湖南大学机自英语教程 (8)
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:152.50 KB
- 文档页数:20

机械设计制造及其自动化自我介绍英文English:Hello, my name is [Your Name], and I am a mechanical design and manufacturing major at [Name of University]. I am passionate about this field because it combines my interest in engineering, problem-solving, and creativity. I have always been fascinated by how things work and how they can be improved, which is why I chose to study mechanical design and manufacturing.Throughout my studies, I have gained a solid foundation in mechanical engineering principles, including mechanics, materials science, thermodynamics, and fluid mechanics. I have also developed strong technical skills in computer-aided design (CAD) software, such as SolidWorks and AutoCAD. I believe that having a strong theoretical understanding combined with practical skills is essential in becoming a successful mechanical designer and manufacturer.In addition to my academic achievements, I have also participated in several extracurricular activities related to mechanical design andmanufacturing. For instance, I was part of a team that competed in the annual Robotics Challenge, where we designed and built a functioning robotic arm. This experience allowed me to apply my knowledge in a real-world setting and enhanced my problem-solving abilities. I have also completed an internship at a local manufacturing company, where I gained hands-on experience in product design, manufacturing processes, and quality control.I am a highly motivated individual who thrives in a team setting, as I believe that collaboration and communication are vital in achieving optimal results. I enjoy working with diverse individuals who bring different perspectives and ideas to the table. I am also a quick learner and adapt easily to new technologies and software, which is crucial in today's rapidly evolving technological landscape.In conclusion, my passion for mechanical design and manufacturing, combined with my strong technical skills and practical experience, make me well-suited for a career in this field. I am eager to apply my knowledge and contribute to the development of innovative and efficient mechanical systems. Thank you for considering my application.中文翻译:大家好,我叫[你的名字],我是 [大学名称] 机械设计与制造专业的学生。

Self-Introduction for Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation MajorGood day, esteemed panel. My name is [Your Name], and I am delighted to have the opportunity to introduce myself for the Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation program.My academic journey in this field began with a fundamental understanding of mechanical principles and designs. Through rigorous coursework and practical experiences, I have honed my skills in CAD software, manufacturing processes, and automation technologies. My coursework has not only equipped me with theoretical knowledge but also allowed me to apply it to real-world problems.My interest in this field is rooted in my curiosity about how things work and the desire to create efficient and innovative solutions. I am passionate about the integration of technology and mechanics to improve manufacturing processes and increase productivity. My goal is to contribute to the advancement of this field by developing sustainable and cost-effective manufacturing systems.Outside the classroom, I have gained valuable experience through internships and projects. One of my most notable achievements was my involvement in a project that aimed to automate a manufacturing process, reducing operational costs and increasing output quality. This experience has given me insights into the practical challenges of mechanical manufacturing and the importance of innovative thinking.I am excited about the opportunities that lie ahead in this rapidly evolving field. I am committed to continuous learning and am eager to apply my knowledge and skills to make a meaningful contribution to the world of mechanical manufacturing and automation.Thank you for considering my application. I look forward to the possibility of further discussing my qualifications and how I can contribute to this program.尊敬的各位面试官,大家好。

湖南的大学英语教材书目大学英语教材对于培养大学生的英语语言能力和跨文化交际能力起着重要的作用。
湖南的大学英语教材书目也在不断提升和发展,以满足学生的学习需求。
以下是湖南大学的英语教材书目推荐:一、大学英语教材1. 《大学英语》(第四版)- 王梦芸、姜丽萍编著这是湖南省高校大学英语教材的主要版本之一。
该教材分为四册,以培养学生的听、说、读、写和翻译能力为主要目标。
教材内容涵盖了语法、阅读、写作、听力、翻译等方面,同时注重培养学生的综合运用能力。
2. 《全新版大学英语》(综合教程)- 韩礼元、王玲编著该套教材为湖南省高校大学英语综合教程的重要版本之一。
教材引入了任务型教学法,通过生动的对话、主题文章和多媒体资源进行教学,使学生能够在实际语境中运用英语进行交际和表达。
教材内容设计灵活,同时包含了听说读写翻译等多个层面。
二、阅读教材1. 《大学英语阅读》(第二版)- 王梦芸主编该教材旨在提高学生的阅读速度和阅读理解能力,涵盖了各种不同主题和体裁的短文。
教材通过选取有代表性的文章,帮助学生了解不同的文化背景和观点,提高他们的跨文化交际能力。
2. 《大学英语阅读与翻译》- 陆向华主编该教材旨在培养学生的阅读理解和翻译能力。
教材内容包括了不同主题和体裁的文章,如社会热点、科技进展和文化交流等。
通过练习和任务的设计,学生能够提高在阅读和翻译方面的能力。
三、语法教材1. 《英语语法与写作》(第三版)- 施宏明主编该教材主要用于提高学生的语法意识和写作能力。
教材内容结构清晰,包括了基础语法知识、句型转换、作文写作等部分。
通过系统性的学习,学生能够在英语表达和写作上得到提升。
2. 《英语语法精讲精练》(第二版)- 张天红主编该教材主要面向学生的语法系统训练和巩固。
教材内容包括了语法知识的讲解、练习和测试题等。
学生可以通过自主学习和练习,快速提高对英语语法的掌握程度。
总结湖南的大学英语教材书目包括了大学英语教材、阅读教材和语法教材等多个方面。

机械专业英文教程机械类专业英语应用教程一、机械类专业术语作为机械类专业的学生,掌握专业术语是必不可少的。
本章节将介绍一些常见的机械类专业术语,包括但不限于:机械零件、机械装置、机械系统、机械设计、机械制造、机械工程等。
通过学习这些术语,学生可以更好地理解机械类专业的基础知识。
二、机械设计基础机械设计是机械工程的重要组成部分,它涉及到如何根据实际需求设计出性能优越、结构合理的机械装置。
本章节将介绍机械设计的基本原理和方法,包括载荷分析、强度计算、结构设计等。
此外,还将介绍一些常用的机械设计软件,如AutoCAD、SolidWorks等。
三、制造工艺与装备制造工艺与装备是实现机械设计的重要手段。
本章节将介绍一些常见的制造工艺与装备,如切削加工、铸造、焊接、热处理等。
此外,还将介绍一些先进的制造技术,如数控加工、3D打印等。
通过学习这些内容,学生可以更好地了解如何将设计转化为实际产品。
四、数控技术与编程数控技术是现代制造技术的代表,它具有高精度、高效率的特点。
本章节将介绍数控技术的基本原理和编程方法,包括数控机床的组成、数控编程语言、加工工艺等。
此外,还将介绍一些常用的数控编程软件,如Mastercam、CNC 编程等。
五、自动化与机器人技术自动化与机器人技术是现代工业发展的重要趋势。
本章节将介绍自动化与机器人技术的基本原理和应用,包括工业机器人、自动化生产线等。
此外,还将介绍一些先进的自动化与机器人技术,如机器视觉、智能机器人等。
六、机电一体化技术机电一体化技术是将机械技术与电子技术相结合的一种综合技术。
本章节将介绍机电一体化技术的基本原理和应用,包括传感器、电机驱动、控制系统等。
此外,还将介绍一些典型的机电一体化产品,如数控机床、自动化生产线等。
七、液压与气压传动液压与气压传动是一种常见的传动方式,具有传递力大、传动平稳等特点。
本章节将介绍液压与气压传动的基本原理和应用,包括液压泵、液压缸、气瓶等。
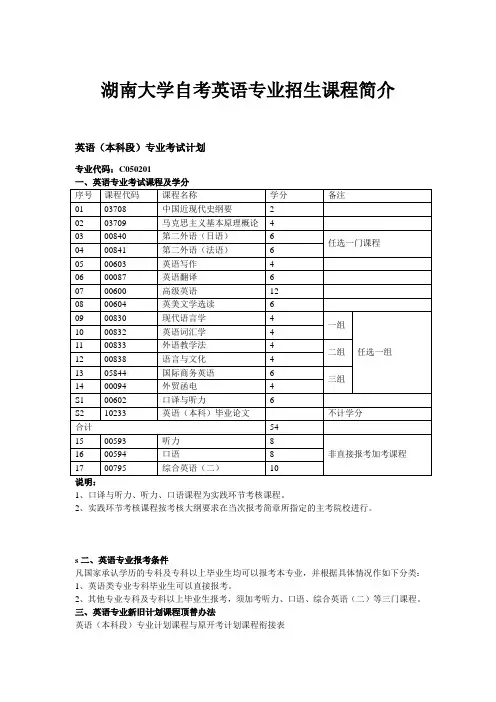
湖南大学自考英语专业招生课程简介英语(本科段)专业考试计划专业代码:C050201一、英语专业考试课程及学分 序号 课程代码 课程名称 学分 备注 01 03708 中国近现代史纲要 2 02 03709 马克思主义基本原理概论 403 00840 第二外语(日语) 6 任选一门课程 04 00841 第二外语(法语) 6 05 00603 英语写作 4 06 00087 英语翻译 6 07 00600 高级英语 12 08 00604 英美文学选读 6 09 00830 现代语言学 4 一组 任选一组10 00832 英语词汇学 4 11 00833 外语教学法 4 二组 12 00838 语言与文化 4 13 05844 国际商务英语 6 三组 14 00094 外贸函电 4 S1 00602 口译与听力6 S2 10233英语(本科)毕业论文不计学分 合计 5415 00593 听力 8 非直接报考加考课程 16 00594 口语8 1700795综合英语(二)10说明:1、口译与听力、听力、口语课程为实践环节考核课程。
2、实践环节考核课程按考核大纲要求在当次报考简章所指定的主考院校进行。
s 二、英语专业报考条件凡国家承认学历的专科及专科以上毕业生均可以报考本专业,并根据具体情况作如下分类: 1、英语类专业专科毕业生可以直接报考。
2、其他专业专科及专科以上毕业生报考,须加考听力、口语、综合英语(二)等三门课程。
三、英语专业新旧计划课程顶替办法英语(本科段)专业计划课程与原开考计划课程衔接表新计划中课程原开考计划中课程序号课程代码课程名称01 00840 第二外语(日语)8027 日语07302 00841 第二外语(法语)8011法语07403 00603 英语写作080 英语写作04 00087 英语翻译072 英语翻译05 00600 高级英语069 高级英语06 00604 英美文学选读075 英美文学选读075 美国文学史及作品选读、076 英国文学史及作品选读07 00830 现代语言学077 现代语言学08 00832 英语词汇学078 英语词汇学09 00833 外语教学法076 外语教学法、教育学10 00838 语言与文化058 语言与文化、心理学11 05844 国际商务英语00834 英语经贸知识05912 00094 外贸函电060 外贸函电13 00602 口译与听力066 口译与听力14 00593 听力8049 英语听力064英语听说15 00594 口语8048 英语口语07016 00795 综合英语(二)067 综合英语(二)、基础英语(二)、基础英语17 10233 英语(本科)毕业论文7072 毕业论文参考文章来源:湖南大学自考网/html/zkzy/20120820181.htm l。

机械设计制造及其自动化英语Mechanical Design, Manufacturing and AutomationMechanical design, manufacturing, and automation play a crucial role in modern industrial processes. These processes involve the creation of products and machines, as well as the development of automated systems to streamline production and increase efficiency.The process of mechanical design starts with conceptualizing a product or machine, followed by detailed design and analysis. This is often done using computer-aided design (CAD) software, which allows engineers to create 3D models and simulate the behavior of the product under various conditions. Once the design is finalized, it is then sent for manufacturing.Manufacturing involves a variety of processes, including machining, casting, molding, and additive manufacturing. Each of these processes has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of manufacturing method depends on the specific requirements of the product. Advanced manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, are also becoming more prevalent, offering new possibilities for design and production.Automation is another key aspect of modern manufacturing, with many processes being fully or partially automated. This includes the use of robots and machinery to perform repetitive tasks, as well as the implementation of advanced control systems to optimize production. Automation not only increases efficiency but also improves safety by reducing the need for manual labor inhazardous environments.Overall, mechanical design, manufacturing, and automation are essential components of modern industry, driving innovation and enabling the production of high-quality products in a cost-effective manner. As technology continues to advance, the role of these processes will only become more important in shaping the futureof manufacturing.当谈到机械设计、制造和自动化时,值得注意的是这些领域的发展也在不断受到数字化和智能化的影响。


机械制造及其自动化专业英语自我介绍As a student pursuing a degree in Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation, I am excited to share my passion for this dynamic field. This specialized major encompasses a wide range of interdisciplinary subjects, from advanced engineering principles to cutting-edge technological developments. Through my studies, I have gained a deep appreciation for the intricate workways of modern manufacturing processes and the transformative power of automation.At the core of Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation lies the fundamental understanding of mechanical systems and their underlying principles. This includes a comprehensive knowledge of materials science, thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, and machine design. By delving into these foundational areas, I have developed the ability to analyze complex mechanical systems, optimize their performance, and devise innovative solutions to engineering challenges.One of the key aspects of this major is the integration of automationtechnologies into manufacturing processes. The rapid advancements in robotics, computer numerical control (CNC) machines, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) have revolutionized the way products are designed, fabricated, and assembled. As a student in this field, I have gained hands-on experience with these cutting-edge technologies, learning how to program, operate, and maintain automated systems.The integration of automation has significantly improved the efficiency, precision, and quality of manufacturing operations. Through the use of sensors, feedback control systems, and advanced software, production processes can be streamlined, waste can be minimized, and product consistency can be achieved. Furthermore, the incorporation of additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, has opened up new avenues for customized and on-demand production, revolutionizing the way we approach product development and supply chain management.Beyond the technical aspects of Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation, this major also emphasizes the importance of sustainable and environmentally-conscious practices. As the global community becomes more aware of the need for sustainable development, the role of mechanical engineers and automation specialists has become increasingly crucial. I have learned about the principles of green manufacturing, which involve the optimization ofenergy consumption, the reduction of waste and emissions, and the implementation of recycling and reuse strategies.Through my coursework, I have had the opportunity to work on projects that tackle real-world challenges in the manufacturing industry. For example, I have collaborated with my peers to design and prototype automated systems for material handling, quality control, and assembly line optimization. These hands-on experiences have not only honed my technical skills but have also fostered my ability to work effectively in a team, communicate complex ideas, and think critically to solve problems.Furthermore, the Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation major has provided me with a solid foundation in project management, data analysis, and decision-making. These transferable skills are highly valued in various industries, as they enable professionals to navigate the complexities of modern manufacturing environments and contribute to the development of innovative products and processes.As I look towards the future, I am excited about the potential career paths that this major can open up. Graduates of Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation programs are sought after in a wide range of industries, including automotive, aerospace, electronics, consumer goods, and renewable energy. The demand for skilledprofessionals who can bridge the gap between mechanical engineering and automation is only expected to grow as the manufacturing landscape continues to evolve.In my pursuit of this degree, I have developed a deep appreciation for the intricate workways of modern manufacturing and the transformative power of automation. I am passionate about leveraging my knowledge and skills to contribute to the advancement of this dynamic field. Whether it is optimizing production processes, designing innovative manufacturing systems, or developing sustainable solutions, I am committed to making a positive impact on the industry and society as a whole.As I continue my journey in Mechanical Manufacturing and Automation, I am eager to further expand my knowledge, hone my technical expertise, and collaborate with industry leaders and fellow professionals. I am confident that the skills and experiences I have gained through this major will serve me well in my future endeavors, empowering me to drive the evolution of manufacturing and contribute to the shaping of a more efficient, sustainable, and technologically advanced world.。

机电一体化技术所学课程自我介绍英语Hello, my name is [Your Name], and I am a student learning 机电一体化技术 (Integrated Technology of Mechanical and Electrical Engineering). 你好,我叫[你的名字],是一名学习机电一体化技术的学生。
This course is a combination of mechanical engineering and electrical engineering, integrating the two disciplines to create innovative solutions in various industries. 这门课程是机械工程和电气工程的结合,将这两个学科整合在一起,以在各个行业中创造创新解决方案。
One aspect of this course that I find particularly intriguing is the blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. 这门课程让我特别着迷的一个方面是理论知识和实践技能的结合。
We not only learn about the principles behind machine design and electrical systems, but we also have the opportunity to apply this knowledge in hands-on projects and experiments. 我们不仅学习机械设计和电气系统背后的原理,而且还有机会将这些知识应用于实践项目和实验中。
In addition, the 机电一体化技术 course provides a comprehensive understanding of mechatronics systems, which are essential intoday's technology-driven world. 此外,机电一体化技术课程提供了对机电一体化系统的全面了解,这在当今技术驱动的世界中是至关重要的。
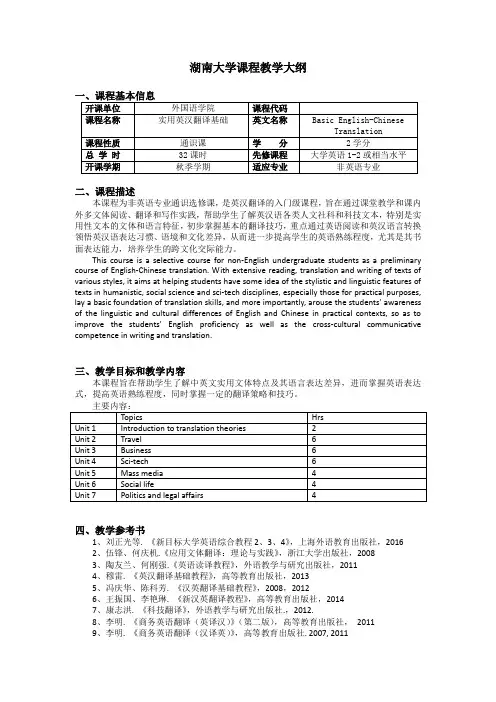
湖南大学课程教学大纲二、课程描述本课程为非英语专业通识选修课,是英汉翻译的入门级课程,旨在通过课堂教学和课内外多文体阅读、翻译和写作实践,帮助学生了解英汉语各类人文社科和科技文本,特别是实用性文本的文体和语言特征,初步掌握基本的翻译技巧,重点通过英语阅读和英汉语言转换领悟英汉语表达习惯、语境和文化差异,从而进一步提高学生的英语熟练程度,尤其是其书面表达能力,培养学生的跨文化交际能力。
This course is a selective course for non-English undergraduate students as a preliminary course of English-Chinese translation. With extensive reading, translation and writing of texts of various styles, it aims at helping students have some idea of the stylistic and linguistic features of texts in humanistic, social science and sci-tech disciplines, especially those for practical purposes, lay a basic foundation of translation skills, and more importantly, arouse the students’ awareness of the linguistic and cultural differences of English and Chinese in practical contexts, so as to improve the students’English proficiency as well as the cross-cultural communicative competence in writing and translation.三、教学目标和教学内容本课程旨在帮助学生了解中英文实用文体特点及其语言表达差异,进而掌握英语表达式,提高英语熟练程度,同时掌握一定的翻译策略和技巧。

Automatic Control Principles 8th Edition - CourseDesign (English Version)AbstractThe course design of Automatic Control Principles 8th Editionfocuses on the application of theoretical knowledge and practical skills. It ms to enhance students’ understanding of automatic controlprinciples and their ability to analyze and design control systems. This document contns a summary of the course design, including the course objectives, content, teaching methods, materials, assessments, and expected outcomes.Course ObjectivesUpon completion of this course, students should be able to:•Understand the fundamental principles of automatic control and the mathematical models of dynamic systems.•Analyze the stability, performance, and robustness of control systems using frequency response and time domn methods.•Design control systems using classical and modern control techniques.•Implement and simulate feedback control systems using computer tools (e.g., MATLAB, Simulink).•Evaluate the effectiveness and limitations of different control strategies in specific applications (e.g., robotics,automotive systems, industrial processes).Course ContentThe course is structured into 14 lectures and 10 lab sessions. The lectures cover the following topics:1.Introduction to automatic control principles2.Mathematical models of dynamic systems3.Time domn analysis of control systems4.Stability analysis of control systems5.Root locus method for control system design6.Frequency domn analysis of control systems7.Bode and Nyquist plots for control system design8.Feedback compensation techniques9.State space analysis of control systems10.Controllability and observability11.Pole placement and observer design12.Nonlinear control systems13.Digital control systems14.Advanced topics in control systems (e.g., adaptivecontrol, fuzzy control, neural networks)The lab sessions provide hands-on experience in designing andtesting control systems using MATLAB and Simulink. The lab topics include:1.Modeling and simulation of dynamic systems2.Time and frequency response analysis of control systems3.Design of proportional-integral-derivative (PID) controllers4.Root locus and frequency response design of control systems5.State space design of control systems6.Robust control design using H-infinity and µ-synthesis7.Nonlinear control system design using feedback linearizationand sliding mode control8.Digital control system design using discretization anddigital filtering9.Experimental validation of control system designs10.Final project on control system design andimplementationTeaching MethodsThe course adopts a blended learning approach, combining face-to-face lectures with online resources and activities. The lectures provide the theoretical foundations of automatic control principles, while the lab sessions offer hands-on practice and experimentation. The online resources include recorded lectures, slides, notes, quizzes, and forums. Students are expected to read the course materials before each lecture and participate in class discussions and group projects. The teaching methods also emphasize the integration of real-world applications and examples into the course content.MaterialsThe required course materials include the textbook。
机械设计制造及其自动化专业英语Mechanical Design, Manufacturing, and Automation in EnglishIntroduction:Mechanical Design, Manufacturing, and Automation is a specialized field within engineering that focuses on the design, development, and production of mechanical systems and automated processes. This field requires a strong knowledge of engineering principles, manufacturing techniques, and automation technologies. In this text, we will explore the key concepts, methodologies, and technologies associated with Mechanical Design, Manufacturing, and Automation.1. Mechanical Design:Mechanical design is the process of creating and developing mechanical systems, components, and products. It involves various stages, including conceptualization, analysis, and detailed design. The main objective of mechanical design is to ensure that the resulting product meets the desired functionality, performance, and safety requirements.1.1 Conceptualization:During the conceptualization stage, engineers brainstorm and generate ideas for new products or improvements to existing ones. They consider factors such as market needs, customer requirements, and technological advancements. This stage often involves sketching, prototyping, and conducting feasibility studies.1.2 Analysis:In the analysis stage, engineers evaluate the proposed designs using computer-aided design (CAD) software and simulation tools. They assess factors such as structural integrity, thermal performance, fluid dynamics, and ergonomics. This analysis helps identify potential issues and refine the design before moving to the detailed design phase.1.3 Detailed Design:During the detailed design phase, engineers develop the final design specifications and create detailed drawings and models. They consider factors such as material selection, manufacturing processes, and assembly requirements. This stage involves collaboration with manufacturing engineers to ensure that the design can be efficiently manufactured.2. Manufacturing:Manufacturing is the process of transforming raw materials into finished products through various production techniques. It involves a series of steps, including material preparation, machining, assembly, and quality control. Efficient manufacturing plays a crucial role in ensuring product quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery.2.1 Material Preparation:Material preparation involves selecting and preparing the appropriate raw materials for the manufacturing process. This may include cutting, shaping, and treating the materials to meet the desired specifications. Material properties, such as strength, durability, and corrosion resistance, are carefully considered during this stage.2.2 Machining:Machining is the process of shaping and forming materials using various cutting tools and machines. Common machining techniques include milling, turning, drilling, and grinding. Computer numerical control (CNC) machines are often used to automate and enhance the precision of these processes.2.3 Assembly:Assembly is the process of combining individual components to create a final product. This may involve manual labor or the use of automated assembly systems. Assembly techniques vary depending on the complexity of the product and can include methods such as welding, soldering, and fastening.2.4 Quality Control:Quality control is an essential aspect of manufacturing. It involves inspecting and testing the products at various stages to ensure they meet the specified standards. This may include dimensional checks, material testing, and functional testing. Quality control helps identify and rectify any defects or deviations from the desired specifications.3. Automation:Automation refers to the use of technology and machines to perform tasks with minimal human intervention. In the context of mechanical design and manufacturing, automation plays a significant role in improving productivity, efficiency, and consistency.3.1 Robotics:Robotic automation involves the use of robots to perform repetitive or complex tasks. Robots can be programmed to handle tasks such as material handling, assembly, and quality inspection. They can significantly increase production speed and accuracy while reducing the risk of human error.3.2 Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM):Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) involves the use of computer software to control and optimize manufacturing processes. CAM systems generate instructions for machines, such as CNC machines, based on the design specifications. This automation reduces manual intervention and improves the precision and efficiency of manufacturing.3.3 Internet of Things (IoT):The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that can communicate and exchange data. In the context of manufacturing, IoT enables the integration and monitoring of various machines and systems. This connectivity allows for real-time data collection, analysis, and control, leading to improved efficiency, predictive maintenance, and quality control.Conclusion:Mechanical Design, Manufacturing, and Automation is a multidisciplinary field that combines engineering principles, manufacturing techniques, and automation technologies. It involves the design, development, and production of mechanical systems and automated processes. By understanding the key concepts and methodologies discussed in this text, professionals in this field can contribute to the advancement of technology and innovation in various industries.。
自动化专业英语教程Automatic Control Engineering English CourseUnit 1: Introduction to Automatic Control Engineering1.1 Introduction to Automatic Control EngineeringAutomatic Control Engineering is a branch of engineeringthat deals with the design, construction, and operation ofcontrol systems. These control systems are used to regulate and manipulate the behavior of dynamic systems. In this course, wewill learn about the fundamental principles and techniques usedin Automatic Control Engineering.1.2 Control Systems1.3 Feedback Control SystemsUnit 2: Modeling and Analysis of Control Systems2.1 System ModelingSystem modeling is the process of representing a physical system in terms of mathematical equations. It allows us to analyze and design control systems using mathematical techniques. This unit will cover various methods of system modeling.2.2 Transfer FunctionsTransfer functions are a mathematical representation of the relationship between the input and output of a system. They areused to analyze the stability, transient response, and frequency response of control systems. In this unit, we will learn how to derive and use transfer functions.2.3 Block DiagramsUnit 3: Control System Design3.1 Classical Control DesignClassical control design refers to the design of control systems using classical control theory. This theory is based on the principles of proportional, integral, and derivative (PID) control. It provides simple and intuitive methods for designing control systems.3.2 PID Control3.3 State-Space Control DesignState-space control design is a modern approach to control system design. It represents the system in terms of state variables and uses linear algebra and matrix theory to design controllers. State-space control design provides moreflexibility and control over the system's behavior.Unit 4: Digital Control Systems4.1 Introduction to Digital Control Systems4.2 Discrete-Time Systems4.3 Digital Controller DesignUnit 5: Advanced Topics in Automatic Control Engineering5.1 Robust ControlRobust control is a control design approach that takes into account uncertainties and variations in system parameters. It aims to design controllers that can maintain acceptable performance even in the presence of uncertainties. In this unit, we will learn about robust control techniques.5.2 Nonlinear ControlNonlinear control deals with the control of dynamic systems with nonlinear behavior. It requires advanced techniques such as Lyapunov stability analysis, sliding mode control, and adaptive control. This unit will provide an introduction to nonlinear control.5.3 Intelligent ControlConclusion。