基础写作讲义、写作基本要求①字数(字数不够怎么办)②信息完整③语法可接受④行文连贯⑤词汇与句式多变二、写作规范①标点顿号、’”英语没有顿号,一般用逗号取代。
汉语中用顿号表示一句话中间并列的词和词组之间的停顿。
书名号汉语书名号为《》,表示书籍、报刊等名称。
英语中不用书名号,而是用斜体字表示,以区别于印刷体;但打字或书写时,因没有斜体字,便在书名或刊名下划一横线。
句号英语的句号是是实心的小圆点,即“.”常用于陈述句和祈使句之后。
而汉语的句号是空心圆圈,即。
”。
省略号英语的省略是三个实心的小圆点,位于一行的中间。
②字母大小写(题目应放在第一行的中间,第一个单词的首字母和每一个名词、动词、形容词、副词等的首字母都要大写。
)③选词在写作中特别要注意,不能过多使用过于口语化的词汇,要书面化。
Cool - very good④书写(注意格式)三、写作基本结构框架文章结构:-±-Begi nnin g+Body1+...+Body N+ EndingBody 的结构:Topic sentence+ Supporting sentence+ Concluding sentence段落是文章的基本构成成分,其作用是围绕文章的主题或中心思想从不同角度进行有组织的、逻辑性强的说明或阐述。
段落由一系列围绕同一主题的句子组成。
当新的主题出现时,就应开始新的段落。
段落一般由三部分构成:主题句(topic sentence、支撑句(supporting sentence 或扩展句(developing sentence 和结尾句(concluding sentence。
请看下面的一篇短文:What is a topic sentence?The topic sentence in troduces the paragraph.What does it do?It tells the reader what your paragraph will be about.Example:There are three reasons why I want to learn English. One reas on is that En glish hasbecome an international Ianguage. It is now used by most international compa ni es, in clud ing the compa ny where I work, for bus in ess com muni catio n. Another reason why I want to learn English is so that I can travel to English-speaking countries. The United States,England, Australia and many other countries all use English as their primary Ianguage.Finally, I want to learn English because I plan to move to the U.S. in the future. I willbecome a manager for my compa ny soon. For all these reas on s, I am very excited about lear ning En glish.ANALYSIS:What are you going to tell the reader about?Topic Sentence There are three reas ons why I want to lear n En glish.文章中的第一句就是段落的主题句,顾名思义,段落的主题句是表达该段落主题或中心思想的句子,段落的其他句子都是对该主题句的进一步扩展或论证。
所以,写好主题句往往是写好文章的关键。
在构思主题句时,应注意两个常见的问题,一是主题句太空泛,没有具体内容;二是因一个段落中出现一个以上的主题句而使得段落的中心内容不明确。
段落的主题句一般位于段落的开头,尤其是对议论文更是如此。
同样是这篇文章,我们再来看一下它的支撑句。
Support ing Senten cesWhat are supporting sentences?support ing senten ces come after the topic senten ce, to expla in your topic senten ce. The support ing senten ces with their support ing details make up the body of a paragraph.What do supporting sentences do?They give information to develop and support the main idea of the paragraph.How do I write supporting sentences?You should give in formati on, facts, details, and examples. support ing senten ces ofte n an swer the questi on "Why?"Example:There are three reasons why I want to learn English. One reason is that Englishhas become an international language!! is now used by most internationalcompanies, including the company where I work, for business communication.Another reason why I want to learn English is so that I can travel to English-speaking countries. The United States, England, Australia and many othercountries all use English as their primary Ianguage. Finally, I want to learn Englishbecausel plan to move to the U.S. in the future. I will become a man ager for mycompa ny soon. For those reas on s, I want to lear n En glish.ANALYSIS:Why do you want to learn English?Main point: because En glish has become an intern ati on al la nguage一篇文章要有始有终,到了文章的结束部分,往往会出现结尾句。
Closing Sentence (Conclusion)What is the closing sentence?The clos ing sentence is the last sentence in a paragraph.What does it do?It restates the main idea of your paragraph. It tells the reader what you were writing about.How do I write a closing sentence?Restate the main idea of the paragraph using differe nt words.Example:There are three reasons why I want to learn English. One reason is that English hasbecome an intern ati on al la nguage. It is now used by most intern ati onal compa ni es, in cludi ng the compa ny where I work, for bus in ess commu ni catio n. Ano ther reas on why I want to learn English is so that I can travel to English-speaking countries. The UnitedStates, England, Australia and many other countries all use English as their primary Ianguage. Fin ally, I want to learn En glish because I pla n to move to the U.S. in the future. I will become a manager for my company soon. For all these reasons, I am very excitedabout learning English.ANALYSIS:What did you tell the reader about?Closing Sentence: For all these reas on s, I am very excited about lear ning En glish.ConclusionThis is your last senten ce, therefore the most importa nt. This will be the sentence that is most fresh in the readers' mi nd after they put the paragraph dow n. A good way to form your con clusi on is to reform the introductory paragraph in reverse form. In other words, have the conclusion contain the following, in the order written:Restate your topic senten ce, but in differe nt words tha n before.Close with a gen eral stateme nt that reflects in sight on your topic.四、写作实践①选题(考试一般为任务性写作题目已给出)②拟提纲Outline1首先要理解题目和主题句。