制程检验报告 中英文版
- 格式:xls
- 大小:50.00 KB
- 文档页数:1

制程检验员一天的工作流程【中英文实用版】英文文档:The daily work process of a process inspector involves several key steps to ensure the quality and efficiency of the manufacturing process.Here is an overview of a typical day for a process inspector:1.Morning Check-In: The inspector arrives at work and logs into the system to check for any urgent messages or notifications.They review the daily production schedule and inspect the necessary documents, such as work orders and quality specifications.2.Pre-Shift Inspection: Before the production line starts, the inspector conducts a pre-shift inspection to ensure that all equipment and tools are in proper working condition.They check for any signs of damage or malfunction and ensure that all safety measures are in place.3.In-Process Inspection: During the production process, the inspector randomly selects samples from the batch and checks them against the quality specifications.They examine the products for any defects, dimensional accuracy, or compliance with the required standards.Any non-conforming products are documented and segregated for further analysis or disposal.4.Documentation: Throughout the day, the inspector maintains detailed records of their inspections, including the date, time, batchnumber, and any issues identified.They also document any corrective actions taken or communicated to the production team.5.Collaboration with Production Team: The inspector works closely with the production team to address any quality-related concerns or issues.They provide feedback, suggest improvements, and collaborate on resolving any production bottlenecks or defects.6.Lunch Break: The inspector takes a scheduled lunch break to relax and recharge.They return to work promptly after the break to continue their duties.7.Final Inspection: Before the end of the shift, the inspector conductsa final inspection to ensure that the production batch meets the required quality standards.They check the final output against the production records and specifications.8.Shift Handover: The inspector completes a handover report, summarizing the day"s activities, inspections, and any issues encountered.They communicate this information to the incoming inspector or supervisor to ensure a smooth transition.9.Cleaning and Maintenance: Before leaving for the day, the inspector ensures that the inspection area is clean and organized.They also perform routine maintenance on inspection tools and equipment, as necessary.10.Evaluation and Continuous Improvement: At the end of the day,the inspector reflects on their work and identifies areas for improvement.They may participate in training sessions or meetings to enhance their skills and knowledge.In conclusion, a process inspector"s daily work process involves various steps to maintain quality standards and ensure efficient production.Their role is crucial in identifying and addressing any issues promptly, contributing to the overall success of the manufacturing operation.中文文档:制程检验员的一天工作流程包括多个关键步骤,以确保生产过程的质量和效率。

质检实习报告英文回答:During my quality inspection internship, I had the opportunity to learn and experience a lot. One of the most important things I learned is the importance of attention to detail. In quality inspection, even the smallest details can make a big difference in the overall quality of a product. For example, I was responsible for inspecting electronic components, and I learned that even a tiny scratch or dent can affect the functionality of the component.I also learned the importance of communication and teamwork in quality inspection. For instance, there was a time when I found a defect in a product, and I had to communicate effectively with the production team to ensure that the issue was addressed and resolved. This experience taught me the importance of clear and respectful communication in a professional setting.Furthermore, I gained a better understanding of the quality standards and regulations in the industry. I had to familiarize myself with the specific requirements and criteria for the products I was inspecting, and I had to ensure that all the products met these standards. This experience helped me develop a keen eye for identifying deviations from the quality standards.Overall, my quality inspection internship was a valuable learning experience that allowed me to apply my knowledge in a real-world setting. I am grateful for the opportunity to learn from experienced professionals in the field and to contribute to the quality assurance process.中文回答:在我的质检实习期间,我有很多学习和经验的机会。

Out-going Inspection Product出货检查程序一、目的Purpose:规定出货检查工作在有效受控下进行。
To ensure that out-going inspection is performed under effective control.二、适用范围说明Scope:一般情况下,本公司产品终检后不再做出货检查:但在以下四种情况任一种出现时,必须进行出货检查。
对于特别的部品(如尼龙用料部品)在某种情况必需做出货检查的,由项目部、QC部门等相关人员共同确定。
Generally, no need out-going inspection after final inspection. But in any one of the following situations, out-going inspection is necessary.Related personnel in Program Dept and QC section are responsible for determining whichparts need to do out-going inspection.1.产品库存期超过6个月(若FQC当月已对待出货产品进行了仓贮品质评估,可根据其《仓库物资评估报告》QF-PW-009的结果进行,反之,则必须做出货检查)。
Stored more than 6 months (If the waiting-for-delivery product has been assessed byFQC in the same month, then FQC conduct in accordance with the result of thecorresponding <<Material/product assessment report>> QF-PW-009, otherwise it is amust for FQC to perform out-going inspection.)2.因受外界环境的影响发生异常,影响到产品质量Product quality is effected by thechanging of environment;3.包材被损坏.Damage of package;4.出货海外(包括香港)或客户指定产品。

质检英文作文英语模板英文:As a quality inspector, my job is to ensure that the products meet the required standards before they are released to the market. This involves checking the products for defects and making sure they are safe for consumers to use.One of the main challenges that I face as a quality inspector is identifying defects that may not beimmediately apparent. For example, a product may look fine on the surface, but upon closer inspection, I may discovera small crack or chip that could potentially cause harm to the user. In such cases, it is important to document the defect and work with the production team to find a solution.Another challenge is dealing with non-compliance issues. Sometimes, the production team may not follow the required procedures or use the correct materials, which can resultin a product that is not up to standard. In such cases, it is important to communicate the issue clearly and work with the team to find a solution that meets the required standards.In addition to identifying defects and addressing non-compliance issues, I also work to improve the overall quality of the products. This involves analyzing data, identifying trends, and implementing changes to the production process to ensure that the products meet the required standards consistently.Overall, my job as a quality inspector is challenging but rewarding. By ensuring that the products meet the required standards, I am helping to protect consumers and maintain the reputation of the company.中文:作为一名质检员,我的工作是确保产品在发布到市场之前符合所需标准。
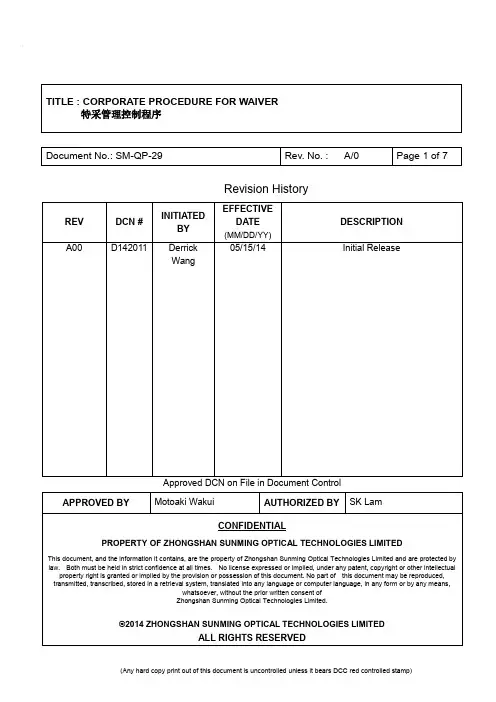
Revision HistoryApproved DCN on File in Document Control1.0 PURPOSE目的对于不符合公司品质之原物料进料,制程中半成品,成品,若不影响产品使用功能特性之前提件下,可依据本程序特采使用,以免影响正常生产或交期。
2.0 SCOPE 范围2.1生产急用,于限期内必须完成的生产作业。
2.2本程序适用于进料检验及制造过程检验,成品检验等程序。
3.0 ASSOCIATED DOCUMENTS 有关文件无4.0 DEFINITIONS 定义无5.0RESPONSIBILITY职责5.1品质部:提交原材料检验报告,对检验报告中内容必要时进行说明;5.2工程部:特采尺寸之判定;5.3采购部:依据需求对原材料提出特采申请;5.4生产部:全检执行、标准作业规范执行,依据实际情况对制程中的半成品及成品提出特采;5.5销售部:依据需求对成品提出特采申请5.6各单位主管:审核特采申请,提列特采相关意见;5.7总经理:对特采申请进行最终裁决。
6.0 PROCEDURE 流程6.1.原物料特采流程:6.1.1原物料经IQC判定不合格时,将不良内容及数量填写在【进料检验报告】中交品质工程师审核。
6.1.2品质工程师核准后仍然判为不合格(拒收)物料,遇下列情况由供应商或采购向品质部提出予以特殊审核或提出特采申请:(1)供应商或采购人员认定判定有误时(2)该批物料生产急需使用时,且短期内无法采购到更好原物料时(3)该缺陷对后续加工、生产影响甚微时(4)其他特殊情况时6.1.3采购依据生产计划需求提出特采申请,填写“特采申请单”,并附【来料检验报告】交品质部总监。
6.1.4品质总监与相关部门的责任人根据实际的情况召开物料特采(MRB)会议,并做出如下判定:(1)由品质部门重新抽样(2)指定某单位执行全数检验予以筛选(3)放宽标准特准使用(让步接收)(4)经加工后使用(5)维持不合格判定6.1.5若各主管会签同意特采,则交总经理核准,如有不同意见,则由总经理裁决,如不允许特采,则拒收该批物料。

质量体系缩写中英文对照AAR:外观批准报告ADV:分析/开发/验证ADV-DV:ADV设计验证A/S/V P &R:分析/开发/验证计划和报告ADV-PV:ADV产品验证AIAG:汽车工业行动集团AP:先期采购APQP:产品质量先期策划APO:(通用)亚太分部APQP Project Plan:APQP项目策划ASQE:先期供应商质量工程师BOM:材料清单BOP:过程清单Brownfield Site:扩建场地CMM:三坐标测试仪M Complex System/Subassembly:M复杂系统/分总成CPK:过程能力指数CTS:零件技术规范Defect outflow detection:缺陷检测DFM/DFA:可制造性/可装配性设计DFMEA:设计失效模式分析DPV:每辆车缺陷数DRE:设计发放工程师Error Occurrence Prevevtion:防错EWO:工程更改指令FE1,2,3:功能评估GD&T:几何尺寸&尺寸GM:通用汽车公司GME:通用汽车欧洲分部GM9000:指QS9000GP:总体步骤GPDS:全球产品描述系统GPS:全球采购系统GQTS:全球质量跟踪系统GR&R:量具的重复性与再现性Greenfield Site:新建工厂GVDP:全球车辆开发工程IPTV:每千辆车缺陷数KCC:关键控制特性KCDS:关键特性指示系统Kiek-Off Meeting:启动会议KPC:关键产品特性LAO:(通用)拉丁美洲分部LCR:最低生产能力MCR:最大生产能力MOP:制造/采购MPC:物料生产控制MPCE:欧洲物料生产控制MRD:物料需求日期MSA:测量系统分析MVBns:非销售车制造验证MVBs:销售车制造验证NAO:(通用)北美分部NBH:停止新业务OEM:主机客户PAD:生产装配文件PC&L:生产控制&物流PDT:产品开发小组PFMEA:潜在失效模式分析PPAP:生产件批准程序PPM:1)项目采购经理2)每百万件的产品缺陷数PPK:过程能力指数PQC:产品质量特性PR/R:问题报告及解决PSA:潜在供应商评审QSA:质量系统评审QTC:工装报价能力RASIC:负责、批准、支持、通知、讨论RFQ:报价要求RPN:风险顺序数RPN Reduction Plan:降低RPN值计划SDE:供应商开发工程师SFMEA:系统失效模式失效SMT:系统管理小组SOA:加速开始SOP:正式生产SOR:要求声明:SPC:统计过程控制SPO:(通用汽车)零件与服务分部SQ:供应商质量SQE:供应商质量工程师SQIP:供应商质量改进过程SSF:系统填充开始SSTS:分系统技术规范M Subcontractor:M分供方Team Feasibility Commitment:小组可行性承诺UG:UG工程绘图造型系统VDP:车辆开发过程VLE:车辆平台负责人WWP:全球采购序号缩写英文原文解释1 OTS overall tooling sample用批量生产的工模器具制造出的样件2 PVS Produktions – Versuchs - Serie 批量试生产3 TMA Trial Manufacturing Agreement 试制协议4 QSV Qualitaes-Sicherungs-Vereinbarung 质量保证协议5 BMG Bau-Muster-Genehmigung产品工程样件性能检验认可6 B- Freigabe 采购认可7 D- Freigabe 试制/0批量的认可8 P- Freigabe 计划认可9 TL 技术资料汇编10 LH LastenHeft 要求汇总书11 Pflichtenheft 责任汇总书12 ME Markt-Einfuehrung 市场导入13 MIS Management Informations-System 管理信息系统14 Nullserie 零批量15 QPN Qualifizierungs-Programm Neuteile 新零件质量提高计划16 SOP Start-Of-Production 批量生产启动Standard Operating Procedure 标准操作程序17 QSR 质量体系要求18 APQP Adavanced part quality plan 高级产品质量计划19 PPAP product part approval procedure 生产件批准程序20 QSA 质量体系评审21 MSA measurement system analysis 测量系统分析22 FMEA 失效模式及结果分析23 SPC 统计过程控制QC(Quality Control)质量控制,就是质检,通俗说就是检验QA(Quality Assurance)QA中文全称:质量保证IPQC(In-Process Quality Control)品质管理项目制程检验IQC来料检验,就是原材料检验QC的层次要比QA低,通俗来说就是检验员QA人员的主要任务就是监督药品从原料进厂到成品出厂的全过程的质量;QC 就是对药品原料和成品的所含主要成分进行检测,主要是给出原料和成品的检测数据.在药厂QC比QA轻松一点,但QA不需要懂得仪器的操作,只要知道成品和原料的指标,并用QC提供的数据来判断原料和成品是否合格同意进厂或出厂.在液相中设置这个主要是为制药厂考虑的,能减少很多不必要的重复工作.IQC 是来料控制,也就是进货检验OQC 是出货检验也就是出厂检验QC 是质量检验QA 指质量测试IPQC 制程控制PE 指制程工程师IE 指文件工程师-----------------------------------------------QC中文全称: 即英文QUALITY CONTROL的简称,中文意义是品质控制,质量检验。
实验报告纸英文AbstractThis experiment aimed to investigate the effects of temperature on the rate of enzymatic activity. The enzyme used in this study was α-amylase, and its activity was measured by observing the breakdown of starch. Different temperatures were tested, ranging from 5C to 60C, in order to determine the optimum temperature for enzyme activity. The results showed that enzymatic activity increased with temperature initially, reached its peak at 37C, and then declined rapidly. These findings highlight the critical role of temperature in enzymatic reactions and provide insights for further biotechnological applications. IntroductionEnzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions within living organisms. They play a crucial role in various physiological processes, including digestion, metabolism, and synthesis. Enzymes are highly selective and efficient in their catalytic functions, but their activity is influenced by several factors, such as pH, substrate concentration, and temperature. Temperature is a critical factor that directly affects enzyme activity. Enzymatic reactions are highly temperature-dependent, as temperature affects the three-dimensional structure of enzymes, their substrate binding, and the rate of molecular collisions. This experiment aimed to investigate the effects of temperature on the rate of enzymaticactivity using α-amylase as the model enzyme.Materials and MethodsMaterials:- α-amylase solution- Starch solution- Iodine solution- Water bath- Thermometer- Test tubes- StopwatchMethods:1. First, prepare five test tubes and label them as 5C, 25C, 37C, 50C, and 60C, respectively.2. Add 2 mL of α-amylase solution and 2 mL of starch solution to each test tube.3. Place the test tubes in the water bath set at the respective temperatures.4. Start the stopwatch as soon as the reagents are mixed in each test tube.5. Observe the color change in each test tube every 30 seconds until a blue-black color is observed, indicating the complete breakdown of starch.6. Record the time taken for each test tube to reach the end point.7. Repeat the experiment three times for each temperature condition and calculate the average time taken for starch breakdown.ResultsThe results of the experiment are summarized in the table below: Temperature (C) Time taken for Starch Breakdown (seconds)-5 54025 24037 18050 24060 480DiscussionThe results of the experiment demonstrate the effects of temperature on enzymatic activity. At lower temperatures (5C), the rate of enzyme activity was noticeably slower. This can be attributed to the reduced kinetic energy of the molecules, resulting in fewer successful collisions between the enzyme and its substrate. As the temperature increased, the rate of enzymatic activity also increased. The optimum temperature for α-amylase activity was observed to be 37C, at which point the rate of starch breakdown was the fastest. At higher temperatures beyond 37C, the rate of enzymatic activity started to decline rapidly. This can beexplained by the denaturation of the enzyme, as excessive heat disrupts the enzyme's three-dimensional structure, rendering it less effective in catalyzing the reaction.The findings of this experiment are consistent with the principles of enzymology and provide insights for various biotechnological applications. Understanding the effects of temperature on enzymatic activity is crucial for optimizing enzymatic reactions in industrial processes, such as food production, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and biofuel production. By controlling the temperature, scientists and engineers can enhance the efficiency and yield of enzymatic reactions. ConclusionThe experiment successfully demonstrated the effects of temperature on the rate of enzymatic activity, using α-amylase as the model enzyme. The results highlighted the optimum temperature for α-amylase activity and the decline in enzymatic activity at higher temperatures due to denaturation. These findings contribute to our understanding of enzyme kinetics and have practical implications in biotechnological applications. Future studies can explore other factors, such as pH and substrate concentration, to further optimize enzymatic reactions for various industrial purposes.。