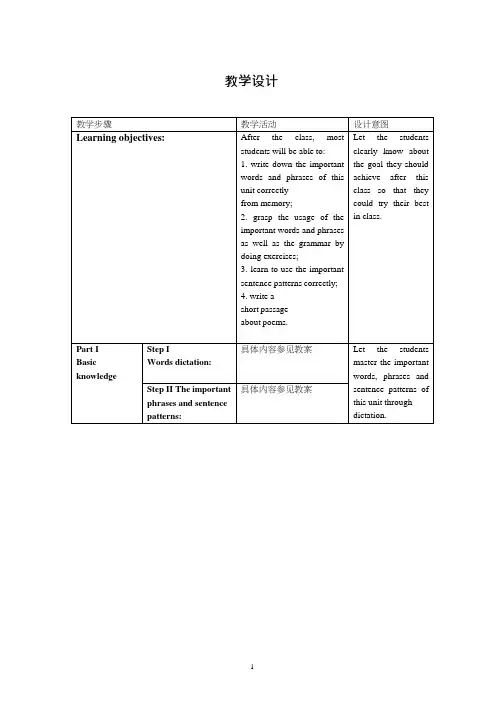
高中英语Unit2PoemsSectionⅤWriting改写诗歌教学案新人教版选修6
- 格式:doc
- 大小:81.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

高中英语Unit 2 Poems Reading and Writing 教案设计(最新版)编制人:__________________审核人:__________________审批人:__________________编制单位:__________________编制时间:____年____月____日序言下载提示:该文档是本店铺精心编制而成的,希望大家下载后,能够帮助大家解决实际问题。
文档下载后可定制修改,请根据实际需要进行调整和使用,谢谢!并且,本店铺为大家提供各种类型的经典范文,如语文资料、数学资料、英语资料、幼儿资料、教案大全、案例分析、教学反思、教育笔记、说课稿、其他资料等等,想了解不同范文格式和写法,敬请关注!Download tips: This document is carefully compiled by this editor.I hope that after you download it, it can help you solve practical problems. The document can be customized and modified after downloading, please adjust and use it according to actual needs, thank you!In addition, this shop provides various types of classic sample essays, such as Chinese materials, mathematics materials, English materials, children’s materials, lesson plans, case analysis, teaching reflection, education notes, lecture notes, other materials, etc. if you want to know the difference Please pay attention to the format and writing of the sampleessay!高中英语Unit 2 Poems Reading and Writing 教案设计Unit 2 Poems Reading and Writing教学内容分析The teaching materials of this period contain two parts. The first part is the reading passage on page 14 with the title of I've Saved the Summer, which is a poem telling a parent speaking to a young adult child. The older person has experienced his/her own journey through life and is offering love to the young person to help him/her begin on his/her own journey through life. The second part is the Writing Task on page 16,which asks the students to write a poem.目标设计Knowledge and skills1. To enable the students to listen to the "music" of the poem, to know how it makes them feel and what it make them think about.2. To get the students to know about the useful new words and phrases.3. To get the students to learn the following useful structures:If I + past tense..., I would...4. To help the students learn how to write a poem starting with "If I..." .Process and methodsReading for specific information, summarizing,discussing and practicing.Emotion ,attitude and value1. To stimulate the students' love to poetry.2. To inspire the students to write poems of their own.教学重、难点1. The under standing of the reading passage.2. The use of the subjunctive mood in poem writing.3. Teaching the students how to write a list poem of their own.教学过程Step 1 RevisionAre these statements true or false?...Step 2 Pre-readingListen to the poem "I've saved the summer" and answer these questions:1. Does the poem have a rhythmic pattern?2. Does the poem have rhyming words?Step 3 Reading1. Circle the words that rhyme. What is unusual about the rhyming words in the last four lines?2. Now listen to the beats of the rhythm are marked below:I’ve saved the summerAnd I give it all to youTo hold on winter morningsWhen the snow is new.I’ve saved some sunlightIf you should ever needA place away from darknessWhere your mind can feed.And for myself I've kept your smileWhen you were but nineteen,Till you’re older you’ll not knowWhat brave young smiles can mean.I know no answersTo help you on your wayThe answers lie somewhereAt the bottom of the day.But if you’ve a need for loveI’ll give you all I ownIt might help you down theroadTill you’ve found your own.Step 4 DiscussionIn small groups discuss these questions:1.Who is the speaker in the poem and who is he /she speaking to ? Give reasons to support your answer.2.Which of the following is the closest to the speaker’s message?A. If it’s cold, I’ll warm you; if it’s dark, I’ll give you light; if you’re hungry, I’ll feed you; if you want to love , I’ll give it to you .B. Although the future may be difficult for you, whenever you need warmth and love, remember I’ll have some to give you.C. While you’re away I’ll remember your smile and I’ll love you always. When you return, I hope you will love me.Step 5 Writing1. Revise the grammar.1). If I had done ..., I would have done ...2). If I did... , I would do...2. Write a list poem.1).Work in groups. The teacher guides the students to writea list poem starting with "If I..." like poem C on page 10. It doesn't have to rhyme.Example:The little girlShe would have survived...If the first driver had been more careful,If the first driver had stopped to give first aid,If the passers-by had given a hand.She would have survived...If the second truck hadn't rolled her.2). Ask the students to watch a video and discuss with their paterners :What would you do if you had a million dollars? After that ask them to write a list poem with the title of If I had a million dollars.Step 6 Summary1. In this class, we've learned a poem "I've saved the summer" through listening,reading and discussing.2.We've also learned how to write a simple list poem.Step 7 Homework1. Reread the poem "I've saved the summer" and appreciate the beauty of the poem.2. Make more sentences with "If I had done ..., I would..."3. Write a poem that starts with “I feel happy when ...”or“Slowly”.。


Unit 2 Poems【美文阅读】THE WINDWho has seen the wind?Neither I nor you;But when the leaves hang trembling,The wind is passing through.Who has seen the wind?Neither you nor I;But when the trees bow down their heads,The wind is passing by.【诱思导学】1.Do you know about the author of the poem?________________________________________________________________________ 2.Who has seen the wind according to the poem?________________________________________________________________________ 【答案】 1.略 2.Nobody.Period ⅠPreviewing●教学目标本课时主要是通过学生对学案所给出的内容的学习,了解本课文中所出现的词汇,初步了解课文以及相关的背景知识,对下一堂课课文的全面理解起到一个铺垫作用。
●教学地位本单元话题是“诗歌”。
文中涉及诗歌的韵律、节奏,并介绍了几种不同内容和形式的简单诗歌。
本单元引导学生讨论这些内容,目的在于让他们了解诗歌的一些基本特征和写作方法,自己尝试写简单的诗歌,并学会欣赏这些优美的文学作品。
●新课导入建议可以通过给学生看地图,拼地形图卡片,看幻灯片等,尽可能多的直观地向学生介绍有关英国概况的知识,使学生对当代英国的经济与政治,城市与乡村等诸多方面有一个整体认识。
老师要尽量给学生自主学习的时间和空间,通过自学、自做、自悟、自助等方式,让学生体会和理解文章的内容,探讨英国的文化。

Section ⅤWriting诗歌改写技法指导本单元的写作任务是诗歌改写。
改写是用不同形式表达同一内容,使之成为与原文意思相同而表达方式、文体不同的作品。
改写可以变换文章的人称、顺序,可以改变原文的体裁、结构,也可以灵活运用自己的语言,尽可能用多种方法来表达、替换原文的内容。
一、基本框架具体写作步骤一般是“三段式”,具体为:第一段:简要介绍诗歌的内容。
第二段:详细论述诗歌的主题。
第三段:总结照应上文。
二、注意事项1.改写必须忠实于原作的中心思想。
这就要求想象和联想要符合原作精神,不能任意想象,谈得漫无边际。
2.改写要注意创作性。
改写是再创作的过程。
作者并不是单纯地翻译诗歌,不能仅就诗歌的内容进行简单的扩充,而是要进一步展开种种想象,使人物形象有血有肉,栩栩如生,使故事情节更加完整生动。
3.改写时可以插入丰富的想象,将原来文中没有的东西,如人物的表情、动作、语言、神态和行为等都加进去,在不改变原作主题思想的基础上,写成一篇完整的文章。
总之,诗歌改写应该把握原文的主题,结合自己的理解,用通俗易懂的语言进行创作,加入自己的语言,使文章符合主题,流畅易懂。
黄金表达1.开头①The poem is written by the famous poet ...②It is rhymed at the end of every line.2.中间①As far as I am concerned, this poem is ...②Compared with other poems, ...③In the poem, we can sense/find ...④The poet expressed his/her feeling of ... in the poem.⑤This poem has successfully touched the hearts of the readers.⑥In my opinion, we should learn ...⑦Therefore, we can find that ...⑧If I were the poet, I would ...⑨We can appreciate the image of ... through the piece of poem. 3.结尾①In conclusion, ...②Through the poem, ...[典题演练]请将下面的英文短诗,以“Reading Is Valuable”为题改写成为一篇短文。

Lesson Plan Unit2 PoemsThe fourth period Using LanguageBackground informationStudents: 50 senior high school students, Grade 2Materials: PEP Book 6 unit 2 _ PoemsType of lesson: speaking and listeningTeaching method: TBLT PPPLesson duration: 45 minutesAids: ppt , blackboardTeachi ng im portan t point s (教学重点):1.Know how to catch the key words when do the listening2.Learn the usages of some important new words and phrases.Teaching difficult points (教学难点):1. Grasp the usages of some important new words and expressions.Teaching methods (教学方法):Communicative Approach, Task -based teaching method, discussion, pair -workTeaching aids (教具): Teaching objectives(教学目标):1.Review the poem I've saved the summer by listening exercise.2.Learn and grasp the usages of some important new words and expressions.3.Share some poems with others.PPT, a tape recorder,blackboardContents (教学内容) :1. Speaking and listening2. Pair-work3. Key words and phrasesTeaching procedures and Time Allotment:I.Getting students ready for learning (3mins)T: Good morning, boys and girls.Ss:…Task 1 Presentation: a student will do a presentation according to the list.II.Lead-in(4mins)Task 1 Pair-work1)Imagination: If you had a bottle which could save everything, what would you put into it and why?e.g. I would save the good old days, so when I grow old I can taste it again.2)Discussion:If you could save a season for someone you love, which one would you choose? Why? Then invite some students to express their ideas.Aims: (1) to catch students’ attention about the topic.(2)to set up develop interest in poems.III.Presentation(12mins)Task 1 Listening: play the tape and fill in the blanks. I’ve saved the summerAnd I ___give___it all to youTo hold on winter___mornings___When the __snow___ is new.I’ve saved some __sunlight___If you should ever__need____A place away from ___darkness____Where your mind can feed.And for myself I’ve kept your __smile__When you were but __nineteen____,Till you’re older you’ll not knowWhat __brave__ young smiles can mean.I know no answersTo __help___ you on your wayThe answers lie somewhereAt the __bottom___ of the day.But if you’ve a need for __love__I’ll give you all I ownIt might help you down the __road__Till you’ve found your own.Aims: (1) to review the poem by listening.(2) to grasp the key words when do the listening.Task 2 Group work: Translate the poem into Chinese Then invite some students to share their opinions.I've saved the summerI’ve saved the summer我把夏天省下,And I give it all to you全部交给了你To hold on winter mornings当雪花儿初降时When the snow is new .让冬天的早晨停住I’ve saved some sunlight我把阳光省下If you should ever need以供你不时之需A place away from darkness在那远离黑暗的地方Where your mind can feed你的心灵会得到养料And for myself I've kept your smile 那年你才十九岁I know no answers我不知道有什么办法To help you on your way帮你踏上你人生的旅程The answers lie somewhere答案也许就在某处At the bottom of the dayBut if you've a need for love但是如果你需要爱I’ll give you all I own我会献上我所有的爱It might help you down the road它也许能帮你踏上旅程Till you've found your own.直到你也找到属于你的爱.When you were but nineteen珍藏了你的微笑Till you'll not know等你长大成人以后What brave young smiles can mean才知道年轻勇敢的微笑的奥秘Aims: (1) to have a better understanding about the poem by translation.(2)to improve the teamwork between group members by discussion.nguage points (15mins)1. appropriate adj. 适当的;正当的e.g. 1)Match the beginning of each sentence with the appropriate ending.把每句话的开头和结尾进行适当的连线搭配。

Unit 2诗歌改写[文体指导]本单元的写作任务是诗歌改写。
改写是用不同形式表达同一内容,使之成为与原文意思相同而表达方式、文体不同的作品。
改写可以变换文章的人称、顺序,可以改变原文的体裁、结构,也可以灵活运用自己的语言,尽可能用多种方法来表达、替换原文的内容。
具体写作步骤一般是“三段式〞,具体为:第一段:简要介绍诗歌。
第二段:详细论述诗歌的主要内容。
第三段:发表看法。
改写诗歌时,应遵循以下原那么:1.要忠实于原作的中心思想这就要求想象和联想要符合原作精神,不能任意想象,漫无边际。
2.适当拓展,服务主题诗歌用词比较精炼、含蓄,感情色彩较浓厚,也就是说它们的内在含义比较丰富,改写时,有发挥想象的余地,可以把原作简洁的词句拓展成具体的景象,形成一篇与主题相关的文章。
3.避免简单翻译,要有创作性改写是再创作的过程,并不是单纯的翻译诗歌,不仅能就诗歌的内容进行简单的扩充,而是要进一步展开种种想象,使人物形象有血有肉,栩栩如生,使故事情节更加完整生动。
总之,诗歌改写应该把握原文的主题,用通俗易懂的语言进行创作,加入自己的语言,使文章符合主题,流畅易懂。
[亮点句式]1.The poem is written by the famous poet...这首诗是由著名的诗人……写的。
2.Its concrete content goes as follows.它的具体内容如下。
3.We can appreciate the image of...through the piece of poem.我们可以通过这首诗歌欣赏到……的意境。
4.In the poem,we can sense/find...在诗歌中,我们能够意识到/发现……5.The writer expressed his/her feeling of...in the poem.作者在诗歌中表达了自己……的感情。
6.This poem has successfully touched the hearts of the readers.这首诗歌成功地触动了读者的心弦。

Unit 2 Poems Ⅰ. 单元教学目标Ⅱ. 目标语言Ⅲ. 教材分析与教材重组1. 教材分析本单元以Poems为话题,从学生初次接触诗歌,一直谈到诗歌创作的动机、有关诗歌的一些基本知识(包括诗歌的种类、风格)等。
旨在通过本单元的学习,使学生在初步了解和掌握诗歌这一文学形式的基本常识的基础上,进行简单的诗歌创作。
1.1 Warming Up部分要求学生回顾所学诗歌,启发学生以小组活动形式分析、列举人们进行诗歌创作的原因。
1.2 Pre-reading 部分首先要求学生说出自己最喜欢的中英文诗歌并阐明理由;然后通过快速阅读Reading部分内容填写列表,区分诗歌种类。
1.3 Reading部分是一篇介绍诗歌基础知识的文章。
文章从诗歌创作的动机、种类、特点及读者对象等方面简要介绍了五种不同风格、特色的诗歌。
1.4 Comprehending 部分根据阅读内容设置了三个习题。
第一个习题要求学生通过读文章、听录音感受诗歌特色,判断自己所喜欢的诗歌类型并说出理由;第二个习题就文章总体内容提出了五个问题,帮助学生进一步了解不同类型诗歌的不同特点;第三个习题通过十一个具体问题考查学生对文中某些细节内容的理解并要求分析诗歌创作者的情感、态度。
1.5 Learning about Language分words and expressions和structures两部分。
第一部分设置了两个练习:第1个练习要求从所学诗歌中找出与所给词汇压韵的词并添加其它韵词;第2个练习要求用所给词汇的正确形式填空。
第二部分通过四个小练习对所学诗歌中出现的两种结构形式进行训练。
1.6 Using Language共设置了三个任务:第一项任务通过一首小诗展开听力、口语、阅读训练,加深学生对诗歌韵律知识的理解;第二项任务通过Miss Jiang与学生谈论诗歌竞赛的一段录音学习,练习“意愿(intentions)”的表达。
第三项任务要求学生运用所学诗歌知识,根据所给提示进行模仿习作训练。

人教版高中英语选修6《Unit2Poems》教案人教版高中英语选修6《Unit 2 Poems》教案【一】教学准备教学目标教学目标(Teaching Aims)知识与技能(Knowledge and Skills)1. 了解教学大纲关于语法填空的命题特点。
2. 能够根据语法填空的命题特点自己编语法填空的题目3. 掌握语法填空的解题方法与技巧过程与方法(Process and Methods) 让每一位同学都能参与到课堂教学与活动中来,以小组或结对的形式进行相互学习和讨论。
情感态度与价值观(Feeling, Attitudes and Values) 学习应对语法填空是与课文相结合,让学生在了解各种不同诗歌形式的背景下学习语法填空的设题与解题特点,从而更加理解英语诗歌的特色,更加懂得如何阅读和欣赏英语诗歌。
教学重难点教学重点(Important Points) :1. 让学生了解语法填空的命题特点2. 掌握语法填空的解题方法与技巧教学难点(Difficult Points):语法填空中词性的转换教学过程(Teachers’ Activities)Step I: Lead-in① Review the new words and expressions of this unit by them together, and then do Task 1---speak out the other forms according to the giv en words② Listen to the song Jingle Bells and try to fill a word intoeach blank.Step II : Pre-practising1. Questions① Do you think it is difficult to complete the items of blank-filling with grammar knowledge?② Have you figured out the characteristics of the i tem?2. ExplainingIn this item there are 10 blanks for you to fill in with less than one proper word① some blanks with a given word while others with none② fill in the blanks with the proper form of the given word according to its grammatical and logical meaning.③ choose a preposition, pronoun, conjunction or an article to fill in the blank without any given word.3. DiscussionHow can we finish the items step by step with our grammar knowledge?① ___________________________________________.② _ __________________________________________.③ ___________________________________________.Step III : While-practising1. Making an item of grammatical blank-filling based on the para graph of the text.① more than 5 blanks.② some blanks with given word.③ other s with none.2. exchange the item you made for your partner to complete it .3. The whole class finis h the one the teacher prepared for them.Step IV : Post-practising1.Check some of the students’ anwsers and give comments.2.Draw a conclusionStep V: Homework Assign ment1. Further improve your skills of dealing with the grammar filling.plete Ex.2 on Page 10, Nanfang New Class人教版高中英语选修6《Unit 2 Poems》教案【二】教学准备教学目标Teaching goals1. Target languagea. Important words and phrasesPoem, poetry, recite, aspect, convey, nursery, rhyme, diamond, cottage, balloon, sparrow, tease, salty, endless, translate, nursery rhyme, take it easy, run out of, make up ofb. Important sentencesWhich poem is about things that don’t make sense?Poets use many different forms of poems to express themselves.I hadn’t taken my eye off the ball.We hadn’t taken it easy.The poem is made up of five lines.A lot of Tang poetry has been translated into English. The translations have a free form that English people like to copy.2. Ability goalsa. Enable Ss to talk about different types of poems: nursery rhymes; list poems; cinquain,; haiku; T ang poemsb. Enable Ss to talk about different purposes of writing poems.c. Understand the main theme of each poem.d. Enable Ss to chant some of their favorite poems.3. Learning abilityEnable Ss to distinguish different types of poems教学重难点Teaching important points1. Talk about five main types of poems.2. Understand the main purpose of writing the poems.Teaching difficult points1. Find the rhythm of each poem.2. Chant the poem.3. Understand the main purpose of writing the poems.教学过程Teaching procedures & waysStep 1. GreetingsStep 2. PresentationAsk Ss to think back and try to remember poems from their early childhood, either in Chinese or in English.Talk about some famous poets both home and abroad, either ancient ones or modern ones.Brainstorming: What will you think of when we talk about the word “poem”?Step 3. Warming upRead the questions in this part, reminding Ss what they notice about the above poems.(e.g. they have a strong beat, or they have rhyme, or they play with words and sounds, or perhaps some of them are funny because they make no sense.) Tell Ss that there are many reasons why people write poetry. Give the examples on the Bb. Ask Ss why they think the poets wrote the poems they have just recited.. Write their suggestionson the board.Give Ss a time limit of a few minutes. Divide the class into groups of four to discuss the purpose of writing poems. Ask one p erson from each group to read their group’s list and add their suggestions to the list on the board. (Suggested reasons: to create certain feelings or images in the reader; to share a feeling or experience; to describe something in detail or give an impression; to get the reader to think about an idea; to express a point of view; to make the reader experience the sight, sounds, smells, feel and tastes of something; to create a mood, to play with words--- their sounds, rhyme and rhythm.)If time permits, in small groups or as a class, discuss the kinds of topics that poets write about.( people, animals, nature, landscapes, the sea, the seasons, stories, death, war, youth and old age, feeling and experiences, emotions like love, hate, sadness, regret and desire, etc.)Step 4. Pre-readingPeople from different countries write different kinds of poems. Get Ss to discuss the questions on Page 9 with their partners: Do you have a favorite poem in Chinese? Why ? Do you have a favorite poem in English? Why?As to exercise 2, give Ss practice in an important reading skill: scanning a text, that is, looking through a text quickly to find specific information. Read the table in exercise 2 with the Ss. Tell them that they are going to look for the information in the table, just in the poems themselves, not in the other parts of the text. They are to look only for those pieces of information and not read every word. Do an example with them.Suggested answers to exercise 2:Step 5. ReadingScanningGet the Ss to read the passage quickly and accurately and meanwhile help the Ss to form a good habit of reading. Teacher gives Ss a couple of minutes to look through the whole passage. Tell them to read the text silently and then ask some detailed questions about the text on the slide show . Teacher should encourage Ss to express their ideas.Q1. Why do people write poetry?Q2. How many forms of poems are mentioned in the passage? What are they?Q3. What does “nursery rhyme” mean? Why do they delight small children?Q4. What’s the characteristic of “list poems”? What about “cinquain”?Q5. Why do English People like “Haiku”?Q6. Are you familiar with Tang Poems? Do you know the title of the last poem in the text?ListeningBefore Ss read the text, have them close their books and listen to the text with their eyes closed. This gives Ss the opportunity to listen to the sounds or “music” of the poems before reading them in detail. Tell them that it doesn’t matter if they don’t understand every word.First readingGet Ss to read the text carefully, finding the one sentence that sums up the paragraph of each part.. Underline the topic sentence.Second readingTell Ss that they are going to look at the rhythm of two of the poems. Make sure they know what rhythm is. Read the limerickaloud and have Ss listen for the strong beats. Then have them clap the strong beats as you read. Mark the strong beats on the limerick on the board.There was an old man with a beardWho said “it is just as I feared”.“Four insects and the nTwo birds and a henHave all made a home in my beard”.Now read the poem A & B. Ask them to mark the strong beats on the two poems that have a strong rhythm. Check their answers . Then play the tape and get them to clap to the strong beats in those two poems.Third readingJust as any scene can serve as the subject of a painting, so any part of daily life can provide material for a poem.. Of course, the choice that the artist or poet makes relates to his or her purpose. Poetry is usually short and compact, so it should be read several times, preferably aloud, to appreciate its meaning. Read the last poem (Poem H), and answer the following questions: Q1. What parts of the poem suggest that the woman loves her husband?Q2. How do you understand the sentence”Should the journeyer return, this stone would utter speech.”? Explain the sentence in your own words.Q3. What picture do you have in your mind when you read the above sentences?Q4. Do you know the Chinese title of this poem? Do you know the Chinese version of the poem?Step 6. Make a short summary of this period.课后习题Homework1. Surf some websites to find out more information about poets.2. Review the content of the reading passage.3. Finish the exercises on Page 12& 13.。


高二英语教案:Unit 2Poems
【摘要】鉴于大家对十分关注,小编在此为大家搜集整理了此文“高二英语教案:Unit 2Poems”,供大家参考!
本文题目:高二英语教案:Unit 2Poems
Unit 2Poems
单元要览
本单元的中心话题是诗歌。
阅读文章中涉及诗歌的韵律和节奏,并介绍了几种不同内容和形式的简单诗歌。
本单元语言知识的选择和听说读写等语言技能的训练主要围绕“诗歌”这一主题进行。
本单元的目的在于帮助学生掌握与“诗歌”这一主题有关的词汇知识,让学生了解诗歌的一些基本特征和写作方法,从而学会欣赏这些优美的文学作品,最终能够自己尝试写简单的诗歌。
本单元的主要教学内容如下表所示:
类别课程标准要求掌握的内容
话题Different types of poems;reading,writing and listening to poetry。
unit,2,poems教案篇一:Unit2Poems教案Unit2Poems★教材分析本单元的中心话题是诗歌。
文中涉及诗歌的韵律、节奏,并介绍了几种简单的不同内容和形式的诗歌。
本单元引导学生讨论这些内容,目的在于让他们了解诗歌的一些基本特征和写作方法,自己尝试写简单的诗歌,并学会欣赏这些优美的文学作品。
★单元目标导读知识目标单元重点词汇、短语与句型。
能力目标通过本单元的学习让学生做到1.掌握本单元教学目的和要求中词汇的用法。
2.掌握虚拟语气的基本用法。
3.培养学生听、说、读、写的能力,并能概括、归纳文章大意、深层理解文章内容、动手解决实际问题的能力。
情感目标通过本单元的学习让学生简要了解文中涉及诗歌的韵律、节奏和几种简单的不同内容和形式的诗歌。
引导学生讨论这些内容,让他们了解诗歌的一些基本特征和写作方法,自己尝试写简单的诗歌,并学会欣赏这些优美的文学作品。
教学设想教材重组1.单元预习,文章整体理解,涵盖了warming-up(热身),Pre-reading(读前),Reading(阅读),comprehending(理解)和UsingLanguage(语言运用)等五部分内容,锻炼学生听说读写的技能,能运用自身已有的知识和经验思考本单元话题,逐渐加深对其的理解。
⑴从单元的话题内容方面把warmingup,Pre-reading,Reading合在一起上一节听说阅读课。
⑵把comprehending以及UsingLanguage中的文章理解部分合在一起上一节课文理解课。
⑶从单元知识方面,把词汇、短语和重点句型合在一起上一、二节知识点的讲授课。
⑷把虚拟语气的基本用法合在一起上一节语法课。
⑸根据本单元话题上一节关于某个问题如何写一封给出自己建议的写作课。
2.课型设计与课时划分①SectioniTextcomprehending(Period1-2)②SectioniiLanguagepointsstudying(Period3-4)③SectioniiiGrammar(Period5)④SectioniVwriting(Period6)SectioniTextcomprehending教学目标1.ToarouseSs’interestinlearningaboutpoems.2.Todevelopsomebasicreadingskills.3.Tolearnsomenewwords.4.Toknowaboutthedifferentstylesofpoems.教学流程StepiLeading-in Showthepoemwrittenbywangzhihuanandaphotographofthewriter.askSstor eadthepoemand.andseeiftheycanrememberanypoemsthattheyhavelearnt,ei therinchineseorinEnglish,andthenaskthemtoreciteoneofthem.Step2:warmingUpPurpose:ToleadSstothetopicofthisunitthroughadiscussion.1.PairworkGetSstoasktheirpartnersthequestions,andthenaskthemtopresentitbeforethe class.(1)whichpoemiswrittentotellastory?(2)whichpoemiswrittentoexpressfeelings?(3)whichpoemiswrittentomakeotherlaugh?…2.GroupworkGetSstotalkabouttheworldfamouspoets.ThepicturesbelowcanbeusedforSst otalkabout,andSscanalsotalkasmuchastheycan.StepiiFast-reading(1)askSsiftheyarecuriousaboutsomeEnglishpoems.dotheywanttoappreciat esomekindofpoems?andgetthesomeSstoanswerthisquestion.(2)Readthroughthetext,preferablytheparagraphsbesidethesevenpoemsandt hendecidewhichpoemyoulikebest?Givereasons.(3)Trytoanswerthequestionsaboutthepassage.①whatisthemaintopicofthereadingpassage?②whatfivekindsofpoemsdoesthereadingpassagetalkabout? Suggestedanswers:①:ThemaintopicofthereadingpassageisaboutsomesimpleformsofEnglishp oems.②:Thefivekindsofpoemsthatthereadingpassagetalksaboutare:nurseryrhym es,listpoems,thecinquain,haikuandTangpoems. Stepiiicomprehending一、Readthetextcarefullyandtrytogetsomedetailsfromthetext.workinpairsandtr ytoaskandanswerquestionsfromthetext.Questionscanbelikethese.①Therearetwopoemsthathaveastrongrhythm.whichonesarethey?②whichtwopoemshaverhyminglines?circlethepairsofrhymingwords.③whichpoemsgiveyouoneclearpictureinyourmind? Suggestedanswers:Q1.TheyarePoemaandPoemB.Eachpoemhasfourbeatsaline.Forexample:hu sh,baby,don’t,word;Pa,buy,don’t,mockingbird;etc.Q2.TheyarePoemsaandB.Poema’srhymingpairs:word/mockingbird,sing/ring,brass/looking-glass,broke/bill y-goat,away/today;PoemB’srhymingpairs:fire/squire,high/sky,lead/dead,race/lace,cat/hat,too/true.Q3.inmyopinion,mostprobablytheyarePoemsF,G,H.StepiVSummary ThepassagemainlysummarizedthecharacteristicsoffivesimpleformsofEngli shpoems,suchasnurseryrhymes,listpoems,cinquain,haikuandTangpoems,e xamplesoftheseformsincluded. SectioniiLanguagepointsstudying重点单词1convey双语释义v.表达,传递,传达(communicate);运送;输送(transport)(1)完成句子①words_cannot_convey_howangryiamwithher.语言无法表达我对她有多么的生气。
人教版高中英语选修六Unit 2 Poems教学设计一、教材分析(一)本单元的中心话题是诗歌。
文中涉及诗歌的韵律、节奏,并介绍了几种不同内容和形式的简单诗歌。
为了让学生能对诗歌的认识和理解有一定的基础和鉴赏水平,笔者将本单元的课时安排进行了处理和调整。
第一课时听说训练,引导学生谈论对诗歌的喜好以及诗歌创作灵感的汲取;第二课时学习Using language “ I’ve saved the summer ”, 让学生通过听读理解诗歌内容,辨认诗人的身份,体会感受,找出诗歌的韵律,并表达由诗歌所激起的联想。
继而,引导学生边打拍子边朗读,在欣赏中加深对诗歌的理解。
阅读后,由五个学习小组分别翻译该诗歌的五小节。
经过两个课时的学习,学生已经不惧怕诗歌,同时还有了创作的愿望。
在此基础上,笔者着手教学Reading--- A few simple forms of English poems。
(二)Reading教学内容分析:该部分介绍了几种简单的英语诗歌。
第一段总括全文,阐述写诗的目的;第二段起,分析不同种类的诗歌,并举例说明。
儿歌节奏明快,韵律和谐、朗朗上口、不断重复、利于记忆,是语言学习的有效手段;清单诗,尤其是那些不断重复短语和节奏的诗歌,比较容易创作。
五行诗,顾名思义,由五行组成,寥寥数语,言简意赅。
俳句起源于日本,由17个音节组成。
唐诗,被英国等所借鉴,许多唐诗被译成英文,广为传诵。
(三)教学目标知识目标:To read for t the characteristics of different forms of poems.能力目标:Enable the students to give their ideas about poets and poems to other group members, using the target language.情感目标:To encourage the Ss to learn to appreciate poems.学习策略:To some extend, students develop the abilities of study, effective communication, dealing with information and thinking and expressing in English.教学重难点:Help the students to understand what the rhyme and rhythm are.To learn the characteristics of different forms of poems.To improve students' reading ability.To practice writing simple poems.Using subjunctive mood correctly in different situations.(四)教学方法:小组合作探究、诗歌朗读、讨论法、竞赛活动(五)教学用具:多媒体、黑板、音乐播放器、小音箱二、学情分析授课班级学生素质较好,具备一定的自主学习能力,特别是本学期年级开展学习合作互助小组以来,学生之间的合作精神、竞争意识都在一定程度上有了较明显的提升。
如何使用英语Unit2Poems的教案进行教学。
一、教材概述鉴于本教案是围绕“Unit2 Poems”展开的,因此,我们需要先对“Unit2 Poems ”进行一个整体性的了解。
关于“Unit2 Poems ”,它是英语教材中的一个单元。
在这个单元里,我们将学习诗歌的写作技巧以及创作灵感,也将了解到一些英语经典诗篇的意境和韵律。
二、教学目标1.了解英语诗歌的写作技巧和创作灵感;2.掌握英语诗歌的基本韵律和诗体;3.学会分析英语经典诗篇的意境和文化内涵;4.能够自行创作英语诗歌。
三、教学重点1.英语诗歌的写作技巧和创作灵感;2.英语诗歌的基本韵律和诗体;3.英语经典诗篇的意境和文化内涵。
四、教学方法1.书面讲解,帮助学生了解诗歌的写作技巧和创作灵感;2.字面训练,让学生对英语诗歌的韵律有实际掌握;3.分析诗歌,帮助学生认识英语经典诗篇的意境和文化内涵。
五、教学步骤1.教师向学生介绍“Unit 2 Poems”单元,并简要讲解本单位置的教学目标和教学重点;2.介绍英语诗歌的基本知识,包括英语诗歌的韵律和诗体等;3.教师帮助学生了解诗歌的写作技巧和创作灵感,并通过介绍一些经典的英语诗歌进行解析;4.通过字面训练,让学生练习英文诗歌的韵律和韵脚;5.分析英语经典诗篇,帮助学生认识诗歌的意境和文化内涵,并引导学生分析和创作英语诗歌;6.教师和学生互动交流,确保学生真正理解和掌握了所学知识。
六、教学效果的评估在教学的过程中,教师可以通过以下方式来评估教学的效果:1.听学生发言,了解学生是否真正明白了所学知识;2.通过分组讨论或个人笔试等方式来评估学生所掌握的知识程度;3.教师可以看学生的创作成果,来看学生是否真正掌握了诗歌的写作技巧。
七、总结通过对“Unit2 Poems ”教案的解析,可以看出,在教学过程中,我们需要充分利用各种教学资源,特别是教案资源,来为我们的教学提供有力支持。
而在具体上课过程中,我们还需要把握好教学的目标、方法和效果评估等关键点,才能真正帮助学生掌握英语诗歌的基本知识和创作技巧,从而提高学生英语语言和文学素养的水平。
Unit 2 Poem (诗歌)Text-understandting (课文理解)Teching aims( 教学目标)1.Know a few simple forms of English poems.2.Learn the charactristics of English poems.Teaching steps as follows:Step 1 Leading-in (课文导入)Listen to a nursey rhyme in the break and then ask students to answer some questions. (课间童谣导入课题)(This step is to arouse students’ interest in learning about poems.)Boys and girls,at the break of the class,we have listened to a very interesting song-Twinkle,twinkle little star.Step 2. Warming up(热身)(This step is intended to excite students to learn about poems)I ofter the questions as follows toexcite students1.Do you like the song ?2.Now,do you want to listen to it again?3.Can you sing the song?4.Can you tell me what kind of poem is it?Is it a nursery rhyme or a haiku? Do you want to know more about English poems?Step 3. Fast reading (快速阅读)(This step is to teach students to get the general idea of the passage )1.Why do people write poems ?2.Read the whole text silently and quickly, and then fill the form below.Step 4Listening(听力)(This step is to train students’listan ability .Explain to them that they should pay specisl attention to the key information)Five kinds of poems areand .Step5. Careful reading (细节阅读)(This step is to deal with prombles in detail )Task1.Answer the questions according to each poem1.Poem A1). What is the baby’s father going to buy if the mirror gets broken?2)What is the baby’s father going to do if goat runs away?2.Poem C1. )What sport do you think the speaker is writing about?2)Why didn’t the players win? Write down three excuses that the speaker gives3)Translate the following sentence into Chinesseif we hadn’t taken it easy,if we hadn’t run out of energy,we would have won3.Poem D,E1.) What subject is the speaker writing about?Poem D:PoemE:2.) 2.) Does the speaker like the subject?Give a reason for your answerPoem D: Yes. Although the speaker describes a couple of negative aspects of his/ her brother, the reader can feel the affection that the speaker feels for his/ her brotherPoem E: No. The reader gets the feeling that the speaker can’t wait until the summer is over. The words drooping, dreading, week in week out and endless convey this feeling.4.Poem H1)What is the story that the poem tells? Tell the story in your own wordsA woman’s husband has gone away. The woman waits for him by the river where she last saw him. she waits and waits never moving form that spot and never speaking, while the river continues to flow and the wind and rain come and go.2)The woman may have the feelings of :loneliness: she was alone watching her husband on the mountain top. love:she waited year after year despite wind and rain.trust:she believed her husband would come back one day. sorrow: year after year, she waited and waited without seeing any hope of her husband’s coming back, she was very sad.Task 2. Fill in the chart as the examples given.Step 6 .Outline(提纲)(This step is to help students know the passage much more clearly) Outline: (课文行文顺序)1 the purpose of writing poems2.nursery rhyme3 list poems4 the cinquain5. the haiku6.Tang poemsStep 7. Consolidation(After the above reading, students can understand the text very well,so I arrange this step to consolidate what they have learned)Poems are used to tell a story or ________ certain emotions. Poets use many different ____________ of poems to ________________ themselves. For example, nursery rhymes _____________ small children because they have strong __________ and _______________and have a lot of _____________ , while, list poems is the _____________ kind ofpoems. Another simple form is the Cinquain ,____________ poem ________________ 5 lines. Haiku is a ______________ form of poetry that consists of 17___________________. In ________________,a lot of Tang poetry has also been ________________________ into English. Step 8.Discussion and performance(This step is helpful to strengthen the cooperation among students and use what they have learned. )1.Are poems good for our life?2 What can we get from poems?Poems bring passion (激情)to our lifePoems help us to understand life, virtues, beauty and romance.Poems make us know we are here and that we can make our life and the world more colorful and beautiful!Step 9.Summary and Homework (小结及作业)1.Summary:In this period,we have learned much about English poems.Only if you have a good knowledge of poems can you understand English literature and culture.2.Homework:Write a composition according to the following poem阅读下面这首由英国诗人爱默生写的英语诗,然后用英语写一篇评价这首诗的短文: A Nation’s Strength 《民族的力量》Not gold,but only man can makeA people great and strong; 不是黄金,只有人才能使民族伟大而强盛;Men who for truth and honor’s sake为了真理,为了荣誉,Stand fast and suffer long. 他们意志坚定,历尽艰辛Brave men who work while others sleep,他们无所畏惧,别人睡觉他们做工Who dare while others fly;别人逃遁他们大显神勇;They build a nation’s pillar deep他们深深地埋下民族的支柱,And lift them to the sky.并将石柱举起支撑天空。
Unit 2 Poems Section Ⅱ Warming amp ;Reading Language Points一、这样记单词二、这样记短语三、这样记句式1.(教材P10)Others try to convey certain emotions. 而有些(诗)则试图传达某种感情。
convey vt.传达;运送请向你的妻子转达我的谢意。
②His determined look conveyed (convey) his meaning that all the injured should be conveyed from the spot to the hospital at once.他坚定的表情表达了他的想法:所有的伤员应该立即从现场转移到医院。
2.(教材P10)List poems have a flexible line length and repeated phrases which give both a pattern and a rhythm to the poem.清单诗可长可短较为灵活且有重复的短语,这就形成了这种诗的固定句型和节奏。
flexible adj.灵活的;可弯曲的;柔顺的这个月,我的日程安排有很大的灵活性。
②The company appreciates a more_flexible design.这家公司喜欢更灵活的设计。
③Leather and rubber are flexible, while glass and iron are not.皮革和橡胶都是易弯曲的,而玻璃和铁则不然。
④Computers offer a much greater degree of flexibility (flexible) in the way work is organized.利用计算机,工作安排可以灵活得多。
3.(教材P10)... if we hadn't taken it easy.……如果我们没有放松警惕。
Unit 2 Poems Section Ⅴ Writing —改写诗歌
本单元的写作任务是诗歌改写。
改写是用不同形式表达同一内容,使之成为与原文意思相同而表达方式、文体不同的作品。
改写可以变换文章的人称、顺序,可以改变原文的体裁、结构,也可以灵活运用自己的语言,尽可能用多种方法来表达、替换原文的内容。
一、基本结构
具体写作步骤一般是“三段式”,具体为:
第一段:简要介绍诗歌的作者及内容。
第二段:详细论述诗歌的主题。
第三段:启迪与感想。
二、注意事项
1.改写必须忠实于原作的中心思想。
这就要求想象和联想要符合原作精神,不能任意想象,扯得漫无边际。
2.改写要注意创作性。
改写是再创作的过程。
作者并不是单纯地翻译诗歌,不能仅就诗歌的内容进行简单的扩充,而是要进一步展开种种想象,使人物形象有血有肉,栩栩如生,使故事情节更加完整生动。
3.改写时可以插入丰富的想象,将原来文中没有的东西,如人物的表情、动作、语言、神态和行为等都加进去,在不改变原作主题思想的基础上,写成一篇完整的文章。
总之,诗歌改写应该把握原文的主题,用通俗易懂的语言进行创作,加入自己的语言,使文章符合主题,流畅易懂。
三、增分佳句
(一)开头常用句式——介绍诗歌及作者
Here is a poem entitled “...” by ..., which enjoys great popularity among readers.
……是……写的一首诗,它深受读者欢迎。
(二)主体常用句式
1.Young as we are, we come to realize that as long as we try, nothing is impossible.
尽管我们年轻,但我们认识到只要我们尝试,一切皆有可能。
2.She often encourages me to face everything, sad or happy.
她常常鼓励要我面对一切,无论是悲伤还是幸福。
3.Remember, the best love is to love others unconditionally rather than make demands on them.
记住,最好的爱存在于对别人的无条件的爱之中,而不是从中有所索求。
(三)结尾常用句式
1.I'm deeply moved by the above poem reminding me of the importance of trying to seize every chance to do what we should before it's too late in our life.
上面这首诗告诉我们抓住机遇及时做好该做的事情对我们人生的重要性,为此我很感动。
2.We should call on people all over the world to change our living ways before all hopes have gone.
我们应该号召全世界的人们在希望破灭之前改变我们的生活方式。
[题目要求]
下面是唐朝诗人李绅的名作《悯农》(Sympathy on the Farmers),请写一篇短文解释一下诗的意思及诗中所蕴含的作者的思想感情。
《悯农》
锄禾日当午,汗滴禾下土。
谁知盘中餐,粒粒皆辛苦。
第一步:审题构思很关键
一、审题
1.确定体裁:本文为诗歌改写;
2.确定人称:本文的主要人称应为第三人称和第一人称;
3.确定时态:主要使用一般现在时。
二、构思
第一部分,诗歌的作者:李绅;时代:唐朝;地位:深受欢迎。
第二部分,介绍诗歌所表达的内容。
第三部分,诗歌的写作意图及现实意义。
第二步:核心词汇想周全
1.be_popular_with 受到……欢迎
2.frequently 频繁地
3.delicious 美味的
4.remind_..._of_... 提醒某人某事
5.waste_food 浪费食物
6.treasure 珍惜
第三步:由词扩句雏形现
1.《悯农》是唐朝诗人李绅写的一首诗。
(过去分词作后置定语;被动语态)
The_poem_entitled_“Sympathy_on_the_Farmers”_is_written_by_Li_Shen_in_the_ Tang_Dynasty.
2.夏日正午时刻,外面天气炎热;农民依然在地里劳作。
(although引导的让步状语;主谓结构;现在进行时)
Although_it's_so_hot_outside_at_this_summer_noon_time,_the_farmers_are_stil l_working_in_the_fields.
3.他们全身湿透,汗水频繁地掉在庄稼生长的土地上。
(主系表结构;and连接的并列句;主谓结构;where引导的定语从句)
They_are_wet_all_over_and_their_sweat_are_frequently_falling_into_the_soil, _where_the_crops_grow.
4.我认为对于当代年轻人来理解这首诗歌并珍惜粮食是很重要的。
(it is+adj.+for sb. to do sth.)
I_think_it's_very_important_for_the_young_generation_today_to_understand_th e_poem_and_treasure_every_grain.
第四步:句式升级造亮点
1.用as引导的倒装句改写句2
Hot_as_it_is_outside_at_this_summer_noon_time,_the_farmers_are_still_workin g_in_the_fields.
2.用with的复合结构改写句3
They_are_wet_all_over_with_their_sweat_frequently_falling_into_the_soil,_wh ere_the_crops_grow.
3.用“it is of+抽象名词+主语从句”结构改写句4
I_think_it's_of_great_importance_that_the_young_generation_today_should_und erstand_the_poem_and_treasure_every_grain.
第五步:过渡衔接联成篇
Here_is_a_poem_entitled_“Sympathy_on_the_Farmers”_by_Li_Shen_in_the_Tang_ Dynasty,_which_enjoys_great_popularity_among_Chinese_readers._It_goes_like_this :_Hot_as_it_is_outside_at_this_summer_noon_time,_the_farmers_are_still_working_ in_the_fields._They_are_wet_all_over_with_their_sweat_frequently_falling_into_t he_soil,_where_the_crops_grow._But_who_on_earth_knows_exactly_all_the_delicious _dishes_on_our_table_come_from_the_hard_work_of_the_farmers?
Li_Shen_wrote_this_poem_in_order_to_remind_people_of_the_importance_of_the_farm
ers'_hard_work._Nowadays,_many_young_people_waste_a_lot_of_food._I_think,_it's_ of_great_importance_that_the_young_generation_today_should_understand_the_poem_ and_treasure_every_grain.。