浙江大学2007–2008学年秋季学期《数据结构基础》课程期末考试
- 格式:doc
- 大小:133.50 KB
- 文档页数:6

《数据结构》期末考试试题及答案一、单项选择题1. 数据结构是计算机科学的基础学科之一。
下列哪个选项正确描述了数据结构的定义?A. 数据结构是一种计算机程序B. 数据结构是一种存储和组织数据的方法C. 数据结构是一种人工智能技术D. 数据结构是一种操作系统答案:B2. 链表和数组是常见的数据结构,它们之间的主要区别是:A. 数组可以存储不同类型的数据,而链表只能存储相同类型的数据B. 数组的元素在内存中是连续存储的,而链表的元素在内存中是分散存储的C. 链表可以随机访问元素,而数组只能顺序访问元素D. 链表的插入和删除操作更高效,而数组的访问操作更高效答案:B3. 在二叉树中,每个节点最多可以有多少个子节点?A. 1B. 2C. 3D. 无限多个答案:B二、填空题1. 假设有一组数据 [5, 8, 3, 2, 9],按照从小到大的顺序进行冒泡排序的过程中,经过三次交换后的结果是__2__,__3__,__5__,__8__,__9__。
2. 请完成以下代码,实现栈的入栈和出栈操作:```pythonclass Stack:def __init__(self):self.stack = []def push(self, item):self.stack.append(item)def pop(self):if not self.is_empty():return self.stack.pop()def is_empty(self):# 示例代码s = Stack()s.push(1)s.push(2)s.push(3)print(s.pop()) # 输出 3print(s.pop()) # 输出 2print(s.is_empty()) # 输出 False ```答案:```pythonclass Stack:def __init__(self):self.stack = []def push(self, item):self.stack.append(item)def pop(self):if not self.is_empty():def is_empty(self):return len(self.stack) == 0# 示例代码s = Stack()s.push(1)s.push(2)s.push(3)print(s.pop()) # 输出 3print(s.pop()) # 输出 2print(s.is_empty()) # 输出 False```三、简答题1. 请简要介绍树的基本概念及常见的树结构。
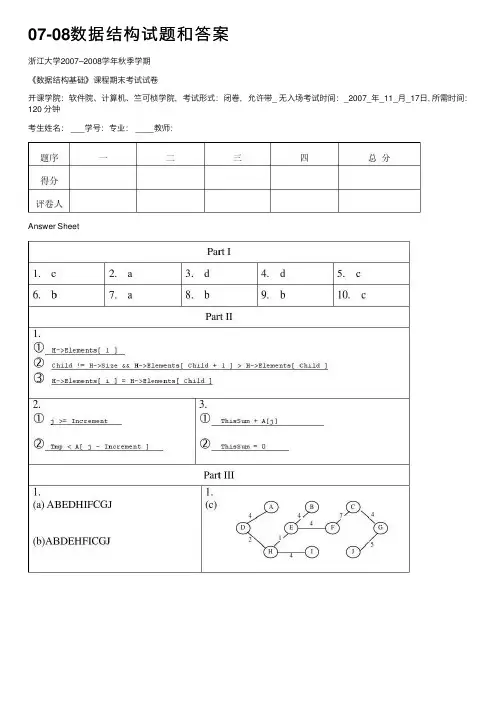
07-08数据结构试题和答案浙江⼤学2007–2008学年秋季学期《数据结构基础》课程期末考试试卷开课学院:软件院、计算机、竺可桢学院,考试形式:闭卷,允许带_ ⽆⼊场考试时间:_2007_年_11_⽉_17⽇, 所需时间:120 分钟考⽣姓名: ___学号:专业: ____教师:Answer SheetNOTE: Please write your answers on the answer sheet.注意:请将答案填写在答题纸上。
I. Please select the answer for the following problems. (20 points)(1)The time complexity of the following piece of code is (2 points) for(i=0; ifor(j=i; j>0; j/=2)printf(“%d\n”, j);a. O(n)b. O(n*n)c. O(nlogn)d. O(n*i)(2)Suppose that the time complexities of two programs are given by T1(N)=O(f(N))and T2(N)=O(f(N)). Which of the following equations is true? (2 points) a. T1(N)+T2(N)=O(f(N)) b. T1(N)-T2(N)=o(f(N))c. T1(N)/T2(N)=O(1)d. T1(N)=O(T2(N))(3)Given an empty stack S and an empty queue Q. A list of characters are pushedinto S in the order of a, b, c, d, e, f and every character that is popped from S will be inserted into Q immediately. If the output of Q is b, d, c, f, e, a, the minimum capacity of S must be . (2 points)a. 6b. 5c. 4d. 3(4)Suppose that the size of a hash table is 11, and the hash function isH(key)=key%11. The following 4 elements have been inserted into the table as Addr(14)=3, Addr(38)=5, Addr(61)=6,Addr(86)=9. When open addressing with quadratic probing is used to solve collisions, the address of the element withkey=49 will be . (2 points)a. 4b. 7c. 8d. 10(5)For a binary tree, given the postorder traversal sequence FDEBGCA and theinorder traversal sequence FDBEACG, the corresponding preorder traversal sequence is . (2 points)a. ABDFEGCb. ABDEFCGc. ABDFECGd. ABCDEFG(6)Insert 10, 12, 1, 14, 6, 5, 8, 15, 3, 9, 7, 4, 11, 13, 2 into an initiallyempty binary min heap one at a time, after performing three DeleteMin operations, the last element of the heap is . (2 points)a. 10b. 11c. 8d. 5(7)Let T be a tree created by union-by-size with N nodes, then the height ofT can be . (2 points)a. at most log2(N)+1b. at least log2(N)+1c. as large as Nd. anything that is greater than 1(8)Given a weighted and connected undirected graph G, there is/are minimumspanning tree(s) of G. (2 points)a. only oneb. one or morec. more than oned. zero or more(9)To find the shortest path between a pair of given vertices, methodcan be used. (2 points)a. Kruskalb. Dijkstrac. Hashingd. Critical Path(10)Among the following sorting algorithms, has the average run timeO(NlogN) with O(N) extra spaces. (2 points)a. Quick sortb. Heap sortc. Merge sortd. Insertion sortII. Given the function descriptions of the following three (pseudo-code) programs, please fill in the blank lines. (24 points) (1)The function is to delete the maximum element in a max heap. (12 points) ElementType DeleteMax( PriorityQueue H ) {int i, Child;ElementType MaxElement, LastElement;MaxElement = ① ;LastElement = H->Elements[ H->Size-- ];for( i = 1; i * 2 <= H->Size; i = Child ){ Child = i * 2;if( ② )Child++;if( LastElement < H->Elements[ Child ] )③ ;else break;}H->Elements[ i ] = LastElement;return MaxElement;}(2)The function is to sort a list of N elements A[] in non-decreasing orderby Shellsort with Shell’s increments. (6 points)void Shellsort( ElementType A[ ], int N ){int i, j, Increment;ElementType Tmp;for ( Increment = N / 2; Increment > 0; Increment /= 2 )for ( i = Increment; i < N; i++ ) {Tmp = A[ i ];for ( j = i; ① ; j - = Increment )if(② )A[ j ] = A[ j - Increment ];else break;A[ j ] = Tmp;}}(3)The function is to find maximum sum value of the subsequence in A[0], A[1], A[2], … A[N-1]. (6 points)int MaxSubsequenceSum(int A[], int N){int ThisSum, MaxSum, j;ThisSum=MaxSum=0;for(j=0; jThisSum = ① ;if (ThisSum >MaxSum)MaxSum= ThisSum;else if (ThisSum <0)② ;}return MaxSum;}III. Please write or draw your answers for the following problems on the answer sheet.(41 points)(1)Please list:(a)the depth-first search sequence;(b)(c)the minimum spanning tree.Note: All the adjacent vertices are to be visited by alphabetical order.(15 points)(2)Insert the numbers 40, 28, 6, 72, 100, 3, 80, 91, 38 into an initially emptybinary search tree. Please show(a)the resulting binary search tree; (10 points) and(b)the resulting binary search tree after 72 is deleted. (3 points)(3)The array representation of the disjoint sets is given by { 2, –4, 2, 2,-3, 5, 6, 9, -2 }. Please list the resulting array elements after invokingUnion(7, 9) with union-by-size. Keep in mind that the elements are numberedfrom 1 to 9. (5 points)(4)Given a list of N elements and an integer k. Please describe two differentalgorithms for finding the kth largest element and give the time complexities.(8 points)IV. If each vertex in an undirected weighted graph has a number of balloons assigned.Explain how to modify Dijkstra's algorithm so that if there is more than one minimum path from v to w, a path with the maximum number of balloons is chosen.(15 points)Note : T[ V ].balloon contains the number of balloons at vertex V.void Dijkstra( Table T )。

__________________学院__________级___________班 姓名_______________ 学号_______________………………………………(密)………………………………(封)………………………………(线)………………………………密 封 线 内 答 题 无 效2007-2008学年度第二学期期末考试数据结构试卷 B 卷答卷说明:1.本试卷共9页,五个大题,满分100分,120分钟完卷。
2.本试卷为闭卷考试,请将所有题目直接做在试卷上。
一、单项选择题(每题21.单循环链表的尾结点的指针域的值为( )。
A) NULL B) 0 C) 首结点地址 D) 尾结点地址2.设有一个足够大的栈,入栈元素的顺序为wxyz,,则栈的可能输出序列是( )。
A )zwyx B )ywxz C )wxyz D )zxyw3.设串s1=’ABCDEFG’,s2=’PQRST’,函数con(x,y)返回x 和y 串的连接串,subs(s, i, j)返回串s 的从序号i 开始的j 个字符组成的子串,len(s)返回串s 的长度,则con(subs(s1, 2, len(s2)), subs(s1, len(s2), 2))的结果串是: A) BCDEF B) BCDEFG C) BCPQRST D) BCDEFEF4.若广义表A=((a,b,c),(d,e,f )),则式子GetHead(GetTail(GetHead(GetTail(A))))的值为()。
A )(a,b,c )B )(d,e)C )eD )f5.下列程序段的时间复杂度是()。
i=1;while (i<=n) i*=2;A)O(1) B)O(㏒2n) C)O(n) D)O(n2)6.已知一算术表达式的中缀形式为A+B*C-D/E,后缀形式为ABC*+DE/-,其前缀形式为()。
A)–A+B*C/DE B)–A+B*CD/EC)–+*ABC/DE D)–+A*BC/DE7.假设有60行70列的二维数组a[1…60, 1…70]以列序为主序顺序存储,其基地址为10000,每个元素占2个存储单元,那么第32行第58列的元素a[32,58]的存储地址为()。

《数据结构》期末考试试卷试题及答案一、选择题(每题5分,共20分)1. 下列哪个不是线性结构?A. 栈B. 队列C. 图D. 数组2. 下列哪个不是栈的基本操作?A. 入栈B. 出栈C. 查找D. 判断栈空3. 下列哪个不是队列的基本操作?A. 入队B. 出队C. 查找D. 判断队列空4. 下列哪个不是图的基本概念?A. 顶点B. 边C. 路径D. 环二、填空题(每题5分,共20分)5. 栈是一种______结构的线性表,队列是一种______结构的线性表。
6. 图的顶点集记为V(G),边集记为E(G),则无向图G=(V(G),E(G)),有向图G=(______,______)。
7. 树的根结点的度为______,度为0的结点称为______。
8. 在二叉树中,一个结点的左子结点是指______的结点,右子结点是指______的结点。
三、简答题(每题10分,共30分)9. 简述线性表、栈、队列、图、树、二叉树的基本概念。
10. 简述二叉树的遍历方法。
11. 简述图的存储结构及其特点。
四、算法题(每题15分,共30分)12. 编写一个算法,实现栈的入栈操作。
13. 编写一个算法,实现队列的出队操作。
五、综合题(每题20分,共40分)14. 已知一个无向图G=(V,E),其中V={1,2,3,4,5},E={<1,2>,<1,3>,<2,4>,<3,4>,<4,5>},画出图G,并给出图G的邻接矩阵。
15. 已知一个二叉树,其前序遍历序列为ABDCE,中序遍历序列为DBACE,请画出该二叉树,并给出其后序遍历序列。
答案部分一、选择题答案1. C2. C3. C4. D二、填空题答案5. 后进先出先进先出6. V(G),E(G)7. 0 叶结点8. 左孩子右孩子三、简答题答案9. (1)线性表:一个线性结构,其特点是数据元素之间存在一对一的线性关系。

数据结构期末考试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在数据结构中,线性表的顺序存储结构通常使用什么数据结构来实现?A. 链表B. 数组C. 栈D. 队列答案:B2. 以下哪个是二叉树的性质?A. 每个节点最多有两个孩子B. 每个节点最多有三个孩子C. 每个节点最多有四个孩子D. 每个节点最多有五个孩子答案:A3. 在图的遍历算法中,深度优先搜索(DFS)和广度优先搜索(BFS)的区别是什么?A. DFS使用队列,BFS使用栈B. DFS使用栈,BFS使用队列C. DFS和BFS都使用栈D. DFS和BFS都使用队列答案:B...20. 以下哪个排序算法的时间复杂度为O(n^2)?A. 冒泡排序B. 选择排序C. 插入排序D. 所有上述排序算法答案:D二、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 简述链表和数组的区别。
答案:链表和数组都是用来存储数据的线性数据结构。
数组是连续的内存空间,可以随机访问,但插入和删除操作效率较低;链表由一系列节点组成,每个节点包含数据部分和指向下一个节点的指针,不支持随机访问,但插入和删除操作较为高效。
2. 什么是递归?请给出一个递归算法的例子。
答案:递归是一种算法设计技术,它允许函数调用自身来解决问题。
递归通常包含基本情况和递归情况。
例如,计算阶乘的递归算法:f(n) = n * f(n-1),其中基本情况是f(1) = 1。
...三、算法设计题(每题25分,共50分)1. 给定一个整数数组,请设计一个算法找出数组中的第k大元素。
答案:可以采用快速选择算法,类似于快速排序的划分过程,通过随机选择一个元素作为基准,将数组分为两部分,一部分包含比基准大的元素,另一部分包含比基准小的元素。
然后根据k与基准元素的位置关系,决定是继续在左侧子数组还是右侧子数组中进行查找。
2. 描述如何使用哈希表解决字符串匹配问题。
答案:哈希表可以用于实现字符串匹配的KMP算法。
首先,构建模式字符串的前缀函数,该函数用于记录模式字符串中每个位置的最长相同前缀和后缀的长度。

期末考试试卷(B)卷2007 ——2008 学年第一学期课程名称:数据结构适用年级/专业: 06/计应、计教试卷类别开卷()闭卷(√)学历层次本科考试用时 120分钟《.考生.......................》...注意:答案要全部抄到答题纸上,做在试卷上不给分一、单项选择(每小题2分,共20分)()1.以下数据结构中,()是非线性数据结构。
A.树 B.字符串 C.队 D.栈()2.下面关于线性表的叙述中,错误的是哪一个?A.线性表采用顺序存储,必须占用一片连续的存储单元。
B.线性表采用顺序存储,便于进行插入和删除操作。
C.线性表采用链接存储,不必占用一片连续的存储单元。
D.线性表采用链接存储,便于插入和删除操作。
()3.对于栈操作数据的原则是()。
A. 先进先出B. 后进先出C. 后进后出D. 不分顺序()4.最大容量为n的循环队列,队尾指针是rear,队头是front,则队空的条件是()。
A. (rear+1) % n=frontB. rear=front C.rear+1=front D. (rear-l) % n=front()5.数组A[0..4,-1..-3,5..7]中含有元素的个数()。
A. 55B. 45C. 36D. 16。
()6.串是一种特殊的线性表,其特殊性体现在:A.可以顺序存储B.数据元素是一个字符C.可以链式存储D.数据元素可以是多个字符()7.已知某二叉树的后序遍历序列是dabec, 中序遍历序列是debac , 它的前序遍历是()。
A.acbed B.decab C.deabc D.cedba()8.关键路径是事件结点网络中()。
A.从源点到汇点的最长路径 B.从源点到汇点的最短路径C.最长回路 D.最短回路()9.链表适用于查找A.顺序 B.二分法 C.顺序,也能二分法 D.随机()10.在排序算法中,每次从未排序的记录中挑出最小(或最大)关键码字的记录,加入到已排序记录的末尾,该排序方法是()。

“数据结构”期末考试试题一、单选题(每小题2分,共12分)1.在一个单链表HL中,若要向表头插入一个由指针p指向的结点,则执行( )。
A. HL=ps p一>next=HLB. p一>next=HL;HL=p3C. p一>next=Hl;p=HL;D. p一>next=HL一>next;HL一>next=p;2.n个顶点的强连通图中至少含有( )。
A.n—l条有向边B.n条有向边C.n(n—1)/2条有向边D.n(n一1)条有向边3.从一棵二叉搜索树中查找一个元素时,其时间复杂度大致为( )。
A.O(1)B.O(n)C.O(1Ogzn)D.O(n2)4.由权值分别为3,8,6,2,5的叶子结点生成一棵哈夫曼树,它的带权路径长度为( )。
A.24 B.48C. 72 D. 535.当一个作为实际传递的对象占用的存储空间较大并可能需要修改时,应最好把它说明为( )参数,以节省参数值的传输时间和存储参数的空间。
A.整形B.引用型C.指针型D.常值引用型·6.向一个长度为n的顺序表中插人一个新元素的平均时间复杂度为( )。
A.O(n) B.O(1)C.O(n2) D.O(10g2n)二、填空题(每空1分,共28分)1.数据的存储结构被分为——、——、——和——四种。
2.在广义表的存储结构中,单元素结点与表元素结点有一个域对应不同,各自分别为——域和——域。
3.——中缀表达式 3十x*(2.4/5—6)所对应的后缀表达式为————。
4.在一棵高度为h的3叉树中,最多含有——结点。
5.假定一棵二叉树的结点数为18,则它的最小深度为——,最大深度为——·6.在一棵二叉搜索树中,每个分支结点的左子树上所有结点的值一定——该结点的值,右子树上所有结点的值一定——该结点的值。
7.当向一个小根堆插入一个具有最小值的元素时,该元素需要逐层——调整,直到被调整到——位置为止。

数据结构期末考试试题及答案数据结构期末考试试题及答案随着信息时代的到来,数据的处理和管理变得愈发重要。
数据结构作为计算机科学的基础课程之一,对于培养学生的编程思维和解决问题的能力具有重要意义。
数据结构期末考试是对学生掌握该课程知识的一次全面检验。
本文将为大家提供一些常见的数据结构期末考试试题及答案,希望能够对大家复习备考有所帮助。
1. 请解释什么是数据结构,并举例说明。
数据结构是指在计算机中组织和存储数据的方式。
它关注的是数据的逻辑关系和操作,而不仅仅是数据本身。
常见的数据结构有数组、链表、栈、队列、树等。
举例来说,数组是一种线性结构,它将相同类型的数据元素按照一定的顺序存储在一块连续的内存空间中,可以通过索引来访问和修改元素。
2. 请说明数组和链表的区别,并分别列举它们的优缺点。
数组和链表都是常见的线性数据结构,但它们在存储方式和操作上有所不同。
数组将元素存储在连续的内存空间中,通过索引可以直接访问和修改元素。
链表则通过节点和指针的方式将元素串联起来,每个节点包含数据和指向下一个节点的指针。
数组的优点是访问速度快,可以通过索引直接定位元素,适合随机访问。
缺点是插入和删除操作比较耗时,需要移动其他元素。
链表的优点是插入和删除操作简单高效,只需要修改指针即可,不需要移动其他元素。
缺点是访问速度较慢,需要遍历链表才能找到指定位置的元素。
3. 请解释什么是栈和队列,并分别列举它们的应用场景。
栈和队列都是常见的线性数据结构,它们在数据的插入和删除操作上有所不同。
栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构,只允许在栈顶进行插入和删除操作。
队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构,允许在队尾进行插入操作,在队头进行删除操作。
栈的应用场景有很多,比如函数调用栈、表达式求值、括号匹配等。
函数调用栈用于保存函数的局部变量和返回地址,保证函数的正确执行顺序。
表达式求值中,栈可以用于保存运算符和中间结果,实现正确的计算顺序。

《数据结构》期末考试试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 下列哪种数据结构是线性结构?A. 栈B. 树C. 队列D. 图答案:A2. 在计算机科学中,什么是最基本的数据结构?A. 数组B. 链表C. 栈D. 树答案:C3. 下列哪种操作的时间复杂度是O(1)?A. 在链表中插入元素B. 在数组中查找元素C. 在树中删除节点D. 在图中寻找最短路径答案:B4. 下列哪种数据结构常常用于实现栈和队列?A. 数组B. 链表C. 树D. 图答案:A5. 下列哪种数据结构是有序的?A. 栈B. 队列C. 链表D. 图答案:C二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 在数据结构中,栈是一种后进先出(____)的数据结构。
答案:线性表2. 队列是一种先进先出(____)的数据结构。
答案:线性表3. 链表是一种____数据结构,由一系列节点组成。
答案:非线性4. 二叉树是一种特殊的树,它的每个节点最多有两个____。
答案:子节点5. 哈希表是通过____函数将关键字映射到表中的位置来访问数据。
答案:哈希三、判断题(每题2分,共20分)1. 树是一种线性结构。
()答案:错误2. 链表的插入和删除操作时间复杂度都是O(1)。
()答案:错误3. 图是一种线性结构。
()答案:错误4. 哈希表是一种基于顺序结构的的数据结构。
()答案:错误5. 在数据结构中,时间复杂度O(n)表示算法随着输入规模的增加而线性增长。
()答案:正确四、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 请简述栈和队列的特点和应用场景。
答案:栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构,应用场景包括函数调用栈、表达式求值等。
队列是一种先进先出(FIFO)的数据结构,应用场景包括任务队列、缓冲区等。
2. 请简述链表的优缺点。
答案:链表的优点包括动态扩容、插入和删除操作时间复杂度为O(1)、可以方便地实现各种复杂数据结构。
缺点包括占用内存空间较大、不如数组支持随机访问。

《数据结构》期末考试试题及答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 下列哪一个不是线性结构的基本特征?A. 有且只有一个根结点B. 每个结点最多有一个前驱和一个后继C. 有且只有一个叶子结点D. 有序对中第一个元素是根结点答案:C2. 在单链表中,存储元素的数据域称为元素的哪个部分?A. 指针域B. 数据域C. 结点域D. 头结点答案:B3. 在顺序存储结构中,数据元素之间的逻辑关系由哪个因素决定?A. 数据元素的存储顺序B. 数据元素的存储位置C. 数据元素的类型D. 数据元素的大小答案:A4. 下列哪种排序算法的时间复杂度不是O(nlogn)?A. 快速排序B. 归并排序C. 堆排序D. 冒泡排序答案:D5. 在二叉树中,具有度为2的结点的个数是n0,度为0的结点个数是n2,则有()。
A. n0 = n2 - 1B. n0 = n2 + 1C. n0 = n2D. n0 = n2 + 2答案:B6. 在线索二叉树中,哪个结点被称为线索结点?A. 有左子树的结点B. 有右子树的结点C. 既没有左子树也没有右子树的结点D. 具有左右子树的结点答案:C7. 在双向链表中,查找结点的时间复杂度是()。
A. O(1)B. O(n)C. O(nlogn)D. O(n^2)答案:B8. 在栈的操作中,下列哪个操作是非法的?A. 先进先出B. 后进先出C. 可以插入任意元素D. 可以删除任意元素答案:D9. 在顺序表中进行插入操作时,平均移动次数为()。
A. 0B. n/2C. nD. n-1答案:C10. 在下列排序算法中,哪个算法是不稳定的?A. 冒泡排序B. 快速排序C. 插入排序D. 归并排序答案:B二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 线性表的顺序存储结构称为顺序表,其基本特点是()。
答案:元素顺序存储2. 在单链表中,每个结点包括两个域:数据域和()。
答案:指针域3. 在二叉树中,度为0的结点称为(),度为2的结点称为()。

数据结构期末考试试题及答案一、选择题1. 以下哪种数据结构是线性存储结构?A. 树B. 图C. 链表D. 哈希表答案:C2. 在二叉搜索树中,若删除一个节点,则需要进行以下哪些操作?A. 仅删除操作B. 删除操作和调整树结构操作C. 插入操作D. 忽略操作答案:B3. 快速排序算法的时间复杂度在最坏情况下是:A. O(log n)B. O(n)C. O(n log n)D. O(n^2)答案:D4. 下面哪个排序算法适用于大数据量的排序?A. 冒泡排序B. 快速排序C. 插入排序D. 归并排序答案:D5. 哈夫曼树是一种特殊的:A. 二叉树B. 多叉树C. 哈希表D. 图答案:A二、填空题1. 链表的基本操作包括__________、__________、__________和__________。
答案:创建、插入、删除、查找2. 栈是一种后进先出(LIFO)的数据结构,其添加元素的操作称为__________,移除元素的操作称为__________。
答案:push、pop3. 在图的遍历算法中,按照遍历方向的不同,可以分为__________和__________。
答案:深度优先遍历、广度优先遍历4. 红黑树是一种自平衡的__________。
答案:二叉搜索树4. 散列表(哈希表)的主要优点是__________。
答案:查找速度快三、简答题1. 请简述数组和链表的区别及各自的优缺点。
答案:数组是一种顺序存储结构,通过索引直接访问元素,访问速度快,但是插入和删除操作需要移动大量元素,效率较低。
链表是一种非顺序存储结构,通过指针连接元素,插入和删除操作只需要改变指针,效率较高,但是访问元素需要从头开始遍历,速度较慢。
2. 请解释二分查找法的工作原理及其适用条件。
答案:二分查找法是一种在有序数组中查找特定元素的算法。
工作原理是将数组分为两部分,判断目标值与中间元素的大小关系,然后在相应的一半中继续查找,重复此过程,直到找到目标值或范围缩小到无法再分。
数据结构期末考试题及答案一、单项选择题(每题3分,共30分)1. 在数据结构中,最基本的数据结构是()。
A. 线性结构B. 树形结构C. 图形结构D. 非线性结构答案:A2. 栈是一种特殊的线性表,其特点是()。
A. 先进先出B. 先进后出C. 后进先出D. 后进后出答案:C3. 在二叉树中,度为2的结点数为n,度为1的结点数为m,度为0的结点数为p,则m的值为()。
A. n-1B. n+1C. p-1D. p+1答案:A4. 哈希表的构造方式是()。
A. 线性结构B. 树形结构C. 链式结构D. 索引结构答案:D5. 在图的遍历过程中,深度优先搜索算法采用的是()。
A. 队列B. 栈C. 链表D. 树答案:B6. 快速排序算法的时间复杂度在最坏情况下是()。
A. O(n)B. O(nlogn)C. O(n^2)D. O(2^n)答案:C7. 以下哪个排序算法是不稳定的排序算法()。
A. 冒泡排序B. 快速排序C. 归并排序D. 堆排序答案:B8. 在数据库中,索引通常采用哪种数据结构()。
A. 线性表B. 树形结构C. 图形结构D. 散列表答案:B9. 以下哪个不是二叉搜索树的性质()。
A. 左子树上所有结点的值都小于它的根结点的值B. 右子树上所有结点的值都大于它的根结点的值C. 左、右子树也分别为二叉搜索树D. 所有结点的值都相等答案:D10. 在图的表示方法中,邻接矩阵适用于表示()。
A. 稠密图B. 稀疏图C. 有向图D. 无向图答案:A二、填空题(每题4分,共20分)1. 在数据结构中,一个算法的空间复杂度是指算法在执行过程中需要的___________。
答案:存储空间2. 堆排序中,调整堆的过程称为___________。
答案:堆化3. 在图的遍历中,广度优先搜索使用的辅助数据结构是___________。
答案:队列4. 一个长度为n的链表,删除第i个元素的时间复杂度是___________。
数据结构期末考试试题(含答案)数据结构期末考试试题(含答案)第一题:多项式相加(20分)将两个多项式 P(x) 和 Q(x) 相加,结果存储在另一个多项式 S(x) 中,请写出相应的算法,并给出其时间复杂度分析。
答案:算法如下:1. 初始化一个空多项式 S(x)。
2. 分别取多项式 P(x) 和 Q(x) 的第一项,判断指数的大小关系,并将指数较小的项加入 S(x)。
3. 若指数相同,则将两项系数相加,并将结果加入 S(x)。
4. 重复步骤2和步骤3,直到两个多项式中的所有项都被处理完。
5. 返回结果多项式 S(x)。
时间复杂度分析:- 假设 P(x) 和 Q(x) 的项数分别为 m 和 n。
- 在最坏情况下,需要比较 m+n 次指数大小,并进行 m+n-1 次系数相加。
- 因此,该算法的时间复杂度为 O(m+n)。
第二题:循环队列设计(30分)请设计一个循环队列,实现入队、出队等基本操作,并给出时间复杂度分析。
答案:定义循环队列的结构体如下:```ctypedef struct {int *data; // 存储队列元素的数组int front; // 队首指针,指向队首元素的位置int rear; // 队尾指针,指向队尾的下一个位置int maxSize; // 队列的最大容量} CircularQueue;```基本操作的实现如下:1. 初始化循环队列:```cvoid initQueue(CircularQueue *queue, int maxSize) {queue->data = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * maxSize);queue->front = queue->rear = 0;queue->maxSize = maxSize;}```2. 入队操作:```cint enqueue(CircularQueue *queue, int value) {if ((queue->rear + 1) % queue->maxSize == queue->front) { return 0; // 队列已满,插入失败}queue->data[queue->rear] = value;queue->rear = (queue->rear + 1) % queue->maxSize;return 1; // 插入成功}```3. 出队操作:```cint dequeue(CircularQueue *queue, int *value) {if (queue->front == queue->rear) {return 0; // 队列为空,出队失败}*value = queue->data[queue->front];queue->front = (queue->front + 1) % queue->maxSize; return 1; // 出队成功}```时间复杂度分析:- 入队和出队操作的时间复杂度均为 O(1)。
《数据结构》试题答案A卷姓名班级一、回答下列问题 (每题5分,共40分)1.给定序列(67,45,87,19,55,32,70,60,90,23),写出它的初始堆序列。
答:调整后的初始堆序列(小根堆)为:19,23,32,45,55,87,70,60,90,67或者是大根堆:90, 67, 87, 60, 55, 32, 70, 45, 19, 232.设一个序列奇数项和偶数项分别由小到大有序,用什么方法可以最快得到一个有序序列,分析它的时间复杂度。
答:把奇数项和偶数项分为2个有序序列,然后进行合并,时间复杂度为O(n)。
实际上就是把2个有序表合并为一个有序表。
见教科书算法2.7。
3.二叉排序树中的最大值在二叉排序树的何处?答:最大值应该位于二叉排序树中根的右子树的最右叶子上。
1923 3245 55 7060 904.在2048个互不相同的关键码中选择最小的5个关键码,用堆排序是否比用锦标赛排序更快?为什么?答:此题用锦标赛排序比堆排序要快。
理由是;①在首次求最小值时,锦标赛排序对2048个结点建树得到最小码只需比较n-1(即2047)次,而此时堆排序建初始堆得到最小码却可能需要比较4072次(因为每个结点的调整都要与左右两边的孩子相比。
从第1024个结点往前调整,有512个结点可能调整1次,但要与左右孩子都比较,有256个结点可能调整2次,每次都要与左右孩子比较,有128个结点可能调整3次,……有32个结点调整5次,……根结点可能要调整10次,每次都会与左右孩子比较,所以可能会比较2036×2=4072次)。
而两种算法对求后面4个次小码的平均效率相同,都是log2n,所以,此题用锦标赛排序会比堆排序快。
5.n个顶点、m条边的全连通图,至少去掉几条边才能构成一棵树?答:因为树的结构是一对多,即n个结点的树只有n-1条边与双亲结点相连。
只要再多添一条边就会成为图结构。
所以,m条边的图要去掉m-(n-1)=m-n+1条边才能构成一棵树。
浙江大学2007–2008学年秋季学期《数据结构基础》课程期末考试试卷开课学院:软件学院、计算机、竺可桢学院,考试形式:闭卷,允许带_ 无入场考试时间:_2007_年_11_月_17日, 所需时间: 120 分钟考生姓名: ___学号:专业: ____教师:Answer SheetNOTE: Please write your answers on the answer sheet.注意:请将答案填写在答题纸上。
I. Please select the answer for the following problems. (20 points)(1)The time complexity of the following piece of code is (2 points)for(i=0; i<n; i++)for(j=i; j>0; j/=2)printf(“%d\n”, j);a. O(n)b. O(n*n)c. O(nlogn)d. O(n*i)(2)Suppose that the time complexities of two programs are given by T1(N)=O(f(N))and T2(N)=O(f(N)). Which of the following equations is true? (2 points) a. T1(N)+T2(N)=O(f(N)) b. T1(N)-T2(N)=o(f(N))c. T1(N)/T2(N)=O(1)d. T1(N)=O(T2(N))(3)Given an empty stack S and an empty queue Q. A list of characters are pushedinto S in the order of a, b, c, d, e, f and every character that is popped from S will be inserted into Q immediately. If the output of Q is b, d, c, f, e, a, the minimum capacity of S must be . (2 points)a. 6b. 5c. 4d. 3(4)Suppose that the size of a hash table is 11, and the hash function isH(key)=key%11. The following 4 elements have been inserted into the table as Addr(14)=3, Addr(38)=5, Addr(61)=6, Addr(86)=9. When open addressing with quadratic probing is used to solve collisions, the address of the element with key=49 will be . (2 points)a. 4b. 7c. 8d. 10(5)For a binary tree, given the postorder traversal sequence FDEBGCA and theinorder traversal sequence FDBEACG, the corresponding preorder traversal sequence is . (2 points)a. ABDFEGCb. ABDEFCGc. ABDFECGd. ABCDEFG(6)Insert 10, 12, 1, 14, 6, 5, 8, 15, 3, 9, 7, 4, 11, 13, 2 into an initiallyempty binary min heap one at a time, after performing three DeleteMin operations, the last element of the heap is . (2 points)a. 10b. 11c. 8d. 5(7)Let T be a tree created by union-by-size with N nodes, then the height ofT can be . (2 points)a. at most log2(N)+1b. at least log2(N)+1c. as large as Nd. anything that is greater than 1(8)Given a weighted and connected undirected graph G, there is/are minimumspanning tree(s) of G. (2 points)a. only oneb. one or morec. more than oned. zero or more(9)To find the shortest path between a pair of given vertices, methodcan be used. (2 points)a. Kruskalb. Dijkstrac. Hashingd. Critical Path(10)Among the following sorting algorithms, has the average run timeO(NlogN) with O(N) extra spaces. (2 points)a. Quick sortb. Heap sortc. Merge sortd. Insertion sortII. Given the function descriptions of the following three (pseudo-code) programs, please fill in the blank lines. (24 points)(1)The function is to delete the maximum element in a max heap. (12 points) ElementType DeleteMax( PriorityQueue H ){int i, Child;ElementType MaxElement, LastElement;MaxElement = ① ;LastElement = H->Elements[ H->Size-- ];for( i = 1; i * 2 <= H->Size; i = Child ){ Child = i * 2;if( ② )Child++;if( LastElement < H->Elements[ Child ] )③ ;else break;}H->Elements[ i ] = LastElement;return MaxElement;}(2)The function is to sort a list of N elements A[] in non-decreasing orderby Shellsort with Shell’s increments. (6 points)void Shellsort( ElementType A[ ], int N ){int i, j, Increment;ElementType Tmp;for ( Increment = N / 2; Increment > 0; Increment /= 2 )for ( i = Increment; i < N; i++ ) {Tmp = A[ i ];for ( j = i; ① ; j - = Increment )if(② )A[ j ] = A[ j - Increment ];else break;A[ j ] = Tmp;}}(3)The function is to find maximum sum value of the subsequence in A[0], A[1],A[2], … A[N-1]. (6 points)int MaxSubsequenceSum(int A[], int N){int ThisSum, MaxSum, j;ThisSum=MaxSum=0;for(j=0; j<N; j++) {ThisSum = ① ;if (ThisSum >MaxSum)MaxSum= ThisSum;else if (ThisSum <0)② ;}return MaxSum;}III. Please write or draw your answers for the following problems on the answer sheet.(41 points)(1)Please list:(a)the depth-first search sequence;(b)(c)the minimum spanning tree.Note: All the adjacent vertices are to be visited by alphabetical order.(15 points)(2)Insert the numbers 40, 28, 6, 72, 100, 3, 80, 91, 38 into an initially emptybinary search tree. Please show(a)the resulting binary search tree; (10 points) and(b)the resulting binary search tree after 72 is deleted. (3 points)(3)The array representation of the disjoint sets is given by { 2, –4, 2, 2,-3, 5, 6, 9, -2 }. Please list the resulting array elements after invokingUnion(7, 9) with union-by-size. Keep in mind that the elements are numberedfrom 1 to 9. (5 points)(4)Given a list of N elements and an integer k. Please describe two differentalgorithms for finding the kth largest element and give the time complexities.(8 points)IV. If each vertex in an undirected weighted graph has a number of balloons assigned.Explain how to modify Dijkstra's algorithm so that if there is more than one minimum path from v to w, a path with the maximum number of balloons is chosen.(15 points)Note : T[ V ].balloon contains the number of balloons at vertex V.void Dijkstra( Table T )。