应激性高血糖的治疗及护理
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:918.00 KB
- 文档页数:13



心脏外科病人术后应激性高血糖的护理发表时间:2016-04-18T16:06:31.153Z 来源:《医师在线》2015年11月第23期供稿作者:沈静[导读] 兰州大学第二医院CICU 应激性血糖升高是无糖尿病史的突如其来的严重疾病或创伤后,造成人体血糖迅速升高的现象。
沈静兰州大学第二医院CICU 甘肃兰州 730000摘要:心脏手术过程中的创伤可引起机体强烈的应激反应,导致内分泌代谢紊乱、糖耐量异常,从而出现术后应激性高血糖。
术后持续高血糖会造成机体内环境呈高渗状态,导致组织细胞损伤及水、电解质失衡,最终影响病人的手术效果和临床预后。
因此,加强对心脏手术病人的应激性高血糖护理,合理控制血糖水平,对提高临床治疗效果具有重要的意义。
本文对心脏外科病人术后应激性高血糖的护理进行了分析。
关键词:心脏外科病人术后;应激性高血糖;护理引言应激性血糖升高是无糖尿病史的突如其来的严重疾病或创伤后,造成人体血糖迅速升高的现象。
心脏外科术后是临床比较常用的治疗方法,机体因此种治疗方法造成的创伤会表现出强烈的应激,从而使全身代谢和神经内分泌情况发生改变,引起糖耐量出现异样变化,最终发展成应激性高血糖,机体一旦处于高血糖状态,就非常容易导致组织高渗透性以至于发生水电解质紊乱和细胞损伤的情况,免疫功能不断下降,感染发生率较高,对手术整体效果以及预后造成非常不利的影响。
1资料与方法1.1一般资料2013年1月—2014年12月,本科共收治心脏手术术后发生应激性高血糖的病人35例,其中男20例,女15例;年龄45岁~76岁(55.3岁±10.3岁)?病人于术前均经过心电图?超声心动图等确诊需行心脏手术?手术采用常规全身麻醉,并在浅低温无糖预充液的体外循环下施行手术?35例病人中,术前诊断心功能不全15例,所有病人术前无肝肾功能不全及糖尿病病史?住院期间发生肺部感染2例,死亡1例,其余病人均痊愈出院,住院天数17.6d±3.2d?1.2方法入院后立即心电监护,血糖、心肌酶谱、电解质和肝、肾功能等进行检测,记录患者的年龄、性别、CK-MB、心脏Killip功能分级情况。


ICU 患者应用肠内营养剂期间血糖管理由于肠内营养(EN)在维护肠道黏膜屏障、肠道动力及内分泌功能方面的特殊作用,已成为重症患者最理想的营养支持途径。
伴有胰岛素抵抗的高血糖是重症患者糖代谢改变的特点,不论既往是否有糖尿病史,高血糖是营养支持的常见合并症。
很多研究表明,应激性高血糖可作为一个独立的因素影响危重症患者的预后。
因此,在EN 支持期问应关注血糖并给予恰当的血糖控制。
一、应激性高血糖1、定义:应激性高血糖是在各种危重病人,如高热、急性心肌梗死,脑出血或脑血栓形成、大手术、创伤如骨折、重度烧伤等由于处于应激状态,升糖激素如糖皮质激素分泌比平时增加10倍以上,胰高血糖素、儿茶酚胺、生长激素等也分泌增多,暂时出现的高血糖、尿糖以及糖耐量减低的病理现象。
2、诊断标准:两次空腹血糖水平≥7mmol/L 或随机血糖≥11.1mmol/L3、应激性高血糖对机体影响:应激性高血糖细胞内氧化作用升高 自由基与过氧化物产生升高 诱导单核细胞炎症因子表达 细胞因子释放增加损伤中性粒细胞及吞噬细胞的杀伤能力及补体功能。
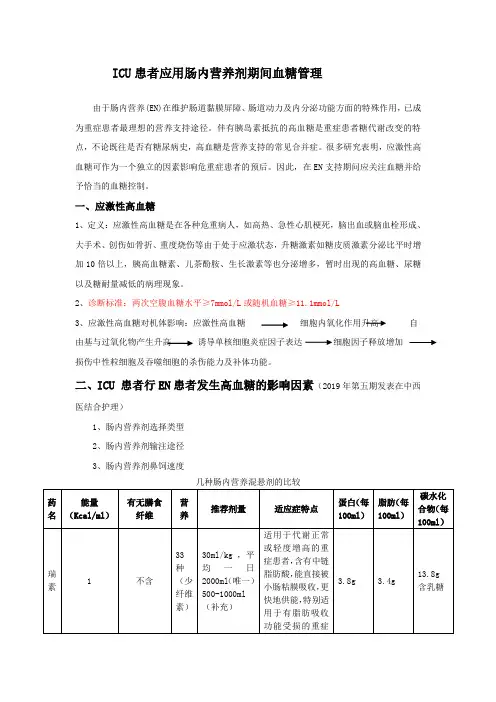
二、ICU 患者行EN 患者发生高血糖的影响因素(2019年第五期发表在中西医结合护理)1、肠内营养剂选择类型2、肠内营养剂输注途径3、肠内营养剂鼻饲速度几种肠内营养混悬剂的比较2、常用的EN输注途径:(1)用肠内营养泵经空肠插管,24h持续均匀输入;(2)靠重力经胃管持续滴入(3)间歇少量分次滴入(口服摄入),一般每2-4h一次每次50-250m左右。
3. EN鼻饲速度:24h持续输入时血糖波动最小,肠内营养输注速度对患者血糖控制影响比较大,随着速度的加快,血糖升高。
肠内营养液中含有一定浓度的钠离子,而在鼻饲速度较快的情况下,进入肠腔的钠离子浓度越高,可通过影响小肠上皮细胞葡萄糖转运体的顺浓度扩散作用而诱发高血糖。
2019年护理学杂志:对照组:患者肠内营养液达全量耐受的速度输注,一般控制在70~100 mL/h,实验组:自肠内营养达全量后第1天根据血糖调整营养泵输注速率。



护理干预在ICU患者应激性高血糖血糖控制中的应用效果廖中梅;唐志红【摘要】Objective To investigate the effect of nursing intervention on blood glucose control of ICU patients with stress hyperglycemia.Methods A total of 120 ICU stress hyperglycemia patients were randomly divided into observation group and control group,with 60 cases per group.The control group received routine nursing and the observation group was given intensive glucose control nursing,and blood glucose control,insulin dosage,recovery and prognosis of the two groups were compared.Results The insulin dosage in the observation group was less than that in the control group,the blood glucose after intervention was lower,the blood glucose was less,the time of blood glucose reaching standard was shorter than the control group,and the hypoglycemia was less than that in the control group,the differences were statistically significant (P <0.05).The mechanical ventilation time and ICU time in the observation group were shorter,the incidence rate of MODS was lower than that in the control group,and the differences were statistically significant (P <0.05).Conclusion Intensive hypoglycemic nursing can improve the level of blood glucose control,reduce the dosage of insulin,and improve the prognosis of patients with ICU stress hyperglycemia.%目的探讨护理干预在ICU患者应激性高血糖血糖控制中的应用效果.方法将ICU收治的120例ICU应激性高血糖患者随机分为观察组和对照组各60例.对照组给予常规护理,观察组给予强化降糖护理,比较2组的血糖控制情况、胰岛素用量、恢复情况及预后等.结果观察组的胰岛素用量少于对照组,干预后的血糖低于对照组,血糖达标时间短于对照组,低血糖例次少于对照组(P<0.05);观察组的机械通气时间、住ICU时间短于对照组,MODS发生率低于对照组(P<0.05).结论强化降糖护理能够提高ICU应激性高血糖患者的血糖控制水平,减少胰岛素用量,改善预后.【期刊名称】《实用临床医药杂志》【年(卷),期】2017(021)018【总页数】4页(P23-26)【关键词】护理干预;ICU;应激性高血糖;血糖控制【作者】廖中梅;唐志红【作者单位】四川大学华西医院重症医学科,四川成都,610041;四川大学华西医院重症医学科,四川成都,610041【正文语种】中文【中图分类】R473.5ABSTRACT: Objective To investigate the effect of nursing intervention on blood glucose control of ICU patients with stress hyperglycemia. Methods A total of 120 ICU stress hyperglycemia patients were randomly divided into observation group and control group, with 60 cases per group. The control group received routine nursing and the observation group was given intensive glucose control nursing, and blood glucose control, insulin dosage, recovery and prognosis of the two groups were compared. Results The insulin dosage in the observation group was less than that in thecontrol group, the blood glucose after intervention was lower, the blood glucose was less, the time of blood glucose reaching standard was shorter than the control group, and the hypoglycemia was less than that in the control group, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The mechanical ventilation time and ICU time in the observation group were shorter, the incidence rate of MODS was lower than that in the control group, and the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Intensive hypoglycemic nursing can improve the level of blood glucose control, reduce the dosage of insulin, and improve the prognosis of patients with ICU stress hyperglycemia.KEY WORDS: nursing intervention; ICU; stress hyperglycemia; blood glucose controlICU是危重患者的集中治疗病区,其护理问题也为大家所关注。

ICU患者应激性高血糖胰岛素强化治疗的监测与护理发表时间:2016-05-17T16:30:51.977Z 来源:《医药前沿》2016年1月第2期作者:蒋莉莉袁丽萍[导读] 皖南医学院第一附属医院弋矶山医院重症监护室对危重病人实行胰岛素强化治疗并进行动态血糖监测及护理干预可有效的控制血糖,改善疾病的预后。
(皖南医学院第一附属医院弋矶山医院重症监护室安徽宣城 241001)【摘要】目的:探讨胰岛素强化治疗ICU患者应激性高血糖过程中的血糖监测及护理措施。
方法:选择123例入住我院ICU,既往无糖尿病病史出现应激性高血糖的的危重患者,采用胰岛素强化治疗控制血糖,并实施动态监测及护理措施。
结果:123例患者中116例血糖控制在安全范围(10.O~11.1mmol/L),血糖控制率为94.3%,效果满意,其中7例因原发疾病加重死亡。
结论:对危重病人实行胰岛素强化治疗并进行动态血糖监测及护理干预可有效的控制血糖,改善疾病的预后。
【关键词】胰岛素;应激性高血糖;监测护理【中图分类号】R473.5 【文献标识码】B 【文章编号】2095-1752(2016)02-0250-02在ICU患者中,应激性高血糖的发生较为普遍,而对于这一概念却并没有严格的标准。
应激性高血糖即指在无糖尿病史患者在应激状态下出现的高血糖,其诊断标准为入院后随机两次以上测量,其空腹血糖≥6.9mmol/L(126mg/dl)或随机血糖≥11.1mmol/L(200mg/dl)。
在应激状态下儿茶酚胺、糖皮质激素、胰高血糖素、生长激素、胰岛素以及多种细胞因子等共同因素调节糖代谢。
从而加重原发疾病,进而诱发多种并发症如严重感染、多器官功能衰竭乃至死亡等。
我科医护人员通过对ICU应激性高血糖患者进行强化胰岛素治疗,减低感染发生率,从而降低了病人的病死率。
取得较为显著的成效,现报道如下:1.资料与方法1.1 一般资料选自2011年12月~2013年1月,入住我院ICU病房患者123例既往无糖尿病病史的急危重患者,其中男68例,女55例;年龄为22~78岁。
35例急性胰腺炎合并应激性高血糖的治疗及护理
刘芳
【期刊名称】《中国保健营养》
【年(卷),期】2012(000)007
【摘要】目的探讨急性胰腺炎合并应激性高血糖患者的治疗及护理。
方法回顾性分析总结2010年1月-2011年1月我科收治的35例急性胰腺炎伴发高血糖患者的临床资料。
结果 35例患者中33例治愈出院,2例病情加重转上级医院继续治疗,无死亡病例。
结论对急性胰腺炎合并高血糖病人进行有效的监测、治疗及护理提高了患者的生活及生存质量。
【总页数】2页(P2840-2841)
【作者】刘芳
【作者单位】龙泉驿区第一人民医院
【正文语种】中文
【中图分类】R473.5
【相关文献】
1.35例急性胰腺炎合并应激性高血糖的治疗及护理 [J], 刘芳
2.危重病儿应激性高血糖临床分析(附35例报告) [J], 余咏文;张强英
3.ICU内应激性高血糖患者胰岛素治疗及护理 [J], 张艳艳;唐丹
4.危重病儿应激性高血糖临床分析:附35例报告 [J], 余咏文;张强英
5.老年重症急性胰腺炎合并应激性高血糖患者血清miR-223、HMGB1检测及意义 [J], 金旭;包先丽;张春芳;杨科
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。