高速钢 硬质合金
- 格式:ppt
- 大小:3.94 MB
- 文档页数:75
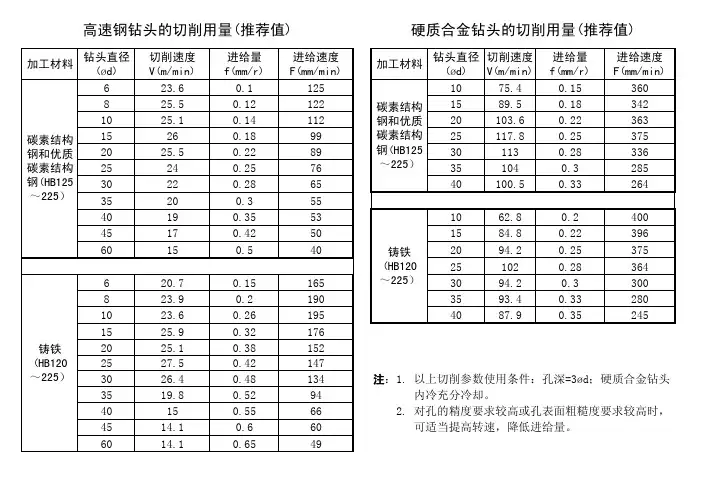
加工材料钻头直径(ød)切削速度V(m/min)进给量f(mm/r)进给速度F(mm/min)加工材料钻头直径(ød)切削速度V(m/min)进给量f(mm/r)进给速度F(mm/min) 623.60.11251075.40.15360 825.50.121221589.50.18342 1025.10.1411220103.60.22363 15260.189925117.80.25375 2025.50.2289301130.28336 25240.2576351040.3285 30220.286540100.50.33264 35200.35540190.35531062.80.2400 45170.42501584.80.22396 60150.5402094.20.25375251020.28364 620.70.151653094.20.3300 823.90.21903593.40.33280 1023.60.261954087.90.35245 1525.90.321762025.10.381522527.50.421473026.40.481343519.80.529440150.55664514.10.6606014.10.65492. 对孔的精度要求较高或孔表面粗糙度要求较高时,内冷充分冷却。
高速钢钻头的切削用量(推荐值)铸铁(HB120~225)硬质合金钻头的切削用量(推荐值)碳素结构钢和优质碳素结构钢(HB125~225)铸铁(HB120~225)注:1. 以上切削参数使用条件:孔深=3ød;硬质合金钻头 可适当提高转速,降低进给量。
碳素结构钢和优质碳素结构钢(HB125~225)钻头直径mm 15φ< 30~15φφ< 50~30φφ<进给量 mm/r0.05~0.15 0.15~0.25 0.20~0.30硬质合金钻头线速度 min /120~100m =ν高速钢钻头(HSS) 1> Q235-A min /30m =ν 2> 16Mn min /20m =ν切削速度ν:刀类相对于工件的线速度转速即圆周长ו•=n d πν高速钢钻头线速度:min /03~25m =ν进给量(吃刀量)mm/r 钻头每转一转走的长度(轴向),取:0.2mm/r(齿数)刃Z /×mm 取0.1~0.2 mm/刃硬质合金钻头线速度min /120~100m =ν孔的精度:孔径公差;孔的表面光洁度 钻孔精度:孔距公差;孔的垂直度THE TWIST DRILLSThe twist drill is the more simple tool for drilling holes cylindrical, usually from solid.The twist drill is formed by:x by a cylindrical or conical shank to center on the spindle of the machine and transmit the cutting torque (by friction or drag tooth)x by a cylindrical part in which are carried two opposing helical grooves, which intersect with surface ends form the two main cutting edges.The two helical grooves allow the evacuation of the chip that is formed at the cutting edges, and lead near the same, the lubricating/coolant fluid .Characteristic elements of endsThe check or driving surfaces (with rake angle lower by about 2°) are formed by two off-set diametrically opposed to the limit of the helical grooves and have a dual function: à driving the tip into the hole without even the jam during drilling, because thecontact between the drill and sides of the hole is limited.à finishing the cylindrical surface of the hole.The central core (central scraping edge) between the two grooves has a diameter (0.1~0.2) × D and provides to give the torsional strength to the drill during machining. However for a hole made by a twist drill we can be obtained the maximum standard ofIT 10 and a roughness Ra> 1.8 mm, which often must be finished with other processes such as boring or grinding.Caracteristic anglesİ :Inclination angle of helix .It is formed ythe tangent of the helix average with axisof the drill. Its value is so smaller as harderSEZ N-Nis the material to machining.ij:Angle of cutters. It is the angle formedby the two main cutter.Ȗ:Upper rake angleȕ:Cutting angleĮ:Lower rake angleThe characteristic angles can assume different values in according to the material to be machined and the diameter of the drill.WORKING CONDITIONS IN DRILLINGRelative motion and cutting parametersThe main relative motions are the motion of cutting and the move of advance or feed. The motion of cutting is the main motion of the machine, and is what determines the removal of chip.On the drilling machine it is rotating type and is acted by the tool.The motion of cutting can be expressed both as cuttingspeed, both as rotary speed.The cutting speed, denoted by V (m / min), represents therelative speed between tool and workpiece, at the pointwhere it be removed the chip, therefore the speedwherewith the material can be cut.It is equivalent to peripheral speed of the tool, that is thespeed of point P shown in the figure, which is tangent tothe circle of point P in same sense of rotation. The cuttingspeed is not constant along all points of the cutting edge,but varies from a maximum (cutting speed rated) at thepoint P to a zero value at the axis of the tool.The value set depends on: material processing, material ofthe tool and diameter of the drill.There are tables indicating the value needed depending onworking conditions.The cutting speed and the speed of rotation are related by:This relation calculates the number of rounds to select on the drilling machine, after determining the cutting speed more suitable for processing.The movement of advance or feed aims to bring new material from the tool contact. It is a movement much slower than the motion of cutting.On drilling machine it is a translational motion and is impressed to the tool, according to its axis, in a continuous and simultaneous movement of the cutting.The movement forward can be expressed as feed per revolution, both as speed of advancement.Advancement per revolution, indicated by a (mm / rev), representing the movement of the tool for every lap completed by the same tool.Its value depends on the diameter and material of tool, as well as the material processing. For the selection of the advanced exist tables that suggest the value needed depending on conditions of work.Speed of advancement, indicated by Va (mm / min), represents the speed with which the tool moves, hence the speed with which the processing proceeds.The two magnitude are related by the following relation:Indeed, if a indicates the tool displacement per revolution, multiplying its the number for the revolutions n made in a minute, you get the movement of the tool for each minutes; that is its speed of advancement.SECTION OF THE CHIPThe section of the chip, denoted by q, in the case of a twist drill,takes the form of a parallelogram equivalent to a rectangle ofheight equal to half of the feed per revolution and a basis equalto the radius of the drill. (D / 2 represents the depth of cut in thecase of drilling a hole from solid).Indeed, if for every round of the drill advances of a step equal to a(advancement per revolution), each of cutters to remove a chipwith a side a / 2.In this case, the section area of the chip removed from each edge is:Cutting forceCutting forces required on both edges of the twist drill to detach the chip depend :x from material of workpiece, through the load or pressure to tear Ks (N/mm2).x from total chip section Q = 2 x q (mm 2) detached from the tool.These forces, one for each main cutting edge, supposedly applied approximately half the length of the cutting edge.Each of them takes the value:section of one cutter chipthere is a cutting force :withThen foreach cutterOn average it is considered that : xKs = (4,2 y 5) Rm for cast ironwitch Rm the diameter of drill nd with higher values he total cutting force is :x Ks = (4,8 y 6) Rm for steels and non-ferrous materials In is strength of the material in N/mms decreases with increasing of the advanced. However keep in mind that the value of K a TCUTTING POWERcreate a torque (cutting moment). with dimension b in metres.Looking where the cutting forces are positioned you can see that they form a couple of forces that The value is:aller values forrittle materials (cast iron), higher values for lasting materials (steel).sional stress, where the torque is equal and opposite to the utting moment.sics we know that in rotary motion, the power is calculated using the followinglation:The value of arm b is assumed, the approximate equivalent to D / 2, but in reality its value varies with the type of material that is drilled. In particular b = (0.45÷ 0.60) × D : sm b The tool is subject to a tor c From phyre Where M is sum of torques applied to the body respect to its axis of rotation. nd Ȧ is the angular velocity of the body. the case of drilling:xM represents the moment of cutting forces, then as we saw earlier.with dimension b in metresxȦ is the angular velocity of twist drills.with n number of rounds of the drill ino the cutting power is:aInSWhereand :he power required for the advancement of twist drills can be neglected, because little. tearing of the chip, but also all the sses may be present in transmission of motion.o account for this power dissipation introduces the mechanical efficiency: echanical efficiencyom which flows: T So that the processing is possible, the engine power of the drill must be capable of winning not only the moment of resistance due to lo T m fr that allows us to calculate the engine outputen we known the effective power of cutting and the mechanical efficiency of the achine.he mechanical efficiencyȘ depends on the state of the machine: h = 0.6 ¸ 0.8. power, wh m T It has the condition of maximum utilization of the drilling machine when the power eveloped by its motor c Working timedoincides with the available power of the engine.The relation that calculates the working time is the following:he tool, is With reference to the figure we see that the travel,that is the distance that who must run t e sum of four quantities, namely:th L is the depth of the holee 1 is the overtravel attack : e 1 = 1÷ 2 mm e 2 is the overtravel output : e 2 = 1 2 mml p is the height of the drill cone : l p = ~ 0.33 × DRegarding the height of th edges, with the following considerations of trigonometry.angle OAB is noted that:e drill cone, the approximate value lp = ~ 0.33 × D, can bereplaced by the correct value function of the cuttingFrom the tri from the definition of tangent:which is calculated:For example in the case of a twist drillø 20 for drilling steel with Rm <700 N/mm2 withngle of the cutting edges M = 118 ° is calculated:aE XEMPLEecessary power and time to drill a trough hole ( Tool in high speed steel ) eatures:nd N/mm 2Mechanical efficiency Ș = 0,75alculation of poweralculation of working timeel with Rm <700 N/mm2 and with angle of thecutting edges M = 118°, it is calculated:N F Hole diameter D = 16 mm Hole deep L = 25 mm Feed a = 0,2 mm/rou Cutting speed V = 32 m/min Material strength Rm = 600C We can assume:We think to can select exactly this speed on drilling machineCutting powerOutput power of motorC If we use a twist drillø 20 for drilling ste We assume。

到底啥是高速钢;高速钢钻头、白钢钻头、硬质合金钢钻头区别高速钢介绍:高速钢(HSS)是一种具有高硬度、高耐磨性和高耐热性的工具钢,又称高速工具钢或锋钢,俗称白钢。
高速钢刀具是一种比普通刀具要坚韧,更容易切割的刀具。
高速钢名称的由来:高速钢比碳素工具钢具有更好的韧性、强度、耐热性,切削速度比碳素工具钢(铁碳合金)高很多,因此得名高速钢;而硬质合金刚比高速钢的性能更好,切削速度可以再提高2-3倍。
在常用的钻头都是高速钢和硬质合金钻头!高速钢与合金钻头关系:首先高速钢钻头属于合金钻头!一般的工具钢也属于合金钢只不过是铁碳合金,高速钢的还分普通高速钢和优质高速钢,因此现在合金钻头一般是指硬质合金钻头。
高速钢钻头在高速切削产生高热情况下(约500℃)仍能保持高的硬度,HRC能在60以上。
硬质合金钻头(一般为钨钢材质)具有硬度高、耐磨、强度和韧性较好、耐热、耐腐蚀等一系列优良性能,特别是它的高硬度和耐磨性,即使在500℃的温度下也基本保持不变,在1000℃时仍有很高的硬度。
高速钢钻头和硬质合金钻头材质介绍:高速钢钻头材质是一种成分复杂的合金钢,含有钨、钼、铬、钒、钴等碳化物形成元素。
合金元素总量达10~25%左右。
它在高速切削产生高热情况下(约500℃)仍能保持高的硬度,HRC能在60以上。
这就是高速钢最主要的特性——红硬性。
而碳素工具钢经淬火和低温回火后,在室温下虽有很高的硬度,但当温度高于200℃时,硬度便急剧下降,在500℃硬度已降到与退火状态相似的程度,完全丧失了切削金属的能力,这就限制了碳素工具钢制作切削工具用。
而高速钢由于红硬性好,弥补了碳素工具钢的致命缺点。
高速钢钻头主要用来制造复杂的薄刃和耐冲击的金属切削刀具,也可制造高温轴承和冷挤压模具等,如车刀、钻头、滚刀、机用锯条及要求高的模具等。
钨钢钻头材质(硬质合金)具有硬度高、耐磨、强度和韧性较好、耐热、耐腐蚀等一系列优良性能,特别是它的高硬度和耐磨性,即使在500℃的温度下也基本保持不变,在1000℃时仍有很高的硬度。

第一章、第二章简答题1、刀具在什么条件下工作?答:刀具工作时,要承受很大的压力,同时,由于切削是产生的金属塑性变形以及在刀具、切屑工件相互接触表面间产生的强烈摩擦,使刀具切削刃上产生很高的温度和受到很大的应力。
另外,在加工脆性材料,断续切削,粗加工过程中,刀具切削部分要承受一定的冲击力的作用。
2、高速钢、硬质合金、陶瓷、金刚石、立方氮化硼各有何性能特点,适用于何处?答:高速钢的特点:耐热温度低,切削速度低;强度高,工艺性最好。
主要低速加工铸铁,结构钢硬质合金的主要特点:(1)随碳化物含量的提高,其熔点、硬度、耐磨性提高;(2)化学稳定性好,热稳定性好(3)切削速度高(4)抗弯强度低,冲击韧性低主要应用:加工铸铁,结构钢,不锈钢,耐热合金,钛合金等陶瓷刀具的主要特点:(1)硬度高,耐磨性好,切削速度高(2)热化学稳定性好,耐热温度高(3)抗弯强度低,冲击韧性差(4)导热性能差主要应用:氧化铝基陶瓷刀具主要用于高速精车、半精车铸铁及调质结构钢;氮化硅基陶瓷刀具加工铸铁,镍基合金。
金刚石主要特点:(1)具有极高的硬度和耐磨性(2)切削刃可以刃磨得非常锋利(3)导热性能非常好(4)热稳定性能较低(5)高温下和黑色金属(铁碳合金)在加工中会发生化学磨损应用:主要用于磨料,用作刀具时,多用于在高速下对有色金属及非金属进行精细车削,镗孔3、常用高速钢有哪些牌号?其化学成分和性能特点如何?目前通过那些途径提高高速钢的切削性能?答:W18Cr4V(W18),化学成分中含钨量18%主要特点:(1)综合性能较好(2)淬火过热倾向小,热处理易控制,刃磨性能好(3)含碳量高,塑性变形抗力大(4)碳化物分布不均,剩余碳化物颗粒大(30μm(5)抗弯强度、韧性较低,钨钼钢W6Mo5Cr4V2(M2)特点:优点:(1)碳化物细小均匀,机械性能好,可做大尺寸刀具;(2)热塑性好;(3)刃磨性好。
(4)热稳定性稍低于W18,V>40m/min时,性能稍差;(5)热处理时脱碳倾向大,易氧化,淬火温度范围较窄。

GT35钢-高韧性粉末高速钢的特性和应用(1)模具钢的特性新型含TiC硬质相的钢结硬质合金,是一种高韧性粉末高速钢,具有高耐磨粒磨损、、高韧性、高抗压强度,有较高的硬度和耐磨性,但不耐高温和腐蚀,淬火状态硬度69~73HRC,=1400~1800MPa,冲击韧性值6J/cm2。
强度σbb东莞弘超模具钢材钢结硬质合金是用粉末冶金的方法制造的铬钼合金钢,其中钢为黏结相,TIC为硬质相。
它的性能介于钢与硬质合金之间,可进行淬火等热处理,因此加工硬质合金方便,而硬质比钢却高很多。
具有硬质合金的高硬度、高耐磨性及高耐腐蚀性,又具有钢的加工性、锻压性、焊接性及热处理性。
⑵供货状态硬度38~46HRC。
⑶典型化学成分(质量分数,%)C0.5、Cr2.0、Mo2.0、余为Fe,硬质相TIC的含量约为35%。
⑷典型应用举例①可用于冷挤压模凹模,推荐硬度65~67HRC,模具寿命很高。
每打光一次凹模,可连续拉伸1000件工件。
而同样情况下,Cr12MoV 钢仅为数十件。
②可用于钢板冷冲模具,当批量大于100万件,被冲材料为δ<1mm的软态低碳钢板。
③含80%镍的特殊合金材料,在退火状态的硬度值为130HBS,极易与模具表面发生强烈的咬合,采用Cr12MoV钢(硬度为59~61HRC)制作的凹模,每拉伸十余件,模具表面就出现咬合拉毛现象;当使用特殊润滑剂以后,也只能拉伸数十件,只好将凹模卸下抛光,否则,将使工件拉毛;在采用CT35型钢结硬质合金制作凹模以后,硬度为65~67HRC,大大减少咬合倾向,每打光一次凹模,可连续拉伸近1000个工件。
④适用于各种冷挤、冷冲、冷镦和冷剪模具。
⑤镗杆、轧辊、液压工具及卡具、量具等。
⑥重载荷、形状复杂的大、中型模具。

刀具材料的种类很多,常用的材料有工具钢、硬质合金、陶瓷和超硬1、碳素工具钢碳素工具钢是指碳的质量分数为0.65%~1.35%的优质高碳钢。
用做刀具的牌号一般是T10A和T12A。
常温硬度60~64HRC。
当切削刃热至200~250℃时,其硬度和耐磨性就会迅速下降,从而丧失切削性能。
碳素工具钢多用于制造低速手用工具,如锉刀、手用锯条等。
2、合金工具钢为了改善碳素工具钢的性能,常在其中加入适量合金元素如锰、铬、钨、硅和钒等,从而形成了合金工具钢。
常用牌号有9SiCr、GCrl5、CrWMn等。
合金工具钢与碳素工具钢相比,其热处理后的硬度相近,而耐热性和耐磨性略高,热处理性也较好。
但与高速钢相比,合金工具钢的切削速度和使用寿命又远不如高速钢,使其应用受到很大的限制。
因此,合金工具钢一般仅用于取代碳素工具钢,作一些低速、手动刀具,如手用丝锥、手动铰刀、圆板牙、搓丝板等。
3、高速钢高速钢是一种含钨、铝、铬、钒等合金元素较多的高合金工具钢。
高速钢主要优点是具有高的硬度、强度和耐磨性,且耐热性和淬透性良好,其允许的切削速度是碳素工具钢和合金工具钢的两倍以上。
高速钢刃磨后切削刃锋利,故又称之为“锋钢”和“白钢”。
高速钢是一种综合性能好、应用范围较广的刀具材料,常用来制造结构复杂的刀具,如成形车刀、铣刀、钻头、铰刀。
拉刀、齿轮刀具等。
高速钢按其用途和性能不同,可分普通高速钢和高性能高速钢;按其化学成分不同,又可分为钨系高速钢和钨钼系高速钢。
1) 普通高速钢是指加工一般金属材料用的高速钢。
常用牌号有W18Cr4V和W6Mo5Cr4V2。
① W18Cr4V属钨系高速钢,它具有性能稳定,刃磨及热处理工艺控制方便等优点,但因钨价较高,且使用寿命短故使用较少。
② W6Mo5Cr4V2属钨钼系高速钢,它的碳化物分布均匀,抗弯强度,冲击韧度和高温塑性都比W18Cr4V好,但磨削工艺略差。
因其使用寿命长、价格低,故被广泛使用。
2) 高性能高速钢是在普通高速钢中再加入一些合金元素,以进一步提高它的耐热性、耐磨性。

3.2.2 加工中心刀具的材料⑴ 高速钢(High Speed Steel)自 1906 年 Taylor 和 White 发明高速钢以来,通过许多改进至今仍被大量使用着,大体上可分为W系和M O系两大类。
其主要特征有:合金元素含量多且结晶颗粒比其他工具钢细,淬火温度极高(12000C)而淬透性极好,可使刀具整体的硬度一致。
回火时有明显的二次硬化现象,甚至比淬火硬度更高且耐回火软化性较高,在6000C仍能保持较高的硬度,较之其他工具钢耐磨性好,且比硬质合金韧性高,但压延性较差,热加工困难,耐热冲击较弱。
因此高速钢刀具仍是数控机床刀具的选择对象之一。
目前国内外应用WM O、WM O AI、WM O C O为主,其中WM O AI是我国所特有的品种。
⑵ 硬质合金(Cemented Carbide)硬质合金是将钨钴类WC,钨钦钴类WC-TiC ,钨钦钽(铌)钴类WC TiC-TaC等硬质碳化物以C O为结合剂烧结而成的物质,于1926年由德国的Krupp公司发明,其主体为WC-C O 系在铸铁、非铁金属和非金属的切削中大显身手。
1929~1931 年前后,TiC以及TaC等添加的复合碳化物系硬质合金在铁系金属的切削中显示出极好的性能,从而使硬质合金得到了很大程度的普及。
按ISO标准,主要以硬质合金的硬度,抗弯强度等指标为依据,将硬质合金刀片材料分为P、M、K三大类,大致如下。
a. WC+Co;K类、YG类b. WC+ TiC+ Co,P类、YT类:c. WC+ TiC+TaC+Co:;M类、YW类。
K类(相当与旧牌号YG)适于加工短切屑的黑色金属、有色金属及非金属材料,如铸铁、淬硬钢,铜铝合金、塑料等。
主要成分为碳化钨和3%~10%的钴,有时还含有少量的碳化钮等添加剂。
P 类(相当与旧牌号YT)适于加工长切屑的黑色金属,如钢,铸钢等。
主要成分为碳化钦、碳化钨和钴(或镍),有时还加人碳化担等添加剂。
M类适于加工长切屑或短切屑的黑色金属和有色金属。

高速钢刀具与硬质合金刀具比较分析刀具是工业生产中必不可少的工具,其中高速钢刀具和硬质合金刀具是常用的两种刀具材料。
本文将对这两种刀具进行比较分析,探讨它们的特点和适用领域,以便读者更好地理解和选择合适的刀具。
首先,我们来看高速钢刀具。
高速钢是一种含有多种合金元素(如钼、钨、钴、铬等)的高碳钢。
这种刀具具有以下特点:1. 高硬度和耐磨性:高速钢刀具经过热处理具有较高的硬度,能够在切削过程中保持刀刃的尖锐。
同时,高速钢具有出色的耐磨性,可以长时间保持刀刃的锋利。
2. 良好的韧性:高速钢具有较高的韧性,能够抵抗较大的冲击和振动。
这使得它在切削过程中不易断裂,提高了使用寿命。
3. 较低的成本:相比于硬质合金刀具,高速钢刀具的制造成本较低。
这使得它成为广泛应用于一般金属切削加工中的经济型选择。
然而,高速钢刀具也存在一些局限性。
尽管它在一般金属加工中具有出色的性能,但在高强度、高硬度和耐高温材料的切削中性能可能有所不足。
此外,高速钢刀具在切削速度较高时容易发生刀尖火花,从而影响切削质量。
接下来,我们来看硬质合金刀具。
硬质合金刀具以钨钴碳合金为主要材料,与高速钢相比它具有以下特点:1. 极高的硬度:硬质合金刀具具有极高的硬度,通常在摩氏硬度达到90以上。
这使得它具有出色的耐磨性和耐热性,能够在高温、高硬度和高强度材料切削中发挥较好的性能。
2. 较好的切削性能:硬质合金刀具由于硬度高、切削角度容易控制,可以获得更高的切削速度和更好的切削质量。
它能够完成更高效、更精细的切削加工,提高生产效率。
3. 长寿命:硬质合金刀具的耐磨性能非常突出,因此它的使用寿命通常比高速钢刀具更长。
这进一步降低了生产成本和换刀频次。
然而,硬质合金刀具的制造成本较高,在某些应用领域可能不太经济。
此外,硬质合金刀具的韧性相对较差,容易受到冲击和振动的影响,因此需要在使用过程中加以注意,以防止刃口断裂。
综上所述,高速钢刀具和硬质合金刀具在不同应用领域有各自的优势和局限性。


第一章复习题1、为什么不宜用碳素工具钢制造拉刀和齿轮刀具等复杂刀具?为什么目前常采用高速钢制造这类刀具,而较少采用硬质合金?答:因为碳素工具钢耐热性较低,适合低速切削。
高速钢的耐热性、硬度和耐磨性虽低于硬质合金,但强度和韧度却高于硬质合金,工艺性较硬质合金好,而且价格较硬质合金低,适用高速刀具。
2、在一般情况下,K类硬质合金适于加工铸铁件,P类硬质合金适于加工钢件。
但在粗加工铸钢件毛坯时,却要选用K20类硬质合金,为什么?答:铸钢的毛坯表面粗糙度高,不易连续切削,易受冲击。
而K20耐冲击大,及抗磨损性,韧性更好,所以选用K20.3、选择下列刀具的材料:麻花钻、手用铰刀、整体圆柱铣刀、端铣刀刀齿、锉刀、机夹刀片。
答:高速钢,合金工具钢,高速钢,硬质合金,碳素工具钢,硬质合金。
4、切削用量指的是什么?包括哪些内容?答:切削用量是切削过程中的切削速度、进给量和吃刀量的总称。
5、常见的零件表面成形方法有哪些?各举两个例子.答: 1轨迹法:车外圆,刨平面 2成形法:车球面,拉孔 3展成法:插齿,锉削外圆弧面。
6、切削热对切削加工有什么影响?答:切削热传入工件,使工件温度升高,产生热变形,影响加工精度;传入刀具,使刀具温度升高,加剧刀具磨损,甚至使刀具丧失切削能力。
7、对刀具材料的性能有哪些基本要求?答:高硬度,高耐磨性,高耐热性,足够的强度和韧性,有一定的工艺性能。
8、在车外圆时,切削功率主要依据哪个切削分力来计算?为什么?答:切削力Fc,其数值大小一般是三个分力中最大的,消耗动力最多,占机床总功率的95%-99%。
9、高速钢和硬质合金在性能上的主要区别是什么?各适合做何种刀具?答:高速钢有很高的强度和韧性,制造钻头、铰刀、拉刀、铣刀等。
硬质合金:抗弯强度低,不能承受较大的冲击载荷,制造车刀、铣刀、刨刀的刀片等。
10、切削刚性较差的细长轴时,产生弯曲变形的原因是什么?如何改进?答:由于细长轴刚性较差,径向力将会把细长轴顶弯,使其在水平面内发生弯曲变形。

常用刀具材料的性能及应用一、概述刀具材料是指刀具上参与切削部分的材料。
刀具的切削部分不但要求具有一定的几何形状,还要求有相应的刀具材料。
目前广泛应用的刀具材料有高速钢和硬质合金。
二、刀具材料应具备的性能(一)高的硬度和良好的耐磨性(二)高的强度和韧性(三)高的耐热性(四)良好的工艺性总之,刀具应具备的性能主要就这四个方面,当然还有经济性、切削性能的可预测性等要求。
三、常用刀具材料目前在切削加工中常用的刀具材料有:碳素工具钢、合金工具钢、高速钢、硬质合金及陶瓷等。
一)碳素工具钢碳素工具钢是一种含C量较高的优质钢(含C一般为0.65~1.35%)。
1、常用牌号有T7A、T8A……T13A等2、主要性能淬火后硬度较高,可达HRC61~65;红硬性为200℃~250℃,价格低廉,不耐高温,切削速度因此而不能提高,允许切削速度VC≤10m/min,只能制作低速手用刀具,如板牙、锯条、锉等。
二)合金工具钢在碳素工具钢中加入一定量的铬(Cr)、钨(W)、锰(Mn)等合金元素,能够提高材料的耐热性、耐磨性和韧性,同时还可以减少热处理时的变形。
1、主要牌号有9SiCr CrWMn2、主要性能淬火后的硬度可达HRC61~65,红硬性为300℃~400℃,允许切削速度Vc=10~15m/min,制作低速、形状比较复杂、要求淬火后变形小的刀具。
如板牙、拉刀、手用铰刀(孔的精加工)等。
三)高速钢高速钢是一种高合金工具钢,钢中含有W、Mo、Cr、V等合金元素。
(一) 高速钢的性能:具有较高的强度和韧性;良好的耐磨性;红硬性为600℃;允许切削速度V C=25~30m/min;良好的制造工艺性;可获得锋利的刀刃(锋钢之称);加工范围较大(铸铁、有色金属、钢)。
(二)高速钢的分类钨系高速钢:W18C r4V (最常用,刃磨性好)普通高速钢钼系高速钢:W6M O5C r4V2高速钢高碳高速钢:95W18C r4V (含C量为0.95%)高钒高速钢:W6M O5C r4V3 (提高耐磨性)高性能高速钢钴高速钢:W6M O5C r4V2C O8铝高速钢:W6M O5C r4V2A l四)硬质合金硬质合金= 硬质相(TiC或WC)+粘结相(Co、Ni、Mo等,其中Co比较常用)上图为各种硬质合金刀头(一)主要性能1)常温硬度HRC74~81.5,红硬性800℃~1000℃,耐磨性优良;2)允许切削速度V C=100m/min以上,最高不能超过200m/min;硬质合金3)脆性较大,怕冲击和振动。

车床加工基本知识图书搜索一、车刀材料在切削过程中,刀具的切削部分要承受很大的压力、摩擦、冲击和很高的温度。
因此,刀具材料必须具备高硬度、高耐磨性、足够的强度和韧性,还需具有高的耐热性(红硬性),即在高温下仍能保持足够硬度的性能。
常用车刀材料主要有高速钢和硬质合金。
1.高速钢高速钢又称锋钢、是以钨、铬、钒、钼为主要合金元素的高合金工具钢。
高速钢淬火后的硬度为HRC63~67,其红硬温度550℃~600℃,允许的切削速度为25~30m/min。
高速钢有较高的抗弯强度和冲击韧性,可以进行铸造、锻造、焊接、热处理和切削加工,有良好的磨削性能,刃磨质量较高,故多用来制造形状复杂的刀具,如钻头、铰刀、铣刀等,亦常用作低速精加工车刀和成形车刀。
常用的高速钢牌号为W18Cr4V和W6Mo5Cr4V2两种。
2.硬质合金硬质合金是用高耐磨性和高耐热性的WC(碳化钨)、TiC(碳化钛)和Co(钴)的粉末经高压成形后再进行高温烧结而制成的,其中Co起粘结作用,硬质合金的硬度为HRA89~9 4(约相当于HRC74~82),有很高的红硬温度。
在800~1000℃的高温下仍能保持切削所需的硬度,硬质合金刀具切削一般钢件的切削速度可达100~300m/min,可用这种刀具进行高速切削,其缺点是韧性较差,较脆,不耐冲击,硬质合金一般制成各种形状的刀片,焊接或夹固在刀体上使用。
常用的硬质合金有钨钴和钨钛钴两大类:(1)钨钴类(YG)由碳化钨和钴组成,适用于加工铸铁、青铜等脆性材料。
常用牌号有YG3、YG6、YG8等,后面的数字表示含钴量的百分比,含钴量愈高,其承受冲击的性能就愈好。
因此,YG8常用于粗加工,YG6和YG3常用于半精加工和精加工。
(2)钨钛钴类(YT)由碳化钨、碳化钛和钴组成,加入碳化钛可以增加合金的耐磨性,可以提高合金与塑性材料的粘结温度,减少刀具磨损,也可以提高硬度;但韧性差,更脆、承受冲击的性能也较差,一般用来加工塑性材料,如各种钢材。
车刀适用的钢种及牌号在汽车制造工业当中,车刀是一种重要的工具,它被广泛应用于车削、切断、铣削、刻划等加工过程中。
然而,不同种类的车刀需要适用不同的钢种和牌号,以确保加工过程的高效性和品质。
在本篇文章中,我们将按类划分,介绍车刀适用的钢种及牌号。
1. 高速钢高速钢是车刀制造的主要材料之一,具有高硬度、强度和切削性能,在高温下仍能保持稳定。
车刀制造中常用的高速钢主要包括W6Mo5Cr4V2、W18Cr4V、W9Mo3Cr4V等。
2. 硬质合金硬质合金是一种由耐磨金属和结晶等不同材料构成的复合材料,具有高硬度、强度、耐磨、防腐蚀等特性。
硬质合金车刀具有高精度、高效率、高切削速度等特点。
硬质合金车刀制造常用的牌号有YG8、YG15、YK20等。
3. 难切削合金难切削合金是一种为了提高材料性能而制造的特殊合金,通常具有高韧性、耐热性、耐腐蚀性、高强度等特点,但也因此具有难切削性。
为了加工这种材料,车刀需要有强大的耐磨性、耐高温性和耐腐蚀性,适用的钢种常有T15、M42、S600等。
4. 铸铁铸铁是一种常用的材料,但其硬度和强度较低,易于断裂和开裂。
为了解决这种问题,可以采用未淬火的原材料生产车刀。
常用的铸铁车刀牌号有K、P、M等。
5. 不锈钢不锈钢具有良好的抗腐蚀性和机械性能,因此被广泛应用于汽车制造领域。
由于其高硬度和难切削性,加工过程中需要特殊的车刀。
常用的不锈钢车刀牌号有P20、M2等。
综上所述,车刀适用的钢种及牌号因其性能的差异而不同。
选择适合的车刀和钢种,可以提高汽车制造的工艺质量和生产效率。
硬质合金科技名词定义中文名称:硬质合金英文名称:hardmetal;cemented carbide定义:由作为主要组元的难熔金属碳化物和起黏结相作用的金属组成的烧结材料,具有高强度和高耐磨性。
应用学科:机械工程(一级学科);机械工程(2)粉末冶金(二级学科);粉末冶金材料与制品(三级学科)本内容由全国科学技术名词审定委员会审定公布编辑本层的厚度不过几微米,但是与同牌号的合金刀具相比,使用寿命延长了3倍,切削速度提高25%~50%。
20世纪70年代已出现第四代涂层工具,可用来切削很难加工的材料。
硬质合金是怎样烧结而成的?硬质合金是将这种或多种难熔金属的碳化物和粘接剂金属,用粉末冶金方法制成的金属材料。
编辑本段主要生产国家世界上有50多个国家生产硬质合金,总产量可达27000~28000t-,主要生产国有美国、俄罗斯、瑞典、中国、德国、日本、英国、法国等,世界硬质合金市场基本处于饱和状态,市场竞争十分激烈。
中国硬质合金工业是50年代末期开始形成的,60~70年代中国硬质合金工业得到了迅速发展,90年代初中国硬质合金总生产能力达6000t,硬质合金总产量达5000t,仅次于俄罗斯和美国,居世界第3位。
编辑本段分类与牌号WC刀具①钨钴类硬质合金主要成分是碳化钨(WC)和粘结剂钴(Co)。
其牌号是由“YG”(“硬、钴”两字汉语拼音字首)和平均含钴量的百分数组成。
例如,YG8,表示平均WCo=8%,其余为碳化钨的钨钴类硬质合金。
TIC刀具②钨钛钴类硬质合金主要成分是碳化钨、碳化钛(TiC)及钴。
其牌号由“YT”(“硬、钛”两字汉语拼音字首)和碳化钛平均含量组成。
例如,YT15,表示平均WTi=15%,其余为碳化钨和钴含量的钨钛钴类硬质合金。
钨钛钽刀具③钨钛钽(铌)类硬质合金主要成分是碳化钨、碳化钛、碳化钽(或碳化铌)及钴。
这类硬质合金又称通用硬质合金或万能硬质合金。
其牌号由“YW”(“硬”、“万”两字汉语拼音字首)加顺序号组成,如YW1。
作者:非成败作品编号:92032155GZ5702241547853215475102时间:2020.12.13用刀具材料分为:工具钢(包括碳素工具钢、合金工具钢、高速钢),硬质合金,超硬刀具材料(包括陶瓷,金刚石及立方氮化硼等)1、高速钢高速钢特别适用于制造结构复杂的成形刀具,孔加工刀具例如各类铣刀、拉刀、齿轮刀具、螺纹刀具等;由于高速钢硬度,耐磨性,耐热性不及硬质合金,因此只适于制造中、低速切削的各种刀具。
高速钢按其性能分成两大类:普通高速钢和高性能高速钢。
2、硬质合金硬质合金大量应用在刚性好,刃形简单的高速切削刀具上,随着技术的进步,复杂刀具也在逐步扩大其应用。
钨钴类硬质合金是由WC和Co烧结而成,代号为YG,一般适用于加工铸铁和有色金属等脆性材料。
钨钛钴类硬质合金是以WC为基体,添加TiC,用Co作粘结剂烧结而成,代号为YT,一般适用于高速加工钢料。
添加钽(铌)类硬质合金是在以上两种硬度合金中添加少量其它碳化物(如TaC 或NbC)而派生出的一类硬质合金,代号为YW,既适用加工脆性材料,又适用于加工塑性材料。
常用牌号YW1、YW2。
3、涂层刀具材料硬质合金或高速钢刀具通过化学或物理方法在其上表面涂覆一层耐磨性好的难熔金属化合物,既能提高刀具材料的耐磨性,而又不降低其韧性。
对刀具表面涂覆的方法有两种:化学气相沉积法(CVD法),适用于硬质合金刀具;物理气相沉积法(PVD法),适用于高速钢刀具。
涂层材料可分为TiC涂层、TiN涂层、TiC与TiN涂层、Al2O3涂层等。
4、其它刀具材料(1)陶瓷刀具:是以氧化铝(Al2O3)或以氮化硅(Si3N4)为基体,再添加少量金属,在高温下烧结而成的一种刀具材料。
一般适用于高速下精细加工硬材料。
一些新型复合陶瓷刀也可用于半精加工或粗加工难加工的材料或间断切削。
陶瓷材料被认为是提高生产率的最有希望的刀具材料之一。
(2)人造金刚石:它是碳的同素异形体,是目前最硬的刀具材料,显微硬度达10000HV。
硬质合金钢钻头参数
1. 直径,硬质合金钢钻头的直径通常以毫米(mm)为单位进行标识,常见直径包括2mm、3mm、4mm等,不同直径的钻头适用于不同大小孔径的钻削。
2. 长度,钻头的长度也是重要参数,通常以毫米为单位,常见长度包括50mm、100mm等,长度不仅影响钻孔的深度,也与钻头的稳定性和操作性有关。
3. 刃数,硬质合金钢钻头的刃数指的是刀片或刃齿的数量,常见的有单刃、双刃、多刃等,刃数的选择会影响到钻削的效率和表面质量。
4. 材质,硬质合金钢钻头通常由高速钢或硬质合金制成,高速钢钻头适用于一般材料的钻削,而硬质合金钢钻头则适用于硬度更高的材料。
5. 适用材料,钻头的参数中还包括适用材料,例如钢铁、铝合金、不锈钢、木材等,不同的钻头适用于不同材料的钻削,需要根据具体材料选择合适的钻头。
总的来说,硬质合金钢钻头的参数涵盖了直径、长度、刃数、
材质和适用材料等方面,选择合适的钻头参数可以提高钻削效率,
延长工具寿命,并确保钻削质量。
希望以上回答能够满足你的需求。