2010-2011学年英语国家概况教案
- 格式:doc
- 大小:128.00 KB
- 文档页数:23

英语国家概况范文《英语国家概况》课程标准一、课程定位《英语国家概况》是高职应用英语专业学生的专业知识必修课。
本课程的设置是为了使学生了解英美等几个主要英语国家的地理、历史、经济、政治等方面的概况,了解英语国家的文化传统、风俗习惯和社会生活的其它情况,以提高学生对文化差异的敏感性、宽容性和处理文化差异的灵活性,培养学生的跨文化交际能力;加深对语言的理解,提高分析和批判的能力;提高学生的思想道德素质、文化素质和心理素质。
为学生毕业后所从事的中小学英语教学工作打下扎实的英语文化根底知识和英语语言应用能力。
前导课程是《语音》课程、《精读》、《听说》等语言根底课程,通过这些课程的学习使学生具备扎实的英语听、说、读等根本功底,掌握英语的根本知识、为《英语国家概况》的学习打下根底。
后续课程是《商务礼仪》、《英美文学》和《英美文学欣赏》。
二、课程教学目标本课程的教学目标是使本专业学生了解六个主要英语国家的地理、历史、经济、政治等方面的概况,了解英语国家的文化传统、风俗习惯和社会生活的其它情况,使学生养成不断联系当前实际,密切关注国际局势的习惯,并能迅速准确地查阅资料,在储藏丰富背景知识的同时,稳固和提高英语水平。
1、知识目标:系统了解英美国家的地理、历史、政治、经济、文化等知识。
理解和掌握英美国家重要历史变革、重要人物、政治体制、经济政策。
分析中西文化的差异,深刻理解洋为中用,求同存异的思想。
2、能力目标:进一步扎实学生的英语根底,扩大词汇量,扩大阅读量,用英语进展展示和演讲,学以致用,加强语言表达的流利性和准确性。
能运用英语讨论和讲解地理、历史等相关的学科知识。
能运用英语分析和阐述与生活严密相关的政治、经济和文化等问题,培养良好的思辨能力。
3、素质目标:增强学生们对文化差异的敏感性和宽容性,及处理这些文化差异的灵活性。
渗透了积极向上的西方人文思想,有利提升学生的人文素养,培养学生独立自信、诚信守法、回报社会的良好操守。

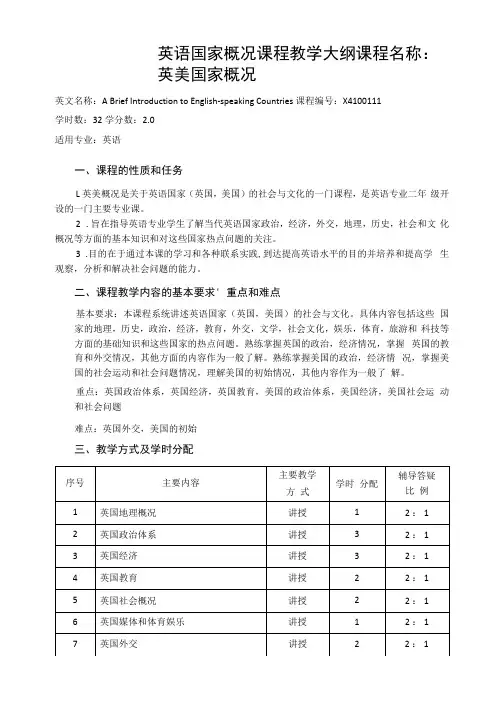
英语国家概况课程教学大纲课程名称:英美国家概况英文名称:A Brief Introduction to English-speaking Countries课程编号:X4100111学时数:32学分数:2.0适用专业:英语一、课程的性质和任务L英美概况是关于英语国家(英国,美国)的社会与文化的一门课程,是英语专业二年级开设的一门主要专业课。
2.旨在指导英语专业学生了解当代英语国家政治,经济,外交,地理,历史,社会和文化概况等方面的基本知识和对这些国家热点问题的关注。
3.目的在于通过本课的学习和各种联系实践,到达提高英语水平的目的并培养和提高学生观察,分析和解决社会问题的能力。
二、课程教学内容的基本要求' 重点和难点基本要求:本课程系统讲述英语国家(英国,美国)的社会与文化。
具体内容包括这些国家的地理,历史,政治,经济,教育,外交,文学,社会文化,娱乐,体育,旅游和科技等方面的基础知识和这些国家的热点问题。
熟练掌握英国的政治,经济情况,掌握英国的教育和外交情况,其他方面的内容作为一般了解。
熟练掌握美国的政治,经济情况,掌握美国的社会运动和社会问题情况,理解美国的初始情况,其他内容作为一般了解。
重点:英国政治体系,英国经济,英国教育,美国的政治体系,美国经济,美国社会运动和社会问题难点:英国外交,美国的初始三、教学方式及学时分配四、课程其他教学环节的要求.要求改变以教师为中心的教学模式,注重培养学生的学习能力和研究能力,采用多种教学方式,除课堂教学外还要安排学生看录像片和相关书籍,布置讨论题目。
1.学生要主动,全面的预习课文,积极配合教师完成课堂教学,课后要阅读相关书籍报纸杂志关于英国和美国的热点新闻,扩展知识面,能积极思考,参与讨论,并能提出问题。
最后做出全面的复习。
五,本课程与其他课程的联系先修课程:综合英语(学生在对英美国家的社会文化背景有了初步的了解之后可以更好的学习掌握英美概况的相关知识)后续课程:英美文学(对英美国家概况知识有了充分的了解之后才能更好的学习英美文学)六'教学参考书目《英语国家社会文化与入门》上下册朱永涛主编高等教育出版社1998年1月第一版《英美文化基础教程学习手册》朱永涛主编外语教学与研究出版社1994年6月第一版《英美文化辞典》胡文仲主编外研社1995年10月第一版《世界文化史故事大系》英国卷毕继万主编上海外语教育出版社2003年2月第一版《世界文化史故事大系》美国卷倪世雄乔长森主编上海外语教育出版社2003年2月第一版。



英语国家概况》课程实施细则《英语国家概况》(上)课程实施细则一、教学建议本教材课文并非按语言难易循序渐进,而是按内容编写。
教学的重点是帮助学生了解英美国家的政治、历史、地理、社会、文化、教育等概况。
以阅读和理解为主,语法分析和语言点的掌握不作要求。
学习的重点以书后的Focal Points和练习为主。
要求学生能将每个章节所学的内容用英语进行概述。
二、教学进度两学期学完全书共二十四章。
上学期学完英国部分(共十二章),对澳新部分也应有所了解。
下学期学完美国部分(共十二章),对加拿大部分也应有所了解。
本课程以自学结合面授辅导,教师的面授辅导以讲解难点, 归纳重点、要点及课堂练习为主。
三、学习要点和考核目标第一编英国概况 The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland Introduction: The United Kingdom1.A complicated country with a complicated name2.The effects of its imperial past3.A member of the European Union4.A multiracial society5.Remarkable class, regional and economical differences6.Significant role of LondonChapter 1: Great Britain1.A cultural and economic dominance of England2.Invasion from the Roman empire3.Settlement of the Anglo-Saxons4.William the Conqueror5.Parliament's dominance over the throne6.Physical features of Scotland7.A cultural division between highland and lowland8.The battle of Bannockburn9.Independence of Scotland for 300 years10.Union with England in 170711.A strong Scottish identity12.A brief introduction of Wales13.A history of invasions14.Wale's unification with the UK15.Campaigns for independenceChapter 2: Northern Ireland1.Physical features of Northern Ireland2.Economy of Northern Ireland3.The Home Rule Bill4.The Easter Rising of 19165.The Sinn Fein Party6.The religious conflicts between the Irish and the British7.A partition of Ireland in 19218.Civil Rights Movement9.The presence of British soldiers on Northern Ireland since 196910.IRA's violence in the 1970s11.Bloody Sunday12.The collapse of the power-sharing13.Cooperation between the British and Irish governments Chapter3: The Government of the United Kingdom1.King Egbert2.Divine right of kings3.The civil war4.Charles I5.Roundheads6.Magna Carta7.The Great Council8.William of Orange9.The Bill of Rights of 168910.The Cabinet11.The prime minister12.George I13.The Constitution14.The power and the functions of the Parliament15.The roles of the monarch16.The house of Lords17.Life peers18.The House of CommonsChapter 4: Politics1. 1. The importance of general elections2. 2. The formation of the government3. 3. Vote of no confidence4. 4. The electoral campaigns5. 5. The procedure of general elections6. 6. The Conservative party and the Labour party7. 7. The Liberal Democrats8. 8. The National Health Service9. 9. Margaret Thatcher10. 10. John Major11. 11. Tony BlairChapter 5: The UK Economy1. 1. The privatization in the 1980s2. 2. The main sectors of the UK economy3. 3. Primary industries4. 4. Secondary industries5. 5. Tertiary/service industries6. 6. Agriculture7. 7. Energy production8. 8. The offshore oil industries9. 9. The manufacturing industry10. 10. The city of London11. 11. The London Stock Exchange12. 12. The aerospace industry13. 13. ConcordeChapter 6: British Literature1. 1. Early British literature concerned with Christianity2. 2. Beowulf3. 3. The Canterbury Tales by Geoffrey Chaucer4. 4. The stories of King Arthur and his knights5. 5. The development of drama in the Renaissance6. 6. William Shakespear7. 7. Characteristics of the Romance writers in the 19th century8. 8. The Brontes9. 9. Charles Dickens10. 10. Sir Walter Scott11. 11. Robert Louis Stevenson12. 12. Characteristics of the twentieth century literature13. 13. Modernism14. 14. Postmodernism15. 15. Joseph Conrad16. 16. Virginia Woolf17. 17. D.H. Lawrence18. 18. E.M. Foster19. 19. George Orwell20. 20. John FowlesChapter 7: Sports in Britain1. 1. Popular sports in Britain2. 2. The FA and the FA Cup3. 3. Wimbledon4. 4. Equestrianism5. 5. The Grand National6. 6. The Royal Ascot7. 7. Hunt saboteursChapter 8: British Holidays and Festivals1. 1. Christmas and its traditions2. 2. The Boxing Day and its traditions3. 3. Easter4. 4. Ramadan5. 5. Trooping the Colour6. 6. Bonfire Night (Guy Fawkes Night) and the traditions7. 7. Hogmanay8. 8. Halloween and the traditionsChapter 9: British Education System1. 1. The purpose of the British education system2. 2. The relationship between education and social class3. 3. The influence of the church on schooling4. 4. Comprehensive school5. 5. Grammar school6. 6. The national Curriculum7. 7. Public school8. 8. Open UniversityChapter 10: British Society: Housing, Class and Race1. 1. Owner-occupation2. 2. Four main types of British home3. 3. Class system in the British society4. 4. Upper middle-class and lower middle-class5. 5. The hereditary aristocracy6. 6. Oxbridge7. 7. Life peers8. 8. Ethnic relations in BritainChapter 11: British Foreign Relations1. 1. Active in setting up the United Nations2. 2. Foreign policy influenced by its history and geopolitical traits3. 3. A parliamentary democracy4. 4. Relations with other countries and organizationsChapter 12: The British Media1. 1. Popularity and functions of the media2. 2. British main newspapers3. 3. The tabloids4. 4. The broadcast media第二编澳大利亚概况 Australia1. 1. Land, people and history2. 2. The political life3. 3. Economy4. 4. The cultural and social life第三编新西兰概况 New Zealand1. 1. Land, people and history2. 2. Political system, education and economy英语国家概况》(下)课程实施细则一、教学建议本教材课文并非按语言难易循序渐进,而是按内容编写。



《英语国家概况》课程教学大纲A Survey of the English-speaking Countries课程负责人:宋力英执笔人:高丽娜编写日期:2012 年5 月课程编号:06010210课程类别:专业课课程性质:限选课学时:34(理论34)学分:1.5适用专业:英语一、课程教学目标及学生能达到的能力《英语国家概况》是一门集英语国家背景知识和英语语言知识为一体的英语专业必修课程,旨在向学生介绍主要英语国家的历史、社会和文化等背景知识,拓宽其知识面,帮助学生了解英、美国家的地理、历史、文化、社会生活与政治体系概貌,使学生从上述五个角度更加深刻地理解和掌握所学语言知识和技能,提高学生对文化差异的敏感性、宽容性和处理文化差异的灵活性,培养学生跨文化交际能力。
二、课程教学内容与基本要求Chapter 1 Philosophy of Western Civilization(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the outline of western philosophy, understand different trends and memorize important figures and historical facts.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the outline of western philosophy and understand its core values.2. Learn different trends and the representative philosophers.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The outline of western philosophy2. Greek rationalism,Plato and Aristotle3. Renaissance4. Modern trends难点:1. Greek rationalism and its influence on western culture2. Renaissance3. Pragmatism(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the structure of western philosophy and philosophers by PPT.2. Learning quotations of these philosophers and help students to understand their ideas.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§1-1 Introduction§1-2 Greek Rationalism§1-3 The Middle Ages§1-4 The Renaissance§1-5 Modern Philosophy§1-6 Modern Philosophical Trends§1-7 SummaryChapter 2 Geography of the United Kingdom(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the general features of British geography, the key feature --- water and four political regions, and memorize important terms and figures.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the general features of British geography and four political regions.2. Learn geographical history and the Commonwealth.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The general features of British geography2. Four political regions3. Water system4. The Commonwealth难点:1. Topography of the UK2. Geographical features of Scotland and England3. The geographical history(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the topography and four political regions by PPT.2. Helping students understand the features of British geography by a lot of pictures, evenvideos.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§2-1 Introduction§2-2 General Characteristics of the UK§2-3 Water: the Key Geographical Features§2-4 Geographical History§2-5 Surface Features and Geography --- by Political Region§2-6 Current Situation§2-7 CommonwealthChapter 3 History of the United Kingdom(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the course of British history and the basic historical facts, and memorize important terms and key points.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the basic historical facts about British history.2. Remember key figures and key points in British history.3. Learn and remember the terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The course of British history2. Major historical events: the Civil War, the Reformation, the Glorious Revolution, theIndustrial Revolution, the First and the Second World Wars.3. Important historical figures4. The definition of important terms难点:1. The bourgeois revolution and the Reformation2. The British Empire and its decline3. The definition of important terms(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the course of British history and major historical events.2. Understanding historical events by learning the life of the important historical figures.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§3-1 Prehistory to the Norman Conquest§3-2 The Making of a Nation: From the Norman Conquest to the Renaissance§3-3 The Tudors: Sea Power and Protestantism§3-4 Founding of the British Empire§3-5 England in Revolution: Representative and Constitutional Government§3-6 England in the Eighteenth Century: The Age of Reason§3-7 Napoleonic Wars and a Century of Slow Reforms§3-8 Nineteenth Century Imperialism§3-9 Twentieth-Century England: Crisis of IdentityChapter 4 British Economy(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the characteristics and development of British economy, understand the present economic policies and memorize important data.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the characteristics and system of British economy.2. Understanding economic dictators and basic economic structure.3. Memorize important data.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The characteristics and system of British economy2. The economic dictators and basic economic structure3. Taxation and other economic policies难点:1. Economic dictators2. Industrial structure3. Economic policies(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the structure of British economy and important economic dictators by pictures and charts.2. Helping students understand characteristics of British economy by examples of world-famous brands or products.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§4-1 Introduction§4-2 Highlights of Britain's Economic Development§4-3 Britain's Prosperity Today§4-4 Britain's Economic System: A Unique Mix§4-5 Consumer Expenditure§4-6 Industrial Structure and Output§4-7 International Trade§4-8 Taxation and Public Spending§4-9 Economic PolicyChapter 5 British Culture(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the meaning of culture and the characteristics of British culture. Remember the representatives and major schools in British art, literature and music.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the characteristics of British culture.2. Learn representatives and major schools in British art, literature, and music.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The outline of British culture2. British arts, media, literature, social customs, sports and religion3. Representatives and their achievements难点:1. British arts and literature2. Religion(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the components of British culture by PPT.2. Learn representatives and their achievements by pictures and videos.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§5-1 Introduction§5-2 The British People --- General Traits§5-3 Entertainment§5-4 ConclusionChapter 6 British Education(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the history and characteristics of British education, acknowledge a profile of British higher education and memorize important terms.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the history and characteristics of British education.2. Acknowledging the basic information of British higher education.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The history and characteristics of British education.2. The British higher education.难点:1. The history of Britain education2. Higher education and elite universities(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the history of British education using demonstrations and charts on PPT.2. Helping students grasp the outline of British higher education by introducing world-famous colleges and universities.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§6-1 Introduction§6-2 Medieval England---Church and Class§6-3 Renaissance Education§6-4 Eighteenth Century---What Is Correct English§6-5 Nineteenth Century---Class Struggle and Change§6-6 Twentieth Century---Reform, Socialism and Conservatism§6-7 ConclusionChapter 7 Geography of the United States(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the general features of American geography, the physiographic subdivisions, energy and mineral resources, and memorize important terms and figures.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the general features of American geography and physiographic subdivisions.2. Learn geographical history, energy and resources.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The general features of American geography2. Physiographic subdivisions3. Living patterns难点:1. Topography of the US2. Physiographic subdivisions3. The geographical history(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the topography and Physiographic subdivisions by PPT.2. Helping students understand the features of British geography by a lot of pictures, even videos.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§7-1 Introduction§7-2 Economic Activities§7-3 Rural, Suburban and Urban Living Patterns§7-4 Physiographic Subdivisions of the United States§7-5 Geologic Processes Shape the Nations Physical and Human Geography§7-6 Energy and Mineral Resources Required for a Modern Society§7-7 Summary: The United States---“A Land of Contrasts”Chapter 8 History of the United States(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the course of American history and the basic historical facts, and memorize important terms and key points.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the basic historical facts about American history.2. Remember key figures and key points in American history.3. Learn and remember the terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The course of American history2. Major historical events: the Independence War, the founding of the new nation, the Civil War, the Industrial Revolution, the First and the Second World Wars, the post-war period.3. Important historical figures4. The definition of important terms难点:1. The Independence War and the founding of the new nation.2. The Capitalism and Monopolies3. The definition of important terms(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the course of American history and major historical events.2. Understanding historical events by learning the life of the important historical figures.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§8-1 Introduction§8-2 Native Americans§8-3 Colonial North America§8-4 The Founding of the United States§8-5 Forming A New Nation§8-6 Nationalism and the Economy Westward Expansion§8-7 The Industrial Revolution and Social Reforms§8-8 The American Civil War and Reconstruction§8-9 Industrialization,Capitalism,and Monopolies§8-10 The United States Becomes a World Power§8-11 The Post World War I Period§8-12 World War Ⅱ§8-13 The Post World War Period (1945- 1989)§8-14 Modern Times§8-15 ConclusionChapter 9 Britain and American Government(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the basic structure and departments of British and American governments, the similarities and differences between the two governments, and memorize important terms and key points.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the basic structure of British and American governments.2. Understand the features and functions of departments in the governments.3. Learn and remember the terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The basic structure and departments of British and American governments2. The similarities and difference3. Important political figures4. The definition of important terms难点:1. The core principles and structure of British and American governments2. The Checks and Balances3. The definition of important terms(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the structure of British and American governments by charts.2. Understanding the checks and balances by charts.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§9-1 Introduction§9-2 Politics§9-3 Political Legitimacy§9-4 Absolutism and Constitutionalism§9-5 Democracy§9-6 Indirect or Representative Democracy§9-7 Elections§9-8 The Assembly Model§9-9 ConclusionChapter 10 The Economy of the United States(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the characteristics and development of American economy, understand the present economic policies and memorize important data.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the characteristics and system of American economy.2. Understanding economic dictators and basic economic structure.3. Memorize important data.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The characteristics and system of American economy2. The economic dictators and basic economic structure3. Taxation and other economic policies难点:1. Economic dictators2. Industrial structure3. Economic policies(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the structure of American economy and important economic dictators by pictures and charts.2. Helping students understand characteristics of British economy by examples of world-famous brands or products.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§10-1 Introduction§10-2 Introduction and Overview§10-3 History and Growth§10-4 Commercial and Nonprofit Firms§10-5 Households§10-6 Government and the Economy§10-7 International Trade§10-8 Problems and Challenges for the U.S. EconomyChapter 11 American Society(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the characteristics of American society, understand the social conventions and values, and memorize important data.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the characteristics of American society.2. Understanding conventions and values.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The characteristics and system of American society2. The conventions and values难点:1. The conventions and values2. Social problems3. Race and ethnicity(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the characteristics of American society and social conventions by pictures and charts.2. Helping students understand American values by instances and cases.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§11-1 Introduction§11-2 Individuals§11-3 Families§11-4 Groups§11-5 Organizations§11-6 Socioeconomic Classes, Status and Roles§11-7 Race and Ethnicity§11-8 Other Social IssuesChapter 12 American Culture(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the meaning of culture and the characteristics of American culture. Remember the features and main points in American food, manners and holidays.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the characteristics of American culture.2. Learn features and main points in American food, manners and holidays.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. The outline of American culture2. American food, manners and holidays, social customs, sports and religion难点:1. Materialism2. Religion3. Manners(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the components of American culture by PPT.2. Learn manners and holidays by pictures and videos.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§12-1 Introduction§12-2 Materialism and the Mass Media§12-3 Individual Style and Personal Rites of Passage§12-4 Manners§12-5 Food and Meals§12-6 Pets§12-7 Housing§12-8 Leisure Activities§12-9 HolidaysChapter 13 British Education(一)教学目的和任务Students should grasp the characteristics of American education, acknowledge a profile of American basic and higher education and memorize important terms.(二)教学基本要求1. Grasp the characteristics of American education.2. Acknowledging the basic information of American basic and higher education.3. Memorize important terms.(三)教学重点和难点重点:1. American basic education2. American higher education难点:1. The characteristics of Britain education2. Higher education and elite universities(四)教学建议与说明1. Presenting students with the characteristics of American education using demonstrations and charts on PPT.2. Helping students grasp the outline of American higher education by introducingworld-famous colleges and universities.3. Asking students to make a presentation.(五)教学内容§13-1 Introduction§13-2 Issues in American Basic Education§13-3 Higher Education§13-4 Conclusion三、习题、课程讨论及要求英美概况课程要求学生在课余进行英美国家文化相关资料搜索和整理,课堂授课以理论和知识讲授,学生讨论和总结汇报相结合的方式进行,学生还要通过一定的学习和广泛阅读完成对文化热点问题的相关学期论文。

课程名称:大学英语授课对象:非英语专业本科生课时:2课时教学目标:1. 了解主要英语国家的基本概况,包括历史、地理、政治、经济、文化等方面。
2. 提高学生的英语阅读理解能力、口语表达能力和跨文化交际能力。
3. 培养学生的自主学习能力和团队合作精神。
教学内容:1. 主要英语国家的地理位置和历史背景2. 主要英语国家的政治体制和经济制度3. 主要英语国家的文化特点和社会习俗教学步骤:一、导入1. 教师简要介绍英语国家的分布和重要性,激发学生的学习兴趣。
2. 提问:你们知道哪些英语国家?它们分别位于哪个洲?它们的历史背景是怎样的?二、课堂讲解1. 主要英语国家的地理位置和历史背景- 以地图展示主要英语国家的地理位置。
- 介绍英国、美国、加拿大、澳大利亚等主要英语国家的历史背景。
2. 主要英语国家的政治体制和经济制度- 介绍英国、美国、加拿大、澳大利亚等主要英语国家的政治体制(如君主立宪制、总统制等)。
- 介绍这些国家的经济制度(如市场经济、计划经济等)。
3. 主要英语国家的文化特点和社会习俗- 介绍英国、美国、加拿大、澳大利亚等主要英语国家的文化特点(如语言、宗教、艺术等)。
- 介绍这些国家的社会习俗(如节日、饮食、礼仪等)。
三、课堂活动1. 小组讨论:学生分组讨论各自感兴趣的主要英语国家,总结其特点。
2. 角色扮演:学生扮演不同国家的代表,进行跨文化交际活动。
四、课堂总结1. 教师总结本节课所学内容,强调重点和难点。
2. 鼓励学生课后自主学习,拓展知识面。
教学资源:1. 教科书:《大学英语国家概况》2. 地图:展示主要英语国家的地理位置。
3. 课件:展示主要英语国家的政治、经济、文化等方面的信息。
教学评价:1. 课堂参与度:观察学生在课堂活动中的表现,如讨论、角色扮演等。
2. 课后作业:检查学生课后自主学习的成果,如完成相关练习题、撰写心得体会等。
教学反思:1. 根据学生的学习情况和反馈,调整教学策略,提高教学效果。
Chapter 1 Introduction of UK Teaching Aims and Requirements: To make a short introduction to UK; To fully understand the details of the four parts of UK; To know something more about the important Ages of England, Scotland and Wales.
Teaching Importance: England and Scotland Teaching Periods: 4*50‟
Teaching Procedure: 1. Introduce all the important points in this chapter. 2. Explain them as detailed as possible. 3. Rationalism It refers to the belief that reason is the primary source of knowledge, and Human beings could understand Nature through reasoning because Nature followed rational laws.
1) Major Greek philosophers A. Thales (624-550 BC) a. He claimed that Nature is rational; therefore, human beings could use their reasoning abilities to understand Nature. b. He reasoned that water is the basis of everything. B. Anaximander (611-547 BC) a. He disagreed that water or any single substance could explain everything, but viewed the world in terms of opposites. b. He incorporated mathematical ideas to describe the world. C. Pythagoras (570-500 BC) Pythagorean theory (勾股定理); explaining the entire natural world with numbers. D. Heraclitus (535-475 BC) a. He introduced the concept of change as the only unchanging reality in the universe. b. He compared life to a flowing river: a person cannot step into the same river twice. c. Opposites are inherently connected. d. „Unity in opposition‟ created for perpetual change. E. Parmenides (515-440 BC) a. Change was an illusion. b. Human reasoning could discover the hidden universal truth(s) disguised by the facade of change. F. Democritus (460-390 BC) a. Everything in the universe obeys the laws of necessity; they are the result of mechanical laws. b. atomic theory, explaining that nothing actually changes. 2) Socrates, Aristotle, Plato A. Socrates (470-399 BC) a. He disagreed with the Sophists, and argued that some norms are universally valid and absolute. b. two types of knowledge: innate or a priori knowledge and empirical or a posteriori knowledge. c. question-and-answer technique, called the Socratic method. B. Plato (428-347 BC) a. There were a limited number of forms (ideas), transcending the sensory world. b. True, absolute and eternal knowledge must be a priori, or innate within human beings. c. Idealism: Mind over Matter—Human senses provide inexact concepts of things; only human reason can give us true knowledge about the world. d. the Republic—Every person could reach the highest level of wisdom and virtue possible in his society. C. Aristotle (385-323 BC) a. To Plato, the highest reality was gained through reason; to Aristotle, the highest reality was gained through the physical senses. b. Plato‟s motto was „Mind over Matter‟, but Aristotle‟s motto was „Matter over Mind‟. c. Reason depended on the senses. d. Four causes for why events occur in the natural world: material, efficient, formal and final. e. He founded the science of logic: syllogism. f. Geocentric theory: the earth was the center of the universe; women were „incomplete‟ men.
4. The Middle Ages/ the Medieval Period It is a thousand-year-feudal era which occurred between Antiquity and the Modern Age, when the Christian dominated Western Europe. a. Christianity b. Christians accepted some earlier ideas. c. religious interpretation/the study of theology
5. The Renaissance It refers to the rebirth of knowledge in Europe, particularly the rediscovery of the Greco-Roman texts, based on a new humanism which focused on Man and characterized by changes in all areas of human endeavor.
1) Rene Descartes (1596-1650) the father of modern Rationalism and the father of modern Western philosophy a. mathematical logic b. dualism c. „What am I?‟—I am a thinking, conscious being for as long as I am thinking. 2) John Locke (1632-1704) the modern father of Empiricism a. Reflection b. Nurture Vs Nature //concept of the blank mind c. corresponding theory d. some political views 3) David Hume (1711-1776) a. impressions & ideas b. concept of open mindedness c. the law of Causation 4) George Berkeley (1685-1753) a. Locke and Hume said that ideas come from the mind‟s reflection on the physical world; Berkeley argued that ideas come from the mind of a supernatural All-perceiver. b. The foundation of all scientific knowledge is sense experience.
6. Modern Philosophy 1) Immanuel Kant (1724-1804) Combining elements of both Rationalism and Empiricism into one new comprehensive system to explain how humans know the world. 2) Georg Hegel (1770-1831) a. paradoxical nature of change b. concept of dialectal change