第五章对流换热分析
- 格式:pdf
- 大小:2.25 MB
- 文档页数:83






第五章对流换热分析通过本章的学习,读者应熟练掌握对流换热的机理及其影响因素,边界层概念及其应用,以及在相似理论指导下的实验研究方法,进一步提出针对具体换热过程的强化传热措施。
5.1 内容提要及要求5.1.1 对流换热概述1.定义及特性对流换热指流体与固体壁直接接触时所发生的热量传递过程。
在对流换热过程中,流体内部的导热与对流同时起作用。
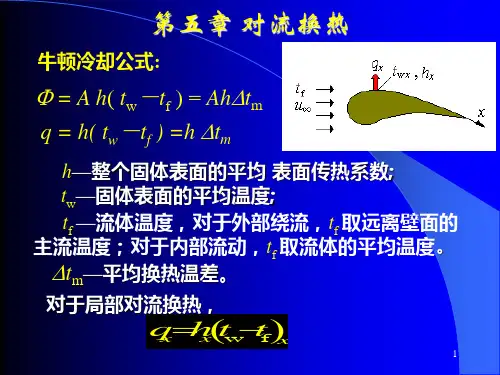
牛顿冷却公式q h(t w t f ) 是计算对流换热量的基本公式,但它仅仅是对流换热表面传热系数h 的定义式。
研究对流换热的目的是揭示表面传热系数与影响对流换热过程相关因素之间的内在关系,并能定量计算不同形式对流换热问题的表面传热系数及对流换热量。
2.影响对流换热的因素(1)流动的起因:流体因各部分温度不同而引起密度差异所产生的流动称为自然对流,而流体因外力作用所产生的流动称为受迫对流,通常其表面传热系数较高。
(2)流动的状态:流体在壁面上流动存在着层流和紊流两种流态。
(3)流体的热物理性质:流态的热物性主要指比热容、导热系数、密度、粘度等,它们因种类、温度、压力而变化。
(4)流体的相变:冷凝和沸腾是两种最常见的相变换热。
(5)换热表面几何因素:换热表面的形状、大小、相对位置及表面粗糙度直接影响着流体和壁面之间的对流换热。
综上所述,可知表面传热系数是如下参数的函数h f u, t w , t f , , c p , ,,, l这说明表征对流换热的表面传热系数是一个复杂的过程量,不同的换热过程可能千差万别。
3.分析求解对流换热问题分析求解对流换热问题的实质是获得流体内的温度分布和速度分布,尤其是近壁处流体内的温度分布和速度分布,因为在对流换热问题中“流动与换热是密不可分”的。
同时,分析求解的前提是给出正确地描述问题的数学模型。
在已知流体内的温度分布后,可按如下的对流换热微分方程获得壁面局部的表面传热系数由上式可有h xtt x yW/(m 2 K)w,x其中为过余温度,h xxyW/(m 2 K)w,x对流换热问题的边界条件有两类,第一类为壁温边界条件,即壁温分布为已知,待求的是流体的壁面法向温度梯度;第二类为热流边界条件,即已知壁面热流密度,待求的是壁温。




第五章 对流换热分析对流换热是发生在流体和与之接触的固体壁面之间的热量传递过程。
牛顿冷却公式:)(f w t t h q -= W/m 2 A t t h f w )(-=Φ W 对流换热问题分析的目的是:确定h 的数值。
确定的方法有4种:分析法、类比法、实验法、数值法。
第一节 对流换热概述影响对流换热的因素很多,但不外是影响流动的因素及影响流体中热量传递的因素。
这些因素可归纳为以下五个方面:1.流体流动的起因按流体运动的起因不同,对流换热可区分分为:自然对流换热和受迫对流换热。
(1)自然对流(natural convection ):流体因各部分温度不同而引起的密度不同,在密度差的作用下产生的流动。
(举例:暖气片)(2)受迫对流(forced convection):在外力的作用下产生的流动。
(举例:泵、风机) 流动的起因不同,流体中的速度场也有差别,所以换热规律也不一样。
2.流体的流动状态层流(laminar flow):流层间不掺混,依靠流体分子的热运动传递热量; 紊流(turbulent flow):有流体微团的掺混,换热作用增强。
3.流体的热物理性质流体的热物理性质对于对流换热有较大的影响。
流体的热物性参数主要包括: ① 导热系数λ:λ大,则流体内的导热热阻小,换热强;② 比热容p c 和密度ρ:p c ρ大,单位体积流体携带的热量多,热对流传递的热量多; ③ 粘度μ:粘度大,阻碍流体流动,不利于热对流。
温度对粘度的影响较大。
④ 体积膨胀系数:在自然对流中起作用。
定性温度(reference temperature):确定流体物性参数值所用的温度。
常用的定性温度主要有以下三种:1 流体平均温度f t2 壁表面温度w t (有时对物性参数作某种修正时,以此作定性温度)3 流体与壁面的平均算术温度:2wf t t +4.流体的相变流体发生相变时的换热有新的规律。
无相变时:主要是显热;有相变时:有潜热的释放或吸收。
wton’s law of cooling:−=W/m 2dxdtq λ−=Contents第一节对流换热概述Analysis on Convection第二节对流换热微分方程组The Convection Heat Transfer Equations第三节边界层换热微分方程组Convection Differential Equations of Boundary Layer 第四节边界层换热积分方程(自学)第五节动量传递和热量传递的类比(自学)第六节相似理论基础Basis of similarity theoryConvection is the mode of energy transfer between a solid surface and the adjacent liquid or gas that is in motion, and it involves the combined effects of conduction and fluid motion.(流体与固体壁直接接触时所发生的热量传递过程,称为对流换热)The faster the fluid motion, the greater the convection heat transfer.We will study how to calculate the convection heat-transfer coefficient h in Chapter 5 and Chapter 6.5-1 Analysis on Convection(对流换热概述) Convection transfer problemHeat exchangers Tubes in steamboiler (蒸汽锅炉的管束)Tube-shell heat exchanger (管壳式换热器)Condenser ofrefrigerator Tubes withfins (翅片管束)图5-1几种常见的换热设备示意图Factors influencing convection heat transfer :Flow causes of fluid (流体流动的起因)、flow states ( 流动状态)、properties of fluid (流体物性)、change of phase of fluid (流体物相变化)、geometry parameters (壁面的几何参数),and so on 。
1.Causes and States of Flow (流动的起因和状态)(1) Causes of flow(流动起因)Forced convection(受迫对流):if the fluid is forced to flow over the surface by external means such as a fan ,pump,or the wind .naturalforced h h >Natural (or free) convection(自然对流):if the fluid motion is caused by buoyancy (浮力) forces that is induced(引起) by density difference due to the variation of the temperature in the fluid.Examples :air free convection :h=5~25W/(m 2.K )air forced convection :h=10~100W/(m 2.K )(2) flow states ( 流动状态)Whatever the causes of flow are ,the flow states are consist of laminar flow (层流)and turbulent flow (紊流)Laminar flow ——characterized by smooth streamlines (流线) and highly ordered motion due to the fluid flowing in laminae(层) or layers(整个流场呈一簇互相平行的流线)Turbulent flow ——characterized by velocity fluctuation (波动) and highly disordered motion (流体质点做复杂无规则的运动)lt h h >2.The thermal properties of fluid (流体热物性)Properties:density(密度) ρ[kg/m 3], specific heat(比热) c [J/(kg. ℃)]thermal conductivity(导热系数) λ[ W/(m. ℃)],dynamic viscosity(动力粘度) μ[kg/(s.m)]kinematic viscosity(运动粘度) ν(m 2/s ),volume expansion coefficient (体积膨胀系数) α(1/K),ρμ=v p p T T ⎟⎠⎞⎜⎝⎛∂∂−=⎟⎠⎞⎜⎝⎛∂∂=ρρυυα11自然对流换热增强↑⇒α)( 多能量单位体积流体能携带更、↑↑⇒h c ρ)( 热对流有碍流体流动、不利于↓↑⇒h μ↑↑⇒h λ)(间导热热阻小流体内部和流体与壁面where Ideal gasα=1/T***Characteristic temperature (定性温度)Average temperature of fluid (流体平均温度)t fthe surface temperature of wall (壁表面温度)t wthe arithmetic average temperature of the fluid and the wall surface (流体与壁的算术平均温度)(t f +t w )/2.3.Change of phase (流体的相变)Change of phase heat transfer(相变换热):Condensation (凝结)、Boiling(沸腾)、sublimation(升华)、freeze(凝固)、thaw(融化) and so onSingle phase heat transfer (单相换热)glechange h h sin >4. Geometry parameters of convection surface(换热表面几何因素)shape, sizes, position and roughnessExterior flow (外掠): flow across the flat plate,flow across cylinders and tubes (外掠平板、外掠圆管及管束)Interior Flow (内流): flow in a pipe ,flow in slot (管内、槽内流动)。
Forced convectionNatural convectionLower surface of a hot plateUpper surface of a hot plate Flow in a pipe Flow across a pipe***Characteristic Length (定型尺寸) l由于壁面几何形状的影响,在分析计算中可采用对换热有决定意义的特征尺寸作为依据,这个尺寸称定型尺寸。
Example :for a flat plate, l is the length of the plate in the flow direction .If the fluid flow in a pipe , l is the diameter d of the pipe, l=d),,,,,,,,(l c t t u f h p f w μαρλ=5. Sorts of ConvectionGenerally ,the convection heat transfer coefficient h can be expressed the function of those factors mentioned above5-2 The Convection Heat Transfer Equations对流换热微分方程组To simplify the analysis we assume:(1)The fluid is incompressible and Newton-style ;(2)The properties of fluid are constant and no heat resources. ;(3)The energy generated by viscosity is negligible (粘性耗散产生的耗散热可以忽略不计)。
**Newton-style fluid (牛顿型流体)服从y u∂∂=μτ定律的流体称牛顿型流体。
The viscous forces are described in terms of a shear stress between the fluid layers ,that this stress is assumed to be proportional to the normal (法线)velocity gradient .yu∂∂=μτ2-1 Differential Equation for the convection heat transfer process(对流换热过程微分方程式)xy q u Where y=0,u=0,no-slip conditionHeat transfer from the solid surface to the fluid layer adjacent to the surface is by pure conductionThe fluidlayer ismotionlessHeat transfer can be expressed as xw x y t q ,⎟⎟⎠⎞⎜⎜⎝⎛∂∂−=λ:0=y W/㎡λis thermal conductivityof fluidx w y t ,⎟⎟⎠⎞⎜⎜⎝⎛∂∂——is the temperature gradient at the surface x from leading edge of the flat plate(x 点帖壁处流体的温度梯度,K/m)According to Newton’s law of coolingxx x f w x x t h t t h q Δ⋅=−=)(h x ——the local convection heat transfer coefficient at surface x (壁面x 处的局部表面传热系数),W/(m 2.K )。