(优选)STAR踝关节置换操作
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:7.29 MB
- 文档页数:87

关节置换术手术流程Joint replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty, is a procedure in which an injured or damaged joint is removed and replaced with an artificial joint, or prosthesis. 关节置换手术,也称为关节成形术,是一种将受伤或受损的关节切除并更换为人工关节或假体的手术。
This surgery is often performed to relieve pain and improve mobility for patients with severe arthritis or joint injuries. 这种手术通常用于缓解严重的关节炎或关节损伤患者的疼痛并改善可动性。
It is commonly performed on the hip or knee, but can also be done on other joints such as the shoulder, elbow, or ankle. 它通常在髋关节或膝关节上进行,但也可以在其他关节如肩关节、肘关节或踝关节上进行。
The process of joint replacement surgery involves several key steps, including preoperative evaluation, the surgical procedure itself, and postoperative recovery and rehabilitation. 关节置换手术的过程涉及几个关键步骤,包括术前评估、手术过程本身以及术后康复和康复。
The first step in the joint replacement surgery process is the preoperative evaluation. 关节置换手术过程中的第一步是术前评估。

全踝关节假体研究进展黄迪超;张弓皓;黄加张;马昕;王旭;张超;陈立;王晨【摘要】目前临床上应用较多的全踝关节假体有Salto、STAR和INBONE假体等.Salto假体是模拟人体正常踝关节解剖结构的活动负载假体,具有较好的生物力学特性,但同时也存在垫片受力不均、并发症较多等问题;STAR假体是三组件活动负载结构假体,兼具稳定性与活动度;INBONE假体是首个采用髓内固定的全踝关节假体,具有较好的稳定性及安装精准性,但亦存在截骨量过多、损伤较大等问题.该文就全踝关节假体研究进展作一综述.【期刊名称】《国际骨科学杂志》【年(卷),期】2017(038)004【总页数】4页(P229-232)【关键词】全踝关节置换;Salto假体;STAR假体;INBONE假体【作者】黄迪超;张弓皓;黄加张;马昕;王旭;张超;陈立;王晨【作者单位】200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科;200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科;200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科;200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科;200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科;200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科;200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科;200040 上海,复旦大学附属华山医院骨科【正文语种】中文自1970 年由法国医生Lord完成首例全踝关节置换术(TAA)以来,TAA已有40余年历史。
随着假体及手术技术的发展,TAA越来越为广大足踝外科医生所青睐,但相比于髋、膝关节置换术,TAA尚不成熟,其在提高假体生存率和减少并发症发生率上还有很大的空间。
自20世纪70年代 Smith 成功设计第一种全踝关节假体以来,全踝关节假体已经历了40余年的发展与改进,假体5年生存率逐渐提高至90%,10年生存率提高至89%[1]。
目前具有代表性的第一代全踝关节假体有Mayo、Newton、Smith假体等,这些假体都需骨水泥固定。

踝关节骨关节炎的治疗进展骨关节炎(OA)是比较常见的关节疾病,因为关节软骨退变和损伤导致关节疼痛和功能障碍,最常见于膝关节和髋关节。
踝关节OA的发病率要比髋膝关节OA低,以创伤性多见,这和髋膝OA大都是原发OA不同,原发性踝关节OA大概占所有OA的13%,但在亚洲人群中发病率相对较高,有研究认为和亚洲一些国家有盘腿坐的习惯有关。
病因和流行病学原发性踝关节OA的发病率不高,大概占世界人口的1%,虽然踝关节OA与膝关节发病机制和进展相似,但踝关节OA70%是足踝部创伤的后遗症。
在一项对踝关节OA的放射学相关横断研究和相关因素研究中,共纳入864例研究对象,其中女性患者68%(非洲裔34%),平均年龄72岁和体重指数(BMI)31kg/m2。
27%的研究对象有放射学2级以上的关节炎,结果提示年龄增长、BMI增加、踝关节外伤病史、临床表现都是踝关节OA的独立因素,其发病率与性别、种族无关。
一项对社区老人踝关节痛和关节炎的回顾性研究发现踝关节痛的发病率11.7%,在放射学上2级以上OA占调查人群的3.4%,女性、50~64岁、从事日常工作和手工劳作的人群有较高的发病率。
下肢力线对关节功能有很大影响,膝关节OA往往存在力线问题,关节置换也往往需要将关节力线矫正,但膝关节的矫正也会导致踝关节后足的柔韧性减少,从而导致踝关节疼痛和骨关节炎的发生。
内翻型膝关节OA在做内侧的撑开截骨后,20%患者会出现踝关节后足新发持续疼痛和不适,膝关节内翻截骨矫正力线后,往往导致HKA角(髋膝踝角)变小,胫骨近端内侧角(MTPA)变大,从而引起胫骨远端外翻(TPI)增大,导致踝关节不适。
踝关节骨折后如果下胫腓联合存在不稳定,术中复位不良很容易导致有临床症状的踝关节OA,有作者对120例踝关节骨折伴有下胫腓不稳定的患者进行研究,发现有13例(11%)患者踝关节出现关节炎。
保守治疗与其他骨关节炎治疗原则一样,踝关节OA同样可以使用非甾体类药物和关节软骨营养药物,另外还包括一些保守治疗,如使用支具和鞋垫等。




第六章踝及膝关节置换术第1节踝关节置换术全踝关节置换术失败后的补救手术第二节膝关节置换术一. 膝关节假体的演变及设计(1) 初期的设计(2) 铰链式假体(3) 双关节间室型假体(4) 三关节间室型假体(5) 限制型髁假体(6) 带半月板型假体(7) 单关节间室型假体(8) 分级系统的概念二. 人工膝关节置换的生物力学运动学(1)膝关节的纵向与旋转对线(2)髌股关节(3)聚乙烯材料(4)假体固定三. 全膝人工关节置换术的适应证与禁忌证(一)三关节间室型膝关节置换术(二)单关节间室型膝关节置换术的适应证与禁忌证(三)髌骨表面置换术的适应证(四)同时或分期行双侧全膝关节置换术的适应证四. 初次全膝关节置换术功能和X线效果评价的效果五. 假体的寿命六. 术前评价七. 初次三关节间室型膝关节置换术的手术方法(1) 麻醉的选择(2) 手术入路(3) 骨准备1. 屈膝-伸膝间隙技术2. 测量截骨方法3. 关节线抬高4. 髓内与髓外对线导向器(4) 韧带平衡1. 内翻畸形2. 外翻畸形3. 屈曲挛缩4. 平衡后十字韧带(5) 骨缺损的处理(6) 髌骨股骨轨迹(7) 假体植入(8) 伤口缝合8. 单髁型膝关节置换术的手术方法9. 术后处理10. 对于特殊问题的手术处理(1) 有胫骨高位截骨史(2) 有髌骨切除史(3) 神经病变性关节病(4) 其它疾病11. 全膝关节置换术的并发症(1) 血栓栓塞(2) 感染治疗全膝关节置换术感染的使用髓内针的关节融合术(3) 髌骨-股骨并发症(4) 血管神经并发症(5) 假体周围骨折12. 全膝人工关节翻修术(1) 首次全膝关节置换术的无菌性失败(2) 翻修的显露(3) 假体的取出(4) 重建的原则(5) 人工膝关节翻修术的效果-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------第一节踝关节置换术随着髋及膝关节置换术的成功,许多外科医生—工程师小组设计和发展了踝关节假体(图6-1)。


TAR total ankle replacement TAA total ankle arthroplasty 全踝关节置换术(PLUS 适应症禁忌症及手术步骤)[原创2010-11-30 12:59:59]患者信息:M/66术前诊断:OA ankle Rt.治疗方案:TARA, Rt.手术医师:professor Chu In Tak(St. Mary's hospital)手术日期: 2010-11-30手术体会:chu教授做踝关节置换手术非常熟练,术中几乎不要截骨定位器。
入路是标准的前入路,他建议从胫前肌腱内侧入路,骨膜分离用手术刀而非骨膜剥离器,他认为这样损伤小。
先在流行的踝关节假体有11种,他所用的假体是法国的Hintegra Sensitive假体,而在教科书上大部分都是讲解利用PE 假体,组件不同手术方式也有不同。
以上3图为术前X线表现手术选择前正中切口胫骨截骨定位器截骨完成后安装试模安装试模后透视胫骨假体组件标签距骨假体组件标签PE垫标签术后拍片所见术后到Catholic University图书馆查阅有关踝关节置换的内容,摘录如下:假体组件Hintegra Sensitive Prosthesistibial component(CoCr)talar component(CoCr)Fixation screws(Titanium alloy)intermediary sliding core(UHMW Polyethylene)适应症Indications:systemic caused arthritis of the ankle(eg. rheumatoid arthritis,hemochromatosis); primary arthritis(eg. degenerative disease);secondary arthritis(eg. posttraumatic,infection,avascular necrosis);salvage for failed total ankle replacement;salvage for non-union and malunion of ankle arthrodesis.禁忌症Contraindications:relative controindications:severe osteoporosis;immunosuppressive therapy;high demanding sport activities(eg.contact sports,jumping);patients with a poor soft tissue envelope;absolute contraindications:active infection;charcot neuroarthropathy;neurologic disease of the lower extremities;advanced peripheral vascular disease;absence of distal leg muscular functionsuspected or documented metal allery or intolerance;avascular necrosis of the talus/tiba of more than1/2;evere malalignment(if not surgically correctale);severe instability;diabetic syndrom最常用的3种假体although there are currently 11 different ankle implants being used throughout the world,attention in the united states has been focused on three second-generation ankle implant devices:Buechel Pappas total ankle repalcement(Endotec, South Orange,NJ,USA)Agility total ankle system (DePuy,Warsaw,IN,USA)scandinavian total ankle replacement(STAR Waldemar-Link,Hamburg,Germany)术前准备preoperative considerations:instability of the ankle often accompanies hindfoot or tibiotalar deformity that necessitates repair or reconstruction of the lateral ligaments during implantation.the condition of the soft tissues envelope is an important preoperative consideration that may influence complications.preoperative evaluation of plain films,MRI, and CT scan can be used for evaluation of ankle deformity.手术步骤Surgical technique1.the patient is operated with spinal or general anesthesia;2.the patient is placed on the operating table in the supine position with a sandbag placed under the ipsilateral hip;3.a well-padded thigh tourniquet is used for hemostatic control;4.the leg is surgically prepped and draped above the knee;5.an anterior midline incision is centered over the ankle joint extending 10-13cm in length between the anterior tibial and extensor hallucis longus tendons;6.the incision is carried through to the subcutaneous tissues, being careful to identify and protect the superficial peroneal nerve;7.the extensor retinaculum is incised between the tendons of the anterior tibialis and the extensor hallucis longus;it is advisable to place a suture tag along the retinaculum on either side;8.a deep incision is made through this space incising the ankle capsule down to the the tibial periosteum;9.the osteophytes must be removed with bone cutters and rongeurs to expose the joint,next medial and lateral subperiosteal elevation provides exposure of the anterior ankle joint and the neck of the talus.the surgeon must be able to visualize the medial and lateralgutter and proximal tibial surface approximately 4.0 cm above the level of the joint.distally exposure must provide visualization of the talar body and neck;10.tibial preparation11.preparation of the talus.ponent sizing.13.final component implantaton14.closure:a final radiographic exam is performed to ensure proper size and placement of the components.motion of the ankle joint is evaluated again to assure adequate dorsiflexion.the wound is closed over a hemovac drain using nonabsorbable ethibond suture to close the ankle joint capsule and the extensor retinaculum.absorbable sutures are used to close the subcutaneous layers and the skin is closed with 4-0 nylon sutures;15. the surgical site is infiltrated with plain, long acting local anesthesia;16.after a sterile surgical dressing is placed, a well padded below the kness fiberglass splint is placed to maintain the ankle joint at 90 degrees.17. the tourniquet is released and vascular status evaluated, the tourniquet time should not exceed two hours.术后处理:石膏固定4周第五周:双拐部分负重,活动踝关节第六周:单拐部分负重第七周:不用拐杖负重。
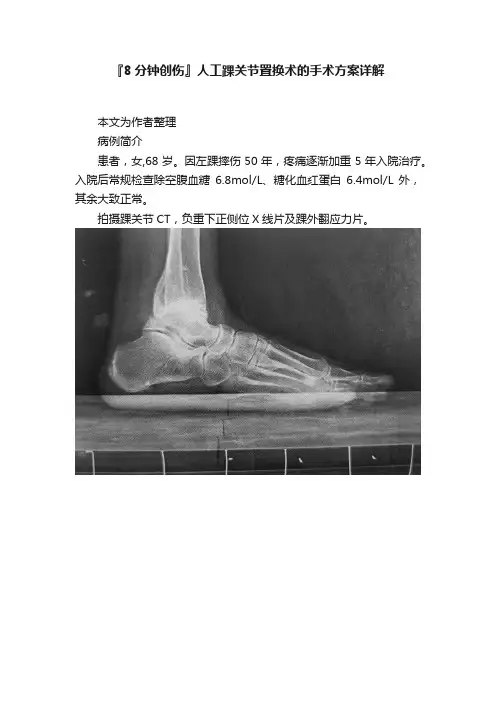
『8分钟创伤』人工踝关节置换术的手术方案详解本文为作者整理病例简介患者,女,68岁。
因左踝摔伤50年,疼痛逐渐加重5年入院治疗。
入院后常规检查除空腹血糖6.8mol/L、糖化血红蛋白6.4mol/L外,其余大致正常。
拍摄踝关节CT,负重下正侧位X线片及踝外翻应力片。
A:踝关节负重侧位片示创伤性关节炎B:正位X线片示距骨内翻15°畸形,踝创伤性关节炎C:矢状面CT示距骨内翻畸形,踝关节周围增生等D:踝外翻应力像,距骨内翻畸形改善不明显入院诊断:①踝关节创伤性关节炎(左);②踝关节骨折(左,陈旧);③糖尿病(2型)。
手术指征的选择•患者为高龄女性,踝关节创伤性关节炎较严重疼痛剧烈,距骨内翻畸形约15°;踝关节活动度:背伸5°,跖屈15°;无距骨缺血坏死及足踝部肌力失衡,无严重的骨质疏松。
A:正位X线片示距骨内翻15°畸形,踝创伤性关节炎B:矢状面CT示距骨内翻畸形,踝关节周围增生•患者有明确人工踝关节置换手术指征。
糖尿病病情控制较好,未见明显手术禁忌。
•患者为高龄知识分子,常年受踝关节疼痛困扰,踝关节创伤性关节炎严重。
•患者在细致了解踝关节融合术及置换术之优缺点后,实际接触了数例人工踝关节置换术后患者,遂坚决要求选择人工踝关节置换术。
术前计划•患者有常年形成的踝关节内翻畸形,应在术中通过距骨顶截骨方法纠正足踝力线。
•我们考虑患者在此位置上负重已40年,如平行距骨关节面截骨,会造成距下关节软组织失衡反而引起疼痛。
术中还应注意避免截骨不慎所造成的内、外踝骨折。
•针对糖尿病病史,应在围手术期采用控制血糖,预防应用抗生素等方法避免感染。
手术技巧•患者采用连续硬膜外麻醉,平卧位,将患侧(左侧)臀部垫高20°,标记出足背动脉走行。
•取踝关节前方纵弧形切口,暴露踝关节并清理内外踝、前踝及距骨周围的增生骨赘。
▲切口位置:自踝上6cm经踝关节中点,沿第2跖骨方向止于距舟关节水平•在胫骨远端前方安装胫骨截骨板及定位杆,截取胫骨远端5mm 之关节面。

踝关节置换术的治疗及护理方法发表时间:2016-05-12T11:22:08.637Z 来源:《心理医生》2015年17期供稿作者:毕娜[导读] 黑龙江省大庆让胡路铁路医院目前认为接受踝关节置换术大多是关节畸形、关节破坏、关节功能丧失、股骨头坏死等患者。
毕娜(黑龙江省大庆让胡路铁路医院黑龙江大庆 163712)【摘要】目的:本文旨在分析和总结踝关节置换术的治疗及护理方法,以便形成文本材料,为以后的治疗提供可行的依据。
方法:回顾性分析我院2014年1月~2015年3月收治患者,随机选取45例,通过对接受踝关节置换术患者的的治疗及其护理方法的记录,进行分析和总结经验。
结果:患者通过手术及护理大部分都已痊愈。
并发症:局部疼痛、伤口感染和愈合不良最为常见。
结论:对于接受踝关节置换术的患者来说,经过精密的治疗和守护精心的护理,绝大部分患者是完全可以治愈的。
【关键词】踝关节;置换术;并发症;护理【中图分类号】R472 【文献标识码】B 【文章编号】1007-8231(2015)17-0153-02目前认为接受踝关节置换术大多是关节畸形、关节破坏、关节功能丧失、股骨头坏死等患者,由于各种原因导致了他们的关节发生了结构上的改变后单纯使用药物治疗是不可取的,因为药物只能部分缓解疼痛症状除急性感染性疾病,所以采用人工关节置换手术。
已达到缓解疼痛、稳定关节、矫正畸形和改善关节功能使原来僵硬、活动受限的关节能够恢复关节的正常功能[1]。
1.临床资料1.1 一般资料选择于2014年1月至2015年3月在本院住院的45例患者为研究对象。
其中男性患者为15例,女性患者为30例。
年龄范围是45~65岁,平均年龄是45.6岁。
1.2 治疗及结果1.2.1手术方法:患者仰卧位,取踝关节前方纵形弧切口,自踝上10cm经踝关节中点沿向第1 跖骨,显露踝关节的同时注意保护血管神经。
胫骨远端安置选定的5mm的SIZER连接的胫骨截骨板,定位于固定于平行胫骨前脊中线上。
踝关节置换的截骨和假体安装宁波市第一医院骨科浙江大学宁波医院宁波市骨科研究所(315010)毛宾尧踝关节截骨是人工踝关节置换成功的第一环节,接下来,假体正确安装(STAR)则是第二个重点,其重要性不言而谕。
目前,由于我国只有STAR假体在各地应用,其安装工具的局限性,乃至改进后第二套工具(SBi)也未见得有若干新意,但切骨乃至安装假体,还必须遵循沿革和些许不可轻怠的程序,方可使手术成功并稳定疗效【1,2】。
一、截骨是基础,截骨尽量要少当然,适应证确认、术前准备、假体型号(大小)的选择,无疑是不能轻视的,但截骨,是不可稍有懈怠的环节,是人工踝关节的基础中的基础【1-3】,若稍有疏失,造成假体安装困难,甚至安装失败,或安装不上去,留下关键性遗憾【3,4】。
1.胫骨远端二个切骨面(1)先作内踝切骨面:根据术者判断,该踝关节大小和内、外踝发育状况和完善程度,确定先作内踝切骨:依标杆和切骨导板指示,切除胫骨远端和穹窿顶在内的软骨和软骨下骨成一个平面之前,先切内踝内侧关节面,使与预计切除胫骨穹窿部水平面成90°相交【2,4】。
切除软骨与软骨下骨厚度约3mm,面积约12×17mm2。
若先切胫骨穹窿部,则电动摆锯虽在胫骨截骨导引器限宽框内切骨,摆锯的震击仍有可能造成术中并发症—内踝骨折【2,3】。
笔者77例中3例术中踝部骨折,其中2例内踝骨折,1例外踝骨折。
因此,把握好切骨顺序,可使术中踝部骨折减少,后期笔者无一例发生。
Wood (2003)报告术中踝部骨折4例(足)【4】;Coester, Saltzman和Leupoid 等【5】(2001)报道6例术中踝部骨折;Giannini, Leardini等等【6】(2001) (2000)报道5例术中踝部骨折。
因此,认为踝部骨折是常见术中并发症,但是如何完全避免发生,正是一个重要课题【1,2,4-7】。
1(2)再切胫骨远端穹窿部紧贴胫骨切骨导板下缘,作垂直于胫骨纵轴线的水平面,将胫骨远端连带穹窿部切除至少3~4mm, 多切不宜。