妊娠合并宫颈上皮内瘤变80例分析
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:128.22 KB
- 文档页数:2


中外医疗China &Foreign Medical TreatmentDOI:10.16662/ki.1674-0742.2021.36.022宫颈上皮内瘤变患者行LEEP 刀宫颈环切术深度对妊娠率及妊娠结局的影响李巧婵,陈卫梅吴川市妇幼保健计划生育服务中心妇产科,广东湛江524500[摘要]目的探讨子宫颈上皮内瘤变患者行LEEP 刀宫颈环切术深度对妊娠率及妊娠结局的影响。
方法便利选取该院2016年3月—2017年3月确诊的子宫颈上皮内瘤变CINⅡ~Ⅲ级并拟行宫颈环切术的未孕者80例为研究对象,根据切割深度(≥或<15mm)分为观察组和对照组。
观察组切割深度≥15mm,对照组<15mm。
术后对两组患者进行随访,对比分析两组患者受孕时间及妊娠结局有无差异。
结果术后随访3年,观察组成功妊娠28例,妊娠率为70.0%,对照组成功妊娠31例,妊娠率为77.5%,两组比较差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.581,P>0.05)。
两组孕妇妊娠结局方面,胎儿病死率、剖腹产率、妊娠时间、新生儿体质量及Apgar 评分差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);术后随访3年,对照组复发6例,观察组复发0例,对照组术后复发风险高于观察组,差异有统计学意义(χ2=4.505,P<0.05)。
结论宫颈上皮内瘤变患者行LEEP 刀宫颈环切术深度对妊娠率及妊娠结局无明显影响,但切割深度≥15mm 可显著降低术后复发风险。
[关键词]宫颈上皮内瘤变;LEEP 刀;宫颈环切术;妊娠率;妊娠结局[中图分类号]R737.33[文献标识码]A[文章编号]1674-0742(2021)12(c)-0022-04Influence of the Depth of Circumcision with LEEP Knife on Pregnancy Rate and Pregnancy Outcome in Patients with Cervical Intraepithelial NeoplasiaLI Qiaochan,CHEN WeimeiDepartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology,Wuchuan Maternal and Child Health and Family Planning Service Center,Zhanjiang,Guangdong Province,524500China[Abstract]Objective To investigate the influence of the depth of LEEP knife circumcision on pregnancy rate and pregnancy outcome in patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.Methods A total of 80non-pregnant patients withcervical intraepithelial neoplasia CIN Ⅱ-Ⅲwho were diagnosed with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia from March 2016to March 2017and planned to undergo cervical circumcision were conveniently selected as the research objects.According to the cutting depth (greater than or less than 15mm)were divided into observation group and control group.The cutting depth of the observation group was ≥15mm,and the control group was <15mm.After the operation,the two groups of patients were followed up,and the two groups of patients were compared and analyzed for differences in pregnancy time and pregnancy outcome.Results After 3years of follow-up,28cases were successfully pregnant in the observation group,the pregnancy rate was 70.0%,and 31cases in the control group were successfully pregnant,and the pregnancy rate was77.5%.There was no statistically significant difference between the two groups (χ2=0.581,P>0.05).In terms of pregnancyoutcomes between the two groups,there was no statistically significant difference in fetal mortality,caesarean section rate,pregnancy time,newborn weight and Apgar score (P>0.05).After 3years of follow-up,there were 6recurrences in the control group and 0recurrences in the observation group,the risk of recurrence in the control group was higher than that inthe observation group,and the difference was statistically significant(χ2=4.505,P<0.05).Conclusion In patientswith cervical intraepithelial neoplasia,the depth of[基金项目]湛江市科技计划项目(2019B01218)。



宫颈上皮内瘤变发生的相关危险因素分析目的调查分析宫颈上皮内瘤变(cervical intraepithelial neoplasia,CIN)发生的相关危险因素。
方法对入组的148例宫颈疾病患者(包括CIN组105例和宫颈炎组43例)通过问卷调查的形式采集相关资料分析CIN发生的相关危险因素。
结果经单因素非条件Logistic回归分析,首次性生活年龄、妊娠次数、性生活频率和性生活前清洗习惯这4项因素差异有统计学意义(P 3次是CIN发生的危险因素(P 0.05),具有可比性。
1.2 方法在纳入研究的调查对象知情同意的基础上,采用自编问卷进行调查,其内容主要包括被调查对象的年龄、受教育程度、职业、吸烟史、饮酒史、既往病史及用药史、月经史、初次性行为的年龄、首次生产年龄、孕产史、避孕史、宫颈癌家族史、宫颈细胞学检查史、行为与习惯、相关知识的了解程度等。
调查问卷均由调查员进行一对一详细询问填写。
1.3 统计学方法建立Epi Data和Excel数据库,应用SPSS 13.0软件对数据进行统计分析,采用单因素及多因素非条件Logistic回归分析CIN发生的相关影响因素,以P 3次是CIN发生的危险因素,性生活前双方清洗阴部是CIN的保护因素。
见表2。
3 讨论CIN是宫颈癌的癌前病变,反映了宫颈癌的连续发展过程。
从宫颈癌前病变发展成宫颈癌,是一个较长时间的渐进性病理过程。
CIN有可能发展为宫颈癌,也有可能自发消退或逆转[6]。
宫颈癌是由HPV感染引起的,是一种感染性疾病。
生殖道HPV在有性活动的人群中普遍存在,每一名妇女在一生中都有可能接触到HPV的一种或多种亚型,大多数HPV的感染是暂时性的。
国外一项研究观察到,608例女大学生中HPV的感染率为43%,其中90%以上感染在2年内自然消退,仅有不足5%的人发展为CIN[7-9]。
从HPV携带者发展到CIN甚至宫颈癌还依赖其他因素的共同作用。
国际肿瘤研究机构多中心的研究资料表明,多次妊娠可能会增加HPV阳性妇女患CIN及宫颈癌的风险。





中晚期妊娠合并CIN 患者HPV 感染状况、外周血T 细胞亚群细胞水平变化及临床意义雷盼盼,刘妮渭南市妇幼保健院妇科,陕西渭南714000【摘要】目的探讨中晚期妊娠合并宫颈上皮内瘤变(CIN)患者人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)感染状况、外周血T 细胞亚群细胞水平变化及临床意义。
方法回顾性分析2020年7月至2021年12月在渭南市妇幼保健院诊治的60例中晚期妊娠合并CIN 孕妇的临床资料,将其设为观察组,另选择同期产检的60例健康中晚期孕妇作为对照组。
比较两组孕妇产前人乳头瘤病毒(HPV)阳性状况、产前及产后6个月免疫功能指标(包括CD4、CD8)水平及观察组CIN 分级不同孕妇产前与产后6个月HPV 感染、HPV DNA 载量和免疫功能指标水平。
结果观察组孕妇的单一感染、多重感染、HPV 阳性率分别为56.67%、23.33%、80.00%,明显高于对照组的13.33%、0、13.33%,差异均有统计学意义(P <0.05);产前,CIN Ⅲ级孕妇的HPV 感染率为100.00%,明显高于Ⅰ级、Ⅱ级的71.43%、85.00%,差异有统计学意义(P <0.05),三级孕妇的HPV DNA 载量比较差异无统计学意义(P >0.05);产后6个月,CIN Ⅲ级孕妇HPV 转阴率为8.33%,明显低于Ⅰ级、Ⅱ级的64.29%、50.00%,HPV DNA 载量为(1.73±0.27)ng/L ,明显高于Ⅰ级、Ⅱ级的(0.46±0.11)ng/L 、(0.71±0.14)ng/L ,差异均有统计学意义(P <0.05);产前及产后6个月,观察组孕妇的CD4水平分别为(36.37±8.05)%、(37.26±4.99)%,明显低于对照组的(41.56±6.23)%、(43.42±5.89)%,CD8水平分别为(28.93±8.49)%、(24.55±3.81)%,明显高于对照组的(24.13±3.90)%、(22.79±3.17)%,差异均有统计学意义(P <0.05);产前及产后6个月,不同CIN 分级孕妇的CD8水平比较差异无统计学意义(P >0.05);产前及产后6个月,CIN Ⅲ级孕妇的CD4水平分别为(35.21±7.21)%、(36.20±4.99)%,均明显低于Ⅰ级、Ⅱ级的(40.46±6.47)%、(37.26±7.03)%和(42.92±5.37)%、(39.42±4.89)%,差异均有统计学意义(P <0.05)。
LEEP治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变86例疗效观察
窦洪涛;张清华;董翠霞
【期刊名称】《山东医药》
【年(卷),期】2009(49)38
【摘要】@@ 2008年3月~12月,我们采用高频电波刀(LEEP)治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变(CIN)86例,疗效较好.现报告如下.rn临床资料:86例患者中的年龄26~52岁,均为经产妇.其中CIN Ⅰ级且伴高危型HPV阳性28例,CIN Ⅱ级46例,CIN Ⅲ级12例.术前均行液基薄层细胞学(TCT)检查和阴道镜下宫颈活检病理证实.
【总页数】1页(P55)
【作者】窦洪涛;张清华;董翠霞
【作者单位】淄博市中心医院,山东淄博255036;淄博市中心医院,山东淄博255036;淄博市淄川区城区卫生院
【正文语种】中文
【相关文献】
1.LEEP术治疗轻至中度宫颈上皮内瘤变的疗效观察 [J], 罗芳
2.LEEP联合外用溃疡散治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变的临床疗效观察 [J], 顾玲珠
3.复方沙棘籽油栓配合LEEP术治疗高级别宫颈上皮内瘤变的疗效观察 [J], 曹玲君
4.LEEP刀宫颈锥切术联合重组α-2b干扰素栓治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变疗效观察 [J], 谢秀梅;徐芳
5.干扰素凝胶联合LEEP刀治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变伴hr-HPV感染患者的疗效观察[J], 柳书勤; 殷敏敏
因版权原因,仅展示原文概要,查看原文内容请购买。
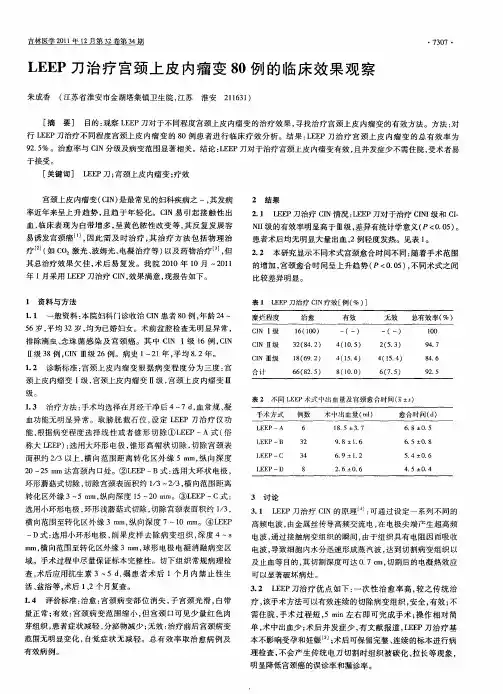
LEEP刀治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变临床疗效分析摘要目的:探讨leep刀对于不同程度宫颈上皮内瘤变的临床治疗效果,寻找治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变的有效方法。
方法:回顾性分析80例不同程度宫颈上皮内瘤变的患者行leep刀治疗的临床疗效。
结果:leep刀在治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变的总有效率为92.5%,治愈率与cin级别及病变范围有明显关系。
结论:leep刀在治疗宫颈上皮内瘤变具有明显的有效,简单方便,并发症少,得到患者的认同。
关键词leep刀宫颈上皮内瘤变疗效宫颈上皮内瘤变(cin)是妇科的最常见疾病之一,近年来随着leep刀技术的不断推广应用,其治疗预后取得较好的临床效果。
2009年10月~2010年11月采用leep刀治疗cin疗效显著。
现报告如下。
资料与方法一般资料:2009年10月~2010年11月收治cin患者80例,年龄24~56岁,平均32岁。
均为已婚妇女,就诊症状主要是白带多异味,血性白带,接触性出血,腰部酸痛不适。
其中cin ⅰ级16例,cin ⅱ级38例,cin ⅲ级26例。
病史1~21年,平均8.2年。
治疗方法:80例患者均应用leep刀治疗,术前盆腔检查无明显异常,排除滴虫念珠菌感染及宫颈癌,术后常规送病检。
手术在月经干净后4~7天进行。
患者取膀胱截石位,根据患者一般情况和具有问题来采用个性化治疗方案,分别选取leep-a式、leep-b式、leep-c式、leep-d式对患者进行手术治疗[1]。
用3%醋酸涂宫颈,以9点为起点,顺时针环形切除病变组织,切割深度(深度指宫颈管中央部分组织最大深度)1.5~2.5cm,切除范围应达到病灶外0.3~0.5cm;对于cin ⅲ,leep术切除范围应达到病灶外0.5~1.0cm,锥切深度2~3cm[2]。
创面边缘及基底部出血点用球状电极止血,若球状电极无法控制出血,可以使用针状电极止血。
术后1、2个月复查。
结果leep刀治疗cin临床疗效:cin ⅰ级和cin ⅱ级的有效率明显高于cin ⅲ级,差异有统计学意义(p<0.05)。
阴道镜下活检诊断宫颈上皮内瘤样病变与LEEP刀术后病理检查结果的差异观察摘要:目的:观察阴道镜下活检诊断宫颈上皮内瘤样病变与LEEP刀术后病理检查结果的差异;方法:选择我院2012年1月至2014年1月收治的接受阴道镜下活检诊断为宫颈上皮内瘤样病变患者80例,全部患者均接受LEEP切除术并将切除病理组织送至病理检查,对两种诊断结果进行对比分析;结果:术前阴道镜下多点活检结果与LEEP刀术后病理检查结果的总符合率为67.5%(54/80)。
结论:在对宫颈上皮内瘤样病变进行诊断时,阴道镜下活检具有一定的诊断价值,但是因为取材受到一定的限制不能有效获得颈管内病变组织,所以漏诊情况比较多,和宫颈锥切病理组织诊断相结合,能让诊断准确性得到有效提升。
关键词:宫颈上皮内瘤样病变;阴道镜;活检;LEEP刀术后病理检查宫颈上皮内瘤样病变主要包括宫颈原位癌和宫颈不典型增生,是一组宫颈癌前病变[1]。
在临床诊断宫颈上皮内瘤样病变时可以选择的方法较多,而阴道镜下多点活检因为其快速和简便等优势,在早期诊断和筛查宫颈上皮内瘤样病变时具有非常重要的作用,但是因为阴道镜下多点活检在取材时存在一定的限制,所以就会出现漏诊的情况。
本研究主要观察了阴道镜下活检诊断宫颈上皮内瘤样病变与LEEP刀术后病理检查结果的差异,现将具体情况汇报如下。
1.资料与方法1.1一般资料选择我院2012年1月至2014年1月收治的接受阴道镜下活检诊断为宫颈上皮内瘤样病变患者80例,年龄23-58岁,平均年龄(37.5±3.1)岁。
妇科检查发现,患者存在宫颈阴道细胞学检查阳性,肉眼观察发现存在慢性宫颈炎症或者可疑病变等。
全部患者均在经期后3-7天进行LEEP刀切除术治疗。
1.2方法全部患者均给予常规阴道镜检查,同时对可疑病变部位组织进行采集并将其送到病理检查。
患者给予50mg哌替啶针肌肉注射,取膀胱截石位,同时消毒铺巾,利用无菌棉球擦拭干净患者阴道分泌物。