冷轧辊使用维护检测2013
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.88 MB
- 文档页数:3


锻钢冷轧辊使用(维护)指导书锻钢冷轧辊分为支承辊、中间辊、工作辊三类,采用高碳合金工具钢经复杂的冷、热加工制造而成。
锻钢冷轧辊常用的材料根据其含铬量的不同,分为2Cr系列如9Cr2Mo、85Cr2MoV(86CrMoV7),3Cr系列如85Cr3MoV(MC3)、70Cr3Mo、70Cr3NiMo,4Cr系列如45Cr4NiMoV,5Cr系列如5Cr5NiMoV、85Cr5MoV(MC5)等。
锻钢冷轧辊在轧制中承受巨大的交变应力,常见的失效形式有:清洁度不够造成的辊印压痕;断带等轧制事故造成的粘钢;轧制周期过长、冷却不足造成的表面裂纹或剥落;修磨量不当造成的剥落;轴承烧损抱辊、轧制过载等应力集中造成断辊等。
锻钢冷轧辊的设计、制造、使用(维护)质量直接影响使用寿命,合理的轧辊使用、维护和管理能明显地提高轧辊使用寿命,为此,我们建议轧辊使用单位从下述方面采取措施:(1)储存和运输:应储存在干燥通风的室内(储存期一般在半年以上);运输时避免碰撞;修磨后应及时防锈处理。
(2)轧制控制:检验控制坯料质量;严格按照轧制工艺操作,防止超负荷轧制;轧材要洁净;防止跑偏、叠轧、断带等轧制事故。
(3)定期修磨和检测:根据轧机性能、轧制工艺和产品结构等,统计、分析、确定合理的轧制周期和修磨量。
确定轧制周期的原则是:辊身硬度上升不超过3%。
(针对黑色金属);确定修磨量的原则是:最小的修磨量必须消除轧制疲劳层,特别是辊面微裂纹必须彻底磨去。
对于事故轧辊应反复进行磨削和检测,消除事故影响层,并连续跟踪三次以上。
(4)建立质量档案:轧辊投入使用前应检验并建立轧辊质量卡。
记录轧辊号、规格及相关检测结果;记录每次换辊原因(如正常换辊、变规格换辊、划伤、剥落、粘钢、卡钢、裂纹、换辊等),记录每次修磨量,轧制钢号、规格、轧制量(轧制公里数或吨位)等。
(5)新换轧辊应先预热辊面至70~80℃并保温1~2h;冷轧工作辊应预热至30~50℃,保温后方可正常使用。

轧辊生产使用检测及表面强化基础知识第一节轧辊基础知识1547.什么是轧辊,轧辊的种类有哪些?轧辊是使(轧材)金属产生塑性变形的工具,是决定轧机效率和轧材质量的重要消耗部件。
轧辊种类按成型方法可分为铸造轧辊和锻造轧辊;按工艺方法分为整体轧辊、冶金复合轧辊和组合轧辊。
整体轧辊分为整体铸造和整体锻造轧辊两种。
冶金复合铸造轧辊要紧有半冲洗复合铸造、溢流(全冲洗法)复合铸造、离心复合铸造三种,此外还有连续浇铸包覆(CPC—Continuous Pouring Process for Cladding)、喷射沉积法、热等静压(HIP—Hot Isostatically Pressed)、电渣熔焊等专门复合方法制造的复合轧辊种类。
组合轧辊要紧是镶套组合轧辊。
1548.轧辊按材质要紧分为哪几种类别?轧辊按制造材料要紧划分为铸钢系列轧辊、铸铁系列轧辊和锻造系列轧辊三大类别。
其中碳含量小于2.2%的铸造铁基材料称为铸钢系列;碳含量大于2.2%的铸造铁基材料称为铸铁系列;锻造铁基材料称为锻造系列。
1549.什么是整体轧辊?整体轧辊是相关于复合轧辊而言的,整体轧辊的辊身外层与心部以及辊颈采纳单一材质铸造或锻造而成,辊身外层和辊颈不同的组织、性能通过铸造或锻造工艺以及热处理工艺过程来操纵和调整。
锻造轧辊和静态铸造的轧辊均属于整体轧辊。
1550.什么是铸造轧辊,铸造轧辊要紧有哪些种类?铸造轧辊是指将冶炼钢水或熔炼铁水直截了当浇注成型这一生产方式制造的轧辊种类。
铸造轧辊按材质又可分为铸钢轧辊和铸铁轧辊两类;按制造方法又可分为整体铸造轧辊和复合铸造轧辊两类。
1551.什么是整体铸造轧辊?整体铸造轧辊是指轧辊辊身外层与心部以及辊颈采纳同一成分的金属液浇铸成型的轧辊,采纳此种方法生产的轧辊,辊身外层和辊颈不同的组织、性能,是通过操纵轧辊铸造过程中不同部位的冷却速度以及热处理工艺过程而取得的。
1552.哪些轧辊适合于整体铸造生产?初轧机、钢坯连轧机、大型型钢和轨梁轧机、热轧椽带钢轧机破鳞和轧边机、型钢万能轧机的轧边机,还有小型型钢、线棒材轧机的粗轧机架等轧机使用的轧辊,大多采纳整体铸造方法生产,这类轧辊使用层较厚,孔型较深。
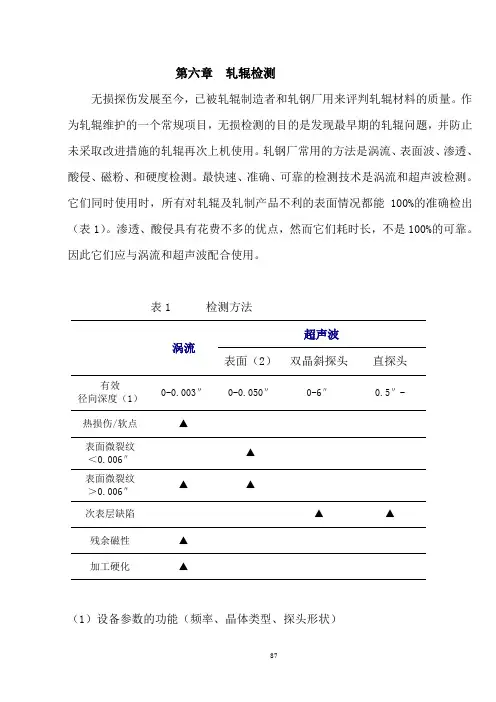
第六章轧辊检测无损探伤发展至今,已被轧辊制造者和轧钢厂用来评判轧辊材料的质量。
作为轧辊维护的一个常规项目,无损检测的目的是发现最早期的轧辊问题,并防止未采取改进措施的轧辊再次上机使用。
轧钢厂常用的方法是涡流、表面波、渗透、酸侵、磁粉、和硬度检测。
最快速、准确、可靠的检测技术是涡流和超声波检测。
它们同时使用时,所有对轧辊及轧制产品不利的表面情况都能100%的准确检出(表1)。
渗透、酸侵具有花费不多的优点,然而它们耗时长,不是100%的可靠。
因此它们应与涡流和超声波配合使用。
表1 检测方法超声波涡流表面(2)双晶斜探头直探头有效0-0.003″0-0.050″0-6″0.5″- 径向深度(1)热损伤/软点▲表面微裂纹▲<0.006″表面微裂纹▲▲>0.006″次表层缺陷▲▲残余磁性▲加工硬化▲(1)设备参数的功能(频率、晶体类型、探头形状)(2)圆周方向(要求扫描3次)轴向(要求扫描2次)一、涡流探伤涡流探伤是轧辊磨削之后,确定缺陷位置如软化区(热损伤)、宏观裂纹和磁化的一种方法。
磨床上,一个双线差分探头放置在辊身一端,靠近辊面处,随着轧辊以设定的速度转动,探头慢慢移动跨过整个辊身长度。
探头移动速度和轧辊转速的同步性是设定好的,以确保辊面的每一点都通过探头。
随着探头在辊身移动,在交流电流的作用下线圈间的辊面上产生涡流。
线圈间电流的导电性和路径长度的瞬间变化都能被检测出来,并显示在两个独立的频道。
一个称为压伤/热损伤频道,一个称为裂纹/剥落频道。
涡流探伤的特殊步骤取决于使用的涡流设备,由设备生产者提供。
导电率的变化可在压伤/热损伤频道上检出。
它是辊面相邻点间的硬度和显微组织变化的结果。
磁化区内所有相邻点间也会引起导电率的连续变化。
高斯通量可用来证实剩余磁性的存在。
(大于30Gauss)。
能引起辊面上导电性反复变化的一般条件包括(但不限于此)局部超温、局部工作硬化、表面粗化和外来夹杂物嵌入辊面。
这些情况在压伤/热损伤频道表现为超过噪音水平的单独的波峰或超过噪音水平的大面积的草状波峰(图2)。

轧机维护与检修摘要:轧机由于工作条件的因素,故障的种类繁多,严重影响正常生产。
本文主要介绍轧机 主要部件的日常维护保养,使轧机保持良好的工作状态,通过轧机的检测方式总结出各种较 为常见故障的产生原因,以及所对应的检修措施。
以此来做好轧机的维护减少轧机的故障率, 提高轧机使用寿命和工作性能进而降低在设备维修上的投入资金,降低生产成本高为企业提 高经济效益。
关键词:轧机检修 维护 润滑所谓轧机,就是使轧件在转动的轧辊间产生塑性变形, 轧出所需断面形状和尺寸的钢材。
主要由轧辊、轧辊轴承、机架压下装置、轨座和导位装置等组成。
轧机的工作环境是极其恶劣的,高温、摩擦、重载荷、介质等等,这些因素使轧机的各 部件容易产生种种故障。
如不及时发现和处理,不仅会影响正常生产,造成企业重大经济损 失,甚至会酿成灾祸。
轧机的检测:(1) 机械测量法。
是利用机械器具对对被测物理量进行直接测量。
如用杠杆应变计测量 应变,用机械测振仪测量轧机振动参量等。
(2) 光测法。
是利用光学的基本理论, 用实验的方法去研究物体中的应力、应变和位移等力学问题。
如光弹法、云纹法、红外测温仪测温以及激光扫描测径仪测量轧辊直径等。
(3) 声测法。
是利用声波或超声波在介质中的传播速度和波形衰减情况估价被测物质的 质量。
如超声波测量仪来检测轧机部件的抗拉强度和内部缺陷等。
(4)电测法。
是先将被测物理量转换成电量,再用电测仪表进行测量的方法。
如用电阻 应变仪表测量应力应变,用热电高温计测温度,用涡流检测仪检测轧辊内部缺陷等。
下面来介绍轧机轧机两个故障率较高的主要部件的维护与检修: 轧机轧辊维护检修:(1)辊身表面剥落,出现崩坑。
(2) 轧辊出现裂纹。
1- 2 -3'4 5 6-10-.11-传动端; 辊颈; 辊身; 圆锥过渡区; 紧固件槽; 键槽;辊颈润滑油沟; 平口; 内孔; 双圆锥过渡区; 心轴; 硬质合金套; 螺钉; 轴向紧定用螺母轧辊是轧机轧制过程中 轧辊失效方式:变形的工具,是轧机的主要部件。

轧辊的使用与维护技术部胡国红针对近段时间薄板车间频繁爆辊现象,技术部前期已制订并发放了《冷轧工作辊和支承辊技术要求》,近期又陆续发放了《轧辊的使用和维护规定》,《轧辊磨削前后时效规定》等制度性文件。
要求各相关环节从轧辊进货、储存、运输到使用、修磨和事故处理等过程都严格按规定执行。
这将有利于减少轧辊质量事故的发生,延长轧辊使用寿命,降低轧辊消耗,提高各分公司的生产效益。
通常,轧辊出现不正常爆辊、剥落等早期失效事故,有着很复杂的原因,可能与轧辊内在质量(包括轧辊的坯料材质、浇注、锻造与热处理等冶金缺陷)直接有关;也与我们使用和维护过程中存在欠缺密切相关,质量好的轧辊如果没有正确操作和维护,也很容易出现事故。
现在我们已经提高了对轧辊的验收要求,凡不符合轧辊验收标准的,一律拒收。
我们除了对进货验收从严控制,还必须加强平时在轧辊使用和维护上的管理工作。
用于冷轧薄板的轧辊,常用高碳铬钢,铬钼钢或铬钼钒钢锻造而成,俗称锻钢冷轧辊。
轧辊的工作条件十分恶劣,在轧制过程中,它要承受压应力,弯曲应力、扭转应力、接触疲劳应力和热疲劳应力。
为了使轧出的薄板达到规定的尺寸精度和较好的表面粗糙度,要求轧辊辊身表面具有极高的硬度和硬度均匀性。
由于轧辊连续进行轧制作业,表面磨损,易形成橘皮状缺陷或裂纹,经常需要修磨后再继续使用,因此还要求轧辊具有较深的有效硬化层深度。
为使轧辊具备这些基本性能,在加工制造中,对合金钢制作的轧辊进行强烈的喷水淬火和低温回火处理,使轧辊内部存在很高的残余内应力,当它与轧制应力综合作用超过轧辊的疲劳强度时轧辊就会产生表面疲劳裂纹、剥落或断辊等早期失效,严重影响轧辊的使用寿命。
关于轧辊的使用和维护应该注意哪些事项,在《轧辊的使用和维护规定》都有明确规定,这里需要再强调两点:第一,轧辊硬度的选择,应根据轧制要求进行确认。
通常冷轧工作辊表面硬度的技术要求在HS85-95之间,粗轧一般选用85-90,精轧一般选用90-95;中间辊选用HS80-85,支承辊选用HS65-70,连轧机最后一台的支承辊硬度可以相应提高点但也不应高于HS75。


冷轧机设备保养维护方案
冷轧机设备保养维护方案主要包括以下几个方面:
1. 日常保养:每天对设备进行清洁,检查设备的各个部件是否有异常,检查设备的油位、油质、冷却水等是否正常。
2. 定期保养:按照设备的规定,定期对设备进行全面的保养,包括更换机油、清理油路、清理散热器等,以及检查电气系统是否正常。
3. 预防性维修:根据设备的磨损规律和使用情况,提前对设备进行维修,以防止设备出现故障。
4. 应急处理:对于突然出现的故障,应尽快联系专业维修人员进行维修,以免影响生产。
具体的保养维护方案应根据冷轧机的型号、使用环境、工作条件等因素来制定,建议查阅设备的维修保养手册,或咨询厂家及专业维修人员。

轧辊生产使用检测及表面强化基础知识前言轧辊是金属加工行业中一种常用的工具和设备,用于轧制金属材料,如钢材、铝材等。
轧辊在使用过程中面临着高强度的冲击和磨损,因此需要进行检测和表面强化。
本文将介绍轧辊的生产使用检测流程以及表面强化的基础知识。
轧辊生产检测轧辊的生产检测是为了保证轧辊的质量,提高其使用寿命和稳定性。
主要包括以下几个方面的检测:材料检测轧辊主要由高铬铸铁、高铬铸钢等材料制成。
在生产过程中,需要对材料进行检测,确保其符合相关标准要求。
常用的材料检测方法包括化学成分分析、金相组织分析等。
尺寸检测轧辊的尺寸精度对轧制产品的质量有着重要影响。
因此,在生产过程中需要对轧辊的尺寸进行检测,确保其符合设计要求。
常用的尺寸检测方法包括三坐标测量、外径测量等。
表面质量检测轧辊的表面质量直接影响轧制产品的表面质量。
因此,在生产过程中需要对轧辊的表面进行检测,确保其表面光洁度和平整度满足要求。
常用的表面质量检测方法包括平行度测量、表面粗糙度测量等。
轧辊使用检测轧辊在使用过程中,会受到冲击和磨损,因此需要进行定期检测,以确保其安全可靠地运行。
主要包括以下几个方面的检测:磨损检测轧辊在使用过程中,会因为与金属材料的摩擦而产生磨损。
定期检测轧辊的磨损情况,可以及时更换磨损严重的轧辊,以保持轧辊的工作性能。
常用的磨损检测方法包括测量磨损凹槽深度、测量表面损失量等。
裂纹检测轧辊在使用过程中,可能会因为冲击或其他原因产生裂纹。
裂纹的存在会降低轧辊的工作性能,甚至导致轧辊断裂。
因此,需要定期检测轧辊的裂纹情况,及时修补或更换有裂纹的轧辊。
常用的裂纹检测方法包括超声波检测、磁粉检测等。
接触应力分析轧辊在使用过程中,由于冲击和磨损会受到较大的应力。
通过对轧辊接触应力的分析,可以评估轧辊的工作状态和剩余寿命,以制定合理的维护计划。
常用的接触应力分析方法包括有限元分析、应力测量等。
表面强化基础知识由于轧辊在使用过程中受到的冲击和磨损较大,为了延长轧辊的寿命和提高其使用性能,常常需要对轧辊进行表面强化处理。

邢台轧辊(锻钢)小冷辊使用说明(总4页)-本页仅作为预览文档封面,使用时请删除本页-邢台轧辊(锻钢)小冷辊使用说明一、搬运与储藏1、轧辊在搬运过程须采用吊装带装卸,防止出现磕碰伤现象。
2、轧辊应贮存在干燥通风的室内,防止受潮,也不要在酸、碱等化学腐蚀环境中存放,储存前轧辊表面应涂防锈油保护。
3、安装拆卸轧辊应十分小心,防止擦伤或碰伤辊面。
4、下机热辊不可堆放湿冷的地面上,并应避免轧辊之间相互碰撞。
5、修磨后的待上机轧辊应注意防锈,严禁就地搁置。
二、轧辊的管理1、投入使用前应建立轧辊使用卡,记录轧辊辊号、规格尺寸、轧辊使用寿命结束后将轧辊使用卡作为原始记录归档。
2、轧辊上下机应在轧辊使用卡上记录上下机时间、本次轧制钢号、规格、轧制量和修磨原因(如正常换辊、变规格换辊、划伤、剥落、粘钢、裂纹等)。
3、轧辊每次修磨后均应记录开始磨削时间、磨削前后直径、重磨量及修磨原因。
4、根据轧制材料制定合理的轧制工艺(使用道次、单道次压下量和轧制速度等),针对不同的轧制工艺建立相应的换辊制度。
5、根据轧辊用途、轧制材料、粗精轧工序,合理选用工作辊辊身硬度及粗糙度相当的轧辊上机使用。
同时保证中间辊、支承辊硬度的合理搭配。
6、使用轧辊的原则是:新(高硬度)辊适用于宽带、薄带的精轧;旧(低硬度)辊适用于窄带、厚带的初轧。
轧辊必须实行分机使用的原则,避免误用混用,勿精作粗用。
7、定期维修、检查和监控轧机运行状况,轧辊装配、传动装置要安装精确、运行自如,避免带“病”设备运行、超期服役。
注意防震,确保轧辊在良好的状态下工作。
三、轧辊的使用1、使用前,应擦去表面油污、灰尘和锈迹,然后进行常规检测。
特别应仔细检查辊身和辊颈表面是否有划痕、压痕、锈斑和裂纹等缺陷,不允许有表面缺陷的轧辊上机使用。
2、轧制前应仔细检查轧制坯料的板面质量、板材成分和硬度等,需要接带时接口要平整,无凸起现象,在轧制中严格按轧制工艺进行操作,防止超负荷轧制,注意观察轧制力的变化和轧材硬化速率,硬度较高时中间要进行退火处理。

P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE 8 3DX. United KingdomTel +44 (0)191 402 5200. Commercial Fax +44 (0)191 477 8821 Web email enquiries@The Davy Roll Company LimitedE x c e l l e n c e i nF o r g e d a n d C a s t R o l l T e c h n o l o g yInspection and Maintenance of Cast Rolls.The following information is intended to aid roll shop personnel with the every day maintenance and inspection of static and rocast work rolls.By optimizing grinding operations and introducing targeted inspection procedures significant improvements in roll performance and reliability can be achieved.Roll Shop Inspection Equipment.Automated eddy current systems are used in a large proportion of roll shops across the world. They provide a rapid and efficient means of testing large areas of a rolls surface allowing the operator to manage and where necessary, remove rolling generated defects.These systems are however limited to testing near surface defects. Many roll shops feel it is necessary to introduce complementary, deep inspection systems in the form of ultrasonic equipment. This can be in the form of an automated system used in cooperation with the eddy current units or manual handheld units.In roll shops were eddy current equipment is not available manual ultrasonic equipment as well as visual crack detection procedures, such as magnetic particle or die penetrant inspection become essential.Ultrasonic InspectionThe Davy Roll Company inspection departments use portable ultrasonic units for the day -to-day inspection requirements of both work and back up rolls during manufacture and at the customer’s site. A high level of operator skill and specific training is requi red to fully utilise these units as well as a range of tailored ultrasonic probes. The Davy Roll Company is able to offer guidance and training to suitably experienced personnel in roll inspection practices.Ultrasonic ProbesThe following probes are recommended for roll inspection duties and available from most manufacturers.Compression Probes.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomTel +44 (0)191 402 5200. Commercial Fax +44 (0)191 477 8821 Web email enquiries@Registered in E ngland Registration no: 162966 Registered offi c e: P O Box 21, Coulthards Lane, Close Work s, Gateshead, T yne and Wear, NE8 3DX The Davy Roll Company Limited is a member of the Union Electric Steel Corporation Group of companies.Twin Shearwave Probes.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomTel +44 (0)191 402 5200. Commercial Fax +44 (0)191 477 8821 Web email enquiries@Registered in E ngland Registration no: 162966 Registered offi c e: P O Box 21, Coulthards Lane, Close Work s, Gateshead, T yne and Wear, NE8 3DX The Davy Roll Company Limited is a member of the Union Electric Steel Corporation Group of companies.Calibration.Accurate calibration of test equipment is essential to ensure minimum stock removal and ensure the complete removal of defects, optimizing roll performance and reliability. To ensure accurate results compression probes should be calibrated with test blocks manufactured to the same material specification as that of the roll to be tested.For shearwave probes a steel angle calibration block, for example a V2 type is required to ensure precise trigonometric calibration is achieved.The following values may be used for the calibration of compression probes when specific test blocks are not available. These values are approximate only as variations between material grades, for example enhanced Apex grade and standard iron grade as well as between manufacturers will exist.Dye Penetrant Inspection.Die penetrant systems are useful in determining the presence of gross cracking in back up and work rolls. The system is relatively inexpensive and requires a limited degree of operator training. There is however some limitation to this method for roll inspection. The process relies on the dye being drawn into open surface cracks by capillary action and as such anything that impedes this process can reduce or even eradicate the effectiveness of crack detection. For example;∙When cracks contain large amounts of oil or debris out of the mill.∙After grinding the cracks may be sealed by mechanical deformation of the surface or by grinding debris.As such additional inspection methods are advised to compliment this procedure to ensure complete removal of defects.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomMagnetic Particle Inspection.Magnetic particle inspection is an effective and reliable system for the detection of cracks in rolling mill rolls. This system is preferred for the detection of smaller cracks especially on ground or turned surfaces.The system works by attraction of a ferrous based dye on the roll surface towards the magnetized crack faces. This attraction occurs across the full face, at the surface and at depth. As such the system does not suffer the limitations of the dye penetrant system when the cracks are closed at the surface or filled with debris.Many systems are available on the market consisting of either mains powered electro-magnets or permanent hand held magnets.Hardness Testing.Hardness testing of cast rolls is primarily carried out with EQUOTIP type instruments. These devices determine hardness by measuring the level of rebound energy from the surface of the test piece or roll.One of the many uses of harness testing is determining if work hardened material has been removed from the barrel surface during grinding, especially of back up rolls.These devices are very sensitive to surface cleanliness and finish. Hardness measurements taken on a rolled or rough ground surface will in general give a lower result than on a polished ground surface. Accurate measurements can only be obtained on a 400-grade grit equivalent or better surface finish.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomP O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE 8 3DX. United KingdomUltrasonic Inspection Procedures.Measuring Crack Depths.When cracks are generated in the barrel of a roll they can be parallel to or perpendicular to the surface. For example, fire cracking will initially form at right angles to the surface but as they are subjected to the forces of rolling will propagate circumferentially and turn parallel to the surface as shown below.Working with the probe away from the crack on a curved surface can result in the beam moving back up the crack face towards the barrel surface resulting in deeper than actual crack depths.When using a shearwave probe crack depths should be checked from both edges to ensure the maximum depth is obtained. Cracks will not always be aligned exactlyperpendicular to the surface but may be entering at an angle. If the probe angle and crack angle are similar the crack may not be detected when tested from only one side.Cracking may not always break the surface, for example a roll which has been subjected to an impact or localized overload may initiate cracks below and aligned parallel to the barrel surface.It is therefore always advisable to inspect the area surrounding a surface crack or bruise with a compression and angle probe to ensure detection of the deepest component.Care should always be taken when assessing crack depths on curved surfaces. Withshearwave probes an angle should be chosen that will allow you to work as close to the surface crack as possible.Inspection of Centrifugally Cast Shell to Core Bond Zone (Interface).Centrifugally cast work rolls are inspected prior to delivery to ensure an interface bond strength sufficient for standard mill operating conditions to discard size.However if rolls are subjected to abuse during rolling it is advisable to inspect the bond zone or interface area to ensure there has been no detrimental effect that could ultimately result in the rolls failure.The test procedure described below compares the amount of energy returned to the probe from the interface related to the amount transmitted into and dispersed within the core material. A low energy return indicates a poor reflector or well-bonded interface while a high-energy return indicates a good reflector and hence poorer bonding.The principle is shown below with echoes for a well and poor bonded interface at the same decibel level.Poor InterfaceP O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomTest procedureThis procedure can be used for all types of ROCAST centrifugally cast rolls.EquipmentKrautkramer USN 50 or similar calibrated to BS44331 part 2 or equivalent.A 2.5 MHz twin crystal compression probe.Test block (20x40x50mm) manufactured from the same grade material as the roll to be examined.ProcedureCalibrate the time base at 100mm using the above test block. Measure and record the gain in decibels (db) required to obtain a full screen height (100%) back wall echo from the test block. This value (A) is then used as the minimum or theoretical value for total interface separation.Test the roll beginning at the top end (marked T on neck end face) working towards the barrel bottom end.Record the average background db level (B) required to achieve a 100% full screen height echo for each of the top, middle and bottom zones of the roll barrel.Record the highest db value for any localized defects (D) found within each zone.Shell depth measurements should also be taken at each position for comparison with the test block used.Fail CriteriaThe following formula should be used to asses interface bonding, were (F) is the minimum background db level allowable in each zone:F= (B-A) x 0.6 +AP O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomCommentsFor example if the average value for (B) obtained during manufacture was 68 db and the test block value was 40 db the minimum allowable db value F will therefore be = 56.8 dbWhere (D) is a small area < 20mm in size and is not approaching value (A) this may be allowed unless a significant number are grouped in the same zone.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomBack Up Roll Ultrasonic Inspection.Full ultrasonic inspection is carried out on all back up rolls prior to delivery to ensure reliable operation in service. The user may also wish to implement in service inspection at routine intervals throughout the rolls long service life.EquipmentDetector: Panametrics, Krautkramer or equivalent.Probes: 0.5MHZ, Normal Beam, 2 X Single Probe, Dual Mode.Transverse TestThis test is carried out across both necks and full barrel width. The aim of the test is to assess deep barrel and centre line discontinuity such as porosity, centre line segregation and voids.The test requires a back wall echo (BWE) to be obtained across the neck and barrel diameters. This echo is measured in decibels (dB) at 100% of the detectors screen height. The decibel level required to achieve this 100% echo is related to the attenuation of the material and is proportional to the severity of any centre line discontinuity. The higher the decibel level required the worse the centre line condition. The attenuation is measured as the difference between lowest dB value obtained anywhere across the necks and barrel and the actual value obtained at a specific position.Longitudinal TestThis test is carried out along the axis of the roll to detect and asses defects perpendicular to the barrel and neck surfaces initiating from the roll centerline.The test requires a 100% FSH BWE to be obtained from the barrel end faces when the probes are positioned on a parallel surface such as the opposite barrel face and neck pintel end face or sleeve end face.Echo’s will also be obtai ned from any reflective surface parallel to the probe. These will be produced by the roll geometry as well as any internal defect. It is essential that any echo detected between the probe and barrel face (BWE) is matched to roll geometry e.g. grooves, faces and keyways. Any echo that cannot be matched is possibly an internal defect e.g. fatigue cracking forming at the neck/barrel zone, and should be monitored routinely.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomStandardsIt should be remembered that differences in ultrasonic response will exist across different grades i.e. 3% and 5% chromium materials and different manufacturing methods e.g. differentially hardened monoblock (DH) and double poured (DP).The above tests can be carried out before the back up rolls first use and the results recorded. The test may then be carried out at routine intervals and the results obtained compared with those from the first inspection. Significant changes in the values obtained will provide an alert to the inspector of changes within the back up roll over time.The Davy Roll Company is happy to provide advice on any results obtained and recommend appropriate action.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United KingdomA Guide to Back Up Roll Maintenance.1. Work Hardening.Control and removal of work hardening is essential to ensure efficient and reliable service from back up rolls. If stock removals between rolling campaigns are not sufficient to remove this worked surface layer an accumulation will occur over successive campaigns, eventuallyleading to crack formation and spalling.Hardness measurements are a simple and efficient means of ensuring the complete removal of work hardening during the grinding operation.The following graph may be used to determine the maximum allowable hardness values after grinding:Example: Maximum roll hardness at delivery (base hardness)= 65HsCAverage hardness after grinding at new (100%) = 68HsCAverage hardness after grinding at mid-life (50%) = 66.5 HsC2. Optimising Performance.Just as too small a stock removal can lead to spalling and loss of valuable roll life, removal of unnecessary stock can severely affect roll performance and cost effectiveness.The Davy Roll Company recommends the following procedure be applied to optimisegrinding amounts and roll performance.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United Kingdom3. Eddy Current and Ultrasonic Inspection.While removal of work hardening is a good means of crack prevention there is always the possibility of cracks and bruising occurring during rolling campaigns.We recommend full eddy current/ultrasonic inspection of back up roll barrel surfaces be carried out on a routine basis to ensure the removal of cracks which could produce a roll failure.P O Box 21, Close Works, Gateshead, Tyne and Wear, NE8 3DX. United Kingdom。
专利名称:一种冷轧辊表面磨削横纹检测工具专利类型:实用新型专利
发明人:周利,陈甚超,李春辉,滕华湘,李春光申请号:CN200820110366.4
申请日:20080911
公开号:CN201311399Y
公开日:
20090916
专利内容由知识产权出版社提供
摘要:本实用新型属于金属材料加工检测领域,涉及一种冷轧辊表面横纹的检测工具,用于冷轧辊磨削后表面横纹的快速检测。
检测工具由弓形板(1)和弹性材料制成的着色带(2)组成,着色带(2)两端固定在弓形板(1)上,着色带(2)的设计半径为工作辊的最大半径尺寸,着色带曲率随轧辊直径的变化发生改变;检测时,首先在着色带(2)上均匀涂抹黑色显色剂,在辊身上反复蹭几下,如果冷轧辊表面存在横纹,显色剂就会在冷轧辊表面留下深浅不同的痕迹,这样就能快速、准确地检测出冷轧辊表面的磨削横纹。
该发明可快速、准确检测出冷轧辊表面的横纹,有效避免带横纹的轧辊上机使用,从而提高了轧机的成材率。
申请人:首钢总公司
地址:100041 北京市石景山区石景山路68号
国籍:CN
代理机构:北京华谊知识产权代理有限公司
代理人:吕中强
更多信息请下载全文后查看。
冷轧工程运行维护标准1 连续退火炉的辐射管和炉辊,以及各设备的装卸应采用专用的吊具进行,需要采用起重机或人工更换时,应采取必要的安全措施。
2 工业炉窑检修和清渣,应严格按照有关危险作业、煤气安全、设备维护规程和操作规程进行,防止发生人员烫伤和中毒窒息事故。
3 进入涉及煤气的设施等有限空间作业,应遵守有限空间作业安全管理和国家相关标准规定要求,先通风,再检测,后作业。
4 轧钢企业强电磁辐射区域应设警示标识,体内安装有心脏起搏器或金属植入物的人员禁止进入。
5 用磨床加工轧辊,操作台应设置在砂轮旋转面以外,不应使用不带罩的砂轮进行磨削。
带冷却液体的磨床,应设防止液体飞溅的装置。
6 剪机应设专门的控制台来控制。
喂送料、收集切头和切边,均应采用机械化作业或机械辅助作业。
7 运行中的轧件,禁止接触,或用棍、管等进行撬动,以防止对操作人员造成伤害。
8 在锌锅地下室、全氢炉地下室等进行作业时,应先进行易燃易爆、有毒有害气体和氧含量的检测。
检测合格后,方可作业。
9 两台及两台以上起重机联合进行吊装作业,应制定专门的、经主管领导审批的作业方案,并采取专门的防护措施。
10 吊具应在其安全系数允许范围内使用。
钢丝绳和链条的安全系数和钢丝绳的报废标准应符合有关规定。
11 在最不利位置和最不利装载条件下,起重机的所有运动部分(吊具和其他取物装置除外)与建筑物的净距规定如下:1 距固定部分不小于0.05m;2 距任何活栏杆或扶手不小于0.10m;3 距出入区不小于0.50m(出入区是指允许人员进出的所有通道,但工作平台除外)。
12 起重机械各运动部分的下界限线与下方的一般出入区(从地面或从属于建筑物的固定或活动部分算起,工作或维修平台及类似物除外)之间的垂直距离不应小于1.7m,与通常不准人出入的下方的固定或活动部分(例如棚顶、加热器、机械部分和运行在下方的起重机等)及与栏杆顶部的垂直距离不应小于0.5m。
13 采用放射性元素检测仪表的区域,应有明显的标志,并有必要的防护措施,并按有关规定定期检测。
锻钢冷轧辊表面无损检测方法1 主题内容与适用范围本标准规定了在役锻钢冷轧辊辊面无损检测的仪器设备、探头、试块及试片、对检验人员的要求、检测方法、检测结果的记录、缺陷的评定及报告等。
本标准适用于在役锻钢冷轧工作辊、中间辊的磨后辊面表面波及磁粉检测。
锻钢支承辊及轴类锻钢工件的表面波检测亦可参照执行。
本标准不适用于声衰减较大的粗晶材料工件的表面波检测。
2 引用标准下列标准所包含的条文通过在本标准中引用而构成为本标准的条文。
本标准出版时所示版本均为有效。
所有标准都会被修订,使用本标准的各方应探讨使用下列标准最新版本的可能性。
GB 9445-1999 无损检测人员技术资格鉴定通则GB/T 13298-91 金属显微组织检验方法JB/T 4730.4-2005 承压设备无损检测第四部分:磁粉检测JB/T 10060-1999 A型脉冲反射式超声波探伤仪通用技术条件3 对检测人员的要求轧辊的无损检测项目参与人员应经过必要的相关技术培训并应持有与所从事项目相应的有效技术资格证书,其资格证书的考核鉴定按GB/T 9445的规定。
4 技术要求4.1 对比试块4.1.1 对比试块材质为调质后的20#或20CrMo等优质锻钢。
4.1.2对比试块的规格、人工缺陷的尺寸及表面粗糙度要求如图1所示。
4.2 探伤仪器和设备4.2.1 超声波探伤仪的性能应按JB/T 10060的规定方法进行测试。
其指标应满足以下要求:4.2.1.1 超声波探伤仪的水平线性误差≤1%;垂直线性误差≤4%;灵敏度余量≥36dB;动态范围≥30dB。
其余Ra6.3图1.锻钢冷轧辊表面波探伤灵敏度校定用钢质试块。
4.2.1.2 要求探伤仪衰减器细调步级≤2dB;衰减器误差≤1dB/20dB。
4.2.1.3 探头和探伤仪的组合灵敏度余量除应满足检验要求外,不少于20dB。
4.2.2 磁粉探伤设备的技术性能按照GB/T 4730.4的规定。
4.2.3 磁粉及磁悬液技术要求按JB4730.4执行。
连铸机的辊子装配的检测与维修一、连铸机的介绍1.连铸机的功能把高温钢水连续不断地浇铸成具有一定断面形状和一定尺寸规格铸坯的生产工艺过程叫做连续铸钢。
完成这一过程所需的设备叫连铸成套设备。
浇钢设备、连铸机本体设备、切割区域设备、引锭杆收集及输送设备的机电液一体化构成了连续铸钢核心部位设备,习惯上称为连铸机。
连铸机是一种用模具进行连续浇注钢水的大型生产线。
生产出的钢坯经轧制,成为成品销售。
提高连铸自动化水平,对保证铸坯质量、提高连铸机的劳动生产率、增加连铸机的金属收得率起着至关重要的作用。
2.连铸机的组成(如图a)(1)钢包回转台:钢包回转台是现代连铸中应用最普遍的运载和承托钢包进行浇注的设备,通常设置于钢水接收跨与浇注跨柱列之间。
所设计的钢包旋转半径,使得浇钢时钢包水口处于中间包上面的规定位置。
用钢水接收跨一侧的吊车将钢包放在回转台上,通过回转台回转,使钢包停在中间包上方供给其钢水。
浇注完的空包则通过回转台回转,再运回钢水接收跨。
钢包回转台是连铸机的关键设备之起着连接上下两道工序的重要作用。
(2)中间包:中间包是短流程炼钢中用到的一个耐火材料容器,首先接受从钢包浇下来的钢水,然后再由中间包水口分配到各个结晶器中去,并且有着分流作用。
对于多流连铸机,由多水口中间包对钢液进行分流。
连浇作用。
在多炉连浇时,中间包存储的钢液在换盛钢桶时起到衔接的作用。
减压作用。
盛钢桶内液面高度有5~6m,冲击力很大,在浇铸过程中变化幅度也很大。
中间包液面高度比盛钢桶低,变化幅度也小得多,因此可用来稳定钢液浇铸过程,减小钢流对结晶器凝固坯壳的冲刷。
保护作用。
通过中间包液面的覆盖剂,长水口以及其他保护装置,减少中间包中的钢液受外界的污染。
清除杂质作用。
中间包作为钢液凝固之前所经过的最后一个耐火材料容器,对钢的质量有着重要的影响,应该尽可能使钢中非金属夹杂物的颗粒在处于液体状态时排除掉。
(3)结晶器:结晶器承接从中间包注入的钢水并使之按规定断面形状凝固成坚固坯壳的连续铸钢设备。