1、定域面的位置和定域 深度
1)定域面的位置由=0确定 2)光源与楔板位置不同时的定域面位置
S
S
S
P
P
a)
b)
P c)
图11-16 用扩展光源时楔行平板产生的定域条纹 a)定域面在板上方 b) 定域面在板内 c) 定域面在板下方
10
3)楔板的角度越小,定域面离板越远,当平 行时,定域面在无限远处;
n2 n2 sin2 1
2
4
Since the interval between the two surfaces may be an actual plate or film, or it may be a gap between plates. We have four possibilities, as the following.
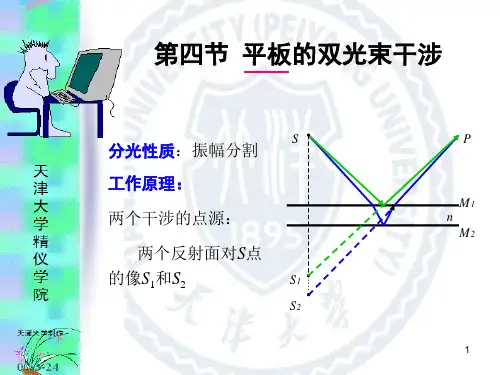
第四节 平板的双光束干涉
分光性质:振幅分割 S
P
工作原理:
M1
两个干涉的点源:
n
M2
两个反射面对S点
的像S1和S2
S1
S2
1
一、干涉条纹的定域
1.条纹定域:能够得到清晰干涉条纹的区域。
非定域条纹:在空间任何区域都能得到的干涉条纹。 定域条纹:只在空间某些确定的区域产生的干涉条纹。
2.平板干涉的优点,取 =0 ,用面光源。
C
n
θ2
n'
B
图11-18 楔形平板的干涉
12
用平行平板公式近似:垂度直h 入的射函时数,,光在程同差一是厚厚度
2nhcos 2
2
的位置形成同一级条纹。
垂直入射时: 2nh
2
3、实验装置:
l'