椎间盘源性下腰痛诊断-英文-翻译1
- 格式:doc
- 大小:55.00 KB
- 文档页数:4

椎间盘源性腰痛护理常规
一、椎间盘源性腰痛的概述
椎间盘源性腰痛(lumbar intervertebral discogenic backache)
是指椎间盘病变所致的腰痛,其病因及病理病程主要包括椎间盘破裂、椎
间盘积液、椎间盘退变等。
病症表现为腰背部疼痛、痛引伸至腰部、大腿
后侧、膝关节及脚跟,伴有侧弯、屈腰等反射性活动障碍。
1、预防与教育
(1)宣传正确的生活习惯,如保证充足的睡眠、定期活动锻炼、戒
烟限酒等,以减轻椎间盘源性腰痛发病的危险因素。
(2)学习正确的体位姿势和活动方法,及时调整不良姿势,加强身
体的活动训练,增强腰腹部的力量,注意避免单一体位作业或坐姿作业,
尽量减少腰部的负荷。
(3)加强饮食管理。
多加食用富含维生素A、C、E、B6、钙、铁等
营养的食物,减少脂肪、膳食纤维及水分的摄入,注意控制体重,加强免
疫力,积极预防腰痛发作。
2、药物治疗
(1)选用复方丹参颗粒、脑淫羊藿、乌鸡白凤丸等中药具有临床疗效,可减轻卒中性腰痛、肌肉拘束及炎性症状,增强机体对疾病的抵抗力。
(2)应用止痛药、抗炎药、肌肉松弛剂等西药。

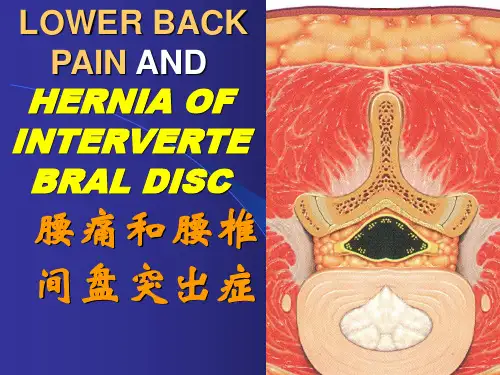




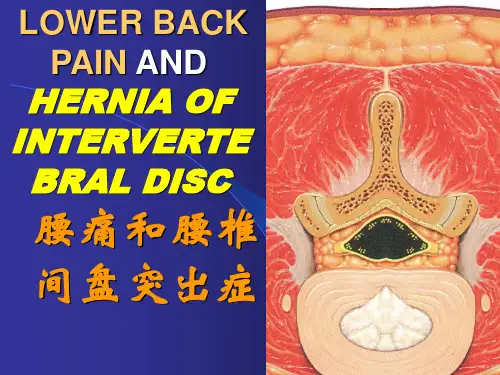

盘源性下腰痛的鉴别诊断With so many possible causes of lower back pain, physicians must pinpoint the source(s) of pain to recommend appropriate action or no action. The IDET procedure is not suitable for every form of lower back pain. Chronic discogenic lower back pain unresponsive to aggressive non-operative therapy is the principal indication for the IDET procedure.IDET不是适合于任何下腰痛患者。
盘源性下腰痛才是IDET的手术指征。
∙Differential diagnosis starts with a detailed history, physical examination and an MRI.鉴别诊断要从相信的病史、体检及MRI检查开始。
∙Non-musculoskeletal causes of back pain such as tumor, infection, aneurysm and renal and vascular pathology should be considered and ruled out.排除非肌肉骨骼原因引起的下腰痛,如:肿瘤、感染、动脉瘤、肾脏疾病等,都需要被考虑到并排除。
∙Fractures and ankylosing spondylitis should also be ruled out.排除骨折及强直性脊柱炎。
∙Discogenic pain should be differentiated from radicular pain, which may also be present.还需与神经根痛相鉴别。

骨科常见疾病英文诊断方位,指示名词上upper下lower外侧lateral内侧medial前anterior后posterior远distal近proximal左left右right部位锁骨clavicle肩胛骨scapula肱骨humerus肱骨外科颈humeral surgical neck肱骨解剖颈humeral anatomic neck肱骨大结节humeral greater tubercle 肱骨髁上epicondylar肱骨髁间intercondylar肱骨外侧髁lateral humeral condyle 肱骨内侧髁medial humeral condyle 肱骨小头humeral capitulum肱骨滑车humeral trochlea尺骨ulna尺骨鹰嘴olecranon尺骨冠状突conoral process桡骨radius腕骨carpal bone舟状骨scaphoid月骨lunate三角骨triquetral豆状骨pisiform大多角骨trapeaium小多角骨trapezoid头状骨capitate钩状骨hamete掌骨metacarpal指骨phalange骨盆pelvis髂骨ilium耻骨pubis坐骨ischium髋臼acetabalum股骨femur股骨颈femeral neck股骨粗隆间femeral intertrochanteric 股骨髁上epicondylar股骨髁间intercondylar股骨内侧髁medial femeral condyle股骨外侧髁lateral femeral condyle 髌骨patella胫骨平台plateau胫骨tibia腓骨fibula内踝medial malleous外踝lateral malleous双踝bimalleous三踝trimalleous距骨talus跟骨calcaneus足舟骨navicular外侧楔骨lateral cuneiform中间楔骨intermediate cuneiform 内侧楔骨medial cuneiform跖骨metatarsal趾骨phalange颈椎cervical spine胸椎thoracic spine腰椎lumbar spine骶骨sacrum寰椎atlas枢椎axis椎间盘intervertebral disc横突transvers process关节突facet joint椎板lamina椎管spinal canal椎弓根pedicle肩锁关节acromiocalvicular joint 肩关节shouder joint肘关节elbow joint上尺桡关节proximal radioulnaris joint下尺桡关节distal radioulnaris joint腕关节wrist joint桡腕关节radiocarpal joint腕掌关节carpometacarpal joint掌指关节phalangiocarpal joint指间关节interphalangical joint骶髂关节sacroilial jioint髋关节hip joint膝关节knee joint踝关节ankle joint胫腓联合distal tibiofibulal combination 跗横关节transversotarsal joint跖跗关节tarsometatarsal joint跖趾关节phalangiometatarsal joint趾间关节interphalangical joint寰枢关节atlasoaxisal joint关节突关节facet joint侧副韧带colateral ligament交叉韧带cruciated ligament滑膜synovium半月板meniscus上臂upper arm前臂forarm手部hand大腿thigh小腿leg足部foot颈部neck胸部thoracic腰部lumbar下腰部lower back脊髓spinal cord神经nerve动脉artery肌腱tendon伸肌腱extensor tendon 屈肌腱flexor tendon 跟腱Archilis tendon疾病骨折fracture脱位dislocation半脱位subluxation断裂rupture损伤injury挫伤contusion裂伤laceration截瘫paraplagia不全瘫痪incomplete paralysis全瘫complete paralysis化脓性septic结核tubercolosis关节炎arthritis骨性关节炎osteoarthritis类风湿性关节炎rheumatoid arthritis椎管狭窄lumbar stenosis滑移spondylolisthesis节段性不稳segmental distablity盘原性腰痛disc genic lower back pain 椎间盘退变性疾病disc degenerative disease 肿块mass肿瘤tumor转移性metastasis原发性primary骨样骨瘤osteoid osteoma成骨细胞瘤/骨母细胞瘤osteoblastoma骨肉瘤osteosarcoma内生软骨瘤enchondroma骨软骨瘤osteochondroma成软骨细胞瘤/软骨母细胞瘤 chondroblastoma软骨肉瘤chondrosarcoma骨纤维结构不良fibrous dysplasia of bone硬纤维瘤fibroma durum恶性纤维组织细胞瘤malignant fibrohistocytoma血管瘤hemangioma/angioma血管球瘤glomus tumor血管肉瘤hemangiosarcomaLangerhans细胞肉芽肿Langerhans cell histiocytosis 尤文肉瘤Ewing sarcoma淋巴瘤lymphoma多发性骨髓瘤multiple myeloma色素沉着性绒毛结节性滑膜炎PVNS滑膜肉瘤synovial sarcoma。
脊柱外科常用英语词汇LUMBAR SPINELumbar disc herniation syndrome 腰椎间盘突出症Fenestration and Discectomy Love method(开窗髓核摘除术Love法) minimally invasive discectomy微创椎间盘切除术MED(micro-endoscopic discectomy) 内镜椎间盘切除术Burst (Compression)fracture of T1-12, L1-5 胸腰椎爆裂(压缩)骨折Open reduction and pedicle screw internal fixation切开复位椎弓根螺钉内固定Decompression and pedicle screw system internal fixation with bone graft减压植骨椎弓根钉内固定Lumbar spine canal stenosis 腰椎管狭窄症spinal stenosisFenestration decompression(开窗减压) laminectomy椎板切除术Degenerative spondylolisthesis 假性(退变性)脊柱滑脱Spondylolitic spondylolisthesis 真性(峡部裂性)滑脱Reduction and interbody fusion (复位椎间植骨融合)anterior approach前入路posterior approach后入路Removal of internal fixation内固定取出术ALIF:anterior lumber interbody fusion前路椎间融合PLIF:posterior lumbar interbody fusion后路椎间融合TLIF:transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion经椎间孔融合Endoscopic operation内镜手术spinal fusion脊柱融合pseudarthrosis假关节chemonucleolysis髓核融解术discogenic back pain椎间盘源性腰痛sacroiliac joint骶髂关节spondylolisthesis脊柱滑脱Removal 取出(术)back pain in children and adolescents儿童和青少年的下腰痛discitis间盘炎CERVICAL SPINEAnold_Chari Deformity 颅底畸形C1 laminectomy and Occipital_C3 Fusion (颈1后弓切除加枕颈融合术)Jefferson Fracture环椎爆裂骨折Halo-vest external fixation (头环背心外固定)Atlantoaxial subluxation 环枢椎脱位Margel Screw(C1-2关节突螺钉)Trans-oral approach(经口咽入路手术)Dens Fracture 齿状突骨折Dens Screw internal fixation(齿状突螺钉内固定)Hangman Fracture C2椎弓骨折Anterior C2-3 Fusion(前路C2-3融合)Posterior C2-3 pedicle screw internal fixation (后路C2-3椎弓根内固定)Cervical spine disc herniation 颈椎间盘突出症Anterior discectomy and fusion(前路间盘摘除植骨融合)Cervical spine canal stenosis 颈椎管狭窄症Cervical spine OPLL(Osification of Posterior Longitudenal Ligarment) 颈椎后纵韧带骨化症Cervical spine dislocation and fracture 颈椎骨折脱位Posterior open reduction and anterior fusion(后路切开复位-前路植骨融合术)Over-extension injury of Cervical spine 颈椎过伸性损伤C3-6 laminoplasty (C3-6椎板成形椎管扩大术)Kurokawa method French door-open(双开门)Hirabayashi method English door-open(单开门)cervical spondylotic radiculopathy神经根型颈椎病cervical spondylotic myelopathy脊髓型颈椎病cervical laminoplasty颈椎椎板成形术upper cervical fracture(Occiput,Atlas and Axis.C0~C1andC2)lower cervical fracture(C3~C7andT1)Thoracic spine canal stenosis 胸椎管狭窄症thoracoscopy of the spine胸腔镜下脊柱手术larproscopic spinal fusion内镜下脊柱融合Thoracic spine OLF(Osification of Ligarmentum Flavum) 胸椎黄韧带骨化症DEFORMITYTetherd cord syndrome 脊髓拴系综合征Spine shortening osteotomy(脊柱短缩截骨术)Degenerative Scoliosis 退变性侧弯Deformity correction (畸形矫正术) Congenital Scoliosis 先天性侧弯Hemivertabra 半椎体Idiopathic Scoliosis 特发性侧弯congenital anomalies of the spinal cord脊髓先天畸形myelomeningocele脊髓脊膜膨出occult spinal dysraphism and tethered cord隐性脊柱裂和脊髓栓系spinal disorders associated with skeletal dysplasias and metabolic diseases脊柱疾病合并骨骼发育不良及代谢性疾病juvenile and adolescent scoliosis青少年脊柱侧弯congenital scoliosis先天性脊柱侧弯idiopathic scoliosis特发性脊柱侧弯neuromuscular scoliosis神经肌肉性脊柱侧弯juvenile kyphosis青年型脊柱后凸TUMORSpinal cord tumor:Neurinoma 神经鞘瘤Neurifibroma 神经纤维瘤Meningioma 脊膜瘤Giant cell tumor 巨细胞瘤Chordoma 脊索瘤INFECTIONTuberculosis 结核Pott’s disease (脊柱结核) Debridment清创(术)OTHERNominature of the disease:spine injury脊柱损伤spinal cord injury脊髓损伤spinal orthoses矫形器spinal tumor脊柱肿瘤spinal infection脊柱感染ankylosing spondylitis强直性脊柱炎rheumatoid arthritis类风湿性关节炎intradural tumors硬膜内肿瘤intraspinal infections椎管内感染,epidural硬膜外,intradural硬膜内arteriovenous malformations of the spinal cord脊髓动静脉畸形syringomyelia脊髓空洞Chronic, acute , haematogenous osteomyelitis急,慢性,血源性骨髓炎dislocation,subluxation脱位,半脱位cervical spinal stenosis颈椎管狭窄scoliosis侧弯,kyphosis后凸,lordosis前凸bone cement骨水泥OPLL:ossification of posterior longitudinal ligment后纵韧带骨化(钙化calcium)OLF: :ossification of ligment flavum黄韧带骨化Operative methods:Expansive open-door laminoplasty单开门椎管扩大成形术hirabayashi 1977 Double-door laminoplasty双开门椎管成形术Kurokawa1982Plaster 石膏corrective operation of scoliosis and kyphosis脊柱侧突及后凸畸形矫形术THA(bipolar):total hip arthroplasty全髋关节置换(双极头)TKA(arthroplasty,replacement)全膝关节置换术ORIF(open reduction and internal fixation) 切开复位内固定Clavical fracture锁骨骨折Acromioclavical 肩锁关节Humeral fracture(distal,proximal,middle,shaft)Radius,ulna,femur,tibia,fibulaepiphyseal,diaphyseal(shaft),metaphyseal干骺端的bone graftCDH(congenital dislocation of the hip)DDH(developmental dysplasia of the hip)DDH(developmental dislocation of the hip)ACL: anterior cruciate ligmentPCL: posterior cruciate ligmentMCL: mdial collateral ligmentLCL: lateral collateral ligmentMeniscus:半月板,repairmentA VN: avascular necrosis缺血性坏死Core decompression and mesenchymal stem cell transplantation髓心减压间充质干细胞移植。
西医疼痛科术语英文翻译以下是常见的西医疼痛科术语英文翻译:1. 疼痛科:Pain Management Department2. 疼痛评估:Pain Assessment3. 疼痛分类:Pain Classification4. 慢性疼痛:Chronic Pain5. 急性疼痛:Acute Pain6. 癌痛:Cancer Pain7. 神经痛:Neuropathic Pain8. 关节痛:Joint Pain9. 头痛:Headache10. 偏头痛:Migraine11. 肌痛:Myalgia12. 疼痛管理:Pain Management13. 药物治疗:Pharmacological Therapies14. 非药物治疗:Non-pharmacological Therapies15. 物理治疗:Physical Therapies16. 神经调节治疗:Neuromodulation Therapies17. 心理治疗:Psychological Therapies18. 针灸治疗:Acupuncture Therapy19. 微创手术:Minimally Invasive Surgery20. 脊柱外科手术:Spinal Surgery21. 关节镜手术:Arthroscopic Surgery22. 硬膜外注射治疗:Epidural Injection Therapy23. 神经阻滞治疗:Nerve Block Therapies24. 射频消融治疗:Radiofrequency Ablation Therapy25. 疼痛教育:Pain Education26. 疼痛康复:Pain Rehabilitation27. 疼痛护理:Pain Nursing28. 疼痛患者自我管理:Self-management for Pain Patients29. 疼痛管理药物经济学:Pharmacoeconomics of Pain Management30. 疼痛管理伦理学:Ethics of Pain Management31. 疼痛管理法律问题:Legal Issues in Pain Management32. 疼痛管理心理学:Psychology of Pain Management33. 疼痛管理多学科合作:Multidisciplinary Collaborations in Pain Management34. 疼痛管理临床实践指南:Clinical Practice Guidelines for Pain Management35. 阿片类药物耐受性与成瘾性管理:Opioid Tolerance and Addiction Management36. 药物治疗安全性监测与管理:Drug Safety Monitoring and Management in Pain Management37. 非药物治疗有效性评估与实施:Evaluation and Implementation of Non-pharmacological Interventions for Pain Management38. 慢性疼痛的预防与管理策略:Prevention and Management Strategies for Chronic Pain39. 癌痛的多学科综合治疗与管理:Multidisciplinary Comprehensive Cancer PainManagement40. 神经痛的治疗与管理策略:Treatment and Management Strategies for Neuropathic Pain41. 关节痛的物理治疗与管理策略:Physical Therapies and Management Strategies for Joint Pain42. 头痛的诊断与治疗策略:Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies for Headache Disorders43. 肌痛的非药物治疗与管理策略:Non-pharmacological Interventions and Management Strategies for Myalgia44. 疼痛管理的患者教育与支持系统建设:Patient Education and Support System Development in Pain Management45. 基于互联网的远程疼痛管理解决方案:Internet-based Remote Pain Management Solutions46. 人工智能在疼痛管理中的应用与前景:Application and Prospects of Artificial Intelligence in Pain Management47. 社会心理因素对疼痛感知与耐受性的影响研究:Studies on the Impact of Psychosocial Factors on Pain Perception and Tolerance48. 个体化疼痛治疗方案的研究与实践进展:Research and Practical Advances in Personalized Pain Management Strategies49. 儿童与老年人的特殊疼痛问题及管理策略研究:Studies on Special Pain Problems and Management Strategies in Children and Elderly Adults50. 国际疼痛管理领域的最新研究动态与合作项目:Recent Research Developments and Collaborative Projects in International Pain Management。
Many patients with back pain, leg pain, or weakness of the lower extremity muscles arediagnosed with a herniated disc.许多患腰腿疼痛,下肢肌端乏力的病患均为椎间盘突出症。
When a disc herniation occurs, the cushion that sits between the spinal vertebra is pushedoutside its normal position.椎间盘突出发生时,脊柱间的缓冲带将发生侧突。
A hrniated disc would not be a problem if it werent for the spinal nerves that are very close tothe edge of these spinal discs.如果脊神经不是离椎间盘特别近的话,椎间盘突出就不是什么大问题了。
HOW ARE THE SPINE AND ITS DISCS *****D脊柱与椎间盘The vertebras are the bony building blocks of the spine.脊椎是建造脊柱的构件。
Between each of the largest parts (bodies) of the vertebrae are the discs.各椎骨之间为椎间盘。
Ligaments are situated around the spine and discs.脊椎和椎间盘周围散布着韧带。
The spine has seven vertebrae in the neck (cervical vertebrae), 12 vertebrae in the mid-back(thoracic vertebrae) , and five vertebrae in the low back (lumbar vertebrae).颈部有7条椎骨,胸部为12条,腰部有5条。
椎间盘源性下腰痛的诊断椎间盘源性下腰痛是一种腰椎间盘退变性疾病引起的慢性顽固性下腰痛,临床表现常不典型,诊断较困难,容易被误诊,导致患者不能得到及时、有效的治疗,增加了经济负担及痛苦。
因此作一综述,希望能引起临床医师的注意。
一概念Crock[1] 1970年提出“椎间盘源性下腰痛”的概念,又称“椎间盘内紊乱”,指由于一个或者多个椎间盘内部结构和代谢功能出现异常,如退变、终板损伤或无菌性炎症释放出某些因子,刺激椎间盘内疼痛感受器所引起的腰痛,它一般不伴神经根性症状或节段间过度活动的放射学证据。
二发病机制确切发病机制尚未研究清楚。
目前认为椎间盘源性腰痛是由纤维环破裂(Internal disc disruption,IDD)引起,不伴有椎间盘突出、脱出、节段不稳或其他影像学上的异常[1,2]。
Bogduk[3]认为椎间盘外层纤维环存在P 物质、降钙素相关基因肽以及血管肠肽,这些物质都属于神经传递素,与痛觉有关。
Shinohara认为:在变性的椎间盘,神经纤维可能伴随肉芽组织沿破裂的纤维环深入到椎间盘深层,无髓纤维裸露在间质液中可以感受到间质内成分的变化而产生疼痛。
目前最新的研究结果倾向于:椎间盘源性腰痛以及椎间盘造影诱发痛不仅与椎间盘承受的压力刺激椎间盘内部的压力传导器引起痛觉,同时与椎间盘内部的物质变化特别是炎症因子的增加引起痛觉的敏感性增加有关。
三临床表现椎间盘源性腰痛的临床表现为:多数病人有久坐、久弯腰、提重物史或腰椎直接暴力外伤史。
疼痛部位:L4/5、L5/S1的棘间、髂后、臀部、腹股沟、股前、股后、大转子等处的自发性胀痛,多痛不过膝;以腰痛为主,不耐受久坐、久弯腰或久站,腰椎前屈、旋转、侧屈加重或诱发疼痛,卧床休息缓解。
典型的病人是保守治疗无效或反复发作,逐渐加重。
查体可见腰椎因疼痛活动受限或正常,腰痛部位深在,压痛轻微,叩击痛明显。
腿痛往往发生于腰痛之后,常常没有精确的定位,通常难以言表,多主诉为臀部和下肢的酸胀、沉重感或抽筋,而且疼痛区域缺乏神经分布的特点,神经系统检查正常,没有皮肤感觉过敏和缺失。
扶他林乳胶剂超声透入治疗椎间盘源性下腰痛的疗效观察随着人们对椎间盘退变疾病的深入研究,腰椎间盘突出症引起的腰痛越来越被医疗工作者所了解,但是椎间盘内部出现病变而髓核没有突出引起下腰痛的病例被人们发现,称为椎间盘源性下腰痛(discogenic low back pain, DLBP)。
Crock在1986年将DLBP定义为一种椎间盘外周部基本保持完整,而内部各种病理(退变、终板损伤、炎症等)刺激椎间盘内疼痛感受器引起的功能丧失性下腰痛,并且不伴有根性症状,无神经或节段过度活动的放射学证据[1]。
DLBP是慢性下腰痛中最常见的疾病,占到其发病率的39%,而椎间盘突出症不到30%,其他疾病如小关节源性疼痛的发病率就更低[2]。
笔者所在科室从2007年11月至2009年2月诊治的DLBP患者共335例,除201例经过微创和开放性手术治疗,其他因不能手术的134例分别采用扶他林乳胶剂超声透入或单独的超声波治疗。
临床效果满意,总结报告如下。
1 资料和方法1.1 一般资料本组病例134例:男85例,女49例;年龄最小24岁,最大57岁;病程最短6个月,最长9年; L3~4间盘病变16例,L4~5者69例,L5~S1者32例,两个以上17例;所有病例均经X线、CT、MRI检查,132例有黑间盘,78例有HIZ,94例有Modic 改变;所有病例均进行椎间盘造影术检查为阳性。
1.2 诊断依据①反复发作下腰痛, 持续时间>6个月, 不能久坐、久站,不能弯腰,部分患者体检有疼痛的中心化现象和棘突骨震动试验阳性,不伴下肢放射痛和间歇性跛行, 无神经根受压体征;②X线检查排除腰椎峡部裂、滑脱和不稳,CT检查无椎间盘突出及椎管狭窄,MRI检查在T2加权像上病变椎间盘呈低信号改变(黑间盘),或者有椎间盘后方有高信号区,或者终板有Modic改变;③椎间盘造影可诱发出一致性下腰痛,V AS≥5,间盘形态异常,注射剂量≥3 ml,有相邻间盘阴性对照。
盘源性下腰痛的鉴别诊断
With so many possible causes of lower back pain, physicians must pinpoint the source(s) of pain to recommend appropriate action or no action. The IDET procedure is not suitable for every form of lower back pain. Chronic discogenic lower back pain unresponsive to aggressive non-operative therapy is the principal indication for the IDET procedure.
IDET不是适合于任何下腰痛患者。
盘源性下腰痛才是IDET的手术指征。
∙Differential diagnosis starts with a detailed history, physical examination and an MRI.
鉴别诊断要从相信的病史、体检及MRI检查开始。
∙Non-musculoskeletal causes of back pain such as tumor, infection, aneurysm and renal and vascular pathology should be considered and ruled out.
排除非肌肉骨骼原因引起的下腰痛,如:肿瘤、感染、动脉瘤、肾脏疾病等,都需要被考虑到并排除。
∙Fractures and ankylosing spondylitis should also be ruled out.
排除骨折及强直性脊柱炎。
∙Discogenic pain should be differentiated from radicular pain, which may also be present.
还需与神经根痛相鉴别。
盘源痛与神经根痛的比较
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙
∙Pain which is unilateral and predominantly below lumbar vertebra 5 is probably not discogenic. 单侧疼痛而且疼痛点低于腰5的情况下大多不是盘源性的。
∙Diagnostic joint blocks can be used to trace the source of pain, which can be attributed to the sacroiliac joint in about 20% of patients and lumbar zygapophysial joint pain in up to 40% of patients.
压痛点有助于医师发现疼痛的根源,大约20%的病人压痛点在骶髂关节,而40%以上的患者压痛点在腰椎小关节处。
∙Patients with discogenic pain may have no abnormalities visible on the MRI or may have a bright spot in the posterior anulus referred to as the high intensity zone or HIZ. This is best seen on sagittal views and indicates a tear in the disc.
大多数盘源性疼痛患者MRI图像没有明显的异常。
或在纤维环后方有高强度区域。
这种情况在矢状面时比较容易看到。
常表明椎间盘有微小的裂纹。
椎间盘源性痛可以通过椎间盘造影刺激并重建症状。
Discography is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure performed while the subject is awake. Sedation and analgesia can be provided to minimize discomfort. Contrast medium is injected into the three or four discs under investigation as the source of the low back pain.
椎间盘造影是一种微创的复制患者症状的检查方法。
操作中可适当给以镇静止痛药物以减轻患者不安,将对比造影剂注射入3-4个椎间盘内以确定疼痛源。
∙The injection of fluid into each disc increases the fluid volume and pressure in the disc and may reproduce the subject’s usual pain pattern.
将造影剂注射入每个椎间盘内可以增加椎间盘内液体体积及压力可以重建患者的疼痛症状。
∙ A positive response in one disc confirmed by the absence of a pain response in one or more other adjacent discs confirms the origin of the pain.
椎间盘内注射出现的阳性反应与患者疼痛区域相同可以证实某个椎间盘为症状根源。
∙In addition, the contrast medium allows the morphology of the disc to be visualized fluoroscopically.
另外,造影剂可以通过透视显示椎间盘的形状。
Since provocation discography is minimally invasive and produces some discomfort, it should only be performed when a definitive diagnosis will lead to treatment that would otherwise not be performed.
尽管椎间盘造影是微创过程仅有较少不适,但这一检查方式仅应在为确定诊断或确定手术部位时才能使用。
确定疼痛源
The disc which is the source of the low back pain can be confirmed when:
如下步骤以证实引起下腰痛的椎间盘:
∙The pain elicited is similar to patient’s usual pain pattern.
复制出的症状与患者平时的症状相同或相似。
∙At least one adjacent disc (preferably two) does not reproduce pain. 至少一个相近的椎间盘不能复制出症状。