煤质化验公式
- 格式:doc
- 大小:42.00 KB
- 文档页数:1

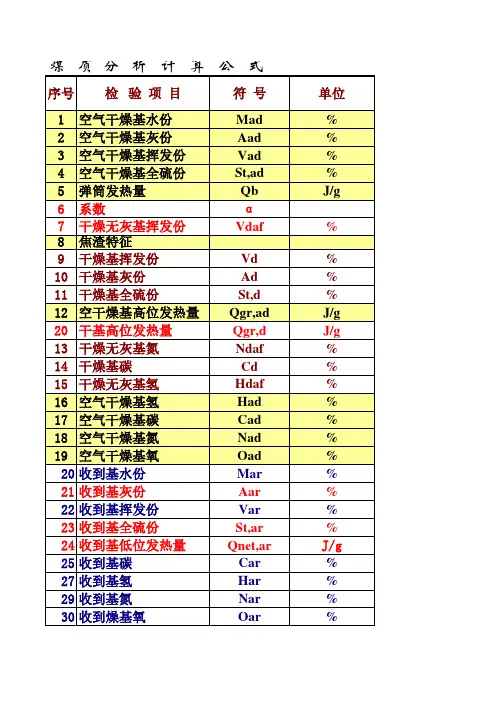
煤炭化验中煤质指标符合及所代表的含义解析煤质化验常规指标英文符号水分全水份(Mt):是煤中所有内在水份和外在水份的总和,也常用Mar表示。
通常规定在8%以下。
空气干燥基水份(Mad):指煤炭在空气干燥状态下所含的水份。
也可以认为是内在水份,老的国家标准上有称之为“分析基水份”的。
灰分(干基灰分--无水分状态;空干基灰分--空气干燥状态下保持的灰分)空气干燥基灰分(Aad)干燥基灰分(Ad)收到基灰分的(Aar)挥发份(全称为挥发份产率)V空气干燥基挥发份(Vad)干燥基挥发份(Vd)干燥无灰基挥发份(Vdaf)收到基挥发份(Var)。
其中Vdaf是煤炭分类的重要指标之一固定碳不同于元素分析的碳,是根据水分、灰分和挥发份计算出来的。
FC+A+V+M=100相关公式如下:FCad=100-Mad-Aad-VadFCd=100-Ad-VdFCdaf=100-Vdaf全硫St空气干燥基全硫(St,ad)干燥基全硫(St.d)收到基全硫(St,ar)发热量煤的弹筒发热量(Qb):煤的弹筒发热量,是单位质量的煤样在热量计的弹筒内,在过量高压氧(25~35个大气压左右)中燃烧后产生的热量(燃烧产物的最终温度规定为25C)。
煤的高位发热量(Qgr) 煤的高位发热量,即煤在空气中大气压条件下燃烧后所产生的热量。
实际上是由实验室中测得的煤的弹筒发热量减去硫酸和硝酸生成热后得到的热量。
煤的恒湿无灰基高位发热量(Qmaf)恒湿,是指温度30C,相对湿度96%时,测得的煤样的水分(或叫最高内在水分)。
煤的恒湿无灰基高位发热量,实际中是不存在的,是指煤在恒湿条件下测得的恒容高位发热量,除去灰分影响后算出来的发热量。
恒湿无灰基高位发热量是低煤化度煤分类的一个指标。
煤的低位发热量Qnet,ar——收到基低位发热量Qnet,daf——干燥无灰基低位发热Qgr,d——干燥基高位发热量;弹筒发热量4种表示方式:Qb,ad——分析基弹筒发热量;Qb,d——干燥基弹筒发热量;Qb,ar——收到基弹筒发热量;Qb,daf——干燥无灰基弹筒发热量。

煤矿常用计算公式及其应用范围1.煤尺寸分布计算公式:煤尺寸分布是指煤在不同粒度上的分布情况,通常通过筛分实验来确定。
常用的煤尺寸分布计算公式有Rosin-Rammler方程和Gates-Gaudin-Schuhmann方程。
- Rosin-Rammler方程:用于描述煤在筛网上的分布情况。
公式:x/xm = exp((-(x/xm)^b))应用范围:通过该公式可以得到煤的粒度分布曲线,并依据曲线来评价煤的破碎性能。
2.煤质计算公式:煤炭质量是煤炭的重要性能之一,影响着其燃烧性能、利用价值等。
常用的煤质计算公式有:洗煤后焦炭机械强度计算公式、元素分析法计算公式等。
-洗煤后焦炭机械强度计算公式:公式:CokeRI = 19.58 - 0.2957×Aad - 0.0531×Mad应用范围:该公式通过对洗煤后焦炭化验数据的分析计算,评价煤质的机械性能,指导焦炭的生产过程。
3.煤炭储量计算公式:煤炭储量是指在一定经济条件下能够被开采出来的煤炭总量。
常用的煤炭储量计算公式有四参数估计法、Kriging法等。
-四参数估计法:公式:Q=N×B×P×r×(1-C)/(B×P+I)应用范围:四参数法通过煤矿开采方法和矿层信息进行计算,可以估计煤矿的储量。
4.煤矿通风计算公式:煤矿通风是维持煤矿工作环境的重要因素之一,通过合理的通风设计可以保证煤矿的安全生产。
常用的通风计算公式有:负压通风系统风量计算公式、鼓风机工作点计算公式等。
-负压通风系统风量计算公式:公式:Q=(P+1)/P×N×P1×P2/60/1000应用范围:该公式用于计算负压通风系统的风量,以确定通风系统是否满足煤矿的通风需求。
5.煤矸石回填计算公式:煤矸石回填是煤炭开采过程中的一个环保举措,通过将煤矸石回填到开采的矿井中,减少环境污染。
常用的回填计算公式有:回填厚度计算公式、回填效率计算公式等。

煤质分析常用公式一、发热量计算公式 1 、热容量计算公式。
E= 2 、弹筒发热量计算公式Q b = 3 、空干基高位热值计算公式Q gr,ad = Q b,ad - (94.1S b,ad + Q b,ad ) 注:当全硫含量低于 4.00% 时,或发热量大于14.60MJ/kg 时,用全硫(按GB/T214 测定)代替 S b,ad 。
一、发热量计算公式1、热容量计算公式。
E=2、弹筒发热量计算公式Q b=3、空干基高位热值计算公式Q gr,ad= Q b,ad-(94.1S b,ad+Q b,ad)注:当全硫含量低于4.00%时,或发热量大于14.60MJ/kg时,用全硫(按GB/T214测定)代替S b,ad。
(引用国标GB/T213-2003《煤的发热量测定方法》中9.3.2条)。
4、收到基低位热值计算公式Q net,ar=(Q gr,ad-206H ad)5、空干基高位热值换算为干基高位热值公式Q gr,d=Q gr,ad×6、硝酸生成热计算公式q n=QG0.00157、冷却校正公式7.1国标公式C=(n-a)V n+aV0当≤1.20时,a=当>1.20时,a=V0=K(t0―t j)+A(测发热量时用)V n=K(t n―t j)+A7.2瑞方公式C=nV0+7.3奔特公式C=式中:E——热容量J/KQ b——弹筒发热量MJ/kgQ gr,ad——空干基高位热值MJ/kgQ net,ar——收到基低拉热值MJ/kgQ gr,d——干基高位热值MJ/kgQ——苯甲酸热值J/gG——试样重量gq1——点火丝热值Jq2——添加物热值Jqn——硝酸生成热J——主期温升K或℃——点火后1'40''时的温升K或℃C——温升冷却校正值K或℃——硝酸校正系数当Q b≤16.7MJ/kg时,=0.001当16.7MJ/K<Q b≤25.1MJ/kg时,=0.0012当Q b>25.1MJ/kg时,=0.0016S t——全硫%M ar——收到基水分%M ad——空干基水分%H ad——空干基氢%V0——初期内筒降温速度K/min(瑞方、奔特为K/0.5min)V n——未期内筒降温速度K/mint j——外筒温度℃t0——点火时的内桶温度℃tn——终点时的内桶温度℃——初期的平均温度℃——末期的平均温度℃m——主期内每30S,温升0.3℃以上的次数,低热值时为温升0.1℃以上的次数。

煤炭水分化验计算公式煤炭是一种重要的能源资源,其水分含量是影响燃烧性能和热值的重要指标。
因此,准确测定煤炭水分含量对于煤炭质量评价和利用具有重要意义。
煤炭水分化验计算公式是用来计算煤炭水分含量的一种方法,通过化验得到的数据和公式计算,可以准确地得出煤炭的水分含量,为煤炭的利用和评价提供了重要的依据。
煤炭水分化验计算公式的基本原理是根据煤炭中水分的含量与煤样的质量和体积之间的关系,通过化验得到的数据,利用计算公式计算出煤炭的水分含量。
一般情况下,煤炭水分含量的计算公式可以分为干燥基和空气干燥基两种计算方法。
下面将分别介绍这两种计算方法的公式和具体步骤。
一、干燥基煤炭水分计算公式。
1. 干燥基煤炭水分计算公式的基本原理。
干燥基煤炭水分计算公式是以煤炭的干燥基为基础,通过化验得到的煤样的湿基水分含量、灰分含量和挥发分含量,结合煤样的质量和体积,计算出煤炭的水分含量。
其中,煤炭的湿基水分含量是指煤样中天然存在的水分含量,灰分含量是指煤样中的无机物含量,挥发分含量是指煤样在加热过程中释放出的挥发性物质的含量。
2. 干燥基煤炭水分计算公式的具体步骤。
(1)首先,根据化验结果得到煤样的湿基水分含量(M_ad)、灰分含量(A_d)和挥发分含量(V_d)。
(2)然后,根据煤样的质量和体积,计算出煤样的干燥基水分含量(M_d)。
(3)最后,利用以下公式计算出煤炭的水分含量(M):M = M_d / (1 M_d)。
其中,M为煤炭的水分含量,M_d为煤炭的干燥基水分含量。
二、空气干燥基煤炭水分计算公式。
1. 空气干燥基煤炭水分计算公式的基本原理。
空气干燥基煤炭水分计算公式是以煤炭的空气干燥基为基础,通过化验得到的煤样的空气干燥基水分含量、灰分含量和挥发分含量,结合煤样的质量和体积,计算出煤炭的水分含量。
2. 空气干燥基煤炭水分计算公式的具体步骤。
(1)首先,根据化验结果得到煤样的空气干燥基水分含量(M_ad)和灰分含量(A_d)。

随着科学技术的不断发展,化验分析在各个领域都发挥着重要作用。
为了提高化验分析工作的准确性和效率,以下是化验分析中常用的一些公式总结,供广大化验工作者参考。
一、基本公式1. 灰分(%)=(烧后总重-灰皿重)/原煤总重×100%2. 挥发分(%)=(原煤重-烧后灰重)/原煤重×100%3. 分析水(%)=(原煤重-烘干后的煤重)/原煤重×100%4. 全水(%)=(原煤重-烘干后的煤重)/原煤重×100%二、化学计量学公式1. 物质的量(mol)= 质量(g)/摩尔质量(g/mol)2. 浓度(mol/L)= 物质的量(mol)/溶液体积(L)3. 摩尔质量(g/mol)= 质量(g)/物质的量(mol)4. 摩尔浓度(mol/L)= 溶质的质量(g)/摩尔质量(g/mol)×溶液体积(L)三、酸碱滴定公式1. 滴定度(g/mL)= 标准溶液的浓度(mol/L)×标准溶液的体积(mL)×摩尔质量(g/mol)2. 标准溶液的浓度(mol/L)= 滴定度(g/mL)/(滴定前溶液的体积(mL)×摩尔质量(g/mol))3. 滴定度(g/mL)= 标准溶液的浓度(mol/L)×滴定前溶液的体积(mL)×摩尔质量(g/mol)4. 滴定度(g/mL)= 滴定后溶液的体积(mL)×标准溶液的浓度(mol/L)×摩尔质量(g/mol)四、氧化还原滴定公式1. 标准溶液的浓度(mol/L)= 滴定度(g/mL)/(滴定前溶液的体积(mL)×摩尔质量(g/mol))2. 滴定度(g/mL)= 标准溶液的浓度(mol/L)×滴定前溶液的体积(mL)×摩尔质量(g/mol)3. 滴定度(g/mL)= 滴定后溶液的体积(mL)×标准溶液的浓度(mol/L)×摩尔质量(g/mol)五、重量分析法公式1. 溶液的浓度(mol/L)= 溶剂的质量(g)/摩尔质量(g/mol)×溶液的体积(L)2. 溶剂的质量(g)= 溶液的浓度(mol/L)×摩尔质量(g/mol)×溶液的体积(L)3. 溶液的体积(L)= 溶剂的质量(g)/摩尔质量(g/mol)×溶液的浓度(mol/L)以上是化验分析中常用的一些公式总结,希望对广大化验工作者有所帮助。

煤质化验指标Document serial number【LGGKGB-LGG98YT-LGGT8CB-LGUT-煤质化验指标水分。
煤中水分分为内在水分、外在水分、结晶水和分解水。
煤中水分过大是,不利于加工、运输等,燃烧时会影响热稳定性和热传导,炼焦时会降低焦产率和延长焦化周期。
现在我们常报的水份指标有:1、全水份(Mt),是煤中所有内在水份和外在水份的总和,也常用Mar表示。
通常规定在8%以下。
2、空气干燥基水份(Mad),指煤炭在空气干燥状态下所含的水份。
也可以认为是内在水份,老的国家标准上有称之为“分析基水份”的。
灰分指煤在燃烧的后留下的残渣。
不是煤中矿物质总和,而是这些矿物质在化学和分解后的残余物。
灰分高,说明煤中可燃成份较低。
发热量就低。
同时在精煤炼焦中,灰分高低决定焦炭的灰分。
能常的灰分指标有空气干燥基灰分(Aad)、干燥基灰分(Ad)等。
也有用收到基灰分的(Aar)。
挥发份(全称为挥发份产率)V指煤中有机物和部分矿物质加热分解后的产物,不全是煤中固有成分,还有部分是热解产物,所以称挥发份产率。
挥发份大小与煤的变质程度有关,煤炭变质量程度越高,挥发份产率就越低。
在燃烧中,用来确定锅炉的型号;在炼焦中,用来确定配煤的比例;同时更是汽化和液化的重要指标。
常使用的有空气干燥基挥发份(Vad)、干燥基挥发份(Vd)、干燥无灰基挥发份(Vdaf)和收到基挥发份(Var)。
其中Vdaf是煤炭分类的重要指标之一。
固定碳不同于元素分析的碳,是根据水分、灰分和挥发份计算出来的。
FC+A+V+M=100相关公式如下:FCad=100-Mad-Aad-VadFCd=100-Ad-VdFCdaf=100-Vdaf全硫St是煤中的有害元素,包括有机硫、无机硫。
1%以下才可用于燃料。
部分地区要求在0.6和0.8以下,现在常说的环保煤、绿色能源均指硫份较低的煤。
常用指标有:空气干燥基全硫(St,ad)、干燥基全硫(St.d)及收到基全硫(St,ar)。

洗煤指标计算公式
洗煤指标是用来评估洗煤产品质量的一种方法,常用的指标有灰分、
硫分、焦渣量等。
下面是一些常见的洗煤指标计算公式。
1.灰分计算公式:
灰分(A)=(干煤质量-焦炭质量-可燃物质量)/干煤质量×100%
其中,干煤质量是指去除水分后的煤样质量;焦炭质量是洗煤过程中
产生的煤炭渣滓经过干燥后的质量;可燃物质量是取样后经过干燥的质量。
2.硫分计算公式:
硫分(S)=(硫含量×煤质量)/干煤质量×100%
其中,硫含量是指洗煤样品中所含有的硫的质量,煤质量是指洗煤样
品的总质量。
3.含水率计算公式:
含水率(M)=(湿煤样质量-干煤样质量)/干煤样质量×100%
其中,湿煤样质量是指煤样中包含的水分的质量,干煤样质量是去除
水分后的煤样质量。
4.热值计算公式:
热值(Q)=(干煤热值×干煤样质量)/煤样质量
其中,干煤热值是指去除水分后的煤样的热容量,干煤样质量是指去
除水分后的煤样的质量,煤样质量是指煤样的总质量。
5.焦渣量计算公式:
焦渣量(R)=(灰渣质量×100%)/煤样焦炭质量
其中,灰渣质量是指洗煤过程中产生的煤炭渣滓的质量,煤样焦炭质量是指洗煤过程中产生的焦炭的质量。
以上是一些常见的洗煤指标计算公式,通过这些公式可以对洗煤产品的质量进行评估和比较。
需要注意的是,在计算指标时需要准确测量煤样的质量和含量,并遵循相关的标准和方法。

煤质化验指标水分:煤中水分分为内在水分、外在水分、结晶水和分解水。
煤中水分过大是,不利于加工、运输等,燃烧时会影响热稳定性和热传导,炼焦时会降低焦产率和延长 焦化周期。
现在我们常报的水份指标有:1、 全水份(Mt ),是煤中所有内在水份和外在水份的总和,也常用 Mar 表示。
通常规定在8%^下。
2、 空气干燥基水份(Mad ),指煤炭在空气干燥状态下所含的水份。
也可以认为是内在水份,老的国家标 准上有称之为“分析基水份”的。
灰分:指煤在燃烧的后留下的残渣。
不是煤中矿物质总和,而是这些矿物质在化学和分解后的残余物。
灰分高,说明煤中可燃成份较低。
发热量就低。
同时在精煤炼焦中,灰分高低决定焦炭的灰分。
能常的灰分指标有空气干燥基灰分( Aad )、干燥基灰分(Ad )等。
也有用收到基灰分的( Aar )。
挥发份(全称为挥发份产率) V:指煤中有机物和部分矿物质加热分解后的产物,不全是煤中固有成分, 还有部分是热解产物,所以称挥发份产率。
挥发份大小与煤的变质程度有关,煤炭变质量程度越高,挥发份产率就越低。
在燃烧中,用来确定锅炉的型号;在炼焦中,用来确定配煤的比例;同时更是汽化和液化的重要指标。
常使用的有空气干燥基挥发份( Vad )、干燥基挥发份(Vd )、干燥无灰基挥发份(Vdaf )和收到基挥发份(Var )。
其中Vdaf 是煤炭分类的重要指标之一 。
固定碳:不同于元素分析的碳,是根据水分、灰分和挥发份计算出来的。
FC+A+V+M=100相关公式如下: FCad=100-Mad-Aad-VadFCd=100-Ad-VdFCdaf=100-Vdaf全硫St:是煤中的有害元素,包括有机硫、无机硫。
1%^下才可用于燃料。
部分地区要求在0.6和0.8以下, 现在常说的环保煤、绿色能源均指硫份较低的煤。
常用指标有:空气干燥基全硫 (St,ad )、干燥基全硫(St.d )及收到基全硫(St,ar )。

煤炭化验公式(Coal test formula)1. ash:The coal pulverizing said 1 grams, put in the muffle furnace 850 degree burn was removed after 1 hours, after cooling (low temperature coal weighing time).Formula: = (total - ash after burning coal, cupel heavy weight) * 100%Note: each record accurate weight cupel2. volatile matter:The coal pulverizing said 1 grams, put in the muffle furnace 900 degree burn for 7 minutes, cooling after weighing (temperature to the exact time)Formula: = (volatile coal - ash after burning heavy weight / weight * 100%-) coal water analysisNote: the total weight of each volatile crucible cover is recorded accurately3. analysis of water:After grinding the coal, weigh 1 grams and put it in a dry oven of 145 degrees. After 30 minutes, remove it and weigh it after cooling.Formula: = (gravimetric analysis of water coal after dryingcoal, coal and heavy weight) * 100%Note: accurate gross weight of each small weighing bottle with cover4. whole water:Take 10 grams of raw coal under 13mm and dry in a 145 degree drying oven. Remove after 30 minutes and weigh after cooling.Formula: water = (coal weight - dried coal / coal heavy weight) * 100%Note: the gross weight of each big weighing bottle with a lid is recorded accurately5. fixed carbon:Calculation formula: fixed carbon =100- ash volatile analysis water6. calories:Analysis of base low calorific value of Joule / gramBituminous coal: 35860-73.7 * volatile, -395.7 * ash, -702 * analysis water, +173.6 coke * char characteristicsAnthracite: 34814-24.7 * volatile, -382.2 * ash, -563 * analysis waterReceive the base low calorific valueThe (23 + X analysis of water based analysis of low calorific value (100-) * (100- / water): water) -23 * full of waterH=2.888+0.393 * V-0.0023 * A *Source: /c52985/news/d51336.html ()A new formula for calculating calorific value of coal is recommendedI. PrefaceCalorific value of coal is an important index to evaluate the quality of coal. It is the main basis for calculating the heat consumption and standard coal consumption of clinker. In addition to a small number of large factories using oxygen bomb calorimeter, the vast majority of cement enterprises are using industrial analysis results, using empirical formula to calculate the calorific value of coal.In the past the formula is not unified, therefore, the original building materials department issued the "notice" provisions on the calculation method of fuel calorific value and unified standard coal in 1980, empirical formula provisions of the notice for the three formula 60s Academy of coal derived late: bituminous coal, anthracite and lignite calorific formula. The formula is listed in the appendix of laboratory manual. The above three formulas play an important role in the heatconsumption of cement, coal and clinker and the assessment of standard coal consumption in cement enterprises. But this formula also has some defects and limitations, such as the calorific value of coal and water, ash, volatile and coke residue features, but then the derivation of the formula, not the quantitative characteristics of coke slag into the formula, but according to the size of packet feature list K char value. When calculating the calorific value of coal, the K value is calculated according to the characteristic size of the coke residue and then incorporated into the formula. It is not only troublesome to calculate, but also the calculation error of some volatile coal samples at the boundary is increased because of the change of K value. Therefore, the coal Coal Institute led by Professor Chen Wenmin in "75" science and technology project, collected a large number of national coal sample data, using multiple regression method, using the computer, a large number of data processing, study to derive a bituminous coal, anthracite, lignite and low calorific value of empirical formula.There are two sets of calculations for the new formula. First, the low calorific value formula of various coals is calculated by elemental analysis. Two is to calculate the low calorific value formula of bituminous coal, anthracite coal and lignite by means of industrial analysis of coal. It is more accurate to calculate the calorific value of coal by elemental analysis, but the measurement work has not been carried out in cement plant. Therefore, a new formula for calculating calorific value by using the industrial analysis results of coal is introduced,The concrete application of cement production coal is brieflyintroduced. In the actual production of each factory, the new and old formulas are calculated and compared. At the appropriate time, the new formula will be listed as the national standard to replace the old formula to calculate the calorific value of coal.The newly established formula for rapid calculation of low calorific value of coal will be of great economic and social benefits for coal and coal producing enterprises.Two. A new formula for calculating the calorific value of coal using the coal industry analysis resultsIn the light of the results of coal industry analysis, the principles and methods for establishing new formulas for calculating low calorific value of coal are no longer detailed. The formula for practical application is only as follows:1. a new formula for calculating low calorific value of bituminous coalA calculation that is expressed in joules:Qnet.ad = 35859.9-73.7Vad-395.7Aad-702.0Mad+173.6CRC Jiao / gOr a formula expressed in cards:Qnet.ad = 8575.63-17.63Vad-94.64Aad-167.89Mad+41.52CRC card / gramQnet.ad - analyze basal low calorific value;Vad - analytical base volatile (%);Aad - analytical base ash (%);Mad - Analysis Base moisture (%);CRC -- characteristics of cinder.2. new formula for calculating low calorific value of anthraciteA calculation that is expressed in joules:Qnet.ad=34813.7-24.7Vad-382.2Aad-563.0Mad Jiao / gOr a formula expressed in terms of cards:Qnet.ad=8325.46-5.92Vad-91.41Aad-134.63Mad card / gramIf the conditions can determine the H value, or obtain the average value of the previous H value from the fixed coal mining area, the low calorific value of anthracite calculated by using the method will be more accurate.A formula expressed in terms of joule:Qnet.ad=32346.8-161.5Vad-345.8Aad-360.3Mad+1042.3Had Jiao / gOr a formula expressed in cards:Qnet.ad=7735.52-38.63Vad-82.70Aad-86.16Mad+249.27Had card / gram3. a new formula for calculating low calorific value of ligniteA formula expressed in terms of joule:Qnet.ad=31732.9-70.5Vad-321.6Aad-388.4Mad Jiao / gOr a formula expressed in cards:Qnet.ad=7588.69-16.85Vad-76.91Aad-92.88Mad card / gram4. when calculating the standard coal consumption in the production of cement, the analytical base heat (Qnet.ad) calculated according to the above formula is converted into the low calorific value (Qnet.ar) of coal by using the following formula, and then the standard coal consumption is calculated.Calculation formula of low calorific value of coal100-Mad 100-MarQnet.ar=Qnet.ad * - -23 (MarMad * -) kJ / g100-Mad 100-MadArticle links: China environmental protection equipment exhibition network/Tech_news/Detail/11393.htmlAll water samples (= [heavy - weight - after the experiment, the same weight tare)] * 100%Ash ash [x = ARB (100 - water (100-), analysis of water).From the base of volatile volatile x = [(100 - water (100-), analysis of water).Air drying base:Ash (= after the experiment, heavy weight and tare) * 100%Analysis of water samples [= weight (weight - the tare)], sample weight x 100%Volatile = [- sample weight (experiment after weight - tare)] / * 100% - Analysis of water sample weight%Fixed carbon =100% (ash volatile water% + of your% + of your%)Dry base:Dry ash ash = / (100 - x 100% analysis of water)Dry volatile volatile 83019 = (100 - x 100% analysis of water)Dry ash free volatile volatile 83019 = (100 - x 100% analysis of water - ash)Calorific value of instrument for measuring coal calorificvalue1) calculate the low calorific value formula of air dried base of bituminous coal:Qnet, ad = 35859.9-73.7Vad-395.7Aad-702.0Mad + 173.6CRC(2) calculation of low calorific value formula for dry air base of anthracite:Qnet, ad = 34813.7-24.7Vad-382.2Aad-563.0Mad(3) calculation of low calorific value formula for dry air base of lignite:Qnet, ad = 31732.9-70.5Vad-321.6Aad-388.4MadFormula: Qnet, ad--, air dried base, low calorific value, J / g;Mad, Aad and Vad-- are dry air, moisture, ash, volatile matter,% of coal;Characteristics of coke residue in CRC-- bituminous coal.Calorific value of coal is an important index to evaluate the quality of coal. It is the main basis for calculating the heat consumption and standard coal consumption of clinker. In addition to a small number of large factories using oxygen bomb calorimeter, the vast majority of cement enterprises are using industrial analysis results, using empirical formula tocalculate the calorific value of coal.In the past the formula is not unified, therefore, the original building materials department issued the "notice" provisions on the calculation method of fuel calorific value and unified standard coal in 1980, empirical formula provisions of the notice for the three formula 60s Academy of coal derived at the end of that bituminous coal, DSC anthracite and lignite low heat formula. The formula is listed in the appendix of laboratory manual. The above three formulas play an important role in the heat consumption of cement, coal and clinker and the assessment of standard coal consumption in cement enterprises. But this formula also has some defects and limitations, such as the calorific value of coal and water, ash, volatile and coke residue features, but then the derivation of the formula, not the quantitative characteristics of coke slag into the formula, but according to the size of packet feature list K char value. When calculating the calorific value of coal, the K value is calculated according to the characteristic size of the coke residue and then incorporated into the formula. It is not only troublesome to calculate, but also the calculation error of some volatile coal samples at the boundary is increased because of the change of K value. Therefore, the coal Coal Institute led by Professor Chen Wenmin in "75" science and technology project, collected a large number of national coal sample data, using multiple regression method, using the computer, a large number of data processing, study to derive a bituminous coal, anthracite, lignite and low calorific value of empirical formula.There are two sets of calculations for the new formula. First,the low calorific value formula of various coals is calculated by elemental analysis. Two is to calculate the low calorific value formula of bituminous coal, anthracite coal and lignite by means of industrial analysis of coal. It is more accurate to calculate the calorific value of coal by elemental analysis, but the measurement work has not been carried out in cement plant. Therefore, a new formula for calculating calorific value by using the industrial analysis results of coal is introduced, and the concrete application of cement production coal is briefly introduced. In the actual production of each factory, the new and old formulas are calculated and compared. At the appropriate time, the new formula will be listed as the national standard to replace the old formula to calculate the calorific value of coal.The newly established formula for rapid calculation of low calorific value of coal will be of great economic and social benefits for coal and coal producing enterprises.Two. A new formula for calculating the calorific value of coal using the coal industry analysis resultsWith the result of coal industry analysis, the principle and method of establishing new formula for calculating low calorific value of coal are no longer detailed. The formula for practical application is only as follows:1. a new formula for calculating low calorific value of bituminous coalA calculation that is expressed in joules:Qnet.ad = 35859.9-73.7Vad-395.7Aad-702.0Mad+173.6CRC Jiao / gOr a formula expressed in cards:Qnet.ad = 8575.63-17.63Vad-94.64Aad-167.89Mad+41.52CRC card / gramQnet.ad - analyze basal low calorific value;Vad - analytical base volatile (%);aad - - 分析基灰分 (%);mad - 分析基水分 (%);the crc - 焦渣特征.煤质化验仪器2.计算无烟煤低位发热量新公式以焦耳表示的计算方式:qnet.ad = 34813.7-24.7vad-382.2aad-563.0mad 焦 / 克或者以卡制表示的计算式:qnet.ad = 8325.46-5.92vad-91.41aad-134.63mad 卡 / 克如果有条件能测定h值, 量热仪或者从固定用煤矿区取得矿区以往h 值的平均值, 用下式计算的无烟煤低位发热量结果精度更高.煤质分析仪器煤炭检测设备以焦耳表示的计算式:qnet.ad = 32346.8-161.5vad-345.8aad-360.3mad + 1042.3had 焦 / 克或者用卡制表示的计算式:qnet.ad = 7735.52-38.63vad-82.70aad-86.16mad + 249.27had 卡 / 克3.计算褐煤低位发热量新公式以焦耳表示的计算式:qnet.ad = 31732.9-70.5vad-321.6aad-388.4mad 焦 / 克或者用卡制表示的计算式:qnet.ad = 7588.69-16.85vad-76.91aad-92.88mad 卡 / 克4.在水泥生产使用中, 计算标准煤耗时, 按上述公式计算的分析基低位发热量 (qnet.ad) 用下式换算成应用煤低位发热量 (qnet.ar) 后, 再计算标准煤耗.应用煤低位发热量计算公式100 - mad 100 - marqnet.ar = qnet.ad× ------- 23 (mar-mad× 焦 / 克...)100 - 100 - mad, mad三、结语利用煤工业分析计算煤炭低位发热量的新公式, 与目前水泥企业应用的旧公式相比, 精度有较大的提高, 其中烟煤计算的低位发热量标准误差为89卡 / 克 (372焦 / 克), 精度比旧公式提高15%, 无烟煤计算的低位发热量标准误差为73卡 / 克 (305焦 / 克), 精度比旧公式提高34%, 褐煤计算的低位发热量标准误差为94卡 / 克(393焦 / 克), 精度比旧公式提高36%.新公式的误差与灰分有关,如灰分 (干燥基) 大于40% 则误差有所增大.而且灰分越高其误差越大.因此使用时要注意当灰分大于40% 以上时, 应另选公式.新创立的煤炭发热量计算公式为没有发热量测定设备的广大水泥企业提供了一个精度比较高的计算方法, 但是当前水泥企业化验室的煤工业分析水平有待进一步提高, 主要问题是分析人员操作规范性比较差, 缺少煤工业分析的专用器皿, 以及设备中的一些问题.因此, 计算公式精度再高, 分析结果不准也会产生很大的误差.。

煤质分析化验基准间的换算
煤质分析化严重,有些基准在实际中是不存在的,是根据需要换算出来的;有些基准在实际存在,但为了方便,有时不进行测试,而是根据已知基准的分析化验结果进行换算,这样就简单多了。
化验室中进行煤质分析化验时,使用的煤样为分析煤样。
分析煤样是经过一次次破碎和缩分得到的,它所处的状态为空气干燥状态。
所以,化验室中用分析煤样进行分析化验时,其基准为分析基(又称为空气干燥基)。
分析煤样分析基化验结果,是化验室中直接测到的,是最基础的化验结果,是换算其它基准的分析化验结果的基础。
各种基准间的换算公式:
1、干基的换算:Xd=100Xad/(100-Mad)%
式中:Xad——分析基的化验结果;Mad——分析基水分;Xd——换算干燥基的化验结果。
2、收到基的换算:Xaf=(100-Mar)/(100-Mad)%
式中:Mar——收到基水分;Xar——换算为收到基的化验结果。
3、无水无灰基的换算:Xdaf=100Xad/(100-Mad-Aad)%
式中:Aad——分析基灰分;Xdaf——换算为干燥无灰基的化验结果。
当煤中碳酸盐含量大于2%时,上式的分母中还要减去碳酸盐中CO2含量。
煤质化验计算公式
一、元素含量计算公式:
1.元素质量分数(%)=元素质量含量/总煤样质量×100%
其中,元素质量含量=煤样中元素的质量/煤样的质量
二、发热量计算公式:
1. 低位发热量(MJ/kg)= 发热量试值/ (1 + 0.1 × 挥发分(%))
2.发热量试值(J/g)=34.8×碳(%)+9
3.7×氢(%)+9×硫(%)
+0.24×氧(%)-3.7×水(%)-0.45×水(%)×灰分(%)
其中,发热量试值(J/g)是指标准工况下,燃烧器压力、温度和湿
度等条件确定时,单位质量燃烧产生的能量。
低位发热量是在燃烧过程中,燃烧产生的水蒸气中蒸发热能被全部回收的情况下计算的发热量。
三、挥发分计算公式:
1.挥发分(%)=(失重/初始试样质量)×100%
其中,失重是初始试样质量与在指定温度下煤样质量的差值。
四、固定碳计算公式:
1.固定碳(%)=(试样质量-挥发分持续加热后质量)/试样质量×100%
五、灰分计算公式:
1.灰分(%)=(灰渣质量/试样质量)×100%
六、硫含量计算公式:
1.硫(%)=(硫的质量/试样质量)×100%
以上是常见的煤质化验计算公式,不同的煤质化验项目可能还会有其他不同的计算公式,具体计算方法需根据具体项目的规定和实验要求进行计算。
煤质分析常用公式一、发热量计算公式 1 、热容量计算公式。
E= 2 、弹筒发热量计算公式Q b = 3 、空干基高位热值计算公式Q gr,ad = Q b,ad - (94.1S b,ad + Q b,ad ) 注:当全硫含量低于 4.00% 时,或发热量大于14.60MJ/kg 时,用全硫(按GB/T214 测定)代替 S b,ad 。
一、发热量计算公式1、热容量计算公式。
E=2、弹筒发热量计算公式Q b=3、空干基高位热值计算公式Q gr,ad= Q b,ad-(94.1S b,ad+Q b,ad)注:当全硫含量低于4.00%时,或发热量大于14.60MJ/kg时,用全硫(按GB/T214测定)代替S b,ad。
(引用国标GB/T213-2003《煤的发热量测定方法》中9.3.2条)。
4、收到基低位热值计算公式Q net,ar=(Q gr,ad-206H ad)5、空干基高位热值换算为干基高位热值公式Q gr,d=Q gr,ad×6、硝酸生成热计算公式q n=QG0.00157、冷却校正公式7.1国标公式C=(n-a)V n+aV0当≤1.20时,a=当>1.20时,a=V0=K(t0―t j)+A(测发热量时用)V n=K(t n―t j)+A7.2瑞方公式C=nV0+7.3奔特公式C=式中:E——热容量J/KQ b——弹筒发热量MJ/kgQ gr,ad——空干基高位热值MJ/kgQ net,ar——收到基低拉热值MJ/kgQ gr,d——干基高位热值MJ/kgQ——苯甲酸热值J/gG——试样重量gq1——点火丝热值Jq2——添加物热值Jqn——硝酸生成热J——主期温升K或℃——点火后1'40''时的温升K或℃C——温升冷却校正值K或℃——硝酸校正系数当Q b≤16.7MJ/kg时,=0.001当16.7MJ/K<Q b≤25.1MJ/kg时,=0.0012当Q b>25.1MJ/kg时,=0.0016S t——全硫%M ar——收到基水分%M ad——空干基水分%H ad——空干基氢%V0——初期内筒降温速度K/min(瑞方、奔特为K/0.5min)V n——未期内筒降温速度K/mint j——外筒温度℃t0——点火时的内桶温度℃tn——终点时的内桶温度℃——初期的平均温度℃——末期的平均温度℃m——主期内每30S,温升0.3℃以上的次数,低热值时为温升0.1℃以上的次数。
煤质化验指标水分:煤中水分分为内在水分、外在水分、结晶水和分解水。
煤中水分过大是,不利于加工、运输等,燃烧时会影响热稳定性和热传导,炼焦时会降低焦产率和延长焦化周期。
现在我们常报的水份指标有:1、全水份(Mt),是煤中所有内在水份和外在水份的总和,也常用Mar表示。
通常规定在8%以下。
2、空气干燥基水份(Mad),指煤炭在空气干燥状态下所含的水份。
也可以认为是内在水份,老的国家标准上有称之为“分析基水份”的。
灰分: 指煤在燃烧的后留下的残渣。
不是煤中矿物质总和,而是这些矿物质在化学和分解后的残余物。
灰分高,说明煤中可燃成份较低。
发热量就低。
同时在精煤炼焦中,灰分高低决定焦炭的灰分。
能常的灰分指标有空气干燥基灰分(Aad)、干燥基灰分(Ad)等。
也有用收到基灰分的(Aar)。
挥发份(全称为挥发份产率)V: 指煤中有机物和部分矿物质加热分解后的产物,不全是煤中固有成分,还有部分是热解产物,所以称挥发份产率。
挥发份大小与煤的变质程度有关,煤炭变质量程度越高,挥发份产率就越低。
在燃烧中,用来确定锅炉的型号;在炼焦中,用来确定配煤的比例;同时更是汽化和液化的重要指标。
常使用的有空气干燥基挥发份(Vad)、干燥基挥发份(Vd)、干燥无灰基挥发份(Vdaf)和收到基挥发份(Var)。
其中Vdaf是煤炭分类的重要指标之一。
固定碳: 不同于元素分析的碳,是根据水分、灰分和挥发份计算出来的。
FC+A+V+M=100相关公式如下:FCad=100-Mad-Aad-VadFCd=100-Ad-VdFCdaf=100-Vdaf全硫St:是煤中的有害元素,包括有机硫、无机硫。
1%以下才可用于燃料。
部分地区要求在和以下,现在常说的环保煤、绿色能源均指硫份较低的煤。
常用指标有:空气干燥基全硫(St,ad)、干燥基全硫及收到基全硫(St,ar)。
煤的发热量: 煤的发热量,又称为煤的热值,即单位质量的煤完全燃烧所发出的热量。
煤的发热量时煤按热值计价的基础指标。
锅炉性能计算需要的煤的元素分析数据(Car、Har、Oar、Nar、Sar、Aar)(应用基数据)化验很不方便,一般电厂无法开展此项工作,而电厂能进行入炉煤的工业分析。
因此可用当前煤质的工业分析数据(Mar、Mad、Aad、Sad、Vad、Qnet,ar )(分析基数据)计算得出元素分析数据,具体计算公式如下:分析基与可燃基进行换算(100-Aad-Mad)Vdaf=100*Vad/(100-Aad-Mad)分析基挥发份计算可燃基挥发份Hdaf=Vdaf/(0.114*Vdaf+2.24) 经验公式Had=Hdaf*(100-Aad-Mad)/100可燃基氢计算分析基氢Ndaf=0.016*Vdaf+0.9 经验公式可燃基挥发份计算可燃基氮Nad=Ndaf*(100-Aad-Mad)/100 可燃基氮计算分析基氮Aar=Aad*(100-Mar)/(100-Mad)Har=Had*(100-Mar)/(100-Mad)Nar=Nad*(100-Mar)/(100-Mad)Sar=Sad*(100-Mar)/(100-Mad)分析基计算应用基(分析基与应用基之间的差别在于水分含量)Qnetar=338.71*Car+1048.48*Har+108.72*(Sar-Oar)-46*Marm1=Aar+Har+Nar+Sar+Marm2=Qnetar-1048.48*Har+46*Mar-108.72*SarCar=(m2+10872-108.72*m1)/447.43Oar=100-m1-Car根据GB/T 3715-1996:工业分析:包括水分、灰分、挥发分和固定碳四个项目的分析(均以质量百分比表示)。
水分一般包括全水分(内水和外水之和)和分析水(内水);灰分:煤样在规定条件下完全燃烧后所得残留物;挥发分:煤样在规定条件下隔绝空气加热,并进行水分校正后的质量损失;固定碳:从测定煤样的挥发分后的残渣中减去灰分后的残留物,通常用100减去水分、挥发分和灰分后得出。
煤化验粘结计算公式煤是一种重要的能源资源,而煤的粘结特性对于其在工业生产中的应用具有重要的影响。
煤的粘结特性主要包括粘结指数、粘结指数和粘结指数等参数。
而煤化验粘结计算公式则是用来计算煤的粘结特性参数的重要工具。
本文将介绍煤化验粘结计算公式的相关知识,并探讨其在工业生产中的应用。
煤的粘结特性是指煤在受热条件下的变形和破裂特性。
煤的粘结特性对于煤的燃烧、气化、液化等过程具有重要的影响。
煤的粘结特性参数包括粘结指数、粘结指数和粘结指数等。
这些参数可以通过煤化验粘结计算公式来计算得到。
煤化验粘结计算公式是根据煤的元素组成和热学性质来推导得到的。
其中,粘结指数是描述煤在高温下的变形特性,粘结指数是描述煤在高温下的破裂特性,而粘结指数则是描述煤在高温下的膨胀特性。
这些参数可以通过煤的元素组成和热学性质来计算得到。
煤化验粘结计算公式的具体推导过程比较复杂,一般需要借助计算机软件来进行计算。
不过,我们可以简单地介绍一下煤化验粘结计算公式的一般形式。
以粘结指数为例,其计算公式一般可以表示为:粘结指数 = a1FC + a2VM + a3灰分 + a4水分 + a5硫分 + a6氧分。
其中,FC表示固定碳的含量,VM表示挥发分的含量,灰分表示灰分的含量,水分表示水分的含量,硫分表示硫分的含量,氧分表示氧分的含量,a1、a2、a3、a4、a5、a6等系数是通过实验测定得到的。
通过煤化验粘结计算公式,我们可以得到煤的粘结特性参数,从而可以更好地了解煤在高温下的变形、破裂和膨胀特性。
这些参数对于煤的燃烧、气化、液化等过程具有重要的指导意义。
除了在科研领域中的应用,煤化验粘结计算公式也在工业生产中得到了广泛的应用。
比如,在煤的燃烧过程中,煤的粘结特性参数可以帮助工程师更好地设计燃烧设备,提高燃烧效率,减少污染物的排放。
在煤的气化和液化过程中,煤的粘结特性参数可以帮助工程师更好地控制反应条件,提高产物的质量和产率。
总之,煤化验粘结计算公式是研究煤的粘结特性的重要工具,它可以帮助我们更好地了解煤在高温下的变形、破裂和膨胀特性,对于煤的燃烧、气化、液化等工业生产过程具有重要的指导意义。
煤质化验指标水分。
煤中水分分为内在水分、外在水分、结晶水和分解水。
煤中水分过大是,不利于加工、运输等,燃烧时会影响热稳定性和热传导,炼焦时会降低焦产率和延长焦化周期。
现在我们常报的水份指标有:1、全水份(Mt),是煤中所有内在水份和外在水份的总和,也常用Mar表示。
通常规定在8%以下。
2、空气干燥基水份(Mad),指煤炭在空气干燥状态下所含的水份。
也可以认为是内在水份,老的国家标准上有称之为“分析基水份”的。
灰分指煤在燃烧的后留下的残渣。
不是煤中矿物质总和,而是这些矿物质在化学和分解后的残余物。
灰分高,说明煤中可燃成份较低。
发热量就低。
同时在精煤炼焦中,灰分高低决定焦炭的灰分。
能常的灰分指标有空气干燥基灰分(Aad)、干燥基灰分(Ad)等。
也有用收到基灰分的(Aar)。
挥发份(全称为挥发份产率)V指煤中有机物和部分矿物质加热分解后的产物,不全是煤中固有成分,还有部分是热解产物,所以称挥发份产率。
挥发份大小与煤的变质程度有关,煤炭变质量程度越高,挥发份产率就越低。
在燃烧中,用来确定锅炉的型号;在炼焦中,用来确定配煤的比例;同时更是汽化和液化的重要指标。
常使用的有空气干燥基挥发份(Vad)、干燥基挥发份(Vd)、干燥无灰基挥发份(Vdaf)和收到基挥发份(Var)。
其中Vdaf是煤炭分类的重要指标之一。
固定碳不同于元素分析的碳,是根据水分、灰分和挥发份计算出来的。
FC+A+V+M=100相关公式如下:FCad=100-Mad-Aad-VadFCd=100-Ad-VdFCdaf=100-Vdaf全硫St是煤中的有害元素,包括有机硫、无机硫。
1%以下才可用于燃料。
部分地区要求在0.6和0.8以下,现在常说的环保煤、绿色能源均指硫份较低的煤。
常用指标有:空气干燥基全硫(St,ad)、干燥基全硫(St.d)及收到基全硫(St,ar)。
煤的发热量煤的发热量,又称为煤的热值,即单位质量的煤完全燃烧所发出的热量。