市场营销原理-亚洲版复习整理
- 格式:docx
- 大小:129.16 KB
- 文档页数:37

Chapter 1Marketing: managing profitable customer relationships营销:管理有价值的顾客关系What is marketing?⏹ A social and managerial process whereby individuals and groups obtain what they need and want through creatingand exchanging products and value with others.⏹广义上,营销是通过创造和交换产品及价值,从而使个人或群体满足欲望和需要的社会和管理过程。
⏹狭义上,营销是指和顾客建立有利可图、充满价值的交换关系。
⏹总之,营销就是企业为了从顾客身上获得利益回报、创造顾客价值和建立牢固顾客关系的过程。
营销过程的五个步骤1.Understand the marketplace and customer needs and wants了解市场及顾客需求和欲望2.Design a customer-driven marketing strategy设计顾客驱动的营销战略3.Construct a marketing program that delivers superior value构建传递卓越价值的营销方案4.Build profitable relationships and create customer delight建立有利可图的关系,并使顾客满意5.Capture value from customers to create profits and customer quality从顾客身上收获价值,从而创造利润和顾客资产顾客驱动下的营销战略●Selecting customers to serve 选择服务对象✧What customers will we serve?✧Marketers select customers that can be served profitably✧通过把市场划分为不同的顾客和选择它将要针对的那部分顾客来实现。

第一章1.市场概念:(1)习惯:商品交换场所。
在日常生活中,人们习惯将市场看做是买卖的场所,如集市、商场、批发市场等。
这是从时间和空间来理解市场的概念。
(2)经济学家:揭示经济实质。
他们认为市场是一个商品经济范畴,是商品内在矛盾的表现,是供求关系,是商品交换的总和,是通过交换反映出来的人与人之间的关系。
经济学家指出,市场是社会分工和商品生产的产物。
在商品生产的条件下,“社会内部分工的前提首先是不同种类劳动的相互独立,即它们的产品必须作为商品相互对立,并且通过交换,完成商品的形态变化,作为商品相互发生关系。
”因此,“哪里有社会分工和商品生产,哪里就有‘市场’。
”市场是为完成商品形态变化,在商品所有者之间进行商品交换的总体表现。
(3)经营者:人们常常把卖方称为行业,而将买方称为市场。
(4)营销学家:认为市场是现实与潜在顾客.(5)管理学家:交换及其经济运行。
在他们看来,市场是供需双方在共同认可的条件下所进行的商品或劳务的交换活动。
(6)我们认为:市场是商品经济中生产者与消费者之间为实现产品或服务价值,满足需求的交换关系、交换条件和交换过程。
2.市场是建立在社会分工和商品生产基础上的交换关系。
3.市场的形成要素:消费者;产品或服务;交易条件。
4.买方需求是决定性的。
5.市场=人口+购买欲望+购买力,市场是利益攸关者的集合。
6.营销是一项有组织的活动,它包括创造“价值”,将“价值”沟通输送给顾客。
以及维示管理公司与顾客之间的关系,从而使得公司及其相关者受益的一系列过程。
市场营销的最终目标是“使个人或群体满足欲望和需要”。
“交换”是市场营销的核心。
交换过程是一个主动、积极寻找机会,满足双方需要和欲望的社会过程和管理过程。
营销的目的是使推销变得不可能,出发点消费者的需求和欲望。
市场营销概念的演进:主体的变化、客体的变化、对象的变化、内容的变化、目标的变化、工具的变化。
7.市场营销的相关概念(1)需要是指人们与生俱来的基本需要。


市场营销复习重点第一章市场营销学与市场营销一、市场的概念:1、从日常生活的角度:市场是买卖的场所2、从经济实质的角度:市场是商品经济的范畴,是商品内在矛盾的表现,是供求关系,是商品交换的总和,是通过交换反映出的人与人之间的关系。
3、从企业治理的角度:市场是供需双方在共同认可的条件下所进行的商品或劳务的交换活动。
4、从营销的角度:市场是指某种产品的实际购买者和潜在购买者的集合。
二、市场存在的条件:1、消费者(有某种需要&欲望,拥有可供交换的资源)2、生产者(能提供满足消费者需求的产品或服务)3、有促成交换双方达成交易的各种条件三、市场营销的概念:1、市场营销是通过制造和交换产品及价值,从而使个人或群体满足欲望和需求的社会过程和治理过程。
2、概念要点:⑴市场营销的最终目的是“使个人或群体满足欲望和需要”;⑵市场营销的核心是“交换”;⑶交换过程能否顺利进行,取决于营销者制造的产品和价值满足顾客需求的程度以及对交换过程治理的水平。
四、市场营销的相关概念:1、需要、欲望、需求⑴需求是指人与生俱来的差不多需要,没有得到某些差不多满足的感受状态。
⑵欲望指对能满足差不多需要的具体满足物的愿望。
⑶需求是指有购买能力并情愿购买某个具体产品的欲望。
2、产品和服务⑴产品是获得服务的载体。
⑵产品是指能够满足人的需要和欲望的任何事物。
⑶产品的价值在于它给人们带来对欲望的满足。
3、效用、费用和满足⑴效用是指消费者对产品满足其需要能力的主观评判。
⑵费用确实是指成本(机会成本)。
4、交换、交易和关系⑴交换是指从他人处取得所需之物,而以自己的某种东西作为回报的行为。
交换是一个过程。
⑵交易是交换双方的价值交换,在交换过程中,假如双方达成一项协议,就称发生了交易。
⑶关系营销:是市场营销者与顾客、分销商、经销商、供应商等建立、保持并加强合作关系,通过互利交换及共同履行诺言,使各方实现各自目的的营销方式。
(建立在交易基础上的营销叫做交易营销,为使企业获得较之交易营销所得到的更多,就需要关系营销)五、宏观与微观市场营销:1、宏观市场营销:资源配置者。

Chapter 1 Marketing:Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Marketing:goal of marketing: attract new customers by promising superior value keep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction definition (it involves satisfying customer needs)process:1. Understanding the marketplace and customer needsNeeds: physical needs (food, clothing, warmth, safety)social needs (belonging and affection)individual needs(knowledge, self—expression)Wants: wants are shaped by one's society and are described in terms of objects that will satisfy needs。
(Food—Big Mac, rice)Demands: given their wants and resources, people demand products with benefits that add up to the most value and satisfaction需要(已有)→欲望→需求(创造)Market offerings: 营销对象physical productsservices, activities or benefits offered for sale(not result in ownership)entities(persons, places, organizations, information, ideas)marketing myopia:营销近视the customer will have the same need but want the new productsolution: look beyond the attributes and existing customer wantsproduct benefits and experiences, and customer’s needsoffer superior customer value(create brand experiences)e。


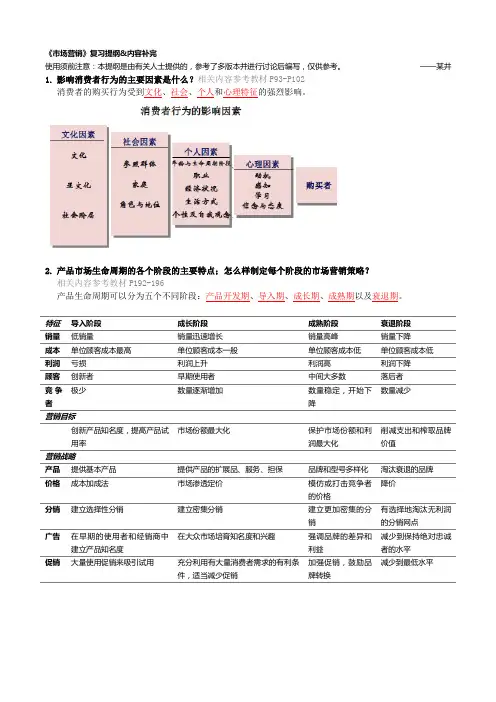
1.影响消费者行为的主要因素是什么1)文化:文化、亚文化、社会阶层2)社会:参照群体和社交网络、家庭、角色和地位3)个人:年龄和生命周期、职业、经济状况、生活方式、个性4)心理:动机、感知、学习、信念和态度2.产品市场生命周期的各个阶段的主要特点,怎样制定每个阶段的市场营销策略产品从进入市场到退出市场的全过程。
包括四个阶段:介绍期、成长期、成熟期、衰退期。
介绍期特点:1)顾客不了解产品,尚未建立理想的分销渠道,销售量少,单位成本高2)产品技术、性能需进一步完善3)无利润或负利润4)竞争者少营销策略:1)加强促销:整合营销传播2)渠道建设:建立销售渠道3)产品性能、质量改进和完善4)目标:提高知名度,培养初始需求成长期特点:1)顾客已了解产品,渠道已建立,销量增长快,单位成本下降2)产品、技术成熟3)利润吸引竞争者加入,竞争激烈策略:1)促销重点转向树立品牌偏好2)提高产品质量和服务质量,增加产品的功能,增强竞争力3)开拓渠道,加强渠道的管理4)目标:提高市场占有率成熟期特点:1)市场需求趋于饱和,潜在顾客已经很少,销售量增长缓慢,市场趋于稳定2)市场竞争激烈,名牌逐渐形成策略:1)市场改进:寻求新的细分市场2)产品改进:不断推出新的功能,延长产品市场寿命3)营销组合改进:调整产品、价格、渠道和促销组合中的因素衰退期特点:1)产品销量迅速下降,消费者兴趣已转移2)产品价格下降到最低水平,利润下降策略:1)继续策略2)收缩策略3)放弃策略3.营销战略计划的四个主要步骤及其内容4.什么是市场定位,市场定位的主要依据是什么定义:强有力地塑造出本企业产品与竞争者不同的、鲜明的个性或形象,并把这种形象生动地传递给顾客,从而使该产品在市场上确定适当的位置。
主要依据:自己的竞争优势,即差异化。
5.市场营销战略是什么,实现途径有哪些6.整合营销传播是什么意思,如何进行整合营销传播定义:将广告、人员推销、销售促进、公共关系、直销等各种沟通渠道通过整合,向市场提供清晰、一致的产品信息,发挥最大的沟通效果。


1.市场(shìchǎng)含义(ch1)市场是商品交换的场所(chǎnɡ suǒ),亦即买主和卖主发生作用的地点或地区。
市场是某一产品的所有(suǒyǒu)现实和潜在卖主的总和。
市场是买主、卖主力量的结合,是商品供求双方(shuāngfāng)的力量相互作用的总和。
市场(shìchǎng)是指商品流通领域,反映的是商品流通的全局,是交换的总和。
2.有人说市场营销就是推销,这种理解正确吗?为什么?(ch1)不正确,市场营销活动是全方位、全过程的,是以满足消费者需求为中心,出发点是市场需求,采用的是整体营销手段,通过满足消费者需求来获取利润;推销活动仅是营销过程中的一个环节,是以现有产品为中心的,出发点是企业产品生产,主要采用人员推销和广告宣传,销售是通过增加销量来获取利润。
3.从理论与实践的结合,阐述市场经营观念的发展?(ch1)生产观念:基本内容是:企业以改进、增加生产为中心,其典型变现是“我们生产什么,就卖什么”。
时间:20世纪20年代;观念:企业致力于提高生产效率和分销效率,扩大生产规模,降低成本来扩展市场;特征:卖方市场、以企业为中心、以产定销。
案例T型车与福特。
产品观念:强调“以质取胜”、“以廉取胜”。
时间:20世纪30年代;观念:企业致力于生产高质量产品,并不断加以改进,做到物美价廉;特征:卖方市场、以产品为中心、以产定销。
推销观念:强调:如果不经过销售努力,消费者就不会大量购买,。
换句话说,只要企业努力推销什么产品,消费者或用户就会更多地购买什么产品。
时间:20世纪40~50年代;观念:企业必须开展积极推销和大力度促销活动,以刺激消费者大量购买本企业产品;特征:买方市场,以产定销,以企业为中心,企业生产什么,就推销什么。
市场营销观念:内容是:消费者或用户需要什么产品,企业就应当生产、销售什么产品。
时间:20世纪50~60年代;观念:企业必须根据消费者需求开发产品,组织产品生产,开展整体营销活动,把能够满足消费者需求的产品送到消费者手中,实现企业的经营目标;特征:买方市场,以需定产,以消费者为中心。

市场营销概论复习要点第一章市场营销及市场营销学名词解释一、市场市场营销市场营销学欲望需求4P组合 4C营销 6P组合二、简答题1.请简述马斯洛需求层次理论的主要内容。
2.请简述市场营销学的产生和开展。
〔四个阶段〕第二章市场营销管理哲学及其贯彻一、名词解释市场营销管理推销观念生产观念产品观念市场营销观念社会营销观念二、简答题1.请比照分析推销观念及市场营销观念。
2.市场营销管理哲学的核心是什么?第三章企业战略及营销管理一、名词解释迈克尔·波特的五力竞争模型前向一体化后向一体化明星类业务问题类业务奶牛类业务瘦狗类业务二、简答题1.简述企业战略的四大特征。
2.简述矩阵的主要内容。
3.简述企业一体化成长战略的类型。
4.请解释金牛类业务和明星类业务的主要特点。
第四章市场营销环境一、名词解释市场营销环境宏观环境因素微观环境因素媒介公众人口环境二、简答题1.简述市场营销环境的构成?2.微观环境因素包括哪些?中间商有哪些主要类别?3.简述市场营销环境的特征。
〔需要展开〕第五章分析消费者市场一、名词解释消费者市场复杂购置行为二、简答题1.简述消费者购置决策过程。
2.简述马斯洛需要层次理论的主要内容。
3.简述消费者行为研究的主要任务。
第八章目标市场营销战略一、名词解释市场细分目标市场市场定位产品专业化二、简答题1.市场细分的主要原则。
〔适当展开〕2.消费者市场细分标准主要有哪几类?人口因素和心理因素分别指的是什么?第十章产品策略一、名词解释产品整体概念产品组合产品线产品工程产品组合的宽度产品组合的长度产品组合的深度产品组合的关联度产品生命周期〔市场寿命周期、经济寿命周期〕二、简答题1.产品的定义及其整体概念的五个根本层次。
〔层次要展开论述〕2.简述产品线延伸策略的三大方式〔向上延伸、向下延伸及双向延伸〕3.简要区分产品的市场寿命及物质寿命。
4.简要论述产品生命周期的四个阶段。
5.请论述成熟期和成长期的企业营销策略。
市场营销原理亚洲版第四版答案
1.市场营销原理的最终目标是什么?
答:市场营销原理的最终目标是创造最大的价值,为客户带来最大的价值,企业及其他利益攸关方也能从中获得最大的成果。
2.根据市场营销原理,市场营销管理有哪些基本原则?
答:市场营销管理的基本原则有:客观分析市场;把客户分类为目标市场;确定目标市场的客户及他们的需要;确定市场营销战略;为目标市场制定市场营销组合;分析、调整和控制市场营销活动。
3.根据市场营销原理,企业在定位市场时应考虑哪些方面?
答:企业在定位市场时应考虑的方面有:(1)企业的优势及其与市场需要的相匹配程度;(2)市场竞争情况及其影响;(3)识别顾客;(4)认识市场机遇;(5)分析投入和预期回报。
4.根据市场营销原理,企业在确定市场营销战略时应考虑哪些因素?
答:企业在确定市场营销战略时应考虑的因素有:(1)产品/服务的价格;(2)渠道分销;(3)促销活动;(4)服务;(5)企业形象;(6)企业文化;(7)竞争对手。
5.根据市场营销原理,按照类别,市场营销组合可以分为几个类别?。
市场营销复习整理资料名词:市场:是由一切具有特定欲望和需求并且愿意和能够以交换来满足这些需求的潜在顾客所组成。
即产品或服务的现实和潜在购买者。
市场营销:市场营销是个人和组织通过创造、提供、并同他人自由交换有价值的产品和服务,以获得其所需所欲的一种社会和管理过程。
市场营销管理:是指企业为实现其目标,创造、建立并保持与目标市场之间的互利交换关系而进行的分析、计划、执行与控制过程。
市场营销观念:是指在一定时期内,占支配地位的、贯穿于企业整个市场营销活动的总体指导思想和行为准则。
它决定着企业生产经营活动的总体方向、决定着企业营销战略和政策。
是企业领导人对于市场的根本态度和看法,是一切经营活动的出发点。
是一定社会经济发展的产物,又反过来指导和推动企业的经营管理活动。
市场导向的战略规划:在组织目标、技能、资源和他的各种变化的市场机会之间建立与保持一种可行的适应性管理过程目标:塑造和不断调整公司业务与产品,以期获得目标利润的发展。
市场营销环境:营销活动的各个参与部分和影响力被称为营销环境要素。
一系列营销环境要素就组成了企业营销活动赖以存在和发展的营销环境可能是一个部门、某类产品、某种产品,或是几个部门、几类产品市场营销信息系统(MIS):由人员、设备和程序组成,它为营销决策者收集、整理、分析、评估和传递所需要的、适时的和准确的信息。
市场营销调研就是运用科学的方法,有目的、有计划、系统的收集、整理和分析有关市场营销方面的信息,提出解决问题的建议,供营销管理人员了解营销环境,发现机会与问题,作为市场预测和营销决策的依据。
消费者市场是指由为了个人消费而购买物品或服务的个人和家庭所构成的市场。
目标市场:企业试图加以满足或拟为之服务的一组明确限定的现有顾客和潜在顾客群目标市场选择:只对每一个小细分市场的吸引力进行评价,然后选择其中的一个或多个作为自己要进入的目标市场。
这一过程称为目标市场选择。
市场定位:定位就是对企业的产品进行设计,从而使其能在目标顾客心目中占有一个独特的、有价值的位置的行动。
Chapter 1 Marketing: Managing Profitable Customer Relationships Marketing:goal of marketing: attract new customers by promising superior valuekeep and grow current customers by delivering satisfaction definition (it involves satisfying customer needs)process:1. Understanding the marketplace and customer needsNeeds: physical needs (food, clothing, warmth, safety)social needs (belonging and affection)individual needs(knowledge, self-expression)Wants: wants are shaped by one’s society and are described in terms of objects that will satisfy needs. (Food—Big Mac, rice)Demands: given their wants and resources, people demand products with benefits that add up to the most value and satisfaction需要(已有)→欲望→需求(创造)Market offerings: 营销对象physical productsservices, activities or benefits offered for sale(not result in ownership)entities(persons, places, organizations, information, ideas)marketing myopia: 营销近视the customer will have the same need but want the new productsolution: look beyond the attributes and existing customer wantsproduct benefits and experiences, and customer’s needsoffer superior customer value(create brand experiences)e.g. Disney World, F1 raceCustomer value and satisfaction:customers form expectations about the value and satisfaction thatvarious market offerings will deliver and buy accordingly价值=总收益-总成本marketers: set the right level of expectationsExchanges交换(包含donation)bring about a response(votes, membership,audience, acceptance)Relationship交易关系goal: retain customers and grow their businessMarkets: marketing means managing markets to bring about profitable customer relationshipsMarketing system:actor: suppliers, company, competitors, intermediaries, final usersaffected by major environmental forces: demographic, economic,physical, technological, political/legal, social/cultural each party adds value for the next level. success depends on the entire system.2. Designing a customer-driven marketing strategyMarketing management: 营销管理Selecting customers to serve: market segmentation, target marketingdemarketing(reduce/shift demand temporarily or permanently, e.g.奢侈品,旅游景点,限量版)customer management, demand management 需求与资源匹配select only customers that it can serve well and profitably Choosing a value proposition: differentiate, position the productMarketing management orientations:经营理念(philosophy guiding these marketingstrategies)Production concept: consumers favor products that are available and highly affordable.生产观念Management focuses on improving production and distribution efficiency.Marketing short-sightedness, losing sight of satisfying customer needs.(e.g.亨利福特T型车,代工企业)Product concept: consumers favor products that offer the most in quality, performance, 产品观念and innovative features.Marketing strategy focuses on making continuous product improvement.Focusing only on products can lead to marketing myopia.(e.g. mousetrap compared with chemical spray, services, 4 Ps)Selling concept: undertaking a large-scale selling and promotion推销观念practiced with unsought goods(buyers do not normally think of buying,e.g. insurance, blood donations)大萧条时期Focus on creating sales transaction rather than on building long-term,profitable customer relationshipsSell what they make rather than making what the market wantsProduct-centered “make and sell ”Marketing concept: customer-centered “sense and respond”营销观念Find the right product for your customers对比:Selling concept & Marketing conceptCustomer driven & Customer driving P10Societal concept: companies should balance three considerations in setting their 社会营销观念marketing strategies: company profits, consumer wants, andsociety’s interests.e.g. 垃圾食品,石油危机,外部性,企业道德(J&J召回)3. Preparing an integrated marketing plan and programdeliver the intended value to target customerstransform the marketing strategy into actionmarketing mix: 营销组合major tools: product price promotion placeintegrated marketing program整合营销计划: blend all marketing mix tools into a comprehensive plan that communicates and delivers theintended value to chosen customers.4. Building customer relationships (most important)Customer relationship management (CRM) 客户关系管理: deals with all the aspects of acquiring, keeping and growing customers.Customer value: buy from the firm that offers greatest perceived value.Do not judge product value and cost accuratelyCustomer satisfaction: higher level satisfaction lead to greater loyalty, thusbetter company performancePromise only what they can deliver, deliver more than promise(Samsung, focus on the delight factor, design, style, image,brand experience, brand personality, overall company culture)Do not attempt to maximize customer satisfactionGenerate customer value profitablyCustomer relationship levels: basic relationship (low-margin customers)full relationship (high-margin customers) Customer relationship tools: frequency marketing programs(reward customers who buy frequently or in large amounts)club marketing programs(offer members special benefits and create member communities)structural ties, financial and social benefits Changing nature of customer relationships:more carefully selected customers: selective relationship managementcustomer profitability analysisrelating for the long term: retain current customersrealities: changing demographics, more sophisticatedcompetitors and overcapacity mean fewer customers,higher cost to attract new onesrelating directly: virtually buying, telephone, mail, online.Partner relationship management:合作伙伴关系管理Inside the company: link all departments to create customer valueevery functional area, electronicallyform cross-functional customer teamsoutside the firm: suppliers, channel partners, and competitorsmarketing channels: distributors, retailers to buyerssupply chain: raw material to final product to buyerssupply chain managementstrategic alliance (e.g. McDonald & Sinopec)5. Capturing value from customersCreating customer loyalty and retention:Aim of CRM is to create not just customer satisfaction but customer delightCustomer lifetime value:顾客生命价值Aim high in building customer relationships (long-term)Growing share of customer:Share of customer:顾客份额Offer greater variety, train employees to cross-sell and up-sell(e.g.Amanzon sell other products, recommend related products)Building customer equity:Ultimate aim of CRM is to produce high customer equityCustomer equity:顾客资产A better measure of a firm’s performance than current sales or market shareView customer as assets that need to be managed and maximizedClassify customers: potential profitability, projected loyalty, requiredifferent relationship management strategies Build the right relationships with the right customersNew landscape: digital age, globalization, ethics and social responsibility, not-for-profit marketing (school, hospital, museum, zoo, church,government agency)Chapter 2 company and marketing strategy: partnering to buildcustomer relationships (overall strategic planning process) Companywide strategic planning公司层面战略规划:1. Defining a market-oriented mission (mission statement使命陈述)market oriented and defined in terms of customer needs. (product-oriented vs. market-oriented)fit the market environmentbased on its distinctive competenciesmotivating(not as making more sales or profits)2. Setting company objectives and goalsTurn mission into detailed supporting objectives for each level of managementA hierarchy of objectives, including business objectives(公司目标,有时间限制,有数据,可测量,具化)and marketing objectives(营销目标)Marketing strategies and programs must be developed to support these marketing objectivesIn this way, translate mission into a set of objectives for the current period3. Designing the business portfolio(业务组合)Fit its strengths and weaknesses to the opportunities in the environmentA. Analyzing the current business portfolio (major activity in strategic planning)(1)Identify the key business making up the companyStrategic business unit (SBU战略业务单元): company division, product linewithin a division, single product or brand(2)Assess the attractiveness of its various SBUs(3)Decide how much support each deservesBCG矩阵growth-share matrix(market growth rate—attractivenessrelative market share—company strength) Stars明星类:need heavy investmentCash cows现金牛:need less investment, produce a lot of cashQuestion marks问题类:require a lot of cash. Management must think hardabout which question marks it should try to build into stars Dogs狗类:do not promise to be large source of cashFour strategies for each SBU: Invest more to build its shareInvest just enough to hold its shareHarvest the SBU (milking short term cash)Divest the SBU (selling or phasing it out) Life cycle of SBU: Q→S→CC→DProblems: difficult in defining SBUs and measuring market share and growth, time consuming and costly to implement, focus oncurrent businesses, not future planningSolution: customized approach, decentralize strategic planning, cross-functional teams.B. Shaping the future portfolio—growth and downsizingGrowth:Finding business and products the company should consider in the futureMarketing has the main responsibility for achieving profitable growth forthe company, must identify, evaluate, and select market opportunities andlay down strategies for capturing themProduct/market expansion grid 产品/市场扩展方格, 安索洛夫方格(Indentify company growth opportunities) Market penetration: new stores, advertising, prices, service, menu市场渗透selection, store designMarket development: new demographic markets, new geographical 市场开发markets出口转内销,发现新用途Product development: modified or new products 新品种,新口味产品开发Diversification: starting up or buying new businesses多样化Downsizing: 精简Environment changes, making some products or markets less profitableFirm may have grown too fast or entered areas where it lacks experienceSome products or business units age and die(prune, harvest, divest them, focus on promising growth opportunities) Planning marketing and other functional strategies (4)Major functional departments work together to accomplish strategic objectives 1. Partnering with other company departmentsValue chain价值链: Each department carries out value-creating activities to design, produce, market, deliver, and support the firm’s products 2. Partnering with others in the marketing systemValue-delivery network 价值传递网络: Company, suppliers, distributors andultimately customers who partner with each otherto improve performance of the entire system Marketing strategy: 营销战略segmentation, targeting, differentiation and positioningMarketing mix: 4 Ps (4 Cs: from buyer’s view) 从4 Cs出发,以4Ps为框架执行Chapter 4 Managing marketing information (marketplace elements) Marketing information system(MIS)营销信息系统P871. Assessing marketing information needsBalances the information users would like to have against what they really need and what is feasible to offerIssues to consider:Amount of information (provide the information decision makers should have) Availability of information (cannot provide needed information, not available or because of MIS limitation, petitor’s strategy, resulting change)Cost (additional information isn’t worth obtaining, costs vs. benefits)2. Developing marketing informationA. Internal data:Internal database: 内部数据库data sources within the company networkAdvantage: can be assessed more quickly and cheaplyDisadvantage: incomplete (记录过去情况)or in the wrong form(不同部门之间格式转换) age quickly, large amount of information, must be wellintegrated and readily accessibleB. Marketing intelligence: 营销情报publicly available informationGoal: improve strategic decision making, assess and track competitors’ actions, provide early warning of opportunities and threatsSources: published information, products, sales, new patents, annual reports, business publications, trade show exhibits, press releases,advertisements, web page.C. Marketing research: 市场调查formal studies of specific situations (e.g.consumer satisfaction, purchase behavior, marketpotential, market share, effectiveness of 4 Ps)(1)Defining the problem and research objectivesTypes of objectives:Exploratory research探索性调查gather preliminary information todefine the problem and suggest hypotheses Descriptive research描述性调查describe things(e.g. market potentialfor a product, demographics and attitudesof consumers who buy the product) Casual research因果性调查test hypotheses about cause-and-effectrelationshipsManagers start with exploratory research and later follow with descriptive or casual research(2)Developing the research plan✧Determine the exact information neededResearch objectives must be translated into specific information needs✧Develop a plan for gathering it effectivelyResearch plan: sources of existing data, specific research approaches, contact methods, sampling plans and instruments to gather new data Secondary data二手数据:Internal database, external database (business, government, internet)Advantage: quickly, lower cost, provide data that an individual company can’tcollect on its own (not directly available, too expensive to collect) Disadvantage:availability (may not exist), relevance (fits needs), accuracy(reliable sources), current (up-to-date) impartial (软新闻)Primary data一手数据:Research approaches:Observational research观察法调查Best suited for exploratory researchObserving relevant people, actions and situationsEthnographic research人类学研究sending trained observersSurvey research问卷调查Most widely used, gathering descriptive information (knowledge,attitudes, preferences, buying behavior), asking directlyAdvantage: flexibilityDisadvantage: unable or unwilling to respond, give misleading orpleasing answers, don’t have time, privacy concerns Experimental research实验法调查Gathering casual information 广告效果测试,口味测试,价格测试Contact methodsMail questionnaires邮寄问卷Telephone interviewing电话采访interviewer biasPersonal interviewing人员调查Individual interviewing: 采用便捷样本Group interviewing(focus group interviewing): 焦点小组访谈6~10人Online marketing researchInternet survey, online panels, experiments, online focus groups Sampling plan:抽样计划Sampling unit(who is to be surveyed)与企业本身产品的目标市场一致Sample sizeSampling procedureProbability sample简单随机抽样,分层抽样(年龄),集群抽样(区域)Nonprobability sample 便捷样本,判断样本,配额样本Research instruments:调查工具Questionnaire: closed-end questions (easier to interpret and tabulate)open-end questions (exploratory)Simple, direct, unbiased wording; in a logical orderMechanical devices: people meters, checkout skinner, eye camera➢Present the plan to managementPresented in a written proposal: problems, objectives, information needed, the way the results will help decision making, research cost(3)Implementing the research planCollecting data: marketing research staff or outside firmsThe most expensive and the most subject to error(Refuse to cooperate, biased, interviewer mistakes or shortcuts) Processing the information: isolate important information and findings, check data for accuracy and completeness, code it for analysis Analyzing the information: tabulate the results, compute statistical measure (4)Interpreting and reporting the findingsManagers and researchers work together closely, share responsibility3. Analyzing marketing informationAdvanced statistical analysis to learn more about the relationships within a set of data, involving a collection of analytical models that will help marketers make better decisionCustomer touch point: customer purchases, sales force contacts, service andsupport calls, web site visits, satisfaction surveys, creditand payment interactions, research studies Analyze and use individual customer data:CRM: managing detailed information about individual customers and carefully managing customer touch point to maximize customer loyaltyConsists of sophisticated software and analytical tools, integratecustomer information from all sources, analyze it in depth, apply theresults to build stronger customer relationshipsData warehouses: 数据仓库a companywide electronic database of finely detailedcustomer informationData mining: sift through data and dig out interesting findings about customersCRM is one part of an effective overall customer relationship management strategy 4. Distributing and using marketing informationChapter 5 Consumer markets and consumer buyer behavior Model of consumer behavior:Stimulus response model: marketing stimuli营销刺激物: 4 PsP117 other stimuli: economic, technological, political, culturalbuyer’s black box: characteristics, decision process Characteristics affecting consumer behavior:●Cultural factors:Culture: the most basic cause of a person’s wants and behavior, from family and other important institutions (school) Cultural shifts: new products Subculture: within a culture民族,宗教,种族,地域Social class: permanent and ordered divisions, measured by a combination of occupation, income, education, wealth, and other variables●Social factors:Groups:群体Membership groups成员群体direct influence, to which a person belongsReference groups参照群体direct or indirect points of comparison or referenceAspirational groups期望群体reference groups to which a person wishes to belongOpinion leaders意见领袖people within a reference group who, because of specialskills, knowledge, personality, or other characteristics, exert socialinfluence on others. (influentials or leading adopters)Buzz marketing口碑营销enlist or even create opinion leaders to spread the wordOnline social networking: blogs, social networking sites like , a newform of buzz marketingFamily: the most important consumer buying organizationHusband-wife involvement: courting the opposite sexChildren: highly regarded in Asian cultures, children-related industry Roles and status: people choose products appropriate to their roles and statues ●Personal factors:Age and life-cycle stage:年龄、生命周期阶段RBC Royal Bank five life-stage segmentsYouth: 小于18,教育资金Getting started: 18—35 贷款,信用卡Builder: 35—50 鼎盛期,贷款Accumulators: 50—60 财富积累,理财Preservers: 大于60 财产转移,继承Occupation: bluecollar workers vs. executivesEconomic situation: include trends in personal income, savings, interest rates Lifestyle: a person’s pattern of living as expressed in his or her psychographics AIO dimension: activity, interest, opinionVALS: lifestyle classification P124 8种Primary motivation: ideals(knowledge and principles)achievements (demonstrate success)self-expression (activity, variety, risk)Resources: income, education, health, self-confidence, energy…Personality andBrand personality: the specific mix of human traits attributed to a particular brandConsumers are likely to choose brands with personalities that match their ownSelf-concept (self-image)Premise: people’s possessions contribute to and reflect their identitiesReal self: 真实self-image:自我looking-glass self:他人ideal self:理想●Psychological factors:Motivation动机: A need that is sufficiently pressing to direct the person to seeksatisfaction of the needSigmund Freud theory: people are largely unconscious about the realpsychological forces shaping their behavior Abraham Maslow: human needs are arranged in a hierarchy, peopleare driven by particular needs at particular timesPhysiological, safety, social, esteem, self-actualization needs Perception感知:Three perceptual processes:Selective attention选择性注意screen out most of the informationSelective distortion选择性歪曲/曲解interpret information in a way that willsupport what they already believe Selective retention选择性保留retain information that supports their attitudes andbeliefsLearning学习Changes in an individual’s behavior arising from experience and occurs through interplay of drives, stimuli, cues, responses and reinforcementMarketer: associating the product with strong drives, usingmotivating cues, and providing positive reinforcement Beliefs and attitudes信念和态度Belief: A descriptive thought that a person has about something based on knowledge, opinion, or faithAttitude: A person’s relatively consistent evaluations, feelings, and tendencies toward an object or idea.It is difficult to change. Fit into existing attitudes.Types of buying behavior decisionBased on degree of buyer involvement and degree of differences among brands:1. Complex buying behavior复杂性购买行为Highly involved, significant differencesExpensive, risky, purchased infrequently, highly self-expressiveMarketer: understand the information-gathering and evaluation behavior of consumers, help buyers learn about attributes and their relativeimportance, differentiate brand’s features, and motivate storesalespeople and buyer’s acquaintancesFocus on product增加产品特性2. Dissonance-reducing buying behavior减少失调购买行为Highly involved, little differenceExpensive, risky, infrequent purchaseBuyers primarily response to a good price or to purchase conveniencePostpurchase dissonance: notice disadvantage or hear favorable words abouta product not purchasedMarketer: after-sale communications should provide evidence and supportFocus on CRM(投诉处理、维修等)3. Habitual buying behavior习惯性购买行为low involved, little differenceLow-cost, frequently purchasedBrand familiarity rather than brand conviction (passively receive information) Marketer: use sales and price promotion to stimulate products trial, ad stresses a few key points, more visual symbols and imaginary, highrepetition of short-duration message, better use TV ad, based onclassical conditioning theory(buyers learn to identify a certainproduct by a symbol repeatedly attached to it)Focus on distribution4. Variety-seeking buying behavior寻求多样化购买行为low involved, significant differencesConsumers do a lot of brand switching for variety rather than dissatisfactionMarket leader: encourage habitual buying behavior by dominating shelf space, keeping shelves full stocked, running frequent reminder advertising Challenger firms: encourage variety seeking by offering lower prices, specialdeals, coupons and free sample, and advertising reasons forsomething newFocus on distribution and promotionThe buyer decision process1. Need recognition需求确认Internal stimuli (normal need rises to a drive) external stimuli (ad, discussion) 2. Information search信息收集Personal sources: family, friends, neighbors, acquaintances) most effectiveCommercial sources: ad, salespeople, web, dealers, packaging, diaplayPublic sources 公开: mass media, consumer-rating organizations, Internetsearches 质量检测Experiential sources体验性: handling, examining, using the product使用经历3. Evaluation of alternatives方案评价process information to arrive at brand choicesCareful calculations and logical thinking; buy on impulse and rely on intuition 4. Purchase decision购买决策Between purchase intention and decision:Attitudes of others, unexpected situational factors5. Post-purchase behavior购买后行为Consumer expectations and products’ perceived performanceCognitive dissonance认知失调: Discomfort caused by postpurchase conflictConsumer satisfaction is a key to building profitable relationships withconsumers—to keeping and growing consumers andreaping their customer lifetime valueMarketer: measure customer satisfaction regularly, set up systems that encourage customers to complainThe buyer decision process for new productsStages in adoption process采纳过程from first learning to final regular user Awareness: become aware, but lack of informationInterest: seek informationEvaluation: consider whether trying it make senseTrial: try the new product in a small scaleAdoption: make full and regular use of itIndividual differences in innovativenessInnovator: venturesomeEarly adopter: guided by respect, opinion leader, early but cautiouslyEarly majority: deliberate, before the average personLate majority: skeptical, after majority of people have tried itLaggards: tradition bound, suspicious, adopt only when they become tradition 采纳曲线/扩散曲线time of adoption/diffusion of innovations P135Firm: research characteristics of innovators and early adaptors and direct market to them Innovators: younger, better educated, higher in income, more receptive to unfamiliar things, rely more on their own values and judgment, more willing to takerisks, less brand loyal, take advantage of special promotionInfluence of product characteristics on rate of adoptionRelative advantage相对优势: superior to existing productsCompatibility: fits the value and experiences of potential consumersComplexity: difficult to understand or useDivisibility: tried on a limited basis (e.g.price)Communicability: results of using can be observed or described to others Chapter 7 Customer-driven marketing strategy: creating value for targetcustomers (STP 营销核心)Market segmentationSegmenting consumer markets1. Geographic segmentation地理划分Nations, regions, states, counties, cities, density, climate, neighborhoodsCompanies: localize products, ad, promotion and sales efforts; cultivate as-yet untapped territory; developing stores in higher-density urban areas2. Demographic segmentation人口划分most popular, consumer needs, wants andusage rates vary closely with it, easier to measure Age and life-cycle stage: guard against stereotype, positive image and appeals Gender: clothing, cosmetics, toiletries, magazinesIncome: automobile, clothing, cosmetics, financial services, travelAffluent or low-income3. Psychographic segmentation心理划分Social class, lifestyle, personality characteristics4. Behavioral segmentation行为划分best starting point for building market segments,buyers’ knowledge, attitudes, uses, or response to a product Occasions: holidays, special occasions (e.g. Valentine’s day, wedding, birth day)Benefits sought: different benefits buyers seek from the producte.g.不同功效的牙膏,match each segment’s benefit preferencesUser status: nonusers, ex-users, potential users, first-time users, regular userse.g. blood banks, recruit new first-time donors and remind ex-donorspotential users: consumers facing life-stage changes(newlyweds) Usage rate: light, medium, heavy product usersHeavy users: a small percentage of the market but account for ahigh percentage of total consumptionLoyalty status: Completely loyal (buy one brand all the time)Pinpoint its target market and develop marketing appealsSomewhat loyal (loyal to two or three brands, favor one brandwhile sometimes buying others)Detect which brands are most competitive with its ownNot loyal (want something different, buy whatever’s on sale)Marketing weaknessUsing multiple segmentation bases: identify smaller, better-defined target Segmenting international marketsUsing one or a combination of several variables: geographic location, economicfactors, political and legal factors, cultural factors Intermarket segmentation: forming segments of consumers who have similar needs and buying behaviors even though they are located in different countries Requirements for effective segmentationMeasurable: 可测量性size, purchasing power, and profiles of the segments Accessible:可接近性can be effectively reached and servedSubstantial:显著性large or profitable enough, a segment should be the largest。