MATLAB多旅行商问题源代码
- 格式:docx
- 大小:71.22 KB
- 文档页数:8

重庆大学(商仆过河模型)开课课程:数学模型指导教师:黄光辉小组成员:庄楚斌(20134760)自动化07班张俊铭(20133227)材料加工01班吴慧(20131966)数学01班时间:2015年3月8日一、问题提出3名商人带3名随从乘一条小船过河,小船每次只能承载至多两人。
随从们密约, 在河的任一岸, 一旦随从的人数比商人多,就杀人越货.乘船渡河的方案由商人决定,商人们如何才能安全渡河呢?二、问题分析商人与随从过河问题可以视为是一个多步决策的过程,通过多次优化,从而得到一个全局最优的决策方案。
决策的每一步,即船从此岸到达彼岸,都要对船上的商人和仆人数做出决策。
在保证河的任一岸均有商人数比随从人数多和小船每次最多只能承载两人的前提下,经有限步使所有人员到达彼岸。
三、模型假设商人和随从都会划船,天气很好,无大风大浪,且船的质量很好,可以保证很多次安全的运载商人和随从。
四、模型建立x~第k次渡河前此岸的商人数,k y~第k次渡河前此岸的随从数kx, k y=0,1,2,3; k=1,2,……kS=(k x, k y, c k )~过程的状态,其中k x, k y, c k 分别表示对应时刻此k岸的商人,仆人数以及船的行进方向,其中c 取值1表示即将向彼岸运行,为0表示即将向此岸运行S ~ 允许状态集合,S={(x , y )| x =0, y =0,1,2,3; x =3 ,y =0,1,2,3; x =y =1,2} k u ~第k 次渡船上的商人数k v ~第k 次渡船上的随从数k d =(k u , k v )~决策,D={(u , v )| 21≤+≤v u ,k u , k v =0,1,2} ~允许决策集合k =1,2,… …因为k 为奇数时船从此岸驶向彼岸,k 为偶数时船从彼岸驶向此岸,所以状态k S 随决策k d 的变化规律是1+k S =k S +k )1(-k d ~状态转移律求k d ∈D(k =1,2, …n), 使k S ∈S, 并按转移律由1S =(3,3,1)到达状态1+n S =(0,0,0(1))。

function [pTS,fmin]=grTravSale(C)% Function [pTS,fmin]=grTravSale(C) solve the nonsymmetrical% traveling salesman problem.% Input parameter:% C(n,n) - matrix of distances between cities,% maybe, nonsymmetrical;% n - number of cities.% Output parameters:% pTS(n) - the order of cities;% fmin - length of way.% Uses the reduction to integer LP-problem:% Look: Miller C.E., Tucker A. W., Zemlin R. A.% Integer Programming Formulation of Traveling Salesman Problems. % J.ACM, 1960, Vol.7, p. 326-329.% Needed other products: MIQP.M.% This software may be free downloaded from site:% http://control.ee.ethz.ch/~hybrid/miqp/% Author: Sergiy Iglin% e-mail: siglin@yandex.ru% personal page: http://iglin.exponenta.ru% ============= Input data validation ==================if nargin<1,error('There are no input data!')endif ~isnumeric(C),error('The array C must be numeric!')endif ~isreal(C),error('The array C must be real!')ends=size(C); % size of array Cif length(s)~=2,error('The array C must be 2D!')endif s(1)~=s(2),error('Matrix C must be square!')endif s(1)<3,error('Must be not less than 3 cities!')end% ============ Size of problem ====================n=s(1); % number of vertexesm=n*(n-1); % number of arrows% ============ Parameters of integer LP problem ========Aeq=[]; % for the matrix of the boundary equationsfor k1=1:n,z1=zeros(n);z1(k1,:)=1;z2=[z1;eye(n)];Aeq=[Aeq z2([1:2*n-1],setdiff([1:n],k1))];endAeq=[Aeq zeros(2*n-1,n-1)];A=[]; % for the matrix of the boundary inequationsfor k1=2:n,z1=[];for k2=1:n,z2=eye(n)*(n-1)*(k2==k1);z1=[z1 z2(setdiff([2:n],k1),setdiff([1:n],k2))];endz2=-eye(n);z2(:,k1)=z2(:,k1)+1;A=[A;[z1 z2(setdiff([2:n],k1),2:n)]];endbeq=ones(2*n-1,1); % the right parts of the boundary equations b=ones((n-1)*(n-2),1)*(n-2); % the right parts of the boundary inequationsC1=C'+diag(ones(1,n)*NaN);C2=C1(:);c=[C2(~isnan(C2));zeros(n-1,1)]; % the factors for objective functionvlb=[zeros(m,1);-inf*ones(n-1,1)]; % the lower boundsvub=[ones(m,1);inf*ones(n-1,1)]; % the upper boundsH=zeros(n^2-1); % Hessian% ============= We solve the MIQP problem ========== [xmin,fmin]=MIQP(H,c,A,b,Aeq,beq,[1:m],vlb,vub);% ============= We return the results ==============eik=round(xmin(1:m)); % the arrows of the waye1=[zeros(1,n-1);reshape(eik,n,n-1)];e2=[e1(:);0]; % we add zero to a diagonale3=(reshape(e2,n,n))'; % the matrix of the waypTS=[1 find(e3(1,:))]; % we build the waywhile pTS(end)>1, % we add the city to the waypTS=[pTS find(e3(pTS(end),:))];endreturn。






走遍全中国方案的研究摘要本文通过对走遍中国各省会城市、直辖市和港澳台的最优路径选择问题进行分析,发现这是一个十分典型的旅行商问题(Traveling Salseman Problem ),即寻找一条遍历n 个城市(在本文中为34个城市)的最短路径。
我们搜索了这34个城市的经纬度和部分列车、航班时刻表等各方面信息,综合省钱、省时、方便等因素,进一步深入并细化,从而得到判断各订票方案的准则。
针对问题一,我们利用欧几里得平面知识,由公式0002901800290A B x R A y R ππ+⎧=⋅⎪⎪⎨-⎪=⎪⎩将该34个城市的经纬度转化为平面直角坐标,从而将其简化成二维平面问题。
目前,解旅行商问题(tsp 问题)的方法有许多种,本文采用了较为先进的遗传算法。
遗传算法是目前解决组合优化问题最有效的工具之一,本文介绍了遗传算法的基本原理,讨论了遗传算法中的有关遗传算子设计等方面的技术。
由于该算法在搜索空间中同时考虑了许多点,这样就减少了收敛于局部极小的可能,也增加了处理的并行性。
同时,我们利用MATLAB 软件编辑了相关程序,计算出了遍历该34个城市的最短路径,其路径长度为14661km 。
对于问题二,在只考虑旅行路线最经济的前提下,结合第一问得出的最优路径,我们收集了这34个城市的列车和航班时刻表等信息,从而找出最经济的订票方案,并得其花费为11426元。
针对问题三,在综合考虑省时、省钱、方便等诸多因素的前提下制定订票方案的评价准则,我们运用了层次分析法对其进行研究。
根据对旅行过程中省时,省钱及方便的偏重程度,我们相应地给出了判断矩阵111571513731⎡⎤⎢⎥⎢⎥⎢⎥=⎢⎥⎢⎥⎢⎥⎢⎥⎣⎦A ,然后对其进行一致性检验,发现其不一致程度在容许范围内。
因此我们利用其最大特征根max λ对应的特征向量w 作为比较因素的权向量,并得到以下评价表达式:12120.0740.2830.643*(0.8330.167)C x x x x =+++。
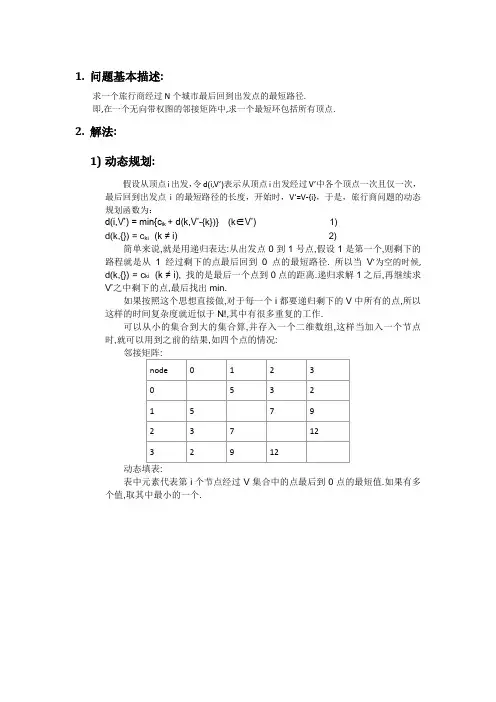
1.问题基本描述:求一个旅行商经过N个城市最后回到出发点的最短路径.即,在一个无向带权图的邻接矩阵中,求一个最短环包括所有顶点.2.解法:1)动态规划:假设从顶点i出发,令d(i,V’)表示从顶点i出发经过V’中各个顶点一次且仅一次,最后回到出发点i的最短路径的长度,开始时,V’=V-{i},于是,旅行商问题的动态规划函数为:d(i,V’) = min{c ik + d(k,V’-{k})} (k∈V’)1)d(k,{}) = c ki (k ≠ i)2)简单来说,就是用递归表达:从出发点0到1号点,假设1是第一个,则剩下的路程就是从1经过剩下的点最后回到0点的最短路径. 所以当V’为空的时候, d(k,{}) = c ki (k ≠ i), 找的是最后一个点到0点的距离.递归求解1之后,再继续求V’之中剩下的点,最后找出min.如果按照这个思想直接做,对于每一个i都要递归剩下的V中所有的点,所以这样的时间复杂度就近似于N!,其中有很多重复的工作.可以从小的集合到大的集合算,并存入一个二维数组,这样当加入一个节点时,就可以用到之前的结果,如四个点的情况:动态填表:表中元素代表第i个节点经过V集合中的点最后到0点的最短值.如果有多个值,取其中最小的一个.这样一共循环(2^(N-1)-1)*(N-1)次,就把时间复杂度缩小到O(N*2)的级别.核心伪代码如下:{for (i =1;i<n;i++) //初始化第0列d[i][0]=c[i][0];for( j=1;j<2^(N-1)-1;j++)for(i=1 ; i<n ;i++){if(子集Vj中不包含i){对Vj中的每个元素k,计算d[i][Vj] = min{c[i][k] + d[k][{Vj-k}] | 每一个k∈Vj};}}对V[2^(n-1)-1]中的每个元素k,计算:d[0][2^(n-1)-1] = min{c[0][k] + d[k][2^(n-1)-2]};输出最短路径:d[0][2^(n-1)-1];}。

function youhuafunD=code;N=50; % Tunablemaxgen=50; % Tunablecrossrate=0.5; %Tunablemuterate=0.08; %Tunablegeneration=1;num = length(D);fatherrand=randint(num,N,3);score = zeros(maxgen,N);while generation<=maxgenind=randperm(N-2)+2; % 随机配对交叉A=fatherrand(:,ind(1:(N-2)/2));B=fatherrand(:,ind((N-2)/2+1:end));% 多点交叉rnd=rand(num,(N-2)/2);ind=rnd tmp=A(ind);A(ind)=B(ind);B(ind)=tmp;% % 两点交叉% for kk=1:(N-2)/2% rndtmp=randint(1,1,num)+1;% tmp=A(1:rndtmp,kk);% A(1:rndtmp,kk)=B(1:rndtmp,kk);% B(1:rndtmp,kk)=tmp;% endfatherrand=[fatherrand(:,1:2),A,B];% 变异rnd=rand(num,N);ind=rnd [m,n]=size(ind);tmp=randint(m,n,2)+1;tmp(:,1:2)=0;fatherrand=tmp+fatherrand;fatherrand=mod(fatherrand,3);% fatherrand(ind)=tmp;%评价、选择scoreN=scorefun(fatherrand,D);% 求得N个个体的评价函数score(generation,:)=scoreN;[scoreSort,scoreind]=sort(scoreN);sumscore=cumsum(scoreSort);sumscore=sumscore./sumscore(end);childind(1:2)=scoreind(end-1:end);for k=3:Ntmprnd=rand;tmpind=tmprnd difind=[0,diff(t mpind)];if ~any(difind)difind(1)=1;endchildind(k)=scoreind(logical(difind));endfatherrand=fatherrand(:,childind);generation=generation+1;end% scoremaxV=max(score,[],2);minV=11*300-maxV;plot(minV,'*');title('各代的目标函数值');F4=D(:,4);FF4=F4-fatherrand(:,1);FF4=max(FF4,1);D(:,5)=FF4;save DData Dfunction D=codeload youhua.mat% properties F2 and F3F1=A(:,1);F2=A(:,2);F3=A(:,3);if (max(F2)>1450)||(min(F2)<=900)error('DATA property F2 exceed it''s range(900,1450]')end% get group property F1 of data, according to F2 value F4=zeros(size(F1));for ite=11:-1:1index=find(F2<=900+ite*50);F4(index)=ite;endD=[F1,F2,F3,F4];function ScoreN=scorefun(fatherrand,D)F3=D(:,3);F4=D(:,4);N=size(fatherrand,2);FF4=F4*ones(1,N);FF4rnd=FF4-fatherrand;FF4rnd=max(FF4rnd,1);ScoreN=ones(1,N)*300*11;% 这里有待优化for k=1:NFF4k=FF4rnd(:,k);for ite=1:11F0index=find(FF4k==ite);if ~isempty(F0index)tmpMat=F3(F0index);tmpSco=sum(tmpMat);ScoreBin(ite)=mod(tmpSco,300);endendScorek(k)=sum(ScoreBin);endScoreN=ScoreN-Scorek;遗传算法实例:% 下面举例说明遗传算法 %% 求下列函数的最大值 %% f(x)=10*sin(5x)+7*cos(4x) x∈[0,10] %% 将 x 的值用一个10位的二值形式表示为二值问题,一个10位的二值数提供的分辨率是每为 (10-0)/(2^10-1)≈0.01 。

%多旅行商问题的matlab程序function varargout = mtspf_gaxy,dmat,salesmen,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,show_prog,show_res % MTSPF_GA Fixed Multiple Traveling Salesmen Problem M-TSP Genetic Algorithm GA% Finds a near optimal solution to a variation of the M-TSP by setting% up a GA to search for the shortest route least distance needed for% each salesman to travel from the start location to individual cities% and back to the original starting place%% Summary:% 1. Each salesman starts at the first point, and ends at the first% point, but travels to a unique set of cities in between% 2. Except for the first, each city is visited by exactly one salesman%% Note: The Fixed Start/End location is taken to be the first XY point%% Input:% XY float is an Nx2 matrix of city locations, where N is the number of cities% DMAT float is an NxN matrix of city-to-city distances or costs% SALESMEN scalar integer is the number of salesmen to visit the cities% MIN_TOUR scalar integer is the minimum tour length for any of the% salesmen, NOT including the start/end point% POP_SIZE scalar integer is the size of the population should be divisible by 8% NUM_ITER scalar integer is the number of desired iterations for the algorithm to run% SHOW_PROG scalar logical shows the GA progress if true% SHOW_RES scalar logical shows the GA results if true%% Output:% OPT_RTE integer array is the best route found by the algorithm% OPT_BRK integer array is the list of route break points these specify the indices% into the route used to obtain the individual salesman routes% MIN_DIST scalar float is the total distance traveled by the salesmen%% Route/Breakpoint Details:% If there are 10 cities and 3 salesmen, a possible route/break% combination might be: rte = 5 6 9 4 2 8 10 3 7, brks = 3 7% Taken together, these represent the solution 1 5 6 9 11 4 2 8 11 10 3 7 1,% which designates the routes for the 3 salesmen as follows:% . Salesman 1 travels from city 1 to 5 to 6 to 9 and back to 1% . Salesman 2 travels from city 1 to 4 to 2 to 8 and back to 1% . Salesman 3 travels from city 1 to 10 to 3 to 7 and back to 1%% 2D Example:% n = 35;% xy = 10randn,2;% salesmen = 5;% min_tour = 3;% pop_size = 80;% num_iter = 5e3;% a = meshgrid1:n;% dmat = reshapesqrtsumxya,:-xya',:.^2,2,n,n;% opt_rte,opt_brk,min_dist = mtspf_gaxy,dmat,salesmen,min_tour, ... % pop_size,num_iter,1,1;%% 3D Example:% n = 35;% xyz = 10randn,3;% salesmen = 5;% min_tour = 3;% pop_size = 80;% num_iter = 5e3;% a = meshgrid1:n;% dmat = reshapesqrtsumxyza,:-xyza',:.^2,2,n,n;% opt_rte,opt_brk,min_dist = mtspf_gaxyz,dmat,salesmen,min_tour, ... % pop_size,num_iter,1,1;%% See also: mtsp_ga, mtspo_ga, mtspof_ga, mtspofs_ga, mtspv_ga, distmat %% Author: Joseph Kirk% Email: jdkirk630gmail% Release: 1.3% Release Date: 6/2/09% Process Inputs and Initialize Defaultsnargs = 8;for k = nargin:nargs-1switch kcase 0xy = 10rand40,2;case 1N = sizexy,1;a = meshgrid1:N;dmat = reshapesqrtsumxya,:-xya',:.^2,2,N,N;case 2salesmen = 5;case 3min_tour = 2;case 4pop_size = 80;case 5num_iter = 5e3;case 6show_prog = 1;case 7show_res = 1;otherwiseendend% Verify InputsN,dims = sizexy;nr,nc = sizedmat;if N ~= nr || N ~= ncerror'Invalid XY or DMAT inputs'endn = N - 1; % Separate Start/End City% Sanity Checkssalesmen = max1,minn,roundrealsalesmen1;min_tour = max1,minfloorn/salesmen,roundrealmin_tour1; pop_size = max8,8ceilpop_size1/8;num_iter = max1,roundrealnum_iter1;show_prog = logicalshow_prog1;show_res = logicalshow_res1;% Initializations for Route Break Point Selectionnum_brks = salesmen-1;dof = n - min_toursalesmen; % degrees of freedom addto = ones1,dof+1;for k = 2:num_brksaddto = cumsumaddto;endcum_prob = cumsumaddto/sumaddto;% Initialize the Populationspop_rte = zerospop_size,n; % population of routes pop_brk = zerospop_size,num_brks; % population of breaks for k = 1:pop_sizepop_rtek,: = randpermn+1;pop_brkk,: = randbreaks;end% Select the Colors for the Plotted Routesclr = 1 0 0; 0 0 1; 0.67 0 1; 0 1 0; 1 0.5 0;if salesmen > 5clr = hsvsalesmen;end% Run the GAglobal_min = Inf;total_dist = zeros1,pop_size;dist_history = zeros1,num_iter;tmp_pop_rte = zeros8,n;tmp_pop_brk = zeros8,num_brks;new_pop_rte = zerospop_size,n;new_pop_brk = zerospop_size,num_brks;if show_progpfig = figure'Name','MTSPF_GA | Current Best Solution','Numbertitle','off'; endfor iter = 1:num_iter% Evaluate Members of the Populationfor p = 1:pop_sized = 0;p_rte = pop_rtep,:;p_brk = pop_brkp,:;rng = 1 p_brk+1;p_brk n';for s = 1:salesmend = d + dmat1,p_rterngs,1; % Add Start Distancefor k = rngs,1:rngs,2-1d = d + dmatp_rtek,p_rtek+1;endd = d + dmatp_rterngs,2,1; % Add End Distanceendtotal_distp = d;end% Find the Best Route in the Populationmin_dist,index = mintotal_dist;dist_historyiter = min_dist;if min_dist < global_minglobal_min = min_dist;opt_rte = pop_rteindex,:;opt_brk = pop_brkindex,:;rng = 1 opt_brk+1;opt_brk n';if show_prog% Plot the Best Routefigurepfig;for s = 1:salesmenrte = 1 opt_rterngs,1:rngs,2 1;if dims == 3, plot3xyrte,1,xyrte,2,xyrte,3,'.-','Color',clrs,:;else plotxyrte,1,xyrte,2,'.-','Color',clrs,:; endtitlesprintf'Total Distance = %1.4f, Iteration = %d',min_dist,iter;hold onendif dims == 3, plot3xy1,1,xy1,2,xy1,3,'ko';else plotxy1,1,xy1,2,'ko'; endhold offendend% Genetic Algorithm Operatorsrand_grouping = randpermpop_size;for p = 8:8:pop_sizertes = pop_rterand_groupingp-7:p,:;brks = pop_brkrand_groupingp-7:p,:;dists = total_distrand_groupingp-7:p;ignore,idx = mindists;best_of_8_rte = rtesidx,:;best_of_8_brk = brksidx,:;rte_ins_pts = sortceilnrand1,2;I = rte_ins_pts1;J = rte_ins_pts2;for k = 1:8 % Generate New Solutionstmp_pop_rtek,: = best_of_8_rte;tmp_pop_brkk,: = best_of_8_brk;switch kcase 2 % Fliptmp_pop_rtek,I:J = fliplrtmp_pop_rtek,I:J;case 3 % Swaptmp_pop_rtek,I J = tmp_pop_rtek,J I;case 4 % Slidetmp_pop_rtek,I:J = tmp_pop_rtek,I+1:J I;case 5 % Modify Breakstmp_pop_brkk,: = randbreaks;case 6 % Flip, Modify Breakstmp_pop_rtek,I:J = fliplrtmp_pop_rtek,I:J;tmp_pop_brkk,: = randbreaks;case 7 % Swap, Modify Breakstmp_pop_rtek,I J = tmp_pop_rtek,J I;tmp_pop_brkk,: = randbreaks;case 8 % Slide, Modify Breakstmp_pop_rtek,I:J = tmp_pop_rtek,I+1:J I;tmp_pop_brkk,: = randbreaks;otherwise % Do Nothingendendnew_pop_rtep-7:p,: = tmp_pop_rte;new_pop_brkp-7:p,: = tmp_pop_brk;endpop_rte = new_pop_rte;pop_brk = new_pop_brk;endif show_res% Plotsfigure'Name','MTSPF_GA | Results','Numbertitle','off';subplot2,2,1;if dims == 3, plot3xy:,1,xy:,2,xy:,3,'k.';else plotxy:,1,xy:,2,'k.'; endtitle'City Locations';subplot2,2,2;imagescdmat1 opt_rte,1 opt_rte;title'Distance Matrix';subplot2,2,3;rng = 1 opt_brk+1;opt_brk n';for s = 1:salesmenrte = 1 opt_rterngs,1:rngs,2 1;if dims == 3, plot3xyrte,1,xyrte,2,xyrte,3,'.-','Color',clrs,:;else plotxyrte,1,xyrte,2,'.-','Color',clrs,:; endtitlesprintf'Total Distance = %1.4f',min_dist;hold on;endif dims == 3, plot3xy1,1,xy1,2,xy1,3,'ko';else plotxy1,1,xy1,2,'ko'; endsubplot2,2,4;plotdist_history,'b','LineWidth',2;title'Best Solution History';setgca,'XLim',0 num_iter+1,'YLim',0 1.1max1 dist_history; end% Return Outputsif nargoutvarargout{1} = opt_rte;varargout{2} = opt_brk;varargout{3} = min_dist;end% Generate Random Set of Break Pointsfunction breaks = randbreaksif min_tour == 1 % No Constraints on Breakstmp_brks = randpermn-1;breaks = sorttmp_brks1:num_brks;else % Force Breaks to be at Least the Minimum Tour Length num_adjust = findrand < cum_prob,1-1;spaces = ceilnum_brksrand1,num_adjust;adjust = zeros1,num_brks;for kk = 1:num_brksadjustkk = sumspaces == kk;endbreaks = min_tour1:num_brks + cumsumadjust;endendend。
MATLAB是一种广泛使用的数学软件,它提供了许多算法和工具,包括启发式算法。
启发式算法是一种基于启发式原理的搜索算法,它通过利用一些启发式信息来减少搜索空间,从而加快搜索速度并提高搜索效率。
下面是一个使用MATLAB实现启发式算法的示例,该算法用于解决旅行商问题(TSP)。
旅行商问题是一个经典的优化问题,要求找到从一个城市到另一个城市的最佳路径,使得总旅行距离最短。
传统的搜索算法可能需要很长时间才能找到解决方案,而启发式算法可以利用一些启发式信息来加快搜索速度。
步骤:1. 定义城市和路径首先,我们需要定义城市的坐标和之间的距离。
这可以通过将每个城市标记为一个数组,并在每个城市之间添加距离来定义。
然后,我们需要为每个城市指定一个优先级或重要性。
这是因为我们的算法会优先考虑访问具有高优先级的城市。
2. 初始化路径接下来,我们需要初始化一个初始路径。
这可以通过随机选择一些城市并将其添加到路径中来实现。
我们还需要将当前路径的长度设置为零,以便我们可以轻松地跟踪总距离。
3. 计算启发式值为了找到最佳路径,我们需要计算每个路径的启发式值。
这可以通过将每个路径的总距离除以未访问城市的数量来实现。
这可以让我们更关注那些距离更短且未访问的城市。
4. 选择下一个城市一旦我们有了所有路径的启发式值,我们就可以选择下一个要访问的城市。
我们选择具有最低启发式值的城市作为下一个目标城市。
这可以确保我们始终在寻找最短路径的同时也访问尽可能多的城市。
5. 更新路径一旦我们选择了下一个城市,我们需要将其添加到当前路径中,并更新路径的总长度。
我们还需要从剩余城市中选择一个具有最高优先级的城市并将其添加到剩余城市列表中。
这将允许我们继续搜索未访问的城市并继续寻找更好的路径。
6. 重复步骤4和5重复步骤4和5直到达到指定的最大迭代次数或找到一个满足要求的解决方案为止。
这就是使用MATLAB实现旅行商问题(TSP)的启发式算法的基本步骤。
%% 连续Hopfield神经网络的优化—旅行商问题优化计算% function main%% 清空环境变量、定义全局变量clear allclcglobal A D%% 导入城市位置load city_location%% 计算相互城市间距离distance=dist(citys,citys');%% 初始化网络N=size(citys,1);A=200;D=100;U0=0.1;step=0.0001;delta=2*rand(N,N)-1;U=U0*log(N-1)+delta;V=(1+tansig(U/U0))/2;iter_num=10000;E=zeros(1,iter_num);%% 寻优迭代for k=1:iter_num% 动态方程计算dU=diff_u(V,distance);% 输入神经元状态更新U=U+dU*step;% 输出神经元状态更新V=(1+tansig(U/U0))/2;% 能量函数计算e=energy(V,distance);E(k)=e;end%% 判断路径有效性[rows,cols]=size(V);V1=zeros(rows,cols);[V_max,V_ind]=max(V);for j=1:colsV1(V_ind(j),j)=1;endC=sum(V1,1);R=sum(V1,2);flag=isequal(C,ones(1,N)) & isequal(R',ones(1,N));%% 结果显示% 计算初始路径长度sort_rand=randperm(N);citys_rand=citys(sort_rand,:);Length_init=dist(citys_rand(1,:),citys_rand(end,:)');for i=2:size(citys_rand,1)Length_init=Length_init+dist(citys_rand(i-1,:),citys_rand(i,:)');end% 绘制初始路径figure(1)plot([citys_rand(:,1);citys_rand(1,1)],[citys_rand(:,2);citys_rand(1,2)],'o-') for i=1:length(citys)text(citys(i,1),citys(i,2),[' ' num2str(i)])endtext(citys_rand(1,1),citys_rand(1,2),[' 起点' ])text(citys_rand(end,1),citys_rand(end,2),[' 终点' ])title(['优化前路径(长度:' num2str(Length_init) ')'])axis([0 1 0 1])grid onxlabel('城市位置横坐标')ylabel('城市位置纵坐标')% 计算最优路径长度[V1_max,V1_ind]=max(V1);citys_end=citys(V1_ind,:);Length_end=dist(citys_end(1,:),citys_end(end,:)');for i=2:size(citys_end,1)Length_end=Length_end+dist(citys_end(i-1,:),citys_end(i,:)');enddisp('最优路径矩阵');V1% 绘制最优路径figure(2)plot([citys_end(:,1);citys_end(1,1)],...[citys_end(:,2);citys_end(1,2)],'o-')for i=1:length(citys)text(citys(i,1),citys(i,2),[' ' num2str(i)])endtext(citys_end(1,1),citys_end(1,2),[' 起点' ])text(citys_end(end,1),citys_end(end,2),[' 终点' ])title(['优化后路径(长度:' num2str(Length_end) ')'])axis([0 1 0 1])grid onxlabel('城市位置横坐标')ylabel('城市位置纵坐标')% 绘制能量函数变化曲线plot(1:iter_num,E);ylim([0 2000])title(['能量函数变化曲线(最优能量:' num2str(E(end)) ')']);xlabel('迭代次数');ylabel('能量函数');elsedisp('寻优路径无效');end% %===========================================% function du=diff_u(V,d)% global A D% n=size(V,1);% sum_x=repmat(sum(V,2)-1,1,n);% sum_i=repmat(sum(V,1)-1,n,1);% V_temp=V(:,2:n);% V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];% sum_d=d*V_temp;% du=-A*sum_x-A*sum_i-D*sum_d;% %==========================================% function E=energy(V,d)% global A D% n=size(V,1);% sum_x=sumsqr(sum(V,2)-1);% sum_i=sumsqr(sum(V,1)-1);% V_temp=V(:,2:n);% V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];% sum_d=d*V_temp;% sum_d=sum(sum(V.*sum_d));% E=0.5*(A*sum_x+A*sum_i+D*sum_d);% % % % 计算dufunction du=diff_u(V,d)global A Dn=size(V,1);sum_x=repmat(sum(V,2)-1,1,n);sum_i=repmat(sum(V,1)-1,n,1);V_temp=V(:,2:n);V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];sum_d=d*V_temp;du=-A*sum_x-A*sum_i-D*sum_d;% % % % % 计算能量函数function E=energy(V,d)global A Dn=size(V,1);sum_x=sumsqr(sum(V,2)-1);sum_i=sumsqr(sum(V,1)-1);V_temp=V(:,2:n);V_temp=[V_temp V(:,1)];sum_d=d*V_temp;sum_d=sum(sum(V.*sum_d));E=0.5*(A*sum_x+A*sum_i+D*sum_d);。
旅行商问题的python代码旅行商问题 (TSP)旅行商问题是一种经典的组合优化问题,涉及寻找一组城市中的最短环路,每座城市只访问一次并返回起点。
贪心算法一种解决 TSP 的贪心算法是最近邻算法。
该算法从任意城市开始,选择与当前城市距离最近的未访问城市,以此类推,直到访问所有城市并返回起点。
Python 代码以下是使用最近邻算法解决 TSP 的 Python 代码:```pythonimport mathdef distance(city1, city2):"""计算两个城市之间的距离。
"""x1, y1 = city1x2, y2 = city2return math.sqrt((x2 - x1) 2 + (y2 - y1) 2) def tsp(cities):"""使用最近邻算法解决 TSP。
"""current_city = cities[0]visited = set([current_city])path = [current_city]while len(visited) < len(cities):next_city = Nonemin_distance = float('inf')for city in cities:if city not in visited anddistance(current_city, city) < min_distance:next_city = citymin_distance = distance(current_city, city)visited.add(next_city)path.append(next_city)current_city = next_citypath.append(cities[0]) # 返回起点return path# 示例城市cities = [(0, 0), (10, 0), (0, 10), (10, 10)]# 求解最短环路path = tsp(cities)# 打印最短环路print(path)```动态规划另一种解决 TSP 的方法是动态规划。
基于遗传算法的旅行商问题求解摘要采用MATLAB,对TSP问题进行基于遗传算法的求解。
TSP 问题是典型的NP完全问题,通过MATLAB进行遗传算法编程,从而有效提出一个较好的TSP解,实现对问题的解答。
进而讨论遗传算法的特点,以及对本问题的可行性。
关键词:TSP问题遗传算法一.问题重述假设有一个旅行商人要拜访n个城市,他必须选择所要走的路径,路径的限制是每个城市只能拜访一次,而且最后要回到原来出发的城市。
路径的选择目标是要求得的路径路程为所有路径之中的最小值。
TSP 问题是一个组合优化问题。
该问题可以被证明具有NPC 计算复杂性。
因此,任何能使该问题的求解得以简化的方法,都将受到高度的评价和关注。
二.遗传算法(GA )概述遗传算法(Genetic Algorithm )是模拟达尔文生物进化论的自然选择和遗传学机理的生物进化过程的计算模型,是一种通过模拟自然进化过程搜索最优解的方法,它最初由美国Michigan 大学J.Holland 教授于1975年首先提出来的,并出版了颇有影响的专著《Adaptation in Natural and Artificial Systems 》,GA 这个名称才逐渐为人所知,J.Holland 教授所提出的GA 通常为简单遗传算法(SGA )。
三.问题分析TSP 问题就是寻找一条最短的遍历n 个城市的最短路径, 即搜索自然数子集W={ 1 ,2 , ⋯, n} ( W 的元素表示对n 个城市的编号) 的一个排列π( W) = { V1 , V2 , ⋯, Vn} , 使len = ∑ d ( Vi , Vi+1) + d ( V1 , Vn)取最小值, 式中的d ( Vi , Vi+1) 表示城市Vi 到城市Vi + 1的距离.遗传算法是具有“生成+检测”的迭代过程的搜索算法。
它的基本处理流程如图1所示。
由此流程图可见,遗传算法是一种群体型操作,该操作以群体中的所有个体为对象。
基于MATLAB的蚁族算法求解旅行商问题作者:李艳平来源:《计算机光盘软件与应用》2013年第14期摘要:目前求解旅行商问题效果最好的混合算法是最大最小蚂蚁算法和局部搜索算法,本文对蚁群算法的仿真学原理进行概要介绍,蚁群算法是受自然界中蚁群搜索食物行为启发而提出的一种智能多目标优化算法,通过蚁群觅食过程中最短路径的搜索策略,给出基于MATLAB的蚁群算法在旅行商问题中的应用,并通过实例仿真结果表明,此算法有一定优越性。
关键词:蚁群算法;旅行商问题;仿真;多目标优化中图分类号:TP301.6旅行商问题(TSP)是一个经典的组合优化问题。
TSP可以描述为:一个商品推销员要去若干个城市推销商品,该推销员从一个城市出发,需要经过所有城市后,回到出发地。
应如何选择行进路线,以使总的行程最短。
从图论的角度来看,该问题实质是在一个带权完全无向图中,找一个权值最小的Hamilton回路。
由于该问题的可行解是所有顶点的全排列,随着顶点数的增加,会产生组合爆炸,它是一个N P完全问题。
随着问题规模的增大,人们对复杂事物和复杂系统建立数学模型并进行求解的能力是有限的,目标函数和约束条件往往不能以明确的函数关系表达,或因函数带有随机参、变量,导致基于数学模型的优化方法在应用于实际生产时,有其局限性甚至不适用。
基于仿真的优化(Simulation Based Optimization,SBO)方法正是在这样的背景下发展起来的。
近年来应用蚁群算法求解旅行商问题,由于其并行性与分布性,特别适用于大规模启发式搜索,实验结果表明这种研究方法是可行的。
1 蚁群算法的仿生学原理蚁群算法最早是由意大利学者M.Dorigo提出来的,它的灵感来源于蚂蚁在寻找食物过程中发现路径的行为,蚂蚁集体寻找路径时,利用称为“外激素”的生物信息激素选择后继行为的智能过程。
蚂蚁是一种群居昆虫,在觅食等活动中,彼此依赖、相互协作共同完成特定的任务。
蚁群的行为是整体协作,相互分工,以一个整体去解决一些对单个蚂蚁来说不可能完成的任务。
1.遗传算法解决TSP 问题(附matlab源程序)2.知n个城市之间的相互距离,现有一个推销员必须遍访这n个城市,并且每个城市3.只能访问一次,最后又必须返回出发城市。
如何安排他对这些城市的访问次序,可使其4.旅行路线的总长度最短?5.用图论的术语来说,假设有一个图g=(v,e),其中v是顶点集,e是边集,设d=(dij)6.是由顶点i和顶点j之间的距离所组成的距离矩阵,旅行商问题就是求出一条通过所有顶7.点且每个顶点只通过一次的具有最短距离的回路。
8.这个问题可分为对称旅行商问题(dij=dji,,任意i,j=1,2,3,…,n)和非对称旅行商9.问题(dij≠dji,,任意i,j=1,2,3,…,n)。
10.若对于城市v={v1,v2,v3,…,vn}的一个访问顺序为t=(t1,t2,t3,…,ti,…,tn),其中11.ti∈v(i=1,2,3,…,n),且记tn+1= t1,则旅行商问题的数学模型为:12.min l=σd(t(i),t(i+1)) (i=1,…,n)13.旅行商问题是一个典型的组合优化问题,并且是一个np难问题,其可能的路径数目14.与城市数目n是成指数型增长的,所以一般很难精确地求出其最优解,本文采用遗传算法15.求其近似解。
16.遗传算法:17.初始化过程:用v1,v2,v3,…,vn代表所选n个城市。
定义整数pop-size作为染色体的个数18.,并且随机产生pop-size个初始染色体,每个染色体为1到18的整数组成的随机序列。
19.适应度f的计算:对种群中的每个染色体vi,计算其适应度,f=σd(t(i),t(i+1)).20.评价函数eval(vi):用来对种群中的每个染色体vi设定一个概率,以使该染色体被选中21.的可能性与其种群中其它染色体的适应性成比例,既通过轮盘赌,适应性强的染色体被22.选择产生后台的机会要大,设alpha∈(0,1),本文定义基于序的评价函数为eval(vi)=al23.pha*(1-alpha).^(i-1) 。
MATLAB多旅行商问题源代码function varargout = mtspf_ga(xy,dmat,salesmen,min_tour,pop_size,num_iter,show_prog,show_res)% MTSPF_GA Fixed Multiple Traveling Salesmen Problem (M-TSP) Genetic Algorithm (GA)% Finds a (near) optimal solution to a variation of the M-TSP by setting% up a GA to search for the shortest route (least distance needed for% each salesman to travel from the start location to individual cities% and back to the original starting place)%% Summary:% 1. Each salesman starts at the first point, and ends at the first% point, but travels to a unique set of cities in between% 2. Except for the first, each city is visited by exactly one salesman%% Note: The Fixed Start/End location is taken to be the first XY point%% Input:% XY (float) is an Nx2 matrix of city locations, where N is the number of cities% DMAT (float) is an NxN matrix of city-to-city distances or costs% SALESMEN (scalar integer) is the number of salesmen to visit the cities% MIN_TOUR (scalar integer) is the minimum tour length for any of the% salesmen, NOT including the start/end point% POP_SIZE (scalar integer) is the size of the population (should be divisible by 8)% NUM_ITER (scalar integer) is the number of desired iterations for the algorithm to run% SHOW_PROG (scalar logical) shows the GA progress if true% SHOW_RES (scalar logical) shows the GA results if true%% Output:% OPT_RTE (integer array) is the best route found by the algorithm% OPT_BRK (integer array) is the list of route break points (these specify the indices% into the route used to obtain the individual salesman routes)% MIN_DIST (scalar float) is the total distance traveled by the salesmen%% Route/Breakpoint Details:% If there are 10 cities and 3 salesmen, a possible route/break% combination might be: rte = [5 6 9 4 2 8 10 3 7], brks = [3 7]% Taken together, these represent the solution [1 5 6 9 1][1 4 2 8 1][1 10 3 7 1],% which designates the routes for the 3 salesmen as follows:% . Salesman 1 travels from city 1 to 5 to 6 to 9 and back to 1% . Salesman 2 travels from city 1 to 4 to 2 to 8 and back to 1% . Salesman 3 travels from city 1 to 10 to 3 to 7 and back to 1%% 2D Example:% n = 35;% xy = 10*rand(n,2);% salesmen = 5;% min_tour = 3;% pop_size = 80;% num_iter = 5e3;% a = meshgrid(1:n);% dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),n,n);% [opt_rte,opt_brk,min_dist] = mtspf_ga(xy,dmat,salesmen,min_tour, ... % pop_size,num_iter,1,1);%% 3D Example:% n = 35;% xyz = 10*rand(n,3);% salesmen = 5;% min_tour = 3;% pop_size = 80;% num_iter = 5e3;% a = meshgrid(1:n);% dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xyz(a,:)-xyz(a',:)).^2,2)),n,n);% [opt_rte,opt_brk,min_dist] = mtspf_ga(xyz,dmat,salesmen,min_tour, ... % pop_size,num_iter,1,1);%% See also: mtsp_ga, mtspo_ga, mtspof_ga, mtspofs_ga, mtspv_ga, distmat%% Author: Joseph Kirk%Email:*******************% Release: 1.3% Release Date: 6/2/09% Process Inputs and Initialize Defaultsnargs = 8;for k = nargin:nargs-1switch kcase 0xy = 10*rand(40,2);case 1N = size(xy,1);a = meshgrid(1:N);dmat = reshape(sqrt(sum((xy(a,:)-xy(a',:)).^2,2)),N,N);case 2salesmen = 5;case 3min_tour = 2;case 4pop_size = 80;case 5num_iter = 5e3;case 6show_prog = 1;case 7show_res = 1;otherwiseendend% Verify Inputs[N,dims] = size(xy);[nr,nc] = size(dmat);if N ~= nr || N ~= ncerror('Invalid XY or DMAT inputs!')endn = N - 1; % Separate Start/End City% Sanity Checkssalesmen = max(1,min(n,round(real(salesmen(1)))));min_tour = max(1,min(floor(n/salesmen),round(real(min_tour(1))))); pop_size = max(8,8*ceil(pop_size(1)/8));num_iter = max(1,round(real(num_iter(1))));show_prog = logical(show_prog(1));show_res = logical(show_res(1));% Initializations for Route Break Point Selectionnum_brks = salesmen-1;dof = n - min_tour*salesmen; % degrees of freedom addto = ones(1,dof+1);for k = 2:num_brksaddto = cumsum(addto);endcum_prob = cumsum(addto)/sum(addto);% Initialize the Populationspop_rte = zeros(pop_size,n); % population of routespop_brk = zeros(pop_size,num_brks); % population of breaksfor k = 1:pop_sizepop_rte(k,:) = randperm(n)+1;pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();end% Select the Colors for the Plotted Routesclr = [1 0 0; 0 0 1; 0.67 0 1; 0 1 0; 1 0.5 0];if salesmen > 5clr = hsv(salesmen);end% Run the GAglobal_min = Inf;total_dist = zeros(1,pop_size);dist_history = zeros(1,num_iter);tmp_pop_rte = zeros(8,n);tmp_pop_brk = zeros(8,num_brks);new_pop_rte = zeros(pop_size,n);new_pop_brk = zeros(pop_size,num_brks);if show_progpfig = figure('Name','MTSPF_GA | Current Best Solution','Numbertitle','off'); endfor iter = 1:num_iter% Evaluate Members of the Populationfor p = 1:pop_sized = 0;p_rte = pop_rte(p,:);p_brk = pop_brk(p,:);rng = [[1 p_brk+1];[p_brk n]]';for s = 1:salesmend = d + dmat(1,p_rte(rng(s,1))); % Add Start Distancefor k = rng(s,1):rng(s,2)-1d = d + dmat(p_rte(k),p_rte(k+1));endd = d + dmat(p_rte(rng(s,2)),1); % Add End Distanceendtotal_dist(p) = d;end% Find the Best Route in the Population[min_dist,index] = min(total_dist);dist_history(iter) = min_dist;if min_dist < global_minglobal_min = min_dist;opt_rte = pop_rte(index,:);opt_brk = pop_brk(index,:);rng = [[1 opt_brk+1];[opt_brk n]]';if show_prog% Plot the Best Routefigure(pfig);for s = 1:salesmenrte = [1 opt_rte(rng(s,1):rng(s,2)) 1];if dims == 3, plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:));else plot(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); endtitle(sprintf('Total Distance = %1.4f, Iteration = %d',min_dist,iter));hold onendif dims == 3, plot3(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),xy(1,3),'ko');else plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'ko'); endhold offendend% Genetic Algorithm Operatorsrand_grouping = randperm(pop_size);for p = 8:8:pop_sizertes = pop_rte(rand_grouping(p-7:p),:);brks = pop_brk(rand_grouping(p-7:p),:);dists = total_dist(rand_grouping(p-7:p));[ignore,idx] = min(dists);best_of_8_rte = rtes(idx,:);best_of_8_brk = brks(idx,:);rte_ins_pts = sort(ceil(n*rand(1,2)));I = rte_ins_pts(1);J = rte_ins_pts(2);for k = 1:8 % Generate New Solutionstmp_pop_rte(k,:) = best_of_8_rte;tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = best_of_8_brk;switch kcase 2 % Fliptmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = fliplr(tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J));case 3 % Swaptmp_pop_rte(k,[I J]) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[J I]);case 4 % Slidetmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[I+1:J I]);case 5 % Modify Breakstmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();case 6 % Flip, Modify Breakstmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = fliplr(tmp_pop_rte(k,I:J));tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();case 7 % Swap, Modify Breakstmp_pop_rte(k,[I J]) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[J I]);tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();case 8 % Slide, Modify Breakstmp_pop_rte(k,I:J) = tmp_pop_rte(k,[I+1:J I]);tmp_pop_brk(k,:) = randbreaks();otherwise % Do Nothingendendnew_pop_rte(p-7:p,:) = tmp_pop_rte;new_pop_brk(p-7:p,:) = tmp_pop_brk;endpop_rte = new_pop_rte;pop_brk = new_pop_brk;endif show_res% Plotsfigure('Name','MTSPF_GA | Results','Numbertitle','off');subplot(2,2,1);if dims == 3, plot3(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),xy(:,3),'k.');else plot(xy(:,1),xy(:,2),'k.'); endtitle('City Locations');subplot(2,2,2);imagesc(dmat([1 opt_rte],[1 opt_rte]));title('Distance Matrix');subplot(2,2,3);rng = [[1 opt_brk+1];[opt_brk n]]';for s = 1:salesmenrte = [1 opt_rte(rng(s,1):rng(s,2)) 1];if dims == 3, plot3(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),xy(rte,3),'.-','Color',clr(s,:));else plot(xy(rte,1),xy(rte,2),'.-','Color',clr(s,:)); endtitle(sprintf('Total Distance = %1.4f',min_dist));hold on;endif dims == 3, plot3(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),xy(1,3),'ko');else plot(xy(1,1),xy(1,2),'ko'); endsubplot(2,2,4);plot(dist_history,'b','LineWidth',2);title('Best Solution History');set(gca,'XLim',[0 num_iter+1],'YLim',[0 1.1*max([1 dist_history])]);end% Return Outputsif nargoutvarargout{1} = opt_rte;varargout{2} = opt_brk;varargout{3} = min_dist;end% Generate Random Set of Break Pointsfunction breaks = randbreaks()if min_tour == 1 % No Constraints on Breakstmp_brks = randperm(n-1);breaks = sort(tmp_brks(1:num_brks));else % Force Breaks to be at Least the Minimum Tour Length num_adjust = find(rand < cum_prob,1)-1;spaces = ceil(num_brks*rand(1,num_adjust));adjust = zeros(1,num_brks);for kk = 1:num_brksadjust(kk) = sum(spaces == kk);endbreaks = min_tour*(1:num_brks) + cumsum(adjust);endendend。