科创学院物流专业英语教案unit1-Part2
- 格式:doc
- 大小:41.00 KB
- 文档页数:3
![物流专业英语(第2版)[电子教案]Chapter XII](https://uimg.taocdn.com/e29aa86d1eb91a37f1115cdc.webp)


《专业英语(物流)》教案课程名称:专业英语(物流)适用专业:商学院物流管理(专)专业规定学时:32学时,2学分开课学期:二年级下学期任课教师:***一、课程说明本课程是物流管理专业开设的一门专业性课程,是物流专业学生的一门必修课程,旨在培养学生在物流实践中的英语交流技能。
通过本课程的学习,学生能够掌握基本的物流专业词汇、常见英文缩略词、国际贸易术语、外贸单据格式,以及具备一定的物流英文文献的阅读能力和日常情境会话能力。
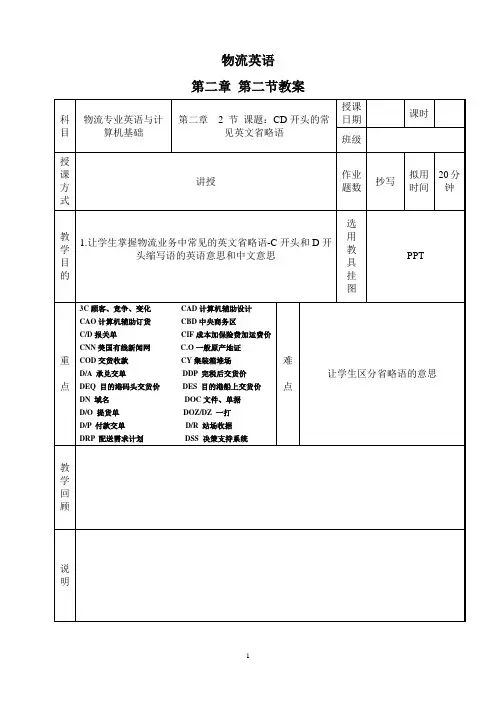
二、教学内容本课程主要包括(一)物流概述1. 主要内容:物流产生的背景,发展过程,概念,内容以及物流业在中国的现状2. 教学要求:掌握物流的基本概念和内容,了解物流的重要性。
(二)供应链1. 主要内容:供应链的定义及供应链管理的特点2. 基本要求:掌握供应链的定义,了解供应链管理的特点(三)采购与订单管理1. 主要内容:采购的概念,方式及其重要性,订单管理2. 教学要求:掌握采购的方式及其流程,掌握订购单的编制流程(四)配送与包装1. 主要内容:配送的概念及流程,包装种类及其作用和重要性2. 教学要求:掌握货物包装的基本方式和功能(五)仓储与库存管理1. 主要内容:仓储与库存管理的界定,仓储规划及运作流程2. 基本要求:掌握仓储与库存管理的定义,了解仓储运作流程(六)运输1. 主要内容:运输的定义,运输的作用和原则,运费的构成2. 基本要求:掌握运输的定义,了解运输的作用和原则,了解多式联运(七)物流单证1. 主要内容:介绍物流单据、信用证2. 基本要求:了解物流单据、信用证(八)物流信息技术1. 主要内容:物流信息系统的定义,条形码及扫描技术2. 基本要求:了解不同信息技术的描述,了解现代信息技术在物流管理中的应用(九)第三/N方物流1. 主要内容:第三/N方物流的概念,重要的知名物流企业的介绍2. 基本要求:了解第三/N方物流的概念以及从事第三/N方物流的知名企业的情况三、本课程的教案主要包括下列教学活动形式1、本章的教学目标及基本要求2、本章教学重点与难点3、本章教学方式(手段)及教学过程中应注意的问题4、教学课时5、本章的主要内容四、课程教学的基本要求本课程的教学环节包括:课堂讲授、习题课、课外作业。

最新物流专业英语教案1(打印版)资料P A R TⅠT h e D e f i n i t i o n o f L o g i s t i c s【步骤一】标题Put forward some questions教师:讲解1.What is the logistics?2.What does the term “logistics”originate from?3.How do you comprehend “logistics encompasses much more than just the transport of goods”?4.In what condition materials management and logistics may be synonymous?5.Please briefly describe evolution of the logistics management concept.【步骤二】 Study the new words教师:讲解,带读学生:跟读,自己理解【步骤三】 Read and understand the text 学生:阅读【步骤四】 Teach the paragraghs[Para.1]“Logistics”is a term, which originates from both the army and French. According to the French, the Baron of Jomini, who of Swiss originwho had s erved in Napoleon’s army before joining the Russians and wholater founded the Military Academy of St. Petersburg, first used theterm in the early 19th century. So in a military sense, the term ‘logistics’encompasses transport organization, army replenishments andmaterial maintenance.“物流”或“后勤”一词其实源于军队,对其词义解释亦有多个不同版本,根据法国人阐述之词义,该词早于十九世纪初被祖文尼男爵率先采用。

授课形式(请打J )授课题目 Logistics company教学目的 Get to know the logistics enterprise annual meeting model and master theuseful sentences about writing letters of thanks教学重点 How to make a statement in an annualmeetingHow to write a thanks letter教学难点 The mail functions of different logistics department使用的教具/多媒体/仪器/仪表/设备等教材,教案,多媒体教学方法理论讲授与实例分析相结合参考资料 齐利梅,牛国崎主编,物流专业英语,北京理工大学出版社毛俊纯主编,物流英语,高等教育出版社纯理论口 纯实践口 理实一体化口 习题课口 其他口授课时间 _________________ 班 周星期第 节 _________________ 班 周星期第—节 __________________ 班 周星期第 节教学基本内容及设计KNOWLEDGE REVIEWITEM 2 OF UNIT ONET: TALKING FACE TO FACELEARN HOW TO MAKE A STATEMENT IN AN ANNUAL MEETING1.NEW WORDS AND EXPRESSIONSclient department storage proportion arrangement cooperation general manager ups and downs make persistent efforts2.DIALOGUEthe main functions of different logistics department:the general manager; human resources department; transport department; storage department; information departmentsecretary3.EXERCISESquestions answeringlistening practice课后作业/思考题教学后记说明:1•课程教案应按授课次数编写;重复班授课不再另行编写教案。




Chapter 1 Introduction to Logistics Management教学目的和要求:1、Understand the brief origins and history of logistics conceptiondevelopment2、Learn the definition and boundary of logistics3、Gain an understanding of competitive advantage through logisticsmanagement4、Understand the mission of logistics5、Learn the factors changing logistics environment6、Get an overview of the changing logistics environment and the newrules of logistics competition7、Get an overview of the logistics network of the 21st century教学重点:1、Origins and history of logistics conception development2、Definition and boundary of logistics3、Competitive advantage through logistics management4、Mission of logistics5、Factors changing logistics environment6、The changing logistics environment and the new rules of logisticscompetition7、Logistics network of the 21st century教学过程:1. New Words and Expressions2. What is Logistics1) Brief History of Logistics Emergence2) Origins and Definition of LogisticsOriginally, logistics is a military term, first used in the Napoleonic ear.the art of moving armies and keeping them suppliedthe integration of transportation, supply, warehousing, maintenance,procurement, contracting and automation into a single function thatensures no suboptimization in any of those areas, to allow the overall accomplishment or a particular strategy, objective, or mission.the branch of military science and operations dealing with the procurement, supply, and maintenance of equipment, and hospitalization of personnel, with the provision of facilities and services, and with related matters.logistics is that part of the supply chain process that plans, implements, and controls the efficient, effective forward and reverse flow and storage of goods, service, and related information between the point of origin and the point of consumption in order to meet customers’requirements.Logistics is the process of strategically managing the procurement, movement and storage of materials, parts and finished inventory (and the related information flows) through the organization and its marketing channels in such a way that current and future profitability are maximized through the cost-effective fulfillment of orders.3) Recognizing the Boundary of Logistics•Material flows•Information flows•Funds flows⏹In-bound logistics⏹Out-bound logistics⏹Dock-to-dock logistics4) Other Types of Logisticsa) Other Types of Logistics•Business logisticsthe efforts of a company to designate the expansion of theseefforts to multiple tiers of suppliers and customers ordistribution•Social logisticsthe setting, maintenance, regulation, and taxation bygovernments of the infrastructure within which companiesoperate, including transportation, communications,controls and law enforcement, taxation, emergencyresponse•Lean logisticsLean logistics tailors approaches to the demand structure ofdifferent items•Production logisticsThe purpose of production logistics is to ensure that eachmachine and workstation is being fed with the right product inthe right quantity and quality at the right point in time.b) Professional logisticianA logistician is a professional logistics practitioner.c) Logistics managementLogistics management is that part of supply chain managementthat plans, implements, and controls the efficient, effective forwardand reverses flow and storage of goods, services, and relatedinformation between the point of origin and the point ofconsumption in order to meet customers’ requirements.Supply chain management is an integrating function with primaryresponsibility for linking major business functions and businessprocesses within and across companies into a cohesive andhigh-performing business modal.3. Mission of Logistics Management1) Logistics Management Provide Competitive Advantagea) Productivity advantageLogistics management can provide a multitude of ways to increaseefficiency and productivity and hence contribute significantly toreduced unit costs.b) Value advantageA number of companies have responded to this by focusing uponservice as a means of gaining a competitive edge.The successful companies will often seek to achieve a positionbased upon both a productivity advantage and a value advantage.2) Gaining Competitive Advantage through LogisticsThe underlying philosophy behind the logistics concept is that of planning and coordinating the materials flow from source to user as an integrated system rather than, as was so often the case in the past, managing the goods flow as a series of independent activities. Thus under a logistics management regime the goal is to link the marketplace, the distribution network, the manufacturing process and the procurement activity in such a way that customers are serviced at higher levels and yet at lower cost. In other words, to achieve the goal of competitive advantage through both cost reduction and service enhancement.3) The Mission of Logistics ManagementThe scope of logistics spans the organization, from the management of raw materials through to the delivery of the final product.Logistics management, from this total systems viewpoint, is the means whereby the needs of customers are satisfied through the coordination of the materials and information flows that extend from the marketplace, through the firm and its operations, and beyond that to suppliers.In this scheme of things, logistics is therefore essentially an integration concept that seeks to develop a system-wide view of the firm.Ideally there should be a one-plan mentality within the business which seeks to replace the conventional stand-alone and separate plans of marketing, distribution, production and procurement.4. The Changing Logistics Environment1) The Customer Service ExplosionCustomer service may be defined as the consistent provision of timeand place utility. In other words products don’t have value until they arein the hands of the customer at time and place required. Essentiallythe role of customer service should be to enhance “value in use”,meaning that the product becomes worth more because service hasadded value to the core product. In this way significant differentiationof the total offer (that is the core product plus the service package) canbe achieved.2) Time CompressionOne of the most visible features of recent years has been the way inwhich time has become a critical issue in management. Product lifecycles are shorter than ever, industrial customers and distributorsrequire just-in-time deliveries, and end users are ever more willing toaccept a substitute product if their first choice is not instantly available.3) Globalization of IndustryThe third of the strategic issues that provide a challenge for logisticsmanagement is the trend towards globalization. A global company ismore than a multinational company. In the global business materialsand components are sourced worldwide, manufactured offshore andsold in many different countries perhaps with local customization.4) Organizational IntegrationThe classical business organization is based upon strict functionaldivisions and hierarchies. It is difficult to achieve a closely integrated,customer-focused materials flow whilst the traditional territorialboundaries are jealously guarded by entrenched management with itsoutmoded priorities.5) The New Rules of competitionSupply chain competition: the fundamental difference from theprevious model of competition is that an organization can no longer actas an isolated an independent entity in competition with other similarlystand-alone organization. Instead, the need to create value deliverysystems that are more responsive to markets and that are much moreconsistent and reliable. In the delivery of that value requires that thesupply chain as a whole be focused on the achievement of thesegoals.a) Responsivenessb) Reliabilityc) Relationships5. Building the Logistics Network of the 21st Century1) Logistics Network Building with E-business Development FrameworkAs supply chains lengthen and become more complex, additional toolsand relationships are needed to plan and coordination activities. Wenow turn our attention to how e-supply chain best practices can beformulated and applied to manage and execute the logisticscomponent.The first question is which component activities should be handledinternally internally and which are better performed externally.The next set of questions deals with how the various best practicesand logistics strengths across the network can be leveraged in themutual fashion to create a logistically excellent value chainconstellation. This leverage must include the best application ofe-commerce and be tied directly to the overall supply chain operationalplan.2) Factors in Optimizing a Logistics Networka) Freight cost and service management•Inbound/outbound rationalization•Carrier management systems•Total transportation cost and service•Operations outsourcing•Administrative serviceb) Fleet management•Total cost analysis•Equipment utilization•Maintenance•Deployment planningc) Load planning•Mode selection•Load building•Load consolidation•Cross-dock planningd) Routing/Scheduling•Inventory management•Trailer capacity utilization•Less-than-truck load shipments e) Warehouse management•Receiving•Picking•Put-away•Load selection•Metrics•Cross-checking•Sales planning coordination•Returns management。

重庆科创职业学院授课方案(教案)课名:成长英语(一)教师:李婷婷班级:软件外包服务ZK1301 编写时间:2013年9月11日3.Listen to Dialogue 1.Students listen to the conversation and try to read it in pairs. Then some Ss read旁批栏:it in pairs. T introduces the etiquette in greeting on PPT. (with smiles on faces;shake hands when first greeting;)4.Perform the activity in pairs.Students read Dialogue 2, discuss in groups and perform it. Then T asks somegroups to perform before the class. Other students give comments and evaluatethe results.Part III. Listening Practice1.Study the New words.students preview the new words on PPT and try to know the meaning, thenread them loudly.2.Listen to Dialogue 1 and fill in the table with information from the dialogue.Dialogue on PPT)3.Check the result and evaluate the students listening ability.4.Learn the useful sentences for the listening.(T presents the useful sentences andexplains them).(1) May I change the major?(2) Have you declared your major?(3) Please fill out the application form over there.(4) I’m sure I will live a colorful life with my dear friends.5. Listen to Dialogues 2 and finish related tasks. Students listen to the dialoguetwice and finish the tasks. T checks the result and evaluates Students listeningability, then explains the key sentences when necessary.Part IV. Summary for Listening and Speakingeful sentences for introduction and greeting on campus; (on PPT)2. Eetiquette in conversations in English.Part IV. Assignments1.Students read Dialogue 3 in pairs out of class and prepare to act in pairs orgroups in class.2.Students finish activities 1-2 on p.4 in groups, T will check the results.重庆科创职业学院授课方案(教案)课名:成长英语(二)教师:李婷婷班级:软件外包服务ZK1301 编写时间:2013年9月11日旁批栏:Part IV. Language points1. (Para. 1) Many high school graduates wrongly assume that college life isfree from worry.Analysis: 本句中含有assume引导的宾语从句“that college life is freefrom worry”, to be free from 意思是“not containing or affected by something harmful or unpleasant”。