例题ABAQUS(全面)
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:985.60 KB
- 文档页数:5
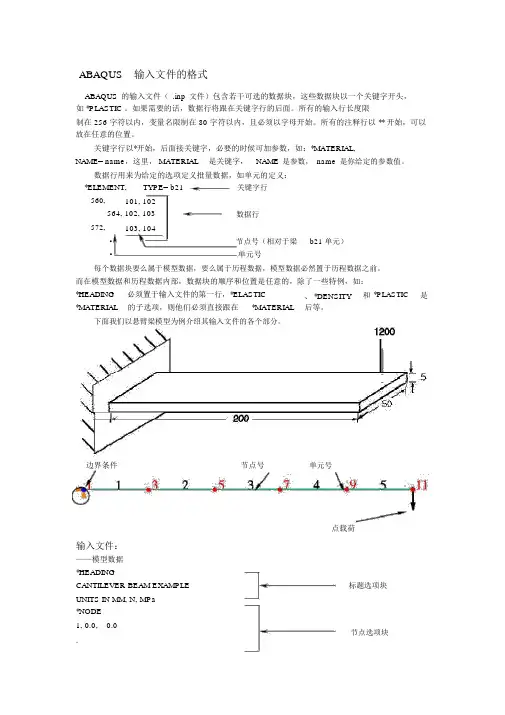
ABAQUS输入文件的格式ABAQUS 的输入文件( .inp 文件)包含若干可选的数据块,这些数据块以一个关键字开头,如 *PLASTIC 。
如果需要的话,数据行将跟在关键字行的后面。
所有的输入行长度限制在 256 字符以内,变量名限制在 80 字符以内,且必须以字母开始。
所有的注释行以 ** 开始,可以放在任意的位置。
关键字行以*开始,后面接关键字,必要的时候可加参数,如:*MATERIAL,NAME= name,这里, MATERIAL是关键字,NAME是参数,name是你给定的参数值。
数据行用来为给定的选项定义批量数据,如单元的定义:*ELEMENT,TYPE= b21关键字行560,101, 102564, 102, 103数据行572,103, 104·节点号(相对于梁·单元号b21 单元)每个数据块要么属于模型数据,要么属于历程数据,模型数据必然置于历程数据之前。
而在模型数据和历程数据内部,数据块的顺序和位置是任意的,除了一些特例,如:*HEADING *MATERIAL 必须置于输入文件的第一行,*ELASTIC的子选项,则他们必须直接跟在*MATERIAL、 *DENSITY后等。
和*PLASTIC是下面我们以悬臂梁模型为例介绍其输入文件的各个部分。
边界条件节点号单元号点载荷输入文件:——模型数据*HEADINGCANTILEVER BEAM EXAMPLE标题选项块UNITS IN MM, N, MPa*NODE1, 0.0, 0.0节点选项块.11, 200.0, 0.0*NSET, NSET=END11,*ELEMENT, TYPE=B21, ELSET=BEAMS 1,1,3..单元集定义单元选项块5, 9, 11属性引用选项块*BEAM SECTION, SECTION=RECT, ELSET=BEAMS, MATERIAL=MAT150.0, 5.0** Material from XXX testing lab注释行*MATERIAL, NAME=MAT1*ELASTIC材料选项块弹性选项块2.0E5, 0.3*BOUNDARY固定边界条件选项块1, ENCASTRE——历程数据*STEP历程数据以第一个 *step 选项开始APPLY POINT LOAD*STATIC指定为静态分析过程*CLOAD载荷定义, 11:节点号, 2:自由度11, 2, -1200.0-1200.0:载荷大小*OUTPUT, FIELD, FREQUENCY=10*ELEMENT OUTPUT, V ARIABLE=PRESELECT*OUTPUT, HISTORY , FREQUENCY=1*NODE OUTPUT, NSET=ENDU输出数据*EL PRINT, FREQUENCY=10S, E*NODE FILE, FREQUENCY=5U*END STEP历程数据以 *end step 选项结束在输入文件中使用集名引用属性:*ELEMENT, TYPE=B21, ELSET=BEAMS1,1,3*BEAM SECTION, SECTION=RECT, ELSET=BEAMS, MATERIAL=MAT150.0, 5.0*MATERIAL, NAME=MAT1*ELASTIC2.0E5, 0.3*BEAM SECTION 为单元集 BEAMS 和材料集 MAT1 建立联系。


Abaqus 使用问答Q:abaqus的图形如何copy?A:file>print>file格式为png,可以用Acdsee打开。
Q:用Abaqus能否计算[Dep]不对称的问题?A:可以,并且在step里面的edit step对话框other里面的matrix solver有个选项。
Q: 弹塑性矩阵【D】与ddsdde有何联系?A: stress=D*stran;d(stress)=ddsdde*d(stran)。
Q:在abaqus中,如果采用umat,利用自己的本构,如何让abaqus明白这种材料的弹塑性应变,也就是说,如何让程序返回弹性应变与塑性应变,好在output中输出,我曾想用最笨地方法,在uvarm中定义输出,利用getvrm获取材料点的值,但无法获取增量应力,材料常数等,研究了帮助中的例子,umatmst3.inp,umatmst3.for,他采用mises J2 流动理论,我在output history 显示他已进入塑性状态,但他的PE仍然为0!!?A: 用uvar( )勉强成功 。
Q: 本人在用umat作本构模型时,*static,1,500,0.000001,0.1 此时要求的增量步很多,即每次增量要很小,*static1,500 时,在弹性向塑性过度时,出现错误,增量过大,出现尖点.?A: YOU CAN TRY AS FOLLOWS:*STEP,EXTRAPOLATION=NO,INC=2000000*STATIC0.001,500.0,0.00001,0.1。
Q: 模型中存在两个物体的接触,计算过程中报错,怎么回事?A: 接触问题不收敛有两个方面不妨试试:一、在*CONTACT PAIR 里调试ADJUST参数;二、调一些模型参数,比如FRICTION等。
。
Q: 在边界条件和加载时,总是有initial这个步,然后是我们自己定义的加载步,请问这个initial步,主要作用是什么?能不能去掉?A: 不能去掉,所有的分析都有,是默认的步。

abaqus问答精华(ABAQUS question and answer essence)Q: pre tensioned prestressed reinforced how, please pointing.Q: I see in the document that you want to define a rebar in the InP file, but rebar can only be used for shell, membrane, and, solid, elements. I want to do now is a prestressed cable, not embedded in the shell, membrane, and solid the unit, a zipper but independent. The cable unit is going to use truss, but how do you use rebar on the truss? Please expert pointingAnother problem, I see someone else's InP file, is as follows: *rebar, element=continuum, material=rebar2, name=ubarTop1,1.005e-4,0.15,0.0,0.5,1The second line, the first is setname (Top1), and the second is the cross-sectional area (1.005e-4) of the rebar. What do the third, fourth and fifth mean? (0.15,0,0.5) the last one should be the direction, the 1 direction. Which expert pointed out the first three or four and five respectively?A: exerts prestressing force*initinial, conditions, type=stress, rebarElset, rebar name, the prestress value, the other prestress hold to keep the prestress value unchanged, my understanding is to prevent other members eat the prestress, caused by prestress loss. With this command, this loss is avoided, and the applied prestressing force is applied to the reinforcement.A: thank you, what you say should be put in prestressed rebar above, but I find that the truss unit cannot be defined as rebar, in fact, I think that truss would have when cable engineering prestressed steel strand tension is to play a role, tension, and in ABAQUS, truss itself is taut, without prestressA: I know simulation reinforced when the need to use rebar, but the bar you can do directly with truss to simulate, and LZ said actually just during the construction of prestressed tension is not the real meaning of prestress, such as prestressed bolt etc.. If it is a cable, it may be a mere personal view of the prestressing force.Q: ask: do a space steel frame structure, beam column with beam element, board with shell element, intended to use tie command (common node), but I don't know how to achieve?A: I think you can use *equation to implement the constraints of the shared node, which is defined by this command.A: because I order more, but I want to use CAE, enter the command editor in CAE, and then edit it, write the *equation command, specifying the constrained degrees of freedom (see the standard manual, written very clearly)Where is the difference between "Q:" Response spectrum analysis (response spectrum analysis) and "Modal dynamic analysis" (modal dynamic analysis)? Such as Response, spectrum, analysis, you can design the structure? But what are the Modal dynamic analysis for?A: as far as I know, modal, dynamic, analysis should be modal decomposition method for dynamic analysis. Decomposition of a single degree of freedom system and a finite combination reaction.How does Q:abaqus apply seismic loads?A: can refer to the example of ABAQUS 6.3, Seismic, Analysis, of, a, Concrete, Dam, Gravity, and so onCan use:1. *amplitude, name=amp, and input=seismicdata.dat input seismic waves2. *boundary, type=acceleration, amplitude=amp to apply the load.In <ABAQUS, Example, Problems, Manual>, 2.1.15, Seismic, analysis, of, a,, concrete, gravity, damA: that's a relative problem. You can deduce that kinetic equation,The result is that ANSYS is the relative time history that takes the foundation to fix the relative base of the structure, and the ABAQUS is applied to the boundary, and the absolute time history of the structure is solved. Thus, there is a difference between the applied acceleration and the time history.Applied on the boundary time history acceleration by explicit calculation speed (mainly depends on your CPU ABAQUS STANDERD) which is the explicit calculation, in addition to its EXPLICT module can also see specific examples, analysis of the of a Concrete Gravity Dam Seismic Analysis; ANSYS is used for solving implicit (mainly depends on you the hard disk speed and CPU), and the big storm (the default output should be a lot of data for it), ANSYS/LSDYNA can be used to explicitly calculate.I have worked together for time analysis, with a little experience.Q: my boss asked me to use the concrete damage plasticity model1. In nonlinear analysis, how do I know the damage to the structure and how to obtain the ultimate bearing capacity of the structure?2. How do you determine concrete, compression, damage, and concrete tension damage? None of the two seems to have been tested. If you can ignore compression damage, then the definition of tension damage is important because of the presence of the tension stiffening (the falling segment is relatively long). In ABAQUS's example of gravity dams, the tension, stiffening, and tension damage data seem to have some relationship.3. When defining concrete tension stiffening, I read some of the papers above about the Tesion stiffening specification, saying that if tensiong stiffening is defined too small, convergence will be difficult. However, the size of tensionstiffening is defined in *concrete tension stiffening, and the first two data are remaining, direct, stress, after, cracking, and direct cracking strain.4. Does the tension stiffenig have anything to do with the rate of reinforcement? If yes, what is the relationship like? Thank you all.I think A: damage plasticity model is mainly used in concrete under cyclic loading, the concrete compression damage and concrete tension damage only when tension stiffening seems to need to define, the definition of concrete in uniaxial tension constitutive relation, tension and damage should Never mind. It doesn't seem to have anything to do with the reinforcement ratio.塑性损伤模型既可以模拟循环拟静荷载的情况,也可计算结构在动力荷载(地震、风以及冲击荷载的作用),通过混凝土压缩损伤和混凝土受拉破坏考虑混凝土的拉压异性,张力加劲则可考虑拉伸屈服后的软还阶段本构行为,同样是混凝土损伤全过程的一部分,它与配筋率及网格划分密度的相互关系很大程度上影响到计算的收敛性。

abaqus例题手册
ABAQUS是一款功能强大的有限元分析软件,广泛应用于各种工程领域。
其例题手册旨在帮助用户更好地理解和使用ABAQUS,通过具体的例题展示软件的使用方法和分析过程。
以下是ABAQUS例题手册中一些常见的例题:
1. 悬臂梁分析:该例题主要演示了如何使用ABAQUS对悬臂梁进行静态和动态分析,包括模型的建立、网格划分、边界条件和载荷的施加、求解过程以及结果的后处理等。
2. 薄板弯曲分析:该例题通过一个简单的薄板弯曲问题,介绍了ABAQUS 在处理弯曲问题时的基本步骤,包括模型的建立、材料属性的定义、边界条件和载荷的施加、求解过程以及结果的解释。
3. 疲劳分析:该例题通过一个简单的疲劳分析问题,介绍了如何使用ABAQUS进行疲劳寿命预测。
该例题展示了如何定义材料的疲劳属性、如何进行循环载荷的施加以及如何解释结果。
4. 冲击分析:该例题通过一个简单的冲击分析问题,介绍了如何使用ABAQUS进行冲击模拟。
该例题展示了如何定义材料的冲击属性、如何设置冲击条件以及如何解释结果。
5. 热分析:该例题通过一个简单的热分析问题,介绍了如何使用ABAQUS
进行温度场模拟。
该例题展示了如何定义材料的热属性、如何设置热边界条件和载荷以及如何解释结果。
以上是ABAQUS例题手册中一些常见的例题,通过这些例题的介绍,用户
可以更好地了解ABAQUS的功能和应用,提高软件的使用效率和分析精度。

作业题1.假设砂井地基中砂井为正方形布置,间距为2m ,长度为8m ,砂井半径为m w 1.0=γ,渗透系数为s m k w /102-=。
地基土厚度m L 8=,土地渗透系数s m k h /108-=。
弹性模量KPa E 410=,不考虑土体的水平方向的变形,取泊松比0.0=ν。
地基土底面不排水,顶面完全透水,土体及砂井表面作用有瞬时施加的荷载KPa P 200=。
在有限元数值分析中,取砂井中的一个单元体进行计算,即长,宽,高,分别为2m,2m,8m ,图形如下图1-1所示;模型底部固定三个方向的约束,不排水;四周仅能容许竖向位移,同样不透水,表面位移自由,且是自由排水面。
载荷瞬时施加,然后根据土体表面的竖向位移求的各个时刻土层的固结度。
1-1模型示意图步骤:1.模型的建立(1)建立部件Part模块中,执行[part]/[create]命令通过Extrusion方法建立一个2mx2mx8m的三维变形体,然后通过执行[Tools]/[partion]命令,在弹出的Creation Partition 对话框中将Type选项设置为Face,将Method 选为sketch,将顶面的砂井画出来,再次执[Tools]/[partion]命令,此时在Creation Partition 对话框将type选项设为Cell,对应的Method 选为Extrude/Sweep edges方法,将砂井的空间形状独立出来。
执行[tools]/[set]/[create]命令,分别建立土体(soil)和砂井(sandwell)的集合。
(2)设置材料及截面特性在property模块中,分别建立soil和sand well的材料,并为问题描述的数据设置相应的参数,执行[section]/[creat]命令,分别设置名称为soil和sand well的section,并执行[Assign]/[section]命令赋予相应的区域。

abaqus经典例题集下面是一些abaqus的经典例题,以帮助大家更好地理解和掌握这款强大的有限元分析软件。
1.线性弹性问题例题1:在一个长方形平板上施加均匀分布的载荷,求解板的应力和应变。
解题步骤:-创建模型,定义几何参数和材料属性;-划分网格;-应用边界条件;-施加载荷;-求解;- 后处理,查看结果。
2.非线性问题例题2:一个简支梁在受力过程中,梁的横截面半径发生变化。
求解梁的挠度和应力。
解题步骤:-创建模型,定义几何参数、材料属性和边界条件;-划分网格;-应用材料的本构关系;-施加载荷;-求解;- 后处理,查看结果。
3.热力学问题例题3:一个平板在均匀温度差的作用下,求解热应力和温度分布。
解题步骤:-创建模型,定义几何参数、材料属性、边界条件和温度差;-划分网格;-应用热力学本构关系;-施加温度边界条件;-求解;- 后处理,查看结果。
4.耦合问题例题4:一个悬臂梁在受到弯曲应力和剪切应力的同时,还受到温度的变化。
求解梁的应力和温度分布。
解题步骤:-创建模型,定义几何参数、材料属性、边界条件、载荷和温度变化;-划分网格;-应用耦合场本构关系;-施加边界条件、载荷和温度边界条件;-求解;- 后处理,查看结果。
5.接触问题例题5:两个物体相互挤压,求解接触面上的应力和接触力。
解题步骤:-创建模型,定义几何参数、材料属性、边界条件和接触属性;-划分网格;-应用接触算法;-施加边界条件和接触力;-求解;- 后处理,查看结果。
通过以上五个经典例题的讲解,相信大家对abaqus的应用有了更深入的了解。
在实际应用中,我们应根据具体问题选择合适的分析类型,并灵活运用所学知识。
希望大家能在实践中不断提高,成为优秀的有限元分析工程师。

2013 年 5 月 8 日现代机械设计方法》课程结业论文( 2011 级)题 目: ABAQUS 实例分析学生姓名 XXXX 学 号 XXXXX 专 业 机械工程 学院名称机电工程与自动化学院指导老师XX目录第一章Abaqus 简介...................................................................................................... 1...一、Abaqus 总体介绍 ......................................................................................... 1..二、Abaqus 基本使用方法................................................................................ 2..1.2.1Abaqus 分析步骤 ................................................................................. 2..1.2.2Abaqus/CAE 界面................................................................................. 3..1.2.3Abaqus/CAE 的功能模块 .................................................................. 3.. 第二章基于Abaqus 的通孔端盖分析实例 ......................................................... 4..一、工作任务的明确 ........................................................................................... 6..二、具体步骤.......................................................................................................... 6...2.2.1 启动Abaqus/CAE .....................................................................................4..2.2.2 导入零件.................................................................................................. 5...2.2.3创建材料和截面属性 ....................................................................... 6..2.2.4定义装配件........................................................................................... 7..2.2.5定义接触和绑定约束(tie )................................................... 1. 02.2.6定义分析步1..42.2.7划分网格 (15)2.2.8施加载荷1..9.2.2.9定义边界条件2..02.2.10提交分析作业................................................................................. 2..12.2.11后处理2..2.第三章课程学习心得与作业体会....................................................................... 2..3第一章:Abaqus 简介Abaqus 总体介绍Abaqus 是功能强大的有限元分析软件,可以分析复杂的固体力学和结构力学系统,模拟非常庞大的模型,处理高度非线性问题。

abaqus悬臂梁例题
ABAQUS是一种常用的有限元分析软件,用于模拟和分析工程结构的行为。
下面是一个简单的ABAQUS悬臂梁的例题,以便说明如何进行有限元分析:
问题描述:
考虑一个简单的悬臂梁,长度为L,截面为矩形,要分析该梁的挠度和应力分布。
步骤:
1.建立模型:首先,在ABAQUS中建立一个新模型。
定义悬臂梁的几何参数,如长度L 和梁截面的宽度和高度。
2.创建网格:划分悬臂梁的几何形状,创建有限元网格。
可以选择合适的单元类型,如梁单元或壳单元,以模拟结构行为。
3.应用边界条件:定义悬臂梁的支持条件,通常悬臂梁的一端是固定支持,另一端是自由端。
在ABAQUS中,你可以定义这些支持条件。
4.施加载荷:定义悬臂梁所受的载荷,如集中力、分布载荷等。
5.设置材料属性:指定悬臂梁所用的材料属性,如弹性模量、泊松比等。
6.运行分析:运行有限元分析,ABAQUS将计算悬臂梁的挠度和应力分布。
7.分析结果:分析完成后,你可以查看和可视化分析结果,包括挠度云图、应力云图等,以了解悬臂梁的行为。
这只是一个简单的悬臂梁分析示例,ABAQUS提供了广泛的功能来进行复杂结构的有限元分析。
具体的模型参数和步骤可能会因实际情况而有所不同。
你可以根据你的具体问题和需求来调整和扩展这个示例。
需要在软件中具体设置和模拟这个问题,以获得详细的分析结果。

1■应用背景概述随着科学技术的发展,汽车已经成为人们生活中必不可少的交通工具。
但当今由于交通事故造成的损失日益剧增,研究汽车的碰撞安全性能,提高其耐撞性成为各国汽车行业研究的重要课题。
目前国内外许多著名大学、研究机构以及汽车生产厂商都在大力研究节省成本的汽车安全检测方法,而汽车碰撞理论以及模拟技术随之迅速发展,其中运用有限元方法来研究车辆碰撞模拟得到了相当的重视。
而本案例就是取材于汽车碰撞模拟分析中的一个小案例 ----------------------------------- 保险杠撞击刚性墙。
2■问题描述该案例选取的几何模型是通过导入已有的*.IGS文件来生成的(已经通过Solidworks软件建好模型的),共包括刚性墙(PART-wall)、保险杠(PART-bumpe)、平板(PART-plane)以及横梁(PART-rail)四个部件,该分析案例的关注要点就是主要吸能部件(保险杠)的变形模拟,即发生车体碰撞时其是否能够对车体有足够的保护能力?这里根据具体车体模型建立了保险杠撞击刚性墙的有限元分析模型,为了节省计算资源和时间成本这里也对保险杠的对称模型进行了简化,详细的撞击模型请参照图1所示,撞击时保险杠分析模型以2000mm/s的速度撞击刚性墙,其中分析模型中的保险杠与平板之间、平板与横梁之间不定义接触,采用焊接进行连接,对于保险杠和刚性墙之间的接触采用接触对算法来定义。
1.横梁(rail)2.平板(plane)3保险杠(bumper)4.刚性墙(wall)图2.1碰撞模型的SolidWorks图为了使模拟结果尽可能真实,通过查阅相关资料,定义了在碰撞过程中相关的数据以及各部件的材料属性。
其中,刚性墙的材料密度为7.83 >10-9,弹性模量为2.07 >05,泊松比为0.28;保险杠、平板以及横梁的材料密度为7.83 >0-9, 弹性模量为2.07 >05,泊松比为0.28,塑形应力-应变数据如表2.1所示。
钣金成型例题讲解一、背景当前,制造行业加工工艺的趋势正朝着高新技术的方向发展。
由于新产品、新技术的开发成本太高、开发时间过长,加上开发成果没有保障,越来越多的公司在研发、制造过程中开始注重仿真技术的应用。
采用ABAQUS对加工工艺进行模拟有着诸多优点:1.数值模拟减少了耗时的原型实验,缩短了产品投放市场的时间;2.合理的参数设计可以降低对工件的损耗;3.合理的坯料设计,减少了飞边,也减少原材料的浪费;4.对模具的设计、加工提供合理建议;5.优化加工过程,提高产品成型质量;采用ABAQUS进行仿真模拟的目的:1.节约开发成本2.加快研发速度3.提高产品质量二、问题的描述本实例模拟油箱的冲压成型过程。
图1为实际的油箱形状,是由两个如图2所示的结构组成,考虑冲压成型过程中,它的结构的对称性,我们通过建立图3所示的结构,对其进行模拟分析,达到分析整个油箱成型分析的目的。
首先,我们将通过ABAQUS/CAE完成图4所示的装配图,其中平面铝板将被冲压成型为图3的结构。
三、建立模型3.1创建成型模具-阳模1、首先运行ABAQUS/CAE ,在出现的对话框内选择Create Model Database 。
2、在主菜单model 中命名新建模型为Forming example ,并保存文件为examle_forming.cae 。
3、从Module 列表中选择Part ,进入Part 模块。
4、选择Part→Create 来创建一个新的零件。
在提示区域会出现这样一个信息。
5、CAE 弹出一个如图5的对话框。
将这个零件命名为punch ,确认Modeling Space 、Type 和BaseFeature 的选项如下图。
输入300作为Approximate size 的值。
点击Continue 。
图 1图2成型模具-阳模金属板压边条成型模具-阴模图4图3图5ABAQUS/CAE 初始化草图,并显示格子。
6、在左侧工具条上点击 ,在提示栏中依次输入下表的坐标点,采用图标 连接1和2点、6和7点,采用连接图中2、3、4点和4、5、6点。
ABAQUS计算指导0:应用梁单元计算简支梁的挠度对于梁的分析可以使用梁单元、壳单元或是固体单元。
Abaqus的梁单元需要设定线的方向,用选中所需要的线后,输入该线梁截面的主轴1方向单位矢量(x,y,z),截面的主轴方向在截面Profile设定中有规定。
注意:因为ABAQUS软件没有UNDO功能,在建模过程中,应不时地将本题的CAE模型(阶段结果)保存,以免丢失已完成的工作。
简支梁,三点弯曲,工字钢构件,结构钢材质,E=210GPa,μ=0.28,ρ=7850kg/m3(在不计重力的静力学分析中可以不要)。
F=10kN,不计重力。
计算中点挠度,两端转角。
理论解:I=2.239×10-5m4,w中=2.769×10-3m,θ边=2.077×10-3。
文件与路径:顶部下拉菜单File, Save As ExpAbq00。
一部件1 创建部件:Module,Part,Create Part,命名为Prat-1;3D,可变形模型,线,图形大约范围10(程序默认长度单位为m)。
2 绘模型图:选用折线,从(0,0)→(2,0)→(4,0)绘出梁的轴线。
3 退出:Done。
二性质1 创建截面几何形状:Module,Property,Create Profile,命名为Profile-1,选I型截面,按图输入数据,l=0.1,h=0.2,b l=0.1,b2=0.1,t l=0.01,t2=0.01,t3=0.01,关闭。
2 定义梁方向:Module,Property,Assign Beam Orientation,选中两段线段,输入主轴1方向单位矢量(0,0,1)或(0,0,-1),关闭。
3 定义截面力学性质:Module,Property,Create Section,命名为Section-1,梁,梁,截面几何形状选Profile-1,输入E=210e9(程序默认单位为N/m2,GPa=109 N/m2),G=82.03e9,ν=0.28,关闭。
ABAQUS输入文件的格式ABAQUS 的输入文件( .inp 文件)包含若干可选的数据块,这些数据块以一个关键字开头,如 *PLASTIC 。
如果需要的话,数据行将跟在关键字行的后面。
所有的输入行长度限制在 256 字符以内,变量名限制在 80 字符以内,且必须以字母开始。
所有的注释行以 ** 开始,可以放在任意的位置。
关键字行以*开始,后面接关键字,必要的时候可加参数,如:*MATERIAL,NAME= name,这里, MATERIAL是关键字,NAME是参数,name是你给定的参数值。
数据行用来为给定的选项定义批量数据,如单元的定义:*ELEMENT,TYPE= b21关键字行560,101, 102564, 102, 103数据行572,103, 104·节点号(相对于梁·单元号b21 单元)每个数据块要么属于模型数据,要么属于历程数据,模型数据必然置于历程数据之前。
而在模型数据和历程数据内部,数据块的顺序和位置是任意的,除了一些特例,如:*HEADING *MATERIAL 必须置于输入文件的第一行,*ELASTIC的子选项,则他们必须直接跟在*MATERIAL、 *DENSITY后等。
和*PLASTIC是下面我们以悬臂梁模型为例介绍其输入文件的各个部分。
边界条件节点号单元号点载荷输入文件:——模型数据*HEADINGCANTILEVER BEAM EXAMPLE标题选项块UNITS IN MM, N, MPa*NODE1, 0.0, 0.0节点选项块.11, 200.0, 0.0*NSET, NSET=END11,*ELEMENT, TYPE=B21, ELSET=BEAMS 1,1,3..单元集定义单元选项块5, 9, 11属性引用选项块*BEAM SECTION, SECTION=RECT, ELSET=BEAMS, MATERIAL=MAT150.0, 5.0** Material from XXX testing lab注释行*MATERIAL, NAME=MAT1*ELASTIC材料选项块弹性选项块2.0E5, 0.3*BOUNDARY固定边界条件选项块1, ENCASTRE——历程数据*STEP历程数据以第一个 *step 选项开始APPLY POINT LOAD*STATIC指定为静态分析过程*CLOAD载荷定义, 11:节点号, 2:自由度11, 2, -1200.0-1200.0:载荷大小*OUTPUT, FIELD, FREQUENCY=10*ELEMENT OUTPUT, V ARIABLE=PRESELECT*OUTPUT, HISTORY , FREQUENCY=1*NODE OUTPUT, NSET=ENDU输出数据*EL PRINT, FREQUENCY=10S, E*NODE FILE, FREQUENCY=5U*END STEP历程数据以 *end step 选项结束在输入文件中使用集名引用属性:*ELEMENT, TYPE=B21, ELSET=BEAMS1,1,3*BEAM SECTION, SECTION=RECT, ELSET=BEAMS, MATERIAL=MAT150.0, 5.0*MATERIAL, NAME=MAT1*ELASTIC2.0E5, 0.3*BEAM SECTION 为单元集 BEAMS 和材料集 MAT1 建立联系。
ABAQUSCAE典型例题18、从主菜单中选择Instance →Translate ,选择Pine ,点击Done ,在CAE 警告信息栏中点击Yes 。
在提⽰栏输⼊(0,0,0)和(0,0,0.02),敲回车。
在提⽰栏点击OK 。
最终的构形如右上图显⽰。
接下来,我们定义分析步,接触,边界条件以及加载。
⼀、定义分析步。
1、进⼊Step 模块,从主菜单中选择Step →Create ,命名这个分析步为Contact ,接受默认的Static, General ,点击Continue 。
在出现的Edit Step 对话框中,接受所有默认选择,并点击OK ,创建⼀个分析步。
2、重复上⼀步,创建⼀个分析步,命名为Load ,在Edit Step 对话框中,进⼊Incrementation ⼦选项,输⼊0.1为Initial Increment Size 。
点击OK ,完成分析步的创建。
3、为输出结果创建⼏何集,在主菜单选择Tools →Set →Create ,命名这个⼏何集为ndisp-output ,点击Continue 。
选择如左下图所⽰的点。
点击Done ,完成该步骤。
4、采⽤相同的技术,定义右上图所选的⾯为fixed-face-output ,所选的边为hole-output 。
5、从主菜单中选择Output →Field Output Requests →Manager ,从出现的对话框中选择F-output-1,点击Edit ,删除变量PE ,PEEQ 和PEMAG ,删除选择Forces/Reactions ,点击OK ,点击Dismiss 退出Field Output Requests Manager 。
6、从主菜单中选择Output →History Output Requests →Manager ,从出现的对话框中选择H-output-1,点击Edit ,在Domain 中选择Set name ,并选择ndisp-output ,去掉Energy 选项,输⼊U1,U2,U3。
abaqus算例ABAQUS实例操作一、型钢梁建模分析1.1 问题描述一型钢梁,尺寸如图所示,利用软件分析其内力。
材料特性:弹性模量E=2.1e11N/m2,泊松比μ=0.3,屈服强度ƒ=3.45e8N/m2。
y1.2创建部件点击创建部件按钮,在对话框中设置参量如右图:模型空间设置为三维的,类型为可变性的,基本特征为实体,可拉伸,比例设为1.1.2生成三维模型首先,在二维的环境下,输入横截面的各点坐标,然后再输入深度6m,便可生成如下图型:1.3创建材料和截面属性创建材料先输入弹性模量,泊松比,以及屈服应力,塑性应变,点击确认即可。
名字命名为section-beam,种类为实体,类型为均质,其他值保持默认,点击确认,接着选择整个部件,将截面性质赋予之。
1.4 定义装配件点击装配功能模块,选择部件为非独立实体其他保持为默认值点解确认即可。
1.5 设置分析步选择分析步模块,点击create instance 在对话框里面,输入名字为step,procedure type 设置为general ,在下拉菜单中选择static general 项,保持其他参数不变,点击确认。
1.6 定义荷载和边界条件选择荷载模块:①施加荷载在 create load对话框中,名字设置为load,step项中选择为step,将荷载设置为pressure,其他值保持不变,点击继续,在荷载的大小后面输入3.5e5,其他参数不变,完成荷载的定义。
②定义便捷条件在对话框中将step 设置为initial,将施加边界条件的方式设置为位移/转角,保持其余参数不变,点击确认。
在弹出的对话框中选择U1=U2=UR2=UR3=0,即对选中面施加铰接约束,点击ok。
同样的方式在另一边同样设置。
1.7 划分网格在列表中选择功能模块,对模型进行网格划分,将环境栏中的object项设为part,即为部件划分网格。
分割下翼缘和腹板,用点和垂线的方法进行分割,先选中下翼缘和腹板的交点,再选中腹板上一条垂线,点击确认,同样的方法分割上翼缘和腹板。