动物生理学6.消化与吸收(五)
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:2.02 MB
- 文档页数:25




动物生理学试题库(含参考答案)一、单选题(共78题,每题1分,共78分)1.近曲小管对Na+的重吸收可促进下列哪一组物质的重吸收A、K+、Cl-B、水、Cl-、HCO3-C、H+、K+D、H+、HCO3-E、水、H+、K+正确答案:B2.肾小管液大量被重吸收的主要部位是A、集合管B、髓袢升支细段C、近曲小管D、髓袢升支粗段E、远曲小管正确答案:C3.消化道内,与蛋白质消化无关的酶是A、糜蛋白酶B、胰蛋白酶C、胰淀粉酶D、羧基肽酶正确答案:C4.下列哪种情况醛固酮分泌将增多?A、血Na+升高、血K+降低B、血Na+降低、血K+升高C、血Ca2+升高D、血Cl-升高E、血中葡萄糖浓度升高正确答案:B5.关于胃液分泌的描述哪一项是错误的A、壁细胞分泌盐酸B、主细胞分泌内因子C、黏液细胞分泌黏液D、主细胞分泌胃蛋白酶原正确答案:B6.能合成血管加压素的是A、雌激素、孕激素和催乳素的租用孕激素和生长激素的作用B、孕激素和生长激素的作用C、雌激素的作用D、雌激素和生长激素的作用E、催乳素和缩宫素的作用正确答案:A7.在出血早期,血小板释放一种抗纤溶酶的活性物质,又称______,它能抑制纤维蛋白溶解酶的作用,使纤维蛋白不发生溶解,有利于血栓的形成。
A、血小板第六因子B、血小板第七因子C、血小板第三因子D、血小板第一因子正确答案:A8.交感神经的生理功能是A、心跳减慢减弱B、瞳孔扩大C、外生殖器血管扩张D、胃肠平滑肌收缩正确答案:B9.抗利尿激素的作用不正确的是A、减少肾小管对水的重吸收B、增加集合管对水的通透性C、使集合管对尿素的通透性增加D、使髓袢升支对NaCl的重吸收增加正确答案:A10.内因子的作用是A、结合维生素B12并促进其吸收B、激活胃蛋白酶原C、促进胃肠运动D、使蛋白质变性正确答案:A11.头期胃液分泌的特点是A、酸度高,胃蛋白酶含量尤其低B、酸度低,胃蛋白酶含量尤其高C、酸度及胃蛋白酶含量均高D、酸度及胃蛋白酶含量均低E、分泌量很少,消化力很低正确答案:C12.动脉血氧分压降低时引起呼吸加强的主要机制是A、刺激颈动脉体化学感受器B、刺激中枢化学感受器C、直接刺激脑桥呼吸调整中枢D、刺激中枢化学感受器E、直接刺激延髓呼吸中枢正确答案:E13.内源性与外源性凝血的主要区别是A、凝血酶激活过程B、纤维蛋白形成过程C、是否需要维生素K的参与D、FⅩ激活物的形成过程正确答案:D14.对汗液的描述,错误的是A、汗液中有少量尿素和乳酸B、大量出汗时不但失水而且失NaclC、汗液是高渗溶液D、汗液流经汗腺时,部分氯化钠被吸收正确答案:C15.胆汁中与消化有关的成分是A、胆固醇B、胆盐C、胆色素D、脂肪酸E、水和无机盐正确答案:B16.下列能激活胃蛋白酶原转变成胃蛋白酶的物质为A、Cl-B、Na+C、H+D、K+E、内因子正确答案:C17.下列关于血小板生理特性,表述错误的是A、疏散B、黏附C、释放D、聚集正确答案:A18.单个骨骼肌细胞A、正常时可接受一个以上运动神经元支配B、具有膜内负于膜外的静息电位C、电兴奋可通过纵管系统传向肌细胞深部D、细胞内不储存Ca2+E、以上都正确正确答案:B19.主动脉瓣关闭见于A、等容收缩期开始时B、等容舒张期开始时C、快速射血期开始时D、快速充盈期开始时正确答案:B20.建立条件反射的必要条件是A、先给无关刺激,后给非条件刺激B、不需要非条件刺激的参与C、要在非条件反射的基础上才能建成D、无关刺激必须用铃声正确答案:C21.心脏收缩力增强时,静脉回心血量增加,这是因为A、血流速度加快B、舒张期静脉压低C、舒张期室内压低D、动脉血压升高正确答案:C22.维生素B12缺乏可导致A、巨幼红细胞性贫血B、再生障碍性贫血C、溶血性贫血D、球形红细胞增多症正确答案:A23.最容易吸收水分及营养物质的主要部位是A、小肠B、十二指肠C、胃D、食管及胃E、大肠正确答案:A24.下列腺垂体分泌的激素不属于“促激素”的是A、促甲状腺激素B、促黑激素C、卵泡刺激素D、黄体生成素E、促肾上腺皮质激素正确答案:B25.使胰蛋白酶原活化的最重要物质是A、肠激酶B、糜蛋白酶C、胰蛋白酶原本身D、盐酸正确答案:A26.呼吸的概念是指A、机体与外界环境之间的气体交换过程B、气体进出组织细胞的过程C、呼吸运动D、肺部气体交换的过程E、气体进出于肺的过程正确答案:A27.不易通过红细胞膜的是A、水B、氧气C、二氧化碳D、钠离子正确答案:D28.以下有关反射中枢的叙述,错误的是A、中枢部位存在多个反射中枢B、大脑皮质是各种反射的高级中枢C、某种反射中枢仅存在中枢神经的某一部位D、是中枢神经中完成某种特定功能的细胞群正确答案:C29.三种主要食物在胃中排空的速度由快至慢的顺序是A、糖类,蛋白质,脂肪B、蛋白质,脂肪,糖类C、脂肪,糖类,蛋白质D、糖类,脂肪,蛋白质正确答案:A30.原尿的成分A、比终尿多葡萄糖B、比血浆多蛋白质C、比终尿少葡萄糖D、比血浆少蛋白质E、比血浆少葡萄糖正确答案:D31.胃肠道激素多产生于A、回肠B、十二指肠C、空肠D、胃正确答案:B32.在运动终板处A、产生终板电位即是肌膜的动作电位B、终板膜不产生动作电位C、终板电位与局部电位无共同之处D、终板膜上的离子通道不是化学依从性通道E、以上都不正确正确答案:B33.钠泵的化学本质是A、载体蛋白B、受体蛋白C、Na+- K+依赖式ATP酶D、糖蛋白正确答案:C34.雌性最重要的雌激素是A、雌三醇B、黄体生成素C、绒毛膜促性腺激素D、雌酮E、β-雌二醇正确答案:E35.神经冲动由神经向骨骼肌传递时发生A、神经末梢不发生去极化B、神经末梢释放去甲肾上腺素C、递质与接头后膜受体结合D、产生可传播的终板电位E、以上都不正确正确答案:C36.膝跳反射是属于A、多突触紧张性牵张反射B、单突触紧张性牵张反射C、多突触位相性牵张反射D、单突触位相性牵张反射正确答案:D37.心肌不发生强直收缩的主要原因是A、心肌的兴奋性较低B、心肌的传导速度较慢C、窦房结的自动节律性较低D、房室结传导延搁正确答案:B38.消化管壁平滑肌的生理特性不包括A、对电刺激敏感B、有自动节律性C、对某些物质和激素敏感D、温度下降可使其活动改变正确答案:A39.肺的弹性回缩力见于A、吸气初B、呼气初C、呼气末D、吸气末E、以上都存在正确答案:E40.催产素的主要生理功能是A、刺激乳腺肌上皮细胞收缩,使乳汁排出B、刺激输卵管收缩,促进卵子运行C、刺激催乳素分泌,促进乳汁分泌D、分娩时使子宫剧烈收缩,娩出胎儿E、促进非孕子宫收缩正确答案:A41.第一心音发生在A、等容舒张期B、心房收缩期C、快速充盈期D、心室收缩期正确答案:D42.快速静脉滴注生理盐水时可出现A、肾球囊囊内压升高B、肾小球毛细血管血压升高C、血浆胶体渗透压降低D、肾小球毛细血管血压降低正确答案:C43.有关平静呼吸的叙述,错误的是A、吸气时膈肌收缩B、吸气时肋间外肌收缩C、呼气时胸廓自然回位D、呼气时肋间内肌收缩正确答案:D44.血清与血浆相似,但血清中几乎不含有A、纤维蛋白原B、钠离子C、白蛋白D、钾离子正确答案:A45.动物胃酸显著缺乏时会导致A、小红细胞高色素性贫血B、大红细胞低色素性贫血C、小红细胞低色素性贫血D、大红细胞高色素性贫血正确答案:C46.子宫内膜增厚,血管和腺体增多。


《动物生理学》期末考试试题及答案版《动物生理学》期末考试试题及答案版一、选择题1、在动物生理学中,研究生物体基本生命活动规律的科学称为: A. 人体生理学 B. 动物生理学 C. 细胞生物学 D. 生物物理学2、关于细胞膜的描述,以下哪一项是正确的? A. 细胞膜只包含蛋白质和糖类 B. 细胞膜是由脂质双层构成的 C. 细胞膜上有多种酶和离子通道 D. 细胞膜没有流动性3、关于生物体内的水的描述,以下哪一项是错误的? A. 水在生物体内含量丰富,是生物体的重要组成成分 B. 水在生物体内以自由水和结合水两种形式存在 C. 自由水是指在细胞内可以自由流动的水,主要起运输和润滑作用 D. 结合水是与细胞内其他物质结合的水,主要参与化学反应4、关于消化和吸收的描述,以下哪一项是正确的? A. 胃是消化食物的主要器官 B. 大肠是吸收营养的主要器官 C. 小肠是消化食物的主要器官 D. 口腔是吸收营养的主要器官二、简答题5、请简述动物细胞的基本结构和功能。
51、请简述人体内酸碱平衡的调节机制。
511、请简述光合作用和呼吸作用的基本过程及其在生态系统中的重要意义。
5111、请简述神经元的基本结构和功能,并说明神经元之间的信息传递方式及其影响因素。
三、论述题9、论述动物体内的血液是如何实现物质运输的,以及血液循环对人体健康的影响。
91、论述动物激素的种类、作用机制及其在动物生命活动中的重要意义。
911、论述动物免疫系统的组成、功能及其在应对疾病中的作用。
四、分析题请分析以下实验现象,并回答问题:在进行某一实验时,研究人员将一种实验药物注射到小鼠体内,结果发现小鼠的细胞分裂活动明显增加。
请用动物生理学的知识解释这一现象,并分析该药物是否可能用于人类疾病的治疗。
12. 分析题:请运用动物生理学的知识,分析以上实验现象,并根据实验结果评价该药物在医学研究中的应用前景。
《动物生理学》期末考试试题及答案版一、选择题(每题1分,共10分)1、B. 动物生理学2、C. 细胞膜上有多种酶和离子通道3、D. 细胞膜没有流动性4、C. 小肠是消化食物的主要器官二、简答题(每题5分,共30分)5、动物细胞的基本结构和功能:动物细胞主要由细胞膜、细胞质和细胞核构成。

《动物生理学》名词解释一、绪论1、内环境:内环境是指机体细胞生存的液体环境,如血浆、组织液、淋巴液等。
2、稳态:内环境的理化性质保持在一个相对稳定的动态平衡状态称为稳态。
3、反射:反射是指在中枢神经系统的参与下,机体对内外环境变化产生的规律性应答。
反射的结构基础是反射弧。
4、反应:反应是指可兴奋组织或细胞对刺激所发生的应答。
二、细胞的基本功能5、量子释放:以小泡为单位的倾囊释放称为量子释放。
6、主动转运:主动转运又名主动运输,是指某些物质在细胞膜上的特殊蛋白质帮助下,同时消耗能量,进行逆电-化学梯度跨膜转运的过程。
7、被动转运:被动转运又名被动运输,是指某些物质顺浓度梯度或电位梯度通过细胞膜的扩散过程,其特点是不需要细胞提供能量。
包括简单扩散、滤过和易化扩散。
8、阈电位:能使Na+通道大量开放从而产生动作电位的临界膜电位称为阈电位。
9、阈刺激:在刺激持续时间和对时间变化率保持中等数值的情况下,引起组织产生动作电位的最小刺激强度称为阈刺激。
是衡量组织兴奋性高低的指标。
10、局部兴奋:阈下刺激引起的膜部分去极化的状态称为局部兴奋。
11、终板电位:终板电位是指终板膜上的N2胆碱能受体与ACh结合后,Na+、K+通道开放,Na+内流、K+外流,尤其是以Na+内流为主,从而使终板膜局部产生的去极化电位。
12、跨膜信号转导:跨膜信号转导是指细胞针对外源信息所发生的细胞内生物化学变化及效应的全过程。
三、血液13、生理性止血:生理性止血是指小血管破损后出血自行停止的现象,包括受损小血管收缩、血小板止血栓形成和血液凝固三个过程。
14、血液凝固:血液凝固是指血液由液体状态转变为凝胶状态的过程。
血液凝固实质是血浆中可溶的纤维蛋白原转变为不可溶的纤维蛋白的过程。
15、交叉配血:将供血者红细胞与受血者血清混合作为主侧,将供血者血清与受血者红细胞混合作为次侧,观察有无凝集反应。
这一过程称为交叉配血。
四、血液循环16、正常起搏点:窦房结是心传导系统中自律性最高的部分,故窦房结称为正常起搏点。

动物生理学-5(总分50,考试时间90分钟)A1型题1. 小肠黏膜吸收葡萄糖时,同时转运的离子是( )。
A. Na+B. Cl-C. K+D. Ca2+E. Mg2+2. 最基本的体温调节中枢位于( )。
A. 大脑皮质B. 下丘脑C. 丘脑D. 延髓E. 小脑3. 下列有关胆汁的描述,正确的是( )。
A. 非消化期无胆汁分泌B. 消化期时只有胆囊胆汁排入小肠C. 胆汁中含有脂肪消化酶D. 胆汁中与消化有关的成分是胆盐E. 胆盐可促进蛋白的消化和吸收4. 通过下列哪项可完成肾脏的泌尿功能( )。
A. 肾小体和肾小管的活动B. 肾小体、肾小管和集合管的活动C. 肾单位、集合管和输尿管的活动D. 肾单位的活动E. 以上都不是5. 消化液的生理作用不包括( )。
A. 水解食物中的大分子B. 为消化酶提供适宜的pH环境C. 稀释食物,使其渗透压与血浆相近D. 保护消化道黏膜E. 有时会损伤消化道黏膜6. 对汗液的描述,错误的是( )。
A. 汗液是高渗溶液B. 大量出汗时不但失水而且失NaClC. 汗液中有少量尿素和乳酸D. 汗液流经汗腺时,部分氯化钠被吸收E. 以上都不是7. 当中枢温度升高时( )。
A. 皮肤温度下降B. 直肠温度升高C. 热敏神经元放电频率增加D. 冷敏神经元放电频率增加E. 以上都不是8. 下列激素不属于胃肠激素的是( )。
A. 胃泌素B. 胆囊收缩素C. 肾上腺素D. 促胰液素E. 生长抑素9. 肠期胃液的分泌主要是通过十二指肠释放哪种胃肠激素实现的( )。
A. 胆囊收缩素B. 促胰液素C. 肠抑胃肽D. 胃泌素E. 生长抑素10. 下列与头期胃液分泌有关的描述,错误的是( )。
A. 分泌的持续时间长B. 分泌量大C. 分泌的酸度高D. 与食欲无关E. 以上都不是11. 关于肾单位的叙述,下列哪项是错误的( )。
A. 是肾脏的基本功能单位B. 与集合管共同完成泌尿机能C. 可分为皮质肾单位和近髓肾单位D. 近髓肾单位数量多于皮质肾单位E. 近髓肾单位与尿液浓缩和稀释关系重大12. 蛋白质主要以下列哪种形式吸收( )。

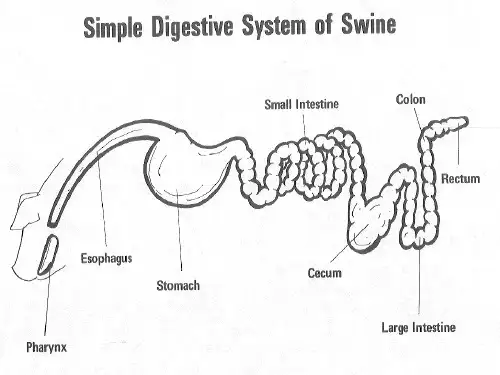
动物生理学中的消化吸收过程动物生理学是研究动物体内各种生理机能的科学,其中消化吸收过程是其中重要的一部分。
在动物体内,消化吸收过程能够将摄入的食物转化为养分,为维持生命活动提供能量和物质基础。
一、胃的消化作用胃是消化系统中的重要器官,主要分为底部、体部和底部三部分。
食物经过食道进入胃后,胃蠕动和胃液的帮助下,开始进行消化作用。
胃液主要由胃壁分泌,包括胃酸、胃蛋白酶和胃粘液等成分。
胃酸的分泌能够使食物降低pH值,起到杀菌的作用,并促进胃蛋白酶的活性。
胃蛋白酶能够将蛋白质分解为多肽和氨基酸,为后续的消化吸收做准备。
胃粘液主要起到保护胃壁的作用,使其不受胃酸的腐蚀。
二、小肠的消化吸收食物进入小肠后,通过胆汁、胰液和小肠粘液的作用,开始进行进一步的消化吸收过程。
小肠截面有大量绒毛,增加了吸收面积。
胆汁来自于肝脏,经由胆管进入小肠。
胆汁中含有胆盐,在脂肪的消化吸收中起到重要作用。
胆盐能够将脂肪乳化,使其表面积增大,便于脂肪酶的作用。
同时,胆盐还可以促进脂肪酶的活性,加速脂肪的水解。
胰液由胰腺分泌,其中含有多种酶类。
胰蛋白酶能够将蛋白质分解为肽和氨基酸,胰淀粉酶能够将淀粉水解为麦芽糖,胰脂酶能够将脂肪分解为甘油和脂肪酸,为后续吸收提供条件。
小肠粘液主要由小肠壁分泌,其中含有黏多糖类物质。
粘液能够保护小肠壁不受胃液和消化酶的腐蚀,同时使腸液黏稠度增加,促进了胃肠道内容物的推进。
三、吸收过程消化后的营养物质通过小肠绒毛进入血液和淋巴系统,完成吸收过程。
小肠黏膜表面有大量微细绒毛,它们具有丰富的血管和淋巴丛。
在这些绒毛上,存在多种摄取机制和运输通道。
醇类和单糖类物质主要通过载体和通道蛋白从小肠绒毛进入血液循环。
肽类物质则通过肽酶的作用分解为氨基酸,在绒毛上的氨基酸转运体与载体蛋白帮助下进入血液循环。
脂肪和脂溶性维生素在小肠绒毛上重新合成为胆酸和脂蛋白,进入淋巴循环。
四、大肠的作用消化吸收过程的最后一部分发生在大肠中。
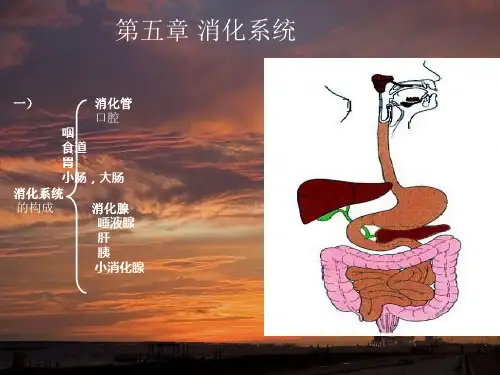
消化系统消化道:口腔、咽、食道、胃、小肠、大肠、肛门——消化食物和吸收营养物质消化腺:唾液腺(唾液)、胃腺(胃液)、肝脏(胆汁)、胰腺(胰液)、肠腺(肠液)消化:食物中的营养物质在消化道内被分解胃可吸收的小分子物质的过程。
吸收:消化后的产物透过消化道黏膜上皮,进入血液和淋巴循环的过程消化方式:物理性、化学性、微生物消化道平滑肌的特性:共性:兴奋性、传导性、收缩性特性:①兴奋性低,收缩缓慢②富伸展性③持续紧张性④自动节律性⑤理化刺激敏感平滑肌电位特性:慢波(基本电节律):自发的、缓慢而短暂的膜电位去极化波。
起源纵行肌。
肌源性峰电位(动作点位):迅速而短暂的去极化波消化道结构:浆膜、纵行肌、环行肌、黏膜下层、黏膜(亚细胞结构—微绒毛)分泌方式:局部分泌:胞吐(肠腺、唾液腺)顶浆分泌:含有分泌物的细胞质的一部分从残留的部分分离而排出(腋窝、脐窝、肛门四周及生殖器)全浆分泌:在一次分泌完了后,腺细胞即死亡,细胞本身被包含在分泌物之中(皮脂腺)消化腺功能:①改变pH,维持酶活性②分解食物为小分子③稀释食物或消化产物,调节渗透压,便于黏膜上皮细胞吸收④分泌粘液、抗体等,保护消化道黏膜消化道功能的调节:神经调节●植物性神经系统●胃肠壁内在神经迷走神经:乙酰胆碱,兴奋胃肠道的运动和分泌交感神经:去甲肾上腺素,意志胃肠道运动和分泌消化道功能的调节:体液调节:胃肠激素1.胃泌素族:胃泌素、CCK2.毅泌素族:促胰液素、胰高血糖素、VIP、糖依赖性胰岛素释放肽3.P物质族:P物质、神经降压素生理作用:1.调节消化道的运动和消化腺的分泌2.调节其他激素的释放咀嚼作用:切碎食物,增加接触面积;混合食物和唾液,形成食团便于吞咽刺激口腔内感受器,引起消化腺分泌、胃肠道运动唾液1.分泌部位:唾液腺:腮腺:浆液细胞,不含粘蛋白颌下腺、舌下腺:浆液细胞、粘液细胞,含粘蛋白口腔小腺体:粘液细胞,含粘蛋白2.成分:水无机物:KCl、NaCl、CaCl、磷酸盐、碳酸氢盐有机物:粘蛋白等3.调节:(1)初级中枢:延髓;高级中枢:下丘脑、大脑皮层(2)神经反射性调节非条件反射:食物对口腔的机械、化学、温度条件反射:食物形状、颜色、气味、采食环境(3)消化道其他部位的反射性调节(如扩大食管或瘤胃内发酵的有机酸等,均能反射性地引起唾液分泌增加)胃液1.成分:(1)胃蛋白酶原:胃酸激活胃胃蛋白酶,pH2.0。
动物生理学考试题+参考答案一、选择题(每题2分,共20分)1. 下列哪种动物的体温不随环境温度变化而变化?A. 狗B. 猫C. 鸟D. 鼠2. 下列哪种动物的生殖方式为有性生殖?A. 蜜蜂B. 鲨鱼C. 鸡D. 蛙3. 下列哪种动物的呼吸系统不具有肺?A. 猪B. 马C. 鱼D. 羊4. 下列哪种动物的心脏具有四个腔室?A. 鸡B. 蛇C. 鲨鱼D. 蜘蛛5. 下列哪种动物的血液循环为单向循环?A. 狗B. 鸟C. 青蛙D. 羊6. 下列哪种动物的神经系统不具有中枢神经系统?A. 鼠B. 猫C. 昆虫D. 蛇7. 下列哪种动物的骨骼系统不具有脊椎骨?A. 牛B. 羊C. 虾D. 鱼8. 下列哪种动物的肌肉组织不具有横纹?A. 狗B. 猫C. 蛙D. 鸟9. 下列哪种动物的消化系统不具有胃?A. 猪B. 马C. 羊D. 蛇10. 下列哪种动物的排泄系统不具有肾脏?A. 狗B. 猫C. 鸟D. 昆虫二、填空题(每题2分,共20分)1. 动物体内的能量供应主要来源于_________。
2. 恒温动物具有能够维持恒定体温的生理机制,如_________和_________等。
3. 昆虫的呼吸系统通过_________进行气体交换。
4. 哺乳动物的牙齿分为_________、_________和_________三种类型。
5. 心脏的结构包括心房、心室、_________和_________等部分。
6. 神经元的基本结构包括细胞体、_________和_________等部分。
7. 动物的内分泌系统由_________、_________和_________等组成。
8. 哺乳动物的繁殖方式为_________,具有_________的特点。
三、简答题(每题10分,共30分)1. 请简要描述动物的体温调节机制。
2. 请简要说明哺乳动物的心脏是如何完成血液循环的。
3. 请简要介绍动物的神经系统是如何传递信息的。
《动物生理学》教学大纲一、课程性质、地位和任务《动物生理学》是研究动物机体生命活动及其规律的学科,是动物科学、动物医学、水产养殖、水族科学与技术、生物学、生物技术等专业必修的专业基础课。
动物生理学在动物生产类、动物医学、动物科学、水产养殖学和水族科学与技术专业的教学计划中具有重要的作用,它对动物生产学、水产增养殖学、动物营养与饲料、动物免疫学、动物疾病学、动物繁殖的生产实习等课程的教学和实践具有重要的基础作用。
动物生理学不仅要描述一个生命活动的现象,还要探讨该生命活动是如何发生、如何进展和如何终结的。
二、课程目标要求认识和了解动物体的生命活动规律,从整体和环境、器官和系统以及细胞和分子的研究水平来解释各种生理现象;从比较的观点掌握生理功能的调节和调控的活动规律,并运用这些规律有效地改善动物的生产性能,预防和治疗动物疾病,保障动物体的健康和动物资源,特别是对濒危动物的保护,促进动物养殖业的发展。
三、教学内容及安排第1章绪论(2学时)教学目标:掌握动物生理学的概念、生理功能的调节方式及其概念。
熟悉动物生理学的三个研究水平、生理功能的调控系统的基本概念。
了解研究方法和学习目的。
重点和难点:重点是生理功能的调节方式及其生理调控方式之间的联系,难点是神经、内分泌、免疫系统及其相互调制作用。
1.1 动物生理学的研究内容(1学时)1.1.1 动物生理学的研究对象1.1.2 动物生理学的三个研究水平1.1.3 动物生理学的研究方法1.2 生理功能的调节及其调控(1学时)1.2.1 生命活动的基本特征1.2.2 生理功能的调节方式1.2.3 动物生理功能的控制系统第2章细胞的基本功能(10学时)教学目标:掌握细胞跨膜物质转运的机制,由离子通道和由G蛋白耦联受体介导的跨膜信号转导过程,生物电的种类、产生、特性、传导和传递机制及其与兴奋性之间的关系,骨骼肌收缩和兴奋-收缩耦联机制。
熟悉细胞膜镶嵌蛋白的生理功能,膜物质转运和跨膜信号转导作用间的相互关系,可兴奋细胞的兴奋性、兴奋及其与离子通道的状态与通透性之间的关系。
1、胆汁中与消化有关的最重要物质是( C )。
A.脂肪酸B.胆色素C.胆盐D.消化酶2.食物在消化道中前进主要是依靠(B )。
A.吞咽B.蠕动C.摆动D.分节运动3. 刺激胃迷走神经可(A )胃运动。
A 促进B 抑制C 无影响4.使胰蛋白酶原活化的最主要的物质是( B )A.盐酸B.肠致活酶C.胰蛋白酶本身D.组织液E.糜蛋白酶5.对脂肪蛋白质消化作用最强的消化液是( D )。
A.唾液B.胃液C.胆汁D.胰液E.小肠液6. 体内哪一种液体的pH值最低?( D )A. 血浆;B. 肠液;C. 胰液;D. 胃液;E. 肝胆汁7.下列关于胃液分泌的描述,错误的是( A )A.主细胞分泌胃蛋白酶B.壁细胞分泌盐酸和内因子C.粘液细胞分泌糖蛋白D.幽门腺分泌黏液E.黏液颈细胞、贲门腺分泌黏液和碳酸氢盐8.氨基酸和葡萄糖在小肠的吸收机制是( B )。
A、渗透与滤过B、主动运输C、入肠作用D、单纯扩散E、易化扩散9.对胃液中盐酸作用的描述,错误的是(E )A.激活胃蛋白酶原B.提供胃蛋白酶所需的最适宜的pH环境C.使蛋白质变性,易于水解D.杀死进入胃内的细菌E.进入小肠后抑制胰液的分泌10. 有关消化道平滑肌生理特性的叙述,错误的是( D )。
A、兴奋性低,收缩缓慢B、经常保持一定的紧张性C、富有伸展性D、具有快而规则的自动节律性E、对化学及牵拉刺激较敏感11. 与维生素B12吸收有关的物质是(D )。
A. 胃蛋白酶B. Na+C. HClD. 内因子12. 与脂肪消化、吸收有关的胆汁成分是( A )。
A. 胆盐B. 胆固醇C. 胆色素D. 卵磷脂13. 刺激交感神经可引起( B )。
A、胃肠运动增强,分泌抑制B、胃肠运动及分泌均抑制C、胃肠运动及分泌均增强D、胃肠运动抑制,分泌增强E、主要引起胃肠运动增强14. 肠上皮细胞由腔肠吸收葡萄糖,是属于(C)A单纯扩散B易化扩散C主动运输D入胞作用E吞噬15. 消化器官不具备哪一功能(D)A 消化食物B. 内分泌C. 免疫 D. 维持酸碱平衡E. 吸收营养16. 有关胃蛋白酶的叙述,错误的是( D )。