利用多点地质统计学方法模拟岩相分布
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:359.95 KB
- 文档页数:5


多点地质统计学原理、方法及应用概述及解释说明1. 引言1.1 概述本文旨在探讨多点地质统计学的原理、方法及应用,为读者提供一个全面了解该领域的概述。
多点地质统计学是一门研究如何有效地利用多变量数值以及空间数据进行地质分析和预测的学科。
它通过综合多种数据,包括物理测量数据、遥感图像数据和野外调查数据等,来实现对不同地质现象和过程的建模与研究。
1.2 文章结构本文按照以下结构组织内容:首先介绍多点地质统计学的基本原理,包括其定义与概念、基本假设以及原理解释。
随后,针对多点地质统计学的方法进行详细阐述,探讨数据收集与预处理、变量选择和缺失值处理以及统计模型拟合与优化算法应用等关键步骤。
接下来,我们将通过具体案例研究来展示多点地质统计学在矿产资源评估与勘探、地下水资源管理与保护以及石油勘探与开发中的应用实践。
最后,在结论部分对全文进行概括总结,并展望未来多点地质统计学研究的发展方向。
1.3 目的本文旨在全面介绍多点地质统计学的原理、方法及应用,以帮助读者对该领域有一个清晰的认识。
通过阐述基本原理和方法,读者可以了解多点地质统计学在地质分析和预测中的重要性。
此外,通过具体案例的引入,读者将能够更好地理解多点地质统计学在实际问题中的应用价值和潜力。
最后,通过对未来研究方向的展望,读者可以获得一些启示,并为自己在该领域开展研究提供参考。
2. 多点地质统计学原理2.1 定义与概念多点地质统计学是一种广泛应用于地质科学领域的统计学方法。
它通过对多个地点上的地质数据进行收集、分析和解释,旨在揭示地下资源的分布规律和空间变异性。
多点地质统计学基于一系列假设和方法,能够提供可靠的预测结果和决策依据。
2.2 基本假设在多点地质统计学中,存在几个基本假设:- 空间自相关假设:相邻位置上的地质现象存在关联性,即一个位置的观测值可能受到相邻位置观测值的影响。
- 空间平稳假设:在整个研究区域内,不同位置上的地质变量具有类似的变异性。

断块油气田2012年9月断块油气田FAULT -BLOCK OIL &GAS FIELD 由两点到多点的地质统计学储层建模陈培元1,姜楠1,杨辉廷1,刘学利2(1.西南石油大学资源与环境学院,四川成都610500;2.中国石化西北油田分公司,新疆乌鲁木齐830011)基金项目:“十二五”国家科技重大专项“大型油气田及煤层气开发”子课题“塔里木盆地大型碳酸盐岩油气田勘探开发示范工程”(2011ZX05049-04)摘要传统的两点地质统计学建模方法,以象元为空间赋值单元、变差函数为工具建立确定性的模型,或者应用各种随机模拟方法建立可选的模型,在精确表征复杂的空间结构及目标体几何形态方面有一定的局限性。
有别于两点地质统计学的多点地质统计学,可有效地解决更广泛的地质模拟问题。
然而,在实际应用过程中,受岩-相模型及与之相对应的训练图像可靠性的影响,结果变得比较复杂。
因此,选择合适的训练图像及恰当的算法可有助于提高储层建模的精度和效率。
以××油田曲流河沉积为例,采用两点和多点统计学方法构建模型。
对比发现,基于多点地质统计学的地质建模方法真实可再现河流相的沉积形态,还降低随机建模的不确定性。
尽管模拟结果与井点真实数据之间存在误差,但通过调整随搜索半径、训练图像大小及概率计算中临近点个数限制,可显著提高模型精度。
关键词两点地质统计学;多点地质统计学;储层;随机模拟中图分类号:TE319文献标志码:A收稿日期:2012-04-01;改回日期:2012-07-10。
作者简介:陈培元,男,1984年生,博士,主要从事油藏描述和油藏地质建模研究。
E -mail :swpua409@ 。
引用格式:陈培元,姜楠,杨辉廷,等.由两点到多点的地质统计学储层建模[J ].断块油气田,2012,19(5):596-599.Chen Peiyuan ,Jiang Nan ,Yang Huiting ,et al.Reservoir stochastic modeling using geostatistics from two -point to multiple -point [J ].Fault -Block Oil &Gas Field ,2012,19(5):596-599.Reservoir stochastic modeling using geostatistics from two -point to multiple -pointChen Peiyuan 1,Jiang Nan 1,Yang Huiting 1,Liu Xueli 2(1.School of Resources and Environment,Southwest Petroleum University,Chengdu 610500,China;2.Northwest Oilfield Company,SINOPEC,Urumqi 830011,China)Abstract:Conventional two -point geostatistics modeling mainly uses the pixel -based method and variogram to establish the deterministic model,or uses all kinds of stochastic simulation methods to establish optional model.But it can not fully reflect the variability of the space structure and geometric shape of object.Unlike the two -point geostatistics,the multiple -point geostatistics can solve the problems of geologic simulation widely.In actual application process,due to the lithofacies and the reliability of corresponding training image,it is necessary choosing the suitable training image and appropriate algorithm to improve the accuracy and efficiency of simulation.Taking the meandering river sedimentation of some oilfield as an example,the reservoir model is built by two -point and multiple -point geostatistics parison results of two models show that the method based on the multiple -point not only represents the real sedimentary form of fluvial facies,but also reduces the uncertainty of stochastic modeling effectively and improves the modeling accuracy at maximum.Although the simulation results do not agree with the real well date completely,the prediction accuracy can be improved through adjusting the search radius,the size of training image and the number limit of nearest -neighbor points used in probability calculation.Key words:two -point geostatistics;multiple -point geostatistics;reservoir;stochastic simulation近年来,随着储层建模技术的不断发展,人们对储层地质模型的要求越来越高。

储层多点地质统计学随机建模方法摘要:多点地质统计学使用训练图像代替变差函数,将更多的地质资料整合到储层建模过程中,使得最终模型更加符合地质认识。
随着研究的不断深入,越来越多的地质工作人员开始熟悉这一方法,凭借自身的独特优势,多点地质统计学将在储层建模领域占得重要的一席。
关键词:多点地质统计学训练图像储层建模一、多点地质统计学与训练图像基于变差函数的传统地质统计学随机模拟是目前储层非均质性模拟的常用方法。
然而,变差函数只能建立空间两点之间的相关性,难于描述具有复杂空间结构和几何形态的地质体的连续性和变异性。
针对这一问题,多点地质统计学方法应运而生。
该方法着重表达空间中多点之间的相关性,能够有效克服传统地质统计学在描述空间形态较复杂的地质体方面的不足。
多点地质统计学的基本工具是训练图像,其地位相当于传统地质统计学中的变差函数。
对于沉积相建模而言,训练图像相当于定量的相模式,实质上就是一个包含有相接触关系的数字化先验地质模型,其中包含的相接触关系是建模者认为一定存在于实际储层中的。
二、地质概念模型转换成图像训练地质工作人员擅于根据自己的先验认识、专业知识或现有的类比数据库来建立储层的概念模型。
当地质工作人员认为某些特定的概念模型可以反映实际储层的沉积微相接触关系时,这些概念模型就可以转换或直接作为训练图像来使用。
利用训练图像整合先验地质认识,并在储层建模过程中引导井间相的预测,是多点地质统计学模拟的一个突破性贡献。
可以将训练图像看作是一个显示空间中相分布模式的定量且直观的先验模型。
地质解释成果图、遥感数据或手绘草图都可以作为训练图像或建立训练图像的要素来使用。
理想状态下,应当建立一个训练图像库,这样一来建模人员就可以直接选取和使用那些包含目标储层典型沉积模式的训练图像,而不需要每次都重新制作训练图像。
三、多点模拟原理进行多点模拟,需要使用地质统计学中的序贯模拟。
但是,多点模拟与传统的基于变差函数的两点模拟是不同的。



复杂断块油藏的三维地质建模方法--以国外某油田为例金春玉;宋扬【摘要】随着油气勘探开发的不断深入,一些具有复杂断块构造特征的油藏已逐渐成为开发的主体目标。
建立精准的复杂断块油藏三维地质模型对指导油田开发有着重要的意义。
三维地质建模技术能够更细致、准确地研究地下的油藏,为油藏的后续开发提供可靠的地质依据。
以国外某油田断块构造发育区块为研究对象,针对研究区地质条件复杂、断层发育的特点,以地质、地震、测井资料为基础,搭建构造框架模型,应用地质统计学理论建立储层岩相及物性参数模型,揭示构造和储层空间分布特征,最终建立一个三维定量的油藏地质模型,在储层计算中各断块误差均小于5%,符合精度要求。
该模型将为该区块数值模拟和井位设计等后续工作提供可靠的地质依据,同时也为同类复杂断块油藏的三维地质建模提供借鉴。
%With the development of oil and gas exploration,some complex fault-block reservoirs have be-come the main objective.3D geologic modeling of complex fault-block reservoirs is an important significance to guide oilfield development.Study on underground reservoirs,3D geologic modeling technology is more particular and accurate,which supplies reliable data for future development.Study on an overseas oilfield which has the complex fault-block,the geologic condition of the complex fault-block is complex.Based on geological,seismic and logging data,the structural modeling had been built.The lithofacies modeling and physical property modeling had been built by geostatistics theory which reveal the structural attitude and spatial distribution.3D geologic modeling of the block had been built at last.The results showed that the reserves error ofthese fault-blocks were within 5%,which meet the requirement.The 3D geologic modeling of the block will provide reliable geological basis forthe numerical simulation and the location and so on, and provide some useful reference for 3D geologic modeling technology of similar complex fault-block res-ervoirs.【期刊名称】《河北联合大学学报(自然科学版)》【年(卷),期】2015(000)001【总页数】6页(P15-20)【关键词】地质建模;复杂断块;构造模型【作者】金春玉;宋扬【作者单位】河北联合大学,河北唐山 063009;大庆油田有限责任公司勘探开发研究院,黑龙江大庆 163712【正文语种】中文【中图分类】TE12随着油气勘探开发的不断深入,一些具有复杂断块构造特征的油藏已逐渐成为开发的主体目标。

第44卷 第5期 新 疆 石 油 地 质Vol. 44,No.52023年10月 XINJIANG PETROLEUM GEOLOGY Oct. 2023文章编号:1001-3873(2023)05-0554-08 DOI :10.7657/XJPG20230506苏里格气田致密砂岩气藏剩余气分布特征及其挖潜石耀东1,王丽琼1,臧苡澄2,张吉1,3,李鹏2,李旭1(1.中国石油 长庆油田分公司 第四采气厂,内蒙古 鄂尔多斯 017300;2.中国石油 长庆油田分公司 勘探开发研究院,西安 710018;3.低渗透油气田勘探开发国家工程实验室,西安 710018)摘 要:苏里格气田中区苏36-11区块已开发17年,开发程度和储量动用程度均高,储集层非均质性强,储量动用不均衡,剩余气分布复杂,剩余气分布的确定及挖潜是气田稳产的关键。
通过储集层构型精细表征,明确剩余气分布的主要影响因素,确定不同类型剩余气分布规律,提出对应的挖潜对策。
研究结果表明:研究区含气砂体主要分布在4级构型单元心滩坝与点坝中,整体规模小,宽度为150~500 m ,长度为300~800 m ,连通性差,受各级次渗流屏障影响大,区块北东—南西向主砂带开发程度最高,地层压力低,剩余气主要分布在区块西北部盒8段下亚段;剩余气分布主要受储集层非均质与开采非均匀影响,可分为井网未控制型、复合砂体阻流带型、水平井未动用次产层型、直定向井未射开气层型和投产未采出型5类;提出井间加密、老井侧钻、查层补孔和老井挖潜4种动用措施,调整方案后,预测可稳产7年,采收率可达45%。
关键词:苏里格气田;致密砂岩;储集层构型;剩余气储量评价;剩余气分布;挖潜对策;开发中—后期;开发调整方案中图分类号:TE122 文献标识码:A©2018 Xinjiang Petroleum Geology. Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License 收稿日期:2022-11-12 修订日期:2023-04-13基金项目:国家科技重大专项(2016ZX05050);中国石油科技重大专项(2016E-0509)第一作者:石耀东(1973-),男,陕西靖边人,高级工程师,气田开发与生产管理,(Tel )************(E-mail )syd_cq@通讯作者:王丽琼(1989-),女,甘肃华池人,高级工程师,硕士,油气田开发,(Tel )************(E-mail )wangliqiong12_cq@petrochina..Distribution and Potential Tapping Strategies of Remaining Gasin Tight Sandstone Gas ReservoirsSHI Yaodong 1,WANG Liqiong 1,ZANG Yicheng 2,ZHANG Ji 1,3,LI Peng 2,LI Xu 1(1.No.4 Gas Production Plant, Changqing Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Ordos, Inner Mongolia 017300, China;2.Research Institute of Exploration and Development, Changqing Oilfield Company, PetroChina, Xi ’an, Shaanxi 710018, China ;3.National Engineering Laboratory for Exploration and Development of Low Permeability Oil and Gas Fields, Xi ’an, Shaanxi 710018, China )Abstract :The Su 36⁃11 block in the central area of Sulige gas field has been developed for 17 years, with high degrees of development and reserves producing. The strong reservoir heterogeneity in this block leads to uneven producing of reserves and complex distribution of re⁃maining gas. Distribution determination and potential tapping of the remaining gas are crucial for maintaining stable production in the gas field. By accurately characterizing the reservoir architecture, the main factors influencing remaining gas distribution were identified, the distribution patterns of different types of remaining gas were determined, and corresponding strategies for recovering the remaining gas were proposed. The research results show that the gas⁃bearing sand bodies in the study area are mainly distributed in the 4th⁃order architec⁃ture units, such as channel bar and point bar, these sand bodies are significantly affected by various levels of flow barriers, with small over⁃all scale, poor connectivity, width of 150-500 m and length of 300-800 m. The main NE⁃SW sand belt in the block has been developed the most, with low formation pressure, and the remaining gas is mainly distributed in the lower He 8 member in the northwestern part of the block. Remaining gas, whose distribution is mainly influenced by reservoir heterogeneity and uneven development, can be divided into five types: gas uncontrolled by well pattern, gas in composite sand body flow barrier, gas in secondary pay zone unexploited by horizontal well, gas in unperforated gas⁃bearing layer in vertical well, and gas unproduced. Four potential tapping measures were proposed, including well infilling, reperforation, sidetracking and potential tapping in exsisting wells. According to the adjusted development plan, it is predicted that stable production can be maintained for 7 years with the recovery efficiency reaching 45%.Keywords :Sulige gas field; tight sandstone; reservoir architecture; remaining gas reserves evaluation; remaining gas distribution; potential tapping; middle-late development stage; adjusted development plan中国致密气资源总量及开发潜力巨大,约占全球资源量的十分之一,主要分布在鄂尔多斯盆地、四川盆地、塔里木盆地等区域。
多点地质统计学Multiple-point geostatistic是相对于传统的两点地质统计学而言的,主要应用于储层表征与建模中.传统的地质统计学在储层建模中主要应用于两大方面:其一,应用各种克里金方法建立确定性的模型,这类方法主要有简单克里金、普通克里金、泛克里金、协同克里金、贝叶斯克里金、指示克里金等;其二,应用各种随机建模的方法建立可选的、等可能的地质模型,这类方法主要有高斯模拟(如序贯高斯模拟)、截断高斯模拟、指示模拟(如序贯指示模拟)等。
上述方法的共同特点是空间赋值单元为象元(即网格),故在储层建模领域将其归属为基于象元的方法。
这些方法均以变差函数为工具,亦可将其归属为基于变差函数的方法。
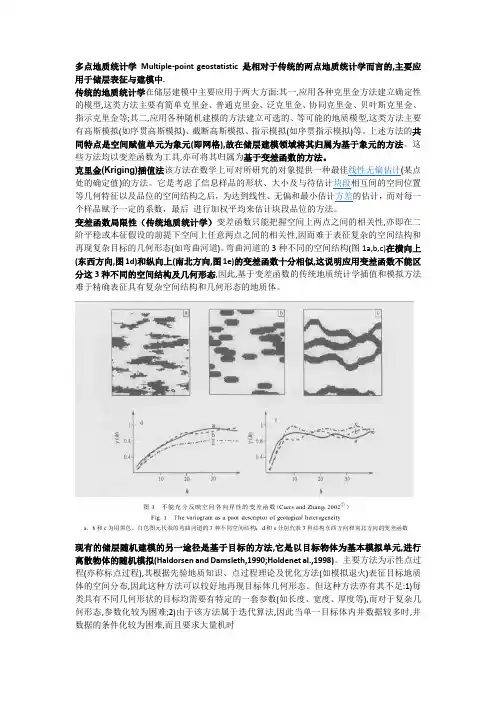
变差函数局限性(传统地质统计学)变差函数只能把握空间上两点之间的相关性,亦即在二阶平稳或本征假设的前提下空间上任意两点之间的相关性,因而难于表征复杂的空间结构和再现复杂目标的几何形态(如弯曲河道)。
弯曲河道的3种不同的空间结构(图1a,b,c)在横向上(东西方向,图1d)和纵向上(南北方向,图1e)的变差函数十分相似,这说明应用变差函数不能区分这3种不同的空间结构及几何形态,因此,基于变差函数的传统地质统计学插值和模拟方法难于精确表征具有复杂空间结构和几何形态的地质体。
现有的储层随机建模的另一途径是基于目标的方法,它是以目标物体为基本模拟单元,进行离散物体的随机模拟(Haldorsen and Damsleth,1990;Holdenet al.,1998)。
主要方法为示性点过程(亦称标点过程),其根据先验地质知识、点过程理论及优化方法(如模拟退火)表征目标地质体的空间分布,因此这种方法可以较好地再现目标体几何形态。
但这种方法亦有其不足:1)每类具有不同几何形状的目标均需要有特定的一套参数(如长度、宽度、厚度等),而对于复杂几何形态,参数化较为困难;2)由于该方法属于迭代算法,因此当单一目标体内井数据较多时,井数据的条件化较为困难,而且要求大量机时2多点地质统计学的基本概念多点统计学着重表达多点之间的相关性。


多点地质统计学python -回复"多点地质统计学python"是一种基于Python编程语言的地质统计学方法,它通过使用多点统计技术来分析地质数据和建立地质模型。
多点地质统计学python可以用于地质建模、矿产资源评估、油气勘探等地质领域。
本文将逐步介绍多点地质统计学python的基本原理、数据处理步骤以及应用案例。
第一步:理解多点地质统计学的基本原理多点地质统计学是一种从多个样本点中提取信息进行推断的统计学方法,它考虑了地质数据在空间上的相关性和变异性。
这种方法的基本原理是通过对多个样本点进行统计分析,揭示地质变量的分布和空间结构。
多点地质统计学方法在地质学领域得到广泛应用,可以实现对地质数据的建模和预测。
第二步:了解多点统计技术在python中的实现Python是一种功能强大且易于使用的编程语言,具有丰富的数据处理和分析库,例如NumPy、Pandas和Matplotlib等。
这些库提供了处理大型地质数据集和执行统计分析的工具。
在python中,可以使用这些库来实现多点地质统计学方法,例如多点统计算法、样本点选择和空间变异性分析等。
第三步:处理地质数据集在使用多点地质统计学python之前,首先需要准备一个地质数据集。
这个数据集包含了地质变量的观测值,例如地层厚度、属性值或矿石品位等。
地质数据集通常以表格形式存储,可以使用Pandas库将数据导入到python环境中进行处理。
第四步:分析地质数据集在有了地质数据集之后,可以使用多点地质统计学python来分析数据。
首先,可以使用NumPy库计算地质数据的统计指标,例如均值、方差和协方差等。
这些统计指标可以用来揭示地质变量的中心趋势和空间关系。
接下来,可以使用多点统计算法来分析地质数据的变异性和空间结构。
其中,常见的多点地质统计学方法包括变差函数、半变异函数和变异权重等。
这些方法可以用来评估地质数据的变异性,并揭示地质变量之间的空间关联性。
尼日尔三角洲盆地重力流沉积模式及储层特征——以AKPO油田为例卜范青;张旭;陈国宁【摘要】通过取芯、分析化验、扫描电镜等资料分析,对尼日尔三角洲的岩石学特征、沉积特征及储层的主控因素进行了研究.结果表明:研究区储层以石英砂岩为主,长石质石英砂岩和岩屑质石英砂岩次之;主要发育水道和朵叶体系,其中水道体系可细分为主水道、砂质天然堤、泥质天然堤、底部滞留沉积;朵叶体系细分为朵叶主体、朵叶侧缘,两者共同由14种岩相类型组成.建立了西非重力流沉积微相的岩相组合模版,提出了重力流复合水道和复合朵叶的沉积模式;明确了储层演化的影响因素.%The petrological characteristics,sedimentary characteristics and main reservoir controlling factors of Niger delta were studied according to the analysis of core,testing,SEM data. It is shown that,the reservoir of the study area is mainly quartz sandstone,and sec-ondarily feldspathic quartz sandstone and lithic quartz sandstone. Channel and lobe systems developed in the delta. The channel system can be subdivided into main channel,sandy natural levee,muddy natural levee and bottom retained deposit microfacies,and the lobe system is subdivided into lobe body and lobe fringe microfacies. The channel and lobe systems are composed of 14 kinds of lithofacies. A lithofacies assemblage template of the West African gravity flow sedimentary microfacies is established,and the sedimentary modes of deepwater channel complex and deepwater lobe complex in West Africa are proposed. The influencing factors of reservoir evolution are clarified.【期刊名称】《西安石油大学学报(自然科学版)》【年(卷),期】2017(032)001【总页数】7页(P64-70)【关键词】尼日尔三角洲;AKPO油田;深水重力流;岩石类型;沉积模式【作者】卜范青;张旭;陈国宁【作者单位】中海油研究总院,北京100027;中海油研究总院,北京100027;中海油研究总院,北京100027【正文语种】中文【中图分类】TE122.1卜范青,张旭,陈国宁.尼日尔三角洲盆地重力流沉积模式及储层特征:以AKPO油田为例[J].西安石油大学学报(自然科学版),2017,32(1):64-70.BU Fanqing,ZHANG Xu,CHEN Guoning.Gravity flow depositional mode and reservoir characteristics of Niger Delta Basin:taking AKPO Oilfield as an example [J].Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University (Natural Science Edition),2017,32(1):64-70.尼日尔三角洲盆地位于非洲大陆西部,盆地主体位于尼日利亚陆上、近海和大陆架海域,对该盆地已进行了60年的勘探开发工作,油气资源十分丰富,目前乃至未来很长时间内深水区的勘探开发仍是广泛关注的热点。
石油天然气勘探开发标准第1章勘探准备与地质调查 (4)1.1 勘探前期资料收集与分析 (4)1.1.1 资料收集范围与内容 (4)1.1.2 资料分析方法 (4)1.2 地质调查与评价 (5)1.2.1 地质调查内容 (5)1.2.2 地质评价方法 (5)1.3 勘探目标确定与设计 (5)1.3.1 勘探目标确定 (5)1.3.2 勘探设计 (5)第2章物探技术与数据处理 (6)2.1 物探方法选择与数据采集 (6)2.1.1 物探方法选择 (6)2.1.2 数据采集 (6)2.2 数据处理与解释 (6)2.2.1 数据处理 (6)2.2.2 数据解释 (7)2.3 物探成果评价与应用 (7)2.3.1 物探成果评价 (7)2.3.2 物探成果应用 (7)第3章钻井与完井技术 (7)3.1 钻井工程设计 (7)3.1.1 设计原则与要求 (7)3.1.2 设计内容 (7)3.1.3 设计步骤 (7)3.2 钻井液与固井 (8)3.2.1 钻井液体系 (8)3.2.2 固井设计 (8)3.3 钻井过程监测与控制 (8)3.3.1 钻井参数监测 (8)3.3.2 井控技术 (8)3.4 特殊钻井工艺与技术 (8)3.4.1 侧钻井技术 (8)3.4.2 水平钻井技术 (8)3.4.3 大位移钻井技术 (9)3.4.4 超深井钻井技术 (9)第4章试油试气与储量评价 (9)4.1 试油试气工艺 (9)4.1.1 试油试气目的 (9)4.1.2 试油试气方法 (9)4.1.3 试油试气工艺流程 (9)4.2 储量参数测定与计算 (9)4.2.1 地质储量参数 (9)4.2.2 可采储量参数 (10)4.2.3 储量分类与评价标准 (10)4.3 储量评价与报告编制 (10)4.3.1 储量评价方法 (10)4.3.2 储量评价结果分析 (10)4.3.3 储量报告编制 (10)4.3.4 储量报告审查 (10)第5章开发方案设计与优化 (10)5.1 开发地质研究 (10)5.1.1 地质条件分析 (10)5.1.2 油气藏评价 (10)5.1.3 油气藏模拟 (10)5.2 开发方案设计 (10)5.2.1 开发原则 (10)5.2.2 开发方式 (11)5.2.3 开发井网设计 (11)5.2.4 开发参数优化 (11)5.2.5 设备与工艺选择 (11)5.3 开发试验与评价 (11)5.3.1 开发试验 (11)5.3.2 开发效果评价 (11)5.3.3 经济效益评价 (11)5.4 开发方案优化与调整 (11)5.4.1 优化依据 (11)5.4.2 优化方向 (11)5.4.3 调整措施 (11)5.4.4 动态监测与调整 (11)第6章油气田生产与动态分析 (12)6.1 油气田生产管理 (12)6.1.1 生产计划与调度 (12)6.1.2 生产过程监控 (12)6.1.3 生产安全管理 (12)6.1.4 生产成本控制 (12)6.2 生产数据分析与处理 (12)6.2.1 数据采集与传输 (12)6.2.2 数据处理与分析 (12)6.2.3 生产趋势预测 (12)6.3 动态监测与评价 (12)6.3.1 动态监测技术 (12)6.3.2 油气藏评价 (13)6.3.3 生产效果评价 (13)6.4.1 生产参数优化 (13)6.4.2 生产工艺改进 (13)6.4.3 生产组织与管理优化 (13)6.4.4 应急预案制定与实施 (13)第7章油气藏改造与提高采收率 (13)7.1 油气藏改造技术 (13)7.1.1 酸化技术 (13)7.1.2 压裂技术 (13)7.1.3 挤压技术 (14)7.1.4 油气藏改造工艺优化 (14)7.2 提高采收率方法与工艺 (14)7.2.1 化学驱油技术 (14)7.2.2 热力驱油技术 (14)7.2.3 气体驱油技术 (14)7.2.4 微生物驱油技术 (14)7.3 改造效果评价与分析 (14)7.3.1 采收率评价方法 (14)7.3.2 改造效果影响因素分析 (15)7.3.3 经济效益评估 (15)7.3.4 环境影响评估 (15)第8章环保与安全 (15)8.1 环境保护措施与实施 (15)8.1.1 环境保护原则 (15)8.1.2 环境保护措施 (15)8.1.3 环境保护实施 (15)8.2 安全生产与应急预案 (16)8.2.1 安全生产原则 (16)8.2.2 安全生产措施 (16)8.2.3 应急预案 (16)8.3 环保与安全监测 (16)8.3.1 环保监测 (16)8.3.2 安全监测 (16)8.3.3 监测数据应用 (16)第9章节能与减排 (16)9.1 节能技术与应用 (16)9.1.1 节能技术概述 (17)9.1.2 节能技术应用 (17)9.2 减排措施与实施 (17)9.2.1 减排措施概述 (17)9.2.2 减排措施实施 (17)9.3 节能与减排效果评价 (18)9.3.1 评价指标 (18)9.3.2 评价方法 (18)第10章石油天然气勘探开发信息管理 (18)10.1 信息采集与处理 (18)10.1.1 信息采集原则 (18)10.1.2 信息采集方法 (18)10.1.3 信息处理技术 (18)10.2 数据库建设与管理 (18)10.2.1 数据库设计 (18)10.2.2 数据库建设 (19)10.2.3 数据库管理 (19)10.3 信息安全与共享 (19)10.3.1 信息安全策略 (19)10.3.2 信息安全防护技术 (19)10.3.3 信息共享机制 (19)10.4 决策支持与智能应用 (19)10.4.1 决策支持系统 (19)10.4.2 智能技术应用 (19)10.4.3 应用案例分析 (19)第1章勘探准备与地质调查1.1 勘探前期资料收集与分析1.1.1 资料收集范围与内容在石油天然气勘探前期,需对相关资料进行全面的收集与分析。
质模型至今还未建立。
因此,需要探索出一套扇三角洲储层构型建模方法,建立研究区扇三角洲前缘精细地质模型,并用于数模分析剩余油分布,为下步油田调整提供可靠的地质依据。
2 方法概述为建立研究区扇三角洲储层构型模型,优选目前应用最广泛的构型建模方法,包括序贯指示、基于目标模拟和多点地质统计方法。
2.1 序贯指示模拟序贯指示模拟通过一系列门槛值,估计某一类型变量或离散化的连续变量低于某一门槛值的概率,以此确定随机变量的分布。
序贯指示模拟实现的关键技术是指示变换、指示克里金和序贯模拟。
在进行模拟计算之前,首先要进行指示变换,即根据不同的门槛值把原始数据编码成0或1的过程。
在模拟不同的网格节点时各变量的比例是不变的。
当存在局部变化时,可应用具有趋势的序贯指示模拟方法。
具有趋势的序贯指示模拟方法通过从地震资料和其他数据中提取信息从而为每一个模拟节点提供一个局部的各变量比例,各变量的比例之和为1。
本次研究采用的带趋势的序贯指示模拟技术流程如下,在单井相数据离散化的基础上通过数据分析获取模拟的方位、主变程、次变程和垂向变程。
以单井累计概率的方式求取垂向比例,用前期研究的沉积微相作为平面约束,共同作为约束条件通过多次概率优选来求取。
2.2 基于目标模拟基于目标方法主要描述各种离散性地质特征(沉积微相、岩相、流动单元等)的空间分布,利用标点过程法建立又离散代码表示的离散性模型。
标点过程法是根据点过程的概率定律,按照空间中几何物体的分布规律产生这些物体的中心点的空0 引言三维构型建模能够刻画储层内部各构型单元间的空间接触关系,表征储层内部复合砂体,单砂体和非储层间的相对空间关系,包括不同构型单元的的三维空间形态、平面和垂向上的分布范围、不同单元的延伸方向、各单元之间的叠置关系。
并在此基础上刻画出各构型单元内部孔隙度、渗透率等物性参数的三维空间展布特征及各个构型单元之间的连通程度、油水运动特征。
储层构型方法自1985年储层构型概念的提出至今[1],取得了多方面的发展。
如何让地质模型更准确关于如何做好建模,每个人都有自己的看法,有人从理论上一套一套的,有人从操作上一套一套的。
那么什么样的模型是一个可靠的地质模型呢,众所周知有一个不是答案的答案:逼近地下真实的模型。
那么问题就来了,怎样来逼近地下真实呢?地下的东西看不见摸不着,谁知道到底如何。
没有调查就没有发言权,看看大伙都是怎么致力于提高模型准确度的吧。
上cnki,上spe,上aapg,国内国外期刊,sci,ei,核心,哪怕非核心都看一看。
结论就出来了,关于如何提高模型的可靠程度,几十年来大概集中在以下四个方面:1、建模算法2、地质认识3、约束建模4、模型优选一、建模算法算法有很多,成熟的(商业化的软件中),不成熟的(没有商业化的,高校与油田发表的文章中多见)。
不管是哪种算法,从数学角度来看,既然是随机模拟,每个模拟的概率是相同的,因此每个模型都是合理的。
但从油田生产角度来看,这些模型无一不经过一而再、再而三的调整,因此这些模型又都是不准确的。
因此,这些模拟实现仅在某种程度上符合储集层的数学特征,逼近其“数学真实”而非“地质真实”。
关于算法也是很多技术人员很了解的内容,这里不谈令人眼花缭乱的公式,只谈应用,认清本质,比会推导公式更重要。
先讨论下大家最为熟悉,用得也最多的序贯指示到底有什么能耐。
首先看个实例效果吧,以基于变差函数的序贯指示模拟为例。
图a是研究区的岩相分布图(蓝色为砂,白色为泥),图b,c是序贯指示两次随机模拟实现。
统计、对比发现,模拟结果砂岩发育长轴与井点统计参数基本一致(图e),而砂体形态及部分细节刻画上与原始相图差别较大,甚至相图上部分泥岩分布区域模拟出连片砂岩。
可见,地质统计学中,变差函数仅仅描述了数据的空间变异程度,而不同形态的地质体可能拥有相同的变异程度,图a,b,c就是这种情况,即井点统计变差函数模拟出来的地质体形态在服从输入数据统计的前提下,可以有无限多个,不确定性极大,但却鲜有与实际吻合,通常需反复多次调整。
多点地质统计学建模的发展趋势石书缘;尹艳树;冯文杰【摘要】从算法研究、训练图像处理和实际应用三个方面详细解剖了国内外多点地质统计学的发展历程,在此基础上,分析了多点地质统计学主流的几种算法的核心原理、适用范围及优缺点,以此来对储层建模的发展趋势作出展望.目前,多点地质统计学虽是随机建模的一种前沿研究热点,但由于其尚未成熟,仍需对建模算法进行研究.为此,在前人研究的基础上,重点分析了多点地质统计学的发展趋势:合理处理训练图像;合理利用软信息;选择合适的相似性方法;选择合适的标准化方法;合理利用平稳性;算法间的耦合;选择合适的过滤器;拓展缝洞型碳酸盐岩模拟.最后,提出多点地质统计学在储层建模方面,应从增加储层的模拟区域、提高模拟精度、扩大储层相的模拟范围和提高计算机模拟效率等方面进行改进.%Starting with algorithm designing, training image,and practical application,the authors analyzed multiple-point statistics research trends both in China and abroad. On such a basis, the core principles of the main four MPS algorithms, their applicable ranges and advantages as well as disadvantages were analyzed,so as to forecast the trend of reservoir modeling. Multiple-point geostatistics is an international forefront research tool in stochastic modeling; nevertheless, as the algorithm is not yet mature, it should be further improved. On the basis of previous researches, the existing problems of the multiple-point geostatistics that need to be modified and the direction of the processing of training images are proposed, such as suitable processing of training image, choice of similarity methods, choice of standardized data,smoothing,couplingamong algorithms,and expansion of the simulation extent for fractured-vuggy carbonate reservoir. In order to improve the usage of multiple-point geostatistics for reservoir stochastic modeling,we should spare no efforts to increase the simulation area,improve simulation accuracy,expand the scope of simulation of reservoir types,save simulation time and improve simulation efficiency.【期刊名称】《物探与化探》【年(卷),期】2012(036)004【总页数】6页(P655-660)【关键词】储层建模;多点地质统计学;模拟精度;缝洞型碳酸盐岩模拟;发展趋势【作者】石书缘;尹艳树;冯文杰【作者单位】中国石油勘探开发研究院,北京 100083;长江大学地球科学学院,湖北荆州 434023;中国石油大学地球科学学院,北京 102249【正文语种】中文【中图分类】TE319目前,中国东部大部分油田进入高含水开发阶段,在新区勘探难度加大的情况下,对老油田进行挖潜寻找剩余油及拓展深层碳酸盐岩勘探开发已成为当前油气勘探开发的几个主要发展方向。
多点地质统计学随机建模方法原理详细教程多点地质统计学随机建模是一种应用于地质领域的统计学建模方法,它主要用于处理地质参数在空间上的变化规律。
该方法的原理基于地质参数的随机性和空间相关性,通过构建具有地质属性的随机模型,可以模拟地质现象的空间分布。
具体而言,多点地质统计学随机建模方法主要包括以下几个步骤:1.数据准备:收集与地质参数相关的数据,例如岩性、厚度、含矿物质等。
要求数据具有一定的地质意义和空间分布规律。
2.变量描述:对收集到的数据进行统计分析,包括计算均值、方差、协方差等统计指标,以描述地质参数的分布特征。
3.变量变换:根据地质参数的实际特征,对数据进行变换,使其符合正态分布、对数正态分布或其他分布类型。
4.空间相关性建模:通过计算地质参数之间的空间相关性,可利用协方差函数、变差函数或半方差函数等,建立地质参数之间的空间相关模型。
5.随机模拟:根据变量的统计特征和空间相关模型,结合随机数生成算法,生成符合实际情况的具有随机性和空间相关性的地质参数数据。
6.模型验证:对生成的地质模型进行验证,比较随机模拟结果与实际数据的吻合程度。
可以使用统计指标如均值、方差、协方差等进行对比分析。
7.地质模型应用:根据随机模拟结果,可以进一步进行岩层插值、矿产资源评估和地质灾害风险评估等相关研究及应用。
总的来说,多点地质统计学随机建模方法是将统计学原理应用于地质参数的空间分布建模,通过对地质参数的统计特征和空间相关性的建模,生成具有随机性和空间相关性的地质模型。
这种方法可以提供地质领域研究的基础数据和分析手段,为地质灾害风险评估、资源勘探和环境评价等问题提供科学依据。
收稿日期:2005-01-18基金项目:国家教育部高等学校优秀青年教师教学科研奖励计划(T RA POYT )资助作者简介:冯国庆(1974-),男,山东荷泽人,博士,主要从事油藏描述和油藏数值模拟研究.文章编号:1673-064X(2005)05-0009-03利用多点地质统计学方法模拟岩相分布Stochastic simulation of lithofacies distribution using multi -point g eostatistics冯国庆1,陈浩2,张烈辉1,李允1(1.西南石油学院油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室,四川成都610500;2.新疆油田分公司陆梁油田作业区,新疆克拉玛依834000)摘要:文中介绍了多点地质统计学的基本原理,并利用该算法模拟了我国东部某砂岩油藏的岩相分布.通过对储层非均质性模拟研究,揭示储层在岩性、物性和含油气性的各向异性或非均质性,揭示砂体展布、连通程度以及在横向、纵向上的变化规律,有利于开发方案的制定及注采井网的布署.模拟结果表明,多点地质统计学模拟方法可以很好地再现砂体局部的变异性和非均质性.由此可得出以下结论:snesim 模拟算法可以快速灵活地进行多点地质统计模拟,多点地质统计学比两点地质统计学更具有优势.关键词:多点地质统计学;随机模拟;训练图像中图分类号:TE19;T E121.1+5 文献标识码:A 传统的地质统计学是利用变差函数描述地质变量的相关性和变异性,通过建立在某个方向上两点之间的地质变量的变化关系来描述空间的变化特性.但是,建立在两点统计关系上的变差函数本身在描述储层非均质性上有很大的不足,它反映的仅仅是空间两点之间的相关性,不能充分描述复杂几何形状砂体如河道砂体和冲积扇砂体空间的连续性和变异性.当井资料较少时,用于计算实验变差函数的点对很少,它也就不能正确反应空间两点之间的相关性.建立在两点基础上的变差函数在储层地质建模中存在一定的不足,而多点地质统计学[1-4]是建立在多个点的相关关系上,所以它在解决描述空间变量的连续性和变异性方面得到越来越广泛的应用.斯坦福大学的Journel 教授曾指出多点地质统计学是今后地质统计学发展的方向,它的优势已越来越显著.1 多点地质统计学的原理在阐述多点地质统计学之前,首先回顾一下变差函数的地质统计学方法是如何模拟储层岩相分布的,以序贯指示模拟算法为例进行说明.该方法的基本原理[5]简述如下:假设在模拟区域有k 种岩相s 1,s 2,,s k ,对于模拟目标区域内的每一相,定义指示变量:I (u )=1 Z(u)I s k0 Z(u)|s k,对于任一待模拟点,其出现第k 种相的概率为:P (I k =1|Z(u A )=s A ,P A ),A 为待估点所包括的条件区域,利用两点地质统计学方法计算该概率是采用克里格方法:P (I k =1|Z(u A )=s A ,P A )=E (I k )+E nA =1KA [1-E (I k )].2005年9月第20卷第5期西安石油大学学报(自然科学版)Journal of Xi c an Shiy ou U niversity(N atural Science Edition)Sep.2005V ol.20No.5其中,K A 为克里格方法确定的权系数,它通过求解由变差函数或协方差函数建立的克里格方程组来确定.多点地质统计学与两点地质统计学的主要区别在于上面的概率的确定方法不同,它首先引入一训练图像,通过在训练图像中寻找与待估点内条件数据分布完全相同的事件的个数来确定概率分布,因此它可以反映出多个位置的联合变异性.例如,计算图1(a)中u 点的概率时,相应的条件数据场为d n ={z (u 1),z (u 2),z (u 3),z (u 4)},其基本方法是首先要在训练图像(b)中寻找与图(a)中数据分布完全相同的事件的个数,即要在训练图像中找出与图(a)几何完全相同的区域,同时在该区域中相同的位置处z (u 1),z (u 2),z (u 3),z (u 4)的值完全相同.在训练图像中一共找到4个既能满足条件数据u 1,u 2,u 3,u 4数值,同时又能满足它们分空间几何形状的事件,在这4个事件中,3个事件的u 点的值为0,只有1个事件中u 点值为1,因此u 点岩相为1的条件概率为P {u =1|d n }=1/4,而P {u =0|d n }=3/4,这样便可求出了u 点的条件概率.图1 多点统计方法估计条件概率的原理上述方法不仅考虑了区域内条件数据的值,而且也考虑了条件数据的几何形状.而两点地质统计学只是依靠z (u 1),z (u 2),z (u 3),z (u 4)的值及各点与u 点距离通过求解克里格方程组来确定u 点的概率,并没有考虑d n 的几何形状和各条件数据的配位关系.基于上述原理,Sebastien Strebelle 提出了snes -im 模拟算法[2],利用该算法可以快速、灵活地模拟岩相分布.该方法的具体步骤为:(1)利用非条件模拟建立三维训练图像;(2)定义通过所有待估结点的随机路径;(3)对随机路径中的任意待估点l(=1,2,,,l):¹定义查找范围内的条件数据;º保留邻区的数据点;»在训练图像中寻找与该区域内条件数据完全相同的事件,计算该点岩相的分布概率.¼由Monto Carlo 法得到位置处的一个模拟值;½将模拟结果归入条件指示数据集中.(4)重复上一步模拟,直到所有的点全被模拟.训练图像既可以通过非条件模拟求出,也可以通过该地区的地质露头资料分析得出.对训练图像的条件非模拟可以选择非条件的布尔模拟方法,其方法和原理参见文献[6].2 实例分析对于开发中后期的砂岩油藏储层参数模拟采用两阶段模拟方法可以较为准确地反映储层的非均质性,而/两步建模0的第一步就是要建立储层结构或流动单元模型,模拟沉积体在空间排列的复杂性;利用多点统计学模拟方法可以较好地完成砂体骨架模拟.模拟区域选择我国东部某砂岩油藏第15小层,在该层一共有64口井,测井资料解释结果表明有26口井钻遇砂体,另外38口井钻遇泥岩,砂体比例为40%.对岩相进行编码,砂岩为1,泥岩为0,图2为该层井位分布图.图2 第15小层井位和井点岩相图采用上述方法模拟砂体的分布.首先建立训练图像,运用布尔模拟方法,把砂体比例40%输入,为保证训练图像数据充足,网格划分为250@250@1,一共由62500个模拟数据组成,布尔模拟结果见图3.把条件数据和布尔模拟生成的训练图像,输入到snesim 模拟算法中进行模拟.根据该区域的特点,椭圆最大搜索半径选为300m,搜索半径内最多)10)西安石油大学学报(自然科学版)的条件数据设为30,搜索主方向选择物源方向5b ,得到该层的砂泥岩分布(图4).从模拟结果看出,它很好地满足了条件数据,即在各井点处的模拟结果与数据相一致,这表明该方法为条件模拟.同时,模拟的砂体展布方向和趋势与依靠地质经验手工绘制的砂体展布图(图5)比较吻合,在模拟的左下角与左上角砂体的展布与手工勾绘的几乎完全一致,但该方法在局部区域表现出砂体展布的非均质性和不确定性,与手工勾画砂体展布的平滑而唯一的表现是具有一定差别的,它充分体现了砂体局部的变异性和非均质性.图3布尔模拟生成的训练图像图4 多点地质统计方法模拟的砂泥岩展布图图5 手工绘制的该小层的砂体展布图3 结 论(1)多点地质统计学是今后地质统计学发展的主要方向,它可以联合反映空间多个位置点的几何形状和相互配位关系;在模拟具有复杂形状地质体分布时,它比两点地质统计学方法具有更大的优势.(2)利用snesim 模拟算法可以快速灵活地进行多点地质统计模拟,模拟的岩相展布图具有一定的真实性,它为储层参数的两阶段模拟奠定了基础.参考文献:[1] Strebelle S.Condit ional simulation of complex geologicalstructures using multiplepoint statist ics[J].M athematical G eolog y,2002,34(1):1-22.[2] Strebelle S,Journel A G.Reser voir modeling using mult-i ple -point stat i stics[C].SPE71324,2001.[3] Jef Caers.Stochast ic Reser voir Characterization U singM ultiple -po int statistics [A ].In:Proceedings o f the I AM G 99,F ifth Annual Conference of the I nternational Associat ion for M at hemat ical Geology [C].L ippars S G,et al ,1999.467-472.[4] Jef Caers.G eostatistical history matching under tr aining -image based geo logical model constraints [A ].SP E77429,2002.[5] 冯国庆,李允.应用序贯指示模拟方法模拟沉积微相[J].西南石油学院学报,2001,23(2):1-4.[6] Deutsch ,Journel.GSL IB:G eostatistical Softw ar e Libraryand U ser .s Guide,2nd ed[M ].New Yor k:Ox ford U n-iversity Press,1998.104-109.编辑:国伍玲)11)冯国庆等:利用多点地质统计学方法模拟岩相分布ABSTRACTS OF THE PRESENT ISSUE(JXSYU ISSN1673-064X)Determination of the geologic age of the bottom interface of Quaternary of Caidamu Basin Abstract:Up to now there are different viewpoints on the geolog ic age the bottom interface of Quaternary. T he determination of the geolog ic age of the bottom interface of Quaternary of Caidamu Basin is not only favor-able to the theoretical study of Quaternary but also of importance to the observation of biog as reservoirs.The ge-ologic age is determined as2.5M a B.P.based on the variation of sporopollen assemblages,the evolution of palaeoclimate,the unconformity formed by intense tectonic movement,the contact state of sediment and the v ariation of archaeom agnetism.The bottom interface is identical w ith that of Quaternary loess in the northwest of China determined by Liu Tun-sheng of our country and that of Quaternary g lacial age beginning determ ined by Shakleto N.T.based on the profile of DSDP site552A hole in North Atlantic Ocean.It is a unconformity surface in w hich the basin g raduates into conformity contact.The palaeoclimate becomes cold suddenly across it.A lot of strong first appears here.Key words:Caidam u Basin;fluvia-l lacustrine sedimentation;bottom interface of QuaternaryZ H U X iao-m in1,K AN G A n2,K AN G Qiang3(1.Key Laboratory of Education M inistry for Hydrocarbon Accumulation M echanism,China University of Petroleum,Beijing,102249,China; 2.China Offshore Petroleum Exploration Corporation,Beijing,100021,China;3.China Oil&Gas Exploration Development Cor-poration,Beijing,100011,China)JXSYU2005V.20N.5p.1-4Effects of volcanic activities on the distribution of accommodation space during the development of volcanic se-quence in Xinyang DepressionAbstract:The effects of the volcanic activities on the formation and the distribution of accommodation space among regressive system tracts of volcanic sequence are discussed w ith Eogene volcanic sequence in Xinyang De-pression being taken as an ex ample.The features of volcanic sequences and the patterns of the accommodation space in regressive system tracts show that,the local accommodation space of the fault-depression lake basin w ith volcanic cones is nonhomogeneous,w hich is different from common fault-depression lake basins.By studying se-quence stratigraphy in Xinyang Depression,it is realized that the volcanic cones in reg ressive system tracts lead to the nonhomogeneous distribution of the accom modation space in this depression,w hich enriches the content of terrigenous sequence stratigraphy.Key words:Xinyang Depression,volcanic activity;sequence;accommodation space;nonhomog eneity L I Ji-shan1,JIANG Zai-x ing2(1.Institute of Porous Flow&Fluid M echanics,Chinese Academy of Sc-i ences,Langfang065007,H ebei,China;2.Faculty of Earth Resource and Information,China U niversity of Petroleum,Dongying257061,Shandong,China)JXSYU2005V.20N.5p.5-8Stochastic simulation of lithofacies distribution using mult-i point geostatisticsAbstract:The research of reservoir heterogeneity is one of the main contents of reservoir description,the heterogeneity of lithology,the heterogeneity of the physical parameters of reservoirs,and the distribution,con-nectivity and vertical and horizontal variations of sandbodies can be revealed by the simulation of reservoir hetero-geneity,which is useful for deploy ing reasonable development plan and arranging w ell netw ork.But traditional g eostatistics describes the correlation and variability of geologic variables by m eans of variate difference function, and it can not fully reflect the correlation and variability of the geologic bodies with com plicated geometric shape since it is only based on two-point geostatistics.M ult-i point geostatistics is based on multiple-point correlation relationship.It has great advantages in reflecting the joint variability of the geolog ical variables.The theory of multiple-point geostatistics is introduced in this paper and a case is also g iven.T he lithofacies distribution of the sandstone reservoir in a oilfield in eastern China is simulated,and the result shows that using multiple-point geo-statistics can reveal the local heterogeneity and variability of sandbodies.Key words:multiple-point geostatistics;stochastic simulation;training im ageÔFEN G G uo-qing1,C H EN H ao2,Z H ANG L ie-hui1,LI Yun1(1.State Key Laboratory of Oil and Gas Reservoir Geology and Exploitation,Southw est Petroleum Institute,Chengdu610500,Sichuan,China; 2.Lu-liang Oilfeild Operational Zone,Xinjiang Oilfield Company,Kelamayi834000,Xijiang,China)JXSYU2005 V.20N.5p.9-11Inorganic geochemical explanation of abnormal vitrinite reflectance:taking Niu-38well in Dongying Sag, Jiyang Depression as an exampleAbstract:The v itrinite reflectance of N iu-38well is restrained,it decreases from0.6%of the upper to 0.45%of the low er of cored interval.T he causes leading to the abnormality of the vitrinite reflectance are ana-lyzed from organic geochemistry and inorg anic geochemistry separately.The explanation from organic g eochem-istry is that,vitrinite reflectance decreases w ith the increase of the contents of sapropelic components,and hy-drogen-rich org anic matters restrain the increase of the vitrinite reflectance.From inorganic geochem istry,the study results in this paper show that,the information w ater in the studied interval becomes fresh and its acidity becomes a little strong from the low er to the upper.The acidic condition is favorable to the m aturation of organic matters.In the studied interval,the contents of K,Na,Mg and Li vary a little,therefore,there are no correla-tions between them and vitrinite reflectance;there are neg ative correlations betw een the contents of Ca,Mn,Sr and B and vitrinite reflectance,they maybe restrain the increase of vitrinite reflectance;there are positive corre-lations betw een the contents of Fe,Ba,Co,Zn,Ni and Rb and vitrinite reflectance,they maybe promote the increase of vitrinite reflectance.Key words:Dongy ing Sag;vitrinite reflectance abnormality;inorganic geochemistry;therm al evolution of organic matterXIE Ming-j u1,2,QI U N an-sheng1,2(1.Key Laboratory of Education Ministry for H ydrocarbon Accumula-tion M echanism,China U niversity of Petroleum,Beijing102249,China; 2.Basin&Reservoir Research Cen-ter,China University of Petroleum,Beijing102249,China)JXSYU2005V.20N.5p.12-16Application of nonlinearly constrained reservoir inversion technique in W eicheng Oilfield Abstract:Linear seismic inversion can only predict the distribution feature of thick sandbodies,but it can. t obtain the know ledge of the thin layer such as substratum to meet the demands of progressive exploration. Based on processing the seismic and log data of target,the distinct know ledg e of the structure of the reservoir can be gained by means of the nonlinear seismic inversion constrained by structure and log conditions,w hich can g uide the adjustment of oilfield deployment.T his study method is used in the progressive ex ploration of Weibei area in Weicheng Oilfield.The target processing of the seism ic and log data improves the resolution of the old data,and then the thin sandbodies are clearly recognized by nonlinearly constrained inversion,w hich are verified by drilling data.The fact demonstrates that nonlinearly constrained inversion has important function to the know ledge of reservoirs and the interpretation and verification of structures,and it is also an important tool to g uide progressive exploration.Key words:nonlinear constraint;reservoir inversion;w avelet frequency-division;logg ing curve reconstruc-tion;prog ressive exploration and developmentL I Zong-tian1,LI U Wei2(1.Department of Petroleum Engineering,China University of Geosciences, Beijing100081,China; 2.No.3Production Plant,Zhong yuan Oilfield Company,Puyang457001,Henan, China)JXSYU2005V.20N.5p.17-21Method of computing the mechanical parameters of formation and its application in Sulige area of Changqing OilfieldAbstract:A set of models for calculating three formation pressure profiles(form ation pore pressure,caving pressure and fracture pressure)and other formation mechanical parameters are established based on the study of borehole wall destabilization,logging data and ordinary empirical formulas.T he calculated m echanical parame-ters can help us design the safe density lim it of drilling fluid to make sure that the borehole w all is stable duringÕ。