外壳防护等级
- 格式:doc
- 大小:117.50 KB
- 文档页数:8

外壳防护等级为IP31,可防止小颗粒进入外壳,Du可同时防止水滴落入外壳,无任何冲击。
外壳防护等级为IP55,可防止有害粉尘的积聚,并支持清洗,无任何危害。
外壳IP代码根据产品的防尘、防异物、防水、防潮等特性对产品进行分类。
不要用工具、手指或其他异物接触灯泡的带电部分,以免触电。
它通常由两个数字组成。
第一个数字表示产品对灰尘和异物的防护等级,第二个数字表示产品防潮和防水的密封程度。
数字越大,保护级别越高。
扩展数据防水层0:无保护1:水滴进入外壳没有影响2:当外壳倾斜15度时,外壳上的水滴没有影响3:从60度角到机柜,不受水或雨水影响4:当液体从任何方向注入外壳时,不会产生有害影响5:用水冲洗是无害的6:可在客舱环境中使用7:可短时间(1米)浸泡8:在一定压力下长时间浸入水中。
外壳IP代码根据产品的防尘、防异物、防水、防潮等特性对产品进行分类。
不要让包括工具和人的手指在内的异物接触灯泡的带电部件,以免触电。
它通常由两个数字组成。
第一个数字表示产品对灰尘和异物的防护等级,第二个数字表示产品防潮和防水的密封程度。
数字越大,保护级别越高。
例如,显示机箱的防护等级(IP代码),如ipxx,粉尘等级(前X表示)0:无保护1:防止大量固体侵入2:防止中等大小固体的侵入3:防止小固体进入和侵入4:防止超过1毫米的固体进入5:防止有害粉尘积聚6:完全防止灰尘进入防水等级(第二个X表示)0:无保护1:水滴进入外壳没有影响2:当外壳倾斜15度时,外壳上的水滴没有影响3:从60度角到机柜,不受水或雨水影响4:当液体从任何方向注入外壳时,不会产生有害影响5:用水冲洗是无害的6:可在客舱环境中使用7:可短时间(1米)浸泡8:在一定压力下长时间浸泡在水中壳牌公司IP编码标准如下:1)IEC起草的国际防护和防水试验标准:IEC 529-598;2)GB 700-86;3)GB 4208等。
IP代码实验室:可进行IP级测试的实验室主要有苏州电气设备研究院、环境可靠性与电磁兼容测试中心、航天环境可靠性测试测试中心。


外壳防护等级及检测要求一、防尘等级防尘等级是指外壳对灰尘的防护能力,通常用字母“IP”后跟两个数字表示,例如IP5X表示防尘等级为5。
数字越高,防尘能力越强。
二、防水等级防水等级是指外壳对水的防护能力,通常用字母“IP”后跟两个数字表示,例如IPX4表示防水等级为4。
数字越高,防水能力越强。
三、防震等级防震等级是指外壳对机械振动的防护能力,通常用字母“IP”后跟一个字母表示,例如IP4表示防震等级为4。
字母越高,防震能力越强。
四、防腐蚀等级防腐蚀等级是指外壳对化学腐蚀的防护能力,通常用字母“IP”后跟一个字母表示,例如IP6表示防腐蚀等级为6。
字母越高,防腐蚀能力越强。
五、防爆等级防爆等级是指外壳对爆炸的防护能力,通常用字母“IP”后跟一个数字表示,例如IP6表示防爆等级为6。
数字越高,防爆能力越强。
六、检测环境条件检测外壳防护等级的环境条件应符合相关标准要求,包括温度、湿度、气压、光照等。
具体要求根据不同的防护等级和检测项目而定。
七、检测方法外壳防护等级的检测方法通常包括以下几种:1.直接观察法:通过肉眼或使用放大镜观察外壳表面是否有损伤、污垢、腐蚀等现象。
2.接触法:使用手套或指套接触外壳表面,检查是否有湿润、沾污等现象。
3.淋水法:对外壳表面淋水,检查是否有渗漏现象。
4.喷水法:使用喷枪对外壳表面喷水,检查是否有水珠附着现象。
5.防尘防潮试验法:将外壳放入防尘防潮试验箱中进行试验,检查其防尘防潮性能。
6.防震试验法:通过振动台对外壳施加振动,检查其防震性能。
7.耐腐蚀试验法:将外壳放入腐蚀性环境中进行试验,检查其耐腐蚀性能。
8.防爆试验法:根据相关标准对外壳进行爆炸试验,检查其防爆性能。
八、检测周期外壳防护等级的检测周期应根据具体使用环境和要求而定,一般建议至少每年进行一次检测。
对于恶劣环境或重要设备的外壳,应适当缩短检测周期。
九、检测设备外壳防护等级的检测需要使用专业的检测设备,包括各种观察仪器、试验箱、振动台等。

外壳防护等级国际标准
外壳防护等级是指电气设备对外部环境的防护能力,通常采用国际标准IEC 60529(GB/T 4208-2017)进行分类和命名。
该标准将外壳防护等级分为七个等级,分别为:
1.等级0:无防护(No protection);
2.等级1:防止直径大于50mm的物体进入(Dust protected);
3.等级2:防止直径大于12mm的物体进入(Protected against harmful ingress of water);
4.等级3:防止水滴进入,垂直滴水(Spray protected);
5.等级4:防止飞溅水进入(Splash protected);
6.等级5:防止低压喷水进入(Water jets protected);
7.等级6:防止高压喷水进入(Immersed in water)。
每个等级都有相应的测试要求和标准,以确保设备具有足够的防护能力。
在实际应用中,需要根据使用环境和设备的特点选择适合的防护等级。
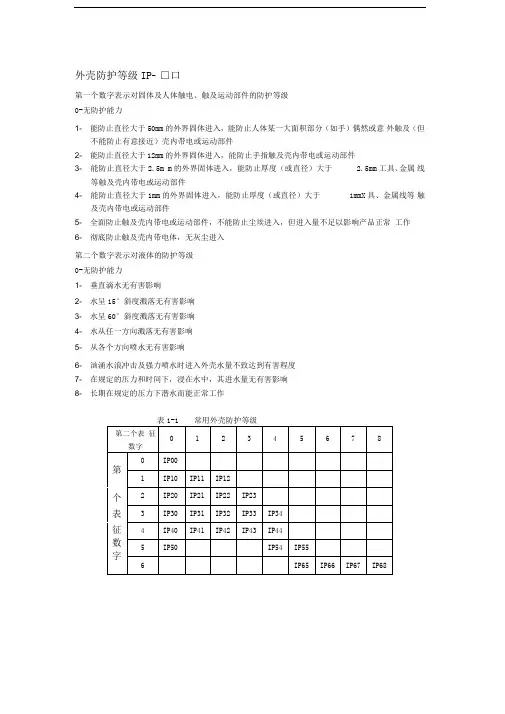
外壳防护等级IP- □口
第一个数字表示对固体及人体触电、触及运动部件的防护等级
0-无防护能力
1- 能防止直径大于50mm的外界固体进入,能防止人体某一大面积部分(如手)偶然或意外触及(但不能防止有意接近)壳内带电或运动部件
2- 能防止直径大于12mm的外界固体进入,能防止手指触及壳内带电或运动部件
3- 能防止直径大于2.5m m的外界固体进入,能防止厚度(或直径)大于 2.5mm工具、金属线等触及壳内带电或运动部件
4- 能防止直径大于1mm的外界固体进入,能防止厚度(或直径)大于1mmX具、金属线等触及壳内带电或运动部件
5- 全面防止触及壳内带电或运动部件,不能防止尘埃进入,但进入量不足以影响产品正常工作
6- 彻底防止触及壳内带电体,无灰尘进入
第二个数字表示对液体的防护等级
0-无防护能力
1- 垂直滴水无有害影响
2- 水呈15°斜度溅落无有害影响
3- 水呈60°斜度溅落无有害影响
4- 水从任一方向溅落无有害影响
5- 从各个方向喷水无有害影响
6- 汹涌水浪冲击及强力喷水时进入外壳水量不致达到有害程度
7- 在规定的压力和时间下,浸在水中,其进水量无有害影响
8- 长期在规定的压力下潜水而能正常工作。


干变外壳防护等级标准干变外壳防护等级是针对电力设备中的干式变压器而设立的一项标准,旨在提供变压器外壳的防护等级,以保护变压器免受灰尘、水分、物理冲击和其他恶劣环境因素的影响。
根据国际电工委员会(IEC)和国家标准,干变外壳防护等级可依据不同的防护需求分类,并通过相应的防护等级代码进行表示。
下面是一些相关参考内容,用于了解干变外壳防护等级标准的概念和应用。
一、国际电工委员会(IEC)标准1. IEC 60529 标准IEC 60529 标准是国际电工委员会制订的防护等级(IP标准)的国际标准。
该标准规定了不同等级的防护构造要求,包括防护等级代码的定义及测试方法等。
在干变外壳防护等级标准中也常使用该标准进行参考。
2. IEC 61892-7 标准IEC 61892-7 标准是国际电工委员会制订的用于海洋上的电气、电子和可编程电子设备的安装设计的标准,该标准也包含了干变外壳防护等级标准的相关内容。
二、干变外壳防护等级标准分类根据不同的防护需求,干变外壳防护等级可分为以下几个分类:1. IP10X该等级表示变压器具备防护物体直径大于50mm的保护能力。
这意味着变压器的外壳能有效地防止大于50mm直径的物体侵入变压器内部。
2. IP20该等级表示变压器具备防护物体直径大于12.5mm的保护能力。
相比于IP10X,该等级提供更高的防护能力,能够有效地防止直径大于12.5mm的物体进入。
3. IP30该等级表示变压器具备防护物体直径大于 2.5mm的保护能力。
相比于IP20,该等级提供了更高的防护能力,能够有效地防止直径大于2.5mm的物体进入。
4. IP40该等级表示变压器具备防护物体直径大于1mm的保护能力。
相比于IP30,该等级提供了更高的防护能力,能够有效地防止直径大于1mm的物体进入。
5. IP50该等级表示变压器具备防护物体直径大于0.5mm的保护能力。
相比于IP40,该等级提供了更高的防护能力,能够有效地防止直径大于0.5mm的物体进入。

外壳防护等级外壳防护等级(IP代码)是将产品依其防尘、防止外物侵入、防水、防湿气之特性加以分级。
这里所指的外物包含工具、人的手指等均不可接触到灯具内之带电部分,以免触电。
它一般是由两个数字所组成,第一个数字表示产品防尘、防止外物侵入的等级;第二个数字表示产品防湿气、防水侵入的密闭程度。
数字越大,表示其防护等级越高。
如:外壳防护等级(IP代码)示例如:IPXX,防尘等级(第一个X表示)0:没有保护1:防止大的固体侵入2:防止中等大小的固体侵入3:防止小固体进入侵入4:防止物体大于1mm的固体进入5:防止有害的粉尘堆积6:完全防止粉尘进入防水等级(第二个X表示)1:水滴滴入到外壳无影响2:当外壳倾斜到15度时,水滴滴入到外壳无影响3:水或雨水从60度角落到外壳上无影响4:液体由任何方向泼到外壳没有伤害影响5:用水冲洗无任何伤害6:可用于船舱内的环境7:可于短时间内耐浸水(1m)8:于一定压力下长时间浸水外壳防护等级(IP代码)的标准有:1)由IEC(INTERNATIONAL ELECTROTECHNICAL COMMISSION)所起草国际防护和防水试验标准:国际电工委员会标准IEC 529 –598;2)国标GB 700–86;3)GB 4208等。
外壳防护等级(IP代码)实验室:目前能进行IP等级试验的实验室主要有苏州电器科学研究所、环境可靠性与电磁兼容试验中心,航天环境可靠性试验与检测中心等。
中华人民共和国国家标准低压电器外壳防护等级Degrees of protecion provided byenolsures for low-voltage apparatusGB/T 4942.2-93代替GB4942.2-85本标准效采用国际标准IEC 947-1(1988)《低压开关设备和控制设备一般规则》,并参照采用IEC 529(1989)《外壳防护等级》等标准中有关低压电器的外壳防护等级的规定和要求。


地址:北京市东四环南路53号邮编:100023 TEL:010-******** FAX:010-******** E-mail:bjhtfk@
外壳防护等级的含义:
IPXX等级中关于防水实验的规定(按照EN60529/IEC529)国际工业标准防水登记IP和日本工业标准的JIS防水等级是接近的,分0-8的9级,IP等级同样对防尘做了规定。
IPxx 防尘防水等级:
防尘等级(第一个X表示) 防水等级(第二个X表示)
IP xx 防尘防水等级的含义
第一个x的数值表示的含义第二个x的数值表示的含义
0:没有保护
1:防止大的固体侵入
2:防止中等大小的固体侵入
3:防止小固体进入侵入4:防止物体大于1mm的固体进入
5:防止有害的粉尘堆积6:完全防止粉尘进入0:没有保护
1:水滴滴入到外壳无影响
2:当外壳倾斜到15度时,水滴滴入到外壳无影响
3:水或雨水从60度角落到外壳上无影响
4:液体由任何方向泼到外壳没有伤害影响
5:用水冲洗无任何伤害
6:可用于船舱内的环境
7:可于短时间内耐浸水(1m)8:于一定压力下长时间浸水
地址:北京市东四环南路53号邮编:100023 TEL:010-******** FAX:010-******** E-mail:bjhtfk@ 更多信息请浏览:
北京恒泰丰科试验设备有限公司
地址:北京市东四环南路53号
邮编:100023
电话: 010-******** (总机)010-********
传真:010-********
手机:159********、135********
E-mail:bjhtfk@。
用电设备的环境条件和外壳防护等级1. 用电环境类型工作环境或生产厂房可按多种方式分类。
根据电击的危急程度,用电环境分为三类:无较大危急的环境、有较大危急的环境和特殊危急的环境。
(1)无较大危急的环境。
正常状况下有绝缘地板、没有接地导体或接地导体很少的干燥、无尘环境,属于无较大危急的环境。
(2)有较大危急的环境。
下列环境均属于有较大危急的环境:①空气相对湿度常常超过75%的潮湿环境;②环境温度常常或昼夜间周期性地超过35℃的酷热环境;③生产过程中排出工艺性导电粉尘(如煤尘、金属尘等)并沉积在导体上或进入机器、仪器内的环境;④ 有金属、泥土、钢筋混凝土、砖等导电性地板或地面的环境;⑤ 工作人员同时接触接地的金属构架、金属结构等,又接触电气设备金属壳体的环境(3) 特殊危急的环境。
下列环境均属于特殊危急的环境:①室内天花板、墙壁、地板等各种物体都潮湿,空气相对湿度接近100% 的特殊潮湿的环境;②室内常常或长时间存在腐蚀性蒸气、气体、液体等化学活性介质或有机介质的环境;③具有两种及两种以上有较大危急环境特征的环境。
2. 电气设备外壳防护等级电机和低压电器的外壳防护包括两种防护: 第一种防护是对固体异物进入内部的防护以及对人体触及内部带电部分或运动部分的防护;其次种防护是对水进入内部的防护。
依据GB4208-84 标准,外壳防护等级按如下方法标志:第一位数字表示第一种防护型式等级;其次位数字表示其次种防护型式等级。
仅考虑一种防护时,另一位数字用“×”代替。
前附加字母是电机产品的附加字母,W表示气候防护式电机,R表示管道通风式电机;后附加字母也是电机产品的附加字母,S表示在静止状态下进行其次种防护型式试验的电机,M表示在运转状态下进行其次种防护型式试验的电机。
如无需特殊说明,附加字母可以省略3.单相电气设备防触电分类根据防止触电的爱护方式,单相电气设备分为以下五类:(1)0级电器。
这种电器仅仅依靠基本绝缘来防止触电。
外壳的防护等级为IP31,这意味着它可以防止小固体进入外壳,并且Du可以同时保持水滴落入外壳,而不会产生任何影响。
外壳的防护等级为IP55,可防止有害粉尘的积聚,并支持水洗而无任何伤害。
外壳的IP代码根据其防尘,防异物,防水和防潮的特性对产品进行分类。
请勿使用工具,手指等异物接触灯泡中带电的部件,以免触电。
它通常由两个数字组成,第一个数字代表产品防尘和防异物侵入的等级,第二个数字代表产品对湿气和水侵入的气密程度。
数字越大,保护级别越高。
扩展数据防水等级0:无保护1:水滴到外壳中没有任何作用2:当外壳倾斜15度时,水滴落到外壳中没有任何作用3:从60度角到机柜没有水或雨水的影响4:从任何方向将液体倒入外壳时,没有有害作用5:用水冲洗无害6:可在机舱环境中使用7:可以在水中短时间(1m)浸泡8:在一定压力下长时间浸入水中。
外壳的IP代码根据其防尘,防异物,防水和防潮的特性对产品进行分类。
请勿使包括工具和人的手指在内的异物接触灯泡中的带电部件,以免触电。
它通常由两个数字组成,第一个数字代表产品防尘和防异物侵入的等级,第二个数字代表产品对湿气和水侵入的气密程度。
数字越大,保护级别越高。
例如,显示了机箱的防护等级(IP代码),例如ipxx,灰尘等级(第一个X表示)0:无保护1:防止大量固体侵入2:防止中型固体侵入3:防止小固体进入和侵入4:防止大于1毫米的固体进入5:防止有害的灰尘堆积6:完全防止灰尘进入防水等级(第二个X表示)0:无保护1:水滴到外壳中没有任何作用2:当外壳倾斜15度时,水滴落到外壳中没有任何作用3:从60度角到机柜没有水或雨水的影响4:从任何方向将液体倒入外壳时,没有有害作用5:用水冲洗无害6:可在机舱环境中使用7:可以在水中短时间(1m)浸泡8:在一定压力下长时间浸泡在水中外壳的IP代码标准如下:1)IEC起草的国际保护和防水测试标准:IEC 529-598;2)GB 700-86;3)GB 4208等IP代码实验室:可以进行IP等级测试的实验室主要包括苏州电气设备研究所,环境可靠性和电磁兼容性测试中心,航空航天环境可靠性测试检测中心等。
NEMA外壳防护等级(与IP等效的标准) NEMA 1:室内应用,保证内部设备不受碰触,提供一定固体异物防护。
(IP30) 2:室内应用,提供一定程度滴水和固体异物防护。
(IP31)3:室外应用,防风沙、防雨和冰雹,不会因外壳结冰而损坏。
(IP64)3R:室外应用,防雨和冰雹,不会因外壳结冰而损坏。
(IP32)3S:室外用,防风沙、防雨和冰雹,结满冰时外部机械装置仍可操作。
4:室内或室外应用,防风沙、溅水和雨、防水管喷水,不会因外壳结冰而损坏。
(IP66)4X:室内或室外应用,防风沙、溅水和雨、防水管喷水,不会因外壳结冰而损坏,防腐蚀。
(IP66)5:尘密,用于水泥、纺织、食品等工业场合。
6:室内或室外应用,可短时间有限深度浸水,不会因外壳结冰而损坏。
6P:室内或室外应用,可长时间有限深度浸水。
7:室内危险区域应用,现场存在危险性气体,I级A、B、C、D组8:危险区域应用,与NEMA7相似,充油后用于现场的危险气体具有腐蚀性的场合。
9:危险区域应用,尘密,II级E、F、D组10:满足美国煤矿联合会防爆要求,适用于有瓦斯泄漏煤矿。
11:室内应用,充油后耐腐蚀性气体和液体。
12:室内应用,尘密、防非腐蚀性液体喷洒。
(IP65)13:室内应用,尘密,防喷水、喷油、喷冷却剂。
(IP65)外壳防护等级(IP)代码(BS EN60529:1992)第一位特征数字防治固体异体异物进去第二位特征数字防止进水造成有害影0 无防护 0 无防护1 固体异物直径大于50mm 1 垂直滴水2 固体异物直径大于12mm 2 倾角75-90滴水3 固体异物直径大于2.5mm 3 淋水4 溅水 4 固体异物直径大于1.0mm5 防尘 5 喷水6 尘密 6 猛烈喷水7 短时间浸水8 连续浸水例如:IP65即要求具有尘密及对喷水的外壳防护功能北美危险等级划分I级(气体和蒸气) II级(粉尘) III级(纤维) A组(乙炔) B(氢气) C(乙烯) D(甲E组(金属粉尘) F组(煤粉) G组(农业粉不分组别烷) 尘)欧洲和北美防爆检验和测试机构机构名称 BASEEFA SCS BVS PTB CESI CSA DEMKO国家英国德国意大利加拿大丹麦机构名称 FM UL INERIS LCIE INIEX KEMA LOM国家美国法国比利时荷兰西班牙。
IP外壳防护等级及其测试方法IP外壳防护等级是用来评估设备外壳对固体颗粒和液体侵入的能力的一种标准。
IP等级由国际电工委员会(IEC)制定。
在IP等级中,第一个数字表示对固体颗粒的保护等级,第二个数字表示对液体侵入的保护等级。
下面将详细介绍IP等级及其测试方法。
1.IP外壳防护等级1.1.固体颗粒防护等级-IP0X:无保护,不防固体颗粒进入设备。
- IP1X:对直径大于50mm的固体颗粒有保护作用,如手指。
- IP2X:对直径大于12.5mm的固体颗粒有保护作用,如手指关节。
- IP3X:对直径大于2.5mm的固体颗粒有保护作用,如工具和铅笔。
- IP4X:对直径大于1mm的固体颗粒有保护作用,如线头和细颗粒。
-IP5X:对灰尘有一定保护作用,但不能完全防止进入。
-IP6X:对灰尘有完全保护作用,不进入设备。
1.2.液体防护等级-IPX0:无保护,不防液体进入设备。
-IPX1:对垂直滴水有保护作用,垂直滴水不会对设备造成损害。
-IPX2:对倾斜滴水有保护作用,倾斜15度范围内的滴水不会对设备造成损害。
-IPX3:对喷水有一定程度的保护作用,喷水不会对设备造成损害。
-IPX4:对飞溅水有保护作用,飞溅水不会对设备造成损害。
-IPX5:对喷射水有保护作用,喷射水不会对设备造成损害。
-IPX6:对大量喷射水有保护作用,如海浪冲击。
-IPX7:在规定时间和压力下,设备在水中放置一定时间后不会受到损害。
-IPX8:在特定条件下,设备可以在一定深度的水中继续工作。
2.IP等级测试方法2.1.固体颗粒防护等级测试-IP0X:不需测试。
- IP1X:使用直径50mm的球形物体对设备进行测试。
- IP2X:使用直径12.5mm的球形物体对设备进行测试。
- IP3X:使用直径2.5mm的球形物体对设备进行测试。
- IP4X:使用直径1mm的球形物体对设备进行测试。
-IP5X和IP6X:使用灰尘对设备进行测试。
2.2.液体防护等级测试-IPX0:不需测试。
外壳防护等级(IP)仪表外壳防护等级(IP)代码(BS EN60529;1992),由字母IP 和后续的两位特征数字表示。
例:IP65 即要求具有尘密及对喷水的外壳防护功能附加数字:防机械冲击第三位特征数字(至EN标准中不包括),适合在某些欧洲国家中通用(参阅法国标准NF C20-010):IP 外壳防护等级"接近等于NEMA 防护等级:IP codesDegrees of Protection Provided by EnclosuresThis standard describes a system for classifying the degrees of protection provided by the enclosures of electrical equipment. Developed by the European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC), these standards are designed to numerically rate an electrical product on the level of protection its enclosure provides. By assigning different number codes, the product's degree of protection can be identified quickly and easily. In the code IP 54, for example, IP identifies this standard, the 5 describes the level of protection from solid objects, and 4 describes the level of protection from liquids.Second Characteristic Numeral DEGREE OF PROTECTION (Second Number in Code)Brief DescriptionDefinition0 Not protected __1 Protected against vertically falling water drops.Vertically falling drops shall have no harmful effects.2Protected against vertically falling water drops when enclosure is titled up to 15 °.Vertically falling drops have no harmful effects when the enclosure is tilted at any angle up to 15° on either side of the vertical. 3 Protected against spraying water. Water sprayed at an angle up to 60° degrees on either side of the vertical shall have no harmful effects. 4 Protected against splashing water.Water splashed against the enclosure from any direction shall have no harmful effects. 5 Protected against water jets. Water projected in jets against the enclosure from any directionshall have no harmful effects.6 Protected against powerful water jets.Water projected in powerful jets against the enclosure from any direction shall have no harmful effects.7Protected against the effects of temporary immersion in water.Ingress of water in quantities causing harmful effects shall not be possible when the enclosure is temporarily immersed 1 meter in water under standardized conditions of pressure and time.8Protected against the effects of continuous immersion in water.Ingress of water in quantities causing harmful effects shall not be possible when the enclosure is continuously immersed in water under conditions which shall be agreed between manufacturer and the user, but are more severe than for number 7.International Protection (IP) RatingsThe IP rating system classifies the degree of protection from solid objects and liquids afforded by electrical equipment and enclosures. Recognized in most European countries and meets a number of British and European standards, this rating system includes: Classification of Degrees of Protection Provided by Enclosures, BS (British Standards) 5490:1977; IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) 529:1976.Specifications for Degrees of Protection of Enclosures of Switchgear and Control Gear for voltages up to and including 1000 VAC and 1200 VDC, BS 5420:1977; and IEC 144:1963.First NumberProtection against solid objectsSecond Number Protection against liquids0 no protection1 protected against solid objects up to 50 mm (e.g. accidental touch by hands)2 protected against solid objects up to 12 mm (e.g. fingers)3 protected against solid objects over 2.5 mm (e.g. tools and wires)4 protected against solid objects over 1 mm (e.g. tools and small wires)5 protected against dust-limited to ingress (no harmful deposits)6 totally protected against dust 0 no protection1 protected against vertically falling drops of water (e.g. condensation)2 protected against vertically falling drops of water up to 15° from the vertical4 protected against water sprayed from all directions limited ingress permitted6 protected against strong jets of water—limited ingress permitted (e.g. for use on ship decks)7 protected against the effects of temporary immersion between 15 cm and 1 mNEMA/IEC Enclosure RatingsNEMA/IEC Enclosure Ratings Conversion of NEMA type classifications to IEC classification designation (IP ratings). Note: NEMA standards meet or exceed IEC standards; therefore, the conversion does not work in the opposite direction.NEMAenclosure type no.NEMA definitionIECenclosureclass1General-purpose. Protects against dust, light, and indirect splashing but is not dust-tight; primarily prevents contact withlive parts; used indoors and under normal atmospheric conditions.IP102Drip-tight. Similar to Type 1 but with addition of drip shields;used where condensation may be severe (as in coolingrooms and laundries).IP113 and 3S Weather-resistant. Protects against weather hazards such asrain and sleet; used outdoors on ship docks, in constructionwork, and in tunnels and subways.IP543R Intended for outdoor use. Provides a degree of protectionagainst falling rain and ice formation. Meets rod entry, rain, external icing, and rust-resistance design tests.IP144 and 4X Watertight (weatherproof). Must exclude at least 65 GPM ofwater from 1-in. nozzle delivered from a distance not lessthan 10 ft for 5 min. Used outdoors on ship docks, in dairies,and in breweries.IP565Dust-tight. Provided with gaskets or equivalent to excludedust; used in steel mills and cement plants.IP526 and 6P Submersible. Design depends on specified conditions of pressure and time; submersible in water; used in quarries, mines, and manholes.IP677Hazardous. For indoor use in Class I, Groups A, B, C, and D environments as defined in the NEC.—8Hazardous. For indoor and outdoor use in locations classified as Class I, Groups A, B, C, and D as defined in the NEC.—9Hazardous. For indoor and outdoor use in locations classified as Class II, Groups E, F, or G as defined in the NEC.—10MSHA. Meets the requirements of the Mine Safety and Health Administration, 30 CFR Part 18 (1978).—11General-purpose. Protects against the corrosive effects of liquids and gases. Meets drip and corrosion-resistance tests.—13General-purpose. Primarily used to provide protectionagainst dust, spraying of water, oil, and noncorrosive coolants. Meets oil exclusion and rust resistance designtests.IP54National Electric Code (NEC) RatingsHazardous Classifications:Class I: Areas in which flammable gases of vapors may be present in the air in sufficient quantities to be explosive.Group A: Atmospheres containing acetyleneGroup B: Atmospheres such as butadiene, ethylene oxide,propylene oxide, acrolein, or hydrogen (or gases or vaporsequivalent in hazard to hydrogen, such as manufactured gas)Group C: Atmospheres such as cyclopropane, ethyl ether,ethylene, or gas or vapors of equivalent hazardGroup D: Atmospheres such as acetone, alcohol, ammonia,benzene, benzol, butane, gasoline, hexane, lacquer solventvapors, naphtha, natural gas, propane, or gas or vapors ofequivalent hazardCLASS II: Areas made hazardous by the presence of combustible dustGroup E: Atmospheres containing combustible1.metal dusts, regardless of resistivity2.dust of similarly hazardous characteristics having a resistivity lessthan 100 k½-cm3.electrically conductive dustsGroup F: Atmospheres containing combustible1.carbon black, charcoal, or coke dusts having more than 8% totalvolatile material2.dusts so sensitized that they present an explosion hazard, and dustshaving a resistivity greater than 100 ½-cm but less than or equal to1 x 108 ½-cmGroup G: Atmospheres containing combustible1.dust having resistivity equal to or greater than 100 k½-cm2.electrically nonconductive dustsCLASS III: Areas made hazardous by the presence of easily ignitable fibers or dust, but which are not likely to be in suspension in the air in quantities that are sufficient to igniteDivision 1: Atmospheres where hazardous concentrations existcontinuously, intermittently, or periodically under normaloperating conditionsDivision 2: Atmospheres where hazardous concentrations existonly in case of accidental rupture or breakdown of equipmentExplosion-proof: Enclosures or housings are designed to withstand internal explosions and prevent the spread of fire to the outside.Intrinsically-safe: Systems designed in which electrical energy in the circuits is not present at levels that would ignite a flammable mixture of a gas and air.The IP Code SymbolsThe chart at the right illustrates the use of special symbols in the IP classification system. In the "1st digit" column, not the grid-like symbols net to numbers 5 and 6. In the "2nd digit" column numbers 3-8 are symbolised by teardrop shaped symbols, sometimes enclosed in a box or a triangle, sometimes unenclosed (#7-8). These symbols can be placed on equipment to illustrate the IP protection provided.。