Overview of Repair
Stimuli or stress can lead the cell damage (cell injury, necrosis)
In the same time, injured cells release some soluble factors to star the process of repair
Then the CDK is inactivated and the cyclin breakdown
Tissue Repair: Cell Regeneration and
Fibrosis
Tissue Repair
Cell regeneration Growth factors in cell regeneration and fibrosis Stem cell Repair by connective tissue (fibrosis) Wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair
Cell Proliferation
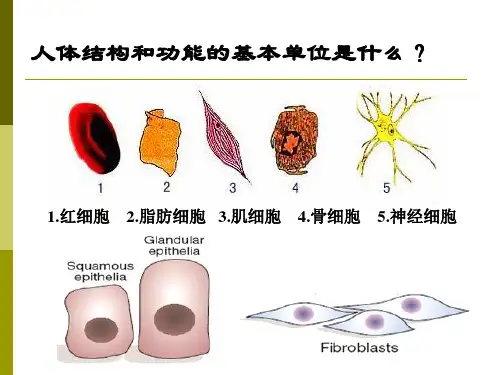
Classification of cells by their proliferative potential Labile (epithelium of skin, respiratory tract,
gastrointestinal tract and urinary tract, lymphoid cell, et al) Stable (parenchymal cells in liver, kidney, pancreas, salivary gland, et al) Permanent (myocardium, skeletal muscle, neuron)