SAP用语(D-E)
- 格式:xls
- 大小:142.50 KB
- 文档页数:5

sap各模块常用todeMM模块:mm01:建物料主数据mm02:更改物料主数据mm03:查看物料主数据(一般1为创建,2为更改,3为查看) xk01:建供应商me11::建采购信息记录me51n::创建采购申请单me55:采购申请的集中批准me57:分配并处理采购申请me41:创建RFQ(request for quote:报价请求)me47:维护报价zme49:采购报价单审核me01:维护货源清单me23n:查询采购订单migo_gr:采购订单收货me21n:创建采购订单mb21:创建预留mb22:修改预留mb23:查看预留概况mmbe:库存总览(查看库存)mb1a:输入发货co01:创建生产订单co02:修改生产订单co03:查看生产订单mb51:查看物料凭证清单me5a:查询采购申请列表me4s:每一汇总号报价请求zme49:采购报价单审核me49:价格比较mkvz:显示多个供应商清单me1m:每个物料信息记录me1e:报价价格历史记录me1p:采购订单价格历史记录me01:创建货源清单me04:更改货源清单me03:显示货源清单me29n:采购订单单独审批me28:采购订单集中审批mrko:寄售结算mir7:发票校验SD模块:xd01:创建客户xd04:现实客户修改历史xd05:冻结/解冻客户xd06:删除客户信息va01:创建销售订单vap1:创建联系人vk11:创建价格(FOB)条件(ZPRO)v/ld:查询价格清单fd32:创建/修改客户信贷记录fd/33:显示客户信贷记录va21:创建报价单va25:查询报价清单(单个客户)va25n:查询报价清单(多个客户)zsd002:销售订单查询与打印(可查询销售订单审批状态及审批人) zsd003:审核销售订单vl01n:创建交货单vl10i:批量创建交货单vl02n:修改交货单vl09:取消交货单vf01:单独开具销售发票vf02:修改发票vf04:集中开具销售发票vf05:集中显示发票清单vf11:取消发票CO常用TCODE--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------成本中心-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- KS01 创建成本中心KS02 修改成本中心KS03 显示成本中心KS04 删除成本中心KS05 成本中心:显示修改KSH1 创建成本中心组KSH2 修改成本中心组KSH3 显示成本中心组KA01 创建成本要素KA02 修改成本要素KA03 显示成本要素KA04 删除成本要素KA05 成本要素:显示修改KA06 创建次级成本要素KAH1 创建成本要素组KAH2 修改成本要素组KAH3 显示成本要素组***************************************************************KK01 创建统计指标KK02 修改统计指标KK03 显示统计指标KB31N 统计指标过帐KB33N 统计指标过帐显示KB34N 统计指标过帐冲销*************************************************************** KSU1 创建实际分摊KSU2 改变实际分摊KSU3 显示实际分摊KSU4 删除实际分摊KSU5 运行实际分摊KSV1 建立实际分配KSV2 改变实际分配KSV3 显示实际分配KSV4 删除实际分配KSV5 运行实际分配*************************************************************** OKEON 标准层次更改OKENN 标准层次显示*************************************************************** S_ALR_87013611 成本中心报表*************************************************************** 成本中心计划:KP06 手工输入成本中心计划KP07 显示成本中心计划KP97 复制成本中心计划到计划KP98 复制成本中心实际数据到计划*************************************************************** 成本中心过帐:KB11N 成本中心重过帐KB13N 显示成本中心重过帐KB14N 冲销成本中心重过帐------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 内部订单------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ KO01 创建内部订单KO02 修改内部订单KO03 显示内部订单KOH1 创建内部订单组KOH2 修改内部订单组KOH3 显示内部订单组*************************************************************** S_ALR_87012993 内部订单报表*************************************************************** 计划:KPF6 创建内部订单计划KPF7 显示内部订单计划KO14 复制内部订单计划到内部订单计划KO15 复制内部订单实际数据到计划*************************************************************** KB11N 内部订单重过帐KB13N 显示内部订单重过帐KB14N 冲销内部订单重过帐------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ 利润中心------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ KE51 创建利润中心KE52 修改利润中心KE53 显示利润中心KE54 删除利润中心KCH1 维护利润中心标准层次KCH5N 更改利润中心标准层次KCH6N 显示利润中心标准层次KCH1 创建利润中心组KCH2 修改利润中心组KCH3 显示利润中心组。

SAP系統操作指示代碼一、目錄------分類代碼:1.目錄“3”:檢驗最終判定結果代碼(UD Usage): 允收----A拒收----B特採----C廠商全檢----D廠內全檢----E免檢----F2. 目錄“9”:檢驗標準之代碼群組變壓器------A001-1電感(含SMD元件)------A001-2PFC電感------A001-3鐵芯------A001-4電解電容------C001-1陶瓷電容(含SMD元件)------C001-2積層電容------C001-3麥拉電容------C001-4金屬皮膜電容------C001-5安規電容(X、Y)------C001-6二极體(含SMD元件)-----S001-1發光二极體------ S001-2三极管(含SMD元件)------ S001-3場效應管------ S001-4可控硅------S001-5集成電路(含SMD元件)------S001-6色環電阻(含SMD元件)------R001-1水泥電阻------R001-2可調電阻------R001-3熱敏電阻------R001-4壓敏電阻------R001-5各規格PCB板------P001-1各規格AI板及SMT板------P001-2輸出線------L001-1電子線------ L001-2AC電源線------ L001-3DC電源線------ L001-4插座------ L001-5排針------L001-6端子排------L001-7I/O開關------B001-1PUSH開關------B001-2線扣/ 線環------B001-5直流FAN------B001-6繼電器------B001-7電壓指示表------B001-8波段開關------B001-9RESET開關------B001-10五金CASE------D001-1鋁合金CASE------ D001-2塑膠CASE------ D001-3散熱片------ D001-4螺絲------ D001-5FAN網------ D001-6FUSE------ D001-7保險座------ D001-8小焊片/ 小鐵片------ D001-9銅腳------ D001-10插頭------D001-11導光柱------D001-12螺母------D001-13貼紙/ 銘版/ 標籤類/ 說明書------F001-1紙箱/ 白盒/ 彩盒/ 黃盒------F001-2隔板/ 圍板/ 刀卡------F001-3PE袋/ 汽泡袋------F001-4間隔柱------E001-1絕緣粒------ E001-2絕緣片------ E001-3麥拉片------ E001-4導熱膠片------ E001-5束線帶------ E001-6熱縮套管------ E001-7腳墊------ E001-8鐵弗龍套管------E001-9矽質套管------E001-103.目錄“1”:特性屬性之代碼群組變壓器之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------A001-1電感(含SMD元件) 之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------A001-2PFC電感之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------A001-3鐵芯之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------A001-4電解電容之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------C001-1陶瓷電容(含SMD元件) 之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------C001-2金屬皮膜電容之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------C001-5安規電容(X、Y) 之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------C001-6 二极體(含SMD元件) 之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗-----S001-1發光二极體之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ S001-2三极管(含SMD元件) 之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ S001-3場效應管之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ S001-4可控硅之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------S001-5集成電路(含SMD元件) 之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------S001-6色環電阻(含SMD元件) 之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------R001-1水泥電阻之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------R001-2可調電阻之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------R001-3熱敏電阻之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------R001-4壓敏電阻之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------R001-5各規格PCB板之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------P001-1 各規格AI板及SMT板之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------P001-2輸出線之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------L001-1電子線之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ L001-2AC電源線之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ L001-3DC電源線之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ L001-4插座之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ L001-5排針之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------L001-6端子排之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------L001-7I/O開關之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-1 PUSH開關之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-2切換開關之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-3公/ 母座之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-4線扣/ 線環之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-5直流FAN之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-6繼電器之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-7電壓指示表之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-8波段開關之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-9 RESET開關之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------B001-10 五金CASE之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------D001-1鋁合金CASE之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ D001-2 塑膠CASE之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ D001-3散熱片之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ D001-4FUSE之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ D001-7保險座之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ D001-8小焊片/ 小鐵片之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ D001-9銅腳之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ D001-10插頭之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------D001-11導光柱之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------D001-12螺母之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------D001-13貼紙/ 銘版/ 標籤類/ 說明書之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------F001-1紙箱/ 白盒/ 彩盒/ 黃盒之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------F001-2隔板/ 圍板/ 刀卡之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------F001-3PE袋/ 汽泡袋之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------F001-4間隔柱之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------E001-1絕緣粒之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ E001-2絕緣片之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ E001-3麥拉片之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ E001-4導熱膠片之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ E001-5束線帶之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ E001-6熱縮套管之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ E001-7腳墊之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------ E001-8鐵弗龍套管之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------E001-9矽質套管之外觀、破壞及其它屬性檢驗------E001-103. 目錄“5”:檢驗異常之不良原因代碼----0001尺寸不良----0002外觀不良----0003其它----0004二、特性選集之目錄、特性選集、代碼群組:1.目錄------“1”特性選集------QS01代碼群組------同“目錄------1”之項,“代碼”以流水號方式編排2.目錄------“3”3.特性選集------DEER-02 允收----A拒收----B特採----C廠內全檢----D廠商全檢----E免檢----F三、檢驗方法之代碼:3.電氣檢驗------IT03 (用儀器或治具測試材料之電性)4.破壞檢驗------IT04 (用相應工具扶助執行須破壞檢驗之材料檢驗) 5.其它檢驗------IT05 (用相應檢驗方式確認材料之其它品質特性)四、檢驗計劃中群組及群組計數器代碼:1.磁性類(A001): 變壓器------1電感(含SMD元件)------2PFC電感------3鐵芯------42. 電容類(C001): 電解電容------1陶瓷電容(含SMD元件)------2積層電容------3麥拉電容------4金屬皮膜電容------5安規電容(X、Y)------63.半導體類(S001): 二极體(含SMD元件)-----1發光二极體------ 2三极管(含SMD元件)------ 3場效應管------ 4可控硅------5集成電路(含SMD元件)------64. 電阻類(R001): 色環電阻(含SMD元件)------1水泥電阻------2可調電阻------3熱敏電阻------4壓敏電阻------55.PCB板類(P001): 各規格PCB板------1AI及SMT板------26.線材類(L001): 輸出線------1電子線------ 2AC電源線------ 3DC電源線------ 4插座------ 5排針------6端子排------77.塑膠類(B001): I/O開關------1PUSH開關------2切換開關------3公/ 母座------4線扣/ 線環------5直流FAN------6波段開關------9RESET開關------108.五金類(D001): 五金CASE------1鋁合金CASE------ 2塑膠CASE------ 3散熱片------ 4螺絲------ 5FAN網------ 6FUSE------ 7保險座------ 8小焊片/ 小鐵片------ 9銅腳------ 10插頭------11導光柱------12螺母------139. 包材類(F001): 貼紙/ 銘版/ 標籤類/ 說明書------1紙箱/ 白盒/ 彩盒/ 黃盒------2隔板/ 圍板/ 刀卡------3PE袋/ 汽泡袋------410. 絕緣類(E001): 間隔柱------1絕緣粒------ 2絕緣片------ 3麥拉片------4導熱膠片------ 5束線帶------ 6熱縮套管------ 7腳墊------ 8鐵弗龍套管------9矽質套管------10三、QM基本資料各部分代碼:1.抽樣計劃------AQL2.抽樣程序------DEER-013.動態切換規則------IQC4.檢驗特性: 定性------DR-01定量------DR-02。

SAP培训知识点集合之SAP术语大全Order Entry--订单输入接收客户订单并把客户所需要的东西转换为企业惯用的术语的过程,最简单的情况是生成成品的发货文件,较为复杂的情况是描述包括按订单生产产品的工程要求的一系列活动。
Order Promising--订货承诺给出发货承诺的过程。
回答诸如什么时候可以发货之类的问题。
对于面向订单生产的产品,订货承诺通常涉及到对物料和能力的检查。
Pegging--反查在MRP中,对于某个指定的物料项目,通过反查显示该项物料的毛需求及已分配量的来源的详细情况。
所以,反查是给出物料实际用在哪里的信息。
Planned Order--计划订单当出现净需求时,MRP即生成订货数量和交货日期的建议,即计划订单。
计划订单由计算机生成并且仅存放于计算机中,如果条件发生变化,下次MRP处理可能改变或删除原来的计划订单。
处于某一层的计划订单将分解成下一个低层物料的毛需求。
计划订单与预计入库量也是能力需求计划的输入,用以计算出未来时区内的能力总需求。
Post-deduct Inventory Transaction Processing--后减库存处理法一种库存记帐方法。
物料项目的帐面(存于计算机中)库存量是在其父项或装配件的活动完成之后才被减去。
这种方法的缺点是帐面记录与实际库存经常不一致。
这种方法也称为倒冲法。
Pre-deduct Inventory Transaction Processing--前减库存处理法一种库存记帐方法。
物料项目的帐面(存于计算机中)库存量在发料之前,即对其父项或装配件产生预计入库量之时即被减去。
这种方法的缺点是帐面记录与实际库存经常不一致。
Production Planning--生产规划编制是确定企业产出整体水平的功能。
其主要目的是通过提高或降低库存或未完成订单水平来确定可以达到管理目标的生产率,同时要努力保持生成均衡。
生产规划通常是用产品类来表述的。

SAP 名詞Enterprise Resource Planning Material Requirement Planning Sales and Distribution Materials Management Production Planning Financial Accounting ControllingWarehouse Management ClientCompanyPlantStorage LocationCustomerMaterialMaterial MasterPurchase Requisition Purchase OrderChart of AccountsCost Center Accounting Financial AccountingFixed AssetsGeneral LedgerInternal OrdersProduct Cost Controlling Project SystemStatistical Key FigureWork in ProcessClientCompanyDistribution ChannelDivisionSales AreaSales Organization Shipping point CustomerMaterialMaterial Master Agreement Consignment Order ContractsCredit/Debit memo QuotationReturn OrderSales Support & Sales Schedule agreement Standard Order DeliveryInvoiceShipmentStock transport Order ConditionSurcharge/Discount Taxes Transportation FreightsGoods IssueGoods receiptBillingOne-time customer OutputPerforma Invoice PlantSold-to partyShip-to partyBill-to partyPayerPlantStorage LocationPurchasing Organization Purchasing GroupMaterial MasterVendor MasterPurchase RequisitionRequest for Quotation QuotationPurchase OrderRelease StrategyPurchasing Info Record Source ListConditionLogistic Invoice Verification Movement TypeMaterial Document Accounting DocumentGoods MovementGoods ReceiptGoods IssuePhysical Inventory ReservationUnrestricted UseQuality InspectionActual Costing/ Material Ledger Accruals/DeferralsAvailability ControlActivity TypeAllocationsAssessmentAssetAsset AcquisitionsAsset ClassAsset NumberAsset Retirement by Scrapping Asset RetirementsAsset Sub-Number Automatic Clearing Automatic PaymentAssets under Construction Balance CarryforwardBill of ExchangeBudget Carryforward BudgetingBusiness AreaBOMCarry ForwardCash JournalChart of DepreciationCash ManagementChart of AccountsClientControlling Area CommitmentsCompany CodeCost CenterCost Center AccountingCost Center PlanningCost Object ControllingCost Center HierarchyCost Center GroupCost ComponentsCost ElementCost Element Accounting Cost Element GroupCost of Sales Statement Cost EstimateCredit limitCredit ManagementCredit MemoCross-CC Transaction DeliveryDepreciationDepreciation Area Depreciation forecast Depreciation Run DistributionDocument TypeDown PaymentDunningEx Rate DifferencesEx Rate TypesEx RatesFinancial Accounting Financial Statement Version Foreign Currency Valuation Fiscal YearFixed AssetsFunctional AreaG/L AccountsGoods IssueGeneral LedgerGR/IR ClearingGroup AssetHouse BanksIncoming Payment Investment Orders Internal Documents Internal OrdersInvoiceLow Value Asset LocationLockMass ReversalMaster DataMaterial Ledger Moving average price Number Ranges OffsettingOne-Time Vendors Open ItemsOperating Concern Order TypesOutgoing Payment OverheadPeriod LockPhysical Inventory List Plan VersionPlan RevaluationsPostPosting Key (PK)Price Calculation PricesPrice Determination Price Differences Product Cost Controlling Product GroupProduction OrderProfit CenterProfit Center Group Profitability AnalysisProject SystemPurchase Order Reconciliation Accounts Recurring EntriesReference Documents RoutingRetirementReverseSettlementSpecial G/L IndicatorStatus ManagementStandard PriceSubcontractStatistical Key FigureUpdate of Standard Price VersionsVariance CalculationWork in ProcessWIP CalculationWork CenterYear-End ClosingAvailability checkBalance SheetsBase unit of measureBOMCapacity EvaluationCapacity LevelingCapacity Planning EnvironmentCapacity Requirement Planning ClientClient / Server Architecture Company CodeCross-plant material status Demand Management Dependent Requirement DisaggregatingEnterprise Data ModelForecastForecast base planningGoods ReceiptIndependent Requirement Industry-SolutionsInspection Characteristic Integrated Real-timeIntegrated SolutionsInternet/IntranetInvoice verificationKanbanLong-Term PlanningMake-to-Order productionMake-to-Stock productionMaterial MasterMPSMRPMulti-Level Bill of Material Structure Multi-national Multi-currencyOpen SystemsOrganization Hierarchy Organizational LevelsPlanned OrderPlanning at assembly levelPlanning CyclePlanning StrategyPlanning with final assembly Planning with planning material Planning without final assembly PlantProcessing a Production Order Production Control Production Control Production OrderProduction PlanProfit & loss StatementsPRTPurchase OrderPurchase requisitionReorder point planning Repetitive manufacturingRepetitive Manufacturing SchedulingReportRoutingSOPSales PlanSchedule lineSettlementSingle-level BOM中文企業資源規劃物料需求規劃銷售與配銷管理物料管理生產管理財務會計成本控制倉庫管理客戶端公司工廠庫位/儲存位置客戶物料物料主檔請購單採購單會計科目表成本中心會計財務會計固定資產總帳內部訂單產品成本控制專案系統統計關鍵數字在製品SD 客戶端公司配銷通道產品部門別銷售區域銷售組織出貨點客戶物料物料主檔協議託售訂單合約借項/貸項通知單(訂單)報價單退貨訂單銷售支援與銷售排程協議標準訂單交貨發票運送庫存轉移/庫存運輸單條件(價格)附加費/折扣稅運輸運費發料/發貨收料/收貨請款一次性客戶輸出預期發票工廠客戶收貨人發票收受人付款人MM工廠庫位/儲存位置採購組織採購群組物料主檔供應商主檔請購單詢價單報價單採購單核發策略採購資訊記錄貨源清單價格發票驗証異動類型物料文件會計文件物料異動收料/收貨發料/發貨盤點預訂單未限制使用檢驗庫存FICO實際成本計算/ 物料分類帳應計/遞延資金可用度控制作業類型分配分攤資產資產取得資產類別資產號碼報廢資產處分資產處分資產子編號自動結清自動付款在建資產結轉餘額匯票預算結轉預算編列業務範圍物料表結轉現金帳折舊表現金管理會計科目表用戶端成本控制範圍承約公司代碼成本中心成本中心會計成本中心規劃成本物件的成本控制成本中心階層成本中心群組成本元件成本要素成本要素會計成本要素群組銷售表的成本成本估算信用額度信用管理折讓單跨公司代碼交易交貨折舊折價範圍折舊預測折舊執行分配文件類型訂金催款匯率差異匯率類型匯率財務會計財務報表版本外幣評價會計年度固定資產功能範圍總帳科目發貨總帳收貨/發票接收結清群組資產往來銀行收款資本投資訂單內部文件內部訂單發票低值資產位置鎖住大量迴轉主檔資料物料分類帳移動平均成本號碼範圍沖銷一次性供應商未結項目營運考量訂單類型付款間接成本期間加鎖盤點清單計畫版本計畫重估過帳過帳碼價格計算價格價格決定價差產品成本控制產品群組生產工單利潤中心利潤中心群組獲利能力分析專案系統採購訂單統制科目經常性分錄參考文件途程處分迴轉結算特殊總帳指示碼狀態管理標準成本委外統計關鍵數字更新標準成本版本差異計算在製品在製品計算工作中心年終結算PP 物料可用量查核資產負債表基礎計量單位物料表產能評估產能平準化產能需求規劃環境產能需求規劃客戶端三階式的主從架構公司跨工廠物料狀態需求管理衍生需求展開最佳業務流程預測依預測為基礎的計畫收料獨立需求特定行業解決方案檢驗工具即時性的整合整合解決方案網路化企業經營環境發票驗證看板長程規劃接單生產存貨生產物料主檔主生產排程物料需求規劃多階層物料表國際化工業規格的系統設計系統組織架構系統組織架構計畫工單依組裝階層需求之規劃策略計畫流程計畫策略依最終完成品需求之規劃策略依重要共用物件之規劃策略未進行最後組裝之規劃策略工廠工單流程生產控制生產控制工單生產計畫損益表生產資源/工具採購單請購單人工再訂購點計畫重複性生產重複性生產排程報表途程銷售及作業規劃銷售計畫叫貨決算單階層物料表MRP SD MM PPFICO WM Org OrgPartner Master Master PRPO COA CCA FIFAG/LI/O PCC PS SKF WIPOrg Org Org OrgOrg Partner Master Master Order 1 Order 1 Order 1 Order 1 Order 1 Order 1 Order 1 Order 1 Order 1 Order 2 Order 3 Order 4 Order 5 Condition Condition Condition Condition Condition GIGRBuyerPRRFQPO簽核流程AVLPricingLIVMat.Doc.GRGI領/退料申請單可正常使用之庫存處於檢驗狀態的庫存COA COCCAFI FA G/LI/O PCCPSPOSKFWIPBill of MaterialPlanning Strategy Planning StrategyPlanning StrategyPlanning StrategyPlanning StrategyPlanning Strategy Production Resources/Tools Sales and Operation Planning。

SD 常用术语汇集SD (Sales and Distribution) : 销售和分销Sold-to-party : 下订单客户Ship-to-party : 收货之客户Bill-to-party : 仅指收发票之客户Payer-to-party : 付款人Customer Code : 客户代码Sales Organization : 销售业务组织,指台达的某一事业部Distribution Channel : 销售通路Division : 产品别Sales Areas : 销售网, 销售业务组织+ 销售通路+ 产品别Company Code : 公司代码Incoterms : 国际交运条件Payment Terms : 付款条件Price Master : 单价主档YWST : 销项税则ZWST : 销退税则内销: 凡以人民币付款的均为内销外销: 凡非以人民币付款的均为外销Order Type : 合约类别ATP check : Available to promise 通过ATP check confirm so 的delivery date 和数量反转: 因SO中某些数据Key in 错误,影响后续出货作业,才执行此动作D/O (Delivery Note) : 出货通知单Shipping Method : 运输方式PP常用术语汇集BOM (Bill of Material): 某机种或组合料号包含所有材料的表列,它分为group bom (client bom)是整个集团的材料表;bom是已经做过allocate的group bom .BLK(Block):工单锁定.Backflush材料: 不按工单领料,仓库也不作扣帐动作.它是由制作部confirm工单时进行扣帐.CFCO: CONFIRM工单,由制造部完成,可以确认实际工时,实际产出数量,BF材料的扣帐动作.DMS(Document Management System): 文件管理系统,目前DELTA 的所有有料号者皆可将其材料数据存放于Server中.Depedent Requirement: 相依需求,相对于独立需求而产生的需求.DLV(Delivery):工单完全入库.ECN (Engineer Change Notification):工程变更通知书.EO/PO: 制程外包订单.Hierarchy: 各工作站可透过一个结构关系将其产能需求及有效产能整合到一个统计性(虚拟)的工作站中,此结构关系的设定称为Hierarchy 的建立.Indepedent Requirement: 根据业务的FORECAST和S/O而产生的需求.Lead Time : 某机种的生产时间.MPS(Main Production Schedule):主生产排程.OP(operation) Code: 制程代码,即是routing中各个制程的序号.Order Date:工单日期.Pilot run: 试制,即是试验性生产.Pro.ord(Production Order):工单,也就是工令,它是生产顺利进行的核心.S/O产生出来的需求.Routing: 制造途程,生产某一机种的过程.Rework: 针对某些不合格的产品,进行重新加工.REL: release工单,由生管完成,它是工单核准作业,release过后的工单才能算作有效工单.Schedule Date:上线日期.TECO(Technical Complete):工单关闭.Work Center: 工作站或工作群组.有生技部IE维护.工时:生产所需时间,它包括:标准工时,实际工时,异常工时,除外工时. MM常用术语汇集MM: materials management,即物料管理.MRP: material requirement planning,即物料需求计划.P/O: purchase order,采购向厂商所下正式订单.P/R: purchase requisition, run MRP时所得的采购需求单.PlOrd: planned order, run MRP时所得的计划订单.ROH: SAP系统中所定义raw material 类别.FERT: SAP系统中所定义成品类别.S/O: sales order, 业务订单.Delivery: 常指业务订单的出货单号码.Schedule: 常指工作计划的时间表或进度表.Master data: 当有增加新厂商时,需维护该厂商的主文件资料,包括Vendor master / Source list / Info record / material master等资料. Source list: 设定料号的供货商名单.Info record: 主要用于维护购买单价.此单价需经采购主管核准后始得键入,并于开立订单时系统自动带出单价.Subcontract process: 指外加作业,可不需开立工单就能将Subcontract BOM带入订单内;可直接于SAP系统直接控管台达及厂商处的库存, 可免除现行手记帐的缺点.Consignment parts: 指厂商将材料寄放于台达仓库,待台达厂需要时,再领出使用;执行优点是厂商交货时不须付款,待台达厂领用后才付款.Components: 成品或机种组成成份的称谓.Confirm: 确认事务的一种行为方式,如采购为使材料能够准确满足生产需求,必须confirm厂商的交期.Release: 采购向厂商下P/O之后,必须透过一定权限经由主管对此张P/O做release后才能收料.Goods receipt: 收料,如厂商送货到台达后,仓库需做收料动作. Goods issue: 发料,如生产线从仓库领走材料后,仓库需做发料动作. Goods transfer: 转仓,如B.F.材料从仓库发料后需做转仓动作.P/N: part number,材料的料号.Spare parts: 呆料,即已不使用的材料.Return delivery: 退货,如当厂商的材料发生质量问题时,仓库配合相关单位所做的退货处理作业.MVT: Movement type, 材料收发料后仓库在SAP系统中所做相应动作产生的异动代码,如101 / 102 / 261 / 262等.Work order: 指工单发料或扣帐中所识别的工单号码,即工令. Cyclecount: 仓库平日库存盘点,盘点数据由YMD2产生.。

SAP常用名词SAP常用名词解释Manufacture: 制造商Vendor: 供应商AML( Approval manufacture list): 合格制造商清单MM( Material management): 物料管理,包括采购和仓库管理.AVL( Approval vendor list): 合格供应商清单Info record: 采购资讯记录,记录Vendor与Material之间的关联信息主要是价格信息和有效期Source list: 来源清单,记录某料有哪些合格vendor供应,各vendor供应有效期限是多久.Quota arrangement: 配额协议,记录某料由哪些vendor供应,各vendor供应比例占多少,供应有效期限是多久.PR (Purchase Requisition): 采购物料前开立的请购单,一般是在Run MRP时根据实际需求自动产生,也可以手工开立,是采购下正式采购单的重要依据.PO (Purchase Order): 采购部开给供应商的正式订单.也是供应商交货和我们收货的重要依据.一般是根据PR转为PO.SA (Scheduling Agreement): 排程协议,相当于采购通常所说的“空白订单”,“Blanket Order”,一般订单数量比较大,而且SA不可以直接收货,必须在SA的每个Item中在维护具体的交货信息才可以作收货.SL (Schedule Line): 交货排程,即SA中所提到的每个Item中在维护具体的交货信息,只有维护了SL的SA才可以收料.一般是在Run MRP时根据实际需求自动产生.GR (Goods receive): 收货.当供应商交货后, 仓库根据PO/SA/SL 将货收入系统仓库.GT(Goods transfer): 物料转移,比如说把11-1231-01这颗料A仓库转移到B仓库.GI (Goods Issue): 发料.比如工单开立后要发料到工单中, 产线才有料做生产的动作.MRP (Material Requirements Planning): 物料需求计划,采购下单的基本依据,根据demand.ROP (Reorder point): 再订购点, run MRP时当库存低于该水位时系统自动产生PR/SL/Plan order.PP: Production Planning 生产计划,与生产相关的事务处理, 如建立BOM, 开立工单, 计划物料需求, 生产排程等。


SAP词汇表ABAP/4 查询ABAP/4 查询给用户提供在不同标准下基本的列表、分类和汇总。
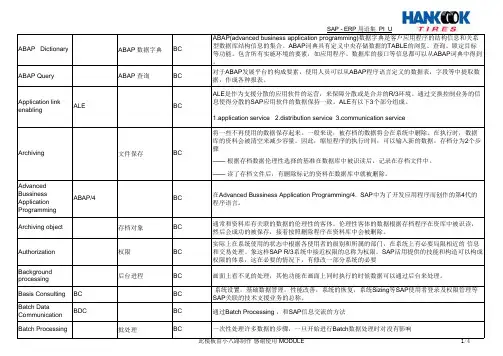
同时还提供统计表和排序列表。
科目设置模板科目设置模板是一个过帐凭证的模板。
它包括在凭证中缺省并方便数据输入的行项目。
它可包含一个不定的行项目号码并包含已过帐的金额,或者使用一个等价因素来展开金额比例。
科目组科目组是总分类帐、供应商和客户主记录的分类特性。
科目组帮助屏幕显示和科目编号。
每一个主记录必须分配到一个科目组。
科目类型过帐行项目时,有5种科目类型可供输入:客户、供应商、G/L 科目、资产和原料。
记帐代码定义正在使用的科目类型。
应计分录应计和递延分录是调整记帐,这是过帐期段末尾所必须的。
典型地,它们在以下期间被冲销。
R/3的应计程序将应计帐记帐到总分类帐,然后指定应当被冲销的数据。
执行冲销程序,选择并冲销可应用的应计凭证。
作业类型作业类型描写了由成本中心引起并以时间和数量为单位度量的作机器小时和劳动小时。
附加科目分配所有的附加到科目号、金额总量和记帐代码的输入在行项目中进行。
包括付款条件、支付方式、成本中心和其它分配字段“分配”字段是凭证行项目的一段附加参照字段。
它包括在所有的已过帐的行项目中。
行项目可以按字段内容在凭证行项目目录中进行排序。
“分配”字段可自动填充 (主记录中的排序码),也可手工填充(行项目中的输入)。
ASAP (加速SAP)ASAP 是SAP的全面执行解决方案,用来将R/3系统连成一个整体。
加速SAP 最优化时间、质量和资源的有效使用。
其中心在于协调使执行得以成功进行的所有元素。
资产类别资产类别提供对固定资产的分类。
它提供科目确定、编号范围和屏幕显示选项。
自动科目分配在过帐事务期间自动进行(在进行财务会计时) ,由此系统将项目分配到合适的科目中,而不要用户进行任何输入。
余额审记线索在某个期段科目中的所有事务的记录。
余额审计线索显示期初余额和期末的总帐增长。
余额结转前一年科目余额的传输。
sap系统编码中常用的英语
SAP系统编码是SAP软件中重要的组成部分,它用于描述不同的对象和过程。
在SAP系统编码中,英语是最常用的语言。
以下是一些在SAP系统编码中常用的英语词汇及其含义:
1. Material number: 物料号码。
它是SAP系统中一个物料的唯一标识符。
2. Vendor: 供应商。
它是向公司提供产品或服务的个人或组织。
3. Customer: 客户。
它是购买公司产品或服务的个人或组织。
4. Sales order: 销售订单。
它是客户和公司之间的商业协议,规定了销售的产品、数量、价格和交货日期等信息。
5. Purchase order: 采购订单。
它是公司向供应商发出的商业协议,规定了采购的产品、数量、价格和交货日期等信息。
6. Invoice: 发票。
它是供应商向客户提供的付款要求,表明了交易的详细信息。
7. Payment terms: 付款条件。
它是在销售订单或采购订单中规定的客户或供应商的付款方式和时间。
8. Production order: 生产订单。
它是公司向工厂发出的指示,要求生产特定数量的产品。
9. BOM (Bill of Materials): 物料清单。
它是指生产产品所需的所有原材料、组件和部件的列表。
10. Routing: 工艺路线。
它是生产特定产品所需的工序和步骤的顺序列表。
以上这些英语词汇在SAP系统编码中非常常用,熟练掌握这些词汇将有助于更好地理解和使用SAP系统。
SAP (Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing)GlossaryInformation Technology has many key words and SAP R/3 has introduced many others. In order to understand the field of SAP even better you should keep those terms in mind.ALE (Application Link Enabling)It provides integration for separate R/3 systems, keeping full interaction. This makes possible distributed enterprise applications.Application serverThe application server is used to run the business application programs in the R/3 client/server concept. The application modules are loaded from the data base server to the application server as required. Thus the application server requires only storage capacity to accommodate UNIX, Swapping and the SAP runtime environment.Batch InputA technique to input data safely. It ensures application data integrity for background interfaces. It pretends to be someone typing. See also direct input.CATT (Computer Aided Test Tool) It allows you to combine and automate sequences of repeatable transactions in test procedures. CATT reduces the number of manual tests, and forces you to test systematically, defining input values and expected test results.CCMS (Computer Center Management System)It allows you to monitor, control and configure your R/3 system. This toolset lets you analyze and distribute client workloads and report on resource consumption for system components.Central SystemIn an R/3 central system, both application and data base software are run on one computer.ClientIn commercial, organizational and technical terms, a self-contained unit in an R/3 system with separate master records and its own set of tables.Client/Server SystemClient/server systems are structured modularly, with components working in a sender/receiver relationship. Software components can also be used in a client/server relationship.Communication ServerIt provides the connection between local area and wide area networks and may be either a router, a bridge or a gateway. In R/3 installations, the communication server must support the TCP/IP protocol over wide area networks.Company codeThe smallest organizational unit for which a complete self-contained set of accounts can be drawn up for purposes of external reporting. This involves recording all relevant transactions and generating all supporting documents for legally-required financial statements, such as balance sheets and profit and loss statements.Computer typeThe R/3 system supports various computer types of SAP's platform partners, such as Bull, DEC, IBM and HP. The suitability of a particular computer type depends on sufficient CPU performance.Common Programming Interface-CommunicationsCommon CPI-C Programming Interface of Communication has been introduced by IBM as a high-level interface to SNA/LU6-2. CPI-C has become the subject of the X/Open standardization and is used by SAP to facilitateprogram-to-program communication between R/3 and external system. SAP offers CPI-C libraries based on TCP/IP. Correction It contains all the objects that a developer has changed or created. It also controls customizing that has been maintained.CSPA system to help SAP employees to give comprehensive support to their clients.Data Base ServerThe data base server stores the SAP application programs and data in the R/3 client/server concept. It also handles the SAP update program and batch jobs.Direct InputA recent technique to input data safely. It ensures application data integrity for background interfaces. See also batch input.DispatcherThe system R/3 agent that identifies the type of task (on-line, update, batch, etc.) and sends the job to an idle work process.EarlyWatchIt is a service that entails having your R/3 installation regularly inspected by SAP employees, in other to ensure high system availability and high data throughput at all time.EthernetIt is a LAN architecture using bus topology. The transmission speed is 10 MBit/s.FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interchange)It is a local high-speed network with ring topology based on light wave conductors. The transmission speed is 100 MBit/s.Field statusIndicator that specifies whether a field can take an entry in the entry screen or if it must be filled.FirewallIt is a means of controlling access through a public network to a private network.FTP (File Transfer Protocol)It is the most commonly used file transmission protocol of the TCP/IP protocol family.GUI (Graphic User Interface)A graphical interface used by SAP environment as part of the three tiers. It is normally called user frontend.IDES (International Demonstration and Education System) It is a model of an international firm. It is a separate demonstration and education system for speeding up the pilot process. IMG (Implementation Management Guide) It is a hierarchical structure that reflects the R/3 component hierarchy and contains every configuration activity. Released from version 3.0 onwards. Instance It means application server and each one has its own set of work processes.IDoc (Intermediate Document)An IDoc is a data container for data exchange between SAP systems or between an SAP system and an external system.ITS (Internet Transaction Server)It links the R/3 application server with one or more Web servers, thus enabling the R/3 to communicate with the Internet.KernelIt means a standard core previously configured. A set of default parameters delivered with the system.LAN (Local Area Network)It is a network for a a tightly limited area with high level data transmission performance. Common LANs include Ethernet, Token Ring and FDDI. These LANs support different transport protocols, such as TCP/IP and IPX.MatchcodeA tool for finding specific records. It is made up of search terms. It is used to find possible entries for an input field.Number rangeA range of numbers that are laid down per file for the assignment of document numbers. It can be internal (carried out automatically by the system) or external (carried out manually by the user).OLEIt is a technique introduced by Microsoft to incorporate objects of one application into another.OSS (Online Service System)SAP's Online Service System offers fast and effective help for R/3 System problems. It is also the basic element of communications between customers, partners, and SAP.RepairIt contains all the objects that a developer has changed but the originals of the objects are located in another system.RFCA way to implement communication between application programs via Abap/4 function call.SemaphoresWhen a work process locks a resource, it sets a semaphore. Another work process that also wants to access it must then wait.SysIDA set of three letters or number that identify a system. Some sets are not allowed because they are used by SAP. They are informed when the system is installed.TCP/IPIt is the most widely used transport protocol for open systems. R/3 clients and servers communicate using TCP/IP.TelnetIt provides terminal access to hosts using TCP/IP protocol. It is a well-known command among System Administrators.Token RingIt is a LAN architecture with ring topology. The transmission speed is 4 MBit/s or 16 MBit/s. This involves a 'free token' which circles the loop picking up transmissions. The receiver station places a confirmation bit into the busy token. As soon as the busy token reaches the sender station again, it is converted back to a free token and sent on to the next station.TransportIt is a request to transport objects from the software development environment, identified as the source system, to the specified target system.WAN (Wide Area Networks)They are normally operated either by the telephone company or by private companies that offer leased lines, switched lines or packet lines.Work processWork processes perform the bulk of the processing carried out by SAP systems. They perform dialog steps in user transactions and carry out updates, lock management, printing services, and so on.WorkbenchThe ABAP/4 Workbench, a graphical programming environment, is used to create application programs. The programming tools are accessed using buttons, dialogs and windows.WorkflowIt consists of time and logical sequence of work items, which are processed by human agents or mechanical processing units.X.25It is a standardized network access protocol for the packet switching network. The maximum transmission speed is 64 KBit/s.美文欣赏1、走过春的田野,趟过夏的激流,来到秋天就是安静祥和的世界。
SAP系统术语SAP (Systems, Applications and Products in Data Processing) GlossaryInformation Technology has many key words and SAP R/3 has introduced many others. In order to understand the field of SAP even better you should keep those terms in mind.ALE (Application Link Enabling)It provides integration for separate R/3 systems, keeping full interaction. This makes possible distributed enterprise applications.Application serverThe application server is used to run the business application programs in the R/3 client/server concept. The application modules are loaded from the data base server to the application server as required. Thus the application server requires only storage capacity to accommodate UNIX, Swapping and the SAP runtime environment.Batch InputA technique to input data safely. It ensures application data integrity for background interfaces. It pretends to be someone typing. See also direct input.CATT (Computer Aided Test Tool) It allows you to combine and automate sequences of repeatable transactions in test procedures. CATT reduces the number of manual tests, and forces you to test systematically, defining input values and expected test results.CCMS (Computer Center Management System)It allows you to monitor, control and configure your R/3 system. This toolset lets you analyze and distribute clientworkloads and report on resource consumption for system components. Central SystemIn an R/3 central system, both application and data base software are run on one computer.ClientIn commercial, organizational and technical terms, a self-contained unit in an R/3 system with separate master records and its own set of tables.Client/Server SystemClient/server systems are structured modularly, with components working in a sender/receiver relationship. Software components can also be used in a client/server relationship.Communication ServerIt provides the connection between local area and wide area networks and may be either a router, a bridge or a gateway. In R/3 installations, the communication server must support the TCP/IP protocol over wide area networks.Company codeThe smallest organizational unit for which a complete self-contained set of accounts can be drawn up for purposes of external reporting. This involves recording all relevant transactions and generating all supporting documents for legally-required financial statements, such as balance sheets and profit and loss statements.Computer typeThe R/3 system supports various computer types of SAP's platform partners, such as Bull, DEC, IBM and HP. The suitability of a particular computer type depends on sufficient CPU performance.Common Programming Interface-CommunicationsCommon CPI-C Programming Interface of Communication has been introduced by IBM as a high-level interface to SNA/LU6-2. CPI-C has become the subject of the X/Open standardization and is used by SAP to facilitateprogram-to-program communication between R/3 and external system. SAP offers CPI-C libraries based on TCP/IP. Correction It contains all the objects that a developer has changed or created. It also controls customizing that has been maintained.CSPA system to help SAP employees to give comprehensive support to their clients.Data Base ServerThe data base server stores the SAP application programs and data in the R/3 client/server concept. It also handles the SAP update program and batch jobs.Direct InputA recent technique to input data safely. It ensures application data integrity for background interfaces. See also batch input.The system R/3 agent that identifies the type of task (on-line, update, batch, etc.) and sends the job to an idle work process.EarlyWatchIt is a service that entails having your R/3 installation regularly inspected by SAP employees, in other to ensure high system availability and high data throughput at all time.EthernetIt is a LAN architecture using bus topology. The transmission speed is 10 MBit/s.FDDI (Fiber Distributed Data Interchange)It is a local high-speed network with ring topology based onlight wave conductors. The transmission speed is 100 MBit/s.Field statusIndicator that specifies whether a field can take an entry in the entry screen or if it must be filled.FirewallIt is a means of controlling access through a public network to a private network.FTP (File Transfer Protocol)It is the most commonly used file transmission protocol of the TCP/IP protocol family.GUI (Graphic User Interface)user frontend.IDES (International Demonstration and Education System) It is a model of an international firm. It is a separate demonstration and education system for speeding up the pilot process. IMG (Implementation Management Guide) It is a hierarchical structure that reflects the R/3 component hierarchy and contains every configuration activity. Released from version 3.0 onwards. Instance It means application server and each one has its own set of work processes.IDoc (Intermediate Document)An IDoc is a data container for data exchange between SAP systems or between an SAP system and an external system.ITS (Internet Transaction Server)It links the R/3 application server with one or more Web servers, thus enabling the R/3 to communicate with the Internet.KernelIt means a standard core previously configured. A set of default parameters delivered with the system.LAN (Local Area Network)It is a network for a a tightly limited area with high level data transmission performance. Common LANs include Ethernet, Token Ring and FDDI. These LANs support different transport protocols, such as TCP/IP and IPX.MatchcodeA tool for finding specific records. It is made up of search terms. It is used to find possible entries for an input field.Number rangeA range of numbers that are laid down per file for the assignment of document numbers. It can be internal (carried out automatically by the system) or external (carried out manually by the user).OLEIt is a technique introduced by Microsoft to incorporate objects of one application into another.OSS (Online Service System)SAP's Online Service System offers fast and effective help for R/3 System problems. It is also the basic element of communications between customers, partners, and SAP.RepairIt contains all the objects that a developer has changed but the originals of the objects are located in another system.RFCA way to implement communication between application programs via Abap/4 function call.Semaphoreswants to access it must then wait.SysIDA set of three letters or number that identify a system. Some sets are not allowed because they are used by SAP. They areinformed when the system is installed.TCP/IPIt is the most widely used transport protocol for open systems. R/3 clients and servers communicate using TCP/IP.TelnetIt provides terminal access to hosts using TCP/IP protocol. It is a well-known command among System Administrators.Token RingIt is a LAN architecture with ring topology. The transmission speed is 4 MBit/s or 16 MBit/s. This involves a 'free token' which circles the loop picking up transmissions. The receiver station places a confirmation bit into the busy token. As soon as the busy token reaches the sender station again, it is converted back to a free token and sent on to the next station.TransportIt is a request to transport objects from the software development environment, identified as the source system, to the specified target system.They are normally operated either by the telephone company or by private companies that offer leased lines, switched lines or packet lines.Work processWork processes perform the bulk of the processing carried out by SAP systems. They perform dialog steps in user transactions and carry out updates, lock management, printing services, and so on.WorkbenchThe ABAP/4 Workbench, a graphical programming environment, is used to create application programs. The programming tools are accessed using buttons, dialogs andwindows.WorkflowIt consists of time and logical sequence of work items, which are processed by human agents or mechanical processing units.X.25It is a standardized network access protocol for the packet switching network. The maximum transmission speed is 64 KBit/s.==============================。