第二章 汽车纵向动力学(20090925制动)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:2.32 MB
- 文档页数:43
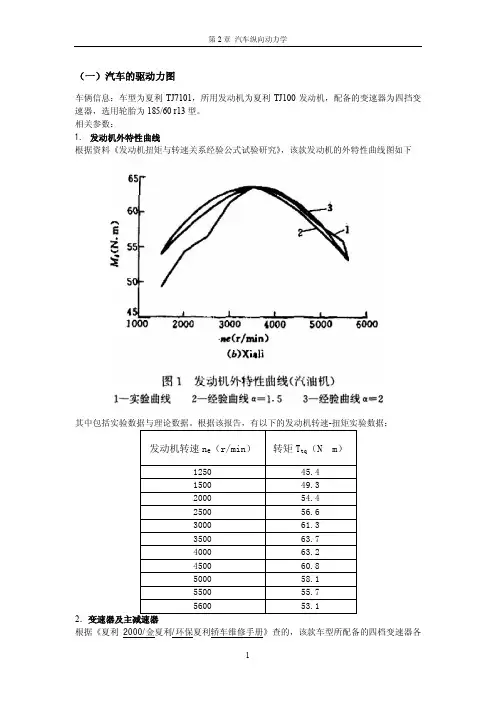






Internal Combustion Engine&Parts・23・汽车纵向动力学研究综述Research Progress of Automobile Longitudinal Dynamics于旺YU Wang(沈阳理工大学汽车与交通学院车辆工程专业,沈阳110159)(Vehicle Engineering,School of Automobile and Transportation,Shenyang University of Technology,Shenyang110159,China)摘要:随着汽车工业的发展,汽车纵向动力学研究不断加深,汽车在道路上行驶,就会存在驱动、制动、滑移等纵向动力学方面的问题。
针对这一问题的研究,人们提出了汽车纵向动力学的概念。
汽车纵向动力学的研究主要包括:汽车制动动力学、汽车防抱死系统、汽车驱动防滑系统、汽车自适应巡航系统、汽车自动刹车系统。
本文将主要介绍汽车纵向动力学控制系统组成和原理、汽车制动动力学控制系统的研究进展、汽车防抱死系统的研究进展、汽车驱动防滑系统的研究进展、汽车自适应巡航控制系统的研究进展、汽车自动刹车辅助系统的研究进展。
Abstract:With the development of the automotive industry,the research on the longitudinal dynamics of automobiles has continued to deepen,and there are problems with longitudinal dynamics such as driving,braking,and slipping when the car is driving on the road.In view of this problem,people have proposed the concept of automobile longitudinal dynamics.The research of automobile longitudinal dynamics mainly includes:automobile braking dynamics,automobile anti-lock braking system,automobile driving anti-skid system, automobile adaptive cruise system,automobile automatic braking system.This article will mainly introduce the composition and principle of automotive longitudinal dynamics control system,the research progress of automotive brake dynamics control system,the research progress of automotive anti-lock system,the research progress of automotive drive anti-skid system,the research of automotive adaptive cruise control system Progress,research progress of auto brake assist systems.关键词:汽车;纵向动力学;防抱死;驱动防滑;制动动力学;自适应巡航;自动刹车;系统Key words:automobile;longitudinal dynamics;anti-lock braking;driving anti-skid;braking dynamics;adaptive cruise;automatic braking;system中图分类号:U469.72文献标识码:A文章编号:1674-957X(2020)24-0023-020引言目前城市的发展和道路的优化设计极大地考验了汽车在道路上的行驶性能,要想在现有的道路上道路上提高交通流量并控制交通事故的发生,这就要求汽车设计者能在提高汽车安全行驶的车速和减小汽车与前后车之间的距离(但能有足够的安全距离)的同时能够保证汽车的各方面的稳定性能。

摘要由于石油等燃料属于不可再生能源,而如今汽车的保有量一直呈现增长趋势,因此电动汽车技术成为解决能源与环境危机的必然发展趋势。
相对于集中式驱动电动汽车,分布式驱动的传动方式可以明显体现出更加良好的动力学操控性,高传动效率以及简化的系统结构,于是分布式驱动电动汽车逐渐开始变成研究热点。
本文以四轮独立驱动电动汽车为研究对象,对纵向动力学控制进行研究。
利用分布式驱动汽车四轮转矩可独立控制的特点,考虑轮胎的动态特性和制动系统执行器的动态特性,基于分层控制理念,利用先进控制分配技术,实现车辆的稳定性控制并提高控制性能。
主要完成了以下研究工作:(1)建立了整车动力学模型,并搭建了CarSim/Simulink联合仿真平台。
利用CarSim软件搭建了模块化的整车动力学模型,并根据控制模型需求,配置了CarSim与MATLAB/Simulink软件之间的I/O口,完成整车模型与控制器模型的连接。
(2)基于逆轮胎模型设计了稳态车轮滑移率控制策略。
首先基于带约束的优化分配方法将目标纵向轮胎力进行分配,然后通过Dugoff逆轮胎模型求出目标滑移率,再利用滑模控制(Sliding Mode Control,SMC)对目标滑移率进行跟踪控制。
最后对基于逆轮胎模型的轮胎力控制分配效果与不考虑轮胎动态特性的轮胎力控制分配效果进行了仿真对比。
结果表明,本文所提出的考虑轮胎动态特性,基于逆轮胎模型,通过滑移率控制进行轮胎力控制分配的策略,有效地提高了轮胎力的控制精度,轮胎力绝对误差至少降低了51.10%。
(3)基于执行器动态控制分配方法设计了极限工况下的滑移率控制策略。
首先在上层控制器中通过滑模控制跟踪滑移率,防止车轮出现滑转和抱死,得到驱动防滑控制(Acceleration Slip Regulation,ASR)转矩和制动防抱死控制(Anti-lock Braking System,ABS)转矩。
然后在制动工况下,下层控制器考虑电机和液压制动系统的动态特性,基于模型预测控制(Model Predictive Control,MPC)动态分配的方法,对电机和机械制动进行转矩分配,实现复合制动。


