腹膜透析患者容量管理
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:4.18 MB
- 文档页数:55






中国血液净化2020年3月第19卷第3期Chin J Blood Purif,March,2020,Vol.19,No.3·护理研究·契约式管理对腹膜透析患者的容量管理效果刘丽1吴燕妮1张蕊1【摘要】目的用契约式管理方式对容量超负荷的腹膜透析患者进行容量管理,并进行效果分析。
方法选取哈尔滨医科大学附属第二医院腹膜透析中心经人体成分分析仪筛选容量超负荷并满足入组标准患者随机分为实验组与对照组,对照组实施常规健康教育,实验组在此基础上实施契约式管理并签订健康管理协议。
观察时间为6个月,比较2组容量管理行为、容量状况和透析相关指标以及实验室检查结果等的差异。
结果观察6个月后,相对于对照组,实验组患者体质量降低(t=-3.201,P=0.002);对血压的监测次数增加(Z=-2.265,P=0.024),液体摄入量减少(Z=-2.285,P=0.022);实验组容量超负荷指标改善(t=-3.623,P=0.001)。
结论契约式管理对腹膜透析患者的容量管理有明显约束作用,能改善其容量管理行为,改善患者容量状况。
【关键词】腹膜透析;契约式管理;容量管理;容量状况;健康管理模式中图分类号:R473文献标识码:A doi:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4091.2020.03.015Contractual management model improved fluid status in peritoneal dialysis patients LIU Li1,WU Yan-ni1,ZHANG Rui11Department of Nephrology,the Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University,Harbin150086,ChinaCorresponding author:LIU Li,Email:****************【Abstract】Objective To evaluate the effectiveness of contractual management on fluid status in perito-neal dialysis(PD)patients.Methods Patients with over hydration screened by human body compositionmonitor and met the inclusion criteria from the Peritoneal Dialysis Center of the Second Affiliated Hospital ofHarbin Medical University were randomly assigned into two groups.Patients in control group received rou-tine health care and those in experimental group adopted contract management on the basis of routine healtheducation and signed a health care agreement.The volume management behavior,volume status,dialysis relat-ed indicators and laboratory examination results were compared before intervention and after intervention for6months.Results In experiment group after the intervention for6months,body weight decreased as com-pared with that in control group(t=-3.201,P=0.002),the times of blood pressure measurement per week in-creased(Z=-2.265,P=0.024),liquid intake decreased(Z=-2.285,P=0.022),and over hydration parameters im-proved(t=-3.623,P=0.001).Conclusion Contractual management is a management mode that obviously re-stricts the volume management of PD patients.This management can improve the volume management behav-ior and volume status in PD patients.【Key words】Peritoneal dialysis;Contractual management;V olume management;V olume status;Healthmanagement model腹膜透析(peritoneal dialysis,PD)是终末期肾病(end-stage renal disease,ESRD)患者尤其是亚裔终末期肾病患者一种成功的肾脏替代治疗方法[1]。

应用品管圈提高腹膜透析患者容量管理依从性的临床实践陈静;王娟;徐鹏飞【期刊名称】《中国医药科学》【年(卷),期】2018(008)023【摘要】目的探讨品管圈管理工具在提高腹膜透析患者的容量管理依从性中的应用.方法成立品管圈小组,确立\"提高腹膜透析患者的容量管理依从性\"为活动主题,进行现况调查、目标设定、原因分析、对策拟定,应用PDCA循环原则实施各项对策.结果我科通过开展品管圈活动,制订规范化容量管理的方法和流程,使腹膜透析患者容量超负荷的发生率由原来的25%降至8%,护士的各项隐性能力也显著提高.结论应用品管圈活动对腹膜透析患者进行容量管理的控制,规范了腹透患者容量管理的流程,降低了腹透患者容量超负荷的发生率,提高了患者的依从性,此种方法和流程值得在临床科室推广.该活动同时增加了护士的主动管理能力,便于更好的促进临床实际问题的解决.【总页数】4页(P138-141)【作者】陈静;王娟;徐鹏飞【作者单位】南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院肾内科,江苏南京 210000;南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院肾内科,江苏南京 210000;南京大学医学院附属鼓楼医院肾内科,江苏南京 210000【正文语种】中文【中图分类】R473.5【相关文献】1.品管圈在提高透析患者治疗依从性中的应用 [J], 程辉;黄秋鹏;庞晴;何霁;2.品管圈活动在提高透析患者控水依从性中的应用 [J], 顾文娟;张红娟;赵黎3.品管圈在提高透析患者治疗依从性中的应用 [J], 程辉;黄秋鹏;庞晴;何霁4.自动化腹膜透析在维持性腹膜透析患者容量管理中的应用 [J], 罗佩婷; 张禹; 李忻阳; 陈洋洋; 赵巧; 苗里宁; 崔文鹏5.5E康复模式联合个案管理对腹膜透析患者容量管理依从性及预后的影响 [J], 田兴;苗金红;姚岚;梁小丽;郑媛;刘晓;袁媛因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。

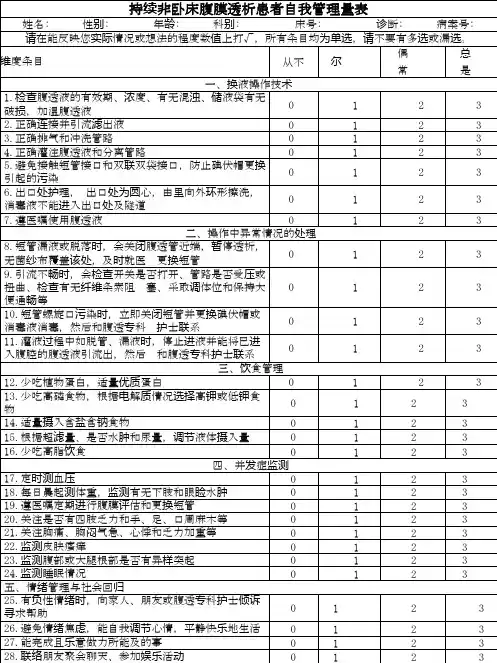

护理实践与研究201 7年第14卷第14期17•腹膜透析患者自我管理行为与营养状况及容量负荷的相关性研究李祥云摘要目的:探讨腹膜透析患者自我管理行为与营养状况及容量负荷的关系。
方法:2014年1月〜2016年12月选取腹膜透析时间大于3个 月的患者150例为研究对象,根据患者容量负荷情况将患者分为无水肿组〇 = 75),轻度水肿组〇 = 40),中度水肿组〇=20)及重度水肿组〇 二15),应用自我管理行为评定量表评定各组自我管理行为,并测定各组患者营养状况。
结果:腹膜透析无水肿组患者血清蛋白、血红蛋白水平高于其余各组(P<〇.〇5),而24 h腹膜液蛋白丢失量少于其余各组(P<0.05),且随着腹膜透析患者容量负荷量增加(P<0.05),患者血清蛋 白、血红蛋白水平明显减少(P<〇.05),而24 h腹膜液蛋白丢失量明显增加(P<0.05)。
腹膜透析无水肿组在饮食及液体摄入、治疗行为、身体 活动、心理社会行为及自我管理行为总分方面均高于轻度、中度及重度水肿组(P<〇.〇5),且随着腹膜透析患者容量负荷量增加患者自我管理行 为总评分及各维度评分明显下降(P<〇.〇5)。
经Pearson单因素分析可知,腹膜透析患者自我管理行为与患者容量负荷量及24 h腹膜液蛋白丢 失量呈负相关(P<〇.〇5),而与血清蛋白、血红蛋白水平呈正相关(P<〇.05)。
结论:容量负荷量增多的腹膜透析患者营养状况恶化,而患者自 我管理行为与营养状况及腹膜透析负荷量有密切的关系,通过提高患者自我管理行为将有助于改善患者容量负荷量及营养状况。
关键词腹膜透析;自我管理行为;营养状况;容量负荷 doi :10.3969/j. issn. 1672 -9676.2017.14.006Research on correlation between self - management behaviors of peritoneal dialysis patients and nutrition condition and capacity loadLI Xiang - yun(The Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University, Xuzhou 221000)Abstract Objective : To discuss the relation between the self - management behaviors of peritoneal dialysis patients and their nutrition condition and capacity load. Methods :Selected 150 patients with peritoneal dialysis duration more than 3 months from January 2014 to December 2016 as the research object, and the patients were divided into no edema group ( n =15) ,slight edema group ( n, = 40) , moderate edema group ( n, = 20) and severe edema group (n = 15),and self - management behavior rating scale was used to evaluate the self - management behaviors of each group and determine the nutrition condition of patients in each group. Results :The serum protein, hemoglobin levels of peritoneal dialysis patients in the no edema group were higher than those of patients in other groups(P <0.05) , while their loss of peritoneal fluid protein within 24h was less than that of patients in other groups(P <0. 05) , and with the increase of capacity load of peritoneal dialysis patients(P <0.05 ) ,the patients5serum protein and hemoglobin levels decreased significantly(P <0.05), while the peritoneal fluid protein within 24h increased(P <0.05). The peritoneal dialysis patients in the no edema group hand total scores of diet and fluid digestion ,treatment behavior, physical activity, psychological and social behaviors and self - management behavior than those of patients in the slight, moderate and severe edema groups(P <0. 05) , and with the increase of capacity load of peritoneal dialysis patients, the total scores and score of each dimension of self - management behavior of patients decreased significantly (P < 0. 05 ). Through Pearson single - factor analysis, the self - management behavior of peritoneal dialysis patients was of negative correlation with the patients5capacity load amount and loss of peritoneal fluid protein within 24h (P < 0.05), while it was of positive correlation with the serum protein and hemoglobin levels(P <0. 05). Conclusion:The peritoneal dialysis patients with increase of load capacity had their nutrition condition aggravated, while the patients5self - management behavior had a close relation with nutrition condition and peritoneal dialysis load capacity, and by improving the patients5self - management behavior, it would be helpful to improve the patients5capacity load and nutrition condition.Key words Peritoneal dialysis ;Self - management behavior; Nutritional status;Capacity load腹膜透析是目前治疗终末期肾病有效的方法,腹膜透析 过程中容量负荷增加是较常见的现象,容量负荷增加不仅会 加重患者营养不良,同时也是导致腹膜透析患者退出及死亡 的重要因素[1]。

1例腹膜透析病人容量管理的健康教育程晓莉;余巧琴;潘琳琳【摘要】分析1例腹膜透析病人在透析期间出现容量超负荷的原因,通过水盐的控制、提高自我管理水平、调整腹膜透析方案、控制感染、保护腹膜功能等相关的健康教育措施,病人能自我有效控制水分摄入,达到容量平衡,体重在理想范围内.【期刊名称】《全科护理》【年(卷),期】2017(015)035【总页数】2页(P4466-4467)【关键词】腹膜透析;容量管理;健康教育【作者】程晓莉;余巧琴;潘琳琳【作者单位】310003 ,浙江大学医学院附属第一医院;310003 ,浙江大学医学院附属第一医院;310003 ,浙江大学医学院附属第一医院【正文语种】中文【中图分类】R473.5欧洲最佳实践指南指出透析充分性不仅包括小分子溶质的清除还包括液体的清除。
容量超负荷是腹膜透析病人常见的临床问题,长期容量超负荷导致左心室肥厚、高血压、心力衰竭等心血管系统并发症[1]。
液体和钠的清除不良是腹膜透析病人死亡的独立危险因素[2]。
因此必须加强对腹膜透析病人及家属的健康教育。
1例病人2014年11月行腹膜透析至今,出现多次容量超负荷现象,对此制定相关健康教育。
现报告如下。
病人,女,25岁,身高182 cm,体重91 kg,学历大专,未婚独居,生活自理。
2014年11月1日因乏力发现血肌酐升高至925 μmol/L,开始腹膜透析。
腹膜平衡试验为低平均转运。
在此期间因饮水控制不佳,心功能减退,容量超负荷出现全身水肿、胸闷、气促,有胸腔积液,出现左心衰竭,住院3次。
在此期间给予控制液体入量、调整透析方案、抗感染、加强心功能等治疗。
现病人无尿状态,体重67.5 kg,与父母同住,继续居家行腹膜透析。
腹膜透析方案为日间不卧床腹腔透析(DAPD)1.5%腹膜透析液10 000 mL,保留3 h。
每日口入饮水量约600 mL,每日腹膜透析超滤约800 mL,血红蛋白63 g/L,血肌酐1 237 μmol/L,活动后无明显胸闷、气促。
居家保姆操作的腹膜透析患者的容量控制培训体会作者:董雅梦周旎娜王娜万梅来源:《中国保健营养·中旬刊》2014年第01期【摘要】目的:提高居家腹透患者的容量控制平衡。
方法:观察71例保姆照顾的腹透居家患者的容量控制情况,制定针对性强的护理干预措施。
结果:有效减少保姆照顾的居家腹透病人容量控制失衡。
结论:针对性强的护理措施,责任心,才能提高腹透病人生存率和生存质量【关键词】腹膜透析居家保姆容量控制【中图分类号】R473.2 【文献标识码】A 【文章编号】1004-7484(2014)01-0073-02腹膜透析(peritoneal dialysis,PD)是一种治疗终末期肾病的肾脏替代治疗方式[1],以居家式为主。
其操作简单、安全有效,并节约医疗资源。
如何维持腹膜透析患者容量平衡,是影响腹膜透析成败的关键。
良好的容量平衡是腹透充分性的重要指标之一。
容量超负荷是腹透高退出率的重要原因。
37.8%的腹透患者容量超负荷[2]。
2010年4月至2013年2月,我科收治腹膜透析病人71例,其中65岁以上病人占49.2 %,因不能自理、家属无法照顾到位选择雇用保姆的占45%。
保姆照顾的病人容量控制不达标的占77.1%。
本文通过针对性的护理干预,有效减少了保姆照顾的居家腹透病人容量控制失衡,总结如下:1 现状:调查发现,保姆中专学历占87%,小学学历占11%,无学历占2%,一例退休护士,在区级医院做临床工作30年。
保姆存在操作不正规,责任心下降,更换频繁现象,致使被照顾的病人有情绪不稳定、与保姆有信任危机,合作关系紧张,导致病人被照顾不周,饮食控制不当,容量控制不理想,使水肿、高血压、心功能衰竭等并发症增多。
同时由于病人年龄偏大,咀嚼能力、消化能力差,只能进软食或半流质,饮食种类有限,只以粥等半流质为主。
或因病人认知功能下降,手眼协调问题,病痛导致无法接受腹透相关知识的学习,且依赖性强,致使自我护理过程不当,出现问题。
【健康教育】亲属督导在腹膜透析患者容量管理中的效果罗 逊(湖南省人民医院,湖南 长沙 410005)【摘要】 目的:探讨亲属督导在腹膜透析患者容量管理中的效果㊂方法:选取进行腹膜透析的52例患者,按随机数字表法分为研究组和对照组,研究组采用亲属督导,对照组不采用亲属督导,比较两组亲属的腹膜透析容量管理知识评分,两组容量管理能力评分和腹膜透析前后血肌酐水平㊂结果:研究组腹膜透析容量管理知识评分明显高于对照组,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05);研究组各项容量管理能力评分均明显低于对照组,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)㊂腹膜透析前,两组血肌酐比较无统计学差异(P>0.05);腹膜透析后,研究组血肌酐明显低于对照组,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05)㊂结论:腹膜透析患者采用亲属督导可有效提高患者的容量管理水平㊂【关键词】 亲属督导;腹膜透析;容量管理doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-0369.2018.05.046中图分类号: R459.5 文献标识码: B 文章编号: 1672-0369(2018)05-0094-02 慢性肾脏病患者需要腹膜透析治疗,应对亲属进行有效的健康知识宣传,加强督导,可提高亲属的督导能力[1],亲属督导可帮助腹膜透析患者提高容量管理能力,从而减少心血管并发症的发生[2]㊂本文探讨亲属督导在腹膜透析患者容量管理中的效果㊂1 资料与方法1.1 一般资料 选取2014年2月至2016年1月于湖南省人民医院进行腹膜透析的52例患者为研究对象,患者基础疾病:糖尿病肾病11例㊁高血压12例㊁冠心病10例㊁COPD19例㊂患者本人和亲属对研究知情同意㊂排除标准:①重要脏器功能不全者;②恶性心律失常㊁恶性肿瘤或精神病患者;③文化程度低,不能理解腹膜透析专职医生宣传教育者㊂按随机数字表法将研究对象分为研究组和对照组各50例,研究组男27例,女23例;年龄40~67岁,平均(53.67±12.82)岁,对照组男25例,女25例;年龄40~69岁,平均(52.16±11.85)岁㊂两组患者一般资料比较,无明显差异(P>0.05),具有可比性㊂1.2 方法 对照组不采用亲属督导,研究组采用亲属督导㊂亲属督导内容包括①心理教育:告知亲属多与患者交流,鼓励患者说出自己内心的感受,强调腹膜透析的重要性,多讲解成功的例子,让患者重拾与疾病抗争的信心;必要时可请有腹膜透析操作经验专家及家属现场讲解,介绍相关经验,消除患者不良情绪,对疾病的康复充满信心;②操作教育:护理人员要掌握告知家属学会正确操作腹膜透析的步骤及方法,必须严格遵守无菌原则,并制定对患者的健康教育计划,通过讲解㊁演示㊁视频放映等方式对家属讲解腹膜透析的正规操作,然后护理人员要亲自示范标准的换液步骤:准备→连接→引流→冲洗→灌注→分离[3]㊂家属要告知其在腹膜透析置管术后两周内不得洗澡,两周后洗澡时也不能盆浴,只能在洗澡袋的保护下进行淋浴,且每次浴后必须进行换药;如果切口出现渗液㊁损伤㊁感染或出血,一定要及时就医处理;导管需固定完好,避免过度牵拉腹膜透析置管,固定时要顺着腹膜透析导管和外接短管的自然走势,不要扭曲㊁弯折;③饮食教育:腹膜透析患者每日蛋白摄入为:1.0~1.5g/(kg㊃d),以优质蛋白质为主,如牛奶㊁瘦肉等,摄入足够的碳水化合物,鼓励患者摄入含不饱和脂肪酸多的植物油,以防止高胆固醇,如出现水肿㊁少尿者应限制饮食,适当补充水溶性维生素,多食含有丰富维生素的蔬菜及水果,少食虾㊁动物内脏等含磷高的食物㊂指导患者尽量在放出腹透液后进餐,以增加食欲㊂1.3 观察指标 对比两组亲属的腹膜透析容量管理知识评分;两组患者容量管理能力评分和腹膜透析前后血肌酐水平㊂在两组健康教育前后通过发放调查问卷的形式通过腹膜透析容量管理知识评分对患者腹膜透析容量管理知识进行评价,项目有腹透的作用㊁腹透排水的途径㊁保持出入平衡策略㊁每天盐的摄入量㊁哪些是高盐食物㊁体内水分过多的原因㊁减轻水肿的方法㊁脱水的表现及脱水时如何处理等㊂问卷满分100分,分数越高,患者容量管理知识掌握越好㊂在患者出院时统一发放调查问卷对患者容量管理能力进行评价,项目有容量管理知识㊁容量管理行为㊁饮食管理㊁少吃高盐高钠食物㊁液体摄入量能力㊁定时测血压㊁晨起测体重及遵医嘱定期检查,每项100分,分数越高,患者容量管理能力越强㊂491.4 统计学方法 采用SPSS17.0软件,计数资料采用(%)来表示,采用x2检验;计量资料用(⎺x±s)表示,t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义㊂2 结果2.1 两组亲属的腹膜透析容量管理知识评分比较 健康教育前,两组亲属的腹膜透析容量管理知识评分比较无统计学差异(P>0.05);健康教育后,研究组亲属的腹膜透析容量管理知识评分明显高于对照组,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1㊂2.2 两组容量管理能力评分比较 研究组各项容量管理能力评分均明显低于对照组,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表2㊂表1 两组亲属的腹膜透析容量管理知识评分比较(分,⎺x±s)组别健康教育前健康教育后对照组(n=50)53.63±5.8763.58±6.38研究组(n=50)49.63±6.3583.36±7.14 t值 6.72 6.88P值<0.05<0.05表2 两组容量管理能力评分比较(分,⎺x±s)组别容量管理知识容量管理行为饮食管理少吃高盐高钠食物液体摄入量能力定时测血压晨起测体重遵医嘱定期检查对照组(n=50)86.35±12.8788.69±5.7491.36±5.3787.63±6.3290.25±4.3691.45±5.8296.35±4.2591.25±4.25研究组(n=50)72.36±5.3568.63±4.2571.39±5.8776.35±6.3373.65±5.2572.55±4.2876.35±6.1377.48±5.28 t值 6.72 6.887.51 6.35 5.28 6.34 5.37 4.52P值<0.05<0.05<0.05<0.05<0.05<0.05<0.05<0.052.3 两组腹膜透析前后血肌酐水平 腹膜透析前,两组血肌酐比较无统计学差异(P>0.05);腹膜透析后,研究组血肌酐明显低于对照组,组间差异具有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表3㊂表3 两组腹膜透析前后血肌酐水平比较(mmol/L,⎺x±s)组别腹膜透析前腹膜透析后对照组(n=50)438.54±45.82125.25±8.55研究组(n=50)426.35±46.02187.52±8.65 t值 6.72 6.88P值<0.05<0.053 讨论通过腹膜透析操作过程是需要患者或者亲属进行操作㊂亲属在这一过程中需要掌握腹膜透析的正规操作,并了解一定的应急处理知识,以便提高患者治疗依从性,这样能够降低腹膜炎等并发症的发生,从而改善患者的生活质量,提高存活率㊂容量负荷过重是引起腹膜透析患者高血压的常见原因,有70%的患者都有容量超负荷[5,6]㊂腹膜透析患者的容量管理与患者的生存质量及并发症的发生密切相关㊂首先腹膜透析患者要使用高浓度的渗透液来排出摄入体内多余的水,但长时期的透析会增强患者对水盐摄入的敏感性,使其静脉血回流量㊁右心室负荷随之升高,最终出现充血性心力衰竭㊂此外体内液体过多会稀释血液,导致溶质清除率降低,同时体内血清白蛋白水平下降,血浆渗透压下降,胃肠道黏膜水肿,增加营养不良发生率㊂影响腹膜透析患者容量管理的因素众多,主要与患者长期患病,心理压力较大有关㊂本研究结果显示,研究组容量管理知识评分明显高于对照组,表明对亲属进行健康教育可以帮助家属对疾病有系统性的认识㊂本研究结果还显示,研究组容量管理能力评分明显高于对照组,表明通过家庭的有效力量,激发患者加强自我管理的信心,调动容量管理的积极性,在患者出现容量负荷时,亲属成为患者的主要精神支撑力量,提高患者容量管理的自我效能㊂综上所述,腹膜透析患者采用亲属督导可有效提高患者的容量管理水平㊂参考文献[1] 卢海霞,张娜,宋艳,等.我国家庭护理对高血压患者健康状况影响的Meta分析[J].中国全科医学,2012,15(24):2799-2802.[2] 肖晓玲,胡秋秋,刘玉萍.家属参与健康教育在2型糖尿病管理中的应用[J].中华护理杂志,2012,47(4):313-316. [3] 赵伟,吴国华,王鹏,等.家庭参与式健康管理对社区2型糖尿病患者自护行为影响研究[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(34): 4062-4064.[4] Kelly M,McCarthy S,Sahm LJ.Knowledge,attitudes and beliefs ofpatients and carers regarding medication adherence:a review of qualitative literature[J].Eur J Clin Pharmacol,2014,70(12): 1423-1431.[5] Cicolini G,Palma E,Simonetta C,et al.Influence of family carerson haemodialyzed patients'adherence to dietary and fluid restric⁃tions:an observational study[J].J Adv Nurs,2012,68(11):2410 -2417.编辑:周金环59。