干旱胁迫对移栽期烟草幼苗光合特性的影响
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:242.04 KB
- 文档页数:3



4个烟草品种干旱胁迫下萌发和苗期生理特性及抗旱性评价烟草是重要经济作物,在我国有较大种植面积。
在干旱胁迫下烟叶会出现水分亏缺,导致烟草产量降低,同时严重影响烟叶品质。
贵州是典型的岩溶高原山区,山高坡陡,岩溶地貌发育强烈,降雨后易产生径流流失,致使水分缺乏,常成为制约烟草种植和品质形成的主要因素,而耕地大多不连片、不平整,目前要实现大面积机械或自动灌溉都是不现实的,且改进耕作栽培方式也不能从根本上解决问题;因此,选育推广抗旱烟草品种是解决干旱威胁的一项经济有效的主要措施。
在烟草抗旱生理指标以及机理研究中,鉴定品种的抗旱性是首要工作,对选育耐旱性品种以减轻干旱危害具有重要意义。
Michel等发现聚乙二醇分子不进入种子,Khajeh-Hoe-seini等发现聚乙二醇没有毒性,所以聚乙二醇可以用来模拟干旱胁迫。
本研究利用15%的聚乙二醇(PEG-6000)溶液模拟干旱胁迫,探讨干旱胁迫对不同品种烟草种子萌发及生理指标的影响,为抗旱品种的筛选提供理论依据。
1.材料与方法1.1材料选用贵州省毕节地区主栽烟草品种毕纳1号、云烟87、韭菜坪2号和黔西1号这4个品种的种子。
种子由贵州省毕节市烟草公司提供。
1.2方法1.2.1种子萌发试验采用培养皿纸上发芽法,参照《国际种子检验规程》进行萌发试验。
将种子均匀置于铺有2层滤纸的培养皿(直径9cm)中发芽,培养皿分为2组,试验组每个培养皿中加入2mL15%PEG-6000作为渗透介质模拟干旱胁迫环境,对照组每个培养皿中加2mL蒸馏水代替2.结果与分析2.1干旱胁迫TN同烟草种子发芽特性的变化2.1.1干旱胁迫下不同烟草种子发芽率的变化发芽率是反映种子活力的常用指标。
从表1可以看出,PEG干旱胁迫对4个品种烤烟种子的发芽具有抑制作用,但不同品种对干旱胁迫的响应程度不同。
云烟87干旱胁迫下发芽率最低,为87.0%,但是相对发芽率最高,为95.3%;毕纳1号的相对发芽率为94.6%,略低于云烟87;黔西1号次之,为93.7%;韭菜坪2号的相对发芽率最低,为90.3%。

引文格式:刘娇, 姜永雷, 蔺璟煜, 等. 外源硅对干旱胁迫下烟草生长及生理特性的影响[J]. 云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2023, 38(2): 306−313. DOI: 10.12101/j.issn.1004-390X(n).202209009外源硅对干旱胁迫下烟草生长及生理特性的影响*刘 娇1, 姜永雷2, 蔺璟煜1,黄晓霞1 **(1. 国家林业与草原局 西南风景园林工程技术研究中心,西南林业大学 园林园艺学院,云南 昆明 650224;2. 云南省烟草农业科学研究院,云南 昆明 650021)摘要: 【目的】探究外源硅对干旱胁迫下烟株生长及生理特性的影响。
【方法】以云烟 87盆栽幼苗为材料,对其进行良好水分处理(90%~95%田间持水量)与干旱胁迫处理(35%~40%田间持水量),并施用不同含量外源硅肥(K 2SiO 3,0、1.0、1.5、2.0 g/kg),待烟株长至旺长期(45 d)时测定不同处理下烟株的生长形态、生物量、叶片光合色素含量、渗透调节物质含量及抗氧化酶活性。
【结果】干旱胁迫下,烟株的株高、叶片数、单叶面积、生物量、叶片光合色素含量及抗氧化酶活性均较良好水分处理组下降,而比叶面积和渗透调节物质含量升高;施加1.0~2.0 g/kg 外源硅对干旱胁迫下烟草的生长有一定的促进作用,主要表现为株高、叶片数、单叶面积、比叶面积、总生物量和根冠比增加,光合色素和渗透调节物质含量增加,抗氧化酶活性增强,丙二醛含量显著降低(P <0.05);且以2.00 g/kg 硅处理效果最明显。
【结论】施用外源硅可缓解干旱胁迫对烟草的伤害,提高其抗旱性。
关键词: 外源硅;烟草;干旱胁迫;生理特性中图分类号: S572.01 文献标志码: A 文章编号: 1004–390X (2023) 02−0306−08Effects of Exogenous Silicon on Growth and PhysiologicalCharacteristics of Tobacco under Drought StressLIU Jiao 1,JIANG Yonglei 2,LIN Jingyu 1,HUANG Xiaoxia 1(1. Southwest Landscape Architecture Engineering Research Center of State Forestry and Grassland Administration,College of Landscape and Horticulture, Southwest Forestry University, Kunming 650224, China;2. Yunnan Academy of Tobacco Agricultural Sciences, Kunming 650021, China)Abstract: [Purpose ]To explore the effects of exogenous silicon on the growth and physiological characteristics of tobacco under drought stress. [Methods ]Yunyan87 potted seedlings were treated with well water (90%-95% field water holding capacity) and drought stress (35%-40% field water holding capacity), and applied with different contents of exogenous silicon fertilizer (K 2SiO 3, 0, 1.0,1.5, 2.0 g/kg). The growth morphology, biomass, photosynthetic pigment content, osmotic regulatory substance content and antioxidant enzyme activity of tobacco plants under different treatments were measured when the tobacco plants grew to the flourishing period (45 days). [Results ]Underdrought stress, plant height, leaf number, single leaf area, biomass, photosynthetic pigment content云南农业大学学报(自然科学),2023,38(2):306−313Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University (Natural Science)E-mail: ********************收稿日期:2022-09-14 修回日期:2023-04-17 网络首发日期:2023-05-08*基金项目:云南省高层次人才青年拔尖人才项目(YNWR-QNBJ-2020-222);云南省科学技术厅基础研究专项(202001AU070006)。

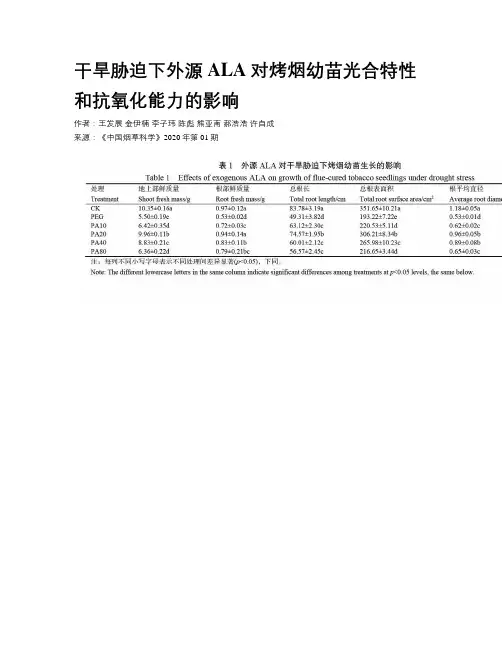
干旱胁迫下外源ALA对烤烟幼苗光合特性和抗氧化能力的影响作者:王发展金伊楠李子玮陈彪熊亚南郝浩浩许自成来源:《中国烟草科学》2020年第01期摘要:為进一步探究外源5-氨基乙酰丙酸(ALA)对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗抗旱能力的作用机理,以烤烟品种豫烟10号幼苗为试验材料,采用营养液培养的方法,研究叶面喷施不同浓度的(0~80 mg/L)外源ALA对干旱胁迫下烤烟幼苗烤烟光合特性和抗氧化能力的影响。
结果表明干旱胁迫下烤烟叶片细胞活性氧和硫代巴比妥酸(TBARS)含量增加,叶绿体遭到破坏,光合速率降低,植物生长受到抑制。
干旱胁迫下外源ALA能够显著降低烤烟叶片活性氧水平,提高抗氧化酶活性,以喷施20 mg/L ALA效果最为显著。
其中与PEG处理相比,净光合速率(P n)、蒸腾速率(T r)、气孔导度(G s)分别提高96.19%、96.79%和132.43%,抗氧化物酶(SOD、POD、CAT、APX)活性分别提高49.05%,61.97%,64.17%和70.08%。
喷施适宜浓度的外源ALA可有效提高烤烟叶片光合特性和抗氧化能力,缓解活性氧伤害,从而增强烤烟幼苗对干旱胁迫的适应能力。
关键词:5-氨基乙酰丙酸;烤烟幼苗;干旱胁迫;光合特性;抗氧化能力Effects of Exogenous ALA (5-aminolevulinic acid) on Photosynthesysand Antioxidant System of Flue-cured Tobacco Seedlings under Drought StressWANG Fazhan1, JIN Yi'nan1, LI Ziwei1,CHEN Biao1,2,XIONGYa'nan1, HAO Haohao3, XU Zicheng1*(1.College of Tobacco Science, Henan Agricultural University, Zhengzhou 450002, China;2. Xuchang Cigarette Factory, China Tobacco Henan Industrial Co., Ltd., Xuchang, Henan 461000, China;3.Zhumadian Branch of Henan Provincial Tobacco Company, Zhumadian,Henan 463000, China)Abstract:To furtherinvestigate the function of exogenous ALA in strengthening the ability of tobacco seedlings to resist drought,the effects of different concentrations (0-80 mg/L) of exogenous ALA on photosynthetic characteristicsand antioxidant activities of flue-cured tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum L.) seedlings of Yuyan 10 were studied using the method of hydroponic nutrient solution withpolyethylene glycol (PEG-6000) simulatingdrought stress artificially. The results showed that chlorophyll contentsand photosynthetic characteristics of flue-cured tobacco seedlings were significantlyinhibited under drought stress. Exogenous ALA could increase chlorophyll contents, photosynthetic characteristics, the activities of antioxidant enzymes,decrease the level of active oxygen metabolism and growthinhibition of flue-cured tobacco seedlings. And 20 mg/L ALA was considered to be the optimal concentration, with 33.09%, 45.04%,31.27% higher net photosynthetic rate (P n), transpiration rate (T r), stomatal conductance (G s), and 49.05%, 61.97%, 64.17%,70.08% higher activities of SOD, POD, CAT and APX. In conclusion,sprayingexogenous ALA with appropriate concentration could effectively enhance the antioxidant capacity andphotosynthetic pigment,relieve oxidative damage, thus enhance the flue-cured tobacco seedling's ability to adapt to drought stress.Keywords:5-aminolevulinic acid; flue-cured tobacco seedlings; drought stress; photosynthetic characteristics; antioxidant capacities煙草(Nicotiana tabacum L.)是我国重要的叶用经济作物之一,烟叶生产是烟区农民增收的主要来源,在国家和地区经济发展中发挥了重要作用[1-2]。

胁迫环境对植物光合作用的影响作者:林琨张鼎华来源:《安徽农业科学》2014年第31期摘要植物的光合作用是植物生理生态上最为重要的一个机制。
本文简述了植物光合作用的概念,并且通过不同胁迫条件下测定光合作用中的各项数据,来验证胁迫环境对植物光合作用的影响。
不同研究证明,胁迫环境确实对植物的光合作用有着不同的影响,主要为气孔因素或细胞内部调控机制受损。
关键词植物;胁迫环境;光合作用中图分类号 S184 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2014)31-10839-02Influence of Environmental Stress on PhotosynthesisLIN Kun, ZHANG Dinghua(Fujian Normal University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350108)Abstract Photosynthesis of plants is one of the most important mechanisms of plant physiology and ecology. The concept of plant photosynthesis was introduced, and data in photosynthesis under different stress conditions were measured, so as to verify the impact of environmental stress on plant photosynthesis. Different experiments show that environmental stress really has different impacts on plant photosynthesis, mainly are stomata factors or cell internal control mechanism damaged.Key words Plant; Environmental stress; Photosynthesis光合作用(Photosynthesis)是绿色自养植物合成有机物、维持其生命的重要途径。
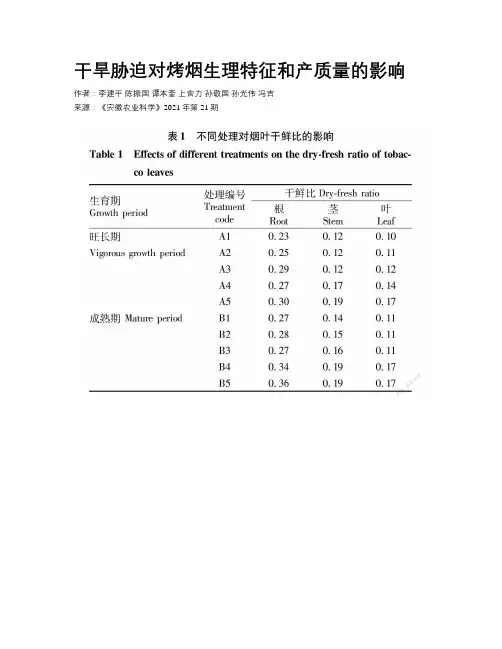
干旱胁迫对烤烟生理特征和产质量的影响作者:李建平陈振国谭本奎上官力孙敬国孙光伟冯吉来源:《安徽农业科学》2021年第21期摘要為了探索干旱胁迫对烤烟的影响,在利川开展烤烟不同生育期不同干旱程度对烤烟某些理化特性及产质量影响的研究。
结果表明,在烟叶干旱过程中,随着干旱程度的加深,烟叶的光合指标和部分生理指标均受到较大影响,各项光合指标和生理指标都呈降低趋势。
烟叶的农艺性状也受到影响,随着干旱程度的加重,烟叶生长受阻,植株矮化,烟叶不能正常成熟,烘烤后烟叶的质量很差,对经济性状造成很大影响。
因此,在烟叶生产中应加强应对高温干旱的应对措施,避免旱灾损失。
关键词烤烟;干旱胁迫;理化特性;产质量中图分类号 S 572 文献标识码 A 文章编号 0517-6611(2021)21-0039-03doi:10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.21.010开放科学(资源服务)标识码(OSID):Effects of Drought Stress on Physicochemical Properties, Yield and Quality of Flue-cured TobaccoLI Jian-ping CHEN Zhen-guo TAN Ben-kui2 et al(1.Tobacco Research Institute of Hubei Province,Wuhan, Hubei 430030;2.Zigui Marketing Department, Yichang Tobacco Company of Hubei Province,Zigui, Hubei 443600)Abstract In order to research the effects of drought stress on flue-cured tobacco, the experiments of different drought degrees at different growing stages of flue-cured tobacco on physicochemical properties, yield and quality were carried out in Lichuan. The results showed that the photosynthetic indexes and some physiological indexes of tobacco leaves were greatly affected with the deepening of drought stress, and all the photosynthetic indexes and physiological indexes showed a decreasing trend. With the increase of drought degree, the agronomic traits of tobacco leaves were also affected. The growth of tobacco leaves were hindered, the plants were dwarfed,the tobacco leaves could not mature normally, and the quality of tobacco leaves after baking was poor, which had a great impact on economic traits. Therefore, the measures to deal with high temperature and drought should be strengthened in tobacco production to avoid drought loss.Key words Flue-cured tobacco;Drought stress;Physicochemical properties;Yield and quality基金项目中国烟草总公司湖北省公司重点项目“烤烟大田生长前期根系发育障碍及应对技术研究与应用”(027Y2020-004)。

干旱胁迫对植物影响摘要:胁迫严重影响着植物的生长发育,如干旱胁迫,可造成经济作物产量的逐年大幅下降[1],它们不能逃避不利的环境变化, 它们需要快速的感应胁迫刺激进而适应各种环境胁迫。
大多数植物遭受干旱逆境后各个生理过程都会受到不同程度的影响。
我们都知道 ,水分在植物的生命活动中起着重要的作用,不仅是光合作用的原料之一,而且还维持着植物的正常体态。
因此,我们要用各种预防途径来减少干旱对植物的影响。
关键词:干旱胁迫植物影响Drought stress impact on plantsAbstract : stress seriously influence the plant growth and development, such as drought stress, which can cause economic crop production has fallen dramatically year by year [1], they cannot escape from adverse environmental change, they need fast induction stress stimulation and adapt to various environmental stresses. Most plants by drought adversity after various physiological processes are subject to the influence of different level. As we all know, water in the plant life activities play an important role, not only is one of the raw material of photosynthesis, but also maintains the normal posture of plants. Therefore, we want to use a variety of preventive ways to minimize the effects of drought on plant.Keywords : plant drought stress inflengce引言:干旱可以分为土壤干旱和大气干旱,而大气干旱往往伴随着较高的温度,这两种干旱有时单独出现,但是,在一般情况下同时出现的,这两种干旱方式对植物的影响是相似的。

干旱胁迫抑制作物光合作用机理研究进展作者:汪本福,黄金鹏,杨晓龙,等来源:《湖北农业科学》 2014年第23期汪本福1,黄金鹏1,杨晓龙2,程建平1,赵锋1,陈少愚1(1.农业部华中地区作物栽培科学观测实验站/粮食作物种质与遗传改良湖北省重点实验室,武汉430064;2.华中农业大学植物科技学院,武汉430070)摘要:从叶绿体色素、叶绿素荧光动力学、光合酶、活性氧代谢等方面阐述了干旱胁迫降低作物光合作用的气孔限制和非气孔限制原因。
现有的研究表明,在作物遭受轻度和中度干旱胁迫时,光合作用下降的主要原因是气孔限制,即气孔导度下降,导致胞间CO2浓度下降,进而降低光合速率;在重度胁迫时,光合作用下降的主要原因是非气孔限制,即光合器官的光合活性下降,非气孔限制影响因素较复杂。
要深入了解干旱胁迫降低光合作用的机理,除了加强形态、生理水平的研究外,还要从分子生物技术水平研究干旱胁迫对光合作用的影响及各相关生理过程,利用基因工程手段,选育新的耐旱高光效品种。
关键词:干旱胁迫;光合作用;气孔限制;非气孔限制中图分类号:S311;Q945.11文献标识码:A文章编号:0439-8114(2014)23-5628-05DOI:10.14088/j.cnki.issn0439-8114.2014.23.003干旱是农业生产中普遍存在的问题,中国每年因干旱造成作物减产达700亿~800亿kg,超过了其他逆境因素减产的总和[1]。
干旱胁迫导致作物减产主要是通过影响作物叶片的光合功能,使光合作用受到抑制,进而使作物减产。
干旱对光合作用的抑制机制前人已做了深入研究,但由于干旱胁迫的作物和胁迫环境的不同,目前的结论还存在一些争议,吕金印等[2]、严平等[3]通过研究干旱胁迫条件下小麦光合作用下降的机理,认为主要是由于气孔导度下降所致。
但Boyer等[4]报道认为光合作用受抑制是来自光合器官光合活性的下降。
随着对干旱胁迫研究的不断深入,有学者发现,在轻度胁迫时,光合速率降低的根本原因在于气孔导度的下降,导致胞间CO2浓度下降(Ci),光合作用随之下降,即光合作用的气孔限制;而在严重胁迫下,光合速率降低的根本原因在于光合器官的叶绿素解体[5]、光系统Ⅱ活性下降[6]、RuBP羧化酶活性受到抑制[7]等非气孔因素,即光合作用的非气孔限制[8-10],这一观点得到很多研究结果的支持[11,12]。

烟叶品质一直是烟草行业的关注焦点,其中水分被认为是烟草生长发育、生理代谢及其品质的一个主要生态因子[1]。
不同时期烟草生长所需最适水分条件有所差异,水分过多或过少都会影响烟叶生长,优质烟叶的生产必须适时、适量地满足烟株的水分需求[2]。
在烟草实际生产中,烟农往往通过经验来判断土壤水分状况,但与烟草生长所需最佳水分相差较大,在一定程度上限制了优质烟叶的生产。
近年来,气候变化剧烈,我国多数植烟地区常出现季节性干旱,以致烟草生长受到影响,其产量及品质下降[3]。
人为灌溉管理劳动力成本较大,且多数植烟区因地形及水资源等因素不能实施灌溉,较大程度上限制了烟草行业的发展。
如何提高烟草抗旱性及品质,以及研究不同时期干旱对烟草生长及后期烟叶品质的影响程度,正受到越来越多的重视。
基于此,综述了干旱胁迫对烟草生长发育、生理代谢及品质的影响,并进一步总结了目前应对干旱胁迫烟草种植的可行性措施和未来发展方向,旨在为干旱胁迫下烟草生产管理提供依据。
1 干旱胁迫对烟草形态建成、养分吸收及品质的影响各时期下烤烟生长所需水分条件不同,因此其干旱胁迫所处域值范围也不同。
研究表明,各生育期下(团棵期、旺长期、现蕾期、成熟期),烤烟生长的最适土壤相对含水量分别为65%、80%、80%、65%[4],评价其干旱胁迫程度可以以此为参考。
严重干旱胁迫导致烟株生长发育受阻,烤烟各器官干物质累积量明显降低,株高降低、叶片小、根系发育不良,其中以旺长期干旱对烟株的危害最大,这是因为旺长期烟株生长快,耗水量最大,此时缺水对烟草危害最大,其次是成熟期,伸根期影响最小[5-7]。
轻度干旱对烟株生长影响相对较小,甚至还有助于烟草生长。
研究表明,烤烟伸根期内轻度干旱有利于烤烟根系发育[8]。
干旱胁迫下烟株器官微结构也有所差异。
研究指出,不同水分条件下烟叶腺毛结构相差较大。
正常水分条件下,烟叶腺头细胞细胞器丰富,细胞质深厚;轻度干旱条件下,表现为细胞器含量减少;而严重干旱条件下,细胞器基本降解,细胞质变小甚至消失[9]。
干旱胁迫对烟草生理生化特征的影响作者:尹福强, YIN Fu-qiang作者单位:西昌学院农学系,四川西昌,615013刊名:安徽农业科学英文刊名:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL SCIENCE年,卷(期):2010,38(21)被引用次数:2次参考文献(11条)1.郑炳松现代植物生理生化研究技术 20062.蒋明义;郭绍川水分亏缺诱导的氧化胁迫和植物的抗氧化作用 1996(02)3.覃鹏转基因SOD高表达烟草抗旱性研究[学位论文] 20034.文建成;陈学宽;符菊芬质膜透性与丙二醛(MDA)含量的变化评价甘蔗品种抗旱性初探 1998(03)5.高丽萍;夏涛;张鹤英猕猴桃衰老中膜脂过氧化指标-丙二醛的研究[期刊论文]-安徽农业大学学报 2000(02)6.王建华;刘鸿先;徐同超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)在植物逆境和衰老生理中的作用 1989(01)7.仵小南;深曾佑水分胁迫对植物线粒体结构和脯氨酸氧化酶活性的影响 1986(04)8.任文伟;钱吉;郑师章不同地理种群在聚乙烯二醇胁迫下含水量和游离脯氨酸含量的比较[期刊论文]-生态学报2000(02)9.汪耀富;韩锦峰;林学语烤烟生长前期对干旱胁迫的生理生化响应[期刊论文]-作物学报 1996(01)10.姜福东;陈德鑫我国丘陵烟区烟草农业机械化发展现状及对策[期刊论文]-畜牧与饲料科学 2009(02)11.吴科瀛;梁玉玲烟草BY2细胞培养及盐胁迫研究[期刊论文]-畜牧与饲料科学 2009(04)本文读者也读过(10条)1.覃鹏.曾淑华.刘飞虎烟草抗旱性生理生化研究进展[期刊论文]-贵州农业科学2002,30(2)2.马新蕾.房燕.王玉军.谢胜利.王玮.Ma Xinlei.Fang Yan.Wang Yujun.Xie Shengli.Wang Wei十个烤烟品种的抗旱性鉴定[期刊论文]-中国烟草学报2005,11(5)3.尚晓颍.刘化冰.张小全.林娟.段旺军.杨铁钊.SHANG Xiao-ying.LIU Hua-bing.ZHANG Xiao-quan.LIN Juan. DUAN Wang-jun.YANG Tie-zhao干旱胁迫对不同烤烟品种根系生长和生理特性的影响[期刊论文]-西北植物学报2010,30(2)4.覃鹏.杨志稳.孔治有.刘凤英.刘飞虎干旱对烟草旺长期光合作用的影响[期刊论文]-亚热带植物科学2004,33(2)5.孙志英.彭克勤.胡家金.蔺万煌.夏石头干旱胁迫对烟叶产量的影响[期刊论文]-湖南农业科学2003(2)6.汪邓民.吴福如.杨红娟.周冀衡干旱对不同烤烟品种的生理及其烟株生长势的影响[期刊论文]-烟草科技2001(10)7.孙梅霞.汪耀富.张全民烟草生理指标与土壤含水量的关系[期刊论文]-中国烟草科学2000,21(2)8.不同烤烟品种抗旱生理特征比较研究[期刊论文]-西北植物学报2009,29(10)9.杨虹琦.周冀衡.罗泽民.林桂华.上官克攀干旱胁迫下供钾水平对烟草生长和钾素吸收及抗旱性的影响[期刊论文]-湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版)2003,29(5)10.农梦玲.刘永贤.李伏生.NONG Meng-ling.LIU Yong-xian.LI Fu-sheng干旱胁迫对烟草生理生化特征影响的研究进展[期刊论文]-广西农业科学2008,39(2)引证文献(2条)2011(5)2.徐萍莉.陈丽萍.周秀杰.何道一枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis)cspB基因转化烟草(Nicotiana tabacuum)的研究[期刊论文]-激光生物学报 2013(4)引用本文格式:尹福强.YIN Fu-qiang干旱胁迫对烟草生理生化特征的影响[期刊论文]-安徽农业科学 2010(21)。
干旱胁迫对烟草不同部位细胞程序化死亡的影响作者:梁栋刘光亮王永马兴华石屹王树声王程栋来源:《中国烟草科学》2020年第04期摘要:为了解干旱胁迫对烟草不同部位细胞程序化死亡的影响,以中烟100(不耐旱)和农大202(耐旱)为材料,采用2.5% PEG-6000模拟干旱,分析了不同耐旱性材料表型差异,用DNA Ladder法、TUNEL法测定烟草不同部位细胞程序化死亡发生的时间及程度差异。
结果表明:(1)干旱胁迫下,农大202和中烟100的生物量、根长、根直径均较对照下降,其中中烟100下降幅度更大且与对照达到极显著差异;(2)中烟100在干旱胁迫第3天,各部位均已发生PCD,但是不同部位对干旱胁迫的响应不同,叶片、侧根的PCD发生程度相近,根尖细胞发生程度明显高于叶片及侧根;(3)根据定位观察可知侧根皮层细胞以及远离叶脉的细胞较早发生PCD;(4)烟草的耐旱性越强,PCD发生较迟,发生程度也越弱。
综上所述,干旱胁迫下烟草不同部位细胞发生PCD的时间和特征是有差异的,耐旱性不同的品种发生PCD的时间也是有差异的。
关键词:烟草;干旱胁迫;细胞程序化死亡Abstract: To understand the effects of drought stress on programmed cell death in different parts of tobacco plants, using Zhongyan 100 (not drought-tolerant) and Nongda 202 (drought-tolerant) as materials, 2.5% PEG-6000 was used to simulate drought stress in analyzing phenotypic difference between plants with different drought tolerance. DNA Ladder method and TUNEL method were used to determine the time and degree of programmed cell death in different parts of tobacco plants. The results showed that:(1) Under drought stress, the biomass, root length and root diameter of Nongda202 and Zhongyan100 decreased compared with the control. The decrease range of Zhongyan100 was larger and the difference with the control was extremely significant. (2) On the third day of drought treatment, PCD had occurred in all parts of Zhongyan 100 plants, but the response of different parts to drought stress was different. The degree of PCD in leaves and lateral roots was similar, and the degree of PCD in root tip cells was significantly higher than that in leaves and lateral roots. (3) According to the localization observation, cells of the lateral root cortex and cells far away from the veins developed PCD earlier. (4) Tobacco plants with higher drought tolerance showed later occurrence of PCD and weaker degree of occurrence. In summary, the time and characteristics of PCD in cells of different parts of tobacco plants under drought stress are different, and the time of PCD in plants with different drought tolerance is also different.Keywords: tobacco; drought stress; programmed cell death干旱對我国农业生产形成巨大威胁,有研究表明其对作物造成的减产量可超过其他自然逆境减产量之和[1],并且干旱在我国各个烟草种植大省中普遍发生,严重影响了我国烟草的产量与品质。
干旱胁迫对植物的影响及植物的响应机制一、本文概述干旱胁迫是植物在生长过程中经常面临的一种非生物胁迫,它严重地限制了植物的生长和发育,并对植物的生存构成了威胁。
本文旨在深入探讨干旱胁迫对植物的影响,以及植物在面对这种环境压力时所采取的响应机制。
我们将从干旱胁迫对植物生理、形态和生态方面的影响入手,详细分析植物如何通过生理生化调整、形态变化以及基因表达等方式来应对干旱胁迫。
通过理解这些响应机制,我们可以为植物抗逆性研究提供理论支持,同时也为农业生产和生态保护提供有益的指导。
二、干旱胁迫对植物的影响干旱胁迫是植物生长过程中常见的非生物胁迫之一,对植物的生长、发育和生存产生深远影响。
干旱胁迫会显著影响植物的水分平衡。
当植物遭遇干旱时,水分吸收和运输受到阻碍,导致细胞水分减少,叶片出现萎蔫现象。
长期的水分不足还会引起叶片黄化、坏死,严重时甚至导致整株植物的死亡。
干旱胁迫对植物的光合作用产生严重影响。
水是光合作用的重要反应物之一,水分不足会直接导致光合作用的效率降低,影响植物的光能利用和有机物合成。
干旱胁迫还会引起叶绿体结构的改变,进一步影响光合作用的进行。
再次,干旱胁迫会对植物的生长发育造成负面影响。
水分不足会限制细胞的分裂和扩张,导致植物株型矮小,根系发育不良。
同时,干旱胁迫还会影响植物的花芽分化和开花结实,降低植物的繁殖能力和种子质量。
干旱胁迫还会引发植物的氧化胁迫和细胞凋亡。
干旱条件下,植物体内活性氧的产生和清除平衡被打破,导致活性氧积累,引发氧化胁迫。
长期的氧化胁迫会损伤植物细胞的结构和功能,严重时导致细胞凋亡,影响植物的生长和生存。
干旱胁迫对植物的影响是多方面的,涉及水分平衡、光合作用、生长发育、氧化胁迫等多个方面。
为了应对干旱胁迫,植物需要发展出一系列的适应和响应机制,以维持正常的生长和生存。
三、植物的响应机制植物在面对干旱胁迫时,会启动一系列复杂的生理和分子机制来应对和缓解干旱带来的压力。
这些机制主要包括形态结构调整、生理生化改变和分子层面的响应。
外源硅对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗生长、叶片光合及生理指标的影响张环纬;陈彪;温心怡;张杰;王小东;李继伟;许自成;黄五星【摘要】采用营养液水培法,研究了施用不同浓度外源硅(0、0.5、1.0 mmol/L)对干旱胁迫(10%PEG、20%PEG)下烟草幼苗生长、叶片光合特性和生理指标的影响.结果表明:干旱胁迫严重抑制了烟草幼苗生长和光合作用,膜质稳定性降低和引起氧化应激反应;施用不同浓度外源硅有效改善了干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗生长,均表现为株高、叶面积、根系体积、根系干重和地上部干重等生长指标增加,提高叶绿素a、叶绿素b、叶绿素a+b和类胡萝卜素含量,显著提高净光合速率(Pn)、蒸腾速率(Tr)、气孔导度(Gs)并降低胞间CO2浓度(Ci),膜质过氧化产物MDA含量显著降低,提高叶片含水量、膜稳定性系数和渗透调节物质(脯氨酸、可溶性糖)含量,显著提高SOD、POD和CAT等抗氧化酶活性,而且1.0 mmol/L Si处理对干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗生长和生理特性的影响显著优于0.5 mmol/L Si处理.以上结果说明,施用外源硅能提高干旱胁迫下烟草幼苗光合作用、抗氧化和渗透调节能力,缓解干旱胁迫对烟草幼苗的伤害,促进其生长.【期刊名称】《生物技术通报》【年(卷),期】2019(035)001【总页数】10页(P17-26)【关键词】外源硅;干旱;烟草幼苗;叶片光合;生理指标【作者】张环纬;陈彪;温心怡;张杰;王小东;李继伟;许自成;黄五星【作者单位】河南农业大学烟草学院,郑州 450002;河南农业大学烟草学院,郑州450002;河南农业大学烟草学院,郑州 450002;河南农业大学烟草学院,郑州450002;河南科技大学农学院牡丹学院,洛阳 471023;河南科技大学农学院牡丹学院,洛阳 471023;中国科学院水利部水土保持研究所,杨凌 712100;河南农业大学烟草学院,郑州 450002;河南农业大学烟草学院,郑州 450002【正文语种】中文随着全球气候变化,农业生产旱情发生强度和频次逐年增加,干旱胁迫在限制农作物生产的所有非生物胁迫中占据首位[1]。