cytoscape教程
- 格式:doc
- 大小:99.00 KB
- 文档页数:12

cytoscape 提取核心处方方法Cytoscape是一款用于生物信息学和计算生物学研究的开源软件,它提供了一种可视化和分析复杂网络的方法。
在生物医学领域中,蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络分析被广泛应用于揭示生物体内重要的生物过程和疾病发生机制。
核心处方是一种从蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络中提取具有重要功能的亚网络的方法,是研究生态系统中的关键物种和关键蛋白质的重要工具。
在Cytoscape中进行核心处方提取需要以下几个步骤:1. 构建蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络:首先,需要从公开的蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用数据库(如STRING、BioGRID等)中获取相关的相互作用数据,并导入到Cytoscape中。
然后,利用Cytoscape提供的网络编辑工具将这些相互作用数据构建成一个网络图。
2. 确定节点重要性指标:为了确定网络中的重要蛋白质节点,我们需要计算每个节点的重要性指标。
常用的指标有度中心性(Degree Centrality)、介数中心性(Betweenness Centrality)、接近中心性(Closeness Centrality)等。
这些指标可以通过Cytoscape中的插件或网络分析工具来计算和显示。
3. 提取核心亚网络:根据节点重要性指标,我们可以选择最重要的节点作为核心节点,并从核心节点开始向外扩展,逐步添加与核心节点相连接的节点,直到满足某种条件(如节点数目、连通性等)。
这样就可以提取到一个具有重要功能的亚网络,即核心处方。
4. 分析核心亚网络:一旦核心亚网络被提取出来,我们可以利用Cytoscape提供的网络分析工具对其进行进一步的分析。
例如,可以计算和显示核心亚网络的网络特征(如平均节点度、连通性、聚集系数等),寻找节点之间的共有模块(如社团检测),进行生物信息学注释(如基因本体注释、通路富集分析等),甚至进行动态网络模拟等。
总之,Cytoscape提供了一种强大的方法来提取和分析核心处方,帮助研究者理解生物体内复杂网络的结构和功能。

cytoscape用法
Cytoscape是一款常用的网络可视化工具,可以用于展示和分析复杂网络数据。
以下是Cytoscape的一些常见用法:
1.导入网络数据:Cytoscape支持导入多种格式的网络数据,包括sif、
csv、txt、xml、json等。
可以通过菜单栏中的File菜单或者Plugins 菜单导入数据。
2.创建网络:如果还没有现成的网络数据,可以使用Cytoscape的
图形界面创建一个新的网络。
在菜单栏中选择New菜单,可以创建一个空的或者基于现有网络的网络。
3.编辑网络:通过Cytoscape的图形界面,可以对网络进行编辑,
包括添加/删除节点、添加/删除边、修改节点/边的属性等。
可以通过菜单栏中的Edit菜单进行编辑。
4.可视化网络:Cytoscape提供了多种可视化网络的方式,包括布局、
颜色、形状、大小等。
可以通过菜单栏中的View菜单进行可视化设置。
5.分析网络:Cytoscape提供了多种网络分析工具,包括网络拓扑分
析、社区发现、网络中心度等。
可以通过菜单栏中的Analyze菜单进行分析。
6.插件管理:Cytoscape支持通过插件扩展其功能,可以通过Plugins
菜单安装和管理插件。
总之,Cytoscape是一款功能强大的网络可视化工具,可以用于展示
和分析复杂网络数据,支持多种数据格式导入、可视化设置、网络分析和插件扩展等功能。
![[重磅]手把手教你玩Cytoscape](https://uimg.taocdn.com/5fc38b8b70fe910ef12d2af90242a8956becaae4.webp)
[重磅]⼿把⼿教你玩Cytoscape⾮常感谢北京协和医学院药⽤植物研究所于猛⽼师的分享。
在这个看颜值的世界,⼀张狂拽酷炫的图不仅有助于解释⽂章的精髓,更能吸引审稿⼈和读者的眼球。
随着⾼通量多组学的兴起,数据分析与整合、以及可视化变得越来越重要。
今天omicsPie将⼿把⼿教你玩Cytoscape!当然,Cytoscape软件的功能⾮常强⼤,本次只针对我们常⽤的关联分析可视化进⾏了整编。
⼀⼝吃不成⼤胖⼦,那都得天天吃。
Learning by doing,且⾏且珍惜!别忘了转发评论点赞打赏,这才对得起于⽼师和⼩编的⾟苦啊!(结尾有彩蛋,⾃⼰慢慢体会)Ready, Go!C. Zhang et al. / EBioMedicine 2 (2015) 968–984⼩伙伴们阅读⽂献看到这样炫酷的关联图时,您是否眼前⼀亮?其实这样的图可以通过很多软件来实现,⽐如Gephi, R, Cytoscape……下⾯我们⼀起⽤最短的时间学习⼀下怎样⽤Cytoscape软件做关联图吧!Cytoscape简介Cytoscape是⼀款图形化显⽰⽹络并进⾏分析和编辑的软件,它⽀持多种⽹络描述格式,也可以⽤以Tab制表符分隔的⽂本⽂档或Microsoft Excel⽂件作为输⼊,或者利⽤软件本⾝的编辑器模块直接构建⽹络。
软件官⽹:/各版本下载地址:/download_old_versions.htmlCytoscape的核⼼是⽹络,最简单的⽹络图包括节点(node)和边(edge)。
节点是你的关联变量,可以是基因、蛋⽩,代谢物质或者miNRA等等;节点与节点之间的连接 (edge) 代表着这些变量之间的相互作⽤。
⼀张简单的⽹络结构,⽐如下图。
但是想要拥有CNS级别的⾼⼤上,就需要下功夫了!格式(⾮常重要)关联数据格式(⾮常重要)Cytoscape关联数据正所谓条条⼤路通罗马,有很多种⽅法可以编辑数据集,数据关联格式也并⾮唯⼀,现在介绍给⼤家的是⾃认为⽐较⽅便的⼀种格式。



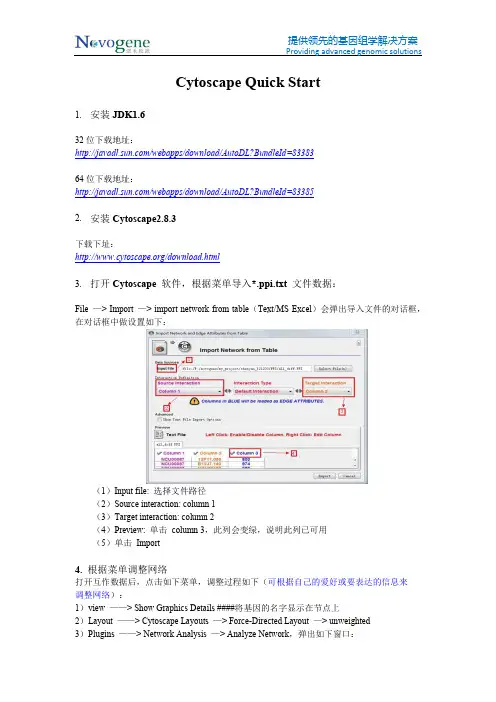
Cytoscape Quick Start1.安装JDK1.632位下载地址:/webapps/download/AutoDL?BundleId=8338364位下载地址:/webapps/download/AutoDL?BundleId=833852.安装Cytoscape2.8.3下载下址:/download.html3.打开Cytoscape 软件,根据菜单导入*.ppi.txt 文件数据:File —> Import —> import network from table(Text/MS Excel)会弹出导入文件的对话框,在对话框中做设置如下:(1)Input file: 选择文件路径(2)Source interaction: column 1(3)Target interaction: column 2(4)Preview: 单击 column 3,此列会变绿,说明此列已可用(5)单击 Import4. 根据菜单调整网络打开互作数据后,点击如下菜单,调整过程如下(可根据自己的爱好或要表达的信息来调整网络):1)view ——> Show Graphics Details ####将基因的名字显示在节点上2)Layout ——> Cytoscape Layouts —> Force-Directed Layout —> unweighted3)Plugins ——> Network Analysis —> Analyze Network,弹出如下窗口:4)如图所选,Treat the network as undirected —> OK ,会弹出如下窗口:5)如上图,点击 Visualize Parameters(用户也可了解网络的其他属性,如Node Degree Distribution 等,具体信息和意义可以参考cytoscape 的在线帮助或联机帮助),弹出如下图:(1)Map node size to: degree(2)Map node color to: Clustering Coefficient(3)Map edge size to: column 35. 结果说明互作网络中节点(node)的大小与此节点的度(degree)成正比,即与此节点相连的边越多,它的度越大,节点也就越大。

Cytoscape史上最全攻略今天还是讲Cytoscape,虽然已经写了很多相关的⽂章,但是依然有童鞋在问哪⾥可以下载Cytoscape这样没有营养的问题,这让本宫⽆⽐⽆⽐的痛⼼!!!所以今天本宫会很详细、⾮常详细、巨详细、史⽆前例地详细、前⽆古⼈,后⽆来者地详细讲解如何使⽤Cytoscape。
Cytoscape是⽤于可视化⽹络数据的⼀个⾮常强⼤的⼯具,⽐如说表现⼀组基因间的相互关系,数据的表现⼒上孰优孰劣⼀⽬了然。
⽂本形式和⽹络图形式,在数据的表现⼒上点(node)和线(edge)是⽹络图的两个核⼼要素。
我们做各种各样的⽹络图,归根结是⽹络图的两个核⼼要素。
我们做各种各样的⽹络图,归根结底是对图中的点和线进⾏注释,我们通过改变点和线的样式来对点和线赋予各种各样的信息,从⽽实现数据的可视化。
息,从⽽实现数据的可视化很多童鞋可能在下载这⼀步就放弃了,因为下载速度可能会很慢,200M的宽带可能只有2kb的见⽂末⽹盘链接)。
下载速度。
本宫送佛送到西,翻过去给你们把⽕种带回来(见⽂末⽹盘链接)安装的时候先安装java,安装好了之后需要设置环境变量在环境变量中,要修改两个地⽅,⼀个是添加JAVA_HOME。
选择“新建”,变量名填上JAVA_HOME,变量值填上C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.8.0_151,在java的安装过程中,默认⼀直下⼀步安装,所以装在C盘,如果你在安装过程中改了,那可能是D盘或者E盘,那么变量值要做相应的更改。
还要修改⼀个地⽅,就是Path,添加JAVA的变量值到Path中,选择Path,然后点“编辑”,在最后⾯添加如下语句;%JAVA_HOME%\bin;打开命令提⽰符cmd,输⼊java -version,如果能正常显⽰,那表明装好了,你就可以装Cytoscape了虽然⽹盘⾥的是最新版本3.60,但是不知道重新安装需不需要重新下载插件什么的,时间所如果⼤家在使⽤过程中发现什么差别,请在迫,今天给⼤家所做的演⽰都是基于3.42版本,如果⼤家在使⽤过程中发现什么差别,请在⽂末留⾔。

Cytoscape2.6使用手册郑国毅译目录目录 (1)一、Cytoscape介绍及其安装的一些要求: (2)Cytoscape2.6的新特点 (2)Cytoscape的安装 (3)系统性能的要求 (3)安装过程 (3)开始应用 (3)内存的消耗说明 (4)栈的大小分配 (4)Cytoscape的界面 (5)菜单 (6)File(文件) (6)Edit(编辑) (7)View(视图) (7)Select(选择) (7)Layout(布局) (7)Plugins(插件) (8)Help(帮助) (8)二、入门Cytoscape (9)三、Cytoscape中基本的数据表达分析 (16)一、Cytoscape介绍及其安装的一些要求:Cytoscape是一个专注于开源网络可视化和分析的软件。
它的核心是提供基础的功能布局和查询网络,并依据基本的数据的结合成可视化网络。
它可以通过插件扩展的,为了适应快速发展的附加的计算分析和和其他功能。
他最先用于生物学,为了整合分子间相互作用的网络(高复杂的,和其他的分子状态信息)。
虽然适应任何分子系统的结构和相互关系。
他是非常强大的,在于联合大的数据库(蛋白质,DNA,和对人类和生物日益重要的遗传)。
Cytoscape允许可视化的网络与文件,显型,其它分子状态信息,和链接网络到功能注释。
Cytoscape的重要组织方式是网络,因子,蛋白质和分子用点表示,两点间的交互关系用链接也就是边Cytoscape的发展Cytoscape软件是由以下的机构联合完成的:Institute for Systems Biology (Leroy Hood lab), theUniversity of California San Diego (Trey Ideker lab), Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (ChrisSander lab), the Institut Pasteur (Benno Schwikowski lab), Agilent Technologies (Annette Adler lab) andthe University of California, San Francisco (Bruce Conklin lab).可以访问 得知详细情况许可Cytoscape是受the GNU LGPL (Lesser General Public License)保护的。
Cytoscape⼗讲之下载安装及使⽤Cytoscape⼗讲之⽹络图的认知Cytoscape的功能集中于两点,⼀个是展⽰蛋⽩/其他features间的⽹络图,⼀个使⽤app⾥的⼩⼯具分析,界⾯操作性相对简单(肯定⽐PS简单)。
软件最好更新⼀下,因为不同软件版本,相同按钮的软件中的位置不太⼀样。
直接点击Download 3.7.1,可以下载最新版本。
软件有点⼤,⼏百M。
JAVA安装:java8是否已安装?如果没有安装或环境变量的配置等,安装Cytoscape时候点击提⽰出:是否安装java,点击是即可。
其他默认安装就可以,可以更改安装⽬录。
(但不建议瞎改)如图。
open source:可以找到不同系统(mac/Linux/Wins)释放的不同版本Release Notes:找到释放的不同版本Samples Visualizations:展⽰出软件可视化图的类型,让你看看不同版本,软件能做什么图cytoscape-tutorials:重点!Cytoscape manual:可以查看Cytoscape的⽹页端学习⼿册Cytoscape YouTube channel:你们可以试试能不能打开Documentation for users:可以获得更多学习材料,如3.x PDF Version:本地下载帮助⼿册,⽬前3.6版本的⼿册249页(⾃学)其他软件内启动Cytoscape等Cytoscape 的核⼼是⽹络,简单的⽹络图包括节点(node)和线/边/连接(edge)。
全部适⽤于点/线的参数,我们可以称之为默认参数。
根据某些属性调节的参数带来的渐变或者离散的变化(这个属性,你可以在⽂件中⾃⼰添加⼀列)。
选中某些/个/条调节后适⽤的变化,如特定⼀条线型需要设置为波浪线。
节点:就是线线焦点 形状:圆型、正⽅形等 填充:Fill color ⾼度:Height 宽度:Width边界:节点周围是否再涂边,⽐如⼀个圆,如果边界线全是灰⾊实线,现可调整为不同粗细线,不同颜⾊线,不同形状线条的属性。

Cytoscape新⼿看过来!分享⽣物信息分析的使⽤⽅法、软件、数据库,分析思路Cytoscape 是⼀个专注于开源⽹络可视化和分析的软件。
Cytoscape的核⼼是⽹络(图),其中的节点(node)是基因、蛋⽩质或分⼦,其中的连接则是这些⽣物结构之间的相互作⽤。
其最强⼤的功能还是⽤于⼤规模蛋⽩质--蛋⽩质相互作⽤、蛋⽩质--DNA和遗传交互作⽤的分析。
通过Cytoscape,你可以在可视化的环境下将这些⽣物⽹络跟基因表达、基因型等各种分⼦状态信息整合在⼀起,还能将这些⽹络跟功能注释数据库链接在⼀起(可以通过插件架构进⾏扩展,开发新功能)。
让我们⼀起来探索吧!1)安装2)运⾏可以选⽤软件下载时⾃带的sampleData⽂件下的数据进⾏测试。
数据背景信息介绍如下:Gal1、Gal4和Gal80都是酵母转录因⼦,在相互作⽤⽹络⾥分别对应YBR020W、YPL248C和YML051W。
相互作⽤有两种类型:protein-protein (pp)和protein-DNA(pd)。
表达量信息分别是Gal1、Gal4和Gal80的表达异常情况下的值。
galFiltered.csv是互作⽹络⽂件,galExpData.csv 是表达量信息(属性)⽂件。
现在我们要看这三个转录因⼦表达异常影响到的基因。
a) 数据⽂件导⼊互作⽹络数据⽂件按照File → Import → Network或者使⽤快捷键导⼊,之后按照要求导⼊互作⽹络数据⽂件;属性⽂件按照File → Import → Node Attributes或者使⽤快捷键导⼊,快捷键导⼊⽂件如下图所⽰:b) 调整node显⽰c) 调整node填充⾊(基于基因表达量)d) 调整node形状(Pvalue)e) 过滤数据(基于互作关系)f) 结合⽬的选择:i. 点击选中3个核⼼基因(Gal1、Gal4和Gal80);ii. 进⼀步选出与核⼼基因相关的周边点和边(Frist Neighbors of Selected Nodes),单独显⽰被选中的点和边;g) 导出图⽚位图:jpg和png,⽮量图:pdf和svg。
Tutorial:Basic Expression Analysis in Cytoscape-HumanSlideshow Basic Expression Analysis in Cytoscape (30 min)Handout Basic_Expression_Analysis_in_Cytoscape-Human.pdf (11 pages)Tutorial Curators Kristina Hanspers, Alex Pico, Mike SmootContents[hide]∙ 1 Loading Network∙ 2 Loading expression data∙ 3 Visualizing Expression Datao 3.1 Set the node coloro 3.2 Set the default node coloro 3.3 Set the node shapeo 3.4 Set the node border∙ 4 Data analysis featureso 4.1 Filter Nodeso 4.2 Search for a nodeo 4.3 Exploring NodesCytoscape is an open source software platform for integrating, visualizing,and analyzing measurement data in the context of networks. This tutorial will introduce you to:▪Combining data from two different sources: experimental data in the form of microarrray expression data and network data in the form of interaction data.▪Visualizing networks using expression data.▪Filtering networks based on expression data.Loading Network▪Start Cytoscape and load the network File:HumanInteractome subset.sif.▪Apply the force-directed layout to organize the layout of the nodes. Select the "Layout->Cytoscape Layouts->Force-Directed Layout" menu.▪The network should now look similar to this:Loading expression data▪Download File:Pellegrini et al Data.txt.zip expression data and unzip it.▪Using your favorite text editor, open the file Pellegrini_et_al_Data.txt. The first few lines of the file are as follows:Gene Symbol Entrez id Probeset CREB kd control p value fold change Sign CREB bindingA2M 2 217757_at 42.24 57.450.4 1.5 yesA2ML1 144568 1553505_at 67.95 206.470.11 0.58A2ML1 144568 1564307_a_at 160.05 183.440.81 0.95You should note the following information about the file:1. The first line consists of labels.2. All columns are separated by a single tab character.3. The first column contains node names, and must match the names of the nodes in yournetwork exactly!4. The second column contains Entrez Gene IDs.5. The third column contains Affymetrix probe set IDs. This column is optional, and the data isnot currently used by Cytoscape, but this column may be useful for analysis in othermicroarray analysis tools.6. The remaining columns contain experimental data; average expression for experimentaland control groups, p value and fold change for the comparison, and data on whether ornot the gene binds CREB. See the manuscript for details on the data generation. NOTE: The expression data used in this example has been pre-processed to work with the interaction network used. The data is a composite of data files from Pellegrini et al, BMC Cancer, 2008.▪Under the File menu, select Import → Attribute from Table (Text/MS Excel).▪Click "Node" for the type of attribute to import.▪Select the file Pellegrini_et_al_Data.txt.▪Click the "Text File Import Options" check box.▪Make sure the "Tab" check box in the "Delimiter" section is selected and that no other check box under "Delimiter" is selected. The preview should indicate that it is importing multiplecolumns of data.▪Click the "Transfer first line as attribute names" check box in the "Attribute Names" section. The preview should now show be using the first row of the input file as column names and the import window should look like the image below.▪Click the "Import" button to import the attribute data.Now we will use the Node Attribute Browser to browse through the expression data, as follows. ▪Select a node on the Cytoscape canvas by clicking on it.▪In the Node Attribute Browser, click the Select Attributes button , and select the attributes "fold change" and "p value" by left-clicking on them. Right-click to close the menu. ▪Under the Node Attribute Browser, you should see your node listed with their expression values, as shown.Visualizing Expression DataProbably the most common use of expression data in Cytoscape is to set the visual attributes of the nodes in a network according to expression data. This creates a powerful visualization, portraying functional relation and experimental response at the same time. Here, we will walk through the steps for doing this.Set the node color▪Double-Click the Node Color row in the Visual Mapping Browser in the Unused Visual Properties Section.▪This action will move Node Color to the top of the Visual Mapping Browser.▪Click the "Please select a value!" cell in the Node Color section.▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available attribute names. Select "fold change".▪Click the "Please select a mapping" cell in the Node Color section.▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available mapping types. Select "Continuous Mapping". ▪This action will produce a basic black to white color gradient.▪Click on the color gradient to change the colors. This will pop-up a gradient editing dialog.▪Drag the left-most, red handle along the top of the gradient. Drag it to an Attribute Value of approx. -1.2▪Drag the white handle to approx 0.5. You can type the Attribute Value in the Handle Settings section to be more precise.▪You can also change the color of each handle by double-clicking or using the Node Color selector button in the Handle Settings section.▪This should produce a Red-White-Green Color gradient like the image below, with min and max extremes colored black and blue, respectively.▪Click 'OK' to save the gradient adjustment dialog and verify that the nodes in the network reflect the new coloring scheme.Set the default node colorNote that the default node color of pink falls within this spectrum. A useful trick is to choose a color outside this spectrum to distinguish nodes with no defined expression value and those with slight repression.▪Click the Defaults network icon in the VizMapper panel.▪Click the Node Color entry and choose a dark gray color.▪Zoom out on the network view to verify that a few nodes have been colored gray.Set the node shapeWe imported both a fold change value and a p value for the comparison between CREB kd and control cells. We can use the p values to change the shape of the nodes so that measurements we have confidence in appear as squares while potentially bad measurements appear as circles.▪Double-Click the Node Shape row in the Visual Mapping Browser in the Unused Visual Properties Section.▪This action will move Node Shape to the top of the Visual Mapping Browser.▪Click the "Please select a value!" cell in the Node Shape section.▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available attribute names. Select "p value".▪Click the "Please select a mapping" cell in the Node Shape section.▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available mapping types. Select "Continuous Mapping". ▪This will create an empty icon in the "Graphical View" row of the Node Shape section. Click on this icon.▪This action will pop-up a continuous shape selection dialog.▪Click the Add button.▪This action will split the range of values with a slider down the middle with a node shape icon to either side of the slider.▪Double-Click on the left node icon (a circle).▪This will pop-up a node shape selection dialog.▪Choose the Rectangle shape and click the Apply button.▪The continuous shape selection dialog should now show both a square and a circle node shape icon.▪Click on the black triangle and move the slider to the left, to slightly lower that 0.05, our threshold for significance.▪Close the continuous shape selection dialog and verify that some nodes have a square shape and some nodes have a circular shape.Set the node borderWe can use the node border color and style to reflect whether a node has been found to be significantly bound by CREB (ref). This data is already available in the dataset as an attribute.▪Double-Click the Node Border Color row in the Visual Mapping Browser in the Unused Visual Properties Section.▪This action will move Node Border Color to the top of the Visual Mapping Browser.▪Click the "Please select a value!" cell in the Node Border Color section.▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available attribute names. Select "Sign CREB binding". ▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available mapping types. Select "Discrete Mapping". ▪This will create a new row for the value "yes", which is the only value available for this attribute.Click on the empty cell to the right of "yes", and then click on the square icon that appears.▪ A color chooser will appear. Pick a color that will stand out against the color scheme, for example a bright yellow. The relevant nodes in the network will be outlined in yellow.Next, we want to also change the border thickness, since the thin yellow border can be hard to see.▪Double-Click the Node Line Width row in the Visual Mapping Browser in the Unused Visual Properties Section.▪This action will move Node Line Width to the top of the Visual Mapping Browser.▪Click the "Please select a value!" cell in the Node Line Width section.▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available attribute names. Select "Sign CREB binding". ▪This will produce a drop-down menu of available mapping types. Select "Discrete Mapping". ▪This will create a new row for the value "yes", which is the only value available for this attribute.The default node border width of 1.5 will be selected to the right of "yes".▪Click in the box specifying the width and type 5.▪Zooming in to part of the network, it now looks like this:Data analysis featuresThis section presents a few examples of features in Cytoscape that can be used to further analyze the network and associated data.First, here is some background on your data. The data is from an experiment in a human myeloid leukemia cell line. The cAMP Response Element Binding Protein, CREB, was knocked down by shRNA and the expression profile of knockdown cells was compared to that of control cells from the same cell line. See Pellegrini et al.Filter NodesIt is possible to filter any network in Cytoscape based on either node or edge attributes. Here, we filter the network based on high and low fold change between the two groups.▪Click the Filters tab in the Control Panel.▪Click the Attribute/Filter chooser in the Filter Definition and choose "node.fold change".▪Click the Add button in the Filter Definition section to add the selected attribute to the filter. ▪This action will create a slider for the fold change in the filter.▪Double-click on the slider to select cutoffs. Set the low bound to 2 and click OK.▪Now, expand the selection to first neighbors of selected nodes byclicking Select→Nodes→First Neighbors of Selected Nodes.▪Create a new network by clicking New→Network→From Selected Nodes, All Edges.▪Apply a force-directed layout to the new network by selecting Layout → Cytoscape Layouts → Force-Directed Layout.▪Navigate to the Network tab in the Control Panel. Rename the new network by right-clicking on it and selecting Edit Network Title. Type in "upregulated".▪The new network should now look like this:▪Repeat the Filter for down-regulated genes with fold change under 0.5. Name the second subnetwork "downregulated".▪The "downregulated" network should look like this:Search for a nodeWe will now search for the CREB1 (CREB) node in the network.▪In the toolbar, to the right of the Search box, click the icon for Configure search options'.▪In the dialog that opens, select the radio button for Nodes and make sure Unique Identifier is selected in the drop-down. Click Apply.▪In the search field, type in "CREB". In the list of hits that is generated, you will see that there is one node named CREB1, which is an alias name for the CREB transcription factor. Select this node from the list and click Enter.▪The CREB node will be highlighted in the network.▪To make it easier to explore the interactions immediately surrounding CREB, we can create a network based on the first degree neighbors of CREB by clicking Select → Nodes → First Neighbors of Selected Nodes.▪ A set of nodes should now be highlighted. Click File → New → Network → From Selected Nodes, All Edges. A new network will be produced.▪Clean up the network by applying a force-directed layout.▪The network should now look like this:▪By examining the network, we can see that CREB interacts with both up- and down-regulated nodes. CREB is known to act both as a transcriptional repressor and transcriptional activator. If you search for CREB in the two subnetworks representing all up- and down-regulated nodes respectively, you will see that CREB is present in both networks.Exploring Nodes▪In the "HumanInteractome_subset" network, right click on the node CREB1.▪Select the menu LinkOut → Entrez → Gene.▪This action will pop-up a browser window and search the Entrez Gene database for CREB.。
Cytoscape软件画图说明1、画图前,先准备两个输入文件。
2、打开cytoscape软件,导入数据。
导入edge.txt文件点击File ----Import ----Network点击ok得到原始图形节点1,文件中第一列节点2,文件中第2列连接类型,文件中第3列点击layout ----Apply Preferred Out 改变图形排列方式此处可以用鼠标在画布中拖动图形到合适的位置。
改变画布背景。
点击左侧Contro Panel ----Style---network ---Backgroud paint设置节点之间连线的宽度和颜色Contro Panel ----Style---Edge颜色宽度导入node.txt个文件点击File ----Import ----Table设置节点图形属性Contro Panel ----Style---Node1、node大小通过设置Height和Width来控制大小2、Node性状通过设置Shape来控制3、Node填充色通过设置Fill Color来控制4、Node标签的设置点击Properties -- Label Position点击Label Position来设置标签位置。
这里是一个示操作,要细致调整标签位置还是要设置Column和Mapping Type两个参数。
设置完成之后图形调节节点之间的距离点击layout ----Scale鼠标拖动最后,画图导出成pdf文件点击File ----Export----Network View as Graphics。
Cytoscape软件画图说明
1、画图前,先准备两个输入文件。
2、打开cytoscape软件,导入数据。
导入edge、txt文件
点击----Network
点击ok得到原始图形节点1,文件中第
一列
节点2,文件中
第2列
连接类型,文件
中第3列
点击layout ----Apply Preferred Out 改变图形排列方式
此处可以用鼠标在画布中拖动图形到合适得位置。
改变画布背景。
点击左侧Contro Panel ----Style---network ---Backgroud paint
设置节点之间连线得宽度与颜色Contro Panel ----Style---Edge
导入node、txt个文件点击----Table 宽度颜色
设置节点图形属性
Contro Panel ----Style---Node
1、node大小
通过设置Height与Width来控制大小
2、Node性状
通过设置Shape来控制
3、Node填充色
通过设置Fill Color来控制
4、Node标签得设置
点击Properties -- Label Position
点击Label Position来设置标签位置。
这里就是一个示范操作,要细致调整标签位置还就是要设置Column与Mapping Type两个参数。
设置完成之后图形
调节节点之间得距离
点击layout ----Scale
最后,
画图导出成pdf文件
点击View as Graphics
鼠标拖动。
Cytoscape中文教程(1)写在前面:•对于我们大多数来说,用图形或图表更比数据本身更能说明问题,更容易让人理解,并且可以赏心悦目。
细胞内部,大量的分子时刻都在发生着变化或相互作用。
对于我们来说,了解这种相互作用是非常重要的。
但就像中国地图,如果抽象的描述东部的东部是谁,一定让人头大,但如果在地图上指出来那效果是完全不一样的。
cytoscape 就给我们提供了一种这种分子地图的可能性,即蛋白互作网络,当然这种网络可以由多种定义形式来产生,比如染色体物理位置,比如共表达性质等;也可以产生多种排布形式(看个人需要)。
所以我觉得这是一个必备的技能,不只会出图,更要会知道出什么样的图,怎么解释这种图。
这样就需要知道作图背后的知识。
所以我翻译并加了自己的理解注释,完成了这份手册。
•这个手册真的有点长,是我早期翻译的,如果你完全不懂Cytoscape,那么你读这些,应该会做出非常漂亮的各种基于cytoscape及插件的图,因为这个教程真的很白。
•cytoscape有很多非常优秀的app,关于cytoscape本身的使用方法完成后,我会稍后发布几个app的使用。
当然,关键还是知道用哪个插件,为什么用,结果怎么解读,其生物学意义是什么。
•原文地址直接从第三部分开始3 命令行参数Cytoscape可以识别很多可选的命令行参数,包括network,节点,边和会话文件等数据文件运行规范,这些文件是可以输出的(有h 或help flag)usage: cytoscape.{sh|bat} [OPTIONS]-h,--help Print this message.-v,--version Print the version number.-s,--session <file> Load a cytoscape session (.cys) file.-N,--network <file> Load a network file (any format).-P,--props <file> Load cytoscape properties file (Java propertiesformat) or individual property: -P name=value.-V,--vizmap <file> Load vizmap properties file (Cytoscape VizMapformat).-S,--script <file> Execute commands from script file.-R,--rest <port> Start a rest service.任何一个指定的文件,都可以被定义为一个路径或URL,例如,你可以指定一个文件为一个网络(假如文件在当前的工作目录存在)cytoscape.sh -N myNet.sif注意:假如文件路径下还有空间,确定在它旁边还要有quotescytoscape.bat -N "C:\Program Files\Cytoscape\sampleData\galFiltered.sif"也可以把一个URL指定为一个网络cytoscape.sh -N [/myNet.sif](/myNet.sif).4 Quick Tour of Cytoscapeimage.png•椭圆形的menu Bar,可以在每个菜单下看详细信息•矩形标记的T ool Bar,有最常用的图标。
Cytoscape基础教程笔记文章目录•第一课新手上路•第三课获取外部数据•第四课表达分析•第五课使用Agilent Literature Search插件•第六课 GO分析•第七课模块和复合物•第八课整合网络服务提供的注释和相互作用网络昨天开始学用Cytoscape,其tutorial分为两个部分,基础的和高级的。
基础教程又分成了四课:Getting Started、Filters & Editor、Fetching External Data和Expression Analysis。
为防忘记,做个摘记。
第一课新手上路地址:/Presentations/01_Get_StartedCytoscape可以本地安装,也可以web start。
软件得用java,所以要装JRE。
我在Ubuntu下装了OpenJDK,可以运行。
因为以前一直没把jnlp文件和java关联起来,所以从没成功web start过,试了一下“课文”里给出的链接,似乎不太靠谱,总之是没法启动。
启动Cytoscape后,得下载两个样例文件。
以sif为后缀名的是蛋白相互作用网络信息,里面的蛋白以数字形式区别,以na为后缀名的是各数字id的注释,似乎两者的文件名必须相同才能关联起来。
sif文件的打开\导入有两种方式:File → Import → Network(Multiple File Types)或者直接Ctrol+L,na文件是File → Import → Node Attributes。
Network导入之后有多种显示风格,2.8版默认风格下,圆圈是各蛋白,称为节点(node),其间各线为edge,代表相互作用。
点中圆圈就选中了一个节点,想要多选,可以采用同时按Shift的方法,也可以先在Select → Mouse Drag Selects 设置好选node还是选edge,然后鼠标拖放,一选一大片。
此外还可以有目的地选择。
Cytoscape基础教程笔记part one昨天开始学用Cytoscape,其tutorial分为两个部分,基础的和高级的。
基础教程又分成了四课:Getting Started、Filters & Editor、Fetching External Data和Expression Analysis。
为防忘记,做个摘记。
第一课新手上路,地址见http://goo.gl/FJLxp。
Cytoscape 可以本地安装,也可以web start。
软件得用java,所以要装JRE。
我在Ubuntu下装了OpenJDK,可以运行。
因为以前一直没把jnlp文件和java关联起来,所以从没成功web start过,试了一下“课文”里给出的链接,似乎不太靠谱,总之是没法启动。
启动Cytoscape后,得下载两个样例文件。
以sif为后缀名的是蛋白相互作用网络信息,里面的蛋白以数字形式区别,以na为后缀名的是各数字id的注释,似乎两者的文件名必须相同才能关联起来。
sif 文件的打开\导入有两种方式:File → Import → Network(Multiple File Types)或者直接Ctrol+L,na文件是File → Import → Node Attributes。
Network导入之后有多种显示风格,2.8版默认风格下,圆圈是各蛋白,称为节点(node),其间各线为edge,代表相互作用。
点中圆圈就选中了一个节点,想要多选,可以采用同时按Shift的方法,也可以先在Select → Mouse Drag Selects设置好选node还是选edge,然后鼠标拖放,一选一大片。
此外还可以有目的地选择。
比如可以Select → Nodes → By Name,然后输入蛋白id,即可选中此节点。
大海捞针即告完成。
此操作的快捷键是Ctrl+F。
如果已经选中了节点,还可以Select → Nodes → First neighbors of selected nodes,可将所选蛋白的直接相互作用蛋白选中,再选File → New → Network → From selected nodes, all edges,即将相互作用网络的一个子网络剥离出来。
Layout菜单的功能比较花哨,是关于相互作用网络图的组织原则的。
可以乱试一通,一张一张放在ppt里唬人,呵呵。
一团乱麻般的相互作用网络图下是查看节点或连线所代表的信息的地方,称为data panel。
按Attributes按钮会弹出一个小窗口,可供选择需要列出的栏目的名字,比如id,或者对应的基因名,当然这个基因名信息是从na文件里导入的。
乱麻左边的窗口是有多个tab的控制面板。
Network那个tab里可以在导入的sif里切换。
VizMapper tab里可以定制显示样式,比如圆圈变成方形,或者变大一些,或者换个底色,连线换个粗细和颜色等等。
如果莫名找不到的话,Cytoscape的菜单栏下有几个快捷按钮,其中有一个可以打开VizMapper。
各种样式设置好之后一定要点Apply,还可以新建或者另存,便于把所有的网络打上自创风格的烙印。
Cytoscape还支持从网上直接导入相互作用网络,也是在File → Import → Network (Multiple File Types)一步,选择remote,然后输入url。
从例题来看应该至少兼容SBML格式的。
不过lin下代理我还是搞不定,这种“奢侈”的功能姐还是表痴心妄想了……Part 2第二课筛选和编辑,地址见http://goo.gl/n2z6V。
首先复习一下,还是以上一课那个sif和na文件。
依次导入、选择显示基因名。
课文里说要用到的插件不仅下载地址作废了,而且似乎并不需要。
可能已经整合到基本的功能包里了。
现在开始玩玩筛选。
首先用拖放选一大堆节点和连线(还是海选),然后Select → Use Filters,控制面板里即出现Filters tab,在此tab中点Options,在弹出的下拉菜单中选Create new filter。
然后开始定义筛选条件,比如连线的类型:在Filter Definition里选edge.interaction,然后点Add。
此时指定了筛选依据,而具体条件还没指明。
在Advanced里,输入non_core或者core之类的连线类型,当然Y2H神马的也行啦。
最后一定要按一下tab左下角的Apply。
此时选中了相互作用类型为non_core的节点和连线。
之后可以进行多种操作。
比如Edit → Delete Selected Nodes/Edges,这样这些non_core的东西就统统删除了,剩下你认为更可信的蛋白及其相互作用。
可是还有一些和其他蛋白没有相互作用的蛋白,我们要把它们找出来、删除。
很简单,如法炮制,仅仅把相互作用筛选条件换成“*”就行,选好后再利用New → Network → From selected nodes, selected edges,调整一下layout:Layout → spring-embedded layout,这张图里只有有相互作用的蛋白。
不过其实任务还剩个尾巴,有些蛋白可与自身相互作用,这部分蛋白还在这张图里。
课文里说可以手动搞定,不过不晓得是否有批量处理的办法。
导入的文件也并不总是完美的,有时需要添加和删除某些节点和连线,此时需要用到控制面板里的Editor tab。
添加节点的话就在标有“Add a Node”的节点上点左键,然后把节点拖到右边的相互作用网络图里,在数据面板的Node Attribute Browser里可以看到新添的节点id为node0。
在此窗口里点相应栏目,即可修改其属性,比如基因名之类的。
添加连线的话,在Editor tab里点“Directed Edge”,如法炮制,拖到右边图里某个节点上,确定相互作用的一方,然后把另一端拖到某个节点之上。
连线属性在数据面板的Edge Attribute Browser里查看和修改。
删除:选中要删的东西,然后Edit → Delete Sele cted Nodes/Edges,此操作的快捷键是Del。
Part 3第三课获取外部数据,地址见http://goo.gl/t5rQl。
这一课要告诉我们:a. 从外部服务(比如SGD和BIND)下载Cytocape格式的数据;b. 用cPath插件获取外部数据,其中cPath从2.4版以后已经整合到Cytoscape核心包里了。
SGD 是酵母的库,Saccharomyces Genome Database,提供physical和genetic相互作用的信息,提供sif格式的下载,地址在:/cgi-bin/batchDownload。
下载页面的说明挺简单,总之是指定想下的东西再重定向到另外一个页面,然后另存为就行了。
BIND是Biomolecular Interaction Network Database,主要提供蛋白相互作用信息,现在整合到BOND库里了。
下载地址是/,要注册,免费。
登录后进入首页,搜索目标分子,搜到的相关信息分成五类:summary、sequences、interactions、complexes和pathways。
打开interactions,在结果栏的右上角有导出功能,选择导出成sif 格式即可。
另外还有Pathway Commons库,地址是/。
课文也不知道啥时候编的,说建成后会超过BIND库,瞧瞧网站的意思,至少上线两年了,应该已经算建成了吧。
目前已经整合的库包括:BioGRID、Cancer Cell Map、HPRD、HumanCyc、IMID、IntAct、MINT、NCI / Nature Pathway Interaction Database,具体的说明见Pathguide。
说起来Pathguide也是个奇网站,是个介绍全部325个途径和相互作用相关的数据库的概况的数据库,相当于目录或者提要。
从这里你可以找到蛋白-蛋白相互作用、代谢途径、信号传导途径、表达途径、转录因子/基因调控网络、蛋白-复合物相互作用、genetic相互作用网络、protein sequence focused等等类型的数据库,查看其概况,然后决定去哪个库搜索信息。
最后是用cPath插件从CPpath数据库直接获取数据,后者从08开始就不更新了,而且建议用户使用Pathway commons。
下载多个源的相互作用网络文件后,可以融合成一张图,需要用到Graph Merge插件。
这个插件可能也整合进核心包了,疑似Plugins下的Advanced Network Merge。
Part 4第四课表达分析,地址见http://goo.gl/Mu6aP。
终于开始做正经事儿了,先唏嘘二点五秒钟~~好了唏嘘完毕,开始学习。
首先下载三个文件:galFiltered.sif、galExpData.pvals和galExpData.mrna。
接下来通过操作下载的示例文件来学习:1. 导入galFiltered.sif,弹出数据面板和结果面板,最大化画布,用spring-embedded风格显示。
2. 文本编辑器打开mrna文件,可以看到第一行是数据标签。
对应于相互作用网络图,第一栏为节点名称,必须和sif文件里的节点名一模一样哟;第二栏是基因座名,Cytoscape里目前不显示;后面各栏是表达信息。
各栏之间用whitespace隔开。
这个mrna应该就是芯片直接导出的数据的格式吧?3. 导入表达信息:Im port → Attribute/Expression Matrix...,快捷键Ctrl+E。
导入后,Node Attribute Browser里就能看到这个节点的表达量了。
基础工作就此结束,下面要玩花哨的活儿了。
4. 首先可以根据表达量高低给节点上不同的颜色。
在V izMapper里先新建个显示风格,然后双击Node color,选择按照某类表达量分类,选continuous mapping,然后点开下面那张颜色图设置阈值和颜色。
别忘了按Apply哟。
下面是一些背景知识。
Gal1、Gal4和Gal80都是酵母转录因子,在相互作用网络里分别对应YBR020W、YPL248C和YML051W。
相互作用有两种类型:protein-protein (pp)和protein-DNA (pd)。
表达量信息分别是Gal1、Gal4和Gal80的表达异常情况下的值。
现在我们要看这三个转录因子表达异常影响到的基因。
5. 首先要把pp相互作用除去。
用filter和Delete Selected Nodes and Edges。