最新第四章晶体中的点缺陷与线缺陷第一讲
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.04 MB
- 文档页数:7










第四章晶体中的缺陷与扩散晶体缺陷的基本类型热缺陷的统计理论晶体中的扩散离子晶体的点缺陷及导电性4-1晶体缺陷的基本类型晶体缺陷(晶格的不完整性):晶体中任何对完整周期性结构的偏离就是晶体的缺陷。
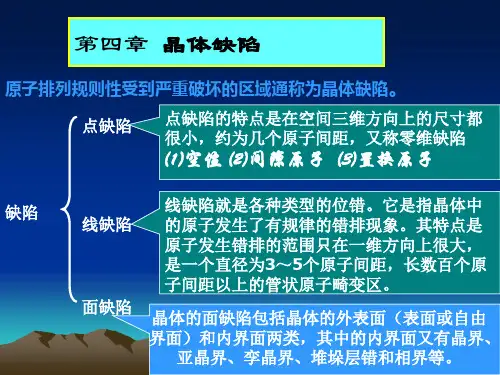
按缺陷的几何形状和涉及范围将缺陷分为:点缺陷、线缺陷和面缺陷。
一、点缺陷点缺陷是在格点附近一个或几个晶格常量范围内的一种晶格缺陷,如空位、填隙原子、杂质等。
由于空位和填隙原子与温度有直接的关系,或者说与原子的热振动有关,因此称他们为热缺陷。
1.弗仑克尔缺陷和肖特基缺陷弗仑克尔缺陷:当晶格中的原子脱离格点后,移到间隙位置形成填隙原子时,在原来的格点位置处产生一个空位,填隙原子和空位成对出现,这种缺陷称为弗仑克尔缺陷。
肖特基缺陷:当晶体中的原子脱离格点位置后不在晶体内部形成填隙原子,而是占据晶体表面的一个正常位置,并在原来的格点位置产生一个空位,这种缺陷称为肖特基缺陷。
2.杂质原子在材料制备中,有控制地在晶体中引入杂质原子,若杂质原子取代基质原子而占据格点位置,则成为替位式杂质。
当外来的杂质原子比晶体本身的原子小时,这些比较小的外来原子很可能存在于间隙位置,称它们为填隙式杂质。
填隙式杂质的引入往往使晶体的晶格常量增大。
3.色心能吸收可见光的晶体缺陷称为色心。
完善的晶体是无色透明的,众多的色心缺陷能使晶体呈现一定颜色,典型的色心是F心。
把碱卤晶体在碱金属的蒸气中加热,然后使之聚冷到室温,则原来透明的晶体就出现了颜色,这个过程称为增色过程,这些晶体在可见光区各有一个吸收带称为F带,而把产生这个带的吸收中心叫做F心。
4.极化子电子吸引邻近的正离子,使之内移。
排斥邻近的负离子,使之外移,从而产生极化。
电子所在处出现了趋于束缚这电子的势能阱,这种束缚作用称为电子的“自陷”作用。
产生的电子束缚态称为自陷态,同杂质所引进的局部能态有区别,自陷态永远追随着电子从晶格中一处移到另一处,这样一个携带着周围的晶格畸变而运动的电子,可看作一个准粒子(电子+晶格的畸变),称为极化子。
第四章晶体缺陷与缺陷运动§4.1 晶体缺陷的基本类型§4.2 位错缺陷的性质、晶体滑移的本质§4.3 热缺陷数目的统计平衡理论§4.4 热缺陷的运动、产生和复合§4.5 晶体中的扩散过程§4.6 离子晶体中的点缺陷与导电性前言理想晶体的主要特征是原子(或分子)的严格规则排列、周期性实际晶体中的原子排列会由于各种原因或多或少地偏离严格的周期性,存在着偏离了理想晶体结构的区域,于是就形成了晶体的缺陷。
晶体中虽然存在各种各样的缺陷,但实际在晶体中偏离平衡位置的原子数目很少(相对于晶体原子总数),在最严重的情况下,一般不会超过原子总数的万分之一,因而实际晶体结构从整体上看还是比较完整的。
缺陷——偏离了晶体周期性排列的局部区域。
前言(续)晶体中缺陷的种类很多,它们分别影响着晶体的力学、热学、电学、光学等各方面的性质。
然而,尽管在晶体中缺陷的数目很少,它们的产生和发展、运动和相互作用、以及合并和消失,对晶体的性能有重要的影响。
因此,晶体缺陷是固体物理中一个重要的研究领域,它对于研究和理解一些不能用完整晶体理论解释和理解的现象具有重要的意义。
例如:塑性与强度、扩散、相变、再结晶、离子电导以及半导体的缺陷导电等现象。
§4.1 晶体缺陷的基本类型一、点缺陷点缺陷——发生在一个或几个晶格常数范围内的缺陷。
如:空位、填隙原子、杂质原子等。
这些空位、填隙原子是由热起伏原因而产生的,所以又称为热缺陷。
晶体中存在的缺陷种类很多,但由于晶体中的晶体结构具有规律性,因此晶体中实际出现缺陷的类型也不是无限制的。
根据晶体缺陷在空间延伸的线度,晶体缺陷可分为点缺陷、线缺陷、面缺陷和体缺陷。
几种重要的点缺陷:1)弗仑克尔缺陷和肖脱基缺陷原子(或离子)在格点平衡位置附近振动,由于存在这样的热振动的能量涨落,使得当某一原子能量大到某一程度时,原子就会克服平衡位置势阱的束缚,脱离格点,而到达邻近的原子空隙中,当它失去多余动能后,就会被束缚在那里,这样产生一个暂时的空位和一个暂时的填隙原子,当又经过一段时间后,填隙原子会与空位相遇,并同空位复合;也有可能跳到较远的间隙中去或跳到晶体边界上去。
材料物理化学-第四章晶体的点缺陷与线缺陷第四章晶体结构缺陷晶体缺陷的产⽣与晶体的⽣长条件,晶体中原⼦的热运动以及对晶体的加⼯⼯艺等有关。
事实上,任何晶体即使在绝对零度都含有缺陷,⾃然界中理想晶体是不存在的。
既然存在着对称性的缺陷,平移操作不能复制全部格点,那么空间点阵的概念似乎不能⽤到含有缺陷的晶体中,亦即晶体理论的基⽯不再牢固。
但缺陷的存在只是晶体中局部的破坏。
作为⼀种统计,⼀种近似,⼀种⼏何模型,缺陷存在的⽐例毕竟只是⼀个很⼩的量(这指的是通常的情况),从占有原⼦百分数来说,晶体中的缺陷在数量上是微不⾜道的。
因此,整体上看,可以认为⼀般晶体是近乎完整的。
因⽽对于实际晶体中存在的缺陷可以⽤确切的⼏何图形来描述,这⼀点⾮常重要。
它是我们今后讨论缺陷形态的基本出发点。
事实上,把晶体看成近乎完整的并不是⼀种凭空的假设,⼤量的实验事实(X射线及电⼦衍射实验提供了⾜够的实验证据)都⽀持这种近乎理想的对称性。
当然不能否认,当缺陷⽐例过⾼以致于这种“完整性”⽆论从实验或从理论上都不复存在时,此时的固体便不能⽤空间点阵来描述,也不能被称之为晶体。
这便是材料中的另⼀⼤类别:⾮晶态固体。
对⾮晶固体和晶体,⽆论在原⼦结构理论上或是材料学家对它们完美性追求的哲学思想上都存在着很⼤差异,有兴趣的同学可以对此作进⼀步的理解。
缺陷是晶体理论中最重要的内容之⼀。
晶体的⽣长、性能以及加⼯等⽆⼀不与缺陷紧密相关。
因为正是这千分之⼀、万分之⼀的缺陷,对晶体的性能产⽣了不容⼩视的作⽤。
这种影响⽆论在微观或宏观上都具有相当的重要性。
4.1热⼒学平衡态点缺陷4.1.1 热缺陷的基本类型点缺陷形成的热⼒学平衡当晶体的温度⾼于绝对零度时,晶格内原⼦吸收能量,在其平衡位置附近温度越⾼,热振动幅度加⼤,原⼦的平均动能随之增加。
热振动的原⼦在某⼀瞬间可以获得较⼤的能量,挣脱周围质点的作⽤,离开平衡位置,进⼊到晶格内的其它位置,⽽在原来的平衡格点位置上留下空位。
第四章晶体缺陷按照点阵结构理论,晶体的主要特征是其结构基元作周期性的排列,但实际晶体中的原子或离子总是或多或少地偏离了严格的晶体周期性,因而出现了各种各样的结构缺陷,并对晶体的各种物理性质产生的重要影响。
根据晶体缺陷在空间延伸的线度晶体缺陷可分为点缺陷、线缺陷、面缺陷和体缺陷。
本章主要讲述晶体缺陷的典型形式以及对晶体性质的主要影响。
§4.1 点缺陷点缺陷,是指那些对晶体结构的干扰仅在几个原子间距范围内的晶体缺陷,空位和间隙原子就是点缺陷的典型例子,它们是晶体中最小的、也是最基本的缺陷形式。
空位就是在晶格中原本应该有原子的位置上缺少了原子,间隙原子则是在原本不应该有原子的点阵间隙位置上出现的原子,也被称为填隙原子。
后面我们会看到,在热作用下完整晶体中会自发地出现空位和间隙原子,这是一种本体性的结构缺陷,称为本征结构缺陷。
与此相对的,晶体中还有另一类点缺陷,称为杂质原子,按照其出现的位置可以分为替位杂质和填隙杂质,由于它们改变了晶体的化学成分,因而也被称为化学点缺陷。
点缺陷影响着晶体的许多物理性质,特别与晶体中物质输运过程有关的一些性质受点缺陷的影响最大。
此外,点缺陷还通过对导电电子的散射影响了金属的电导率,通过对声子的散射影响了晶体的导热性;在半导体晶体中杂质原子作为施主或受主显著地影响着半导体的电学性质;在离子晶体中,由于在带隙中造成缺陷能级而影响其光学性质,而离子晶体的离子导电现象则更是直接来源于点缺陷的运动。
4.1.1热缺陷的形成与平衡浓度晶体中原子或离子由于热振动的能量起伏可能离开理想的晶格位置,从而产生空位或间隙原子,这样形成的点缺陷称为热缺陷。
显然,热缺陷是本征结构缺陷。
晶格中的空位和间隙原子可以籍由不同的机制产生。
在晶格内部的原子可以因为热涨落由格点跳进间隙位置,从而同时产生一个空位和一个间隙原子。
由这种方式产生的空位和间隙原子对被称为弗伦克尔缺陷,如图4.1(a)所示。
邻近表面的原子也可以由于热涨落跳到晶体的表面,从而在晶体内留下一个空位。