新编简明英语语言学教程 翻译
- 格式:doc
- 大小:166.50 KB
- 文档页数:21




新编简明英语语⾔学教程Unit2PHONOLOGY1.Phonetics定义:①Phonetics is defined as the study of the phonic medium of language; it isconcerned with all the sounds that occur in the world’s languages.②A branch of linguistics which studies the characteristics of speech sounds and providesmethods for their description, classification and transcription.e.g. [p] bilabial, stop2.分为哪⼏个Cavity?---Speech organs①The pharyngeal cavity-the throat ②The oral cavity-the mouth ③The nasal cavity- thenose[m],[n],[?]3.The speech organs: ①lips唇; ②teeth齿;③teeth ridge(alveolus)齿龈;④hard palate硬腭;⑤soft palate(velum)软腭; ⑥uvula⼩⾆;⑦tip of tongue⾆尖; ⑧blade of tongue⾆⾯; ⑨back of tongue⾆根; ⑩vocal cords声带; 11pharyngeal cavity咽部; 12 nasal cavity⿐腔4.Broad transcription: used in dictionaries and teaching textbooks for general purposes, withoutdiacritics.This is the transcription normally used in dictionaries and teaching textbooks for general purposes.e.g. clear[ pit ]Narrow transcription: used by phonetician for careful study, with diacritics.This is the transcription needed and used by the phoneticians in their study of speech sounds.e.g. dark [ l ], aspirated [ p ]5.P206.P21The feature ‘unrounded ’ is usually omitted since all front vowels in English are unrounded. Corresponding to the distinction of long and short vowels is the distinction of tense and lax vowels. 7. P22Phonology studies the patterning of speech sounds, that is, the ways in which speech sounds form systems and patterns in human languages.Phonetics & phonology 对⽐⾳位学和语⾳学Both are concerned with the same aspect of language----the speech sounds. But they differ in their approach and focus.Phonetics is of general nature; it is interested in all the speech sounds used in all human languages; it aims to answer questions like: how they are produced, how they differ from each other, what phonetic features they have, how they can be classified, etc.Phonology aims to discover how speech sounds in a language form patterns and how these sounds are used to convey meaning in linguistic communication. 8. P23A phone ⾳素---- a phonetic unit or segment. The speech sounds we hear and produce during linguistic communication are all phones. Phones do not necessarily distinguish meaning, some do, some don’t . e.g. /p/: [p h ] [p]A phoneme ⾳位---- is a phonological unit; it is a unit of distinctive value; an abstract unit, not a particular sound, but it is represented by a certain phone in certain phonetic context. ?Allophones ⾳位变体---- the phones that can represent a phoneme in different phonetic[i:] [l] [?][e][?] [a][?][a:][u][u:] [??] [??] [?]environments.9.P24Phonemic contrast⾳位对⽐----different or distinctive phonemes are in phonemic contrast.Complementary distribution互补分布----allophones of the same phoneme are incomplementary distribution. They do not distinguish meaning. They occur in different phonetic contexts, e.g. dark [l] & clear [l], aspirated [p]Minimal pair最⼩对⽴集----when two different forms are identical (the same) in every wayexcept for one sound segment which occurs in the same place in the strings, the two sound combinations are said to form a minimal pair, e.g. beat, bit, bet, bat, boot, but, bait, bite, boat.10.P25Sequential rules ---- the rules that govern the combination of sounds in a particular language,e.g. in English, ‘k,b,i, I’might possibly form blik, klib, bilk, kilbIf a word begins with a [l] or a [r], then the next sound must be a vowel.If three consonants should cluster together at the beginning of a word, the combinationshould obey the following three rules, e.g. spring, strict, square, splendid, scream.a) the first phoneme must be /s/,b) the second phoneme must be /p/ or /t/ or /k/,c) the third phoneme must be /l/ or /r/ or /w/.10.. Suprasegmental features-超⾳段特征---the phonemic features that occur above the level ofthe segments ( larger than phoneme)11.P27The location of stress in English distinguishes meaning, e.g. a shift in stress in English may change the part of speech of a word.Similar alteration of stress also occurs between a compound noun and a phrase consisting ofthe same elements.复合词和名词词组之间的区别Compound: ‘blackbird; ‘greenhouse; ‘hotdog…noun phrase: black ‘bird; green ‘house; hot ‘dog…The meaning-distinctive role played by word stress is also manifested in the combinations of -ing forms and nouns: modifier:修饰语‘dining-room; ‘reading glasses;doer: ⾏为者swimming ‘fish; flying ‘plane…Sentence stress----the relative force given to the components of a sentence.12.P28⾳调Tones are pitch variations,which are caused by the differing rates of vibration of the vocal cords.The meaning-distinctive function of the tone is especially important in what we call tone languages. English is not a tone language. Our mother tongue Chinese is a typical tone language.e.g.ma 妈(level) ma ⿇(the second rise) ma 马(the third rise) ma 骂(the fourth fall)。

第10章语言习得10.1 复习笔记本章要点:1. Theories of child language acquisition儿童语言习得的理论2. Cognitive development in child language development儿童语言发展中的认知因素3. Language environment and the Critical Period Hypothesis语言环境和临界期假说4. Stages in child language development儿童语言发展的阶段5. Atypical development非典型发展本章考点:行为主义者预言习得观;语法天生主义者的习得观;语言环境和临界期假说。
本章内容索引:I. Theories of child language acquisition1. A behaviourist view of language acquisition2. An innatist view of language acquisition3. An interactionist view of language acquisitionII. Cognitive development in child language developmentIII. Language environment and the Critical Period HypothesisIV. Stages in child language development1. Phonological development2. Vocabulary development3. Grammatical development4. Pragmatic developmentV. Atypical developmentI. Theories of child language acquisition(儿童语言习得的理论)1. A behaviourist view of language acquisition(行为主义者的语言习得观)(1) Main content(主要观点)①A behaviourist view of language acquisition Traditional behaviorists view language as behavior and believe that language learning is simply a matter of imitation and habit formation. A child imitates the sounds and patterns of the people around him; people recognize the child’s attempts and reinforce the attempts by responding differently, the child repeats the right sounds or patterns to get the reward(reinforcement)②So imitation and practice are preliminary, discrimination and generalization are key to language development in this theory. Imitation: word for word repetitionof all or part of an utterance.①传统的行为主义者把语言看作是行为,并且相信语言学习仅仅只是一个模仿和习惯形成的问题。

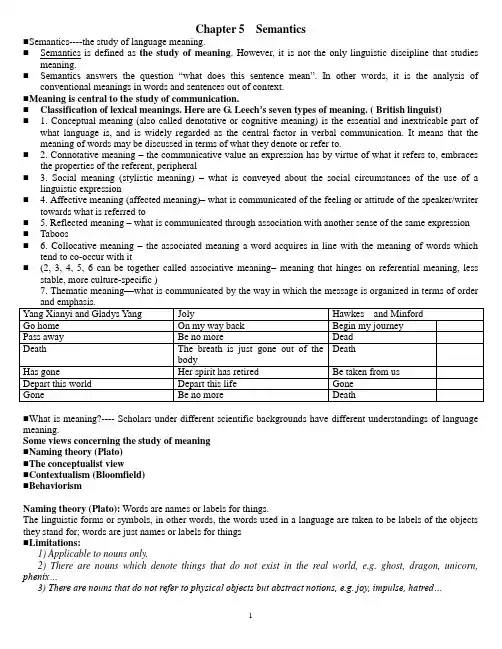
Chapter 5 Semantics⏹Semantics----the study of language meaning.⏹Semantics is defined as the study of meaning. However, it is not the only linguistic discipline that studiesmeaning.⏹Semantics answers the question “what does this sentence mean”. In other w ords, it is the analysis ofconventional meanings in words and sentences out of context.⏹Meaning is central to the study of communication.⏹Classification of lexical meanings. Here are G. Leech’s seven types of meaning. ( British linguist)⏹ 1. Conceptual meaning (also called denotative or cognitive meaning) is the essential and inextricable part ofwhat language is, and is widely regarded as the central factor in verbal communication. It means that the meaning of words may be discussed in terms of what they denote or refer to.⏹ 2. Connotative meaning – the communicative value an expression has by virtue of what it refers to, embracesthe properties of the referent, peripheral⏹ 3. Social meaning (stylistic meaning) –what is conveyed about the social circumstances of the use of alinguistic expression⏹ 4. Affective meaning (affected meaning)– what is communicated of the feeling or attitude of the speaker/writertowards what is referred to⏹ 5. Reflected meaning – what is communicated through association with another sense of the same expression ⏹Taboos⏹ 6. Collocative meaning – the associated meaning a word acquires in line with the meaning of words whichtend to co-occur with it⏹(2, 3, 4, 5, 6 can be together called associative meaning–meaning that hinges on referential meaning, lessstable, more culture-specific )7. Thematic meaning—what is communicated by the way in which the message is organized in terms of order⏹What is meaning?---- Scholars under different scientific backgrounds have different understandings of language meaning.Some views concerning the study of meaning⏹Naming theory (Plato)⏹The conceptualist view⏹Contextualism (Bloomfield)⏹BehaviorismNaming theory (Plato): Words are names or labels for things.The linguistic forms or symbols, in other words, the words used in a language are taken to be labels of the objects they stand for; words are just names or labels for things⏹Limitations:1) Applicable to nouns only.2) There are nouns which denote things that do not exist in the real world, e.g. ghost, dragon, unicorn, phenix…3) There are nouns that do not refer to physical objects but abstract notions, e.g. joy, impulse, hatred…The conceptualist view⏹The conceptualist view holds that there is no direct link between a linguistic form and what it refers to (i.e. between language and the real world); rather, in the interpretation of meaning they are linked through the mediation of concepts in the mind.⏹⏹The referent refers to the object in the world of experience;⏹Thought or reference refers to concept.⏹The symbol or a word signifies things by virtue of the concept associated with the form of the word in the minds of the speaker; and the concept looked at from this point of view is the meaning of the word.⏹Meaning should be studied in terms of situation, use, context—elements closely linked with language behavior. Two types of contexts are recognized:⏹Situational context: spatiotemporal situation⏹Linguistic context: the probability of a word’s c o-occurrence or collocation.⏹For example, “black” in black hair& black coffee,or black sheep differs in meaning; “The president of the United States” can mean either the president or presidency in different situation.calls forth in the hearer⏹Behaviorists attempted to define meaning as “the situation in which the speaker utters it and the response it calls forth in the hearer”.⏹The story of Jack and Jill:Jill JackS_________r--------s_________RLexical meaning⏹Sense and reference are both concerned with the study of word meaning. They are two related but different aspects of meaning.⏹Sense---- is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form. It is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form; it is abstract and de-contextualized. It is the aspect of meaning dictionary compilers are interested in.⏹Reference----what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world; it deals with the relationship between thelinguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.⏹Linguistic expressions stand in a relation to the world. There are two aspects of meaning.⏹Reference is the relation by which a word picks out or identifies an entity in the world. But the referentialtheory fails to account for certain kinds of linguistic expression.⏹Some words are meaningful, but they identify no entities in the real world, such as the words dragon, phoenix,unicorn, and mermaid.⏹It is not possible for some words to find referent in the world, such as the words but, and, of, however, the, etc.⏹Speakers of English understand the meaning of a round triangle although there is no such graph.⏹Sense is the relation by which words stand in human mind. It is mental representation, the association withsomething in t he speaker’s or hearer’s mind. The study of meaning from the perspective of sense is called the representational approach.Note:⏹Linguistic forms having the same sense may have different references in different situations; on the other hand, there are also occasions, when linguistic forms with the same reference might differ in sense, e.g. the morning star and the evening star, rising sun in the morning and the sunset at dusk.Major sense relations⏹Synonymy, Antonymy, Polysemy, Homonymy, HyponymySynonymy⏹Synonymy refers to the sameness or close similarity of meaning. Words that are close in meaning are called synonyms.1) Dialectal synonyms---- synonyms used in different regional dialects, e.g. autumn - fall, biscuit - cracker, petrol –gasoline,lift/elevator, flat/apartment…2) Stylistic synonyms----synonyms differing in style, e.g. kid, child, offspring; start, begin, commence; gentleman/guy…3) Synonyms that differ in their emotive or evaluative meaning, e.g.collaborator- accomplice, attract/seduce4) Collocational synonyms, e.g. accuse…of, charge…with, rebuke…for; …5) Semantically different synonyms, e.g. amaze, astound,…◆Synonyms are frequently used in speaking and writing as a cohesive device. In order to avoidrepetition the writer/speaker needs to use a synonym to replace a word in the previous co-text whenhe/she wants to continue to address that idea. The synonyms together function to create cohesion ofthe text.Antonymy◆Antonyms are words which are opposite in meaning.⏹Gradable antonyms----there are often intermediate forms between the two members of a pair, e.g. old-young, hot-cold, tall-short, …⏹Complementary antonyms----the denial of one member of the pair implies the assertion of the other, e.g. alive-dead, male-female, …⏹Relational/ Reversal opposites----exhibits the reversal of the relationship between the two items, e.g. husband-wife, father-son, doctor-patient, buy-sell, let-rent, employer-employee, give-receive, above-below, … Gradable antonyms⏹Gradable antonyms ----there are often intermediate forms between the two members of a pair, e.g. old-young, hot-cold, tall-short, …Complementary antonyms⏹Complementary antonyms ----the denial of one member of the pair implies the assertion of the other, e.g. alive-dead, male-female, …⏹Antonymy is frequently utilized as a rhetorical resource in language use. Oxymoron and antithesis based onantonymy. Gradable antonyms may give rise to fuzziness.Polysemy⏹Polysemy----the same one word may have more than one meaning, e.g. “table” may mean:⏹A piece of furniture⏹All the people seated at a table⏹The food that is put on a table⏹A thin flat piece of stone, metal wood, etc.⏹Orderly arrangement of facts, figures, etc.Homonymy⏹Homonymy---- the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form, e.g. different words are identical in sound or spelling, or in both.⏹Homophone ---- when two words are identical in sound, e.g. rain-reign, night/knight, …⏹Homogragh ---- when two words are identical in spelling, e.g. tear(n.)-tear(v.), lead(n.)-lead(v.), …⏹Complete/full homonym---- when two words are identical in both sound and spelling, e.g. ball, bank, watch, scale, fast, …⏹Note: Rhetorically, homonyms are often used as puns.⏹A polysemic word is the result of the evolution of the primary meaning of the word (the etymology of the word); while complete homonyms are often brought into being by coincidence.Hyponymy⏹Hyponymy----the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word.⏹Superordinate: the word which is more general in meaning.⏹Hyponyms: the word which is more specific in meaning.⏹Co-hyponyms: hyponyms of the same superordinate.Hyponymy⏹Superordinate: flower⏹Hyponyms: rose, tulip, li ly, chrysanthemum, peony, narcissus, …⏹Superordinate: furniture⏹Hyponyms: bed, table, desk, dresser, wardrobe, sofa, …⏹This kind of vertical semantic relation links words in a hierarchical work.Sense relations between sentences⏹(1) X is synonymous with Y⏹(2) X is inconsistent with Y⏹(3) X entails Y⏹(4) X presupposes Y⏹(5) X is a contradiction⏹(6) X is semantically anomalousX is synonymous with Y⏹X: He was a bachelor all his life.Y: He never got married all his life.⏹X: The boy killed the cat.Y: The cat was killed by the boy.⏹If X is true, Y is true; if X is false, Y is false.X is inconsistent with Y⏹X: He is single.⏹Y: He has a wife.⏹X: This is my first visit to Beijing.⏹Y: I have been to Beijing twice.⏹If X is true, Y is false; if X is false, Y is true.X entails Y⏹X: John married a blond heiress.⏹Y: John married a blond.⏹X: Marry has been to Beijing.⏹Y: Marry has been to China.⏹Entailment is a relation of inclusion. If X entails Y, then the meaning of X is included in Y.⏹If X is true, Y is necessarily true; if X is false, Y may be true or false.X presupposes Y⏹X: His bike needs repairing.⏹Y: He has a bike.⏹Paul has given up smoking.⏹Paul once smoked.⏹If X is true, Y must be true; If X is false, Y is still true.X is a contradiction⏹*My unmarried sister is married to a bachelor.⏹*The orphan’s parents are pretty well-off.X is semantically anomalous⏹*The man is pregnant.⏹*The table has bad intentions.⏹*Sincerity shakes hands with the black apple.⏹Analysis of meaning :⏹Componential analysis⏹Predication analysis⏹Componential analysis⏹Componential analysis---- a way to analyze lexical meaning. The approach is based on the belief that the meaning of a word can be dissected into meaning components, called semantic features. For example,⏹Man: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, +ANIMATE, +MALE]⏹Boy: [+HUMAN, -ADULT, +ANIMATE, +MALE]⏹Woman: [+HUMAN, +ADULT, +ANIMATE, -MALE]⏹Girl: [+HUMAN, -ADULT, +ANIMATE, -MALE]⏹Father: +HUMAN +MALE +ADULT →PARENT⏹Daughter: +HUMAN –MALE 0ADULT ←PARENTPredication analysis⏹1) The meaning of a sentence is not to be worked out by adding up all the meanings of its component words, e.g “The dog bites the man”is semantically different from “The man bites the dog” though their components are exactly the same.⏹2) There are two aspects to sentence meaning: grammatical meaning and semantic meaning, e.g.⏹*Green clouds are sleeping furiously.⏹*Sincerity shook hands with the black apple.⏹Whether a sentence is semantically meaningful is governed by rules called selectional restrictions.⏹Predication analysis---- a way to analyze sentence meaning (British G. Leech).⏹Predication----the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence. A predication consists of argument(s) and predicate.⏹An argument is a logical participant in a predication, largely identical with the nominal elements in a sentence. ⏹A predicate is something said about an argument or it states the logical relation linking the arguments in a sentence.⏹According to the number of arguments contained in a predication, we may classify the predications into the following types:⏹One-place predication: smoke, grow, rise, run, …⏹Two-place predication: like, love, save, bite, beat,…⏹Three-place predication: give, sent, promise, call, …⏹No-place predication: It is hot.Predication analysis⏹Tom smokes.→ TOM (SMOKE)⏹The tree grows well.→ TREE (GROW)⏹The kids like apples.→ KIDS (LIKE) APPLE⏹I sent him a letter.→ I (SEND) HIM LETTERSupplementary Exercises to Chapter 5 SemanticsI. Decide whether each of the following statements is True or False:1. Dialectal synonyms can often be found in different regional dialects such as British English and American English but cannot be found within the variety itself, for example, within British English or American English.2. Sense is concerned with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience, while the reference deals with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form.3. Linguistic forms having the same sense may have different references in different situations.4. In semantics, meaning of language is considered as the intrinsic and inherent relation to the physical world of experience.5. Contextualism is based on the presumption that one can derive meaning from or reduce meaning to observable contexts.6. Behaviourists attempted to define the meaning of a language form as the situation in which the speaker utters it and the response it calls forth in the hearer.7. The meaning of a sentence is the sum total of the meanings of all its components.8. Most languages have sets of lexical items similar in meaning but ranked differently according to their degree of formality.9. “it is hot.” is a no-place predication because it contains no argument.10. In grammatical analysis, the sentence is taken to be the basic unit, but in semantic analysis of a sentence, the basic unit is predication, which is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence.II. Fill in each of the following blanks with one word which begins with the letter given:11. S________ can be defined as the study of meaning.12. The conceptualist view holds that there is no d______ link between a linguistic form and what it refers to.13. R______ means what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world; it deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience.14. Words that are close in meaning are called s________.15. When two words are identical in sound, but different in spelling and meaning, they are called h__________.16.R_________ opposites are pairs of words that exhibit the reversal of a relationship between the two items.17. C ____ analysis is based upon the belief that the meaning of a word can be divided into meaning components.18. Whether a sentence is semantically meaningful is governed by rules called s________ restrictions, which are constraints on what lexical items can go with what others.19. An a________ is a logical participant in a predication, largely identical with the nominal element(s) in a sentence.20. According to the n ____ theory of meaning, the words in a language are taken to be labels of the objects they stand for.III. There are four choices following each statement. Mark the choice that can best complete the statement:21. The naming theory is advanced by ________.A. PlatoB. BloomfieldC. Geoffrey LeechD. Firth22. “We shall know a word by the company it keeps.” This statement represents _______.A. the conceptualist viewB. contexutalismC. the naming theoryD.behaviourism23. Which of the following is not true?A. Sense is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form.B. Sense is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form.C. Sense is abstract and de-contextualized.D. Sense is the aspect of meaning dictionary compilers are not interested in.24. “Can I borrow your bike?” _______ “ You have a bike.”A. is synonymous withB. is inconsistent withC. entailsD. presupposes25. ___________ is a way in which the meaning of a word can be dissected into meaning components, called semantic features.A. Predication analysisB. Componential analysisC. Phonemic analysisD. Grammatical analysis26. “alive” and “dead” are ______________.A. gradable antonymsB. relational oppositesC. complementary antonymsD. None of the above27. _________ deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world ofexperience.A. ReferenceB. ConceptC. SemanticsD. Sense28. ___________ refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form.A. PolysemyB. SynonymyC. HomonymyD. Hyponymy29. Words that are close in meaning are called ______________.A. homonymsB. polysemyC. hyponymsD. synonyms30. The grammaticality of a sentence is governed by _______.A. grammatical rulesB. selectional restrictionsC. semantic rulesD. semantic featuresIV. Define the following terms:31. semantics 32. sense 33 . reference 34. synonymy35. polysemy 36. homonymy 37. homophones 38. Homographs39. complete homonyms 40. hyponymy 41.antonymy 42 componential analysis43.grammatical meaning 44. predication45. Argument 46. predicate47. Two-place predicationV. Answer the following questions:48. Why do we say that a meaning of a sentence is not the sum total of the meanings of all its components?49. What is componential analysis? Illustrate it with examples.50. How do you distinguish between entailment and presupposition in terms of truth values?51. How do you account for such sense relations between sentences as synonymous relation, inconsistent relation in terms of truth values?52. According to the way synonyms differ, how many groups can we classify synonyms into? Illustrate them with examples.53. What are the major views concerning the study of meaning? How they differ?Suggested answers to supplementary exercises:IV. Define the following terms:31. Semantics: Semantics can be simply defined as the study of meaning in language.32. Sense: Sense is concerned with the inherent meaning of the linguistic form. It is the collection of all the features of the linguistic form; it is abstract and de -contextualised.33. Reference: Reference means what a linguistic form refers to in the real, physical world; it deals with the relationship between the linguistic element and the non-linguistic world of experience34. Synonymy :Synonymy refers to the sameness or close similarity of meaning.35. Polysemy :Polysemy refers to the fact that the same one word may have more than one meaning.36. Homonymy :Homonymy refers to the phenomenon that words having different meanings have the same form,i.e. , different words are identical in sound or spelling, or in both.37. homophones :When two words are identical in sound, they are called homophones38. homographs :When two words are identical in spelling, they are homographs.39. complete homonyms.:When two words are identical in both sound and spelling, they are called complete homonyms.40.Hyponymy :Hyponymy refers to the sense relation between a more general, more inclusive word and a more specific word.41. Antonymy :Antonymy refers to the relation of oppositeness of meaning.42. Componential analysis : Componential analysis is a way to analyze word meaning. It was proposed by structural semanticists. The approach is based on the belief that the meaning of a -word can be divided into meaning components, which are called semantic features.43.The grammatical meaning : The grammatical meaning of a sentence refers to its grammaticality, i.e. , its grammatical well-formedness . The grammaticality of a sentence is governed by the grammatical rules of the language.44. predication :The predication is the abstraction of the meaning of a sentence.45. argument : An argument is a logical participant in a predication. It is generally identical with the nominal element (s) in a sentence.46. predicate : A predicate is something that is said about an argument or it states the logical relation linking the arguments in a sentence.47. two-place predication : A two-place predication is one which contains two arguments.Answer the following questions:48. Why do we say that a meaning of a sentence is not the sum total of the meanings of all its components?The meaning of a sentence is not the sum total of the meanings of all its components because it cannot be worked out by adding up all the meanings of its constituent words. For example;(A) The dog bit the man. (B) The man bit the dog.If the meaning of a sentence were the sum total of the meanings of all its components, then the above two sentences would have the same meaning. In fact they are different in meanings.As we know, there are two aspects to sentence meaning: grammatical meaning and semantic meaning. The grammatical meanings of “the dog” and “the man” in (A) are different from the grammatical meanings of “the dog” and “the man” in (B). The meaning of a sentence is the product of both lexical and grammatical meaning. It is the product of the meaning of the constituent words and of the grammatical constructions that relate one word syntagmatically to another.49. What is componential analysis? Illustrate it with examples.Componential analysis, proposed by structural semanticists, is a way to analyze word meaning. The approach is based on the belief that the meaning of a word can be divided into meaning components, which are called semantic features. Plus and minus signs are used to indicate whether a certain semantic feature is present or absent in the meaning of a word, and these feature symbols are usually written in capitalized letters. For example, the word “man” is ana lyzed as consisting of the semantic features of [+ HUMAN, + ADULT, + ANIMATE, +MALE]50. How do you distinguish between entailment and presupposition in terms of truth values?Entailment is a relation of inclusion. Suppose there are two sentences X and Y:X: He has been to France.Y: He has been to Europe.In terms of truth values, if X is true, Y is necessarily true, e.g. If he has been to France, he must have been to Europe.If X is false, Y may be true or false, e. g. If he has not been to France, he may still have been to Europe or he has not been to Europe. If Y is true, X may be true or false, e.g. If he has been to Europe, he may or may not have been to France.If Y is false, X is false, e.g. If he has not been to Europe, he cannot have been to France.Therefore we conclude that X entails Y or Y is an entailment of X.The truth conditions that we use to judge presupposition is as follows:Suppose there are two sentences X and YX: John' s bike needs repairing.Y: John has a bike.If X is true, Y must be true, e.g. If John' s bike needs repairing, John must have a bike.If X is false, Y is still true, e. g. If John' s bike does not need repairing, John still has a bike. If Y is true, X is either true or false, e.g. If John has a bike, it may or may not need repairing. If Y is false, no truth value can be said about X, e.g. If John does not have a bike, nothing can be said about whether his bike needs repairing or not. Therefore, X presupposes Y, or Y is a presupposition of X.51. How do you account for such sense relations between sentences as synonymous relation, inconsistent relation in terms of truth values?In terms of truth condition, of the two sentences X and Y, if X is true, Y is true; if X is false, Y is false, therefore X is synonymous with Ye.g. X; He was a bachelor all his life.Y: He never married all his life.Of the two sentences X and Y, if X is true, Y is false; if X is false, Y is true, then we can say A is inconsistent with Ye.g. X: John is married.Y: John is a bachelor.52. According to the ways synonyms differ, how many groups can we classify synonyms into? Illustrate them with examples.According to the ways synonyms differ, synonyms can be divided into the following groups.i. Dialectal synonymsThey are synonyms which are used in different regional dialects. British English and American English are the two major geographical varieties of the English language. For examples:British English American Englishautumn falllift elevatorThen dialectal synonyms can also be found within British, or American English itself. For example, "girl" is called "lass" or "lassie" in Scottish dialect, and "liquor" is called "whisky" in Irish dialect.ii. Stylistic synonymsThey are synonyms which differ in style or degree of formality. Some of the stylistic synonyms tend to be more formal, others tend to be casual, and still others are neutral in style. For example:old man, daddy, dad, father, male parentchap, pal, friend, companioniii. Synonyms that differ in their emotive or evaluative meaningThey are the words that have the same meaning but express different emotions of the user. The emotions of the user indicate the attitude or bias of the user toward what he is talking about . For example, “collaborator”and “accomplice”are synonymous, sharing the meaning of "a person who helps another", but they are different in their evaluative meaning. The former means that a person who helps another in doing something good, while the latter refers to a person who helps another in a criminal act.iv. Collocational synonymsThey are synonyms which differ in their collocation. For example, we can use accuse, charge, rebuke to say that someone has done something wrong or even criminal, but they are used with different prepositions accuse. . . of, charge. . . with, rebuke. . .for. v. V. Semantically different synonymsSemantically different synonyms refer to the synonyms that differ slightly in what they mean. For example, "amaze" and "astound" are very close in meaning to the word "surprise," but they have very subtle differences in meaning. While amaze suggests confusion and bewilderment, " astound" implies difficulty in believing. "53. What are the major views concerning the study of meaning? How do they differ?One of the oldest was the naming theory, proposed by the ancient Greek scholar Plato, who believed that the words used in a language are taken to be labels of the objects they stand for. The conceptualist view holds that there is no direct link between a linguistic form and what it refers to. The form and the meaning are linked through the mediation of concepts in the mind. Contextualism is based on the presumption that one can derive meaning from or reduce meaning to observable contexts. Two kinds of context are recognized; the situational context and the linguistic context.For example, the meaning of the word "seal" in the sentence "The seal could not be found" can only be determined according to the context in which the sentence occurs:The seal could not be found. The zoo keeper became worried.(seal meaning an aquatic mammal)The seal could not be found. The king became worried.(seal meaning the king's stamp)Behaviorism drew on behaviorist psychology when he tried to define the meaning of linguistic forms. Behaviorists attempted to define the meaning of a language form as " the situation in which the speaker utters it and the response it calls forth in the hearer".。

第1章导言1.1 复习笔记本章要点:1. The definition and main branches of linguistics study语言学的定义和研究的范围2. Important distinctions in Linguistics语言学的一些重要区分3. The definition and the design features of language语言的定义与识别特征4. Functions of language语言的功能本章考点:1. 有关语言学的常考考点语言学的定义;语言学中几组重要区别,每组两个概念的含义、区分及其意义;普通语言学的主要分支学科及各自的研究范畴;宏观语言学及应用语言学的主要分支及各自的研究范畴。
2. 有关语言的常考考点语言的定义;语言的识别特征(任意性、能产性、二重性、移位性、文化传递);语言的功能。
本章内容索引:I. The definition of linguisticsII. The scope of linguistics1. Micro-linguistics2. Macro-linguisticsIII. Some important distinctions in linguistics1. Descriptive vs. Prescriptive2. Synchronic vs. Diachronic3. Speech vs. Writing4. Langue vs. Parole5. Competence vs. Performance6. Traditional Grammar vs. Modern Linguistics IV. The definition of languageV. The design features of language1. Arbitrariness2. Productivity3. Duality4. Displacement5. Cultural Transmission6. InterchangeabilityVI. Functions of language1. Main functions2. Basic functions3. MacrofuntionsI. The definition of linguistics(语言学的定义)Linguistics is generally defined as the scientific study of language.It is a scientific study because it is based on the systematic investigation of linguistic data, conducted with reference to some general theory of language structure.语言学通常被定义为对语言进行科学性研究的学科。
1. 什么是语言学? 1.1定义 语言学常被定义为是对语言进行系统科学研究的学科。语言学研究的不是某一种特定的语言,而是人类所有的语言。为了揭示语言的本质,语言学家首先要对语言实际使用进行观察,并在此基础上形成有关语言使用的概括性假设,这些初步形成的假设要在语言使用中进行进一步的检验,最终形成一条语言理论。
1.2语言学的研究范畴: 语言学研究有不同的侧重。对语言体系作全面研究的语言学研究称为普通语言学。语音学主要是对语言声音媒介的研究,它不只是研究某一特定的语言的声音媒介,而是所有语言的声音媒介。音系学与语音学不同,它主要研究特定语言的语音体系,即音是如何结合在一起产生有意义的单位。形态学主要研究单词的内部语义结构,及这些叫做词素的语义最小单位是如何结合构成单词。句法学主要研究构成潜在句子的句法规则。语义学以研究语义为目的,传统语义学主要研究抽象的意义,独立于语境之外的意义,语用学也是研究语义,但是它把语义研究置于语言使用语境中加以研究。
语言不是一个孤立的现象,而是一种社会现象,各种社会因素都会对语言的使用产生影响。从社会的角度来研究语言的科学被称之为社会语言学。语言和社会之间的关系是社会语言学研究的主要内容。心理语言学主要从心理学的角度来研究语言。它要研究人们在使用语言时大脑的工作机理,如人是如何习得母语的,人的大脑是如何加工和记忆语言信息等问题。把语言学的研究成果应用到实践中的科学形成了应用语言学。狭义上,应用语言学指把语言理论和原则运用于语言教学的科学,在广义上,它指把语言理论与原则应用于解决实际问题的科学。除此之外还有人类语言学、神经语言学、数学语言学、计算语言学等。
1.3语言学研究中的几对基本概念 1.3.1规定性和描述性 语言学研究是描述性的,不是规定性的。这是语言学和传统语法的一个重要区别。语言学研究的目的是对人们使用的语言进行客观描述与分析,而不是对语言的使用作出规定。传统语法是规定性的,它主要建立在笔头语言基础之上,旨在规定一系列的语法规则,并且把这些语法规则强加给语言使用者。一切符合规定规则的被认为是“正确的”,否则就被冠为“错误的”。
1.3.2共时性和历时性 对语言的研究分为共时研究和历时研究。共时研究是对语言的静态特征的研究。它主要对某个时间点上的语言状态的描述。历时研究主要是对语言变化和发展的研究。现代语言学研究主要是共时性研究。
1.3.3口头语和书面语 现代语言学把书面语看作是口头语的记录,认为口头语是第一性的,是语言交际最基本的方式。这是因为从人类社会交际的发展来看,口头语先于笔头语,笔头语是对口头语的记录。从交际的功能来看,人们交际主要采取口头形式。此外,即使是在当今世界,仍然有不少语言只有口头形式,没有笔头形式。所以语言学研究的语料应从口头语中采集。传统语法学家过分重视笔头语料,轻视口头语料。 1.3.4语言和言语 语言和言语的区别是瑞士语言学家索绪尔在20世纪初提出来的。 语言是语言社区所有成员所共有的抽象的语言系统,是一个语言社区所有的人应该遵守的一套约定俗成的规则,它相对稳定,因此索绪尔指出语言学只能研究语言系统本身,既语言。言语是语言体系的实际使用,是具体的。它因人而异,千变万化,所以索绪尔认为无法对言语进行系统的研究。
1.3.5能力和运用 能力和运用的区别由乔姆斯基在20世纪50年代后期提出的。“能力”指一个理想的语言使用者所具有的语言规则的知识,它是一整套内在化语言使用者脑海中的语言规则。“使用”是“能力”的具体使用,是在交际活动中语言知识具体的体现。乔姆斯基认为,语言学家应该研究“能力”,揭示人脑中已经内在化的语言规则,而不是研究“使用”,因为“使用”会受到各种偶然因素的影响,如口误等,因而是不体系的。
乔姆斯基的能力和使用之分与索绪尔的语言和言语之分有其相似性,两人都强调把语言体系与语言的使用区分开来,但是索绪尔是从社会的角度来分析语言,把语言看成社会的约定,而乔姆斯基则是从心理学的角度出发,把语言看成是个人人脑的特性。
2.1语言的定义 语言学家对语言作了不同的定义, 比较普遍地为语言学家所接受的一个定义是“语言是一种用于人类交际的任意的语音符号系统。”这一定义包涵了语言的一些最重要的特征,即语言是一个受规则制约的体系,语言的符号是任意的,语言是有声的。
2.2语言的识别性特征 美国语言学家 C. Hockett提出了人类语言的 12种识别性特征,其中最重要的识别性特种有5种: 即语言的任意性、创造性、二重性、移位性和文化传递性。这些特征是所有人类语言所共有的。人类语言的识别性特征是动物“语言”所不具有的。
1) 任意性:它指音与义之间没有逻辑联系。比如说,不同的语言使用不同的音指相同的事物。 2) 创造性:语言的创造性主要表现在语言使用者能够以有限的语言规则为基础说出和理解无限的句子,包括他们以前从没有听说过的句子。
3) 二重性:它指语言在结构上存在两个层次:低层次和高层次。在低层次是一个个没有意义的音,如/p/,/g/,/i/等,但是这些处在低层次的没有意义的音可以依照一定的语言规则结合在一起形成语言体系的高层次,即:有意义的单位,如词素,单词等。
4) 移位性:移位性指人类可以使用语言来谈论过去的事情,现在的事情或将来的事情;语言也可以用来谈论我们客观世界中的事情,或假想世界中的事情。总之,语言的使用可以脱离交际的直接情景语境,从而不受语言时空距离的影响。
5) 文化传递性:文化的传递性是指,虽然人类习得语言的能力有遗传因素的原因,但是语言体系具体内容的习得不是通过遗传来传递的,而是要通过后天的学习来获得。
第 二 章 音系学 1. 语言的声音媒介 语言的形式有声音和文字。在这两种媒介中,声音是语言最基本的媒介,是第一性的。这是因为在语言的发展过程中,声音媒介早于文字。文字是对声音的记录。在日常交际中,大量信息是通过口头交际来完成的,只有在无法进行口头交际的情况下人们才使用文字形式。除此之外,人们是通过声音媒介来习得自己的母语的。
2. 语音学 2.1什么是语音学 语音学研究的对象是语言的声音媒介, 即人类语言中使用的全部语音。 语音学有三个分支:发声语音学、听觉语音学和声学语音学。它们各有自己的侧重点但又互有联系。发声语音学主要研究语言使用者是如何使用发音器官发出语音,并对所发出的音进行分类。听觉语音学主要是从受话人的角度来研究语音,即语音是如何被受话人感知和理解的。声学语音学主要研究语音的物理特性。通过对语音声波的研究,声学语音学家得出了一些重要的结论。最为重要的结论,所说出的这些通常被认为是同一个话语,如果从声音的物理特性上去分析,其实它们的声波并不相同,只是由于它们之间存在的差异太小,是人耳所不能辨别的。如果它们的声波相同,这只是一种巧合。因此,语音的等同只是一种理论上的理想。
2.2发音器官 人类的发音器官存在于咽腔、口腔和鼻腔腔内。 咽腔内最重要的发音器官是位于喉头的声带, 发音时声带在气流的冲击下发生颤动决定了声音的浊音化(voicing)。浊音化是所有元音以及部分辅音,如[b],[g],[m]等所具有的特性。声带不发生颤动所发出的音是清音,如[t],[k],[f]等。声带颤动的频率决定了声音的高低。口腔中发音器官最多,有舌头、小舌、软腭、硬腭、齿龈隆骨、牙齿和嘴唇。其中舌头是最灵活、最重要的发音器官。发音时,来自肺部的气流在口腔中受到不同的阻碍,从而发出不同的音。
鼻腔和口腔相通。发音时软腭后移关闭鼻腔,气流只能从口腔通过,所发出的音没有鼻音化。但当鼻腔通道打开,允许气流从鼻腔通过,所发出来的音便是鼻音。
2.3音标——宽式和严式标音法 音标是在国际上被广为接受的一套对语音进行标音的标准符号体系。标音分为宽式和严式标音法。宽式标音法是用一个符号来表示一个语音的标音方式。严式标音法是一种使用变音符号的标音方式,旨在记录同一个音在不同的语音环境下所发生的细微的变化,如在star和tar中的/t/的发音就不一样,前者/t/是不送气音,后者/t/是送气音。这些细微区别只有通过严式标音法才能表示。
2.4英语语音的分类 英语中的语音根据气流的受阻情况分为元音和辅音。气流没有受到任何阻碍所发出的音是元音;气流在口腔里受到不同方式的阻碍所发出的音是辅音。
2.4.1英语辅音的分类 根据发音方式,英语的辅音可以分为: 1) 爆破音:发爆破音时,气流开始完全受阻,然后突然释放,如[p],[b],[t],[d],[k],[g] 2) 摩擦音:发摩擦音时,气流部分受阻,气流从狭窄的通道挤出,产生摩擦,如[f],[v],[s],[z],[ θ],[ T ], [∫ ], [ V ], [h]
3) 塞擦音:发塞擦音时,气流开始完全受阻,然后气流从狭窄通道缓慢释放,并伴有摩擦发生,如:[t∫], [dV ]
4) 流音:在发流音时,受阻的气流从舌头与上部(roof of the mouth)形成的通道释放出,如:[l],[r]。
5) 鼻音:发音时,气流从鼻腔释放出所发出的音为鼻音,如[n],[m],[N ] 6) 滑音:滑音又称之为半元音。英语中滑音有[w]和[j]。它们的发音方式与[u]和[i]相同。 根据发音部位,英语辅音可以分为: 1) 双唇音:气流受阻部位在双唇,如[p],[b],[m],[w] 2) 唇齿音:下唇与上齿接触使气流受阻,如[f],[v] 3) 齿音:舌尖与上齿接触使气流受阻,如:[θ],[ T] 4) 齿龈音:舌尖与上齿龈隆骨接触使气流受阻,如:[t],[d],[s],[z],[n],[l],[r] 5) 腭音:受阻部位发生在舌根与硬腭之间,如:[∫], [ V],[ t∫ ], [dV ], [j] 6) 软腭音:舌根与软腭接触使气流受阻,如: [k], [g], [ N ] 7) 喉音:声带短时接触使气流受阻,如:[h] 元音与辅音不同,不能根据辅音的发音方式和发音部位来分类。元音常根据舌位的高低、开口度、嘴唇形状、元音的长度和发音时喉部的紧张程度来分类。
1) 舌位的高低 发音时,舌头前部抬得最高的音为前元音,通常有:[i:] [i] [e] [A] [a]. 发音时,舌头的中部抬得最高为中元音,如:[\:], [[],[Q] 发音时,舌根部位抬得最高为后元音,如:[u:] [J] [ C:], [ ]and [B:].
2) 开口度:根据开口度,通常把元音分为以下四种: 闭元音:如:[i:],[ i],[u:],[J] 半闭元音:如:[e], [з: ] 半开元音:如[ [ ], [ C: ]