麦肯锡 战略分析方法与工具
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:324.27 KB
- 文档页数:33

竞争战略分析工具竞争战略分析工具在企业战略制定和竞争战略选择过程中起着至关重要的作用。
它们帮助企业了解市场环境、竞争对手和自身优势劣势,从而确定最适合的竞争战略。
本文将介绍几种常用的竞争战略分析工具,并分析其应用场景和优势。
一、SWOT分析SWOT分析是一种常用的竞争战略分析工具,它通过评估企业的优势、劣势、机会和威胁,帮助企业确定最佳的竞争战略。
SWOT分析的优势在于它能够全面地评估企业的内部和外部环境,并使企业能够了解自身的优势和劣势,抓住机遇,应对威胁。
然而,SWOT分析也存在一些局限性,例如它只能提供静态的分析结果,不能真正解决企业面临的问题。
二、五力分析五力分析是麦肯锡公司的竞争战略分析工具,它通过评估竞争对手、供应商、买家和潜在进入者的力量,帮助企业了解所处行业的竞争情况。
五力分析的优势在于它能够帮助企业把握行业竞争的核心要素,并制定相应的竞争战略。
然而,五力分析也存在一些限制,例如它无法提供具体的操作指导,而且对于新兴行业或不确定的市场情况,五力分析的有效性会受到影响。
三、价值链分析价值链分析是波特的竞争战略分析工具,它通过评估企业的主要活动和支持活动,帮助企业了解自身在价值链上的定位和竞争优势。
价值链分析的优势在于它能够帮助企业识别自身价值创造的关键环节,从而寻找降低成本和提升价值的机会。
然而,价值链分析也存在一些挑战,例如它需要企业对内部业务流程进行深入的了解和分析,而这可能需要大量的人力和时间资源。
四、BCG矩阵BCG矩阵是波士顿咨询集团的竞争战略分析工具,它通过评估企业产品在市场上的相对市场份额和市场增长率,帮助企业确定产品组合的发展策略。
BCG矩阵的优势在于它能够帮助企业识别优势产品和劣势产品,并制定相应的市场策略。
然而,BCG矩阵也存在一些限制,例如它只考虑了相对市场份额和市场增长率,而忽视了其他重要的因素,如技术发展和市场趋势。
五、市场地图市场地图是一种竞争战略分析工具,它通过评估竞争对手产品在市场上的定位和差异化特点,帮助企业了解市场的竞争格局。


战略分析工具发展历程和分类战略分析工具是指用于帮助组织分析和评估其外部环境、内部资源和能力以及制定相应战略的工具和方法。
随着经济全球化和市场竞争的加剧,战略分析工具的发展逐渐成为组织管理的重要组成部分。
战略分析工具的发展历程可以追溯到20世纪50年代,当时美国波士顿咨询公司(BCG)首次提出了产品组合矩阵和成本收益矩阵等工具。
随后,波特(Michael E. Porter)提出了波特五力模型(Porter's Five Forces Model),并在1980年代进一步发展了价值链分析和竞争优势理论,成为战略分析的经典模型。
在20世纪90年代和21世纪初,麦肯锡全球研究院(MGI)提出了战略性创新矩阵和市场经济周期分析等工具。
威尔森(David C. Wilson)提出了人力资源战略分析模型,为人力资源管理提供了辅助工具。
战略分析工具可以根据其所关注的方面和目标进行分类。
最常见的分类包括外部环境分析工具、内部资源和能力分析工具以及战略制定和评估工具。
外部环境分析工具主要用于评估组织所处的行业竞争环境。
波特五力模型被广泛应用于分析竞争对手、供应商、顾客、替代品和新进入者对组织的影响。
PESTEL分析模型用于分析政治、经济、社会、技术、环境和法律等外部环境因素,并评估其对组织的风险和机会影响。
内部资源和能力分析工具主要用于评估组织内部资源和能力的优劣。
波特的价值链模型用于分析组织的内部价值创造活动,并评估其在行业中的竞争优势。
SWOT分析模型则用于评估组织的优势、劣势、机会和威胁,以制定相应的战略。
战略制定和评估工具主要用于帮助组织制定和评估战略目标和行动计划。
战略地图和平衡计分卡(Balanced Scorecard)用于制定战略目标和评估绩效,以保证组织战略的执行和控制。
战略分析工具的发展历程从上世纪起至今逐渐成熟,分类也变得更加多样化和细分化。
通过合理利用战略分析工具,组织能够更好地了解和应对外部环境的变化,利用内部资源和能力获得竞争优势,并制定和评估相应的战略目标和行动计划。

麦肯锡模型及其详解麦肯锡模型(McKinsey model)是一种管理工具,用于分析和解决复杂的商业问题。
它由全球领先的管理咨询公司麦肯锡公司(McKinsey & Company)开发并广泛应用。
在本篇文章中,我们将详细解释麦肯锡模型的各个方面,包括其定义、应用场景、步骤和示例。
一、什么是麦肯锡模型麦肯锡模型是一种商业问题解决框架,旨在提供结构化的方法来分析和解决各种商业挑战。
该模型由麦肯锡公司的顾问们根据多年的实践经验开发而成,并在全球范围内得到广泛应用。
其核心思想是将问题分解为不同的要素,并通过相互关联的分析来提供解决方案。
二、麦肯锡模型的应用场景麦肯锡模型适用于各种商业问题解决和战略制定的场景。
无论是市场分析、竞争对手研究、产品定位、供应链优化还是企业规模扩张,麦肯锡模型都可以提供有力的解决方案。
该模型被广泛应用于各行各业,包括制造业、金融业、咨询业等。
三、麦肯锡模型的步骤麦肯锡模型的应用通常包括以下几个步骤:1. 定义问题:明确要解决的具体问题,并确保所有相关方都对问题的定义达成一致。
2. 数据收集:收集必要的数据和信息,包括市场数据、竞争信息等,以支持后续的分析和决策。
3. 分析框架:选择适当的分析框架,将问题分解为不同的要素,并建立它们之间的关联。
4. 数据分析:在分析框架的指导下,对收集到的数据进行分析,识别关键问题和机会。
5. 解决方案:基于数据分析的结果,提出切实可行的解决方案,并进行评估和优化。
6. 实施计划:将解决方案转化为可执行的计划,并明确责任和时间表。
7. 监控和调整:跟踪解决方案的实施情况,定期评估并进行必要的调整。
四、麦肯锡模型的示例为了更好地理解麦肯锡模型的应用,以下是一个实际案例的示例:假设一个新兴的科技公司面临市场份额下降的问题。
他们希望通过使用麦肯锡模型来找到解决方案。
遵循麦肯锡模型的步骤,他们首先明确问题为市场份额下降,并与团队成员一致对问题进行定义。

麦肯锡之SWOT分析模型(SWOTAnalysis)在现在的战略规划报告里,SWOT分析算是一个众所周知的工具了,同样SWOT也是来自McKinsey咨询公司的。
SWOT分析代表分析企业优势(strength)、劣势(weakness)、机会(opportunity)和威胁(threats)。
因此,SWOT分析实际上是将对企业内外部条件各方面内容进行综合和概括,进而分析组织的优劣势、面临的机会和威胁的一种方法。
Why SWOT?可以通过分析帮助企业把资源和行动Focus在自己的强项和有最多机会的地方。
1、模型含义介绍优劣势分析主要是着眼于企业自身的实力及其与竞争对手的比较,而机会和威胁分析将注意力放在外部环境的变化及对企业的可能影响上。
在分析时,应把所有的内部因素(即优劣势)集中在一起,然后用外部的力量来对这些因素进行评估。
(1) 机会与威胁分析(OT)随着经济、社会、科技等诸多方面的迅速发展,特别是世界经济全球化、一体化过程的加快,全球信息网络的建立和消费需求的多样化,企业所处的环境更为开放和动荡。
这种变化几乎对所有企业都产生了深刻的影响。
正因为如此,环境分析成为一种日益重要的企业职能。
环境发展趋势分为两大类:一类表示环境威胁,另一类表示环境机会。
环境威胁指的是环境中一种不利的发展趋势所形成的挑战,如果不采取果断的战略行为,这种不利趋势将导致公司的竞争地位受到削弱。
环境机会就是对公司行为富有吸引力的领域,在这一领域中,该公司将拥有竞争优势。
对环境的分析也可以有不同的角度。
比如,一种简明扼要的方法就是PEST分析,另外一种比较常见的方法就是波特的五力分析。
(2) 优势与劣势分析(SW)识别环境中有吸引力的机会是一回事,拥有在机会中成功所必需的竞争能力是另一回事。
每个企业都要定期检查自己的优势与劣势,这可通过“企业经营管理检核表”的方式进行。
企业或企业外的咨询机构都可利用这一格式检查企业的营销、财务、制造和组织能力。

麦肯锡战略分析的工具:解决问题的基本方法(之一)麦肯锡是国际顶级战略管理咨询公司,它有一系列独特的管理理念、方法和工具。
这里介绍他们的一个分析问题的方法。
原文是PPT文档,现在还无法上传,只好这样转贴了。
这里先贴到步骤一。
余下部门,有空时我尽快编好贴出。
有关解决问题常见的迷思迷思―解决问题的高手是天生的,而不是培养出来的。
有的人生来就有这个天赋,而有的人却没有,这是一种天生的创造能力...是教不出来的。
‖事实―善于解决问题的能力通常是缜密而系统化思维的产物,任何一个有才之士都能获得这种能力。
有序的思维工作方式并不会扼杀灵感及创造力,反而会助长灵感及创造力的产生。
‖解决问题的七个步骤1、陈述问题> 2、分解问题(问题树) > 3、去掉所有非关键问题(漏斗法) > 4、制定详细的工作计划 > 5、进行关键分析 > 6、综合调查结果,并建构论证 > 7、讲述来龙去脉:在沟通文件中将数据及论证联系起来第一步-陈述问题清晰地陈述要解决的问题清晰陈述问题的特点:1) 一个主导性的问题或坚定的假设2) 具体,不笼统3) 有内容的(而非事实的罗列或一种无可争议的主张)4) 可行动的5) 以决策者下一步所需的行动为重点首要之务是对问题的准确了解陈述问题的实例-公共图书馆问题评价公共图书馆面临着大家抱怨它不能事实的陈述提供信息服务的问题图书馆是否应努力改善对会员的服务?无可争议能否采取不同的图书馆管理方法以改太空泛善对会员的服务?图书馆有哪些改善会员服务的可能?具体,可行动的是通过延长时间,更好地选择书刊,还是在现有的预算内改善编辑目录使借阅更加容易?其他方面-问题的背景情况1.决策者哪些是你的听众?2.影响决策者的主要因素哪些是他们比较关心的问题?你如何解决互相冲突的问题?3.解决问题的时间多快需要找出解答?4.成功的标准决策者如何判断是否成功地解决了问题?他/她所关心的是什么?5.主要衡量标准哪些是衡量成功的主要变数?6.所需的准确度需要何种准确度?问题背景情况的实例-公共图书馆1.决策者• 图书馆馆长• 理事会• 市长2.影响决策者的主要因素图书馆馆长• 12个月後需再由市长续聘并由理事会批准• 已任职7年市长• 将在9个月后重新选举,并面临着需增加赋税但没有提供足够服务的压力3.解决问题的时间安排必须在6个月内进行改善,所以必须在2月内解决问题4.成功的标准改革必须同图书馆的使命一致• 改革计划必须可在6个月内实施• 改善成果必须在6个月内可以衡量并有所显现• 因为图书馆的工作人员是主要的改革实施者,所以他们必须支持改革5.主要衡量标准不超出预算• 客户满意度调查结果有所改善• 发给市长、报纸或图书馆长的表扬信6.所需的准确度对所需变革种类的强有力的指导比细节的精确度更为重要• 但不能超出预算关心听众所急一定要考虑到决策者的主要标准注意多快需要答案麦肯锡战略分析的工具:解决问题的基本方法(之二)步骤2-分解问题问题陈述:逻辑树问题/假设1分支问题分支问题问题/假设2分支问题分支问题问题/假设3分支问题分支问题为什么使用逻辑树?1.将问题分成几个部分使• 解决问题的工作可以分成智力上能够解决的几个部分• 不同部分可按轻重缓急区分• 工作责任能分派到各人2.保证问题获得完整地解决• 将问题的各个部分解决好,即可解决整个问题• 所分问题的各个部分各不相同,而且包括了各个方面(即没有重叠没有遗漏)3.使项目小组共同了解解决问题的框架4.协助重点使用组织框架及理论步骤3-淘汰非关键的问题• 经常反复推敲过程中的第一步–假设/理论及数据之间的来回穿梭–使用80/20的思考方式• 重点努力解决最重要的问题• 不仅要常问―那又会怎样‖...而且还要问你忘了什么• 进行一项较困难的研究分析时淘汰非关键性问题是掌握合理生活方式的关键步骤4-制定详细的工作计划问题• 从逻辑树中最後一点(或「叶」)开始• 「重要议题」和「未解决议题」定义不同。

麦肯锡1。
麦肯锡7S模型 (1)2. 麦肯锡七步分析法 (4)3. 麦肯锡三层面理论 (5)4. 麦肯锡逻辑树分析法 (6)5。
麦肯锡七步成诗法 (8)6。
麦肯锡客户盈利性矩阵 (12)注1: 新7S原则 (14)麦肯锡咨询公司(Mckinsey & Company)是世界级领先的全球管理咨询公司。
自1926年成立以来,公司的使命就是帮助领先的企业机构实现显著、持久的经营业绩改善,打造能够吸引、培育和激励杰出人才的优秀组织机构。
麦肯锡采取“公司一体”的合作伙伴关系制度,在全球44个国家有80多个分公司,共拥有6500多名咨询顾问。
麦肯锡大中华分公司包括北京、香港、上海与台北四家分公司,共有40多位董事和250多位咨询顾问。
在过去十年中,麦肯锡在大中华区完成了800多个项目,涉及公司整体与业务单元战略、企业金融、营销/销售与渠道、组织架构、制造/采购/供应链、技术、产品研发等领域。
1.麦肯锡7S模型目录1 麦肯锡7S模型简介二十世纪七、八十年代,美国人饱受了经济不景气、失业的苦恼,同时听够了有关日本企业成功经营的艺术等各种说法,也在努力寻找着适合于本国企业发展振兴的法宝。
托马斯·J·彼得斯(Thomas J.Peters)和小罗伯特·H·沃特曼(Robert H.Waterman),这两位斯坦福大学的管理硕士、长期服务于美国著名的麦肯锡管理顾问公司的学者,访问了美国历史悠久、最优秀的62家大公司,又以获利能力和成长的速度为准则,挑出了43家杰出的模范公司,其中包括IBM、德州仪器、惠普、麦当劳、柯达、杜邦等各行业中的翘楚.他们对这些企业进行了深入调查、并与商学院的教授进行讨论,以麦肯锡顾问公司研究中心设计的企业组织七要素(简称7S模型)为研究的框架,总结了这些成功企业的一些共同特点,写出了《追求卓越——美国企业成功的秘诀》一书,使众多的美国企业重新找回了失落的信心.7—S模型指出了企业在发展过程中必须全面地考虑各方面的情况,包括结构(Structure)、制度(Systems)、风格(Style)、员工(Staff)、技能(Skills)、战略(Strategy)、共同价值观(Shared Valueds)。

麦肯锡三部曲读书心得——结构化思维解决问题方法论打造学习型组织是一个组织长久保持领先优势的核心竞争力,最快最有效的统一思想、统一组织语言工具就是共同学习成长。
麦肯锡是世界上最成功的的战略咨询公司,本次阅读的《麦肯锡方法》、《麦肯锡意识》、《麦肯锡工具》,为下一步降低沟通,提升工作技巧,进而提升工作效率打下坚实基础。
一、入脑——整体知识结构1、《麦肯锡方法》介绍解决问题的路径是以事实为基础的,系统化的,大胆假设,小心求证。
其中不同的章节详细介绍了团队组建,层级管理,关键驱动因素,直观简洁汇报,有效沟通等方面,系统化、结构化的介绍麦肯锡人解决问题的思维逻辑。
2、《麦肯锡意识》从界定问题、设计分析内容、数据收集、解释结果、汇报、团队管理、客户管理、自我管理八个方面介绍解决问题过程中遇到的一系列问题,案例详实引人共鸣,借鉴参考意义极强。
3、《麦肯锡工具》主要从人际要素:交流、评价、协助、激励;分析要素:界定、分工、解读、提炼;八个方面详细分析解决问题过程中的技巧,具体章节在实践过程中可以借鉴应用。
二、入心——自身消化理解麦肯锡三部曲核心是解决问题,自身工作岗位的核心定位也是解决问题。
解决问题的路径是以事实为基础的,系统化的,大胆假设,小心求证。
其中不同的章节详细介绍了团队组建,层级管理,关键驱动因素,直观简洁汇报,有效沟通等方面,系统化、结构化的介绍麦肯锡人解决问题的思维逻辑。
三、入髓——躬身实践,知行合一1、MECE原则:麦肯锡学院里面最重要的原则是MECE原则,即:以事实为基础的,穷尽罗列互不相关的组织要素,分析界定问题以及解决问题过程中均可以使用。
例:某项目经营资金方案解决过程中,剖析7中不同的解决方案:a、自有可用资金;b、保函监管资金盘活;c、工抵变现;d、关联项目资金平衡;e、保理商票供应链融资;f、剩余车位、商铺变现;g、股东注资。
经层层分析推理,小心求证,最终只有两种方案能行得通,问题最终得以解决。
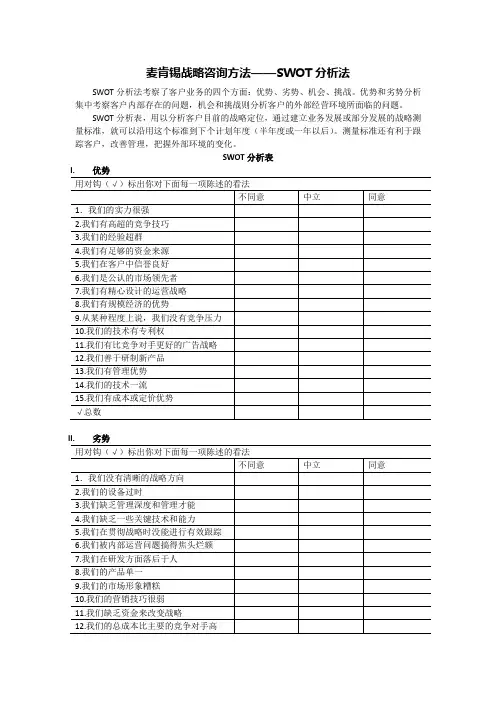
麦肯锡战略咨询方法——SWOT分析法
SWOT分析法考察了客户业务的四个方面:优势、劣势、机会、挑战。
优势和劣势分析集中考察客户内部存在的问题,机会和挑战则分析客户的外部经营环境所面临的问题。
SWOT分析表,用以分析客户目前的战略定位,通过建立业务发展或部分发展的战略测量标准,就可以沿用这个标准到下个计划年度(半年度或一年以后)。
测量标准还有利于跟踪客户,改善管理,把握外部环境的变化。
SWOT分析表
I.优势
II.劣势
III.机会
用对钩(√)标出你对下面每一项陈述的看法
IV.挑战
V.评分说明
1、优势和劣势
(1)选“不同意”得1分
(2)选“中立”得2分
(3)选“同意”得3分
2、挑战和机会
(1)选“不同意”得1分
(2)选“中立”得2分
(3)选“同意”得3分
优势(S)总分挑战(T)总分机会(O)总分劣势(W)总分(S+O)减去(T+W)
总得分(制定战略的基础)。

最全麦肯锡战略分析工具BU Strategic Plan Template Book STRATEGYPLANNING INSTRUCTIONS TABLE OF CONTENTS BU STRATEGIC PLAN DEVELOPMENT IEXECUTIVE SUMMARY IIA INDUSTRY DYNAMICS AND IMPLICATIONS – SUMMARY IIAINDUSTRY DYNAMICS AND IMPLICATIONS – BACK-UP 1 IIA INDUSTRY DYNAMICS-UP 2 IIA INDUSTRY DYNAMICS AND IMPLICATIONS – AND IMPLICATIONS –BACKBACK-UP 3 IIA INDUSTRY DYNAMICS AND IMPLICATIONS – BACK-UP 4 IIB COMPETITIVE ASSESSMENT – SUMMARY IIB COMPETITIVE ASSESSMENT –BACK-UP1 IIB COMPETITIVE ASSESSMENT – BACK-UP2 IIC INTERNAL ASSESSMENT –BACK-UP 1 IIC INTERNAL ASSESSMENT SUMMARY IIC INTERNAL ASSESSMENT –– BACK-UP 2 IIC INTERNAL ASSESSMENT – BACK-UP 3 IIIA STRATEGY ARTICULATION – SUMMARY IIIA STRATEGY ARTICULATION – BACK-UP 1 IIIA STRATEGY ARTICULATION – BACK-UP 2 IIIA STRATEGY ARTICULATION –BACK-UP3 IIIA STRATEGY ARTICULATION – BACK-UP4 IIIB STRATEGICINITIATIVES – SUMMARY IIIB STRATEGIC INITIATIVES – BACK-UP 1 IIIB STRATEGIC INITIATIVES – BACK-UP 2 IIIB STRATEGIC INITIATIVES – BACK-UP 3 IIIBSTRATEGIC INITIATIVES – BACK-UP 4 IIIC FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS –SUMMARYIIIC FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS – BACK-UP 1 IIIC FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS –BACK-UP 2 IIIC FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS – BACK-UP 3 IIIC FINANCIAL PROJECTIONS – BACK-UP 4 IIID RISKSCONTINGENCIES STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVES– SUMMARY IIID RISKSCONTINGENCIES STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVES –BACK-UP 1 IIID RISKSCONTINGENCIES STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVES – BACK-UP2 IIID RISKSCONTINGENCIES STRATEGIC ALTERNATIVES – BACK-UP3 SEGMENTANALYSIS STRUCTURE-CONDUCT-PERFORMANCE SCP MODEL SWOT ANALYSISCAPABILITY PLATFORM ASSESSMENT OF SOURCES OFCOMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE 12 CAPABILITY PLATFORM ASSESSMENT OF SOURCES OF COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGE 22 COMPETITOR CAPABILITY COMPARISON BENCHMARK PERFORMANCE AGAINST RELEVANT INDUSTRY KPIs SEGMENT ANALYSIS TREND ANALYSIS – RETURN ON CAPITAL EMPLOYED ROCE TREND ANALYSIS – CASH INTANGIBLE ASSET CHECKLIST WHERE TO COMPETE VALUE PROPOSITION BUSINESS MODEL STRATEGIC INITIATIVES SOURCES OF VALUE STRATEGIC INITIATIVES VALUE QUANTIFICATION STRATEGIC INITIATIVES RESOURCING REQUIREMENTS DEFINITION OF RISKS C1 What are the key assumptions Profit and loss eg revenues costs margin Balance sheet Corporate center directives Corporate center assumptions BASE CASE Business unit assumptions Revenues Market size Market share Price Costs Input costs Production costs Other costs eg SGA Margins Gross margin Operatingmargin Capital Planned investments divestments Changes in workingcapital 2002 KEY FORECAST ASSUMPTIONS 2003 2004 Growth rate Corporate center assumptions 2002 20032004 Key economic indicators GDP growth Consumer price indexExchange rate PhP USD 91-day T-bill rate Corporate tax rateInstructionsThese are the minimum required assumptions Feel free to add other assumptions relevant to your BU C2 What is your projected net income in the next few years Income statement forecast BASE CASE Historical Sales Cost of goods sold Gross profit Operating expenses Operating profit Other expenses Taxes Net profit 1999 FORECASTED INCOME STATEMENT 2000 In PhP million Forecast 2001 2002 2003 2004 CAGR 1999-2004 Growth analysis SalesGross profit Operating profit Net profit Margin analysis Gross margin Operating margin Net margin Key assumptions not listed earlier should be detailed at the bottom of the chart The impact of planned initiatives on the revenues and costs should be established clearly with additional attachments if required Best estimates on possible actual results InstructionsThese are the minimum required income statement accounts and analyses Feel free to add other accounts and analyses relevant to your BU C3What is your expected cash generation ability over the medium term Cash flow forecast InstructionsThese are the minimum required cash flow statement accounts Feelfree to add other accounts relevant to your BU BASE CASE Operatingprofit Depreciation and amortization Other non-cash operating expenses Net operating cash flow Increasedecrease in working capital Other operating cash flow Total operating cash flow FORECASTED CASH FLOW STATEMENT Historical 1999 2000 Forecast 2001 2002 2003 2004 CAGR 1999-2004 Capital expenditure Other investing cash flow items Total investing cash flow Increasedecrease in debt Dividends Other financing cash flow Total financing cash flow In PhP million Key assumptions not listed earlier should be detailed at the bottom of the chart The impact of planned initiatives on the fixed and working capital investments should beestablished clearly with additional attachments if required Best estimates on possible actual results C4 What is your expected capital productivity Balance sheet forecast ROCE computation ROCE Operating income x 1- tax rate All interest bearing debtshort and long minority interest stockholders equityInstructionsThese are the minimum required balance sheet accounts and analyses Feel free to add other accounts and analyses relevant to your BU BASE CASE Cash Accounts receivables Inventories Other current assets Total current assets Net fixed assets Other assets Total assets FORECASTED BALANCE SHEET Historical 1999 2000 Forecast 2001 2002 2003 2004 CAGR1999-2004 Accounts payable Other current liabilities Total current liabilities Shortans Long-term loans Other liabilities Total -term lo liabilities Minority interest Total stockholders equity In PhPmillion Capital employed ROCE Total liab stockholders equity Ratio analysis Working capital turnover Debt-equity ratio Best estimates on possible actual results D What strategic alternatives have you considered D1What are the associated risks to your chosen strategy D2Re-examining industry opportunities and industrycompetitive threats what alternatives exist to your chosen strategy InstructionsThe answer to thisoverarching questionrequires a recapitulationof the sections mainfindings D3 Beyond the 3-year time frame what breakthrough strategic options may be possible InstructionsThese subsectionscontain a 1-2 sentencesummary of the relevantfindings D1 What are the associated risks to your chosen strategy Identification of significant potential risks and plans to mitigate Sensitivityscenario financial analysis Potential risks Business risk Regulatory risk Technology risk Integrity risk Macroeconomic risk Impact Likelihood Contingency Other D2 Re-examining industry opportunities andindustrycompetitive threats what alternatives exist to your chosen strategy Where to compete Value proposition Business model Alignment with external realities Where to compete Alternative value proposition Alternative business model Alignment with external realities InstructionsBased on a review of the section on Environmental and Internal Assessment Strategy Articulation and the frameworks used Exhibit 2-4 13-15 determine other potential strategic alternatives D3 Beyond the 3-year time frame what breakthrough strategic options may be possible Out-of-the-box ideasInstructionsThink radical Think out-of-the-box IV EXHIBITS Instructions Please include all relevant supporting documentation in this section Exhibit 1 ILLUSTRATIVE Industry boundaries Segments Industry segments Relatively distinct sub-groupings within the industry Market is relatively similar within the segment but different across segments Different industry dynamics may vary in importance in different segments Producers Industry S Technology breakthroughs Changes in government policyregulations Domestic International Economics of demand Availability of substitutes Differentiability of products Rate of growth Volatilitycyclicality Economics of supply Concentration of producers Import competition Diversity of producers Fixedvariable coststructureCapacity utilization Entryexit barriers Industry chain economics Bargaining power of input suppliers Bargaining power of customers Marketing Pricing Volume Advertisingpromotion New productsRDDistribution Capacity change Expansioncontraction Entryexit Acquisitionmerger divestiture Vertical integration Forwardbackward integration Vertical joint ventures Long-term contracts Internal efficiency Cost control Logistics Process RD Organization effectiveness Finance Profitability Value creation Technological progress Employment objectives External shocks Feedback tructure C onduct P erformance Exhibit 2 Exhibit 3 1 Determinants of supplier power Differentiation of inputs Switching costs of suppliers and firms in the industry Presence of substitute inputs Supplier concentration Importance of volume to supplier Cost relative to total purchases in the industry Impact of inputs on cost or differentiation Threat of forward integration relative tothreat of backward integration by firms in the industry 2Determinants of barriers to entry Economies of scale Proprietary product differences Brand identity Switching costs Capital requirements Access to distribution Absolute cost advantages Proprietary learning curve Access to necessary inputs Proprietary low-cost product design Government policy Expected retaliation 5 Rivalry determinantsIndustry growth Fixed or storage costvalue added Intermittentovercapacity Product differences Brand identity Switching costsConcentration and balance Informational complexity Diversity of competitors Corporate stakes Exit barriers 3 Determinants of buying power Bargaining leverage Buyer concentration vs firm concentration Buyer volume Buyer switching costs relative to firm switching costs Buyerinformation Ability to backward integrate Substitute productsPull-through 4 Determinants ofsubstitution threat Relative price performance of substitutes Switchingcosts Buyer propensity to substitute 2 New entrants 3 Buyers 4Substitutes Intensity of rivalry 1 Suppliers Price sensitivity Pricetotal purchases Product differences Brand Identity Impact on qualityperception Buyer profits Decision makers incentives 5 Industry competitors "FORCES AT WORK" FRAMEWORK OpportunitiesThreats How are and supply expected to evolve How do you expect the industry chain demandeconomics to evolve What are the potential major industry discontinuitiesWhat competitor actions do you expect YOUR BU Exhibit 4 CONVERT OPPORTUNITIES BUILD ON STRENGTHS NEUTRALIZE THREATS ADDRESS WEAK-NESSES Strengths Weaknesses What are your BUs assetscompetencies that solidify your competitive position What are your BUs assetscompetencies that weaken your competitive position Can be used as a thought starter forcompetitive analysis and internal assessment Surfaces potential opportunitiesthreats arising from factors external to the BU Physical asset Location"space"Distributionsales network Brandreputation Patent Relationship with "license" allocator BHPs low-cost mines Telecommmedia company with rightsradio spectrum Avons representatives Coca-Cola Pharmaceutical company with a "wonder drug "Favored nation" status with a key minister in liberalizing economy Innovation Cross-functional coordination Market positioning Costefficiency management Talent development 3M with new products McDonalds with QSCV JJ with branded consumer health products Emerson Electrics Best Cost Producer program PG brand management program Privileged assets Distinctive competencies Necessary capabilities in order to succeed in the industry Example Exhibit 5 ILLUSTRATIVE Step 1 Ensure that these are the capabilities required to succeed in the industry Use this list as a thought starter add anddelete as you see appropriate BU Overall Segments A B C Step 2 Assess your overall position relative to the capabilities required to succeedin the industry Also determine if these capabilities are relevant to the segments you serve Physical asset Location"space"Distributionsales network Brandreputation Patent Relationship with "license" allocator Innovation Cross-functional coordination Market positioning Costefficiency management Talent development Privileged assets Distinctive competencies Necessary capabilities in order tosucceed in the industry Exhibit 6 Extremely relevant Somewhat relevant Irrelevant BU Overall Competitors A B C Step 3 Compare the strengths and weaknesses of your competitive position vs the necessary skills Physical asset Location"space"Distributionsales network Brandreputation Patent Relationship with "license" allocator Innovation Cross-functional coordination Market positioning Costefficiency management Talent development Privileged assets Distinctive competencies Necessary capabilities in order to succeed in the industry Exhibit 7 ILLUSTRATIVE Exhibit 8ILLUSTRATIVE KPIs examples Financial indicators Margin Net income ROCEOperating indicators Advertising effectiveness Utilization rate Strategic indicators Market share Percent of revenue from new products Working capital trend External indicators Market prices of raw materials BU Competitor A Competitor B Competitor C Revenue Gross profit Operating profit Assets employed People employed Operatingprofit margin Gross profitmargin ROCE Step 1 Identify the relevant segments Step 2 Provide a segment analysis based on the following minimum financial metrics revenue gross profit and margin operating profit and margin Step 3 Tothe extent assets and people can be disaggregated by segment deployment of assets against returns can be analyzed PhP of total Segment 1 PhP of total Segment 2 PhP of total Segment 3 PhP of totalSegment 4 PhP of total Total Exhibit 9Segment 1 Segment 2 Segment 3 Segment 4 Total NOT EXHAUSTIVE The ROCE tree can be disaggregated to show the other relevant KPIs of a BU ROCE Percent Operating income x 1 - tax rate PhP million Capital employed PhP million ? Revenue PhP million Operating margin Percent x 1 - tax ratePercent x Market share Percent Industry sales PhP million x Exhibit 10 NOT EXHAUSTIVE The cash flow tree can be disaggregated to show the other relevant KPIs of a BU Exhibit 11 Cash flow generated PhP million Operating cash flow PhP million Investing cash flow PhP million Net income PhP million Non-cash expenses PhP million Change in working capital PhP million Financing cash flow PhP million Exhibit 12Intangible assets Ways to extract near-term value Talent Highly motivated and competent workforce leveraging specific skill sets to Generate growth Improveincrease company intangibles Intellectual property Patents generating licensing fees Understanding of customer behavior Risk management Software ILLUSTRATIVE Network Interconnected webs of parties Non-exclusive Additional member lowers costs increases benefits Brandimage Inherent image or brand built upon excellent service and product offerings Lower search costs forcustomers Exhibit 13 Customers Channels Productsmarkets Target customers and segments Which customers are you Geographictrying to target or attract Which are you willing to serve but will not spend resources to attract Which would you prefer not to serve Howdoes the entity reach its target customers Which distribution channels will you use What customer segments can they reach Geographical scope of business activities Geographic limits to the business Local regional multi-local national international or global player If local which localities Quality and breadth of the product line Breadth of the product line Quality of the product line Product bundles or a series of unrelated products A companys specific promise to its target customers of the benefits it will provide at an explicit price It answer the following questions Who is your target customer What are the explicit benefits you provide to your customer What perceived value do you provide to the customer better than competition How much value do your customers attach to the benefits you provide Exhibit 14 Exhibit 15 Understand value desires Select target Chose the value Value proposition Design product process Procure manu- facture Distri- bute Provide the value Service PriceDefine benefitsprice Sales message Communicate the value Business model Integrated set of actions to provide and communicate the value proposition to customers Segmentation Value proposition Adver- tising Promo- tionalPR Value delivery system VDS Each BU must address these 2 issues to define their business model Illustration of how the value proposition will be provided and communicated Identification of existing strengths that can be leveraged and required capabilities that need tobe built to be distinctive in chosen value delivery system 1 2Categories of initiatives 1 Capture greater market share Volume increase EBIT impact via Price increase Cost reduction Other Invest-ment Capital employed impact via Divest-ment Capitalefficiency Other ü 2 Cost reduction eg effective channel management3Obtain higher prices 4 Create new market demand 5 Form strategic alliances partnerships ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü ü Eg improvedworking capital employment increased asset utilization changes to assetownership Specific actionable initiatives Exhibit 16 ILLUSTRATIVE Exhibit 17 ILLUSTRATIVE Estimate of totalongoing operating income andcapital employed impact fromsuccessful implementation ofstrategic initiatives Operating income ongoing impact 2001-2004 PhP millions Capital employed ongoing impact 2001-2004 PhP billions Present operating income Volume increase Price increase Cost reduction benefit Additional costs Total ongoing operating income Present capital employed Improved capital efficiency Divestments Investments capexacquisitionsTotal ongoing capital employed one-time operating income impact one-time costs ––– Exhibit 18 ILLUSTRATIVE Categories of initiatives Specific actionable initiatives Peopleskills Resourcerequirements Funding Ex-Com involvement 1 Capture greater market share 2 Cost reduction 3 Achieve higher prices4 Create new market demand5 Form strategicalliancespartnerships Exhibit 19 Definition Risk of loss due to changes in industry and competitive environment as well as shifts in customer preferences Business risk Risk due to changes in regulatory environment eg deregulation Regulatory risk Risk due to major changes in technology Technology risk Risk of failures due to business processes and operations or peoples behavior either intentional eg fraud or unintentional eg errors Integrity risk Risk of loss due to changes in the political social oreconomic environments Macroeconomic risk Unit of measureFootnote Source Source CONFIDENTIAL Document Date This report is solely for the use of client personnel No part of it may be circulated quoted or reproduced for distribution outside the client organization without prior written approval from McKinsey Company This material was used by McKinsey Company during an oral presentation it is not a complete record of the discussion CONFIDENTIAL Training materials 8 June 2001 This report is solely for the use of client personnel No part of it may be circulated quoted or reproduced for distribution outside the client organization without prior written approval from McKinsey Company This material was used by McKinsey Company during an oral presentation it isnot a complete record of the discussion Jim Ayala – PHO MelissaGil –PHO Regina Manzano – PHO Suresh Mustapha – PHO Steve Shaw – HKO ShellyYeh – PHO Choon-Gin Tan – SIO The objective of these templates is toprovide completeness and consistency of BU strategic plan submissions These templates are not intended to replace or constrain BU strategic thinking and should be adapted to reflect a particular BUs sectoral context as required Each section begins with a summary that is based on a synthesis of questions and analyses that follow The suggested approach would be to first complete the relevant back-up analyses and then worktowards the overall synthesis I Executive summary IIEnvironmental and internal assessment A Industry dynamics and its implications B Competitive assessment C Internal assessment III Strategic definition and implications A Strategy articulation BStrategic initiatives C Financial projection DRiskscontingencies and strategic alternatives IV Exhibits Industry dynamics and implications Environmental and internal assessment Competitive assessment Internal assessment What are the major changes in industry dynamics and resulting opportunities and risks What are your competitive strengths and weaknesses How does your current business emphasis fit with industry opportunity and competitive landscapeStrategy articulation Strategic definition and implications Strategic initiatives Financial projections What strategy will your BU pursue over the next 3 years What will be the impact of major strategic initiatives What are the expected financial returns of your strategy Riskcontingen-cies strategic alternatives What strategic alternatives have you consideredInstructions The Executive Summaryprovides a synthesis of theEnvironmental and InternalAssessments and theresultant BU Strategic Plans II ENVIRONMENTAL AND INTERNAL ASSESSMENT A What are the major changes in industry dynamics and the resulting opportunities and risks A2 How is industry structure changing demand supply and industry chain economics What are the resulting opportunities and risks A3 What is the expected competitor conduct What are the resulting opportunities and risks A4 What are the present and future external factors that could present new opportunities and risks A1What industry are you competing in What are the various segments in the industry InstructionsThe answer to thisoverarching questionrequires a recapitulationof the sections mainfindings InstructionsThese subsectionscontain a 1-2 sentencesummary of the relevantfindings A1 What industry are you competing in What are the various segments in the industry Industry definition Industry segmentation Definition Sizing InstructionsExhibit 1 could providea useful framework foranswering this question Industry definition Industry segmentation A2 How is industry structure changing with respect to demand supply and industry chain economics What are the resulting opportunities and risks Economics of demand By segment Substitutes ability to differentiate Volatility cyclicality Economics of supply Producer concentration and diversity Import competition Capacity utilization Entryexit barriers Cost structure fixed and variable Industry chain economics Customer and supplier bargaining power InstructionsExhibit 23 or 4 could providea useful framework foranswering this question A3 What is the expected competitor conduct What are the resulting opportunities and risks Major industry competitor movesMarketing initiatives Industry capacity changes MAs divestitures Vertical integrationdisaggregation Alliances and partnerships Costcontrol and efficiency improvements InstructionsExhibit 23 or 4 could providea useful framework foranswering this question A4 What are the present and future external factors that could present new opportunities and risks Impact and likelihood of major industry discontinuities Changes in regulationgovernment policy Technological breakthroughs Instructions Exhibit 23 or 4 could providea useful framework foranswering this question B What are your competitive strengths and weaknesses B1 What are the capabilities required to succeed in this industry B2 How do you compare against these necessary capabilities InstructionsThe answer to thisoverarching questionrequires a recapitulationof the sections mainfindings InstructionsThese subsectionscontain a 1-2 sentencesummary of the relevantfindings B1 What are the capabilities required to succeed in this industry Privileged assets that create competitive advantage eg physical assets locationspace distributionsales network intangible assetsintellectual capital network brands talents Distinctive skillscompetencies that create competitive advantage eginnovation talent development InstructionsExhibit 5 could providea useful framework foranswering this question B2 How do you compare against thesenecessary capabilities Strengths and weaknesses of your competitive position vs necessary capabilities Benchmark performance against the industrys relevant key performance indicators KPIs with margin andmarket share as the required minimum Strengths and weaknesses of your competitive position vs necessary capabilities Benchmark performance against therelevant industrys KPIs InstructionsExhibits 6 and 7 couldprovide a useful frameworkfor answering this question InstructionsExhibit 8 could providea useful framework foranswering this question KPIs are a handful of levers that drive the value of the industrybusiness C How does your current business emphasis。

麦肯锡三层面法--企业设计战略规划、学习、管理并不断开拓增长的有效工具1. 概念含义 (3)2. 内容分析 (4)2.1. 主要内容 (4)2.2. 精髓与要点 (6)2.3. 三层面的增长 (8)2.4. 不健康的增长模式 (9)2.5. 界定三层面是否平衡的要点 (9)3. 分析运用 (10)3.1. 运用步骤 (11)3.1.1. 准备工作 (11)3.1.2. 方法与操作模式 (13)3.1.3. 后台支持 (14)3.2. 意义作用 (15)4. 实例分析 (16)4.1. 案例1:澳大利亚C娱乐公司三层面分析 (16)5. 参考书目 (17)1. 概念含义麦肯锡咨询公司资深顾问梅尔达德·巴格海(Mehrdad Baghai)、斯蒂芬·科利(Stephen Coley)与戴维·怀特(David White) 对世界上不同行业的40个处于高速增长的公司进行研究,提出增长阶梯的概念。
他们认为高速增长的公司每一段时间都会前进步,每一步都会带来新行动和新能力;成功的增长公司强调针对近期和远期的远景和策略,真正伟大的公司是能维持增长同时追求增长的公司。
提出了一套关于了解、准备、启动和保持企业获利性持续增长的方法—— 增长的三层级论,通常称之为三层面论。
三层面论是指把企业的业务持续发展的进程分解成三个阶段。
这三个阶段显示了不同的水平:第一层面是守卫和拓展核心业务,第二层面是建立即将涌现增长动力的业务,第三层面是开造有生命力的未来业务,公司实现增长就必须同时管好增长三层面。
如图1所示。
此后,三层面论在三人的《增长炼金术》一书中得到了进一步的阐述和拓展。
麦肯锡三层面论的核心是企业在确保核心业务的基础上,选择第二层面业务,使其迅速发展为第一层面,同时为未来长远发展选择第三层面业务。
2. 内容分析2.1.主要内容这一理论从三个层面来理解和规划企业的业务进程,每个层面代表了开创和发展业务的不同阶段,而每个阶段也分别要求不同的业务举措和管理技能与之相适应。