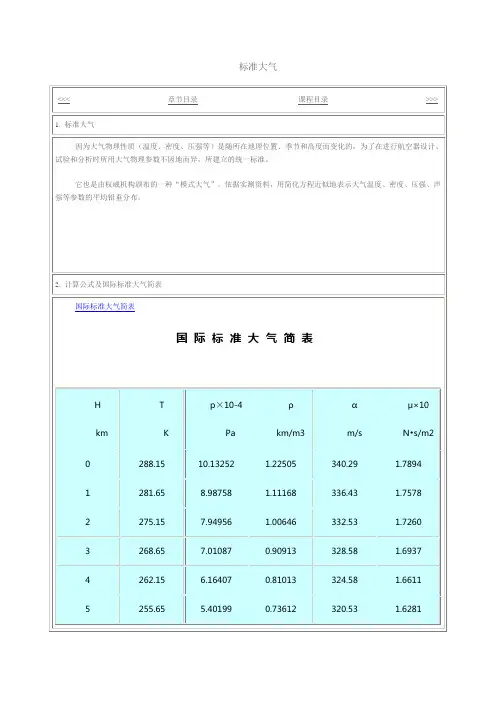
标准大气参数推算
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:468.34 KB
- 文档页数:7

标准大气参数计算公式该套计算公式摘自“杨炳尉 标准大气参数的公式表示 宇航学报1983年1月”,以美标1976标准大气为对照,采用拟合方法,在利用流体静力学得到的大气数据解析计算公式的基础上加上适当的修正因子,缩小公式的计算误差。
计算方法如下:几何高度Z 与重力位势高度H 之间的转换:)/1/(0R Z Z H +=km R 3010356766.6⨯=为地球半径km Z 0191.110≤≤2559.42559.5)(15.2883308.441W W P P K W T HW SLSL===-=ρρ km Z 0631.200191.11≤<W W P P K T H W SLSL11105898.1101953.1)(650.2163416.69647.14exp --⨯=⨯==⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=ρρ km Z 1619.320631.20≤<1629.3521629.342102722.3105158.2)(552.221552.2219021.241----⨯=⨯==-+=W W P P K W T H W SLSLρρ km Z 3501.471619.32≤<2011.1332011.123102618.3108338.2)(350.2504107.897499.391----⨯=⨯==-+=W W P P K W T H W SLSLρρ km Z 4125.513501.47≤<W W P P K T H W SLSL44104920.9109155.8)(650.2709223.76252.48exp --⨯=⨯==⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=ρρ km Z 8020.714125.51≤<2011.1142011.124105280.2101671.2)(021.2472218.884390.591W W P P K W T H W SLSL--⨯=⨯==--=ρρ km Z 0000.868020.71<<0816..1650816.175107632.1102274.1)(590.2002950.1000303.781W W P P K W T H W SLSL--⨯=⨯==--=ρρ km Z 0000.910000.86≤≤()W W H P P K T H W SLSL 663106411.31010042.12730.2)(87.1864700.52848.87exp ---⨯=⨯⨯+==⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛-=ρρ音速、重力加速度、粘度的计算公式对0至90公里范围内各段通用,分别为: 音速:)(0468.20K T a = s m /重力加速度:()2310356766.6/180665.9⨯+=Z g 2/s m 粘度(Sutherland 公式): ⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛⋅+⨯=⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛⋅+⨯=--32373236sec 4.11010487.1sec 4.11010458.1m kg T T m N T T g s m / 海平面大气参数值22242324252/1040294.3/80665.9/12492.0/2250.1/1003323.1/1001325.1108815.2s m a s m g m s kg m kg m kg m N P KT SL SL SL SL SL ⨯==⋅==⨯=⨯=⨯=ρ。

海拔和气压转换公式你知道吗,海拔和气压之间有着很有趣的关系呢。
一般来说,随着海拔的升高,气压是会降低的。
这就像是住在高楼大厦的顶层,空气好像都变得稀薄了一些,其实就是气压变小了。
那具体的转换公式呢,比较常用的一个近似公式是这样的。
气压随海拔高度的变化可以用指数函数来近似表示。
比如说,在标准大气条件下,气压和海拔高度的关系大致可以表示为:P = P₀ * (1 - (Lh / T₀))^(gM / (RL))。
这里面的字母都代表着不同的含义哦。
P₀是海平面的标准大气压,大概是1013.25百帕;L是温度垂直递减率,一般取0.0065 K/m;h就是我们要求的海拔高度啦;T₀是海平面的标准温度,大概是288.15 K;g是重力加速度,约等于9.80665 m/s²;M是空气的摩尔质量,大概是0.0289644 kg/mol;R是理想气体常数,等于8.31447 J/(mol·K)。
这个公式看起来是不是有点复杂呀?其实只要你耐心一点,把每个字母的含义都搞清楚,就会发现它还是很有逻辑的。
不过呢,这个公式也只是一个近似的计算哦。
在实际的情况中,大气的情况是非常复杂的。
比如说,不同的地理位置,大气的温度、湿度、气流等等都会有很大的差异。
就像在海边和在高山上,大气的状况就完全不一样。
海边的空气湿度比较大,这也会对气压产生影响。
而在高山上,地形复杂,气流的运动也很复杂,这都会让实际的气压和按照这个公式计算出来的结果有一些偏差。
但是呢,这个公式在很多情况下还是很有用的。
比如说,气象学家在做天气预报的时候,就会用到这个公式的原理。
他们通过测量不同地方的气压,然后根据这个公式来推测海拔高度,或者反过来,根据海拔高度来预估气压的情况。
这样就能更好地了解大气的运动和变化,从而做出更准确的天气预报。
还有哦,对于那些喜欢登山或者飞行的小伙伴来说,这个公式也很有意义。
登山的时候,随着海拔不断升高,你能明显感觉到气压的变化,身体也会有一些反应。

标准大气压推导全文共四篇示例,供读者参考第一篇示例:标准大气压是指海平面上的大气压力,通常定义为1013.25毫巴(1毫巴≈100帕)或者1013.25千帕。
标准大气压是气象学和大气科学中常用的一个重要参数,用于描述大气中空气的密度、温度和湿度等变化。
标准大气压的推导涉及到气体压强的计算和大气层的结构。
根据理想气体的状态方程PV=nRT,大气压力可以用气体的分子数目、温度和体积等参数来表示。
在海平面上,大气内的气体受地球引力的影响,会受到大气柱的重力作用,因此气体在不同高度上受到的压力会有所不同。
大气的密度随着海拔的增加而递减,这也导致了大气层内气压的不同。
根据气压与海拔的关系公式P=P0*exp(-Mgh/RT),可以推导出不同海拔高度处的大气压力。
其中P为海拔高度处的气压,P0为海平面上的标准大气压,M为气体的平均分子质量,g为重力加速度,h为海拔高度,R为气体常数,T为温度。
综合考虑气体的状态方程和海拔高度对气压的影响,可以得出不同海拔高度处的标准大气压。
在海平面上,标准大气压通常被定义为1013.25毫巴或者1013.25千帕,但随着海拔的增加,实际气压会有所不同。
例如在珠穆朗玛峰的顶峰处,由于海拔高度极高,大气压远低于标准大气压,这也是登山者需要携带氧气瓶来补充氧气的原因之一。
标准大气压的推导对于气象学、气候学和航空航天等领域都具有重要意义。
在天气预报和气候研究中,标准大气压可以用来描述大气层的结构和变化,帮助科学家们更好地理解和预测气候变化。
在航空航天领域,标准大气压可以用来计算飞行器在不同高度上的气动力学特性,以确保飞行安全。
标准大气压的推导是一个涉及到气体物理学和气象学等多个学科知识的综合性问题。
通过对气体状态方程和大气层结构的深入研究,科学家们可以更加准确地描述和理解大气压力的变化规律,为气象预测、气候研究和航空航天技术的发展提供重要参考。
【注:本文共计663字】第二篇示例:标准大气压推导是气象学中一个重要的概念,它在天气预报、航空航天等领域起着至关重要的作用。



标准大气条件标准大气条件是指在一定的气压和温度下,大气的密度、温度和声速等参数的标准值。
在地球上,标准大气条件通常指的是在海平面上的大气条件,这也是工程技术设计和科学研究中常用的参考条件。
在标准大气条件下,大气的压强约为101.325千帕,温度约为15摄氏度。
在这样的条件下,空气的密度约为1.225千克/立方米,声速约为340.29米/秒。
这些数值为工程设计和科学研究提供了重要的参考依据。
标准大气条件的确定对于航空航天、气象学、环境科学等领域具有重要意义。
在航空航天领域,飞行器的设计和性能计算需要考虑大气条件的影响。
在气象学和环境科学领域,大气条件的变化与气候变化、空气污染等问题密切相关。
除了在地球上的海平面上,标准大气条件也可以根据不同的要求进行调整。
例如,在高海拔地区,由于气压较低,大气的密度和温度会有所变化。
在这种情况下,需要根据实际情况对标准大气条件进行修正,以保证工程设计和科学研究的准确性。
在工程设计中,标准大气条件的使用可以帮助工程师进行设计计算和性能预测。
例如在飞机设计中,需要考虑飞机在不同大气条件下的飞行性能,包括爬升率、巡航速度、燃料消耗等。
在这种情况下,标准大气条件可以作为设计的基准,帮助工程师进行性能预测和优化设计。
在科学研究中,标准大气条件的使用可以帮助科学家进行实验设计和数据分析。
例如在气候模拟研究中,需要考虑不同大气条件对气候变化的影响。
在这种情况下,标准大气条件可以作为实验的基准,帮助科学家进行数据分析和模型验证。
总之,标准大气条件是工程设计和科学研究中不可或缺的重要参考条件。
它的准确确定和合理应用对于推动工程技术和科学研究的发展具有重要意义。
希望本文对标准大气条件的理解和应用能够有所帮助。

标准大气压海拔标准大气压是理想气体状态下,在海平面上的压强。
它是巴里定律所得的结果,即将一个压缩空气的容器加热至同温度下保持不变的体积,会得到一个设定的大气压力。
在物理学中,标准大气压的数值为101.325千帕斯卡(kPa),用来作为大气压的标准计量单位。
标准大气压随着海拔的高度而下降。
这是由于大气的压力是由地球表面上的重力引起的,随着海拔的高度逐渐变弱。
这种下降的趋势并不是线性的,而是指数式的。
也就是说,离开海平面越高,每上升一定的高度,标准大气压的变化量就会越大。
为了方便计算和比较,国际上采用了一组标准大气压的值。
这组值是基于一个理想的标准大气的假设情况所得出的。
这个理想的标准大气假设为一束干燥的气体,其中气压按照指数规律随海拔增加而下降,温度随着高度的增加而保持恒定。
根据这个假设,国际上规定了在海平面上的标准大气压为1013.25毫巴(mb),1毫巴相当于 100帕斯卡(Pa)。
这个值还可以通过将功率为1.85的指数函数用于一个海拔中任意高度计算的方法来推算得出。
然而,在真实情况下,大气是非常复杂的。
它包含了水蒸气、氮气、氧气等各种气体的混合物。
而且大气中水蒸气和其他气体的含量和分布也会随着地理位置、时间和季节的变化而变化,在这些因素的影响下,标准大气压也会发生变化。
在气象学中,标准大气压是指在一定的时间和地点下测定的平均大气压值。
总之,标准大气压是大气压的标准计量单位,根据巴里定律,标准大气压在海平面上为101.325kPa,随着海拔的变化而下降,但是这种下降的趋势并不是线性的,是指数式的,国际上有一组标准的大气压值以便于科学计算和比较。

标准大气压计算公式
在标准大气压的计算中,我们可以使用以下的公式:
P=P0*(1-(L*h)/T0)^(gM/RL)
其中:
-P是标准大气压
-L是温度随高度变化的率(一般取为0.0065摄氏度/米)
-h是海拔高度
-T0是参考高度上的温度(一般取为288.15摄氏度)
-g是重力加速度(一般取为9.8米/秒^2)
-RL是气体常数(一般取为8.314千焦耳/(摩尔·开尔文))
这个公式的推导基于气体力学原理,这里给出了一个简化的版本。
在
实际应用中,还需要考虑其他因素,例如地球自转带来的惯性力等。
此外,温度、湿度等因素对气压的影响也需要考虑。
这个公式的基本思想是根据海拔高度的变化和重力加速度的作用,推
导出气压随着高度的变化规律。
当海拔高度变化时,温度和压力都会相应
发生改变,而这些因素又会影响到大气的密度和体积。
因此,通过这个公
式可以计算出不同高度上的标准大气压。
需要注意的是,这个公式是一个推导公式,在实际应用中可能会存在
误差。
因为气象条件的变化是很复杂的,无法完全用一个简化的公式来描述。
因此,在实际应用中,我们往往需要结合气象观测和实际数据,通过
数学建模等方法来计算气压的变化规律。
标准大气压的计算公式为我们理解气压变化提供了一个基本框架,它能够帮助我们理解气象现象、解释天气变化以及进行气象预测等工作。
在气象学、航空航天等领域,对气压变化的研究和预测是非常重要的。
通过不断地发展研究,我们可以更好地理解和预测气象现象,提高气象预报的准确性,为人们的生活和工作提供更好的保障。

海拔与大气密度和温度间的换算关系Revised by Hanlin on 10 January 2021海拔高度与大气密度和温度间的换算关系1、根据大气压力和空气密度计算公式,以及空气湿度经验公式,可得出大气压、空气密度、湿度与海拔高度的关系。
注:标准状态下大气压力为1,相对空气密度为1,绝对湿度为11g/m3。
从表中可以看出,海拔高度每升高1000m,相对大气压力大约降低12%,空气密度降低约10%,绝对湿度随海拔高度的升高而降低。
绝对湿度是指每单位容积的气体所含水分的重量,用mg/L或g/m3表示;相对湿度是指绝对湿度与该温度饱和状态水蒸气含量之比用百分数表达。
2、空气温度与海拔高度的关系在无热源、无遮护的情况下,空气温度随海拔高度的增高而降低。
一般研究所采集的温度与海拔高度的关系:从表中可以看出:空气温度在一般情况下,海拔高度每升高1000m,最高温度会降低5℃,平均温度也会降低5℃。
大气密度(atmosphericdensity)单位容积的大气质量。
空气密度在标准状况(0℃(273k),101KPa)下为1.293g·L-1。
空气的密度大小与气温等因素有关,我们一般采用的空气密度是指在0摄氏度、绝对标准指标下,密度为1.297千克每立方米(1.297kg/m3).大气压力随海拔高度而变化,由经验公式P=P0(1-0.02257h)5.256(kPa)式中h一海拔高度(km).用上面公式,算出压力,然后根据密度=P*29/(8314*T),其中P的单位是帕,T的单位是K,通常也就是273.15+t不同温度下干空气算公式:空气密度=1.293(实际压力/标准物理大气压)*(273/实际绝对温度),绝对温度=+273通常情况下,即30摄氏度时,取1.165KG/M3-60摄氏度时,取1.65KG/M3。

国际标准大气温度1. 介绍国际标准大气温度(International Standard Atmosphere Temperature,简称ISA温度),是指在国际标准大气模型下的大气温度。
它是以海平面为基准,按照一定的规律随高度变化的气温。
ISA温度的定义和计算方法对于航空航天、气象、气候研究等领域具有重要意义。
2. ISA模型国际标准大气模型是一种理想化的气候模型,用于描述大气温度、压力和密度随高度变化的规律。
根据这一模型,大气按照一定的规律分布在不同的层次中,每个层次都有相应的温度和压力值。
ISA模型假设大气是稳定的、由一维气柱组成的,并且假设大气是非湿饱和的。
3. ISA温度的计算方法根据ISA模型,可以计算出不同高度层次的温度。
ISA温度的计算方法如下:3.1 温度梯度ISA模型中,大气温度随高度的变化率称为温度梯度。
温度梯度在不同层次有不同的取值,常用的是以下两个梯度: - 绝热温度梯度(Adiabatic Temperature Gradient):在对流层中,大气温度随高度上升约6.5°C/km。
- 同温温度梯度(Isothermal Temperature Gradient):在平流层中,大气温度保持不变。
3.2 基准温度ISA模型中,海平面的温度被定义为基准温度,记为T0,常取为15°C。
3.3 温度计算公式根据温度梯度和基准温度,可以得到不同高度层次的温度计算公式。
具体计算公式如下:•对流层(0-11km):T=T0−0.0065⋅ℎ,其中T为温度,ℎ为高度(单位:米)。
•平流层(11-20km):T=T11km,其中T11km为对流层顶部的温度。
•中间层(20-32km):T=T20km+0.001⋅(ℎ−20000),其中T20km为平流层顶部的温度。
•局部热层(32-47km):T=T32km+0.0028⋅(ℎ−32000),其中T32km为中间层顶部的温度。
标准大气温度计算公式是pv=NRT其中p表示压强,V表示体积,N是单位体积的气体分子数,R是个常数,T表示温度。
当V、N、R固定不变时,气温越高,气压越高。
当N、R、T固定不变时,体积越小,气压越高。
这个计算公式能够反映某地区(如中纬度)垂直方向上气温、气压、湿度等近似平均分布的一种模式大气。
它能粗略地反映中纬度地区大气多年年平均状况,并得到一国或国际组织承认。
原理
中国国家标准规定的标准大气压,采用海平面温度为15℃,气压为1013.25百帕,密度为1.2250千克/米3。
在11千米以下,高度每增高100米,温度降低0.65℃;在11~20千米,温度保持-56.5℃。
这样规定的标准大气压,与中国中纬度(北纬45°)实际大气十分接近。
大气环境质量标准计算方法化学物质在没有环境空气质量标准和居住区大气环境质量标准情况下,推荐大家采用AMEG值,主要计算公式如下:美国环保局于1977年公布了该局工业环境实验室用模式推算出来的六百多中化学物质在各种环境介质(空气、水、土壤)中的限定值。
又于1980年对其进行了增补,并建议将其作为环境评价的依据值。
这些限定值被称为多介质环境目标值(Multimeedia Environmental Goal,MEG)。
所有目标值都是在最基本的毒性数据基础上,以统一模式推算的,系统性和可比性好。
因而,多介质环境目标值虽然不具法律效力,却可以作为环境评价的依据。
目前,它已在美国环境影响评价中广泛应用。
●以毒理学数据LD50为基础的计算公式为:AMEG=0.107×LD50/1000式中:AMEG-空气环境目标值(相当于居住区空气中日平均最高容许浓度,mg/m3)LD50-大鼠经口给毒的半数致死剂量以环氧乙烷为例,LD50--330mg/kg,计算得AMEG值= 0.04mg/m3,因此推荐居住区环境空气中环氧乙烷最高容许浓度为0.04 mg/m3(日平均值),根据《环境影响评价技术导则-大气环境》(HJ/T2.2-93)“8.1.2.5 如无法获得8.1.2.1中所述的监测资料,一次取样、日、月、季(或期)、年平均值可按1、0.33、0.20、0.14、0.12的比例关系换算”,则计算得相应1小时平均值为0.11 mg/m3。
●以阙限值为基础的计算公式为:AMEG=阙限值/420式中:AMEG-空气环境目标值(相当于居住区空气中日平均最高容许浓度,mg/m3) 阙限值-美国政府工业卫生学家会议(ACGIH)制定的车间空气容许浓度,即每周工作5天,每天工作8小时条件下,成年工人可以耐受的化学物质在空气中的时间加权平均浓度,mg/m3●以健康影响为依据的空气介质排放环境目标值(DMEGAH)可按下式计算:DMEGAH (μg/m3) = 45×LD50式中:DMEGAH——允许排放浓度,LD50——化学物质的毒理数据,一般取大鼠经口给毒的LD50,若无此数据,可取与其接近的毒理学数据。
国际标准大气I S A 集团标准化工作小组 [Q8QX9QT-X8QQB8Q8-NQ8QJ8-M8QMN]A.概述1.国际标准大气(ISA)1.1.标准大气模型的建立大气是指地球周围的大气层。
在世界的不同地区,其特点是不同的。
为此,需要采用一组平均的条件,即:国际标准大气 (ISA)。
1.1.1.温度模型的建立下图(图 A1) 解释了标准大气中温度的变化:图 A1: ISA温度国际标准的基础是海平面温度15°C,气压 hPa1。
海平面空气标准密度为 kg/m3。
1 hPa 等于‘in Hg。
‘hPa’ 表示百帕,‘in Hg’ 表示英寸汞柱。
在对流层顶以下,温度以恒定的速率°C/1000米或°C/1000英尺随着高度变化。
标准的对流层顶的高度为11,000 米或 36,089 英尺。
从对流层顶向上,温度保持恒定的°C。
因此,在ISA模型中被认为是理想气体的空气具有以下特性:在平均海平面 (MSL):在 MSL以上对流层顶以下 (36,089 英尺):为了快速确定在给定高度的标准温度,可以使用以下的近似公式:在对流层顶之上 (36,089 英尺):这个ISA模型作为一个基准,用于比较真实大气条件和相应的发动机/飞机性能。
因此,在给定的高度,大气条件被表达为ISA +/- ISA。
例如:让我们考虑以下条件的飞行:高度 = 33,000 英尺实际温度 = -41oC在 33,000 英尺的标准温度为:ISA = 15 - 2 x 33 = -51oC,而实际温度为 -41oC ,即:比标准温度高10oC 。
结论:飞行条件为ISA+10。
1.1.2. 气压模型的建立为了计算给定高度条件下的标准的压力P ,我们进行以下假设:对应高度,温度是标准的。
空气是理想气体。
通过测量气压得到的高度被称为气压高度(PA ),可以建立一个标准(ISA)表格 (表 A1)。
ZpPRESSURE ALTITUDEP40000300002000010000Zp = f(p) ISA table(hPa)(km)246810122003005008501013.25图 A2:气压高度与气压的函数关系压力 (hPa)气压高度 (PA) FL= PA/100PA 气压高度 PA = f(P)(英尺)(米)2003866111784390250340001036334030030066916430050018287557418085048131467501013000表 A1:用表格表示的气压高度值示例假定一个体积的气体处于静平衡,其气体状态方程为:dP = gdh其中 = 高度 h的空气密度g= 重力加速度 m/s2)dh = 体积单位的高dP = 对应dh的压力变量理想气体方程为:其中 R = 通用气体常数 J/kg/K)结果:在平均海平面 (MSL):P= hPa高于 MSL但低于对流层顶 (36,089 英尺):其中 P= hPa (海平面的标准气压)T= 288 .15 K (海平面的标准温度)= oC/mg 0 = m/s2RTP=ρRg)hT(PPαα01-=R = J/kg/K h = 高度 (m)注: 在低空,气压每降低1 hPa ,气压高度大约增加 28 英尺。
大气气压公式大气气压是指大气中的空气对于地面或物体单位面积的压力。
它是大气物理学中一个重要的参数,对于气象学、地理学以及其他相关领域都具有重要的意义。
大气气压的变化受到多种因素的影响,包括海拔高度、气温、湿度等。
而大气气压的计算则可以通过大气气压公式来进行。
大气气压公式是描述大气气压与高度之间关系的数学表达式。
在大气垂直方向上,气压随着高度的增加呈指数下降的规律。
根据理想气体状态方程以及重力加速度的影响,可以推导出大气气压公式。
大气气压公式的一般形式可以表示为P=P0exp(-Mgh/RT),其中P为某一高度的气压,P0为参考高度的气压,M为气体的摩尔质量,g为重力加速度,h为高度,R为气体常数,T为温度。
在实际应用中,大气气压公式可以帮助我们更好地理解大气的运动规律,预测气象变化以及进行气候研究。
通过对大气气压公式的研究和应用,我们可以更好地理解大气环境的复杂性,并为相关领域的科研工作提供支持。
大气气压的计算在气象学中具有重要的应用。
气象学通过研究大气气压的变化,可以预测气候变化、风暴的形成以及降水的情况。
利用大气气压公式,可以根据不同地区的气压情况来推测天气的变化趋势,为人们的生活和工作提供重要参考。
除了在气象学中的应用,大气气压公式还在地理学、环境科学等领域有重要的作用。
在地理学中,我们可以通过大气气压的分布来推测地球表面的高程,研究地理环境的特点。
而在环境科学中,大气气压的研究可以帮助我们更好地理解大气层的物理特性,推测空气的流动规律以及污染物传播的方向。
大气气压公式的研究不仅涉及理论推导,还包括实际应用。
通过实验数据的采集和分析,我们可以验证大气气压公式的准确度,进一步完善相关理论模型。
同时,在实际工程项目中,我们也可以通过大气气压公式来进行工程设计,确保项目的安全性和可靠性。
总的来说,大气气压公式是描述大气气压变化规律的重要工具,对于气象学、地理学、环境科学等领域都具有重要的意义。
通过对大气气压公式的深入研究,我们可以更好地理解大气环境的复杂性,为相关领域的科研工作提供支持。
1. 标准大气数据参数计算: 1.1 参数列表1.2 计算公式1.2.1 计算气压高度Hpb (m):Hpb=])(1[0RPS PSB T ⨯-ττ( PSB ≥22.631 kp a )Hpb=)631.22(110001PSBLN T R ⨯⨯-1.2.2 计算校正空速Vcb (km/h):Vcb=⎥⎥⎦⎤⎢⎢⎣⎡-⎪⎪⎭⎫ ⎝⎛+-⨯⨯115058.12257/20PS PSB PTB )89293.0(0≤-PS PSBPTB[]1)058.1225()(7058.1225)(9216.1665.22270--⨯⨯⨯=-Vcb Vcb PS PSB PTB)89293.0(>-PS PSBPTB1.2.3 计算马赫数Mb:Mb=51)(7/2⨯⎥⎦⎤⎢⎣⎡-PSB PTB )89293.1(≤PSB PTB5.227)1)(7()(9216.166-⨯⨯=Mb Mb PSB PTB )89293.1(>PSB PTB1.2.4 计算大气静温Tsb (K):)1()(2.012732N Mb Tt Tsb ∆-⨯⨯++=1.2.5 计算真空速Vtb(km/h):Tsb Mb Vtb ⨯⨯=1658.721.2.6 计算大气密度比Sigb:Sigb=TSBPSBPS T ⨯001.2.7 计算压力比Prb:( PSB < 22.631 kp a )Prb=PS PSB1.2.8 计算修正气压高度Hpbc(m):设场压装订的值为PBS ,用代替PSB ,代入公式(1.1),得到一个中间值,设为HPBS; Hpbc=Hpb-HPBS;1.2.9 计算真攻角aoa(º):根据攻角补偿曲线,代入局部攻角LAOA ,插值计算出真攻角;1.2.10 计算爬升率Vyb(m/s): Vyb=)()(s d Hpb d ;1.3 误差计算1.3.1 Ehp=Hp-Hpb; (m)1.3.2 Ehpc=Hpc-Hpbc; (m)1.3.3 Evc=Vc-Vcb; (km/h)1.3.4 Evt=Vt-Vtb; (km/h)1.3.5 EM=M-Mb;1.3.6 Ett=TT-TTI; (℃)1.3.7 Esig=Sig-Sigb;1.3.8 Evy=Vy-Vyb; (m/s)1.3.9 Eaoa=Taoa-aoa; (゜)1.4 计算公式中的常量如下: T 0=288.15K T 1=216.65K τ=0.0065K/m R=29.27m/K PS 0=101.325kPa ΔN=0.0052. 惯性导航系统计算 2.1 参数列表2.2 计算公式R=K ∑∑==n i m j ijiitRER m n 112)(11 (1)式中:R -圆概率径向误差K -系数,可以根据概率的要求得到不同的系数(如:计算常用的圆概率误差CEP 时,K =0.83,计算95%圆概率径向误差时,K =1.73。
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA)Mustafa Cavcar*Anadolu University, 26470 Eskisehir, TurkeyNomenclaturea= speed of sound, m/secg= acceleration of gravity, m/sec2h= altitude, m or ftp= pressure, N/m2 or hPaR= real gas constant for air, 287.04 m2/°Ksec2T= temperature, °K or °Cρ= density, kg/m3Subscripts0= standard sea level conditions11= tropopause caonditionsAbbreviationsICAO = International Civil Aviation OrganizationISA = International Standard AtmosphereMSL = Mean Sea LevelPA = Pressure Altitude1. Standard Atmosphere ModelingFor purposes of pressure altimeter calibrations, aircraft and rocket performance and their design, and so forth, knowledge of the vertical distribution of such quantities as pressure, temperature, density, and speed of sound is required. Since the real atmosphere never remains constant at any particular time or place, a hypothetical model must be employed as an approximation to what may be expected. This model is known as the standard atmosphere. The air in the model is assumed to be devoid of dust, moisture, and water vapor and to be at rest with respect to the Earth (that is, no winds or turbulence). [1]The first standard atmospheric models were developed in the 1920's in both Europe and the United States. The slight differences between the models were reconciled and an internationally accepted model was introduced in 1952 by the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO). [1] The International Standard Atmosphere is defined in ICAO Document 7488/2. The ISA assumes the mean sea level (MSL) conditions as given in Table 1.* Professor, School of Civil Aviation; mcavcar@.tr.Table 1 International Standard Atmosphere, Mean Sea Level ConditionsPressure =0p 101 325 N/m 2 = 1013.25 hPa Density =0ρ 1.225 kg/m 3 Temperature =0T 288.15°K (15°C) Speed of sound=0a 340.294 m/secAcceleration of gravity =0g 9.80665 m/sec 21.1. Temperature ModelingThe following diagram (Figure 1) illustrates the temperature variations in the standard atmosphere:Figure 1 International Standard Atmosphere temperature variation [2].Temperature decreases with altitude at a constant rate of -6.5°C/1000m (-1.98°C/1000ft) up to the tropopause. The standard tropopause altitude is 11,000 m (36,089 ft). Therefore, the air which is considered as a perfect gas in the ISA model presents the following characteristics within the troposphere:1000(m)5.60h T T −= (1) or1000(ft)98.10h T T −= (2)For simple estimations, Equation (2) can be assumed1000(ft)20h T T −= (3)The temperature remains at a constant value of -56.5°C (216.65°K) from the tropopause up to 20,000 m (65,600 ft).This ISA model is used as a reference to compare real atmospheric conditions and the corresponding engine/aircraft performance. The atmospheric conditions will therefore be expressed as ISA +/- ∆ISA at a given flight level [2].Example:Let’s consider a flight in the following conditions:Altitude = 31,000 feetActual Temperature = -37ºCThe standard temperature at 31,000 feet is: 4731215−=×−=T ºC, whereas the actual temperature is -37ºC, i.e. 10ºC above the standard.Conclusion: The flight is operated in ISA+10 conditions1.2. Pressure ModelingTo calculate the standard pressure p at a given altitude, the temperature is assumed standard, and the air is assumed as a perfect gas. The altitude obtained from the measurement of the pressure is called pressure altitude (PA). Both Table 2 and Figure 2 show variation of the pressure altitude as a function of the pressure. The last column of Table 2 shows corresponding flight levels for the given pressure altitudes. The flight level is the altitude expressed in hundreds of feet.Table 2 Pressure altitude versus pressure [2].Figure 2 Pressure altitude versus pressure [2].The pressure variations for the International Standard Atmosphere can be calculated by using the hydrostatic equation, perfect gas law and the temperature lapse rate equation. The hydrostatic equation for a column of air (Figure 3):=(4)dpρ−gdhThe equation of state for the perfect gas:RT p ρ=(5)where R is the real gas constant for the air. Dividing the hydrostatic equation by the equation of state gives:dh RT g RT gdh p dp−=−=ρρ (6)The relationship between the pressure at a troposphere altitude and sea level pressure can be obtained by integrating equation (1) between 00=h and h :∫∫=−−=p p h h h T dh R g p dp 00000065.0Performing the above integration, we obtain:2561.5000065.01−=T h p p (7)In equation (7), the unit of 0T is °K, and h is in meters.Pressure above the tropopauseFor the altitudes above the tropopause, the temperature is constant, so that integrating equation (6) from the tropopause to an altitude above the tropopause:∫∫=−=p p h h dh RT g p dp 11111100011results in)(111111h h RT gep p −−=(8)where the parameters with subscript “11” correspond to the values at the tropopause, and =11p 226.32 hPa, =11T 216.65 °K, and =11h 11,000 m1.3. Density ModelingSince the pressure and standard temperature are known for a given altitude, the standard density can easily be calculated from the perfect gas equation (5):RTp =ρ (9)2. International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) Table [2]The International Standard Atmosphere parameters (temperature, pressure, density) can be provided as a function of the altitude under a tabulated form, as given in Table 3:Table 3 International Standard Atmosphere [2]References[1] Talay, T.A., Introduction to the Aerodynamics of Flight, NASA SP-367, NationalAeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, D.C., 1975, p. 6-9.[2] Airbus, Getting to Grips with Aircraft Performance, Airbus Industrie, CustomerServices, Blagnac, 2000, p. 11-16.。