759线性系统理论Linear System Theory
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:96.50 KB
- 文档页数:10

Linear Systems Theory: A Structural Decomposition Approach线性系统理论: 结构分解法Ben M. Chen (陈本美)新加坡国立大学Zongli Lin(林宗利)美国弗吉尼亚大学Yacov Shamash (雅科夫 司马诩)美国纽约州立大学石溪分校此书献给我们的家人前两位作者谨以这中译版献给他们的母校 厦门大学目录绪论1 导论和预览1.1 背景1.2 各章预览1.3 符号和术语2 数学基础2.1 导论2.2 矢量空间和子空间2.3 矩阵代数和特性2.3.1 行列式、逆和求导2.3.2 秩、特征值和约当型2.3.3 特殊矩阵2.3.4 奇异值分解2.4 范数2.4.1 矢量范数2.4.2矩阵范数2.4.3 连续时间信号范数2.4.4 离散时间信号范数2.4.5 连续时间系统范数2.4.6 离散时间系统范数3 线性系统理论复习3.1 导论3.2 动态响应3.3 系统稳定性3.4 可控性和可观性3.5 系统可逆性3.6 常态秩、有限零点和无限零点3.7 几何子空间3.8 状态反馈和输出馈入的特性3.9 练习4 无驱动和/或无检测系统的分解4.1 导论4.2 自治系统4.3 无驱动系统4.4 无检测系统4.5 练习5. 正则系统的分解5.1 导论5.2 SISO系统5.3 严格正则系统5.4 非严格正则系统5.5 结构化分解特性的证明5.6 系统矩阵的Kronecker型和Smith型5.7 离散时间系统5.8 练习6 奇异系统的分解6.1 导论6.2 SISO奇异系统6.3 MIMO描述系统6.4 定理6.3.1的证明和性质6.5 离散时间奇异系统6.6 练习7 双线性变换的结构化映射7.1 导论7.2 连续到离散时间系统的映射7.3 离散时间到连续时间系统的映射7.4 定理7.2.1的证明7.5 练习8 系统因子分解8.1 导论8.2 严格正则系统8.3 非严格正则系统8.4 离散时间系统8.5 练习9 通过选择传感器/执行器实现的结构配置9.1 导论9.2 同时有限和无限零点结构配置9.2.1 SISO系统9.2.2 MIMO系统9.3 完全结构配置9.4 练习10 通过状态反馈实现的时间尺度和特征结构配置10.1 导论10.2 连续时间系统10.2.1 设计步骤和基本特性10.2.2 控制、控制和干扰解耦10.3 离散时间系统10.3.1设计步骤和基本特性10.3.2 控制、控制和干扰解耦10.4 练习11 通过静态输出反馈实现的干扰解耦11.1 导论11.2 左可逆系统11.3 一般的多变量系统11.4 练习12 软件工具箱12.1 导论12.2 m-函数描述12.2.1 自治系统的分解12.2.2 无驱动和无检测系统的分解12.2.3 正则系统的分解和特性12.2.4 矢量空间的运算12.2.5 奇异系统的分解和特性12.2.6 系统分解12.2.7 通过选择传感器/执行器实现结构配置12.2.8 具有特征结构配置的状态反馈控制12.2.9 通过静态输出反馈实现干扰解耦参考文献索引前言系统的结构特性对我们理解以状态空间表示的线性系统起着重要作用。


线性系统理论学习指南英文回答:Linear system theory is a fundamental topic in thefield of control engineering. It provides a mathematical framework for analyzing and designing systems that can be described by linear equations. In this learning guide, I will explain the key concepts and techniques in linear system theory.Firstly, let's start with the definition of a linear system. A linear system is a mathematical model that can be represented by a set of linear equations. These equations describe the relationship between the inputs and outputs of the system. The behavior of a linear system can be analyzed using techniques such as transfer functions, state-space representations, and frequency domain analysis.One important concept in linear system theory is the transfer function. The transfer function is a mathematicalrepresentation of the input-output relationship of a linear system. It is defined as the ratio of the Laplace transform of the output to the Laplace transform of the input, assuming all initial conditions are zero. The transfer function provides valuable information about the system's stability, dynamics, and frequency response.To illustrate this, let's consider an example of a simple linear system. Imagine a spring-mass-damper system, where a mass is attached to a spring and a damper. Theinput to the system is the force applied to the mass, andthe output is the displacement of the mass. By applying Newton's second law and solving the resulting differential equation, we can derive the transfer function of the system. This transfer function will tell us how the displacement of the mass is related to the applied force.Another important concept in linear system theory isthe state-space representation. The state-space representation provides a more comprehensive description of a linear system by considering both the inputs and outputs as well as the internal states of the system. It consistsof a set of first-order differential equations that describe the evolution of the system's states over time. The state-space representation is particularly useful for analyzing the system's controllability, observability, and stability.To further illustrate this, let's consider a control system that aims to regulate the temperature of a room. The inputs to the system are the heater power and the outside temperature, and the output is the room temperature. By formulating the system dynamics and the output equation in state-space form, we can analyze the controllability of the system and design a suitable controller to achieve the desired temperature regulation.In addition to transfer functions and state-space representations, frequency domain analysis is another important tool in linear system theory. Frequency domain analysis allows us to study the system's behavior in the frequency domain, which is particularly useful for analyzing the system's stability and frequency response. Techniques such as Bode plots, Nyquist plots, and rootlocus plots are commonly used in frequency domain analysis.To illustrate this, let's consider a feedback control system that aims to stabilize an unstable plant. By analyzing the system's transfer function in the frequency domain using Bode plots, we can determine the stability margins and design a suitable controller to stabilize the system.中文回答:线性系统理论是控制工程领域的基础知识。


线性系统理论线性系统理论是一个广泛应用的数学分支,该分支研究线性系统的性质、行为和解决方案。
线性系统可以描述很多现实世界中的问题,包括电子、机械、化学和经济系统等。
在这篇文章中,我们将探讨线性系统理论的基础、应用、稳定性和控制等不同方面。
一、线性系统基础线性系统是一种对于输入响应线性的系统。
当输入为零时,系统的响应为零,称之为零输入响应。
当没有外界干扰时,系统内部存在固有的动态响应,称之为自然响应。
当有外界输入时,系统将对输入做出响应,称之为强制响应。
线性系统具有很多性质,可以让我们更好地理解系统的行为。
其中一个重要的性质是线性可加性,就是说当输入是线性可加的时候,输出也是线性可加的。
换句话说,如果我们有两个输入信号,将它们分别输入到系统中,我们可以在系统的输出中将它们加起来,并得到对应的输出信号。
另外一个重要的性质是时不变性,就是说当输入信号的时间变化时,输出信号的时间变化也会随之发生。
这个性质告诉我们,系统的行为不随着时间的改变而改变。
除此之外,线性系统还有其他很多性质,比如可逆性、稳定性、因果性等等。
二、线性系统的应用线性系统有着广泛的应用,它们可以用来描述很多各种各样的问题,包括但不限于电子电路、航天控制、化学反应、经济系统等等。
下面我们来看看这些应用领域中的具体案例。
1. 电子电路线性系统在电子电路中有着广泛应用。
例如,如果我们想要设计一个低通滤波器,以使高频信号被抑制,我们可以使用线性系统来描述它的行为。
我们可以将电子电路看作一个输入信号到输出信号的转换器。
这个转换器的输出信号可以通过控制电子器件的电流、电压等参数来实现。
这种线性系统可以用来滤掉任何频率的信号,因此在广播和通信中也有广泛的应用。
2. 航天控制航天控制是线性系统理论的一个应用重点。
它包括控制飞行器姿态、轨道以及动力学行为。
在这些问题中,线性可变系统被广泛应用。
这种系统的输出信号是受到飞行器的控制和环境因素的影响。
控制器的任务是计算信号,以引导飞行员和总体系统实现期望的性能和特征。





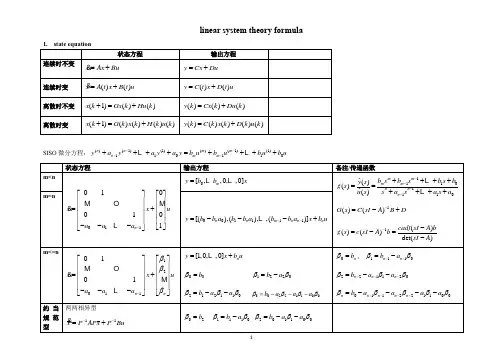
线性系统理论Linear System Theory 1-1 状态空间的基本概念例1-1 图示RLC 网络。
设:u i 为输入变量;u o =u c 为输出变量。
2 状态空间描述中常用的基本概念例1-1 图示RLC 网络。
设:u i 为输入变量;u o =u c 为输出变量。
用矩阵表示状态空间表达式:⎪⎨+−−=u x R x x 11&1-2 线性连续系统状态空间表达式的建立1......)((b s b s b s b s Y G n n ++++−1 N(s)/D(s)的串联分解——可控标准型实现x&x x⎤⎡⎡00010L &状态变量图例1-5 已知系统微分方程:u u T y y y +=ω+ωζ+试求系统的状态空间表达式,并绘制该系统的状态变量图。
21u x x x+ζω−ω−=22&2 可观测标准型实现设可控标准型实现为例1-6 已知系统微分方程:试求可观测标准型实现,并绘制其状态变量图。
3 并联分解——Jordan标准型实现⎤⎡−s L 0001ss s s U s G 89)()(23++==例1-7 已知某系统传递函数:⎡1⎤4 矩阵的特征方程、特征值1)方阵2 线性定常连续系统状态方程的求解2-1 齐次状态方程的解⎢⎣⎥⎦⎢⎣−−=⎥⎦⎢⎣22x 32x &解:用拉氏变换的方法:例2-1 求已知状态方程的状态转移矩阵。
2-2 状态转移矩阵的性质例2-2 已知状态转移矩阵,求Φ-1和系统矩阵A。
性质9 若例2-3已知系统矩阵,求状态转移矩阵及其状态转移矩阵的逆。
非齐次状态方程:例2-4 已知状态空间描述及零初始条件,输入为单位阶跃,求状态方程的解SISO系统:例9-29 已知系统动态方程,试求系统的传递矩阵。
⎡x&9-4-2开环与闭环传递矩阵MIMOU(s)E(s)Y(s)由图可知:3-1 线性系统的可控性与可观性3-1-1 问题的提出例3-2 已知系统状态空间表达式,⎧3-2 可控性问题基本概念考虑线性系统:3-3 可观测性的基本概念3-4 线性定常系统可控性判据考虑线性定常系统:例3-3 判断已知系统的可控性。