PLC应用实例
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:864.33 KB
- 文档页数:16

几个西门子PLC经典实例详解(含程序)
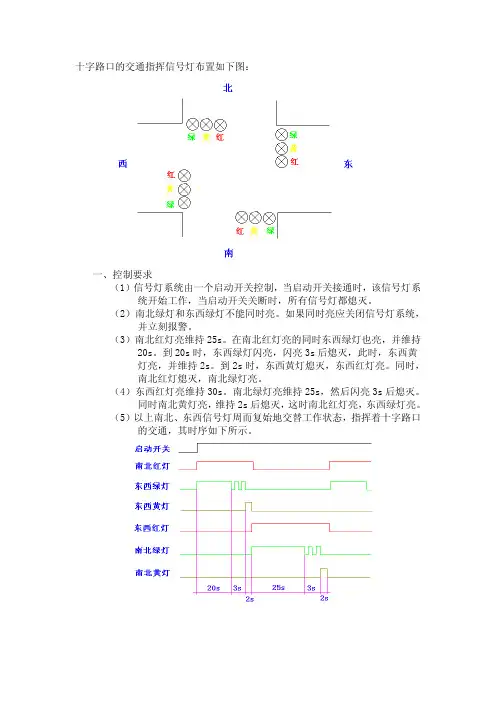
十字路口的交通指挥信号灯布置如下图:
一、控制要求
(1)信号灯系统由一个启动开关控制,当启动开关接通时,该信号灯系统开始工作,当启动开关关断时,所有信号灯都熄灭。
(2)南北绿灯和东西绿灯不能同时亮。
如果同时亮应关闭信号灯系统,并立刻报警。
(3)南北红灯亮维持25s。
在南北红灯亮的同时东西绿灯也亮,并维持20s。
到20s 时,东西绿灯闪亮,闪亮3s 后熄灭,此时,东西黄灯亮,并维持2s。
到2s 时,东西黄灯熄灭,东西红灯亮。
同时,南北红灯熄灭,南北绿灯亮。
(4)东西红灯亮维持30s。
南北绿灯亮维持25s,然后闪亮3s 后熄灭。
同时南北黄灯亮,维持2s 后熄灭,这时南北红灯亮,东西绿灯亮。
(5)以上南北、东西信号灯周而复始地交替工作状态,指挥着十字路口的交通,其时序如下所示。
二、PLC 接线
三、定义符号地址
四、梯形图程序。

plc控制实例200例English Response:Introduction:Programmable logic controllers (PLCs) are widely used in industrial automation and control systems. These devices are capable of performing complex logic operations, sequencing, and data manipulation, making them a versatile solution for various industrial applications. This article presents 200 exemplary PLC control instances that showcase the diverse capabilities of PLCs in various industries.Process Control:1. Temperature control in a manufacturing process: A PLC monitors temperature sensors and adjusts the flow of heating or cooling media to maintain the desired temperature within a specific range.2. Level control in a chemical storage tank: A PLC monitors level sensors and controls the opening and closing of valves to maintain the liquid level within predetermined limits.3. Pressure control in a hydraulic system: A PLC monitors pressure sensors and adjusts the pump speed or valve position to maintain the desired pressure level.Motion Control:4. Conveyor belt control: A PLC controls the speed and direction of a conveyor belt, ensuring smooth material transportation.5. Robotic arm control: A PLC coordinates the movements of a robotic arm, enabling it to perform precise tasks such as assembly or welding.6. Stepper motor control in a machine tool: A PLC precisely controls the movement of a stepper motor, ensuring accurate positioning of cutting tools.Real-Time Monitoring and Data Acquisition:7. Data logger for a water treatment plant: A PLC collects and stores data from sensors monitoring water quality parameters, providing a comprehensive record for analysis and optimization.8. Traffic monitoring system: A PLC records traffic flow data from sensors and displays the information on variable message signs, optimizing traffic patterns.9. Energy consumption monitoring in a building: A PLC tracks the energy usage of different systems and devices, enabling energy-saving measures.Industrial Automation:10. Assembly line control: A PLC coordinates the sequence of operations on an assembly line, ensuring efficient and synchronized product assembly.11. Packaging machine control: A PLC controls the filling, sealing, and labeling operations of a packaging machine, reducing manual labor and waste.12. Machine vision inspection: A PLC integrates with a machine vision system to automatically inspect products for defects, ensuring quality control.Safety and Emergency Response:13. Fire detection and alarm system: A PLC monitorsfire sensors and triggers evacuation alarms and sprinkler systems in case of a fire.14. Gas leak detection and shutdown: A PLC monitors gas sensors and initiates emergency shutdown procedures to prevent accidents.15. Emergency stop system in a manufacturing facility:A PLC detects emergency stop signals and activates safety measures such as machine shutdown and personnel evacuation.Other Applications:16. Lighting control in a warehouse: A PLC manages the on/off status of lighting fixtures based on daylight availability and occupancy sensors, optimizing energy efficiency.17. Irrigation control in a greenhouse: A PLC regulates the flow of water to plants based on soil moisture sensors, ensuring optimal plant growth.18. HVAC system control in a commercial building: A PLC monitors temperature and humidity levels and adjusts the operation of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems for comfort and energy conservation.中文回答:简介:可编程逻辑控制器 (PLC) 广泛应用于工业自动化和控制系统中。





PLC控制伺服电机应用实例,写出组成整个系统的PLC模块及外围器件,并附相关程序.PLC品牌不限。
以松下FP1系列PLC和A4系列伺服驱动为例,编制控制伺服电机定长正、反旋转的PLC程序并设计外围接线图,此方案不采用松下的位置控制模块FPG—-PP11\12\21\22等,而是用晶体管输出式的PLC,让其特定输出点给出位置指令脉冲串,直接发送到伺服输入端,此时松下A4伺服工作在位置模式。
在PLC程序中设定伺服电机旋转速度,单位为(rpm),设伺服电机设定为1000个脉冲转一圈。
PLC输出脉冲频率=(速度设定值/6)*100(HZ).假设该伺服系统的驱动直线定位精度为±0。
1mm,伺服电机每转一圈滚珠丝杠副移动10mm,伺服电机转一圈需要的脉冲数为1000,故该系统的脉冲当量或者说驱动分辨率为0.01mm(一个丝);PLC输出脉冲数=长度设定值*10。
以上的结论是在伺服电机参数设定完的基础上得出的.也就是说,在计算PLC发出脉冲频率与脉冲前,先根据机械条件,综合考虑精度与速度要求设定好伺服电机的电子齿轮比!大致过程如下:机械机构确定后,伺服电机转动一圈的行走长度已经固定(如上面所说的10mm),设计要求的定位精度为0。
1mm(10个丝)。
为了保证此精度,一般情况下是让一个脉冲的行走长度低于0。
1mm,如设定一个脉冲的行走长度为如上所述的0。
01mm,于是电机转一圈所需要脉冲数即为1000个脉冲。
此种设定当电机速度要求为1200转/分时,PLC应该发出的脉冲频率为20K。
松下FP1——-40T 的PLC的CPU本体可以发脉冲频率为50KHz,完全可以满足要求。
如果电机转动一圈为100mm,设定一个脉冲行走仍然是0。
01mm,电机转一圈所需要脉冲数即为10000个脉冲,电机速度为1200转时所需要脉冲频率就是200K。
PLC的CPU输出点工作频率就不够了。
需要位置控制专用模块等方式.有了以上频率与脉冲数的算法就只需应用PLC的相应脉冲指令发出脉冲即可实现控制了.假设使用松下A4伺服,其工作在位置模式,伺服电机参数设置与接线方式如下:一、按照伺服电机驱动器说明书上的“位置控制模式控制信号接线图”接线:pin3(PULS1),pin4(PULS2)为脉冲信号端子,PULS1连接直流电源正极(24V电源需串连2K左右的电阻),PULS2连接控制器(如PLC的输出端子)。
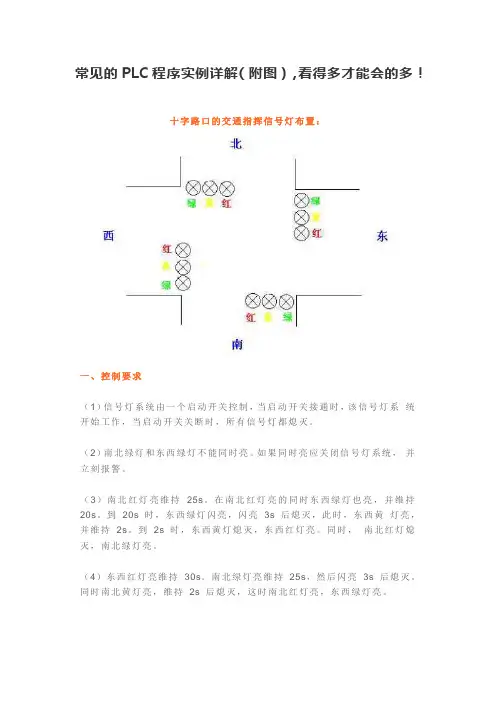
常见的PLC程序实例详解(附图),看得多才能会的多!十字路口的交通指挥信号灯布置:一、控制要求(1)信号灯系统由一个启动开关控制,当启动开关接通时,该信号灯系统开始工作,当启动开关关断时,所有信号灯都熄灭。
(2)南北绿灯和东西绿灯不能同时亮。
如果同时亮应关闭信号灯系统,并立刻报警。
(3)南北红灯亮维持25s。
在南北红灯亮的同时东西绿灯也亮,并维持20s。
到20s 时,东西绿灯闪亮,闪亮3s 后熄灭,此时,东西黄灯亮,并维持2s。
到2s 时,东西黄灯熄灭,东西红灯亮。
同时,南北红灯熄灭,南北绿灯亮。
(4)东西红灯亮维持30s。
南北绿灯亮维持25s,然后闪亮3s 后熄灭。
同时南北黄灯亮,维持2s 后熄灭,这时南北红灯亮,东西绿灯亮。
(5)以上南北、东西信号灯周而复始地交替工作状态,指挥着十字路口的交通,其时序如下所示。
二、PLC 接线三、定义符号地址四、梯形图程序三层楼电梯控制电梯的上升、下降由一台电动机控制;正转时电梯上升、反转时电梯下降。
各层设一个呼叫开关(SB1、SB2、SB3)、一个呼叫指示灯(H1、H2、H3)、一个到位行程开关(ST1、ST2、ST3)。
一、控制要求:(1)各层的呼叫开关为按钮式开关,SB1、SB2 及SB3 均为瞬间接通有效(即瞬间接通的即放开仍有效)。
(2)电梯箱体上升途中只响应上升呼叫,下降途中只响应下降呼叫,任何反方向呼叫均无效,简称为不可逆响应。
具体动作要求,如下表。
(3)各楼层间有效运行时间应小于10S,否则认为有故障、自动令电动机停转。
多种液体自动混合装置的PLC 控制如图所示为三种液体混合装置,SQ1、SQ2、SQ3 和SQ4 为液面传感器,液面淹没时接通,液体A、B、C 与混合液阀由电磁阀YV1、YV2、YV3、YV4 控制,M 为搅匀电动机,其控制要求如下:1.初始状态装置投入运行时,液体A、B、C 阀门关闭,混合液阀门打开20s 将容器放空后关闭。
2.起动操作按下启动按钮SB1,装置开始按下列给定规律运转:①液体 A 阀门打开,液体 A 流入容器。


plc在实际生活中的应用实例PLC(可编程逻辑控制器)是一种广泛应用于自动化领域的控制设备,它可以在实际生活中的许多领域发挥重要作用。
本文将以几个具体的应用实例来说明PLC在实际生活中的应用。
1. 工业生产自动化PLC在工业生产中的应用非常广泛。
例如,在汽车制造业中,PLC可以用于控制生产线上的机器人,通过编程控制机器人的动作和任务,实现汽车组装的自动化生产。
另外,PLC还可以用于控制生产线上的传送带、机器人臂等设备,实现物料的自动输送和加工。
2. 智能家居控制随着智能家居的发展,PLC在智能家居控制系统中的应用也越来越广泛。
通过PLC可以实现对家庭电器的集中控制,例如控制灯光的开关、调节空调的温度、打开窗帘等。
此外,PLC还可以与安全系统集成,实现对家庭安防设备的监控和控制。
3. 水处理系统PLC在水处理系统中的应用也非常重要。
例如,在供水系统中,PLC 可以监测水位、流量等参数,根据设定的条件自动控制水泵的启停,实现对供水系统的自动化控制。
另外,在污水处理系统中,PLC可以控制污水处理设备的运行,确保污水的处理效果。
4. 物流仓储系统在物流仓储系统中,PLC可以用于控制自动化设备,例如堆垛机、输送带等。
通过PLC的编程,可以实现对物料的自动分类、存储和取出,提高物流仓储的效率和精度。
此外,PLC还可以与仓储管理系统集成,实现对仓储库存的监控和管理。
5. 智能交通系统PLC在智能交通系统中的应用也非常重要。
例如,在红绿灯控制系统中,PLC可以监测交通流量和信号灯状态,根据设定的算法和策略,自动控制红绿灯的切换,优化交通流量和减少交通堵塞。
另外,PLC还可以用于控制高速公路收费系统、停车场管理系统等。
PLC在实际生活中有着广泛的应用。
它在工业生产、智能家居、水处理、物流仓储和智能交通等领域发挥着重要作用。
通过编程控制,PLC可以实现对设备和系统的自动化控制,提高生产效率、节省能源、提升安全性。
随着科技的不断发展,PLC在实际生活中的应用将会越来越广泛,为我们的生活带来更多的便利和舒适。
一、小车往返运动用S7-200实现小车往返的自动控制 ,控制过程为按下启动按钮,小车从左边往右边(右边往左边运动)当运动到右边(左边)碰到右边(左边)的行程开关后小车自动做返回运动,当碰到另一边的行程开关后又做返回运动。
如此的往返运动,直到当按下停车按钮后小车停止运动。
▲电气接线图I/O分配表梯形图程序PLC接线图程序调试及结果分析▲控制平台操作面板当按下SB2即i0.0(鼠标点击i0.0f)接通后,Q0.0接通,小车右行(即指示 灯 Q0.0 亮)。
当小车运行碰到右限位开关SQ2即i0.4(用鼠标点击i0.4f,模拟SQ2被压下)接通,此时小车左行(指示灯Q0.0灭,指示灯Q0.1亮),当运行到左边碰到左限位SQ1即i0.3(鼠标点击i0.3f)接通,此时小车又往右运行(指示灯Q0.1灭,指示灯Q0.0亮)。
如此往返运动下去直到按下SB1即i0.2(鼠标点i0.2f)接通,小车停止运行。
附:二、闪光电路当按下启动按钮后,要求在两秒钟内有一秒亮有一秒灭,如此反复,灯一闪一闪 发光。
I/O分配表梯形图程序PLC接线图程序调试及结果分析把编写好的程序下载到西门子s7-200PLC中进行调试。
观察运行结果和实验要求是否相同。
通过在线控制面板进行调试,当按下在线控制面板上的I0.0f(即 I0.0接通)此时Q0.0有输出,Q0.0所接负载灯就亮,同时启动定时器T37开始计时, 当计时一秒后因T37动作,其常闭触点断开,所以Q0.0无输出,所接负载灯灭。
灯灭的同时启动定时器 T38,T38 计时一秒后,把串联在定时器T37的常闭触点断开,所以T37复位,T37常闭触点恢复常闭。
此时Q0.0 又有输出, 所接负载灯又亮。
这样,输出Q0.0上所接的负载灯以接通一秒,断开一秒频率不停的闪烁,直到按下在线控制面板上的 I0.1f(即I0.1接通),闪光电路不在继续工作。
若想改变灯闪烁的频率只要改变定时器的时间就能够达到改变要求。
六个典型PLC程序实例详解(附图),自控项目轻松入门!(1)十字路口的交通指挥信号灯布置一、控制要求(1)信号灯系统由一个启动开关控制,当启动开关接通时,该信号灯系统开始工作,当启动开关关断时,所有信号灯都熄灭。
(2)南北绿灯和东西绿灯不能同时亮。
如果同时亮应关闭信号灯系统,并立刻报警。
(3)南北红灯亮维持25s。
在南北红灯亮的同时东西绿灯也亮,并维持 20s。
到 20s 时,东西绿灯闪亮,闪亮 3s 后熄灭,此时,东西黄灯亮,并维持 2s。
到 2s 时,东西黄灯熄灭,东西红灯亮。
同时,南北红灯熄灭,南北绿灯亮。
(4)东西红灯亮维持30s。
南北绿灯亮维持25s,然后闪亮3s 后熄灭。
同时南北黄灯亮,维持 2s 后熄灭,这时南北红灯亮,东西绿灯亮。
(5)以上南北、东西信号灯周而复始地交替工作状态,指挥着十字路口的交通,其时序如下所示。
二、PLC 接线三、定义符号地址四、梯形图程序(2)电梯控制电梯的上升、下降由一台电动机控制;正转时电梯上升、反转时电梯下降。
各层设一个呼叫开关(SB1、SB2、SB3)、一个呼叫指示灯(H1、H2、H3)、一个到位行程开关(ST1、ST2、ST3)。
一、控制要求:1、各层的呼叫开关为按钮式开关,SB1、SB2 及 SB3 均为瞬间接通有效(即瞬间接通的即放开仍有效)。
2、电梯箱体上升途中只响应上升呼叫,下降途中只响应下降呼叫,任何反方向呼叫均无效,简称为不可逆响应。
具体动作要求,如下表。
3、各楼层间有效运行时间应小于10S,否则认为有故障、自动令电动机停转。
如图所示为三种液体混合装置,SQ1、SQ2、SQ3 和 SQ4 为液面传感器,液面淹没时接通,液体 A、B、C 与混合液阀由电磁阀 YV1、YV2、YV3、 YV4 控制,M 为搅匀电动机,其控制要求如下:1.初始状态装置投入运行时,液体A、B、C 阀门关闭,混合液阀门打开20s 将容器放空后关闭。
2.起动操作按下启动按钮 SB1,装置开始按下列给定规律运转:①液体 A 阀门打开,液体 A 流入容器。
PLC控制实例实例导读●五星彩灯闪烁控制程序设计。
●交通信号灯控制。
●四层电梯PLC控制系统。
●自动送料装车控制实训1 五星彩灯控制实训内容1. 五星彩灯分布图(如图1. 1所示)图1.1 五星彩灯分布图2. 控制要求:十只发光二极管L1-L10 的亮暗规律如下:1 ) 花样1先使全部彩灯复位(熄灭),然后L1 到L10 按图1.2所示的顺序每隔0.5s点亮一个彩灯,直到所有彩灯全部亮起为一个循环,重复轮回三次。
图1.2 花样1流程图2)花样2两组灯亮灭交替,循环闪烁三次。
图1.3 花样2流程图3 ) 花 样 3先 L1 灯亮,延时0.5s 后 L2 灯亮L1 灯灭,延时0.5s 后 L3 灯亮L2 灯灭,依次类推,形成单灯跑马 效果,反复循环三次。
(L10L2 L9L3 L8L4 L7L5 L6图1.4花样3流程图根据以上控制要求,将三种花样连贯起来,完成PLC VO 地址分配、硬件连线和控制程序 的设计。
根据五星彩灯的控制要求,为使程序简单,本实例不使用输入信号, 一通电,彩灯即开始 进行花样循环;使用10个输出点接 L1~L10 十个彩灯,具体 VO 地址分配如表1 所示。
表 1 / O 地址分配表输入元件I/O 地址输出元件 I/O 地址①卫 ③ 四 5 → 6 7④(四L101.主程序梯形图Network 4三个计数器清零SM0.1 C0R3Network 2SM0.0调用花样1子程序3次C0<1 +3SBR O_ENNetwork 3 调用花样2子程序3次SM0.0 C1 C0< ==1+4 +3Network 4 调用花样3子程序3欲SM0.0 C2 C11+4 +424VOC 电源L ⁶1 17 L 81 19 L 10[十>1M 1L+ 0.0 0.10.2 0.3 0. 4 2M 2L + 05 0. 6 0.7 M L+ DCS7-200 CPU224 DC/DC/DC>1M 0.00.10.203040.50.60.72M 1.01.11213141.5 L+L11 L2 L3[ L4| L5|DC24V+PLC 接线图SBR 1_ ENSBR 2 ENNetwork 5C2 ==1 +4 彩灯熄灭Q0.0R10图1.6 彩灯PLC 梯形图控制程序(主程序)2.花样1子程序梯形图图1.7 彩灯PLC 梯形图控制程序(花样1子程序) 3. 花样2子程序Network 1SM0.1让所有彩灯熄灭MOV W EN ENO MOV WENO15#0000=IN OUT □V/0 15#0000-OUT -LWONetwork Z 网络2到网络3为脉冲振荡电路SM0.0 T40 M0.1T39N TON+5{ PTNetwork 3T39 T40 M0.2M0.2T40TONNetwork 4M0.1Network 5M0.2+5{PT网络4到网络5为五星彩灯内圈外圈闪烁电路Q0.5S500.0R )5Q0.55Q0.0SEN5 Network 6Q0.0闪烁次数计数器CU C1CTU]10.4+5+Network 7 子程序运回C1==1 P K—(RET)+4图1.8彩灯PLC 梯形图控制程序(花样2子程序)4.花样3子程序Hctwork1SMM0.1Metwork2C2==1+1 Metwork 3C2+2 Hctwork4SM0.0Network 5,W¹.°Metwork 6T37M11.5(第一次循坏前)辅助继电器复位M¹0.1R )14(第二次循环前)辅助些电器复位M10.1P —(R )14(第三次循环前)辅助继电器复位M10.1P —(R)14同路4到网络9为脉冲生成电路T37 M1.0()T37TOM+2{M10.0)M¹0.1Network12M10.2Network13M10.3Network14M10.4Network15M10.5Network16M10.5Network17M10.7Network18M11.0Network 19M11.1同路11到网路20,形灯单灯跑马效果Q0.0)Q0.1)00.200.3—()Q0.4()Q0.5)Q0.600.7Q10Network 7SI/0.0Network20M11.2M0.1Q1.1)Metwork BM.1Network 9T38 MM⁰0M0.0丽+2世M2.—()循环达数计数器C2CUCTU1.5RNotwork 10MM0.0奇存器移位ENO+4{FVNetwork 23 子程序近回M11.5M1001|DATA ——(RET)M10.1 S BIT+14{图1.8 彩灯PLC 梯形图控制程序(花样3子程序)Network 21Network 22T0H]T38实训2交通信号灯控制1. 交通灯示意图(如图2. 1所示)北西实训内容2东南图2.1 交通灯示意图2.控制要求:SB1位自锁型按钮,功能为手动/自动切换,按下为自动状态,自动状态时SB2,SB3 不起作用。