托马斯·杰斐逊与民主 Thomas Jefferson and Democracy
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:727.00 KB
- 文档页数:60


Thomas Jefferson's Vision: A Synthesis ofDemocratic IdealsThomas Jefferson, a founding father of the United States, left an indelible mark on the political and philosophical landscape with his vision of democratic ideals. Jefferson's thoughts and beliefs were shaped by his education, experiences, and the events of his era, culminating in a unique philosophy that emphasized the rights and freedoms of the individual.Jefferson's belief in the inherent worth of all men was a central tenant of his political philosophy. He was a staunch advocate for the principle of equality, as evident in his Declaration of Independence, where he wrote, "We hold these truths to be self-evident, that all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty, and the pursuit of Happiness." Jefferson's belief in the equality of all men was not just a political ploy;it was a deeply held conviction that shaped his policies and actions.revolutionary. He was a strong proponent of limited government, believing that the role of the state should be to protect the rights of the individual, rather than to encroach on them. This belief led him to oppose the Alien and Sedition Acts, which he saw as an infringement on the freedoms of speech and press. Jefferson's vision of government was one that was small, efficient, and accountable to the people, a far cry from the monolithic and autocratic governments of his era.Jefferson's thoughts on education were also groundbreaking. He believed that education was a fundamental right of all citizens and that it should be accessible to all, regardless of social or economic status. Jefferson founded the University of Virginia, which was designed to be a beacon of Enlightenment thought and a breeding ground for leaders who would uphold his democratic ideals. His belief in the power of education to transform society and create a more enlightened citizenry was a cornerstone of his philosophy.progressive. He was a Deist, believing that reason and science were the surest paths to understanding the universe and our place within it. He saw religion as a personal matter, one that should be kept separate from the affairs of the state. Jefferson's belief in the separation of church and state was a direct challenge to the religious orthodoxy of his time, and it has had profound implications for the religious freedoms enjoyed by Americans today.In summary, Thomas Jefferson's thoughts and beliefs were a powerful blend of Enlightenment ideals and democratic principles. His belief in the equality of all men, his opposition to oppressive governments, his commitment to education as a fundamental right, and his belief in the separation of church and state all contributed to the creation of a more just, free, and enlightened society. Jefferson's vision of a democratic society, one that was based on reason, equality, and freedom, has had a profound impact on the world and continues to inspire people to strive for a more perfect union.**托马斯·杰斐逊的思想综述**托马斯·杰斐逊,这位美国的开国元勋,以他对民主理想的独特见解,在政治和哲学领域留下了不可磨灭的印记。

托马斯·杰斐逊语录标题:托马斯·杰斐逊语录:自由与民主之光引言:托马斯·杰斐逊是美国历史上一位杰出的政治家、思想家和第三任总统。
他的言论和思想对于美国的独立和民主制度的建立起到了重要的推动作用。
在这篇文章中,我们将探讨一些托马斯·杰斐逊的经典语录,并探讨这些语录对于我们理解自由和民主的重要性。
正文:1. “我们认为这些真理不言而喻:人人生而平等,造物主赋予他们若干不可剥夺的权利,其中包括生命权、自由权和追求幸福的权利。
”这是托马斯·杰斐逊在《独立宣言》中的语录,也是美国独立宣言的核心理念。
杰斐逊坚信,每个人都应该享有平等的权利和机会,而这些权利不应该被任何政府或个人剥夺。
这一思想成为了美国民主制度的基石,也影响了世界各国对于自由和平等的追求。
2. “当政府害怕人民,就有自由;当人民害怕政府,就有暴政。
”这句话体现了杰斐逊对于政府权力的警惕。
他认为,政府的权力应该受到限制,以免滥用权力对人民造成伤害。
只有当人民能够自由地表达和行使权利时,才能真正实现自由和民主。
3. “教育是自由社会的最重要的支柱。
”杰斐逊非常重视教育的重要性。
他认为,只有通过教育,人民才能够真正理解和行使自己的权利,才能够参与到民主政治中去。
他在弗吉尼亚大学的创办中,推崇了自由的学术环境,并坚信教育是培养公民责任感和批判性思维的关键。
4. “人民不应该害怕政府,政府才应该害怕人民。
”这句话体现了杰斐逊对于人民参与政治的重要性的看法。
他认为,政府的权力来自于人民,而政府的目标应该是为人民服务。
只有当人民积极参与政治,监督政府的行为,才能够实现真正的民主和自由。
结论:托马斯·杰斐逊的语录体现了他对于自由和民主的追求和理解。
他的思想对于美国独立和民主制度的建立起到了重要的推动作用,也对世界各国的政治发展产生了深远的影响。
通过学习和理解杰斐逊的思想,我们能够更好地理解自由和民主的意义,进一步推动社会的进步和发展。

托马斯·杰斐逊(1743—1826)是美国第一次革命的重要的革命理论家和代言人之一。
在美国人民的心目中,他是与华盛顿、林肯齐名的美国三大伟人之一。
美国人民之所以如此推崇杰斐逊,并不是因为他是美国开国元勋之一,而是因为他是美国民主传统的奠基人,他的民主思想始终是美国人民争取进步的推动力量。
本文不准备对杰斐逊的民主思想作全面的、系统的阐述,因为一则是篇幅所限,二则是外国特别是美国史学工作者在这方面已经作出大量的工作。
这里只是根据个人的管见,就杰斐逊的民主思想的几个主要方面加以初步的探讨和论述。
不当之处,请广大读者多加指正和批评。
对人民群众的无限信任对压迫者的无比仇恨对人民群众抱什么态度?这是杰斐逊与当代美国资产阶级政客特别是联邦党政客之间的重要分水岭。
联邦党领袖之一亚历山大·汉密尔顿在轻视人民、仇视人民方面要算最典型的了。
他辱骂人民是“野兽”,说人民群众没有统治能力。
[1]他曾在1787年制宪会议上大言不惭地宣称:“一切社会都分为少数人和多数人。
前者是富有的,出身名门的,后者是人民群众。
……人民狂暴而变化无常。
他们的判断和决定很少是正确的。
因此,应该使前者在政府中享受一个显著而永久的地位。
他们会制止后者的不稳。
只有这样一个永久性的团体才能抑制民主的轻举妄动。
”与汉密尔顿相反,杰斐逊对人民群众有无限的信心。
首先他深信普通人民的善良和判断能力。
1813年1月13日,在致约翰·梅利什的信里,他写道:“他(指华盛顿——引者注)和我之间的唯一意见分歧在于:我对于人民的天赋完善和判断能力,比起他来,有更大的信心。
”[2]他主张人民群众参加国家管理,因为他相信人民群众有自治和管理国家的能力。
[3]1823年10月31日他在致科里的信里表示:“人民,特别是当他们受到适度的教育时,是公众权利的唯一可靠的保管人(因为他们是唯一正直的),因此应该参加统治,担任他们胜任的职务”。
[4]在给法国重农学派尼摩尔的信里他写道:“我们两个人都爱人民,但是你把它当作幼儿加以爱护,没有保姆你是不相信他们的,而我则把他们看成是大人,他们统治自己我是放心的。

汉密尔顿主义与杰斐逊主义之争我最近一直在看罗荣渠先生的文集《美国历史通论》,对美国建国初期的“汉密尔顿主义与杰斐逊主义”这一章节颇有兴趣,在此与君分享所读所感。
“以汉密尔顿为代表的联邦党人和以杰斐逊为代表的共和党人的斗争,实质上是关于美国未来发展的两条路线和道路的斗争”——这是罗先生的开篇之言。
我首先简介一下罗先生所提的两位人物和两个党派。
亚历山大·汉密尔顿(Alexander Hamilton),美国的开国元勋之一,美国宪法的起草人之一,美国首任财政部部长。
他生于西印度群岛,父亲原是苏格兰商人,家道中衰。
托马斯·杰斐逊(Thomas Jefferson),美国的开国元勋之一,美国《独立宣言》的起草人,当过驻法公使、美国首任国务卿和第三任总统。
他生于弗吉尼亚的一个富裕家庭。
支持汉密尔顿和联邦政府的人就是联邦党人。
汉密尔顿领导的联邦党虽然最早控制政府,却一直是一个比较松散的组织。
杰斐逊领导的共和党是反联邦党的大联合,与美国现今的共和党毫不相干。
自欧洲的英国和法国决裂以来,美国国内亲英的联邦党人和亲法的共和党人也几乎决裂,前者骂后者是无神论者、无政府主义者,后者骂前者是托利党、君主主义者。
随着历史的发展,联邦党日渐衰微,使共和党一党独大,在一个时期内,美国事实上处于一党统治之下,史称“和谐时期”。
人们把早期美国两党的存在称为“第一政党制度时期”。
关于汉密尔顿主义和杰斐逊主义,历史学家大多贬“汉”扬“杰”,但事实远不是如此简单。
在我看来,两者就像太极图中的阴阳双鱼,有差异却又共生。
汉密尔顿是一个“性恶论”者,蔑视人民和民主,崇拜制度和秩序。
他出任财政部部长后,有四大举措:由新政府出面承担和偿还大陆会议和各州在战争时期发行的证券、债券及其他有价契约;设立具有贸易保护主义色彩的关税;模仿英格兰银行,建立一个合众国银行,以20年为期,并有权在全国开设分行;发展制造业。
他所奉行的经济路线代表了美国东北部新兴商人、投机者和债权人的利益,对广大劳动人民和农场主并没有什么好处。

托马斯·杰斐逊思想总结英语作文Thomas Jefferson was one of the founding fathers of the United States and the principal author of the Declaration of Independence. His political philosophy and ideas have had a profound impact on American history and continue to influence political thought today.One of Jefferson's key beliefs was in the importance of individual liberty and limited government. He believed that government should be minimal, with power decentralized and in the hands of the people. This idea is reflected in the Declaration of Independence, with its assertion that all men are created equal and have the right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.Jefferson also championed the idea of a free market economy, with minimal government interference in business and commerce. He believed that a strong economy could only be achieved through free trade and competition, and that government should not play a heavy-handed role in regulating the economy.Furthermore, Jefferson was a strong advocate for education and intellectual freedom. He believed that an educated populacewas essential for a functioning democracy, and that education should be widely accessible to all citizens. He also believed in the importance of a free press and freedom of speech, as essential components of a free society.Another key aspect of Jefferson's political thought was his belief in the importance of states' rights. He believed that the states should have a large degree of autonomy and that the federal government should only exercise the powers explicitly granted to it by the Constitution. This idea of federalism continues to be a central tenet of American political thought.In conclusion, Thomas Jefferson's political philosophy was grounded in the principles of individual liberty, limited government, free markets, education, and states' rights. His ideas have had a lasting impact on American history and continue to shape the political landscape today. Jefferson's legacy as a champion of freedom and democracy is one that will endure for generations to come.。

托马斯·杰斐逊语录标题:托马斯·杰斐逊语录:自由与平等的重要性引言:托马斯·杰斐逊是美国历史上最为重要的政治家之一,他的思想对于美国独立战争和美国宪法的制定起到了关键作用。
他的语录不仅体现了他对于自由与平等的追求,也对世界各地的人们产生了深远的影响。
本文将以托马斯·杰斐逊的语录为线索,探讨自由与平等的重要性。
第一段:自由是人类最基本的权利之一。
杰斐逊曾说过:“我们认为这些真理是不言而喻的,人人生而平等,造物主赋予他们若干不可剥夺的权利,其中包括生命、自由和追求幸福。
”这句话凝聚了杰斐逊对于自由的理解。
自由是每个人天生享有的权利,无论种族、性别、宗教或社会地位如何,每个人都应该有权利追求自己的幸福。
自由不仅仅是个人的权利,也是社会的基石。
只有在自由的环境下,人们才能发挥自己的潜力,追求自己的理想,实现个人的成长。
第二段:平等是社会进步的关键。
杰斐逊曾说过:“我们认为这些真理是不言而喻的,人人生而平等。
”这句话强调了平等的重要性。
平等意味着每个人都应该有平等的机会和权利。
没有人应该因为种族、性别、财富或其他因素而受到歧视或不公平的对待。
平等不仅仅是道德上的要求,也是社会稳定和繁荣的基础。
只有在平等的社会中,每个人都能够充分发挥自己的才能,为社会做出贡献。
第三段:自由和平等相辅相成。
杰斐逊曾说过:“自由和平等是相互依存的。
”这句话揭示了自由和平等之间的密切关系。
自由是实现平等的前提,只有在自由的环境下,每个人才能够追求平等的机会和权利。
而平等则是自由的保障,只有在平等的社会中,每个人才能够真正享受到自由的权利。
自由和平等的共同存在,为社会创造了公正和和谐的环境。
结论:托马斯·杰斐逊的语录体现了他对于自由和平等的追求。
自由和平等是人类最基本的权利,也是社会进步的关键。
只有在自由和平等的环境下,每个人才能够充分发挥自己的潜力,追求幸福和实现个人的成长。
我们应该以杰斐逊的思想为指引,不断努力为实现自由和平等的社会而奋斗。
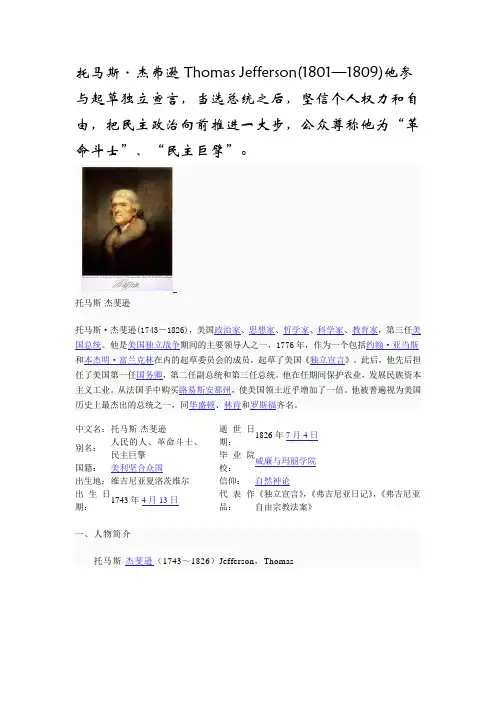
中文名: 托马斯·杰斐逊别名:人民的人、革命斗士、民主巨擎国籍: 美利坚合众国 出生地: 维吉尼亚夏洛茨维尔出生日期:1743年4月13日逝世日期: 1826年7月4日 毕业院校: 威廉与玛丽学院 信仰: 自然神论 代表作品: 《独立宣言》,《弗吉尼亚日记》,《弗吉尼亚自由宗教法案》一、人物简介托马斯·杰斐逊(1743~1826)Jefferson ,Thomas总统(1801~1809)。
1743年4的东西了。
这样一个小箱子,两百年前就相当于今日功能齐全的手提电脑。
思考与启迪这些小玩艺儿,现在我们看来都很简单,不值一提。
它们的意义在于,它们说明了美国立国先贤们对创新之重要性的认识。
杰弗逊和华盛顿总统,是对创新发明非常重视的第一代开国者。
在美国革命的动荡岁月里,两个人都没忘记抽空向英国和欧洲大陆订购花种、菜子,写信给家里关照不要错过了播种新品种的季节。
两个人对于新品种都有异乎寻常的热情,退休以后回到家,都一头扎到田间草地,侍弄新鲜花草。
杰斐逊还改良了一种犁铧,得到过国际组织嘉奖。
当华盛顿担任美国第一任总统的时候,他请杰斐逊担任国务卿。
那个时候,世界上最强大的是英国,制造业中心在英国和欧洲大陆,美国只是偏远落后的农林产品输出地,向欧洲出口棉花,木材,烟草,大米,羊毛,几乎所有工业制品都从欧洲进口。
第一代美国领袖知道,虽然美国有资源,但是如果它不制造,它就永远不是一个强国。
谁制造谁强大,是工业革命时代的铁律。
为此,美国必须广罗技术人才,有人才才会有自己的制造业。
从此开创了美国特别优待技术人才的传统。
至今为止,美国人有一个不成文的共识:美国必须是全世界给人才以最好条件的地方。
什么地方给人才的条件比美国好,美国肯定会提出更好的条件,超过那个地方。
1790年,华盛顿就任总统的第二年,他就让杰斐逊尽快确立专利保护制度。
就在华盛顿总统任内,杰斐逊一手操办,美国通过了保护创新和发明的专利法,从此美国成为世界上保护创新最严格的地方。


托马斯·杰斐逊和美国宪法- 探索权力分立的原则1. 引言1.1 概述在美国历史上,托马斯·杰斐逊是一位重要的政治家和哲学家,他对权力分立原则的思考对于美国宪法的制定和发展起到了重要的影响。
美国宪法作为全球最古老且高度尊崇的宪法之一,奠定了美国政府权力分立和平衡的基础。
1.2 文章结构本文将以托马斯·杰斐逊及其对美国宪法和权力分立原则的贡献为主线,探讨他对这些问题的观点、思想及其意义。
文章将从杰斐逊早年经历开始阐述,然后介绍他在美国独立运动中的作用,接着以详细描述美国宪法的起源和架构,并分析其中关于权力分立原则的表达与实施。
紧接着将探讨杰斐逊在制宪会议中所发挥的角色、他主张权力分立原则理论依据及其对宪法修正案的影响,并提供其对权力分立原则在实践中应用方面的见解与建议。
最后,我们将研究杰斐逊的思想对后世美国政治制度的影响,以及他对权力分立原则在现代社会中的重要性和普遍适用性的见解。
最终,本文将总结讨论并展望这些问题的未来发展。
1.3 目的本文旨在通过托马斯·杰斐逊和美国宪法这两个突出的主题,探索权力分立原则作为一种理念和制度安排如何成为现代民主国家最基本、关键的组成部分。
同时,本文也将尝试回答以下问题:杰斐逊对美国宪法及权力分立原则的贡献是什么?他的思想如何塑造了美国政治体系?以及这些观点和理念如何对现代社会产生影响和启示?通过深入研究和分析,我们希望能够更加全面地理解托马斯·杰斐逊、美国宪法以及权力分立原则之间错综复杂的关系。
2. 托马斯·杰斐逊的背景和影响:2.1 杰斐逊的早年经历托马斯·杰斐逊于1743年出生在美国弗吉尼亚州一个富裕家庭中。
他接受了严格的教育,学习了自然科学、数学、哲学和文学等多个领域的知识。
这些知识使他成为一位卓越的科学家和人文主义者。
2.2 杰斐逊对美国独立运动的贡献作为美国的开国元勋之一,杰斐逊在美国独立运动中发挥了重要作用。

托马斯杰斐逊一 1生平介绍托马斯·杰斐逊(ThmoaSJefferson,1743一1826年),美国的开国元勋,于1743年4月13日出生在弗吉尼亚西部的夏德维尔(Shawdell),父亲是一个种植园主,母亲是一个贵族。
他是《独立宣言》的执笔者,宗教自由法案的起草人,弗吉尼亚大学的创始人,还是学者、作家、思想家和教育家。
当过弗吉尼亚州州长,驻法国公使,第一届国务卿,第二届副总统,第三届总统。
作为美国独立战争时期和战后初期的杰出的政治家和民主主义思想家,他被称为美国民主之父,是美国民主在思想、制度和实践上最伟大的缔造者。
杰斐逊与华盛顿、林肯一起被视为美国历史上的三大伟人。
但正如马隆教授(Pr.oMumasMalone)在其著作((托马斯·杰斐逊和他的时代})(ThmoasJeffersonandHisTime)一书中写道的那样:“华盛顿是独立共和国的主要象征,林肯是维护联邦统一的主要象征,但是杰斐逊在他的许多丰富多彩的成就方面迈越了这两个人。
”〔,l”华盛顿与杰斐逊相比,只是一个杰出的军事统帅和政治活动家,而缺少理论上的建树。
而林肯自称杰斐逊是他的政治和理论导师,他认为杰斐逊不仅是缔造民主社会原则和公理的先哲,而且也是美国民主政治的最伟大的实践者。
林肯在政治活动中不断实践和更新着杰斐逊的思想,不断从杰斐逊那里汲取信念和力量。
可以说,杰斐逊缔造了美国民主主义的政治文化,而林肯则是这种政治文化的更新者。
2主要成就早期起草《独立宣言》《独立宣言》中所体现的原则就一直在全世界为人传诵。
美国的改革家们,不论是出于什么动机,不论是为了废除奴隶制,禁止种族隔离或是要提高妇女的权利,都要向公众提到“人人生而平等”。
不论在什么地方,当人民向不民主的统治作斗争时,他们就要用杰斐逊的话来争辩道,政府的“正当权力是经被治者同意所授予的”。
总统期间的表现及成就在杰斐逊任职期间,他派人赴法国谈判,以期购买新奥尔良和西佛罗里达。
Thomas Jefferson's Vision of Democracy inModern TimesThomas Jefferson, one of the Founding Fathers of the United States, left behind a legacy of profound thoughts and ideas that continue to influence the world today. His belief in the inherent rights of all men, his vision of a government that serves the people, and his commitment to democratic principles have shaped the course of American history and beyond.Jefferson's belief in the equality of all men was a radical departure from the social norms of his time. He firmly believed that all men were created equal and had the right to life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. This 理念 was encapsulated in the Declaration of Independence, which Jefferson drafted, and it has become a fundamental principle of democratic governments around the world.Jefferson's vision of a government that serves the people is also a cornerstone of democratic theory. He believed that the government existed to serve the needs and interests of its citizens, not the other way around. Jefferson advocated for a limited government that protectedthe rights of individuals and did not infringe on their freedoms. This belief led to the creation of a federal system with checks and balances to ensure that no one branch of government could become too powerful.Jefferson's commitment to democratic principles extended to his views on education. He believed that awell-educated citizenry was crucial to the success of a democracy. Jefferson founded the University of Virginia, which was designed to provide a broad-based education that would prepare students to become active and informed citizens. He also advocated for the widespread dissemination of knowledge and information, believing that it was essential for the growth and prosperity of a democratic society.In today's world, Jefferson's ideas continue to resonate. As democracies face challenges ranging from economic inequality to political dysfunction, theprinciples of equality, limited government, and an educated citizenry remain critical to their success. Jefferson's vision of a government that serves the people reminds us that the role of the government is to protect the rightsand freedoms of its citizens, not to infringe on them. His belief in the power of education reminds us that a well-educated citizenry is essential to the health and vitality of a democratic society.Thomas Jefferson's ideas and vision have stood the test of time and continue to inform our understanding of democracy and its essential values. As we move forward in the 21st century, it is important to remember that Jefferson's legacy is not just a part of American history; it is a critical component of the democratic ideal that we all share.**杰斐逊思想在现代的民主愿景**托马斯·杰斐逊,美国开国元勋之一,留下了深刻的思想和理念遗产,至今仍影响着世界。
Thomas Jefferson's Ideological LegacyThomas Jefferson, a towering figure in American history, stands as a beacon of enlightenment and democratic principles. His life and works are a testament to the power of intellectual inquiry and the pursuit of liberty. Jefferson's ideas, particularly his belief in the inherent rights of individuals and the necessity of limited government, have shaped not only the United States but also the global discourse on democracy and freedom.At the core of Jefferson's philosophy was the beliefthat all individuals are born with certain inalienable rights, including the right to life, liberty, and thepursuit of happiness. He firmly believed that these rights were natural and existed independently of any government. This belief underpinned his tireless efforts to securethese rights for all Americans, regardless of their social status or background.Jefferson's commitment to liberty was not limited tothe domestic sphere. As a diplomat and statesman, he advocated for the rights of oppressed peoples across the globe, particularly those enslaved in the Americas. Hisdraft of the Declaration of Independence, which denounced the British monarchy as a tyrant and called for the establishment of a government based on the consent of the governed, was a powerful declaration of these principles.In addition to his commitment to individual rights, Jefferson was a strong proponent of limited government. He believed that government should serve the interests of the people and not vice versa. This belief led him to advocate for the separation of powers and checks and balances, which are fundamental principles of the American political system. Jefferson's distrust of concentrated power and his beliefin the importance of popular participation in governance continue to inform democratic theory and practice.Moreover, Jefferson's thoughts on education and the advancement of knowledge were equally profound. He believed that education was essential for the progress of societyand the cultivation of informed citizens. Jefferson founded the University of Virginia, which emphasized the importance of a liberal education and the pursuit of knowledge across disciplines. His vision of an educated populace capable ofgoverning themselves was a critical aspect of his democratic ideology.Jefferson's legacy is not without its complexities. His views on race and slavery, while evolving over time, were ultimately inconsistent with his broader principles of liberty and equality. However, it is important to remember that Jefferson's era was deeply influenced by the social and cultural norms of his time, and his thoughts and actions must be understood in this context.Nonetheless, Jefferson's contributions to American democracy and his ideas on liberty, limited government, and the importance of education remain relevant and influential today. His vision of a society where individuals are free to pursue their happiness and where government serves the interests of the people continues to inspire generations of Americans and people across the world.**托马斯·杰斐逊的思想遗产**托马斯·杰斐逊,美国历史上的一位巨人,是启蒙思想和民主原则的灯塔。
杰弗逊美国独立宣言的笔者杰弗逊美国独立宣言是美国历史上一份具有重要意义的文献,而它的笔者正是托马斯·杰弗逊。
本文将围绕杰弗逊的背景、宣言的内容以及其对美国独立和后续事件的影响展开论述。
一、杰弗逊的背景托马斯·杰弗逊(Thomas Jefferson)是美国历史上一位杰出的政治家、法学家和作家,他不仅直接参与起草了美国独立宣言,而且担任过美国第三任总统。
他生于1743年,死于1826年,是美国历史上最重要的政治思想家之一。
杰弗逊在早期就受到启蒙思想的影响,他崇尚自由、平等和人权。
他拥有广泛的知识,是一位多产的作家,对于政治和法律等方面有深入的研究。
这样的背景使得他能够成为美国独立宣言的主要撰写者之一。
二、宣言的内容杰弗逊以德国启蒙思想家洛克的政治哲学为基础,将其观点融入到宣言中。
宣言以“我们这样宣布这些真理是毫无疑问的”起头,强调了人人生而平等,并赋予了人们特定的权利和自由。
此外,宣言还谴责了英国政府的暴政,并要求美国人民推翻英国的统治。
宣言接着列举了一系列英国政府违反人民权利的行为,并指出,人民有权利革命并建立一个更加公正和平等的政府。
宣言的最后,杰弗逊明确指出,美国独立是一项正当的行动,并宣布美国与英国彻底分离,成为独立的主权国家。
三、宣言的影响杰弗逊美国独立宣言的影响深远,不仅对当时的美国独立战争产生了重大影响,而且对后来的世界历史产生了深远的影响。
首先,宣言将自由、平等和人权的思想写入正式文件,成为美国价值观的基石。
它提供了一个理论基础,为美国独立战争提供了动力和合法性。
其次,宣言的内容激发了美国人民的爱国热情,团结了起来,为脱离英国的统治进行了长期的斗争。
宣言的宣布将美国确立为一个独立国家,同时也为其他殖民地的独立运动提供了激励和指导。
此外,宣言中关于自由和人权的论述,对于后来世界范围的人权运动产生了重大的影响。
宣言强调人们的自由和平等权利,成为世界其他国家争取自由独立和民主的范例。
托马斯·杰斐逊的思想与遗产Thomas Jefferson, one of the Founding Fathers of the United States, left an indelible mark on the nation heloved and served. His legacy is not only in the Declaration of Independence and the Constitution, which he authored,but also in the principles and ideals he lived by.Jefferson's thoughts on democracy, individual rights, and the role of government are as relevant today as they werein his own era.Jefferson's belief in the sovereignty of the people was central to his political philosophy. He believed that the government existed to serve the people and that it shouldbe limited in its powers to prevent abuse and tyranny. This理念 was reflected in his drafting of the Declaration of Independence, which proclaimed the inalienable rights ofall men and the duty of governments to protect those rights. Jefferson also advocated for a strict interpretation of the Constitution, arguing that it should be a document that enumerated the powers of the federal government and leftthe rest to the states and the people.Jefferson was a staunch advocate of individual rights, particularly the right to property ownership. He believed that property ownership was essential to the pursuit of happiness and the foundation of a free society. Jefferson's own life was a testament to this belief, as he was a successful planter and architect who designed his own home, Monticello. His belief in the primacy of individual rights also extended to issues of slavery, which he saw as a moral wrong that needed to be addressed.Jefferson's thoughts on education were equally as profound. He believed that education was the key to personal growth and societal progress. Jefferson founded the University of Virginia, which was groundbreaking in its time for its emphasis on practical learning and the sciences. He also advocated for the establishment of a national system of public education, believing that it was essential to the democratic process and the development of a well-informed citizenry.Jefferson's thoughts on religion were also noteworthy. He was a Deist who believed in a Creator but rejected organized religion and its dogmas. Jefferson saw religionas a personal matter that should be kept separate from government and politics. His views on this topic were controversial in his time, but they have becomeincreasingly relevant in today's world, where issues of religious freedom and the separation of church and state are once again at the forefront of public debate.Thomas Jefferson's thoughts and contributions have had a profound impact on the United States and the world. His belief in the sovereignty of the people, the primacy of individual rights, the importance of education, and the separation of religion and government are as relevant today as they were in his own era. Jefferson's legacy is a testament to the power of ideas and the importance of upholding democratic principles and ideals.**托马斯·杰斐逊的思想与遗产**托马斯·杰斐逊,美国开国元勋之一,为他所热爱和服务的国家留下了不可磨灭的印记。
托马斯·杰斐逊思想英语作文Thomas Jefferson was a prominent figure in American history, known for his influential ideas and contributions to the development of the United States. His thoughts on various aspects of governance, freedom, and democracy have left a lasting impact on the nation and continue to be studied and celebrated today. In this essay, we will explore the key elements of Thomas Jefferson's ideology and their significance in shaping the American identity.One of the central tenets of Thomas Jefferson's philosophy was the belief in the inherent rights and freedoms of individuals. He famously wrote in the Declaration of Independence that 'all men are created equal, that they are endowed by their Creator with certain unalienable Rights, that among these are Life, Liberty and the pursuit of Happiness.' This assertion laid the groundwork for the American conception of human rights and served as a rallying cry for those seeking to break free from oppression and tyranny. Jefferson's emphasis on the importance of individual liberty and autonomy continues to resonate in modern American society, influencing debates on civil rights, personal freedoms, and the role of government in safeguarding these rights.In addition to his advocacy for individual rights, Thomas Jefferson was a proponent of limited government and the principle of popular sovereignty. He believed in the power of the people to govern themselves and saw the role of the government as being constrained by the will of the governed. Jefferson's vision of a government that derives its authority from the consent of the governed has been enshrined in the American political system, shaping the structure of the nation's democratic institutions and the relationship between the state and its citizens. His ideas continue to inform discussions on the proper balance of power between the government and the people, as well as the mechanisms for ensuring accountability and representation in a democratic society.Furthermore, Thomas Jefferson was a staunch advocate for the separation of church and state, a principle that has become a cornerstone of Americanconstitutional law. He famously articulated this concept in his letter to the Danbury Baptist Association, in which he wrote of the need for a 'wall of separation between church and state.' Jefferson's commitment to religious freedom and the idea that the government should not interfere with matters of faith has had a profound impact on the development of religious pluralism and tolerance in the United States. His views continue to influence contemporary debates on the boundaries of religious expression in public life and the protection of religious minorities from discrimination.Moreover, Thomas Jefferson's vision for the expansion and development of the United States has had a lasting impact on the nation's identity and its place in the world. As the principal author of the Louisiana Purchase, Jefferson played a pivotal role in doubling the size of the United States and opening up vast new territories for exploration and settlement. His belief in the importance of westward expansion and the cultivation of a nation of independent yeoman farmers has left an indelible mark on the American ethos, shaping the country's self-image as a land of opportunity and manifest destiny. Jefferson's ideas continue to inform discussions on the legacy of American expansionism and the ongoing challenges of reconciling the ideals of progress and development with the preservation of natural resources and indigenous rights.In conclusion, Thomas Jefferson's ideas and philosophy have had a profound and enduring impact on the development of the United States and its national identity. His advocacy for individual rights, limited government, religious freedom, and territorial expansion has left an indelible mark on the American ethos, shaping the nation's values, institutions, and self-conception. Jefferson's legacy continues to be celebrated and debated, serving as a touchstone for understanding the complexities of American history and the ongoing pursuit of a more perfect union.。