04 异步电机矢量控制(VC)系统仿真实验
- 格式:pptx
- 大小:1.41 MB
- 文档页数:11

异步电动机矢量控制系统的设计与仿真.异步电动机矢量控制系统的设计与仿真在矢量控制技术出现之前,现代交流调速系统采用了恒压频比控制策略。
这种控制策略的缺点是,当电机低速旋转或在加减速、负载加减等动态条件下,系统性能显著降低,导致交流调速系统在低速、启动时转矩的动态响应和整个系统的稳定性方面不如DC调速系统,无法满足人们对高精度的要求。
后来,交流异步电动机控制开始从标量控制向矢量控制迈进。
以下是矢量控制理论的简要介绍。
矢量控制发展的基础和核心理论支撑是电机的一些概念,如坐标转换原理、机电能量转换理论等。
这种控制的基本思想和方法是将异步电机模拟成DC电机来控制。
只要建立等效于三相交流绕组组的两相绕组,就可以建立等效于异步电机的DC电机模型,并增加相应的比例积分调节环节,从而可以按照DC 电机的控制策略来控制异步电机。
因此,矢量控制可以实现对电机电磁转矩的动态实时控制,从而优化和提高调速性能。
根据这一思想,我在本项目中成功地进行了MATLAB仿真。
关键词:交流电机;矢量控制调速系统;矢量控制系统的设计与仿真交流调速系统的仿真采用常V/f比控制方法,通常称为标量控制。
采用这种方法的系统在电机低速运行时或在加速、减速、增加负载、减少负载等情况下会出现重大缺陷。
采用矢量控制的交流电机可以达到与恒流电机相同的控制性能,从此交流异步电机控制从标量控制向矢量控制迈进了一大步。
以下是矢量控制理论的简要介绍。
矢量控制发展的基础和核心理论支撑是电机的一些概念,如坐标转换原理、机电能量转换理论等。
这种控制的基本思想和方法是将异步电机模拟成DC电机来控制。
只要建立等效于三相交流绕组组的两相绕组,就可以建立等效于异步电机的DC电机模型,并增加相应的比例积分调节环节,从而可以按照DC电机的控制策略来控制异步电机。
因此,矢量控制可以实现对电机电磁转矩的动态实时控制,从而优化和提高调速性能。
根据这一思想,我在本项目中成功地进行了MATLAB仿真。

异步电动机矢量控制系统仿真研究摘要:本文以异步电机矢量控制原理为基础,通过坐标变换和转子磁链位置计算,利用Matlab/Simulink 构建一种异步电动机矢量控制系统的模型。
通过仿真不仅验证了模型的正确性,而且还为实际调速系统控制算法实现提供可靠的分析依据。
关键词:矢量控制;异步电动机;Matlab/Simulink1 引言直流电动机调速系统具有优良的静、动态调速特性,其根本原因在于作为控制对象的他励直流电动机电磁转矩能够容易而灵活地进行控制[1-2]。
在1971 年德国学者提出的矢量变换控制方法中,正交旋转坐标系的直轴励磁轴(M)与转子磁场重合,交轴为转矩轴(T),转子磁场的交轴分量为零,电磁转矩的方程得到简化,即在磁场恒定的情况下,电磁转矩与交轴电流分量成正比,因此,感应电机的机械特性与他励直流电机的机械特性完全一样,实现了磁场和转矩的解耦控制。
像直流调速系统一样,实现了交流电动机的磁通和转矩分别独立控制,从而使交流电动机具有了直流电动机的全部点。
由于直轴和转子磁场重合,因此也称转子磁场定向控制[3-5]。
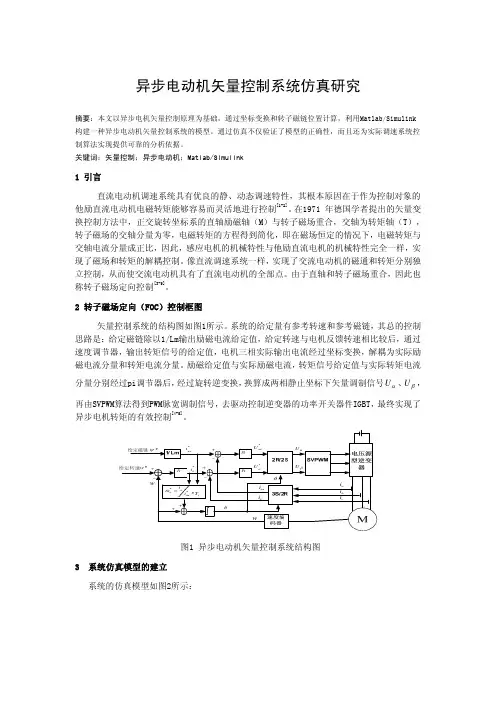
2 转子磁场定向(FOC)控制框图矢量控制系统的结构图如图1所示。
系统的给定量有参考转速和参考磁链,其总的控制思路是:给定磁链除以1/Lm输出励磁电流给定值,给定转速与电机反馈转速相比较后,通过速度调节器,输出转矩信号的给定值,电机三相实际输出电流经过坐标变换,解耦为实际励 磁电流分量和转矩电流分量。
励磁给定值与实际励磁电流,转矩信号给定值与实际转矩电流分量分别经过pi调节器后,经过旋转逆变换,换算成两相静止坐标下矢量调制信号αU 、βU ,再由SVPWM算法得到PWM脉宽调制信号,去驱动控制逆变器的功率开关器件IGBT,最终实现了异步电机转矩的有效控制[4-5]。
PI图1 异步电动机矢量控制系统结构图3 系统仿真模型的建立 系统的仿真模型如图2所示:图2 异步电动机矢量控制系统仿真图3.1 主要仿真模块介绍3.1.1 速度、转矩、磁链调节器模块三个调节器的参数值如表1;三个调节器的内部接线结构如图3所示。
异步电动机矢量控制系统仿真1.异步电机矢量控制系统的原理及其仿真1.1 异步电动机矢量控制原理异步电机矢量变换控制系统和直接转矩控制系统都是目前已经获得应用的高性能异步电机调速系统,对比直接转矩控制系统,矢量变换系统有可以连续控制,调速范围宽的优点,因此矢量变换控制系统为现代交流调速的重要方向之一。
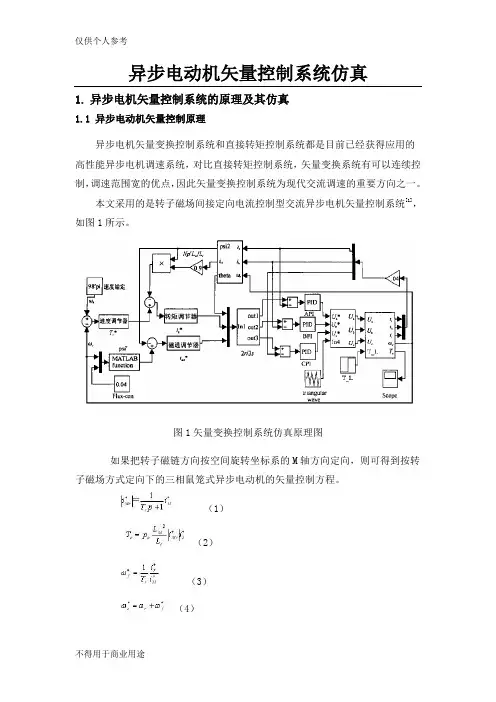
本文采用的是转子磁场间接定向电流控制型交流异步电机矢量控制系统[1],如图1所示。
图1矢量变换控制系统仿真原理图如果把转子磁链方向按空间旋转坐标系的M轴方向定向,则可得到按转子磁场方式定向下的三相鼠笼式异步电动机的矢量控制方程。
(1)(2)(3)(4)(5)上列各式中,是转子励磁电流参考值;是转差角频率给定值;是定子电流的励磁分量;是定子电流的转矩分量;是定子频率输入角频率;是转子速度;是转子磁场定向角度;是转子时间常数;和分别是电机互感和转子自感。
图4所示控制系统中给定转速与实际电机转速相比较,误差信号送入转速调节器,经转速调节器作用产生给定转矩信号,电机的激磁电流给定信号根据电机实际转速由弱磁控制单元产生,再利用式(1)产生定子电流激磁分量给定信号,定子电流转矩分量给定信号则根据式(2)所示的电机电磁转矩表达式生成。
、和转子时间常数Lr一起产生转差频率信号,与ωr相加生成转子磁场频率给定信号,对积分则得到转子磁场空间角度给定信号。
和经坐标旋转和2/3相变换产生定子三相电流给定信号、和,与定子三相电流实测信号、和相比较,由滞环控制器产生逆变器所需的三相PWM信号。
1.2 异步电机转差型矢量控制系统建模在MATLAB/SIMULINK环境下利用电气系统模块库中的元件搭建交流异步电机转差型矢量控制系统[2],电流控制变频模型如图2所示。
图2 电流控制变频模型图整个仿真图由电气系统模块库中的元件搭建组成,元件的直观连接与实际的主电路相像似,其中主要包括:速度给定环节,PI速度调节器、坐标变换模块、磁场定向模块、滞环电流调节器、IGBT逆变器元件、异步电动机元件以及测量和显示模块。

异步电动机矢量控制系统设计与仿真研究THE DISIGN OF THE ASYNCHRONOUS MOTOR VECTOR CONTROL SYSTEM AND IT`S SIMULATION STUDY专业:电气工程及其自动化姓名:高智指导教师:申请学位级别:学士论文提交日期:学位授予单位:天津科技大学摘要本文的研究内容是“异步电动机矢量控制系统设计与仿真研究”。
在矢量控制技术出现之前,交流调速系统多为V / f比值恒定控制方法,又常称为标量控制。
采用这种方法在低速及动态(如加减速)、加减负载等情况时,系统表现出明显的缺陷,所以交流调速系统的稳定性、启动、低速时的转矩动态相应都不如直流调速系统。
随着电力电子技术的发展,交流异步电机控制技术全面从标量控制转向了矢量控制,采用矢量控制的交流电机完全可以和直流电机的控制效果相媲美,甚至超过直流调速系统。
矢量控制是在电机统一理论、机电能量转换和坐标变换理论的基础上发展起来的。
它的思想就是将异步电动机模拟成直流电动机来控制,通过坐标变换,将定子电流矢量分解为按转子磁场定向的两个直流分量并分别加以控制,从而实现磁通和转矩的解耦控制,建立三相交流绕组、两项交流绕组和旋转的直流绕组三者之间的等效关系,从而求出异步电动机绕组等效的直流电机模型,以便按照对直流电机的控制方法对异步电机进行控制。
因此他可以实现对电机电磁转矩的动态控制,优化调速系统的性能。
本文针对异步电动机磁链闭环矢量控制进行研究和探索。
通过空间矢量的坐标变换,对系统进行建模,其中包括直流电源、逆变器、电动机、转子磁链电流模型、ASR、ATR、AΨR等模块。
并对控制系统进行了MATLAB/Simulink仿真分析。
关键词:异步电动机;矢量控制;MATLAB仿真ABSTRACT:The content of this study is the design of the Asynchronous motor vector control system and it's simulation study. Before the advent of vector control technology, most of alternating current speed control system are constant V/f ratio control method which is also often referred as the scalar control. This approach in low-speed and dynamic (such as acceleration and deceleration), such as addition and subtraction load, the system showed obvious defects, so the stability of AC variable speed system, start torque at low speed dynamic response is not such as a DC tune speed system. With the development of power electronics technology, the AC induction motor control technology fully from the scalar control to vector control, vector control of AC motor can be comparable and DC motor control effects, even more than the DC speed control system.Vector control is developed on the basis of the motor unified theory of electrical and mechanical energy conversion and coordinate transformation theory. Its ideology is the asynchronous motor simulation into a DC motor to control, coordinate transformation, decomposition of the stator current vector for the rotor field oriented two DC components were controlled, in order to achieve the decoupling of flux and torque control, three-phase AC winding, two exchanges winding and rotation of the DC winding equivalence between the three, in order to find the equivalent asynchronous motor winding DC motor model, in order to control the DC motor control method for asynchronous motor . So that he can achieve dynamic control of the electromagnetic torque, optimize the performance of the speed control system. In this paper, the closed-loop vector control of asynchronous motor flux research and exploration. By the coordinates of the space vector transformation of the system modeling, including a DC power supply, inverter, motor, the rotor flux current model, the ASR, ATR AΨR and other modules. And control system for the MATLAB / SIMULINK simulation analysis.Key Words:Asynchronous Motor;Vector Control;MATLAB Simulation目录第一章绪论 (1)第一节交直流调速系统的相关概念及比较 (1)第二节交流调速系统的历史和现状 (2)第三节异步电机矢量调速系统的发展 (5)第二章异步电动机的数学建模分析 (7)第一节三相电机的模型分析 (7)第二节同步旋转坐标系上的数学模型及状态方程 (11)第三节异步电动机的数学模型 (12)第四节坐标变换和变换矩阵 (13)第五节异步电动机在不同坐标系下的数学模型 (20)第三章异步电动机矢量控制的基本原理 (23)第一节异步电机的电磁转矩 (23)第二节矢量控制思路的演变过程 (23)第三节矢量控制的磁场定向 (26)第四节转子磁链观测器 (28)第五节异步电机矢量控制系统 (30)第四章异步电动机矢量控制系统的仿真分析 (33)第一节SIMULINK软件基本介绍 (33)第二节异步电机矢量控制系统仿真模型的建立 (33)第三节各模块参数设置 (36)第四节仿真结果 (37)第五章全文总结 (40)参考文献 (41)致谢 (42)第一章绪论第一节交直流调速系统的相关概念及比较电动机+控制装置=电力传动自动控制系统。

摘要摘要由于直流电动机结构复杂,制造费时以及需要经常性维护等缺点,使得人们一直努力寻找能替代直流电动机调速的交流电动机调速。
随着电力电子技术、PWM调制技术、计算机控制技术、交流电动机的控制技术的发展,交流调速系统由于其坚固耐用、运行可靠等众多优点,正在逐步取代以前直流调速系统,在传动领域占据主导地位。
直到20世纪80年代中期,德国学者们在交流电机调速中提出了磁链轨迹控制的思想,在此基础上进一步发展产生了电压空间矢量脉宽调制(SVPWM)的概念。
SVPWM又称磁链追踪型PWM法,它是从电动机的角度出发,着眼于如何使电机获得圆磁场。
本文首先介绍了种种交流调速技术,并逐一的分析其优缺点,然后重点详细的介绍了电压空间矢量脉宽调制(SVPWM)技术,就其如何使电机获得圆磁场进行了具体的分析和推导。
并且推导出在MATLAB/SIMULINK环境下SVPWM控制信号的数学模型,并得到SVPWM控制下的电动机输出电流、电压、转速、转矩、磁链等信号的波形,经分析证实了异步电机在SVPWM控制下,具有启动电流小、转速稳定快、直流利用率高、能量损耗少、谐波少、控制简单等优点。
AbstractAs the DC motor complex, manufacturing time and the need for regu lar maintenance shortcomings, so people have been looking for an alternati ve to DC motor speed control of AC motor speed control. With the powe r electronics, PWM modulation technology, computer control technology, c ommunication technology, the development of motor control, AC drive syst em because of its rugged, reliable operation of the many advantages, is gr adually replacing the previous DC drive system, in drive occupy dominanc e.Until the mid-1980s, the German scholars proposed in the alternating current machine velocity modulation the flux linkage trajectory control's th ought that based on this further developed has had the voltage space vect or pulse-duration modulation (SVPWM) concept. SVPWM said that the flu x linkage tracing PWM law, it is from electric motor's angle embarking, h ow focuses to cause the electrical machinery to obtain the circular field.This paper introduces the various AC variable speed, and the analysis of their advantages and disadvantages of each, and then focus on a detail ed description of the voltage space vector pulse width modulation (SVPW M) technique, on how they get round the motor magnetic field analysis a nd derivation of specific . And derived in the MATLAB / SIMULINK en vironment, the mathematical model of SVPWM control signal, and get SV PWM under the control of motor output current, voltage, speed, torque, fl ux and other waveform, confirmed by the analysis of induction motor und er the control of the SVPWM with a start current, speed stability and qui ck, DC high efficiency, low energy loss, less harmonic control and simple.目录摘要 (I)Abstract ................................................................................................................ I I 第1章绪论.. (1)1.1引言 (1)1.2交流调速的发展历程 (2)1.2.1三大核心技术的突破 (2)1.2.2三个发展阶段 (4)第2章SVPWM调制原理和主电路设计 (10)2.1SVPWM调制技术概述 (10)2.2SVPWM调制原理 (10)2.3主电路拓扑 (15)2.4主电路参数计算 (16)第3章基于MATLAB/SIMULINK的仿真 (18)3.1MATLAB/SIMULINK简介 (18)3.2SVPWM的算法及仿真 (19)3.3异步电机模块的介绍 (27)3.4SVPWM控制下的异步电机仿真 (27)第4章仿真结果与波形分析 (30)4.1SVPWM控制下电机的输出波形 (30)4.2波形分析 (35)结论 (36)参考文献 (38)第1章绪论第1章绪论1.1 引言调速分为直流调速和交流调速两大类。



矢量控制异步电机调速系统仿真研究摘要20世纪70年代德国专家提出了矢量变换控制的思想,矢量变换控制就是采用矢量变换使交流异步电机定子电流励磁分量和转矩分量之间实现解耦,使交流异步电动机的磁通和转矩分别进行独立控制, 从而使交流异步电动机变频调速系统具有了直流调速系统的全部优点。
本文介绍了异步电动机矢量控制的基本原理及转差频率矢量控制的相关概念,结合实际设计出矢量控制异步电机调速系统的结构图,根据异步电机模型和在调速系统中各子系统的模型,在SIMULINK环境下对该系统进行仿真,并得出仿真结果。
从试验和仿真结果可以看出:该方法简单、控制精度高,用于异步电动机调速系统中具有良好动、静态性能。
利用MATLAB/ SIMULINK模块对交流异步电动机矢量控制系统进行了建模仿真,说明了MATLAB/ SIMULINK 对于复杂的交流调速系统来说是一种很好的仿真工具,并且通过仿真波形的分析也验证了交流异步电动机按转子磁链定向的矢量控制系统具有较好的动、静态性能,完全可以适用于高动态性能的交流调速场合。
关键词:交流调速系统;转差频率;矢量控制;仿真建模Vector control of induction motor based on simulation studiesAbstract20th century 70s German experts put forward the idea of vector transform control. transform vector control use vector transformation to make the exchange of excitation of induction motor stator current components and torque decoupling between components, so that the magnetic AC asynchronous motor Qualcomm and independent control of torque, respectively, so that the exchange of asynchronous motor with variable frequency speed regulation system of the DC drive system all the advantages. This article introduces the asynchronous motor of the basic principles of vector control and slip frequency vector control of the basic concepts, practical design combined with vector control of induction motor based on the structure, according to the model of induction motor speed control system and the various sub- system model, in the SIMULINK environment simulation system and simulation results obtained.The simulation results from the tests can be seen: The method is simple, high precision. The control for induction motor speed control system has good dynamic and static performance.Using MATLAB / SIMULINK module of AC asynchronous motor vector control system modeling and simulation. Illustrate the MATLAB / SIMULINK for the complex AC Drive System is a good simulation tools, and through the simulation waveform analysis to verify AC induction motor according to the rotor flux-oriented vector control system has good dynamic and static performance, It can be applied to the exchange of high-speed dynamic performance occasions.Key words : AC Drive System;Slip frequency; Vector Control; Simulation Modeling目录引言 (1)第1章绪论 (2)1.1交流电机调速技术的发展状况 (2)1.2 现代交流调速系统的类型 (3)l.3 现代交流调速系统的发展趋势和动向 (4)1.3.1 控制理念与控制技术方面的研究与开发 (4)1.3.2 PWM模式改进与优化研究 (4)1.3.3 中压变频装置的研究与开发 (4)第2章矢量控制的基本原理 (6)2.1 异步电动机的数学模型 (6)2.2 矢量控制技术思想 (6)2.3 坐标变换 (7)2.3.1 坐标变换的基本思想和原则 (7)2.3.2 三相-两相变换 (10)2.4 转差频率矢量控制的基本概念 (12)2.5 转差频率矢量控制系统 (13)第3章模型的建立及仿真 (15)3.1 仿真软件简介 (15)3.2 矢量控制调速系统仿真和分析 (15)3.2.1电机仿真模块的建立 (16)3.2.2转速调节器模块 (17)3.2.3函数运算模块 (17)3.2.4 坐标变换模块 (17)第4章仿真结果及结果分析 (19)4.1 仿真模型 (19)4.2 仿真结果及分析 (19)结论与展望 (22)致谢 (23)参考文献 (24)附录 (24)插图清单图1-1 现代交流调速系统组成示意图 ....................................................................... - 3 - 图2-1 二极直流电机的物理模型 ............................................................................... - 8 - 图2-2 等效的交流电机绕组和直流电机绕组物理模型 ......................................... - 10 - 图2-3三相、两相静止坐标系与磁通势空间矢量 ................................................. - 11 - 图2-4 转差频率控制的异步电动机矢控制调速系统的结构图 ............................. - 14 - 图3-1转速PI调节器模块 ....................................................................................... - 17 - 图3-2函数运算模块 ................................................................................................. - 17 - 图3-3 坐标变换模块 ................................................................................................. - 18 - 图4-1矢量控制调速系统的仿真模型 ..................................................................... - 19 - 图4-2仿真波形图 ..................................................................................................... - 20 - 图4-3定子磁链轨迹图 ............................................................................................. - 21 -引言交流异步电动机是一个高阶、强耦合、非线性的多变量系统,该系统数学模型比较复杂,将其简化成单变量线性系统进行控制,动态性能不够理想,调节器参数很难准确设计,为了实现高动态性能, 20世纪70年代初德国西门子公司F.Blaschke提出了矢量控制的方法。

异步电动机矢量控制系统的仿真模型设计中文摘要:矢量控制是在电机统一理论、机电能量转换和坐标变换理论的基础上发展起来的,它的思想就是将异步电动机模拟成直流电动机来控制,通过坐标变换,将定子电流矢量分解为按转子磁场定向的两个直流分量并分别加以控制,从而实现磁通和转矩的解耦控制,达到直流电机的控制效果。
本文针对异步电动机磁链闭环矢量控制进行研究和探索。
通过空间矢量的坐标变换,对系统进行建模,其中包括直流电源、逆变器、电动机、转子磁链电流模型、ASR、ATR、AΨR 等模块。
并对控制系统进行了MATLAB/Simulink仿真分析。
关键词:异步电动机、矢量控制、MATLAB仿真Abstract:Vector control(VC) is based on motor unification principle,energy conversion and vector coordinate transformation theory.By transforming coordinate, The stator current is decomposing two DC parts which orientated as the rotator magnetic field and controlled respectively.So magnetic flux and torque are decoupled. It controls the asynchronous motor as a synchronous way. This paper does some research works of the asynchronous motor flux vector control closed-loop research and exploration. Through the space vector coordinate transformation, and the modeling of system,including DC power supply, inverter, AC motor, rotor flux current model, the ASR, ATR,AΨR and modules. And the control system is MATLAB/Simulink analysis.Key Words:Asynchronous Motor,Vector Control,MATLAB Simulation一、绪论1、交直流调速系统的相关概念及比较交流调速系统是以交流电动机作为控制对象的电力传动自动控制系统。

中文摘要异步电动机矢量控制系统设计及仿真摘要现代交流调速系统在矢量控制技术出现以前多用恒压频比的控制策略,采用这个控制策略的不足之处是在电动机低速转动或者在加减速、加减负载等动态情况下,系统性能显著降低,致使交流调速系统在低速、启动时转矩的动态响应以及整个系统的稳定度方面比直流调速系统逊色,这样就不能满足人们的高精度需求。
后来,交流异步电动机控制开始大踏步从标量控制向矢量控制迈进了。
下面就来简要介绍下矢量控制理论。
矢量控制发展起来的基础和核心理论支撑是坐标转换原理,机电能量转换理论等一些电机学的概念。
这一控制的根本思想方法其实就是将异步电动机模仿成直流电动机来控制。
只要建立出与三相交流绕组等效的两相绕组,即可建立与异步电动机等效的直流电机模型,再加上相应的比例积分调节环节,于是就可按对直流电机的控制策略对异步电动机进行控制。
因而使用矢量控制可以实现对电机电磁转矩的动态实时控制,使得调速性能得以优化提高。
这次毕设中我根据这个思路成功地进行了MATLAB仿真。
关键词:交流电动机;矢量控制调速系统;仿真ABSTRACTThe Design and Simulation of Vector Control Systemof Asynchronous MotorAbstractBefore the technique of vector control system was invented, alternating current speed control system used constant V/f ratio control method witch is normally known as scalar control. Systems which take this method show vital defect when the motor running at low speed or under circumstances like acceleration, deceleration, adding load, reducing load. Alternating current motor witch use vector control can achieve the same control performance as constant current motor, even better.Vector control developed from the foundation of the theory of motor integration, mechanical-electric energy transition, coordinates transition. Its main idea is simulating constant current motor to control alternating current motor. Once the equivalent among three-phase alternating current wingding, two-phase alternating current wind and rotating constant current winding is established, the mode of alternating current motor that simulating constant current motor can be created as well. Therefore, asynchronous motor can be controlled in ways according to synchronous motor. So that vector control can achieve dynamic control of electrical torque of asynchronous motor and reach a high level of speed control performance. I have successfully made a MATLAB simulation of the system.Key Words: Asynchronous Motor; Vector Control; Simulation目录摘要 (I)Abstract (II)第 1章绪论 (1)1.1交、直流调速系统 (1)1.2交流调速系统概述 (2)第2章异步电动机之矢量控制理论 (5)2.1异步电动机之数学模型 (5)2.1.1关于异步电动机数学模型之性质 (5)2.1.2数学模型构建 (5)2.2异步电动机的坐标变换 (8)2.3异步地电动机根据矢量控制法则设计的调速系统 (10)第3章矢量控制系统的仿真 (14)3.1 MATLAB仿真工具介绍 (14)3.2 电动机的具体仿真设计 (15)3.2.1总体仿真结构图 (15)3.2.2仿真系统各子模块设计及参数设置 (16)3.3仿真结果分析 (24)3.3.1空载运行结果分析 (24)3.3.2电机带额定负载运行 (26)3.3.3电机动态运行性能 (28)第4章总结与展望 (32)谢辞 (33)参考文献 (34)附录A外文文献原文 (35)附录B外文文献译文 (43)华东交通大学毕业设计(论文)第1章绪论1.1 交、直流调速系统一般来说,电力传动控制系统由电动机和控制装置组成。
异步电动机矢量控制系统设计与仿真研究开题报告一、综述本课题国内外研究动态,说明选题的依据和意义在近二三十年来,各国学者致力于研究无速度传感器控制系统,无速度传感器控制技术的出现开始于常规带速度传感器的传递动力控制系统,处理问题的起始点是运用检测容易检测到的物理量诸如定子电流和定子电压估算它的速度而代替速度传感器。
主要的方面是怎么样进行对转速的信息的准确得到,并且保持有很高的控制准确度,实现即时控制的需要。
对硬件的检测在无速度传感器的控制系统一般不会出现,省去了伴随着带速度传感器的很多必须的麻烦步骤,对该系统的可靠程度进行了增加,减少系统成本的支出,增加了系统的简易程度:另外使得系统的体积小、重量轻,而且减少了电机和控制器之间的连线,无速度传感器的异步电机的调速系统因为这方面的优势得以在工程中得到广泛的应用。
研究人员为了解决速度估计、磁通辨识和参数适应性等基本问题,提出了多种转速估计和磁通辨识的方法,可运用状态估计、间接测量、参数辨识、直接计算等手段,从定子电流和定子电压中提取出与速度有关的量,从而获得转子速度。
在电力电子器件、计算机技术和微处理器的迅猛发展期间,变频调速的控制技术和手段由变压变频、转差频率控制发展到了矢量控制变频调速技术,交流电机无速度传感器矢量控制三电平变频技术最近二三十年才发展起来的一项控制技术。
无速度传感器控制技术的发展从一般的有速度传感器的传递动力控制系统开始,处理问题的方法是运用检测的定子电压、电流等检测出来不复杂的量进行速度估计而代替速度传感器。
最主要的是对于转速信息的获取,且保持较高的控制精度并且满足实时控制的要求。
在中国,这方面的应用才发展了10多年,这一技术的发展,不仅仅是控制技术的进步和调速性能的优良所能概括的,它已经和节约能源和经济效益密切联系,成为影响国民经济发展的重要因素。
在外国,小到家用电器,大到交流电动机,都是采用了这项技术,其变频器类的产品的发展,有每两年也一次的更新速度。
摘要近年来,随着电力半导体器件及微电子器件特别是微型计算机及大规模集成电路的发展,再加上现代控制理论,特别是矢量控制技术向电气传动领域的渗透和应用,使得交流电机调速技术日臻成熟。
以矢量控制为代表的交流调速技术通过坐标变换重建电机模型,从而可以像直流电机那样对转矩和磁通进行控制,交流调速系统的调速性能已经可以和直流调速系统相媲美。
因此,研究由矢量控制构成的交流调速系统已成为当今交流变频调速系统中研究的主要发展方向。
最后,综合矩阵变换的控制策略及异步电动机转子磁场定向理论,采用计算机仿真方法分别建立了矩阵变换仿真模型以及基于矩阵变换的异步电动机矢量控制系统仿真模型,对矩阵变换的控制原理、输入、输出性能以及矢量控制系统的优质的抗扰能力及四象限运行特性进行分析验证,展现了该新型交流调速系统的广阔发展前景,并针对基于矩阵变换的异步电动机矢量控制系统的特点,着重对矢量控制单元进行了软件设计。
关键词:坐标变换矢量控制异步电动机仿真ABSTRACTIn recent years, with the development of the power semiconductor device,the microelectronics component, the microcomputer and large-scale integrated circuit and modern control theory, especially the penetration from vector control technology to electric drive field and application, the feasible AC motor speed regulation technology has become more mature day by day.Depend on the control principle of the MC and the rotor-flux orientation theory, and using the computer simulation technology, the simulation model of the MC and the matrix converter fed induction motor vector control drive system has been build. The input-output characteristic and the ability of four-quadrant operation have been testified, which has proved that the system has wide application field. The software of the vector control unit was designed at the end.Key words: matrix converter vector control induction motor simulation目录摘要 ...............................................................................................................................................1.绪论 01.1行业背景 01.2 交流调速技术概况 (1)1.3 MATLAB 概述 (2)1.4 Simulink 概述 (3)2.矢量控制理论 ............................................................................................................. 错误!未定义书签。
3. 总体模块设计3.1矢量控制结构框图按照上述数学模型建立的矢量控制结构框图如实例图3.1所示。
图3.1矢量控制结构框图为了实现对电机的矢量控制,使电机满足一定的性能指标(稳定性、快速性和准确性),并尽可能使仿真模型简化,而采用电流和转速负反馈控制方式。
为了使仿真时间尽可能短并达到一定的仿真精度,选用离散控制系统。
整个系统主要分成6部分:速度控制器、矢量控制器、电流比较脉冲产生器、全桥逆变电路、异步电机和反馈回路。
其具体结构如实例图3.2所示。
图3.2矢量控制系统结构框图3.2各子系统模块3.2.1求解磁链模块图3.3求解磁链模块3.2.2 求解转子磁链角模块图3.4求解转子磁链角模块该模块是计算θ角,也就是d轴的位置3.2.3 ids*求解模块此模型的作用是根据转子磁通来计算定子电流的励磁分量i d*,模型如下所示图3.5 i ds*求解模块3.2.4 iqs*求解模块此模块的作用是计算定子电流在d、q坐标系下的q分量的给定值i qs*,其内部构造如下所示:图3.6 i qs*求解模块3.2.5 ABC到DQ坐标变换模块ABC-DQ子模块完成从ABC三相定子坐标系到d、q坐标系的变换(3/2变换),在这个模块中,根据定子电流在ABC三相定子坐标系下的分量,经过旋转变换,得出电动机定子电流在d、q坐标系下的转矩分量i qs和励磁分量i ds。
模块的构造如下图:图3.7 ABC到DQ模块3.2.6 DQ到ABC坐标变换模块DQ- ABC子模块是根据定子电流在d、q坐标系下的分量,经过旋转变换得出电动机定子的三相绕组电流的给定值i abc,变换过程如下所示图3.8 DQ到ABC模块3.3 电机参数设置图3.9 异步电动机参数表3.4矢量控制环节模块图3.10 矢量控制环节3.5矢量控制的异步电动机调速系统模块图3.11 矢量控制的异步电动机调速模块交流异步电动机矢量控制系统如上图所示,此系统为转差频率矢量控制方式,按转子磁场定向的异步电机矢量控制框图。